Abstract
Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC) differs from the normal concrete as it has the basic capacity to consolidate under its own weight. The increased awareness regarding environmental disturbances and its hazardous effects caused by blasting and crushing procedures of stone, it becomes a delicate and obvious issue for construction industry to develop an alternative remedy as material which can reduce the environmental hazards and enable high-performance strength to the concrete, which would make it durable and efficient for work. A growing trend is being established all over the world to use industrial byproducts and domestic wastes as a useful raw material in construction, as it provides an eco-friendly edge to the construction process and especially for concrete. This study aims to enlighten the use and comparative analysis for the performance of concrete with added industrial byproducts such as Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBFS), Silica fumes (SF) and Marble Powder (MP) in the preparation of SCC. This paper deals with the prediction of mechanical properties (i.e., compressive, tensile and flexural Strength) of self-compacting concrete by considering four major factors such as type of additive, percentage additive replaced, curing days and temperature using Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs).
1. Introduction
After the production of self-compacting concrete in the 1980s, it has become a very widely used type of concrete, which is highly able to penetrate the closely spaced steel bars without any compaction procedures. SCC differs from normal concrete as it is at a higher end in workability and the issues of segregation and bleeding are encountered in these types of concrete [1]. Nowadays, it is widely used in many developing countries for versatile applications, high rise skyscrapers, urban infrastructure and structural configurations. Use of SCC develops substantial advantages for the productivity of the construction work. The growing trend of utilizing waste materials and industrial byproducts in the production of useful entities is being practiced all over the world. Using materials that are nearly useless for any advantageous purpose to effectively increase the strength of concrete is an efficient way to counter the hazardous effects of such materials. By using different percentages of materials as replacement for cement in concrete mix of grade M20 (Mix ratio 1:1.5:3) and a suitable water-cement (w/c) ratio 0.40, there is a broad analysis of performance of such high strength concrete with respect to the different adding ratios by testing the mechanical properties of concrete such as its compressive strength, split tensile strength and flexural strength [2]. Fresh properties for the SCC have also been monitored and examined, including the V-Funnel test, J-Ring test and Slump test. All these were carried out for the detail examination of fresh concrete behavior. Tests for hardened concrete were carried out using samples of different ratios of materials as a replacement in hardened cylinder and cube form. Many samples were casted for the comprehensive testing process. The samples with replacement ratios of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% and 25% are tested thoroughly to analyze the hardened properties of mixes. By the utilization of these industrial byproducts and waste materials, an elevated level of pollution treatment can be achieved by the construction industry all over the world. This induction of materials in concrete tends to provide efficient and high strength ranging concrete mixes and is eco-friendly, too [3]. Previously much discussion was had on replacement of cement with Fly Ash and Marble Powder [4,5,6,7,8,9], but Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBFS) [4] was limited in use. Therefore, this research has contributed the comparison of Fly Ash and Marble powder with GGBFS not only at room temperature but also at elevated temperature. Furthermore, most previous studies only major focused on compressive strength [4,5,6,8,10,11,12,13]. However, in this research tensile and flexural strength has also been studied. Self-compacted concrete (SCC) is one of the famous types of concrete but addition of industrial waste additives to partially replace the cement and treating concrete at elevated temperature in SCC has been proposed for the first time in this study. Performance of concrete in normal environment and elevated temperature gives a comparative analysis. The property of concrete to sustain in elevated temperature environments provides an opportunity to test its behavior during fire in structures. Employment of such wastes and their beneficial effects for structures are observed in this study.
Although Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is famous in predicting Compressive strength of self-compacting concrete (SCC) [14,15,16,17], in this study, new variables have been tested, which are basically related to change of additives, curing conditions, change of type of additive and percentage of additives. Taking advantage of prediction with multiple inputs and multiple outputs, compression, tensile and flexural Strength have been predicted through ANN.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Major Ingredients
2.1.1. Silica Fume
Silica fume is the term normally used for the micro silica or the condensed silica byproduct produced as a result of the production of Silicon and Ferrosilicon alloys from highly pure form quartz and coal in an electric submerged-arc. The advantage of utilization of Silica fume in concrete gives special characteristics to concrete such as the reduced permeability property, improved corrosion protection for steel bars, increased resistance against the sulfate and chemicals attacks, improved and efficient mechanical strengths and performances and elevated levels of split tensile and flexural strengths [18]. The replacement of cement with different percentages of Silica Fumes, i.e., 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% and 25%, enables analyzing and interpreting clear results of the performances incurred by this valuable replacement. SF reacts with concrete in two different ways: by modifying hydration reaction in concrete and by its very well known “Micro-filler effect”. Upon adding water to the Portland cement in the concrete, hydration process starts; thus, the two primary products are formed [19]. The first resultant product is “Calcium silicate gel”. It is a “glue” of adhesive nature to bind aggregates together in concrete mix. The other product is “Calcium hydroxide”, which comprises up to 25% volume of products formed because of hydration. Calcium hydroxide at higher levels is not useful for the concrete and induces the harmful alkali-aggregate reactions and efflorescence. The second major and efficient process through which the SF improvises concrete is the known “Micro-filler effect” [20]. Average particle size for the dense SF is about 0.1 micrometers, while the ordinary Portland cement has average particle size of about nearly 15 micrometers. The extremity in fineness of SF allows filling in the microscopic voids and gaps between the particles of cement [21]. Micro-filter effect greatly improves and reduces permeability and improves the important “Paste-to-Aggregate bond” in the SF concrete as compared to the conventional ordinary concrete used in common practice. There is no major visible difference in the moisture absorption percentage for both SF and ordinary concrete. The shade of the Silica Fumes depends mainly upon the carbon content in it and pigment inducing variables present in composition contents.
2.1.2. Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBFS)
Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag is a non-metallic powder that consists of some Silicates Aluminates of Calcium and other useful bases [22]. Molten slag is cooled by quenching in water which enables the formation of glassy sand-like material. The basic chemical composition for GGBFS is same as that of cement clinkers. Performance of the slag mainly depends upon the basic chemical composition and fineness. In a similar manner, the Slag is replaced by 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% and 25%. Performance of SCC with the GGBFS is analyzed by testing the basic fresh properties of concrete; in addition, its useful mechanical behavior and durability will be affected by incorporating GGBFS as beneficial replacement of the Portland cement. The effects caused by the replacement of slag depend solely upon the percentage of slag used and the fineness of material. There are different manners by which the replacement of slag with Portland cement affects the basic properties of SCC. Slag affects the important most property of concrete which is workability, by the tests performed and analysis of results it is concluded that higher performance extent is achieved using relatively higher contents of slag (GGBFS) [23]. The degree of fineness of slag does not increase workability for the concrete [24]. The replacement of GGBFS does not significantly affect the bleeding issues for concrete. The risk factor and important issue of the “Autogenously Increasing Temperature” for SCC and major associated “Thermal stresses” and “Cracking” are also considered upon addition of slag elements in SCC [11,25,26]. Setting period for GGBFS concrete mainly depends on the reactivity of the slag used and its employed percentage present in the mix. The use of slag, however, causes a lower gain of initial strength at seven days, while significantly higher strengths at 28 days of sample cured in water. In summers or warm weather sites, the final strength attained can be higher as compared to the ordinary Portland cement [27]. The replacement of the GGBFS in SCC increases its broad resistance against the chloride-ion attack, mainly at some later period of concrete life [28]. This helps to improve chloride binding in concrete. This turns out to be highly beneficial for the key protection of the important element of structures which is the prevention of steel from internal corrosion and deterioration. The resistance against the freeze and thaw cycle for concrete structures in cold climatic areas is not affected by using the GGBFS in a mix of SCC [29]. The following cycle is a direct function related to the evident air-void spacing factor for the concrete, which is mainly obtained by using the additional elements in concrete properly such as the air-entraining admixtures. Sulfate attack resistant concrete with GGBFS entails the replacement of more than 25% by mass of cement used. The replacement of slag in proper fine percentages more than about 20% can be utilized to tackle the expansion due to the alkali-silica reactions in concrete with GGBFS. Carbonation extent in the GGBFS concrete may rise even more than simple concrete if it is not properly treated and cured for the full required period [30]. Durability and the extent of resistance to damage and permeability effects in marine saline environments are far more increased and concrete because of its key useful chloride ion attack resistant nature [31].
2.1.3. Marble Powder (MP)
The addition of Marble Powder as a partial replacement for Portland cement is highly beneficial on large-scale works due to versatile advantages of Marble dust powder. The marble powder obtained by the processing of marble serves as a waste material. In this paper, the usage of marble powder produced during the shaping, grinding and processing of large marble blocks is investigated in the considered concrete mix as an effective acting material. The concrete mix prepared contains varying amounts of Marble Powder: 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% and 25% of the replacement for the total cement used. The prepared samples are observed and cured for 7, 14, 21 and 28 days and tested in the hardened form of cubes and cylinders. During the tests, the hardened properties such as compressive strength, split tensile strength and flexural strength are mainly analyzed. It is observed that the main influence made by the fine to coarse aggregate ratio and also the cement to total coarse aggregate ratio makes a considerably higher effect in improvising strength percentage for the properties of all samples [32]. Phenomenal elevation for compressive strength at seven days for 25% replacement of marble powder with ordinary Portland cement in the cylinder was observed and it shows improved strength properties as compared to the ordinary concrete. Important effects caused by the use of marble powder as a replacement for the fine aggregates in a mortar and the concrete by the partial reduction of cement quantities have been observed for the relative compressive, tensile and flexural strength of the prepared mix [33]. Partially replacing the cement with the waste marble powder and testing it shows that, with increased ratios of MP, greater elevated strengths are achieved. The direct exposure of waste materials to the open environment causes fatal environmental issues leading to increasing the drastic effects of damage for the environment [34]. Basic properties of major additives have been elaborated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Properties of major additives.
2.1.4. Superplasticizer
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is a modified form of concrete with “Superplasticizer” as an essential part of the mix. Superplasticizers are used for producing a flowing concrete in scenarios where placing of concrete is normally inaccessible or in castings where very rapid placement is required [35]. Another key use of plasticizer in concrete is the production of High Strength Concrete with normal workability but a low water–cement ratio. For the production of high strength concrete, when admixtures are added as an integral part of the mix in the form replacement, they absorb water, thus reducing the water content and ultimately hinder the workability and amount of water required for hydration process. These superplasticizers are the sulfonated melamine formaldehyde condensates or sulfonated naphthalene formaldehyde condensates [36]. The plasticizer used in work is the “Super Plasticizer by Ultra Chemicals” and it is the “Sulfonated Naphthalene Formaldehyde condensate” preferred in work because of its prominent dispersing action on cement. The sulfonic acid in it tends to disperse the cement particles by being adsorbed on them and inducing a negative charge on them making them mutually repulsive in nature [37]. This leads to elevating the workability of concrete at given w/c ratio. The main disadvantage of such superplasticizer is the production cost elevates because such plasticizers with high molecular mass are expensive to manufacture [38].
2.2. Concrete Preparation and Testing
2.2.1. Development of Concrete
Self-Compacting concrete is a useful mix prepared by induction of super plasticizer in normal conventional concrete. Similar to many innovative products, SCC was developed out of social necessity. The fine aggregate size is the reason SCC has a lower viscosity as compared to conventional concrete without the demand of increased hydration. An efficient mix design is prepared for the SCC. Different ratios are chosen to test and develop the most efficient and beneficial mix. Self-compacting concrete uses about 2–3% superplasticizer as an admixture to gain high levels of workability. At lower w/c ratios by adding plasticizer, we can achieve a good slump for concrete. It is prepared similar to ordinary concrete, just the addition of plasticizer after water is added to mix develops the qualities of good workability and easy placement for SCC. The J ring, V funnel, fresh mix and Slump tests are performed. A normal mechanical mixer is employed to prepare the SCC. Due to high mobility nature, it is far more easy to handle and place as compared to conventional concrete [4,39]. Fresh concrete is prepared in mixer machine and, during the mixing process, the required replacement for the ordinary cement is done. SF, GGBFS and MP are added to the mixes and cubes of dimensions 150 mm by 150 mm by 150 mm are cast; prisms of size 100 mm by 100 mm by 500 mm; and cylinders with dimensions of 150 mm by 300 mm are cast. All samples were allowed to cure in curing tanks filled with fresh water. The curing process is done for 7, 14, 21 and 28 days. After curing, cube samples are dried in heat ovens at about 300–450 °C for 20 min. Heated cube samples and other sun-dried samples of cylinders and prisms are tested in a Compression Test Machine available in the lab of the institute. The strength tests were carried out carefully on best-attained samples from the stock of casted samples for different percentage replacements. The mixing proportion is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Quantities for mixing and development of concrete.
2.2.2. Properties of Fresh Concrete
Fresh properties of concrete are investigated by the fresh concrete tests of SCC which includes the V-funnel test, J-Ring test and Slump test [39]. Fresh Properties of mix are observed and results are as follows.
Slump Test: The standard apparatus for the slump test was used to carry out the examination of the flow if concrete and its workability. The SCC mixes showed efficient results of a slump for the workability. Slump values are used to visualize the performance of SCC during placement [40].
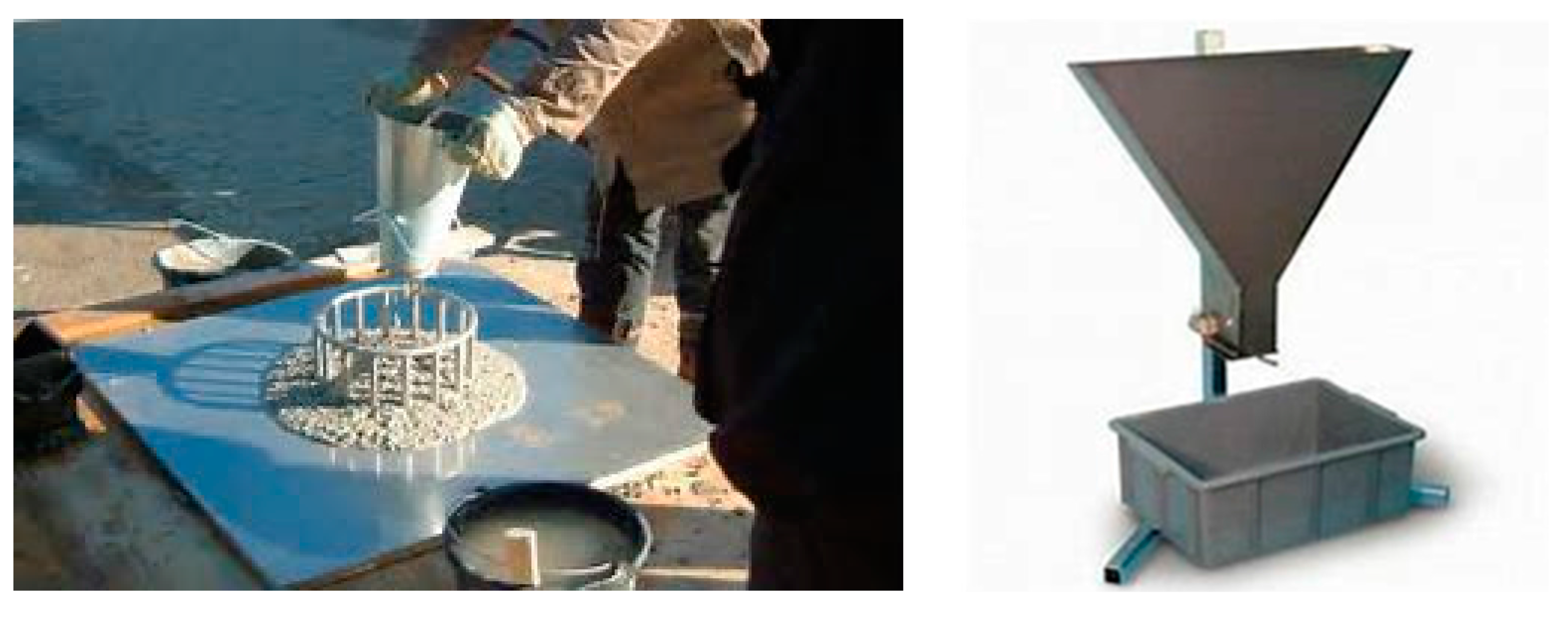
V-Funnel Test: Standard apparatus for the V-funnel test is employed to perform this test. The test was performed in lab and the time was recorded for the flow using a stopwatch. The v-funnel test enables us to analyze the flow pattern of concrete through the congested bars of steel reinforcement in the structure (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Standard J-Ring and V-Funnel test apparatuses.
J-Ring Test: For the analysis of fresh properties of SCC, we performed the J-Ring test for the evaluation of flow ability of concrete with additional replaced percentages of materials [39]. Standard J-Ring apparatus available in the lab made according to BS specifications is used to perform the test. Distance span is carefully examined. This test enables us to overview the pattern of the concrete inside steel bars of reinforcement. The standard testing equipment is shown in Figure 1.
Table 3 explains the results from the tests performed on fresh concrete.

Table 3.
Properties of fresh concrete.
2.2.3. Properties of Hardened Concrete
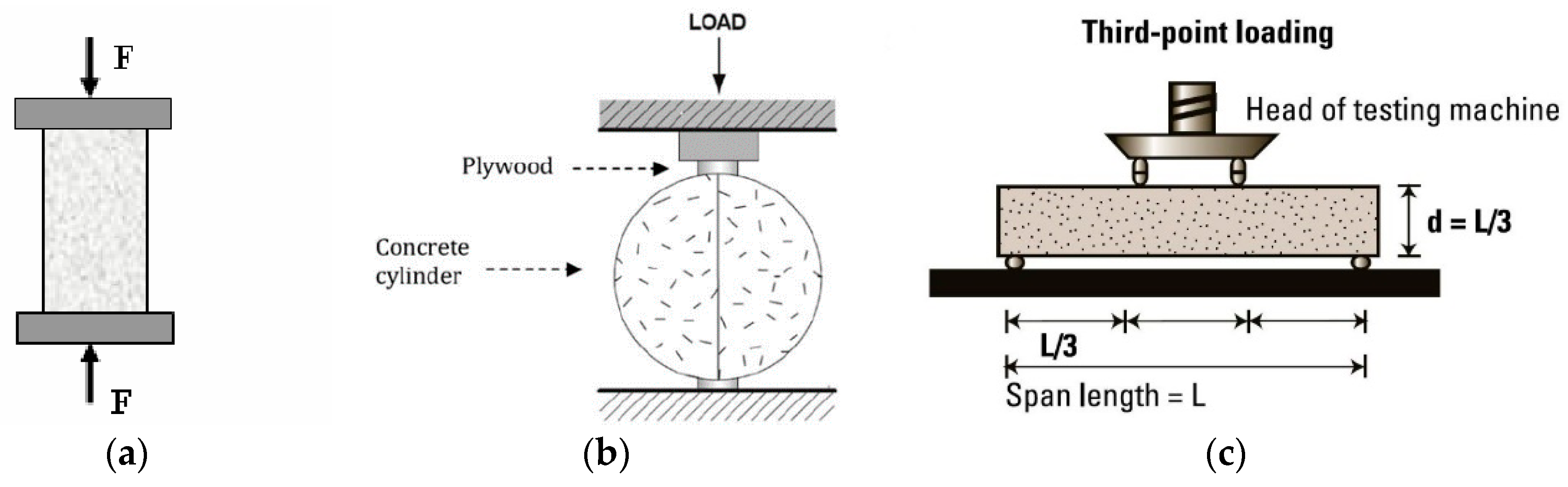
The Mechanical properties are the basic and most important characteristics of concrete upon which the durability, performance and deterioration resistant nature of concrete depend [39]. The properties, such as compressive strength, split tensile strength and flexural strengths are responsible for the behavior of concrete under specific loading conditions. These properties are largely affected by the materials used, size of aggregates, their types and also the WC ratio for the mix [41]. Using SF, Slag and MP as a replacement of cement in the concrete mix render it to achieve an elevated level of durability and strength increment. Testing of handed concrete plays a vital impact in studying the behavior of developed concrete; usually there are three major tests involved in studying concrete behavior: (i) compression test; (ii) indirect tensile test; (iii) flexural strength test (Figure 2).
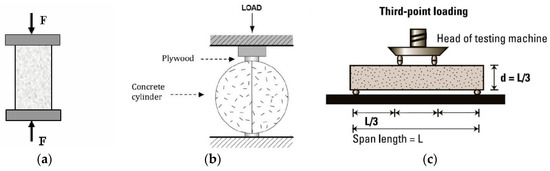
Figure 2.
(a) Compression; (b) split tensile; and (c) flexural strength test mechanisms.
Compression test is related to the testing of load bearing capacity of concrete. To evaluate the strength of concrete, two types of samples are developed: cube (6′′ × 6′′ × 6′′) and cylinder (6′′ × 12′′). The crushing strength or bearing capacity of concrete against crushing determines the load bearing of concrete. Moreover, Indirect Tension test, also known as Brazilian and Japanese test, is conducted to test the vertical impact of compressive load on cylinder subjected to load in horizontal shape to test its tensile strength. To reduce the higher impact of stress on surface of concrete, a plywood strip is placed at point of application. One of the weak points of concrete is its resistance against tension, which is why steel reinforcement is used to bear the tensile loading but it is necessary to know the tensile strength or modulus of rupture [39]. Flexural test is conducted on concrete specimen of beam. Actually, there should be some resistance by concrete before cracking starts and load is shifted to reinforcement. The assembly shown in Figure 2 is a three-point loading mechanism for which cracks can produce at any part of beam. By evaluating concrete performance by these three tests, one can easily evaluate the concrete strength and behavior under changing behavior.
2.2.4. Temperature Treatment
The phenomenon of fire resistance is studied by applying a stage-wise temperature treatment mechanism to concrete to evaluate its resistance to the elevated temperature. Most researchers have tested the behavior of concrete under elevated temperature and observed that there is an increase in strength of concrete in initial stages of temperature (up to 400 °C) and later it tends to decrease with the increase in temperature [27,29]. Presence of dampness in concrete leads to physical and compound changes in the microstructure of concrete and consequently impacts the variety of warm conductivity with temperature. Warm conductivity is typically estimated by methods for “enduring state” or “transient” test techniques. Transient strategies are preferred to measure the conductivity of wet cement over unfaltering state strategies. Researchers have tested Self Compacted Concrete to an elevated temperature within a range from 0 °C to 600 °C and a decrease in strength after 400 °C has been observed during the temperature treatment process.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compressive Strength
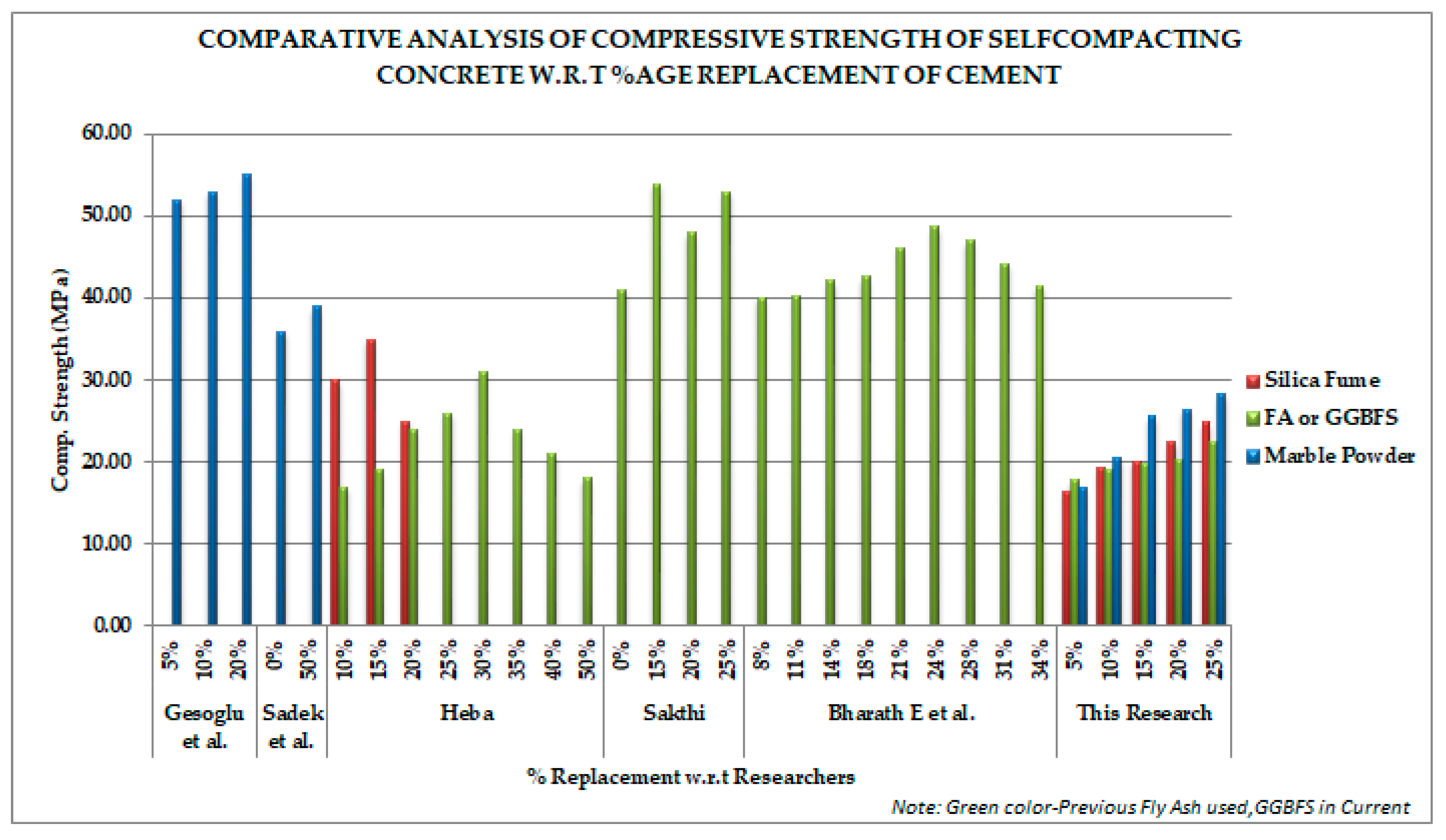
Samples were tested for the determination of compressive strength. Three samples for each ratio (six ratios) and for each material (three materials) were developed and tested. Temperature variation was from room Temperature (27 °C) to 400 °C. Samples were also tested beyond that limit at 500 °C but they were unable to be tested for compressive strength because of spalling. Compressive strength can be observed at both room temperature and elevated temperature in Table 4. With the change of percentage, the behavior of marble powder (MP) was found best compared to its other two competitors (i.e., S.F and GGBFS).

Table 4.
Test Results for hardened self-compacted concrete (compressive strength, MPa).
Furthermore, comparative analysis with previous studies shows that strength of concrete can be explored with all three additives depending on their availability and economics because there is very little difference in highest strength values (Figure 3).
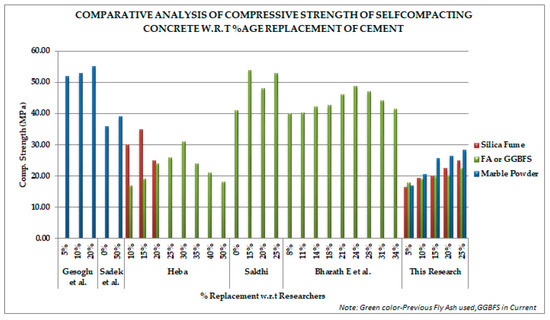
Figure 3.
Comparative compressive strength trend with respect to cement replacement of previous studies (Gesoglu [7], Sadek [9], Heba [8], Sakthi [42] and Bharath [5]).
3.2. Indirect Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is one of the important features, as concrete is highly vulnerable to cracking. A standard test cylinder is placed horizontally between the loading plates of the compression machine and failure of the cylinder along vertical diameter is observed. Three samples for each ratio (six ratios) and for each material (three materials) were developed and tested. Temperature variation was from room Temperature (27 °C) to 400 °C. Samples were also tested beyond that limit at 500 °C but they were unable to be tested for tensile strength because of spalling.
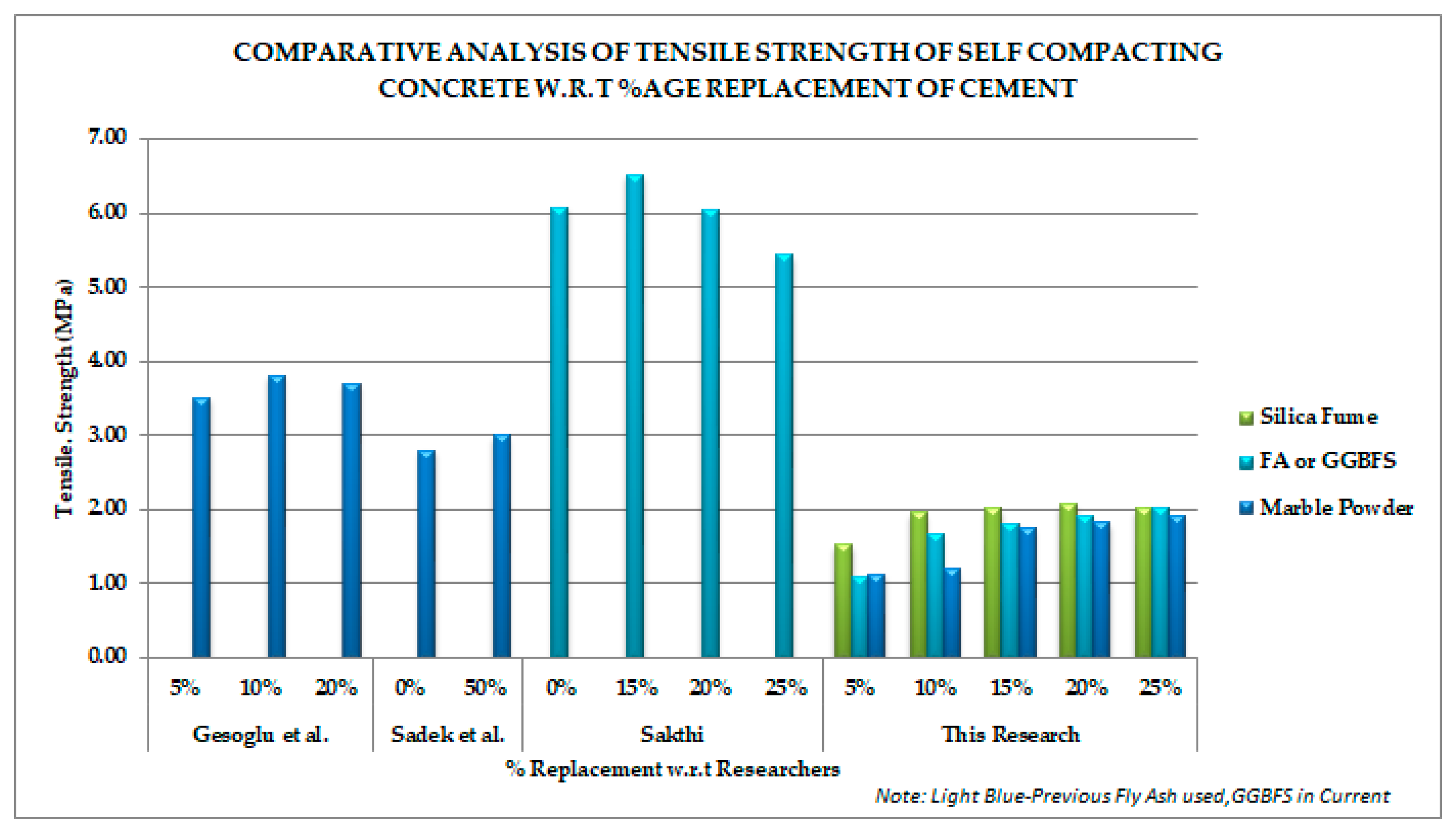
With the change of percentage, the behavior of marble powder (MP) was found best compared to its other two competitors (i.e., S.F and GGBFS). Furthermore, comparative analysis shows that strength of concrete can be explored with all three additives depending on their availability and economics because there is very little difference in highest strength values, as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Test results for hardened self-compacted concrete (tensile strength, MPa).
Comparative analysis with the previous studies shows that trend remains almost same with the change of additive percentage (as shown in Figure 4). Most studies have shown up to 20% higher strength than control samples.
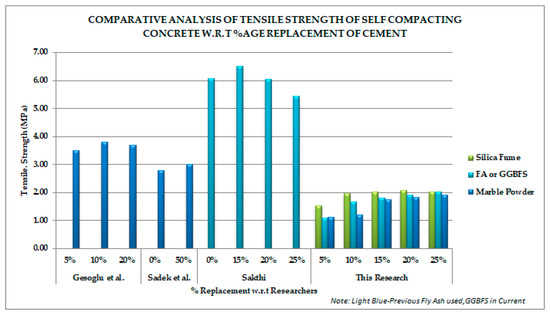
Figure 4.
Comparative tensile strength trend with respect to cement replacement of previous studies (Gesoglu [7], Sadek [9] and Sakthi [42]).
3.3. Flexural Strength
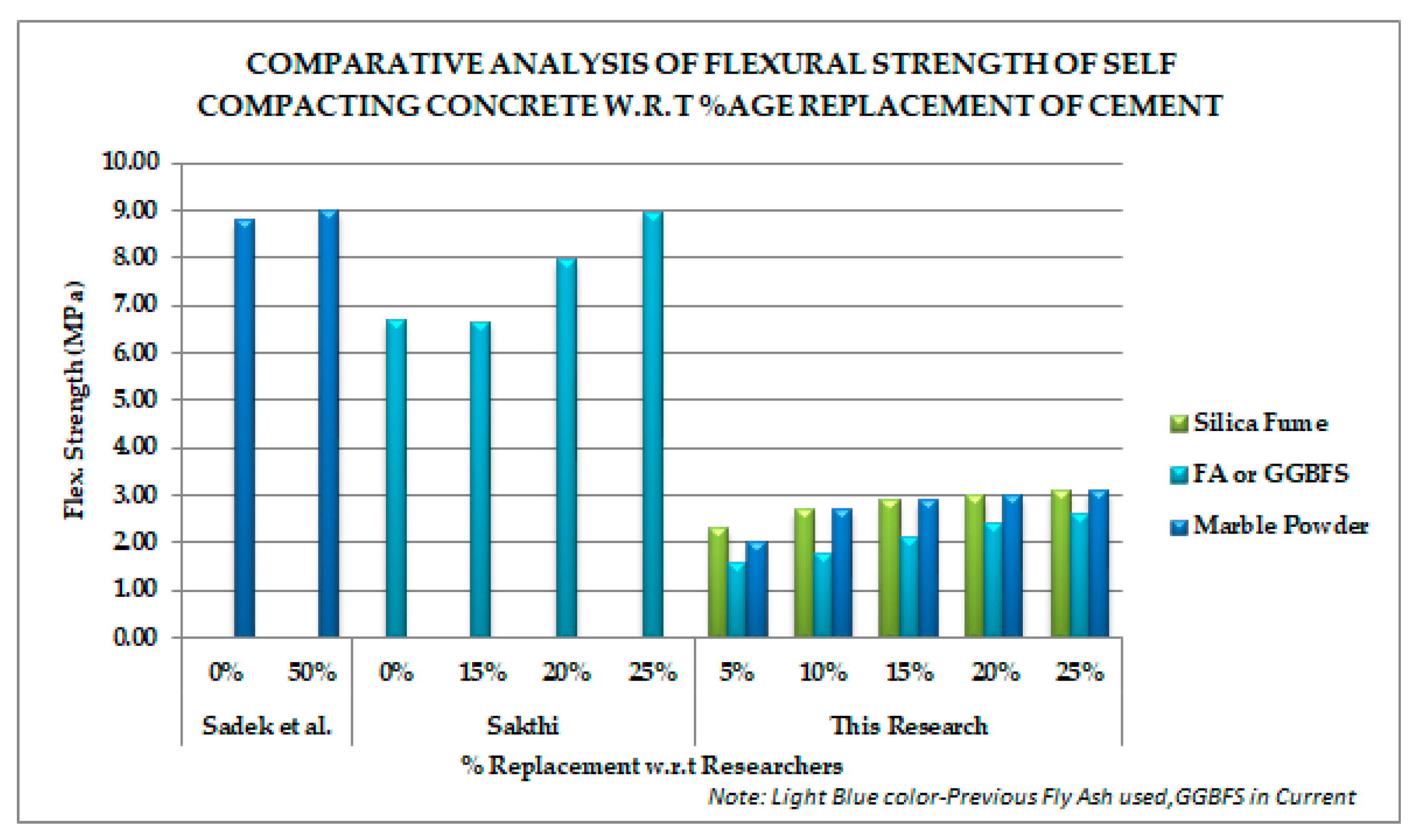
Flexural strength is one measure of the tensile strength of concrete. The resistance of a concrete beam against loading is measured to evaluate flexural strength. Three samples for each ratio (six ratios) and for each material (three materials) were developed and tested. These beams were subjected to three-point loading mechanism. Temperature variation was from room Temperature (27 °C) to 400 °C. Samples were also tested beyond that limit at 500 °C but they were unable to be tested for flexural strength because of spalling. Comparative flexural strength can be seen in Table 6 for comparative analysis.

Table 6.
Test results for hardened self-compacted concrete (flexural strength, MPa).
Flexural strength in comparative analysis shows that trend in the previous research is an increasing one, which is similar to the current study (Figure 5).
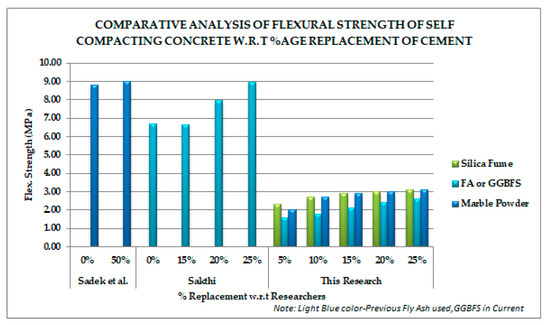
Figure 5.
Comparative flexural strength trend with respect to cement replacement of previous studies (Sadek [9] and Sakthi [42]).
3.4. Strength Prediction and Relationship Analysis
Inside a decade, analysts have investigated the capability of Artificial Neural Networks systems (ANNs), a nonlinear displaying approach, in anticipating the compressive quality of solids, because of its capacity to learn input–yield connection for any difficult issue in a productive way. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) does not require particular condition frame [11]; rather, it just needs adequate input–yield information. It can likewise persistently retrain new information to adjust new information helpfully. ANNs have been explored to manage the issues including inadequate or lost data. The capacity of the manufactured neural system to be an all-inclusive estimator has been generally used to show issues in which the connection among needy and free factors is not unmistakably found. At the point when the quantity of segments increases, the connection between factors turns out to be generally complex. Furthermore, the utilization of a nonlinear displaying approach is required. Recently, ANNs have been connected to numerous structural building applications with some level of progress. ANNs have been connected to geotechnical issues such as the expectation of settlement of shallow establishments [43]. Scientists have additionally utilized ANN in auxiliary building [44]. A few scientists have recently proposed another technique of blend plan and forecast of solid quality utilizing neural organize. Additionally, a few works were accounted for on the utilization of neural organize based demonstrating approach in anticipating the solid quality [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. A few endeavors have been made to portray the compressive quality properties utilizing conventional relapse investigation apparatuses and factual models [15,16,17]. In any case, the improvement of neural system models for anticipating the quality of SCC has not been completely explored. In this manner, it was required to create some reasonable technique to gauge the compressive quality of self-compacting concrete in view of its constituents at the season of the outline. Thus, the goal of the present examination was to inspect the capability of ANN for foreseeing the 28-day compressive quality of SCC blends, with information acquired from writing [11]. These models were additionally connected to forecast of quality at 7, 14, 21 and 28 days to the information acquired tentatively. The perplexing relationship between blend extents and building properties of SCC was produced in view of information acquired tentatively. It was observed that the neural system could successfully anticipate compressive quality, regardless of many-sided information and could be utilized as an instrument to help basic leadership, by enhancing the effectiveness of the procedure. Descriptive data used for ANN modeling purpose are shown in Table 7. Four Major factors were considered that have not previously been discussed for modeling purposes regarding SCC. As the target was to explore and predict the mechanical properties and impact of change of curing days, percentage replacement of cement, change in type of additive and elevation in temperature (from room temperature to 400 °C), this study is a new addition to the existing literature. Previously, only compressive strength was target predictor in research.

Table 7.
Descriptive statistics of parameters for self compacted concrete.
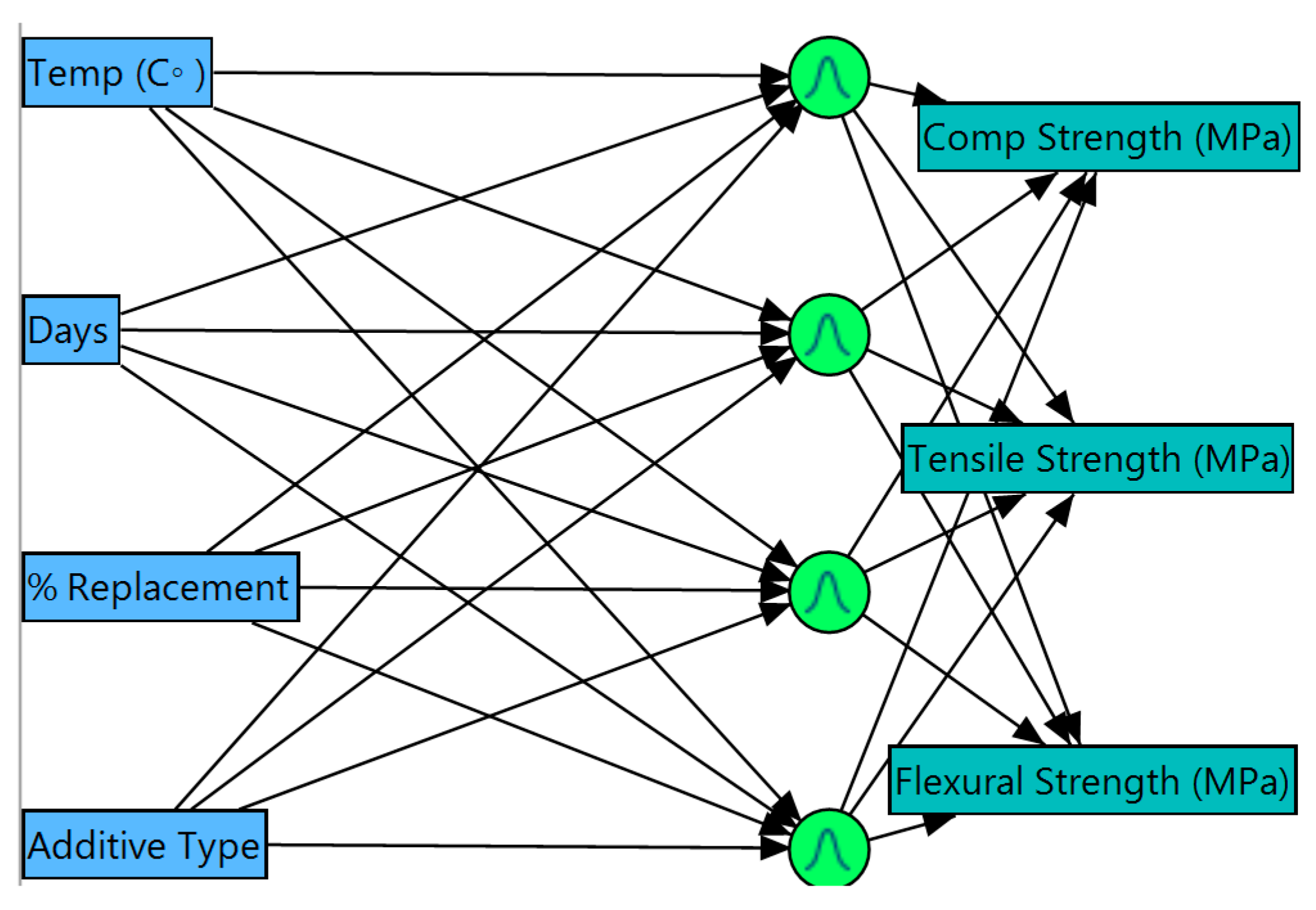
The Artificial Neural System shown in Figure 6 displays analogies to the path varieties of neuron work in organic learning and memory. The major building pieces are units (“hubs”) practically identical to neurons, weighted associations that can be compared to neuro transmitters in organic frameworks. Hubs are straightforward data handling components. The number of hubs in ANNs and the association examples of the hubs can differ. The aggregate number of hubs in the information and yield layers concur with the quantity of information and yield factors in the information set. The perfect number of hubs in the concealed layer must be found through experimentation. It is realized that more neurons give the capacity to retain and lessen the thinking ability of the ANN. When in doubt, an ANN should contain the base number of neurons that are equipped for reproducing the preparation information. Every association between hubs conveys a weight speaking to some past learning process. By shifting these weights, the input–output connection can be simulated. The system must be prepared to imitate this input–yield connection, which is to discover the ideal weights.
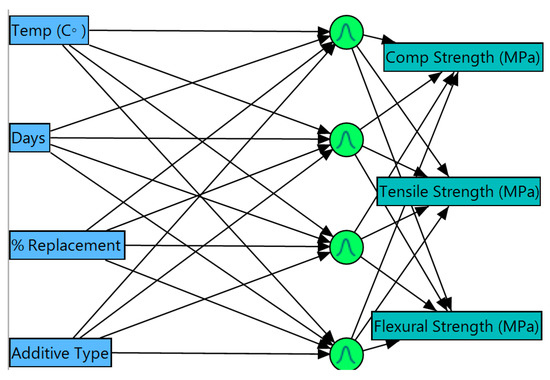
Figure 6.
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) structure for self-compacted concrete.
3.4.1. Model Parameter
Preparation comprises: (i) computing yields from input information; (ii) looking at the deliberate and ascertained yields; and (iii) altering the weights for every node to diminish the distinction between the estimated and computed values. The exactness of the forecasts of a system was measured by the foundation of the root mean squared error (RMSE), between the actual and the predicted values, mean absolute error (MAE) and the various coefficients of determination (R2) [11].
where SSE is sum of squared errors of prediction and SSy is total variation. Mean absolute error is similar to root mean square except using absolute difference instead of squared difference. Usually, performance of a model is compared by coefficient of determination (R2). A classic fit would bring about a R2 of 1 and poor fit almost 0 [11]. The plan of a manufactured neural system requires the assurance of appropriate engineering. A back-propagation neural system based demonstration calculation requires setting up various learning parameters (e.g., learning rate, momentum, etc.), the ideal number of nodes in the hidden layer and the quantity of hidden layers to have a less unpredictable system with a moderately better prediction capacity. In most applications, choice of various hidden layers and the quantity of nodes in hidden layer is finished by utilizing a general guideline or attempting a few subjective structures and choosing one that gives the best execution [11]. Further, a reasonable estimation of parameters such as learning rate is likewise required for chosen hidden layers and nodes. The acknowledgment/dismissal of the model created are resolved by its capacity to anticipate the quality of SCC. Additionally, an effectively prepared model is portrayed by its capacity to foresee quality esteems for the information it was prepared on [11]. A five-folded (k-folded) cross validation is utilized to foresee the quality for the informational collection utilized. Cross-validation is a technique for showing the exactness of an arrangement. The informational index is separated into a few parts (a number characterized by the client), with each part used to test a model fitted to the rest [11]. The relationship coefficient, root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error is utilized to judge the execution of the neural system approach in anticipating the quality. Measurable techniques are regularly utilized as part of the advancement of exact connections between different interfacing factors [11]. This is usually difficult, especially for nonlinear connections. Likewise, to find the measurable model, the essential parameters must be known. By correlation, the displaying procedure in back-propagation neural systems is more straightforward, as there is no need to determine a scientific connection between the input and output factors. Neural systems can be compelled for breaking down a framework containing various factors, to predict the unknown features or properties [11]. Table 8 shows the estimated parameters and prediction of the compressive, tensile and flexural strength of the concrete. Data have been divided into five folds (K-fold mechanism was employed) to get the best results by applying ANN to all parts of the dataset and an average is determined as the most suitable predicted value for both training and validation dataset.

Table 8.
Model parameter estimates for training and validation data.
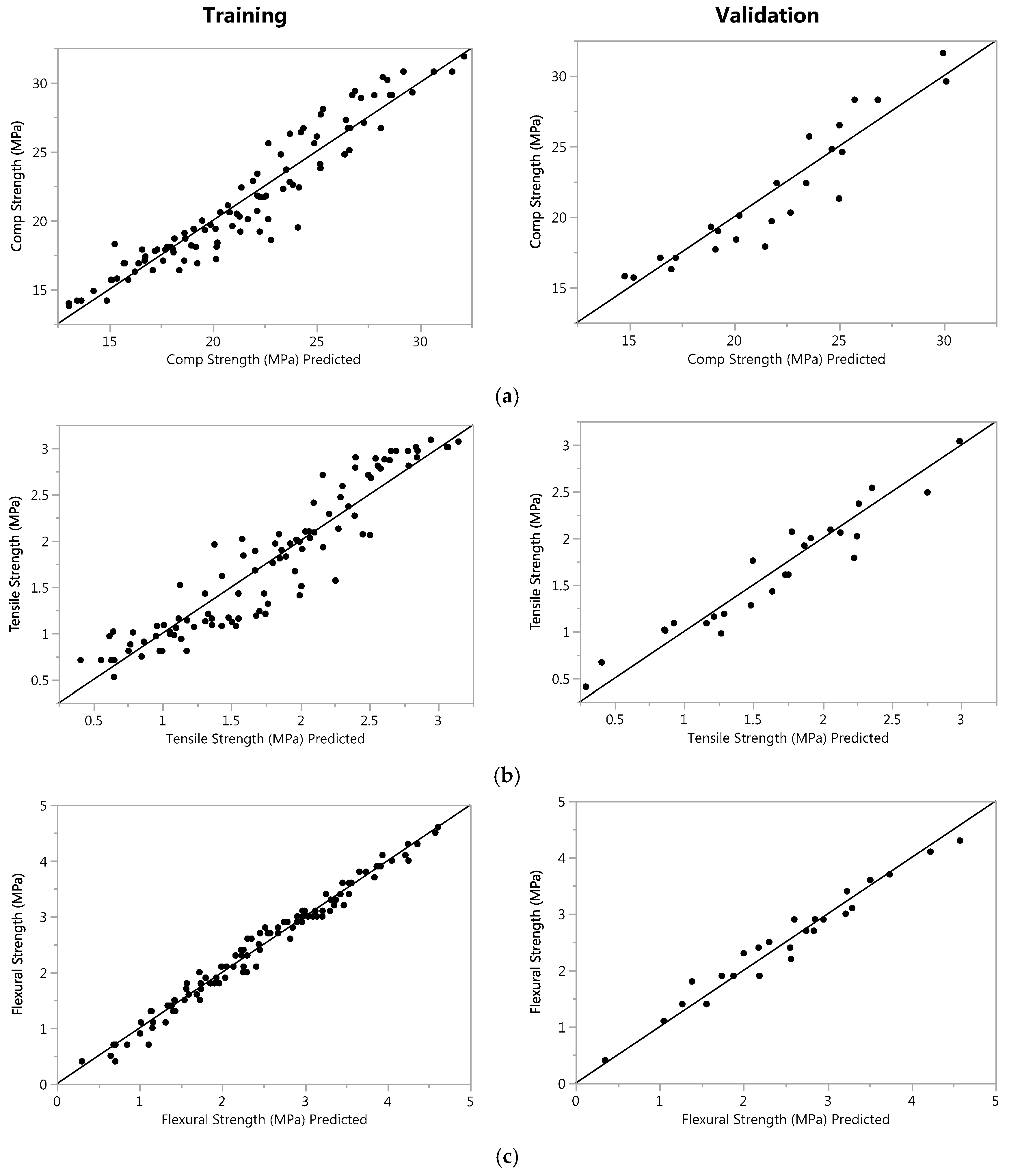
Data were distributed in testing and validation sets. Testing was done through K-validation mechanism (i.e., usually for validation, one third is selected for validation but in case of less number of sample sizes, 5 folded validation techniques better because it divides small subsets and then validate (Figure 7)).
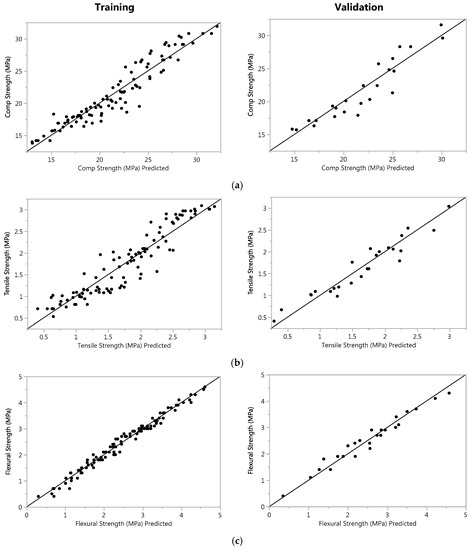
Figure 7.
Training and validation plots for: (a) compressive strength; (b) tensile strength; and (c) flexural strength.
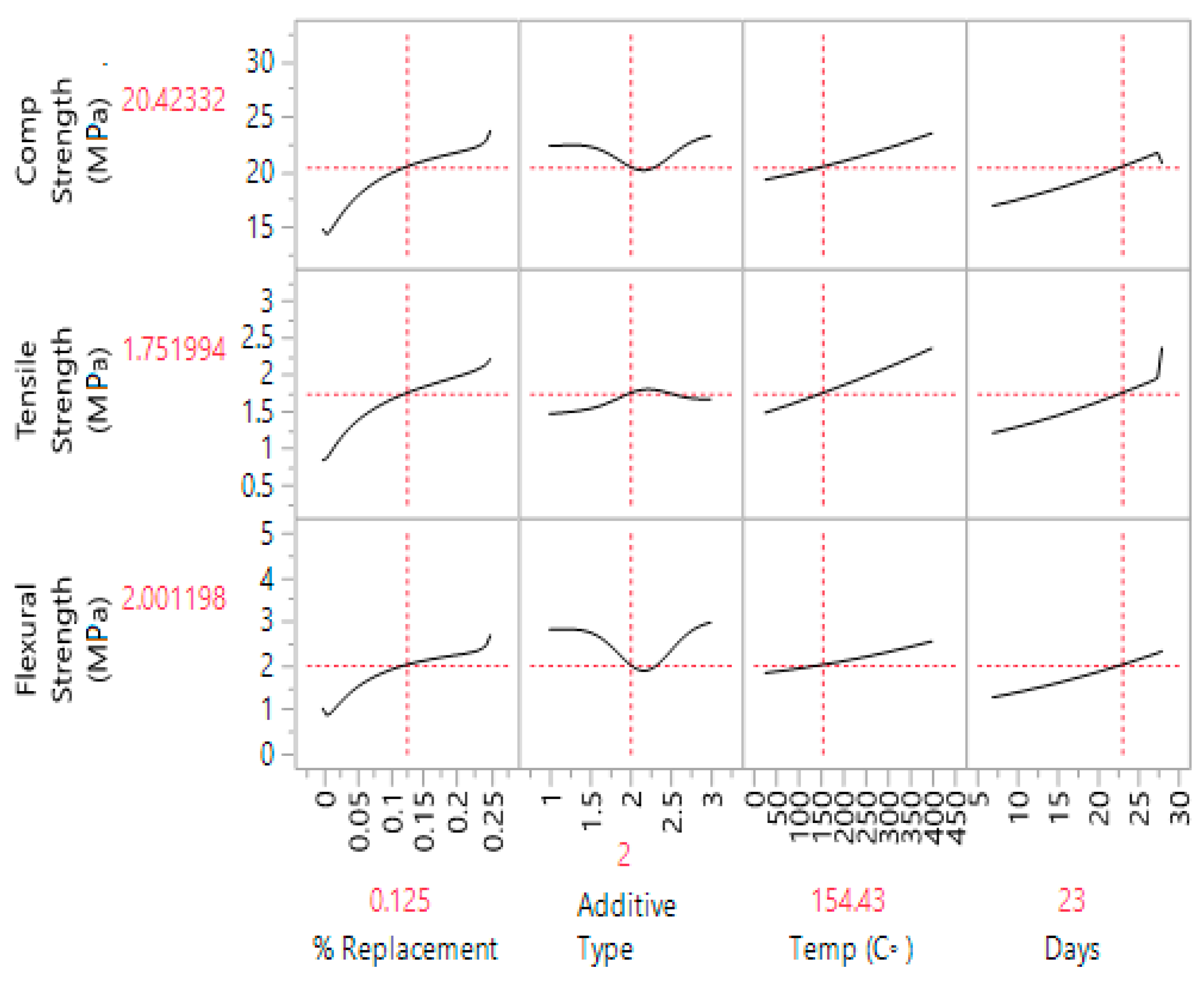
3.4.2. Prediction Profiler
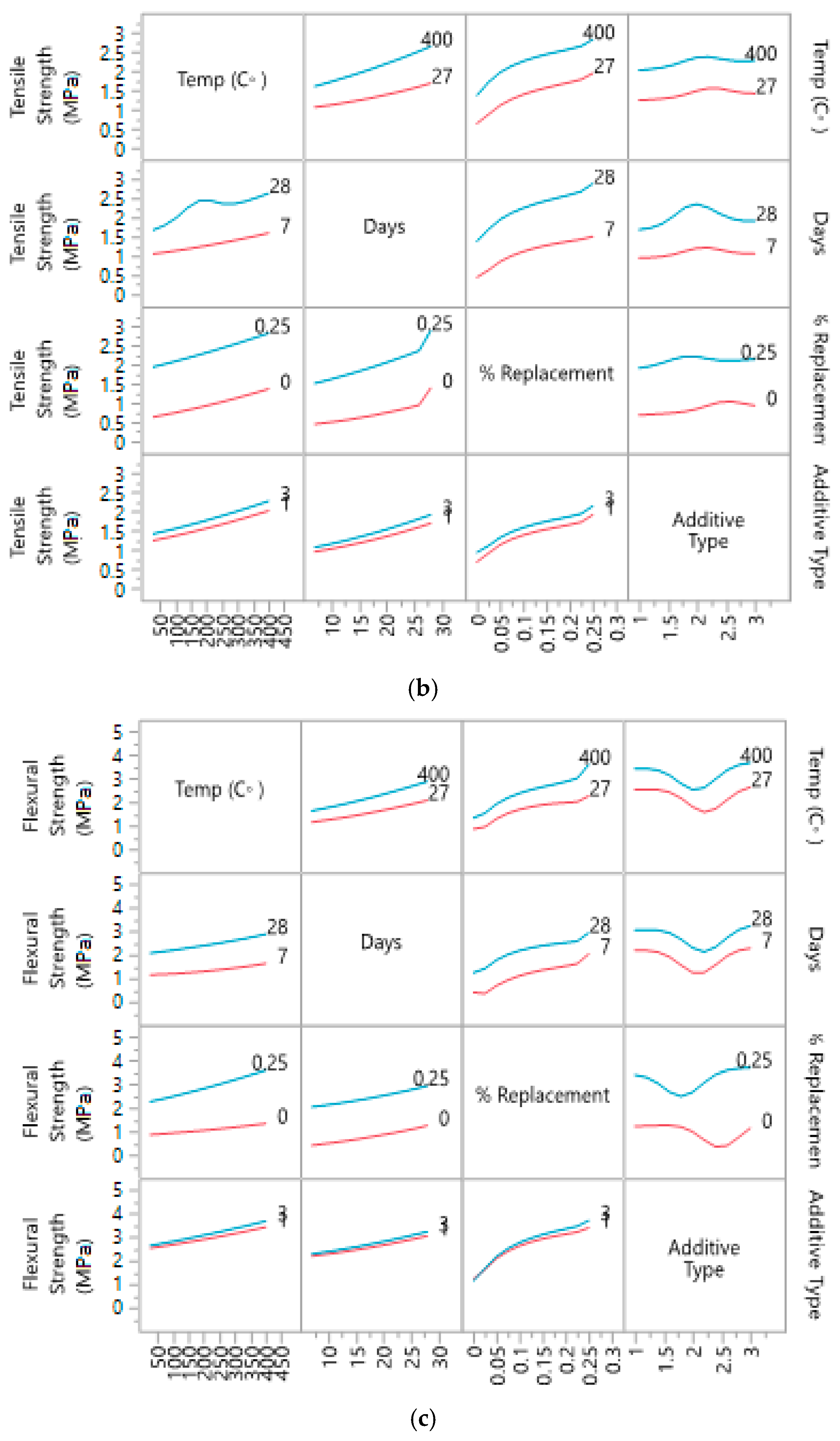
One of the best features of ANN produced during the analysis is the prediction profiler (see Figure 8). A clear trend profile shows the impact of each variable on the compression, tensile and flexural strength. Replacement of additive (in %) shows up to 25% replacement produced higher strength while the type of additive shows Marble powder is the best among the three additives. The behavior of concrete from 27 °C to 400 °C is satisfactory, which shows that it can survive against fire up to that level. Curing conditions are also satisfactory, as it shows the highest strength at 28 days.
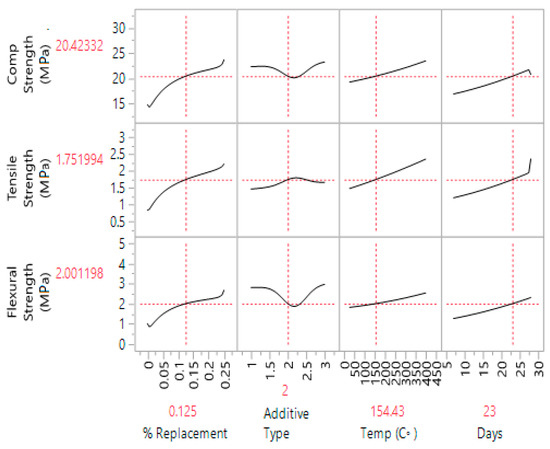
Figure 8.
Prediction profiler for compression, tensile and flexural strength with respect to features.
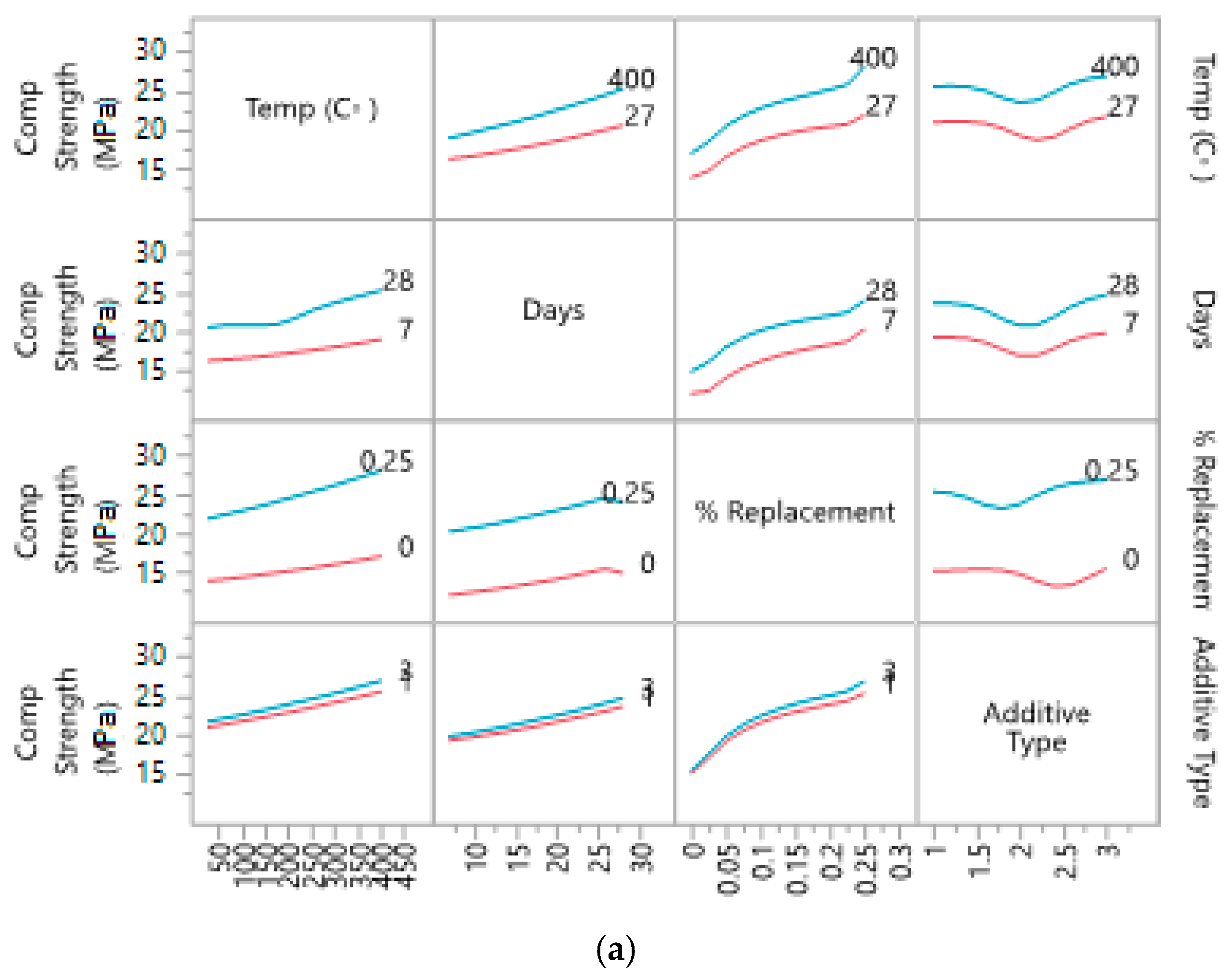
3.4.3. Interaction Profiles
Interaction profile of the variables helps in understanding the individual behavior of variables, especially to understand the behavior of variables within ranges. Figure 9 shows the change of behavior with minimum and maximum ranges of variables. These profiles show that additive type is having a large impact on strength of the concrete.
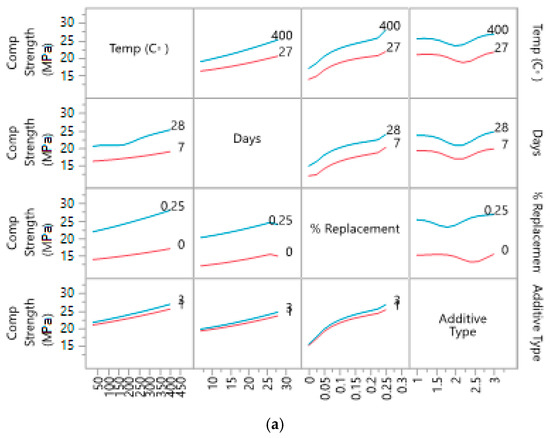
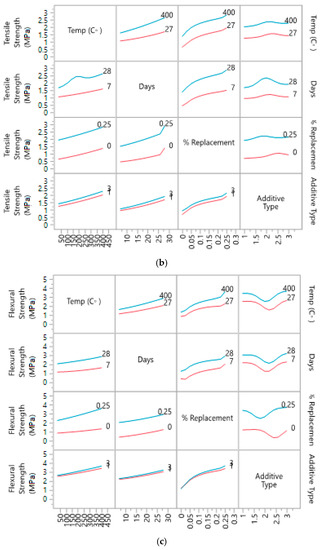
Figure 9.
Interaction profile for ranges of: (a) compressive strength; (b) tensile strength; (c) flexural strength with four variables.
3.4.4. Variable Importance
Sometimes priority setting is an important factor, which can be visualized by variable importance. Overall variable importance results in Table 9 show that replacement percentage and additive type are two major factors for strength prediction. However, in comparison to compressive and flexural strength, which have a similar pattern, tensile strength has an alternative relationship, with the additive type having bigger impact than percentage replacement.

Table 9.
Variable importance and impact of all strength parameters.
4. Conclusions
It is an accepted fact that, normally, concrete structures tend to deteriorate rapidly due to adverse conditions such as challenging weather environments. Thus, it leads to costly repairs during their performance span and before their safety and durability limit ends. Thus, to resolve this crucial issue, construction industry employs all useful and highly effective methods and techniques for improving the quality and extending the lifespan of concrete. From all the results analyzed in this study about the performance of concrete with additives as a partial replacement, we find such mixes to be efficient and useable as a replacement of ordinary concrete in construction work. Series of partial replacement from 5% to 25% partial replacement of cement with three materials are studied at room temperature and elevated temperatures up to 500 °C. It is noted that SF induction in the concrete mix as a replacement effectively improved the base mechanical properties of the concrete. According to this research work, about 20% and 25% SF content serving as the replacement of ordinary cement were concluded to be the optimum quantity for the enhancement and elevation of the compressive and flexural strengths. The workability for fresh concrete (SF based) was at a fine level due to water/cement ratio (w/c = 0.40). The J-ring and V-funnel test results showed that penetration and flow ability for all mixes, especially for MP based mix, are at good levels. The results for the GGBFS based mix of SCC has relatively good compressive, split tensile and flexural strengths as compared to the MP and SF based SCC. It is found that the split tensile strength of sample cylinders increases with incorporation of the waste marble powder at about 25% replacement by the total weight of cement. Any more addition of MP leads to decrease in the Split Tensile strength for sample cylinders. Moreover, upon testing the heated samples of concrete and comparing the results with those of sun-dried samples, we found significant results showing an elevated level of strength gain by the heated ones. This was due to the increased hydration rate and swift gain of strength by the heated sample under heat. Using ANN, we can clearly visualize that Marble powder comes out to achieve successive results. ANN analysis of SF and GGBFS projects the image of predicted behavior by SCC incorporated with these materials as a replacement part to cement and their impact on three major performance indicators of concrete (i.e., compressive, tensile and flexural strength). Predictive strength of ANN provides help in analyzing and predicting SCC strength by multiple inputs and multiple outputs. The relationship developed shows that up to 25% replacement of cement is feasible to produce the SCC for construction purpose. Another property is resistance against the temperature; especially in hot weather and fire condition, it can resist up to 400 °C. Its strength also increases up to 28 days, which is quite normal for production of concrete. The comparison of concrete shows SF and MP are feasible for compression and flexural properties but, in the case of tensile case, GGBFS is ahead. Thus, in the future, a combination of SF with GGBFS or MP with GGBFS could prove better results for all three properties. Using these waste materials and industrial byproducts in concrete mixes, we can achieve high strength levels and reduce the pollution caused by crushing, grinding and preparation procedures of cement. Finding these mixes to be efficient in performances, we conclude that a low-cost mix with far greater strength and durability could serve as a replacement for ordinary concrete in our construction industry. Employing waste reduces the pollution threat and leads to lowering the cost of production at larger levels. By this work, we can reduce the cost of construction work with the usage of GGBFS, SF and Marble powder, which are abundant and cheaply available worldwide in developing and developed countries. Importantly, this research work shows a method for helping the environment by introducing eco-friendly SCC and reducing the environmental pollution levels incurred by the cement manufacture and production as it is our main task to develop facilities by using lowest budgets and maximize the reduction of harmful pollutant aspects in Civil Engineering work.
Acknowledgments
This project has been supported by PIET.
Author Contributions
Syyed Adnan Raheel Shah and Junaid Mansoor conceived and designed the concept; Junaid Mansoor and Abdullah Naveed Sadiq performed literature review; Abdullah Naveed Sadiq, Muhammad Kashif Anwar, Muhammad Usman Siddiq and Hassam Ahmad performed the experimentation; Syyed Adnan Raheel Shah and Mudasser Muneer Khan performed analysis and designed model; and Syyed Adnan Raheel Shah and Junaid Mansoor wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Duval, R.; Kadri, E. Influence of silica fume on the workability and the compressive strength of high-performance concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, M.F.M.; Safiuddin, M.; Mahmud, H. Development of high performance concrete using silica fume at relatively high water–binder ratios. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldred, J.M.; Holland, T.C.; Morgan, D.R.; Roy, D.M.; Bury, M.A.; Hooton, R.D.; Olek, J.; Scali, M.J.; Detwiler, R.J.; Jaber, T.M. Guide for the Use of Silica Fume in Concrete; ACI–American Concrete Institute–Committee: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2006; Volume 234. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaid, M.; Benmarce, A. Behaviour of self compacting concrete mixed with different additions at high-temperature. J. Meter. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Bharath, E.; Shishaila, J.M.; Prakash, P.; Puttiah, P.K.W. Effect of partial replacement of cement in self-compacting concrete by fly ash and metakaolin. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiyari, S.; Allahverdi, A.; Rais-Ghasemi, M.; Zarrabi, B.; Parhizkar, T. Self-compacting concrete containing different powders at elevated temperatures–mechanical properties and changes in the phase composition of the paste. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 514, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesoğlu, M.; Güneyisi, E.; Kocabağ, M.E.; Bayram, V.; Mermerdaş, K. Fresh and hardened characteristics of self compacting concretes made with combined use of marble powder, limestone filler, and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.A. Effect of fly ash and silica fume on compressive strength of self-compacting concrete under different curing conditions. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2011, 2, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, D.M.; El-Attar, M.M.; Ali, H.A. Reusing of marble and granite powders in self-compacting concrete for sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 121, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi, M.R.; Rezaei-Zarchi, S. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their effect on the compressive strength and setting time of self-compacted concrete paste as cementitious composites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4340–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, R.; Aggarwal, P.; Aggarwal, Y. Prediction of compressive strength of self-compacting concrete containing bottom ash using artificial neural networks. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2011, 42, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Taerwe, L. Compressive strength of self-compacting concrete during high-temperature exposure. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, K.; Karatas, M.; Gonen, T. Effect of fly ash and silica fume on compressive strength, sorptivity and carbonation of SCC. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 17, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asteris, P.; Kolovos, K.; Douvika, M.; Roinos, K. Prediction of self-compacting concrete strength using artificial neural networks. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, s102–s122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douma, O.B.; Boukhatem, B.; Ghrici, M.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Prediction of properties of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash using artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehdi, M.; El Chabib, H.; El Naggar, M.H. Predicting performance of self-compacting concrete mixtures using artificial neural networks. Mater. J. 2001, 98, 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Zi-ruo, Y.; Ming-zhe, A.; Ming-bo, Z. Predicting the compressive strength of self compacting concrete using artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Design, Perormance and Use of Self Consolidating Concrete SCC, Beijing, China, 5–7 June 2009; pp. 452–459. [Google Scholar]
- Dinakar, P.; Sethy, K.P.; Sahoo, U.C. Design of self-compacting concrete with ground granulated blast furnace slag. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Lachemi, M.; Hossain, K.M. Effect of metakaolin and silica fume on the durability of self-consolidating concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, K.A.; Carneiro, A.M. Effect of metakaolin’s finesses and content in self-consolidating concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Hsu, K.-C.; Chai, H.-W. A simple mix design method for self-compacting concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristulovic, P.; Kamenic, N.; Popovic, K. A new approach in evaluation of filler effect in cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, B.; Ediz, N. The use of raw and calcined diatomite in cement production. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Sakata, N.; Okamura, H. Evaluation of self-compactability of fresh concrete using the funnel test. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu 1994, 1994, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, M.A.; Elaty, M.A.; Taman, M. Predicting the ingredients of self compacting concrete using artificial neural network. Alexandria Eng. J. 2017, 56, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.; Brooks, J. Concrete Technology; Longman Scientific and Technical: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kodur, V.; Sultan, M. Effect of temperature on thermal properties of high-strength concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; Abo-El-Enein, S.; Hanna, G.; Kotkata, M. Effect of temperature on physical and mechanical properties of concrete containing silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.T.; Lawson, J.R.; Davis, F.L. Effects of elevated temperature exposure on heating characteristics, spalling, and residual properties of high performance concrete. Mater. Struct. 2001, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyamaç, K.E.; Ince, R. A preliminary concrete mix design for scc with marble powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, I.B.; Bilir, T.; Uygunoğlu, T. Effect of waste marble dust content as filler on properties of self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, V.; Moriconi, G. The influence of mineral additions on the rheology of self-compacting concrete. Spec. Publ. 2003, 217, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, M.; Sabah, E. Marble deposits and the impact of marble waste on environmental pollution geological and technical characterization of iscehisar (Afyon–Turkey). J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 6–116. [Google Scholar]
- Türker, P.; Erdogan, B.; Erdogdu, K. Influence of marble powder on microstructure and hydration of cements. Cem. Concr. World J. TÇMB (Turkey) 2002, 7, 38–89. [Google Scholar]
- Türkmen, İ. Influence of different curing conditions on the physical and mechanical properties of concretes with admixtures of silica fume and blast furnace slag. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 4560–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, İ.; Kantarcı, A. Effects of expanded perlite aggregate and different curing conditions on the physical and mechanical properties of self-compacting concrete. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, O.; Uygunoglu, T. Investigation of mechanical properties of waste marble dusty concrete which under the effect of freeze and thaw. In Proceedings of the Turkey 4th Marble Symposium, Afyon, Turkey, 18–19 December 2003; pp. 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Valls, S.; Yagüe, A.; Vázquez, E.; Mariscal, C. Physical and mechanical properties of concrete with added dry sludge from a sewage treatment plant. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, M. Concrete Technology Theory & Practice; CHAND & Company: New Delh, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration; C1202-97, Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997; Volume 4, pp. 639–644. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, D.W.; McDonald, D.B.; Krauss, P.D. The rapid chloride permeability test and its correlation to the 90-day chloride ponding test. PCI J. 1994, 39, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, S. Mechanical and durability properties of self compacting concrete. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2017, 48, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigidi, A.; Garcia, L.A. Parameter estimation in groundwater hydrology using artificial neural networks. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2003, 17, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.L. Simulating structural analysis with neural network. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 1994, 8, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).