Artificial Circulatory Model for Analysis of Human and Artificial Vessels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
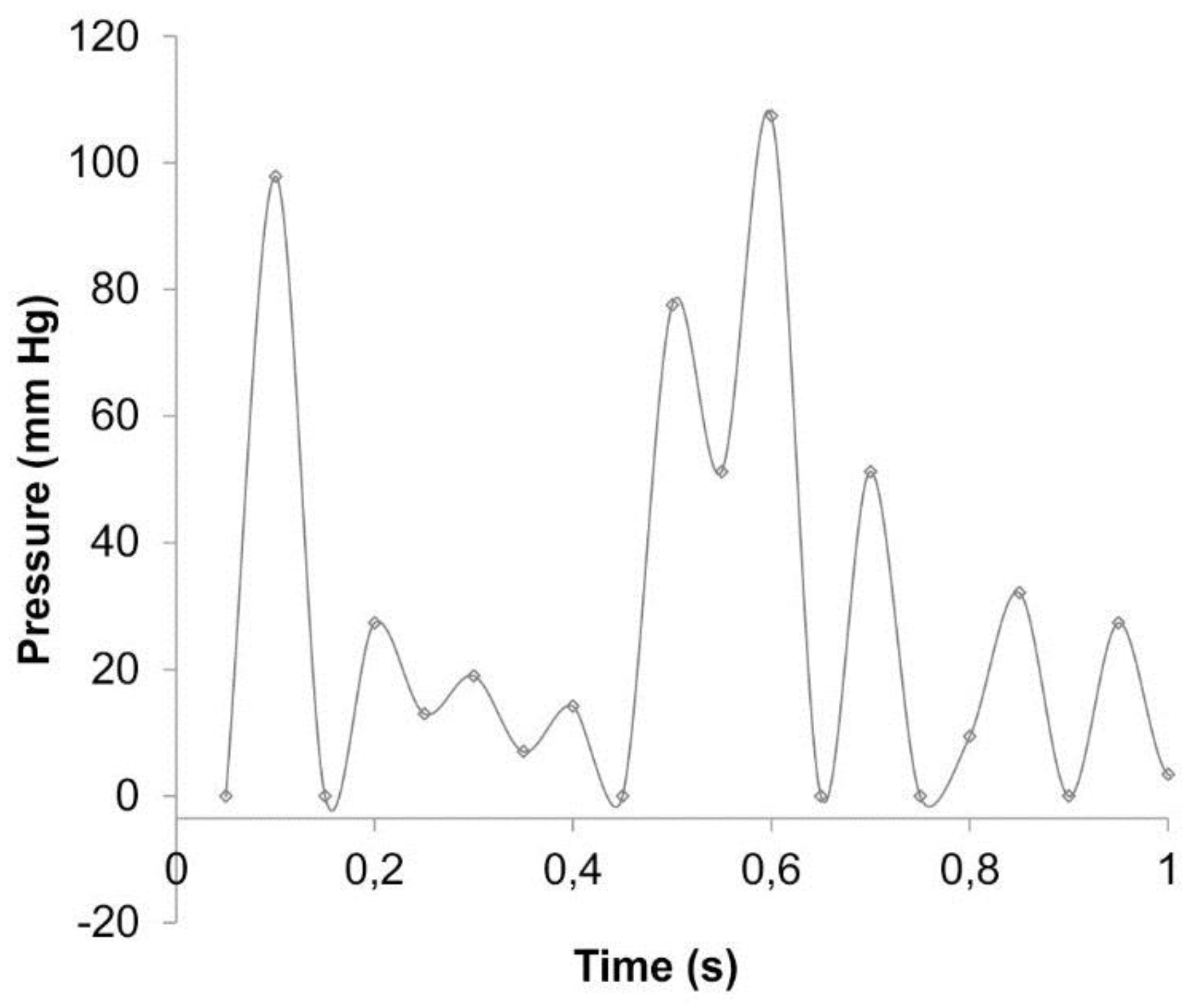
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Analyzed Material
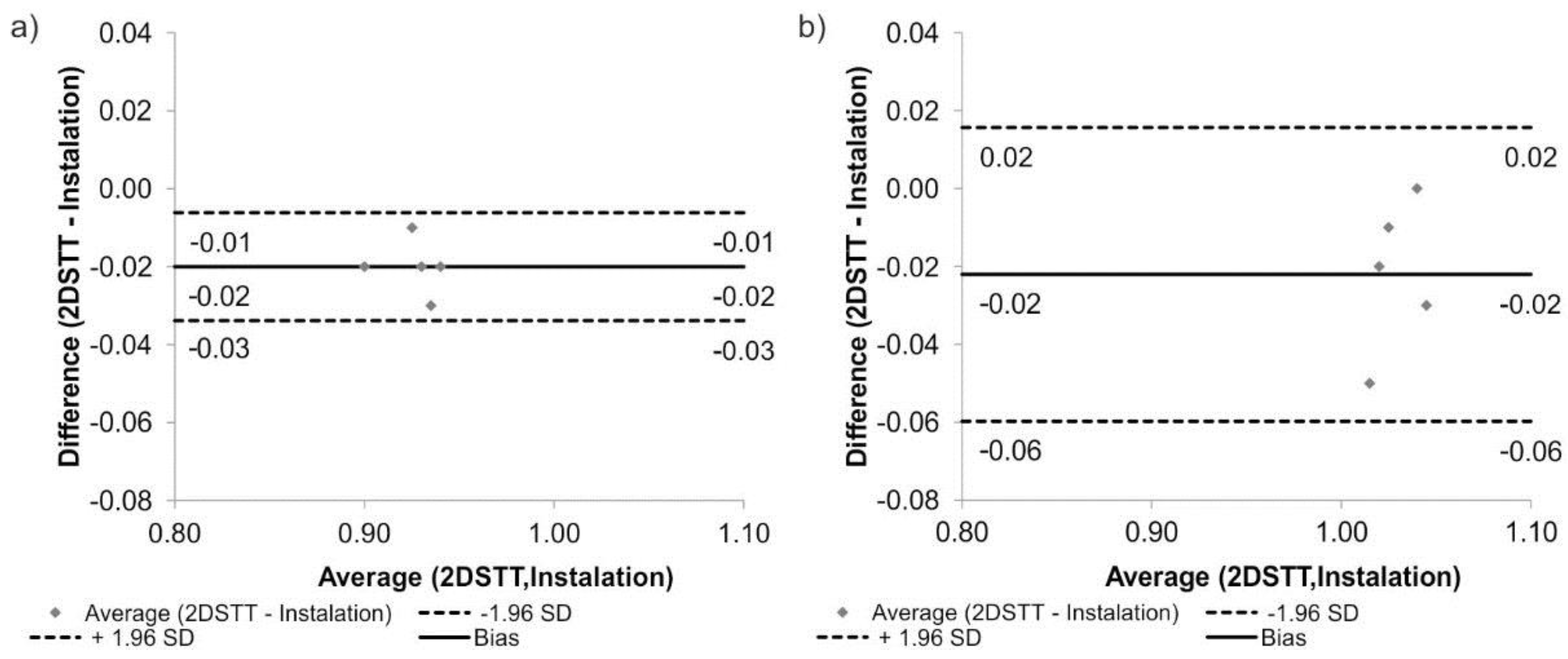
2.3. Statistical Analysis
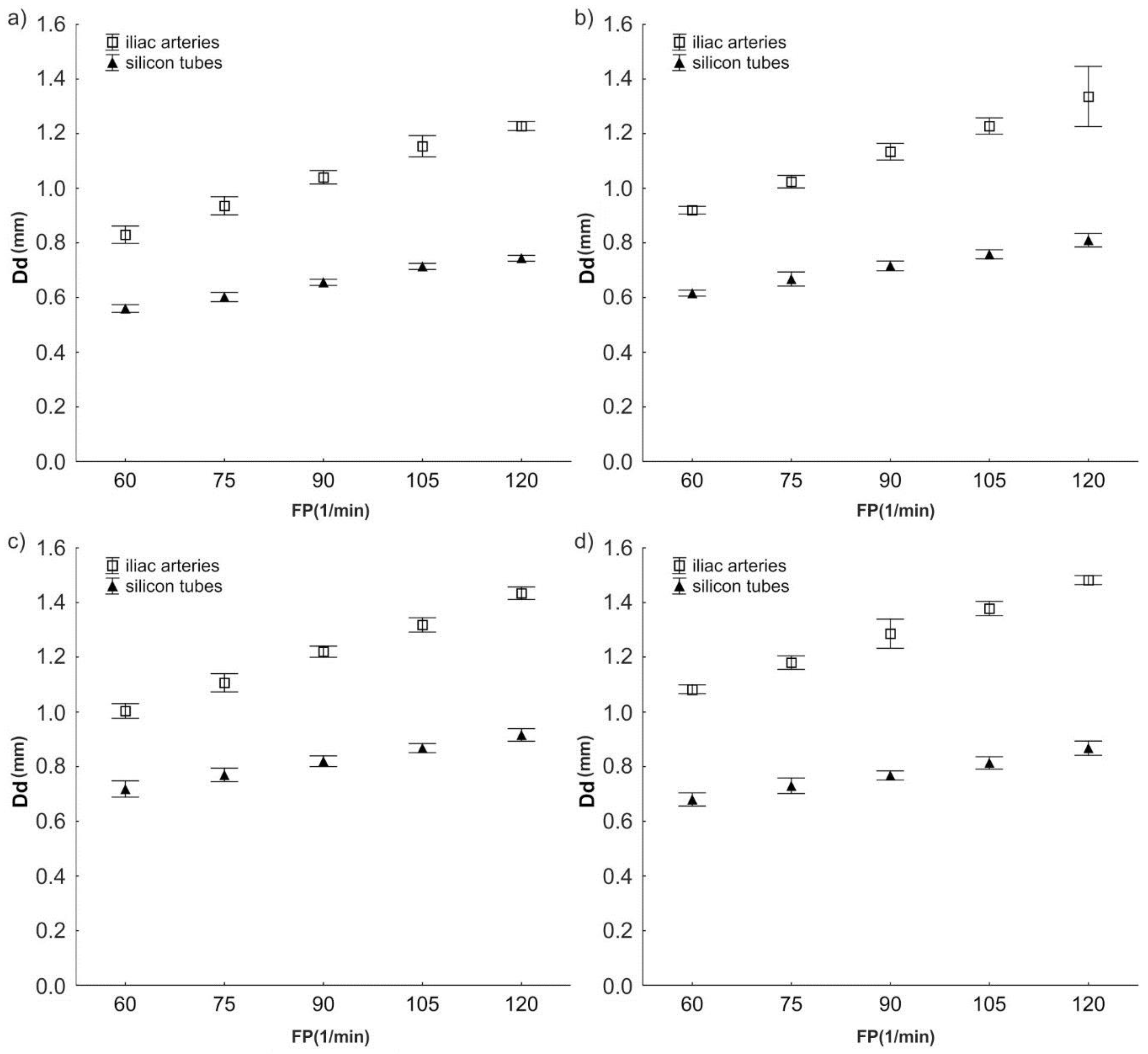
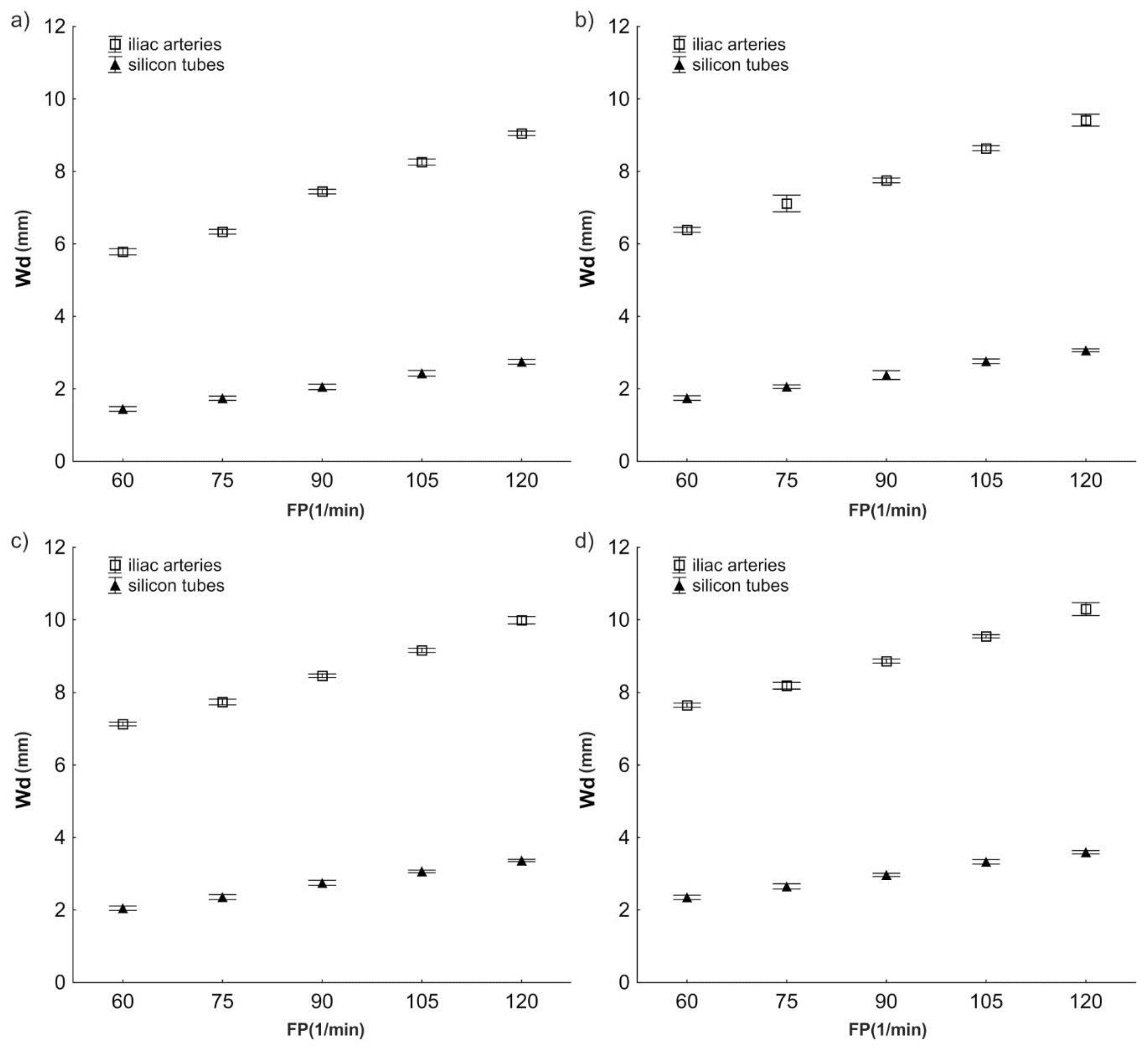
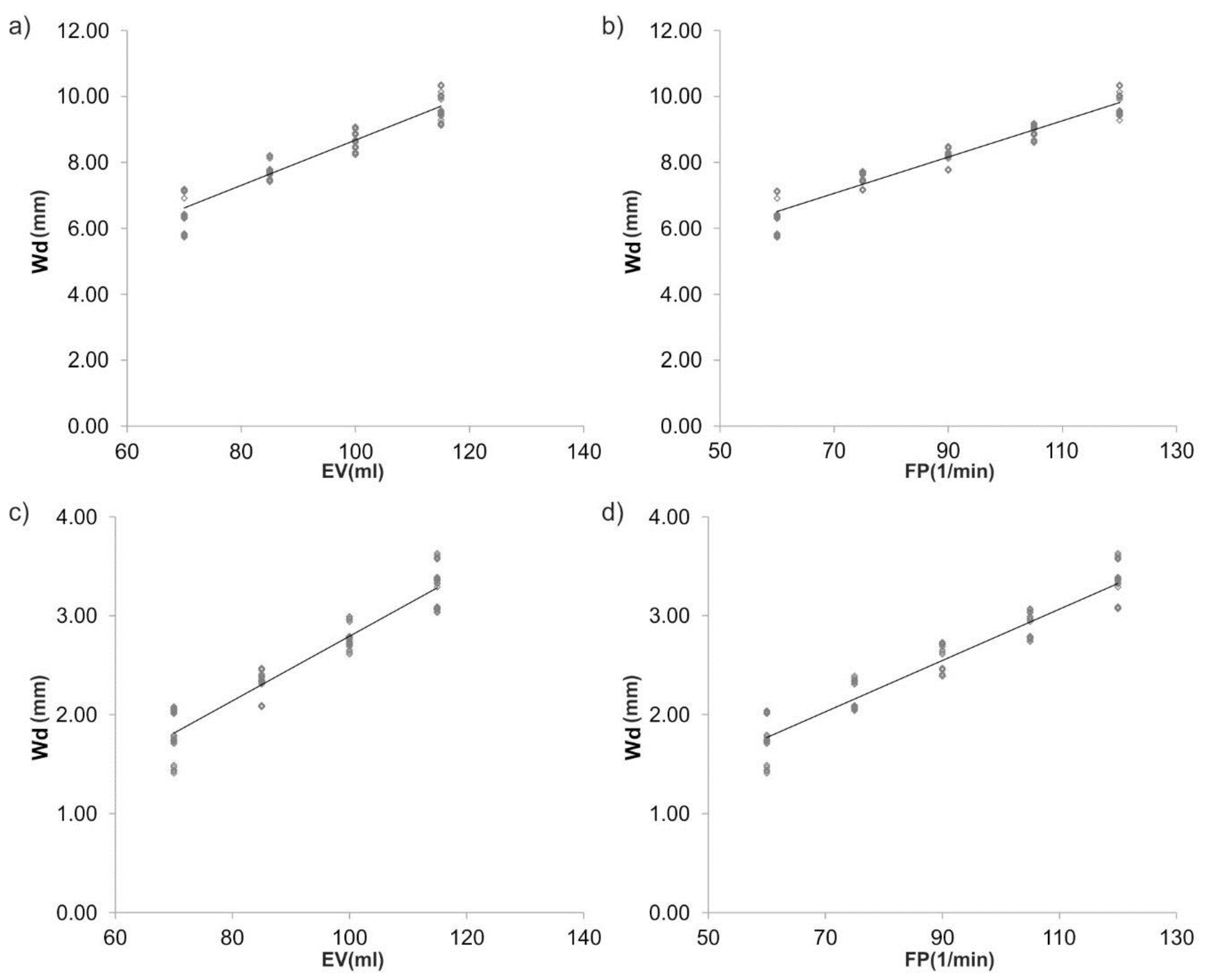
3. Results
3.1. Change of Diameter Dd
3.2. Wall Displacement Wd
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J. The Future of Cardiovascular Epidemiology. Circulation 2016, 133, 2626–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundargi, R.; Venkataraman, D.; Kumar, S.; Mogal, V.; Ortiz, R.; Loo, J.; Venkatraman, S.; Steele, T. Novel Sensor-Enabled Ex Vivo Bioreactor: A New Approach towards Physiological Parameters and Porcine Artery Viability. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 958170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Le Gac, S.; Verdonschot, N.; van den Berg, A.; Koopman, B.; Rouwkema, J. Endothelial cell alignment as a result of anisotropic strain and flow induced shear stress combinations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, R.F.; Snow, H.M. Characteristics of the response of the iliac artery to wall shear stress in the anaesthetized pig. J. Physiol. 2007, 582 Pt 2, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumont, K.; Yperman, J.; Verbeken, E.; Segers, P.; Meuris, B.; Vandenberghe, S.; Flameng, W.; Verdonck, P.R. Design of a new pulsatile bioreactor for tissue engineered aortic heart valve formation. Artif. Organs 2002, 26, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, E.S.; Evans, N.D.; Stevens, M.M. Complexity in biomaterials for tissue engineering. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhdan, V.M.; Holovanova, I.A.; Filatova, V.L.; Khorosh, M.V. Medical evaluation of efficiency of optimized models for early detection and primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Wiad. Lek. 2017, 70 Pt 1, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hicks, C.W.; Obeid, T.; Arhuidese, I.; Qazi, U.; Malas, M.B. Abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in octogenarians is associated with higher mortality compared with nonoctogenarians. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.; Ge, L.; Haraldsson, H.; Hope, M.D.; Saloner, D.A.; Guccione, J.M.; Tseng, E.E. Ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm wall stress analysis using patient-specific finite element modeling of in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 21, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ascuitto, R.; Ross-Ascuitto, N.; Guillot, M.; Celestin, C. Computational fluid dynamics characterization of pulsatile flow in central and Sano shunts connected to the pulmonary arteries: Importance of graft angulation on shear stress-induced, platelet-mediated thrombosis. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 25, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, T.; Veseli, K.; Lausberg, H.; Vohringer, L.; Schneider, W.; Schlensak, C. Regional and directional compliance of the healthy aorta: An ex vivo study in a porcine model. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 23, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piola, M.; Soncini, M.; Prandi, F.; Polvani, G.; Beniamino Fiore, G.; Pesce, M. Tools and procedures for ex vivo vein arterialization, preconditioning and tissue engineering: A step forward to translation to combat the consequences of vascular graft remodeling. Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Xiao, Y.; Voorhees, A.; Qi, Y.X.; Jiang, Z.L.; Han, H.C. Artery Remodeling Under Axial Twist in Three Days Organ Culture. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piola, M.; Ruiter, M.; Vismara, R.; Mastrullo, V.; Agrifoglio, M.; Zanobini, M.; Pesce, M.; Soncini, M.; Fiore, G.B. Full Mimicking of Coronary Hemodynamics for Ex-Vivo Stimulation of Human Saphenous Veins. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 45, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusic, R.J.; Myung, R.; Petko, M.; Gaynor, J.W.; Gooch, K.J. Shear stress and pressure modulate saphenous vein remodeling ex vivo. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakawa, A.A.; Dallan, L.A.; Lacchini, S.; Borin, T.F.; Krieger, J.E. Human saphenous vein organ culture under controlled hemodynamic conditions. Clinics 2008, 63, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piola, M.; Prandi, F.; Bono, N.; Soncini, M.; Penza, E.; Agrifoglio, M.; Polvani, G.; Pesce, M.; Fiore, G.B. A compact and automated ex vivo vessel culture system for the pulsatile pressure conditioning of human saphenous veins. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, E204–E215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prandi, F.; Piola, M.; Soncini, M.; Colussi, C.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Penza, E.; Agrifoglio, M.; Vinci, M.C.; Polvani, G.; Gaetano, C.; et al. Adventitial vessel growth and progenitor cells activation in an ex vivo culture system mimicking human saphenous vein wall strain after coronary artery bypass grafting. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janke, D.; Jankowski, J.; Ruth, M.; Buschmann, I.; Lemke, H.D.; Jacobi, D.; Knaus, P.; Spindler, E.; Zidek, W.; Lehmann, K.; et al. The “artificial artery” as in vitro perfusion model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Daniel Ou-Yang, H.; Lowe-Krentz, L.; Muzykantov, V.R.; Liu, Y. Biomimetic channel modeling local vascular dynamics of pro-inflammatory endothelial changes. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, B.; Reineke, D.; Heinisch, P.P.; Schonhoff, F.; Huber, C.; Kadner, A.; Englberger, L.; Carrel, T. Graft preservation solutions in cardiovascular surgery. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 23, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurel, B.; Sarraf, C.; Bakir, F.; Chai, F.; Maton, M.; Sobocinski, J.; Hertault, A.; Blanchemain, N.; Haulon, S.; Lermusiaux, P. A New Hemodynamic Ex Vivo Model for Medical Devices Assessment. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 29, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, J.; Sotelo, J.A.; Springmuller, D.; Montalba, C.; Letelier, K.; Tejos, C.; Irarrazaval, P.; Andia, M.E.; Razavi, R.; Valverde, I.; Uribe, S.A. Realistic aortic phantom to study hemodynamics using MRI and cardiac catheterization in normal and aortic coarctation conditions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanczyk, A.; Podyma, M.; Trebinski, L.; Chrzastek, J.; Zbicinski, I.; Stefanczyk, L. A Novel Attempt to Standardize Results of CFD Simulations Basing on Spatial Configuration of Aortic Stent-Grafts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polanczyk, A.; Klinger, M.; Nanobachvili, J.; Huk, I.; Neumayer, C. Artificial Circulatory Model for Analysis of Human and Artificial Vessels. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071017
Polanczyk A, Klinger M, Nanobachvili J, Huk I, Neumayer C. Artificial Circulatory Model for Analysis of Human and Artificial Vessels. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(7):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071017
Chicago/Turabian StylePolanczyk, Andrzej, Markus Klinger, Josif Nanobachvili, Ihor Huk, and Christoph Neumayer. 2018. "Artificial Circulatory Model for Analysis of Human and Artificial Vessels" Applied Sciences 8, no. 7: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071017
APA StylePolanczyk, A., Klinger, M., Nanobachvili, J., Huk, I., & Neumayer, C. (2018). Artificial Circulatory Model for Analysis of Human and Artificial Vessels. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071017





