An Improved PSO Algorithm and Its Application in GNSS Ambiguity Resolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Model of GNSS Positioning
2.2. IPSO–AR Method
2.2.1. Standard PSO Algorithm
2.2.2. IPSO Algorithm
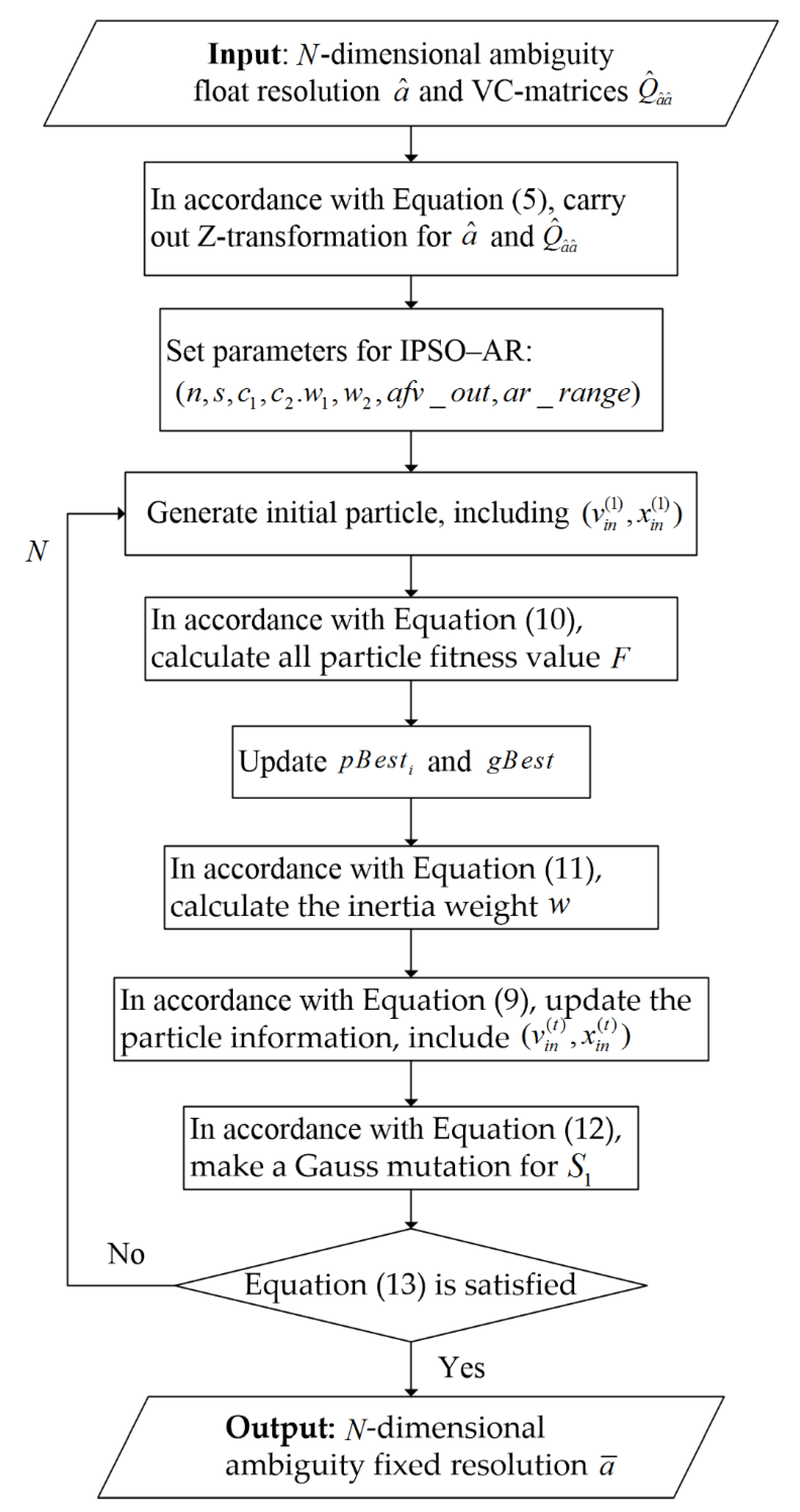
2.2.3. Illustration of the IPSO–AR Algorithm
3. Experiments and Result Analysis
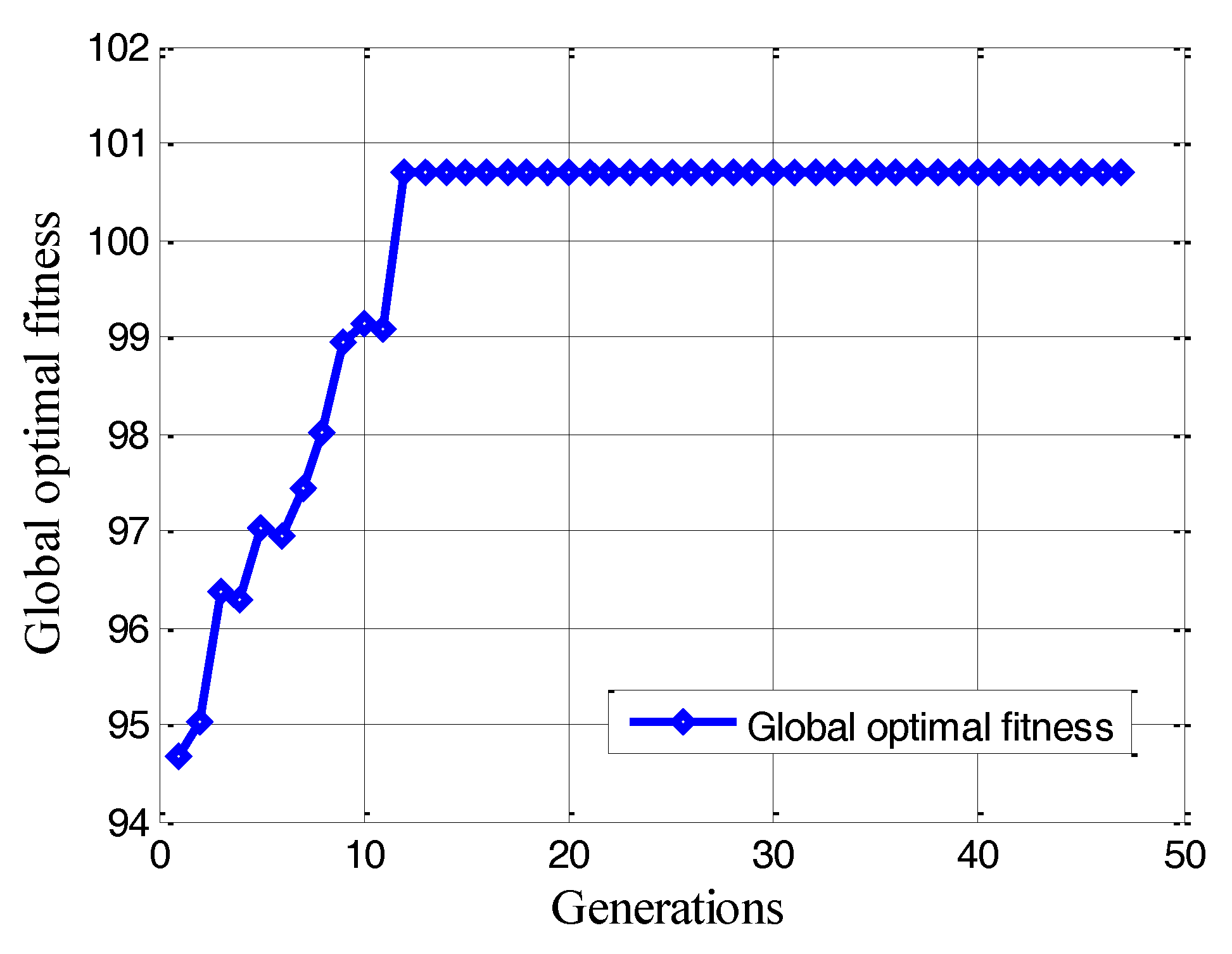
3.1. Search Procedure of IPSO–AR
3.2. Performance Analysis of IPSO–AR
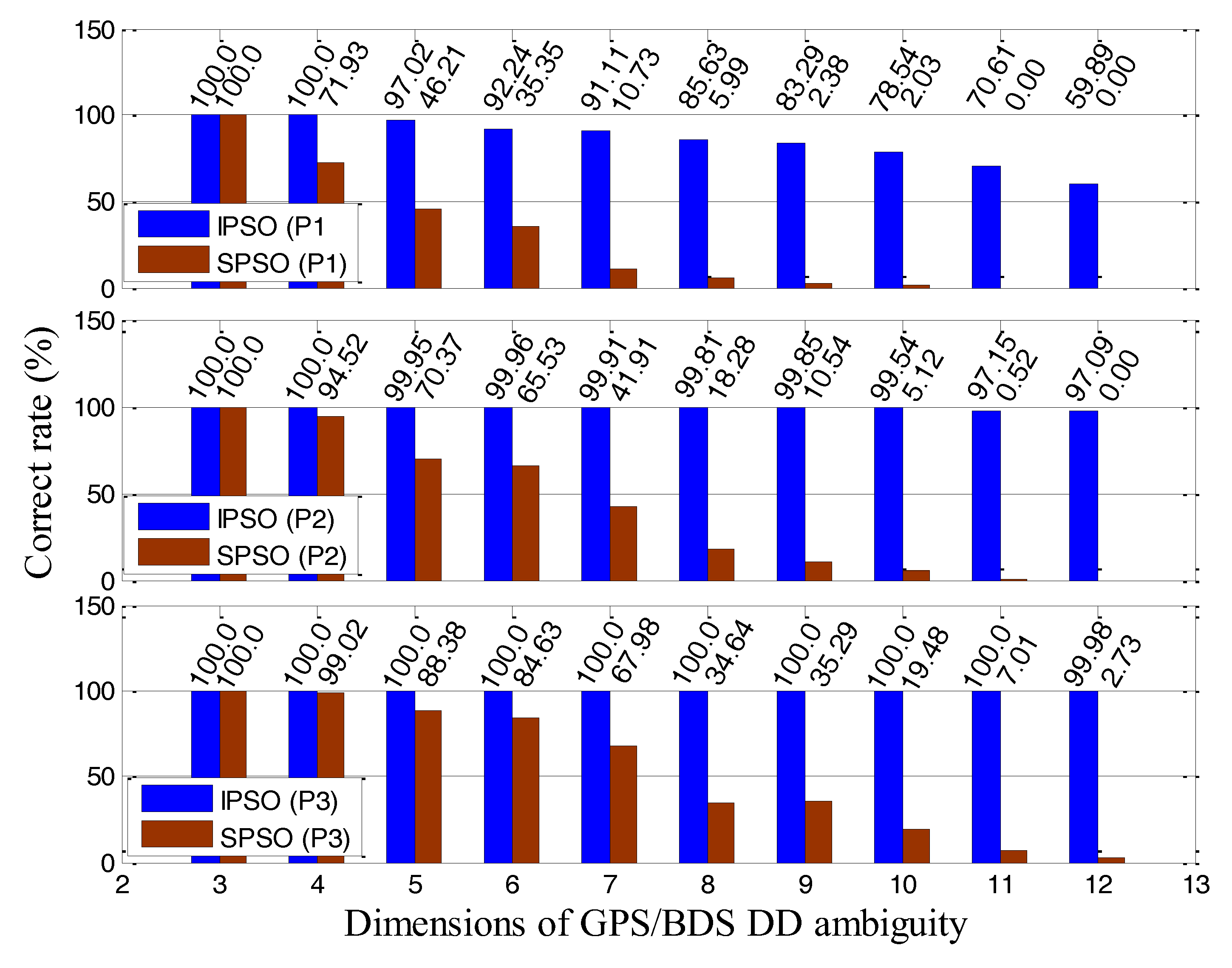
3.2.1. Scheme #1 Experiments
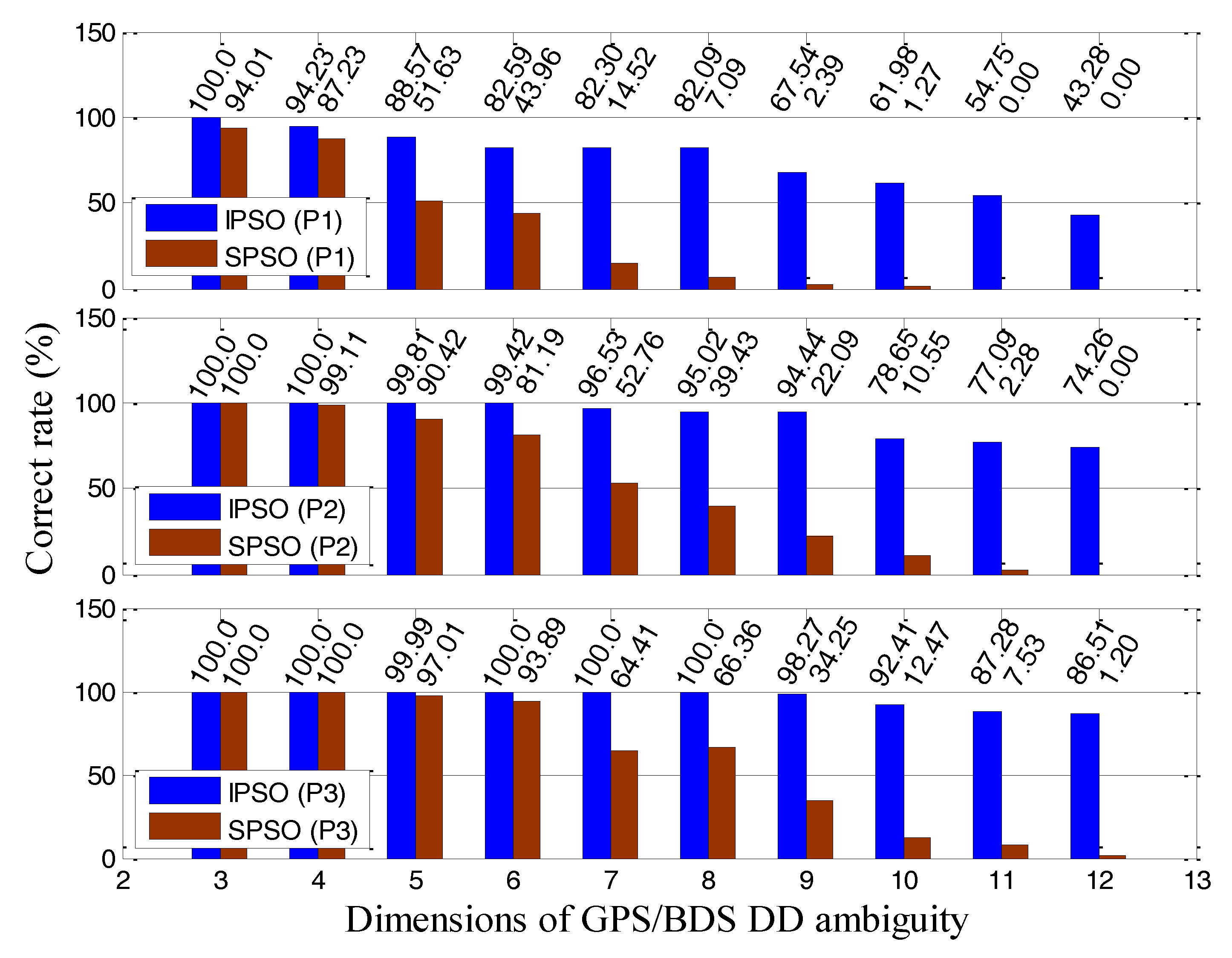
3.2.2. Scheme #2 Experiments
3.2.3. Scheme #3 Experiments
3.2.4. Recommended Parameter Settings for IPSO–AR
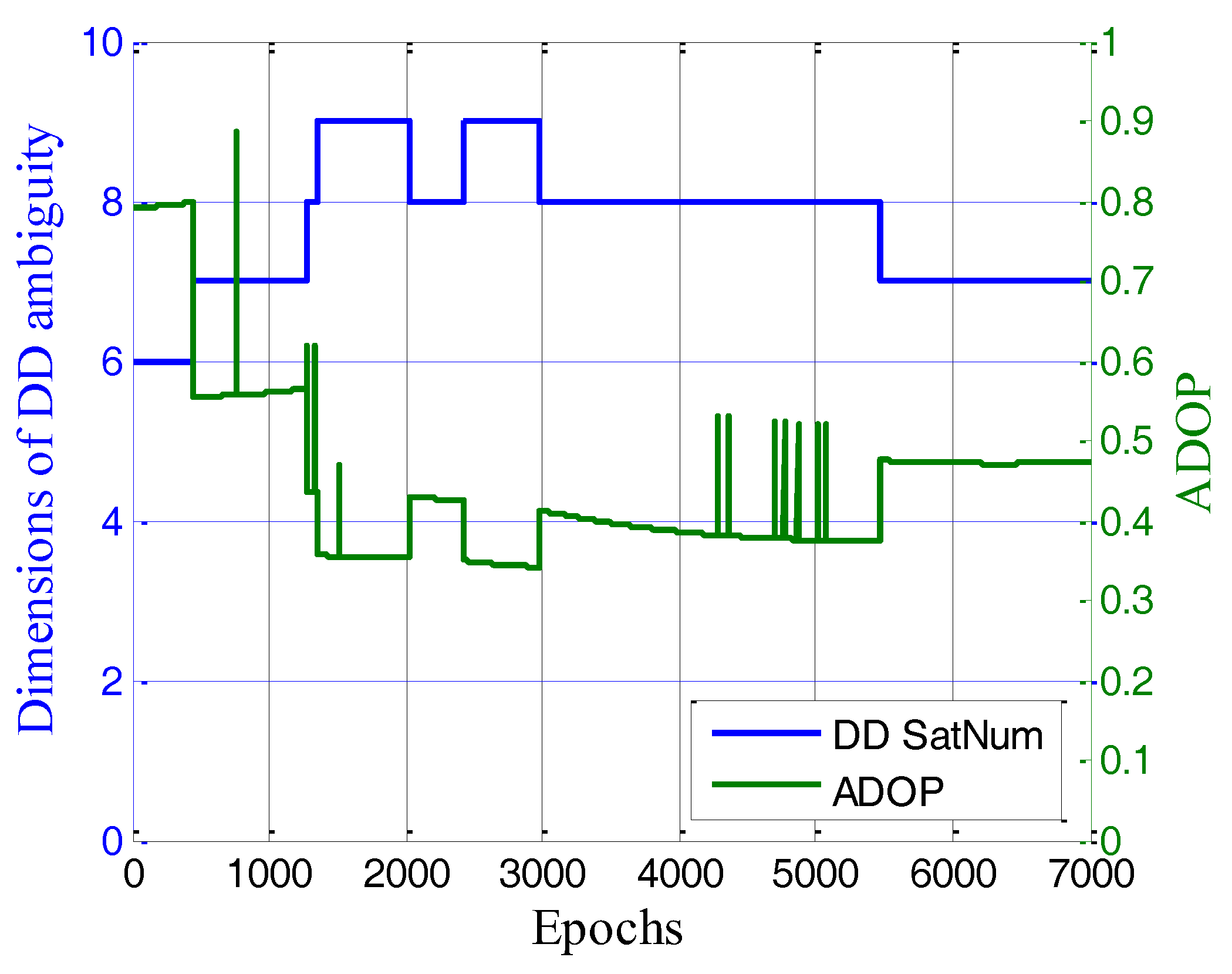
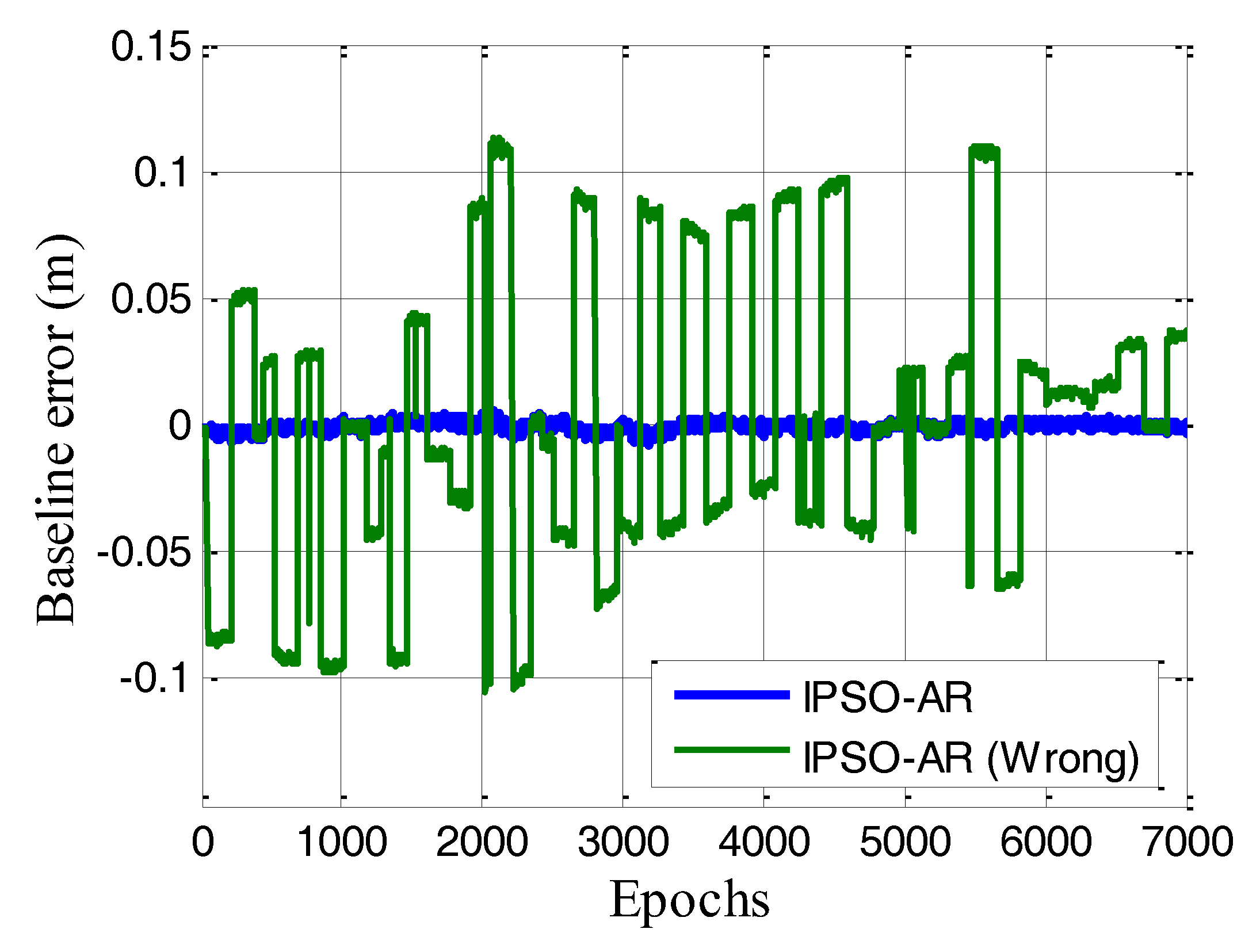
3.3. Validation of the IPSO–AR Algorithm with Known Baseline
4. Conclusions
- (1)
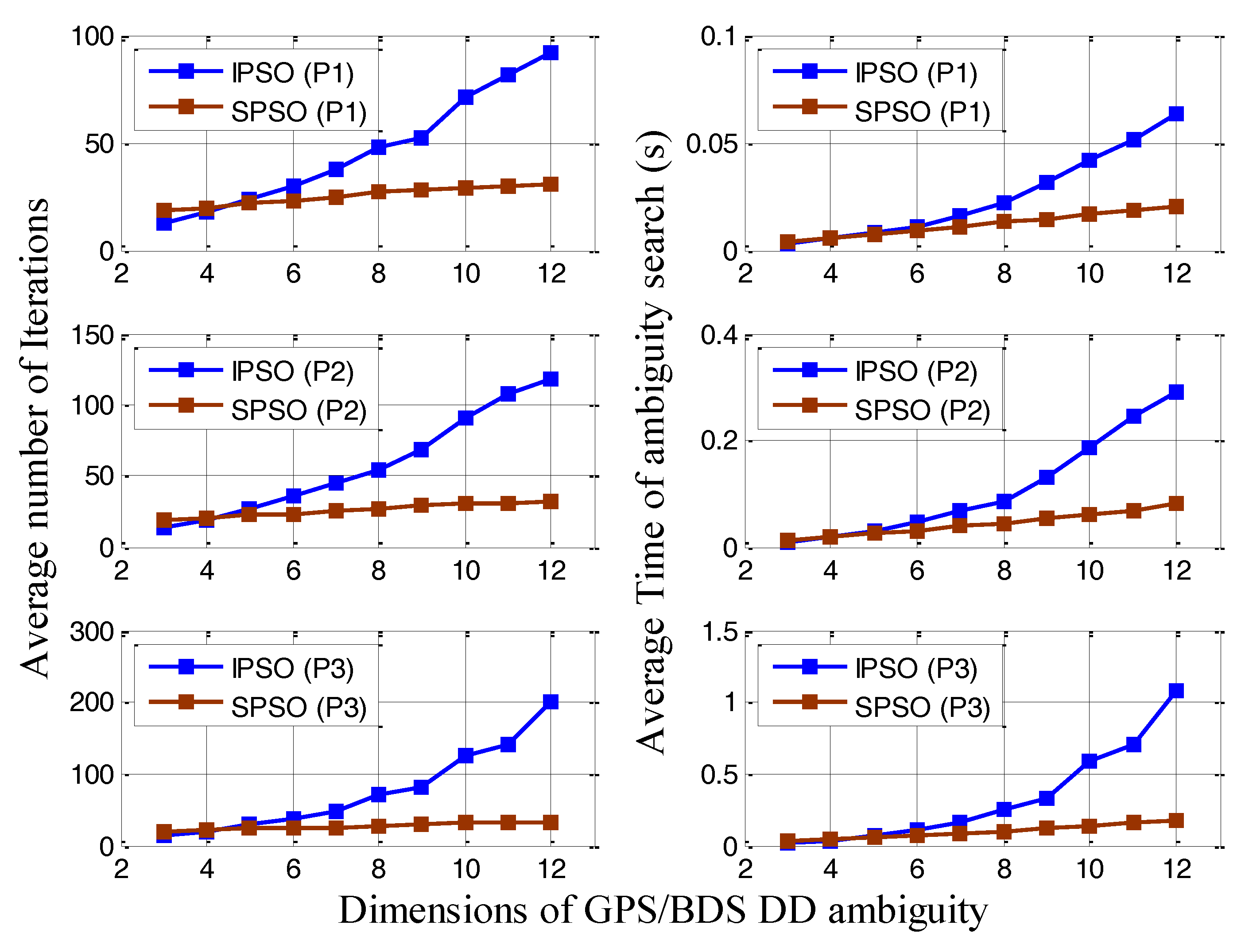
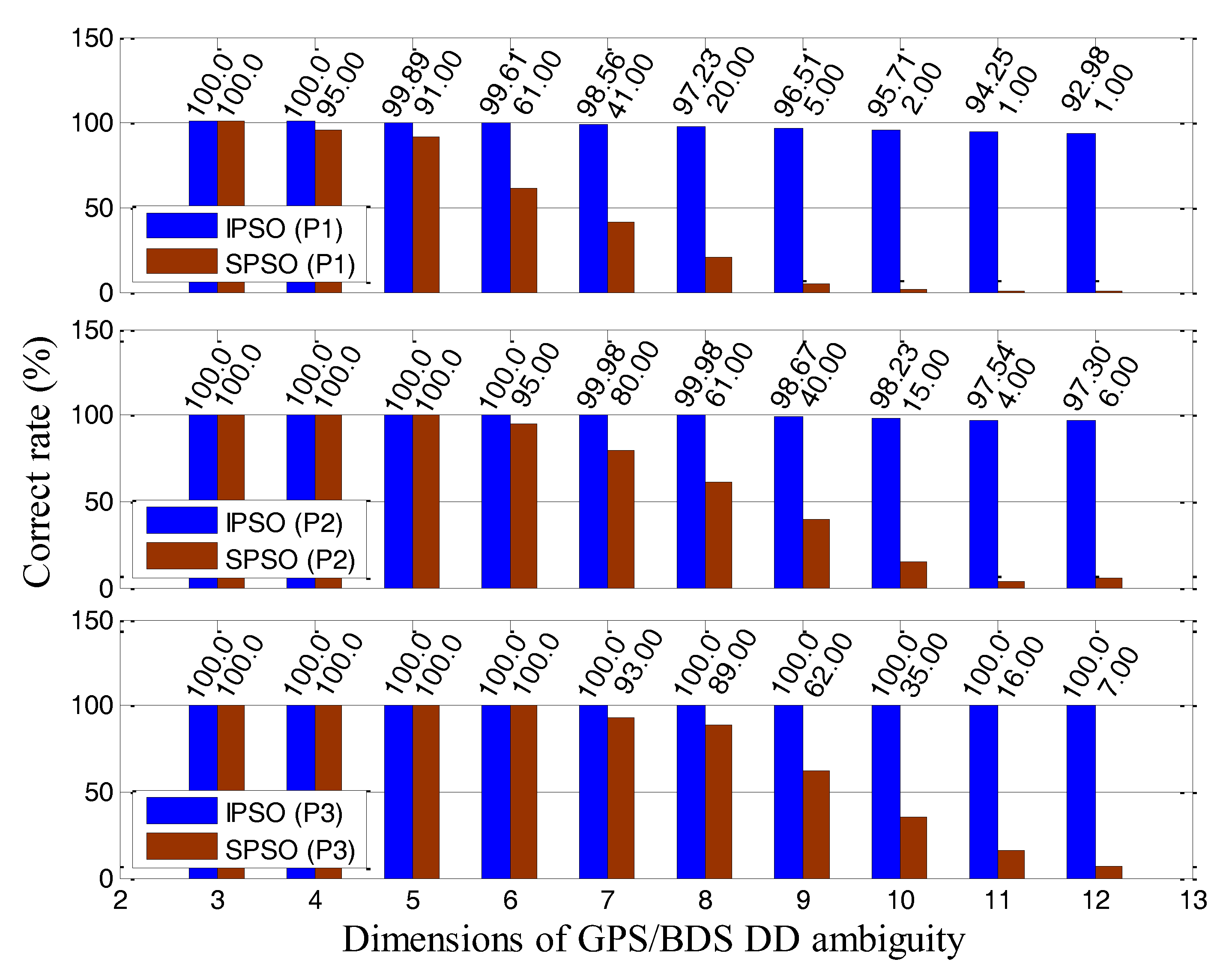
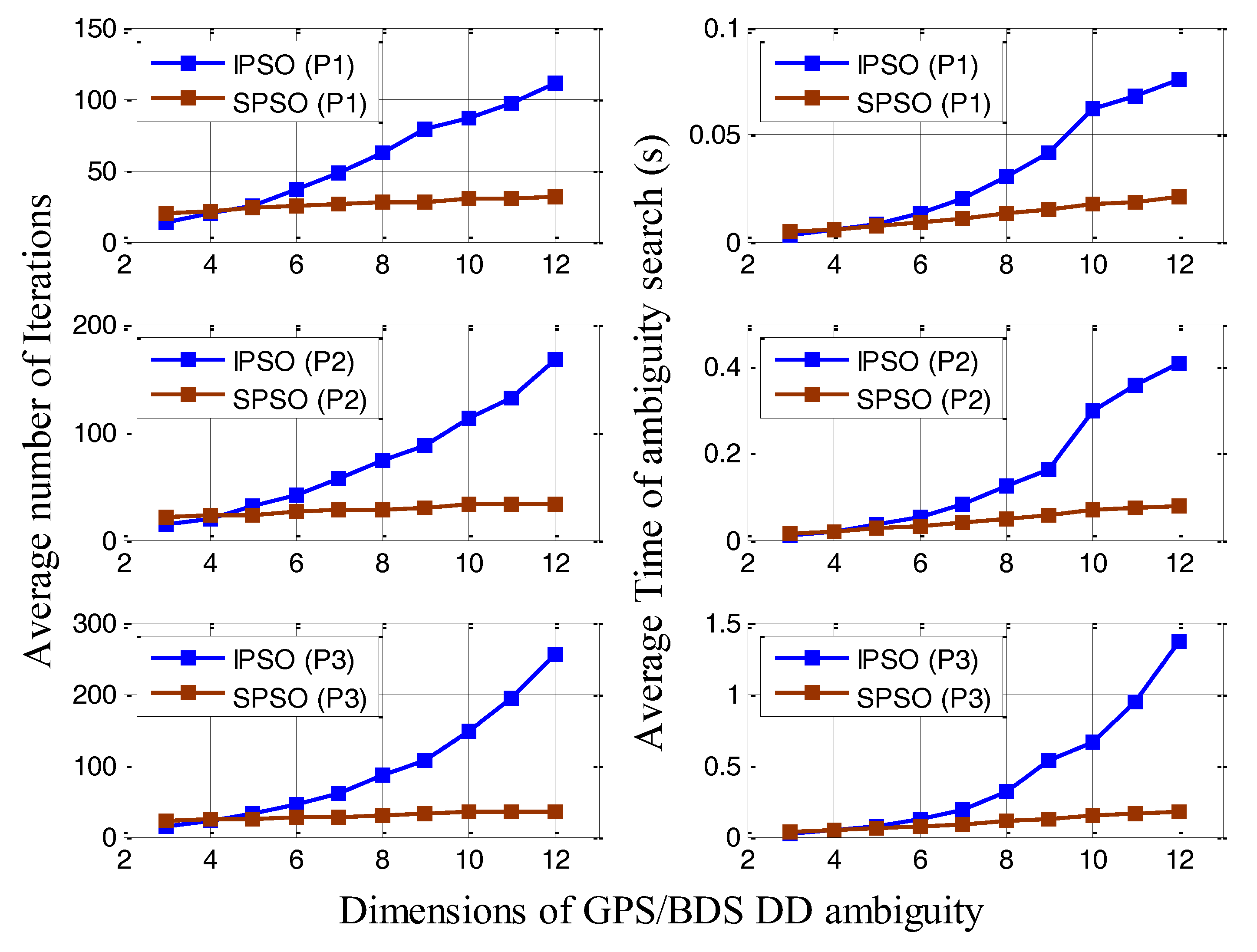
- The correct rate of IPSO–AR is superior to that of SPSO–AR. The superior correct rate of IPSO–AR, however, is obtained at the expense of computational efficiency. The improvement in the correct rate of IPSO–AR is particularly pronounced under high-dimensional ambiguity.
- (2)
- The performance of IPSO–AR is closely related to the property of estimated ambiguity float resolution. Under reasonable parameter settings, the efficiency of IPSO–AR mostly depends on the dimension of the estimated ambiguity float resolution. Meanwhile, the correct rate of IPSO–AR mainly depends on the precision of the estimated ambiguity float resolution. Given this principle, we can adaptively adjust the parameters of IPSO–AR on the basis of the estimated ambiguity float resolution, to achieve high efficiency and high correct rate, simultaneously.
- (3)
- IPSO–AR exhibits high efficiency and high correct rate when the dimension of estimated ambiguity float resolution is low (N < 6). The correct rate of IPSO–AR can be validated when baseline length is known, such as in GNSS attitude determination. Thus, IPSO–AR may have considerable engineering application value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Collins, J. Global Positioning System: Theory and Practice, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Counselman, C.C.; Gourevitch, S.A. Miniature Interferometer Terminals for Earth Surveying: Ambiguity and multipath with Global Positioning System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1981, 19, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. Carrier phase ambiguity resolution for the global positioning system applied to geodetic baselines up to 2000 km. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 94, 10187–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, E.; Beutler, G. Rapid Static Positioning Based on the Fast Ambiguity Resolution Approach “FARA”. Theory and First Results. Manuscr. Geod. 1990, 15, 325–356. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A New Method for Fast Carrier Phase Ambiguity Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–15 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. An Optimality Property of the Integer Least-Squares Estimator. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. New global navigation satellite system ambiguity resolution method compared to existing approaches. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2006, 29, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, P.J.; Tiberius, C. The LAMBDA Method for Integer Ambiguity Estimation: Implementation Aspects; No.12 of LGR-Series; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen, S.; Li, B.; Teunissen, P.J.G. PS-LAMBDA: Ambiguity correct rate evaluation software for interferometric applications. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 54, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, T. MLAMBDA: A modified LAMBDA method for integer least-squares estimation. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Luo, M.; Bai, K.; Chen, S. A Precise Positioning Method for a Puncture Robot Based on a PSO-Optimized BP Neural Network Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T.A. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Clerc, M.; Kennedy, J. The particle swarm-explosion, stability, and convergence in a multidimensional complex space. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, F.V.D.; Engelbrecht, A.P. A study of particle swarm optimization particle trajectories. Inf. Sci. 2006, 176, 937–971. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.J.; Qin, A.K.; Suganthan, P.N.; Baskar, S. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2006, 10, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Wu, C.H.; Ip, W.H.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chan, C.Y.; Yung, K.L. An opposition-based chaotic GA/PSO hybrid algorithm and its application in circle detection. Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 64, 1886–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, O.E.; Turgut, M.S.; Coban, M.T. Chaotic quantum behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving nonlinear system of equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2014, 68, 508–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, Z.; Xie, Y.; Huang, R.; Tan, J. A knowledge-based heuristic particle swarm optimization approach with the adjustment strategy for the weighted circle packing problem. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013, 66, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, T.; Qian, J. Application of particle swarm optimization algorithm on robust PID controller tuning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Natural Computation, First International Conference, ICNC, Changsha, China, 27–29 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, B.; Wen, S.; Yuan, S.; Li, H. PPSO: PCA based particle swarm optimization for solving conditional nonlinear optimal perturbation. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 83, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Han, D.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, J.; Vu, K. Study on attitude determination based on discrete particle swarm optimization. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 3397–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, W. A New Method for Single-Epoch Ambiguity Resolution with Indoor Pseudolite Positioning. Sensors 2017, 17, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazaeri, S.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Sharifi, M.A. Erratum to: Fast integer least-squares estimation for GNSS high-dimensional ambiguity resolution using lattice theory. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.W.; Pan, J.S.; Chen, S.M.; Liao, B.Y.; Hao, S.P. Parallel cat swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Kunming, China, 12–15 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P.W.; Pan, J.S.; Chen, S.M.; Liao, B.Y. Enhanced parallel cat swarm optimization based on the Taguchi method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 6309–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Chien, C.Y. Parallelized genetic ant colony systems for solving the traveling salesman problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leick, A.; Rapoport, L.; Tatarnikov, D. GPS Satellite Surveying, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Guo, J.; Zhou, L. Performance analysis of BDS/GPS kinematic vehicle positioning in various observation conditions. Sens. Rev. 2016, 36, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Ambiguity resolution performance with GPS and BeiDou for LEO formation flying. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneveld, P.W.L.V.; Montenbruck, O.; Visser, P.N.A.M. Epochwise prediction of GPS single differenced ionospheric delays of formation flying spacecraft. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 44, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Feng, Q. The Standard Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Convergence Analysis and Parameter Selection. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC 2007), Haikou, China, 24–27 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bratton, D.; Kennedy, J. Defining a Standard for Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium (SIS 2007), Honolulu, HI, USA, 1–5 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pluhacek, M.; Senkerik, R.; Davendra, D.; Oplatkova, Z.K.; Zelinka, I. On the behavior and performance of chaos driven PSO algorithm with inertia weight. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013, 66, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Guan, Z.H.; Liu, X.Z. Adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamically changing inertia weight. Control Decis. 2008, 23, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, N.; Iba, H. Particle swarm optimization with Gaussian mutation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium (SIS 2003), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 26–26 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Dennis, O. Ambiguity Dilution of Precision: Definition, Properties and Application. In Proceedings of the 10th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1997), Kansas City, KS, USA, 16–19 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Takasu, T.; Yasuda, A. Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. In Proceedings of the International symposium on GPS/GNSS, Seogwipo-si Jungmun-dong, Korea, 4–6 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. GAMP: An open-source software of multi-GNSS precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Main Options | Setting |
|---|---|
| System | GPS/BDS |
| Observation Frequencies | L1/B1 |
| Elevation Cut-Off Angle | 15° |
| Positioning Mode | Static |
| Parameter Estimation | EKF |
| Stochastic Model | Elevation angle |
| Satellite Ephemeris | Broadcast |
| Satellite Antenna Model | IGS08.ATX |
| Receiver Antenna Model | IGS08.ATX |
| Ambiguity Resolution | LAMBDA |
| Ambiguity Validation Threshold | 3 |
| Integer Ambiguity Resolution | Continuous |
| Troposphere Correction | Saastamoinen |
| Ionosphere Correction | Broadcast Ionosphere Model (Klobuchar Mode) |
| Earth Tides Correction | OFF |
| Code/Carrier-Phase Error Ratio | 100 |
| Carrier-Phase Error | 0.003 + 0.003/sin(el) m |
| Experiments | DD Float Ambiguity | Parameter Setting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epochs | ADOP | Precision | ||||
| Scheme #1 | P1 | 10 | (0,0.1] | High | 30 | 10 |
| P2 | 60 | 20 | ||||
| P3 | 90 | 30 | ||||
| Scheme #2 | P1 | 5 | (0.1,0.5] | General | 30 | 10 |
| P2 | 60 | 20 | ||||
| P3 | 90 | 30 | ||||
| Scheme #3 | P1 | 1 | (0.5,2] | Low | 30 | 10 |
| P2 | 60 | 20 | ||||
| P3 | 90 | 30 | ||||
| Dimension | N = 3 | N = 4 | N = 5 | N = 6 | N = 7 |
| Frequency | L1 | L1 | L1 | L1 | L1 + B1 |
| DD Sat | 3G | 4G | 5G | 6G | 6G + 1B |
| Dimension | N = 8 | N = 9 | N = 10 | N = 11 | N = 12 |
| Frequency | L1 + B1 | L1 + B1 | L1 + B1 | L1 + B1 | L1 + B1 |
| DD Sat | 6G + 2B | 6G + 3B | 6G + 4B | 6G + 5B | 6G + 6B |
| ADOP | Dimensions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1,5] | (5,9] | (9,12] | - | |
| (0,0.1] | = 30 = 10 | = 60 = 20 | = 90 = 30 | - |
| (0.1,0.5] | = 30 = 10 | = 60 = 20 | = 90 = 30 | - |
| [0.5,2) | = 60 = 20 | = 90 = 30 | = 120 = 40 | - |
| - | - | - | - | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Guo, J.; Hu, J. An Improved PSO Algorithm and Its Application in GNSS Ambiguity Resolution. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060990
Li X, Guo J, Hu J. An Improved PSO Algorithm and Its Application in GNSS Ambiguity Resolution. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(6):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060990
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Jiming Guo, and Jiyuan Hu. 2018. "An Improved PSO Algorithm and Its Application in GNSS Ambiguity Resolution" Applied Sciences 8, no. 6: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060990
APA StyleLi, X., Guo, J., & Hu, J. (2018). An Improved PSO Algorithm and Its Application in GNSS Ambiguity Resolution. Applied Sciences, 8(6), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060990





