Effects of Post-Synthesis Activation and Relative Humidity on Adsorption Performance of ZIF-8 for Capturing Toluene from a Gas Phase in a Continuous Mode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization
2.3. The Experimental Setup
2.4. Measurement of Toluene Dynamic Adsorption Capacity
2.5. Activation of ZIF-8
2.6. The Effect of RH
3. Results and Discussion
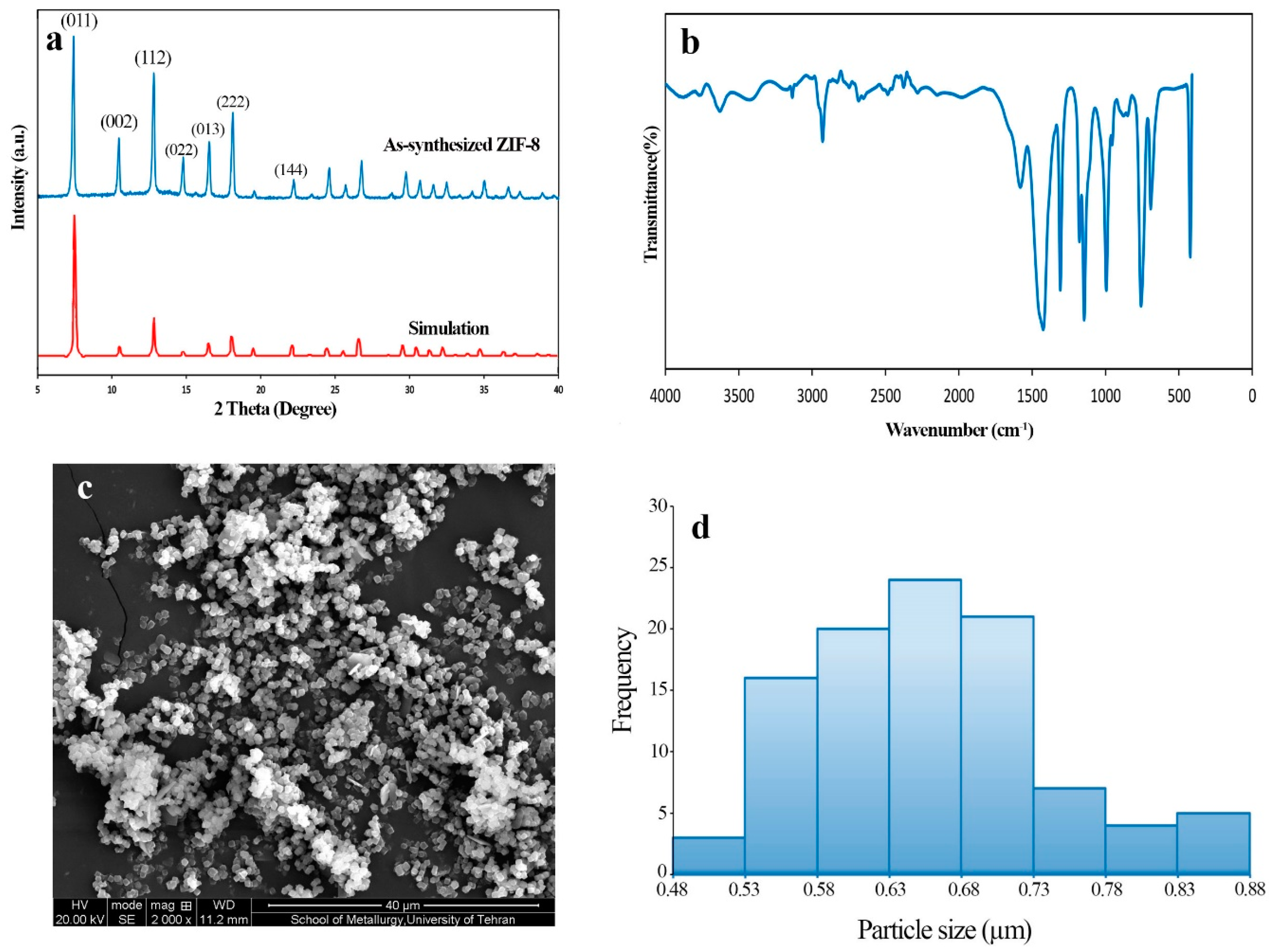
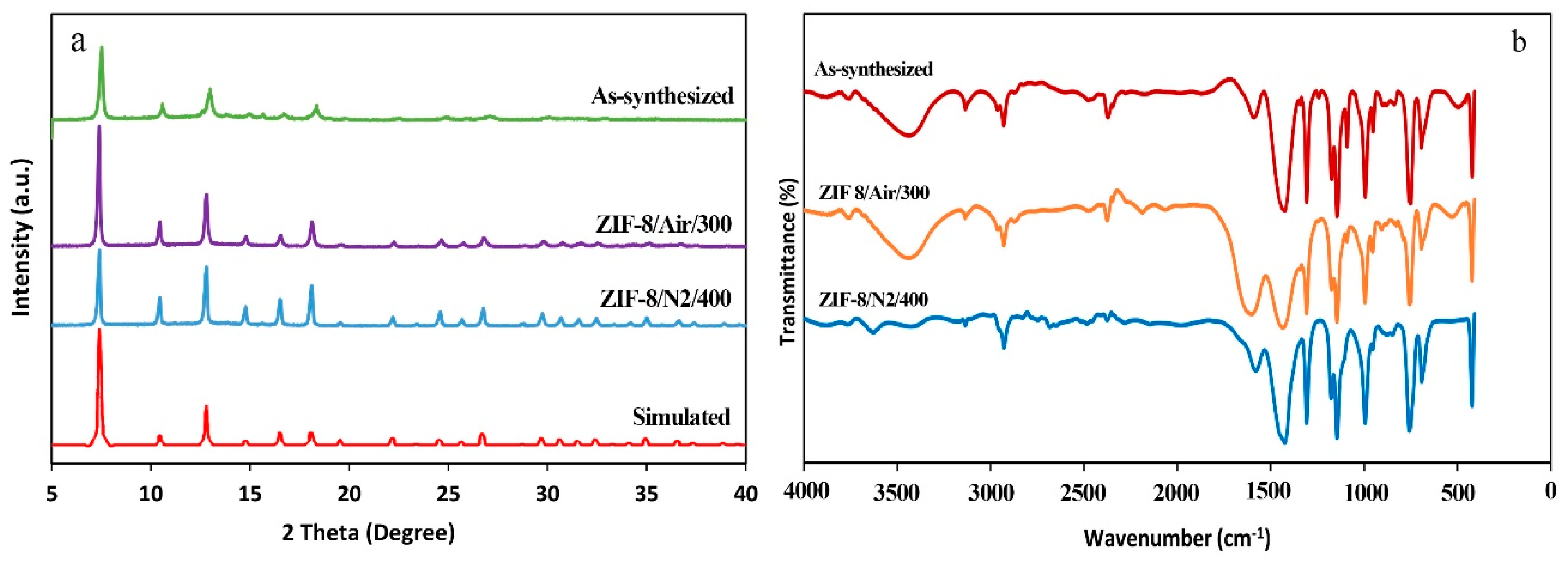
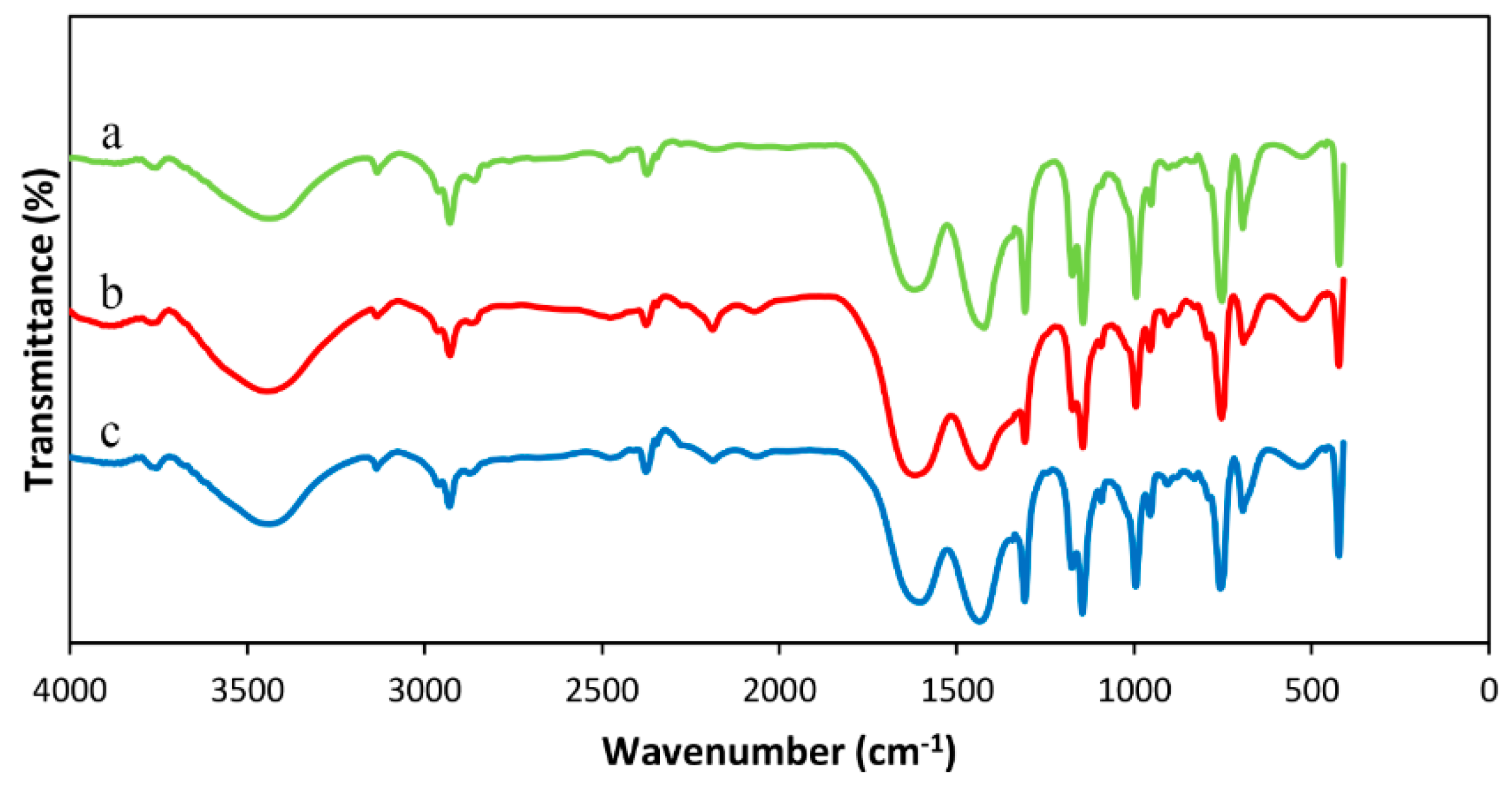
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Effects of Thermal Activation
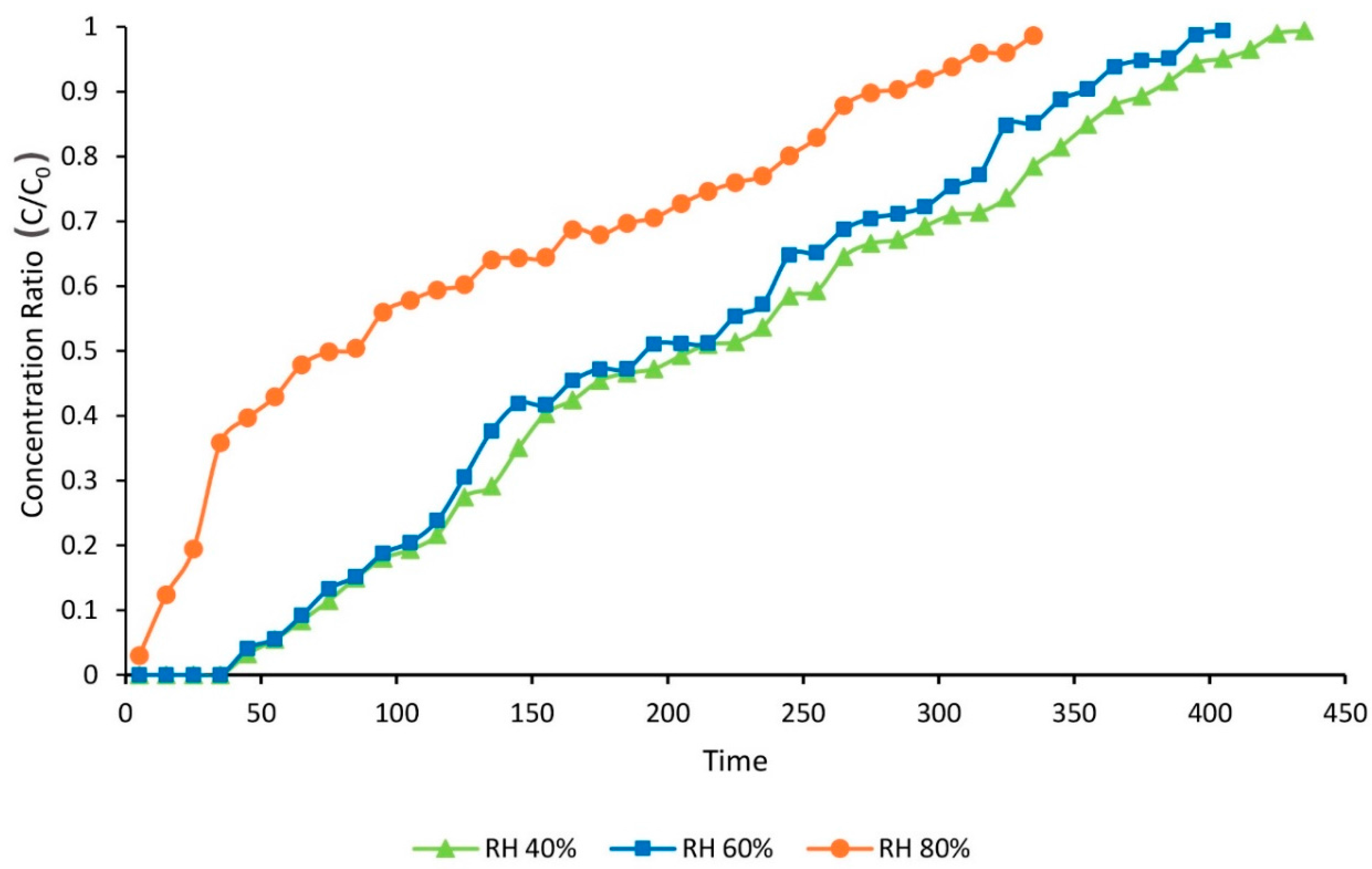
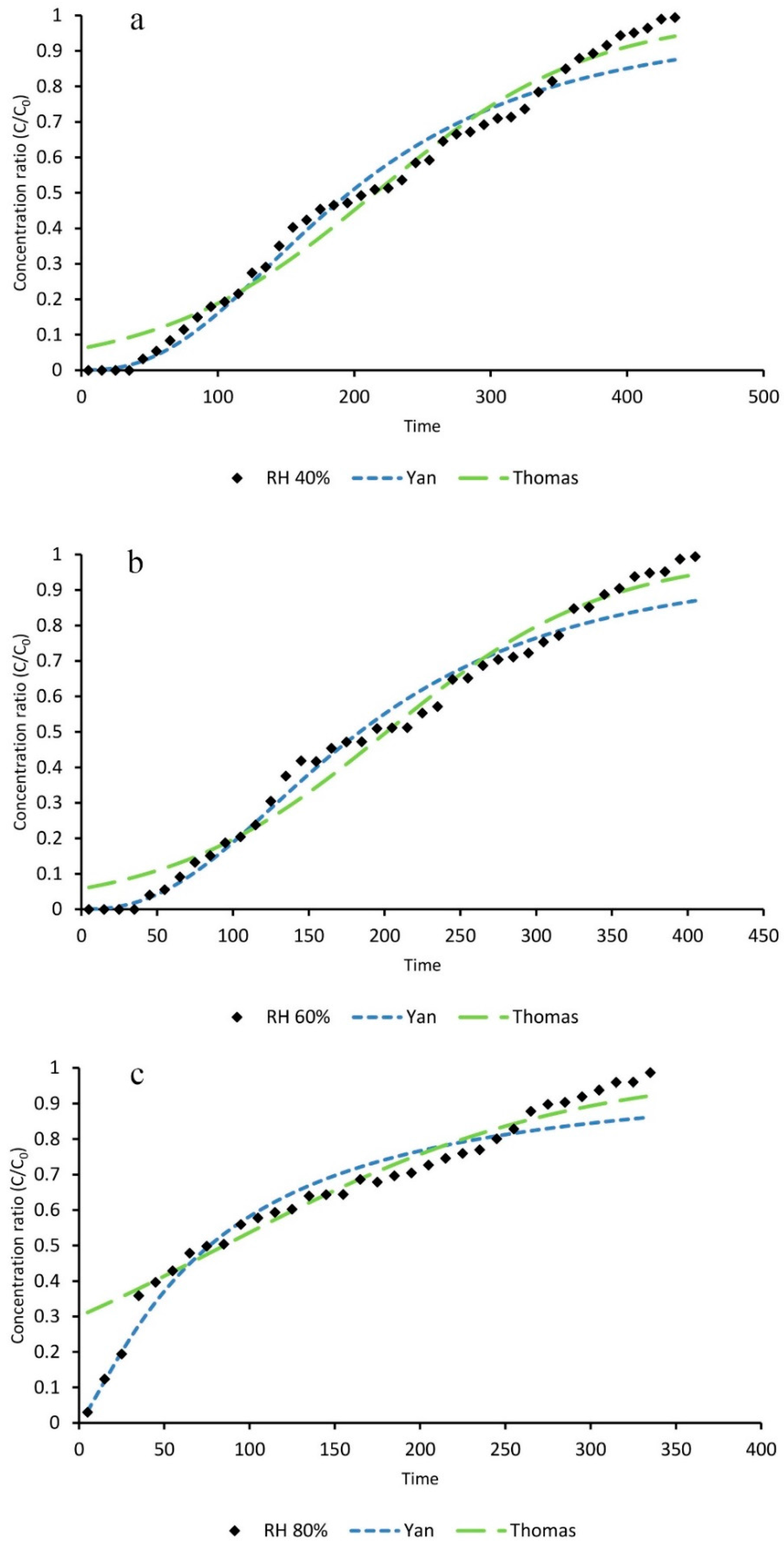
3.3. The Effects of HR on Toluene Adsorption
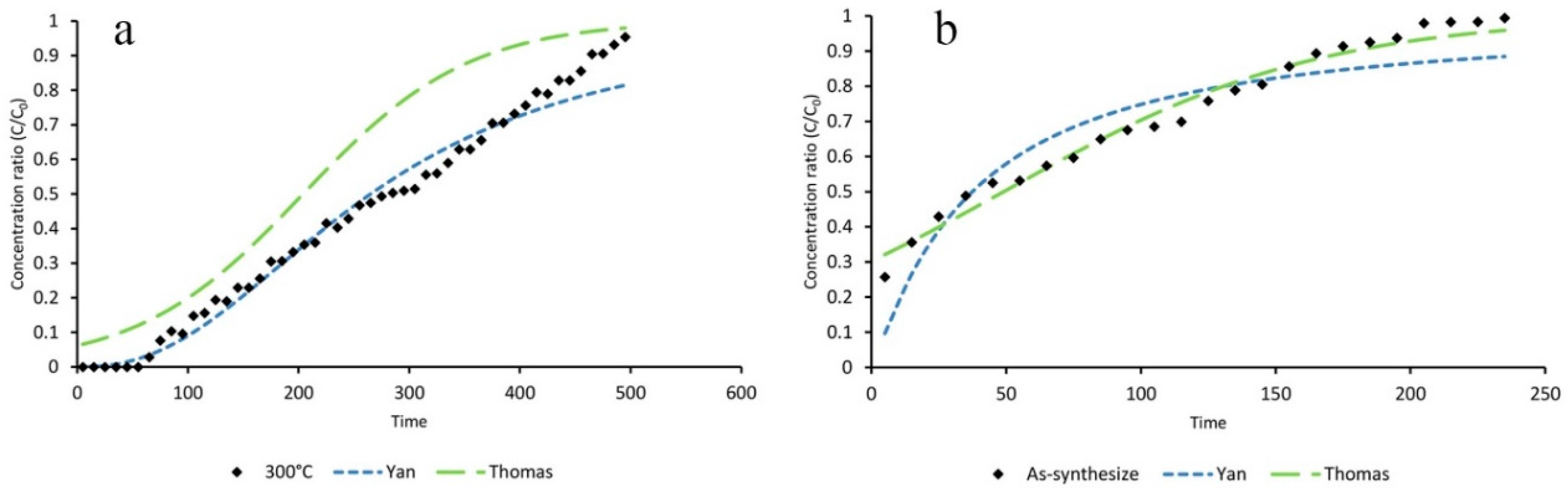
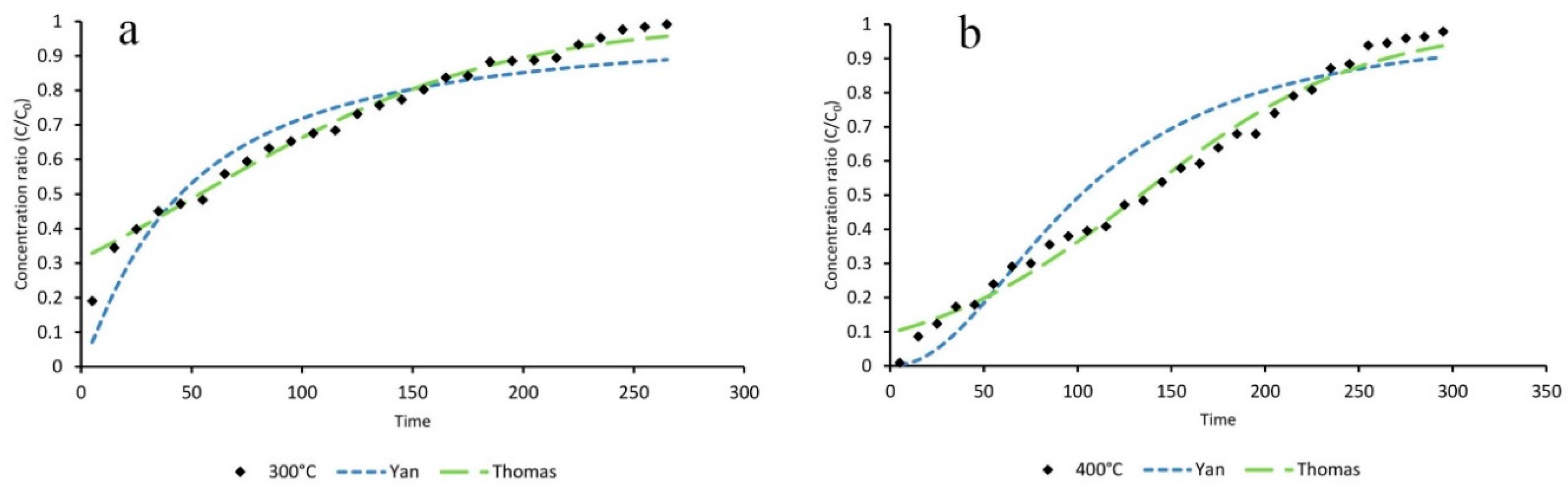
3.4. Mathematical Modeling
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cetin, E.; Odabasi, M.; Seyfioglu, R. Ambient volatile organic compound (voc) concentrations around a petrochemical complex and a petroleum refinery. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 312, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, J.J.; Hao, Z.P.; Li, L.D.; Qiao, S.Z. Dynamic adsorption of volatile organic compounds on organofunctionalized sba-15 materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Kannan, G.K.; Upendra, S.; Subha, R.; Kumar, N.S. Breakthrough of toluene vapours in granular activated carbon filled packed bed reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liotta, L.F. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds on supported noble metals. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 100, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, V.J.; Til, H.P.; de Vrijer, F.; Van Bladeren, P.J. Toxicology of volatile organic compounds in indoor air and strategy for further research. Indoor Environ. 1992, 1, 1016–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Creamer, A.E.; Cao, C.; Li, Y. Adsorption of vocs onto engineered carbon materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ang, H.M.; Tade, M.O. Volatile organic compounds in indoor environment and photocatalytic oxidation: State of the art. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, S.B.; Feng, Q.C.; Liu, J.X. Removal of o-xylene from off-gas by a combination of bioreactor and adsorption. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 3, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahna, F.G.; Golbabaei, F.; Hamedi, J.; Mahjub, H.; Darabi, H.R.; Shahtaheri, S.J. Treatment of benzene, toluene and xylene contaminated air in a bioactive foam emulsion reactor. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosillon, S.; Manero, M.-H.; Foussard, J.-N. Mass transfer in voc adsorption on zeolite: Experimental and theoretical breakthrough curves. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3571–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Long, C.; Li, A. Enhanced adsorption and desorption of vocs vapor on novel micro-mesoporous polymeric adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Deng, L.; Yuan, W.; Tao, B.; Cheng, H.; Chen, F. Facile preparation of hierarchically porous diatomite/mfi-type zeolite composites and their performance of benzene adsorption: The effects of naoh etching pretreatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, S.Z.D.; Cakmak, M.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Vogt, B.D. Large-scale roll-to-roll fabrication of ordered mesoporous materials using resol-assisted cooperative assembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4306–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, Z.; Gurkan, B.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Cakmak, M.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Vogt, B.D. Roll-to-roll fabrication of high surface area mesoporous carbon with process-tunable pore texture for optimization of adsorption capacity of bulky organic dyes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 227, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, H.; Varma, Y.B.G. Air Pollution Control Equipment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.-J.; Liu, S.-X.; Liang, D.-D.; Ren, G.-J.; Wei, F.; Chen, Y.-G.; Su, Z.-M. Adsorption of volatile organic compounds in porous metal–organic frameworks functionalized by polyoxometalates. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 3034–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuge, K.; Kubo, S.; Kikukawa, N.; Takemori, M. Effect of pore structure in mesoporous silicas on voc dynamic adsorption/desorption performance. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, D.; Tranchemontagne, D.; Yaghi, O.M. Metal-organic frameworks with high capacity and selectivity for harmful gases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebbers, M.T.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.; Masel, R.I. Trends in the adsorption of volatile organic compounds in a large-pore metal-organic framework, irmof-1. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11319–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (mofs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouni, R.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. Carbon dioxide adsorption in microwave-synthesized metal organic framework cpm-5: Equilibrium and kinetics study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 175, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouni, R.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. Mathematical modeling and experimental breakthrough curves of carbon dioxide adsorption on metal organic framework cpm-5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9372–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahri, M.; Haghighat, F.; Rohani, S.; Kazemian, H. Metal organic frameworks for gas-phase vocs removal in a ntp-catalytic reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, M.; Haghighat, F.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. A comparative study on metal organic frameworks for indoor environment application: Adsorption evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E.; Szulejko, J.E. Metal–organic frameworks for the control and management of air quality: Advances and future direction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. Mil-53(fe), mil-101, and sba-15 porous materials: Potential platforms for drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 47, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassen, I.; Burtch, N.; Talin, A.; Falcaro, P.; Allendorf, M.; Ameloot, R. An updated roadmap for the integration of metal-organic frameworks with electronic devices and chemical sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3185–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Liang, W.; Li, S.; Zou, F.; Bhaway, S.M.; Qiang, Z.; Gao, M.; Vogt, B.D.; Zhu, Y. A nitrogen doped carbonized metal–organic framework for high stability room temperature sodium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12471–12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Li, N.-X.; Li, Z.-R.; Wang, J.-R.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.-S. Preparation and gas separation properties of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks-8 (zif-8) membranes supported on silicon nitride ceramic hollow fibers. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 8949–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venna, S.R.; Carreon, M.A. Highly permeable zeolite imidazolate framework-8 membranes for co2/ch4 separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 132, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Cote, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Yao, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, H. Facile synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 from a concentrated aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 184, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, D.F.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Chapman, K.W.; Chupas, P.J.; Greathouse, J.A.; Crozier, P.S.; Nenoff, T.M. Capture of volatile iodine, a gaseous fission product, by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12398–12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Langner, E.H.G. The effect of synthesis temperature on the particle size of nano-zif-8. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 221, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ania, C.O.; Garcia-Perez, E.; Haro, M.; Gutierrez-Sevillano, J.J.; Valdes-Solis, T.; Parra, J.B.; Calero, S. Understanding gas-induced structural deformation of zif-8. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhao, L.; Lai, Z. Rapid synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (zif-8) nanocrystals in an aqueous system. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2071–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Yip, A.C.K. Thermal stability of zif-8 under oxidative and inert environments: A practical perspective on using zif-8 as a catalyst support. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 278, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y. In situ high pressure study of zif-8 by ftir spectroscopy. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12694–12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravillon, J.; Munzer, S.; Lohmeier, S.-J.; Feldhoff, A.; Huber, K.; Wiebcke, M. Rapid room-temperature synthesis and characterization of nanocrystals of a prototypical zeolitic imidazolate framework. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, E.L.; Fernandez, J.L.; Zamaro, J.M. Influence of the solvent in the synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (zif-8) nanocrystals at room temperature. J. Colloid. Interface. Sci. 2014, 424, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Q.; Lou, Y.; Xing, T.; Chen, J. Rapid synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (zif-8) in aqueous solution via microwave irradiation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2013, 37, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Ahn, H.-G. The adsorption and desorption characteristics of a binary component system of toluene and methylethylketone on activated carbon modified with phosphoric acid. Carbon 2010, 48, 2198–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Yang, B.; Xue, N.D. Enhanced adsorption of benzene vapor on granular activated carbon under humid conditions due to shifts in hydrophobicity and total micropore volume. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, H.; Zhao, B. Ion exchange adsorption studies of miglitol in a fixed bed. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Ghorbani, F.; Bahrami, A.; Kazemian, H.; Yousefinejad, S. Removal of toluene from air by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8: Synthesis, characterization, and experimental breakthrough curve. Int. J. Sci. Stud. 2017, 5, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, M.J.C.; Balkus, K.J.; Ferraris, J.P.; Musselman, I.H. Molecular sieving realized with zif-8/matrimid® mixed-matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, B.; Zhou, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y. Adsorption of toluene with water on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/graphene oxide hybrid nanocomposites in a humid atmosphere. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z. Adsorption and diffusion of benzene on chromium-based metal organic framework mil-101 synthesized by microwave irradiation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 2254–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lively, R.P.; Zhang, C.; Koros, W.J.; Chance, R.R. Investigating the intrinsic ethanol/water separation capability of zif-8: An adsorption and diffusion study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 7214–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küsgens, P.; Rose, M.; Senkovska, I.; Fröde, H.; Henschel, A.; Siegle, S.; Kaskel, S. Characterization of metal-organic frameworks by water adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.M.; Miró, E.E.; Boix, A.V. Ftir study of toluene adsorption on cs-exchanged mordenites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 127, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Viraraghavan, T.; Chen, M. A new model for heavy metal removal in a biosorption column. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cai, J.-G.; Pan, B.-C. Mathematically modeling fixed-bed adsorption in aqueous systems. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2013, 14, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
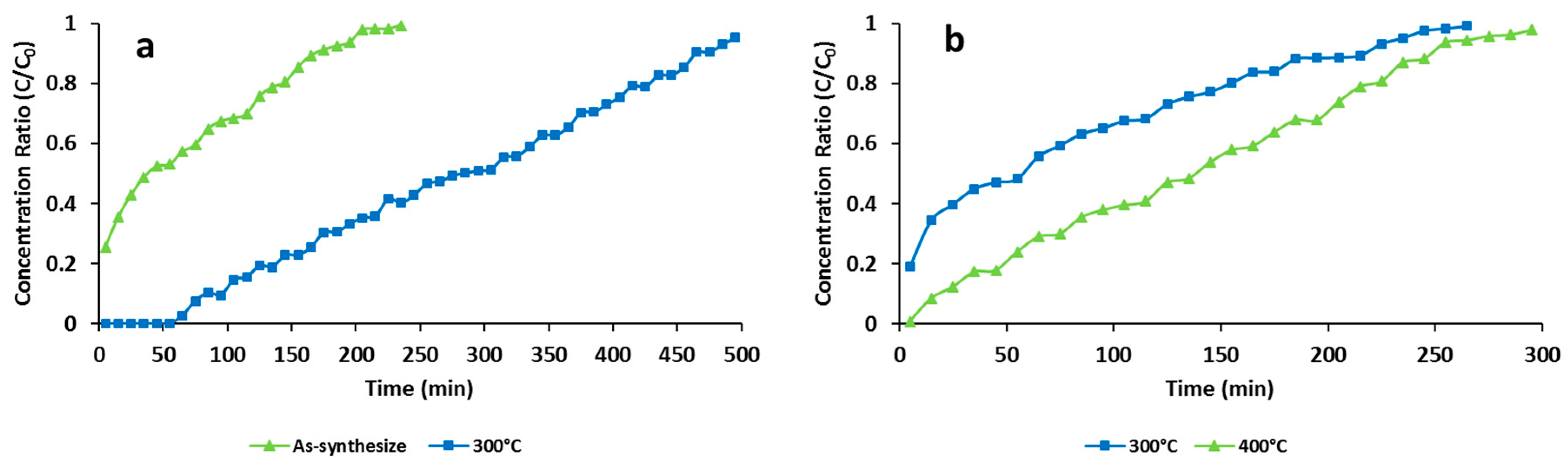
| Pretreatment Condition | Adsorption Capacity (mg∙g−1) | Total Adsorption Percentage (%) | Time of Breakthrough (min) | Time of Equilibration (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-synthesized | 131.43 | 26.84 | 0 | 205 |
| ZIF-8/Air/300 °C | 562.17 | 55.66 | 65 | 495 |
| ZIF-8/N2/300 °C | 155.31 | 27.48 | 0 | 265 |
| ZIF-8/N2/400 °C | 260.87 | 43.95 | 10 | 295 |
| Relative Humidity (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg∙g−1) | Total Adsorption Percentage (%) | Time of Breakthrough (min) | Time of Equilibration (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 410.9 | 48.8 | 55 | 435 |
| 60 | 354 | 48.9 | 55 | 405 |
| 80 | 203.3 | 33.8 | 5 | 335 |
| Statistical Parameters | As-Synthesized | ZIF-8/Air/300 °C | ZIF-8/N2/300 °C | ZIF-8/N2/400 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thomas | KT | 3.26 | 1.98 | 2.75 | 3.33 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| R2adj | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| RMSE | 0.034 | 0.043 | 0.022 | 0.038 | |
| SSE | 0.026 | 0.88 | 0.012 | 0.04 | |
| Yan | Ay | 1.11 | 2.37 | 1.17 | 2.1 |
| R2 | 0.84 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.93 | |
| R2adj | 0.84 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.93 | |
| RMSE | 0.086 | 0.044 | 0.071 | 0.077 | |
| SSE | 0.16 | 0.095 | 0.13 | 0.16 | |
| Adsorption Capacity | As-Synthesize (mg∙g−1) | ZIF-8/Air/300 °C (mg∙g−1) | ZIF-8/N2/300 °C (mg∙g−1) | ZIF-8/N2/400 °C (mg∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qT (Thomas) | 102.3 | 578.2 | 114.4 | 268.3 |
| qy (Yan) | 78.1 | 540.8 | 95.72 | 204 |
| q (Experimental) | 131.43 | 562.17 | 155.31 | 260.87 |
| Statistical Parameters | Relative Humidity (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 60 | 80 | ||
| Thomas | KT | 2.62 | 3.1 | 2.21 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| R2adj | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| RMSE | 0.052 | 0.054 | 0.041 | |
| SSE | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.055 | |
| Yan | Ay | 2.45 | 2.4 | 1.24 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| R2adj | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| RMSE | 0.053 | 0.054 | 0.06 | |
| SSE | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | |
| Adsorption Capacity | Relative Humidity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 60 | 80 | |
| qT (Thomas) | 416.3 | 360.1 | 152.6 |
| qy (Yan) | 379.7 | 328.4 | 137.2 |
| q (Experimental) | 410 | 354 | 203.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jafari, S.; Ghorbani-Shahna, F.; Bahrami, A.; Kazemian, H. Effects of Post-Synthesis Activation and Relative Humidity on Adsorption Performance of ZIF-8 for Capturing Toluene from a Gas Phase in a Continuous Mode. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020310
Jafari S, Ghorbani-Shahna F, Bahrami A, Kazemian H. Effects of Post-Synthesis Activation and Relative Humidity on Adsorption Performance of ZIF-8 for Capturing Toluene from a Gas Phase in a Continuous Mode. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(2):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020310
Chicago/Turabian StyleJafari, Saeed, Farshid Ghorbani-Shahna, Abdulrahman Bahrami, and Hossein Kazemian. 2018. "Effects of Post-Synthesis Activation and Relative Humidity on Adsorption Performance of ZIF-8 for Capturing Toluene from a Gas Phase in a Continuous Mode" Applied Sciences 8, no. 2: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020310
APA StyleJafari, S., Ghorbani-Shahna, F., Bahrami, A., & Kazemian, H. (2018). Effects of Post-Synthesis Activation and Relative Humidity on Adsorption Performance of ZIF-8 for Capturing Toluene from a Gas Phase in a Continuous Mode. Applied Sciences, 8(2), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020310