Neutralization Dynamics of Slow Highly Charged Ions in 2D Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Results on Highly Charged Ion Transmission
2.1. Earlier Work
2.2. Our Work
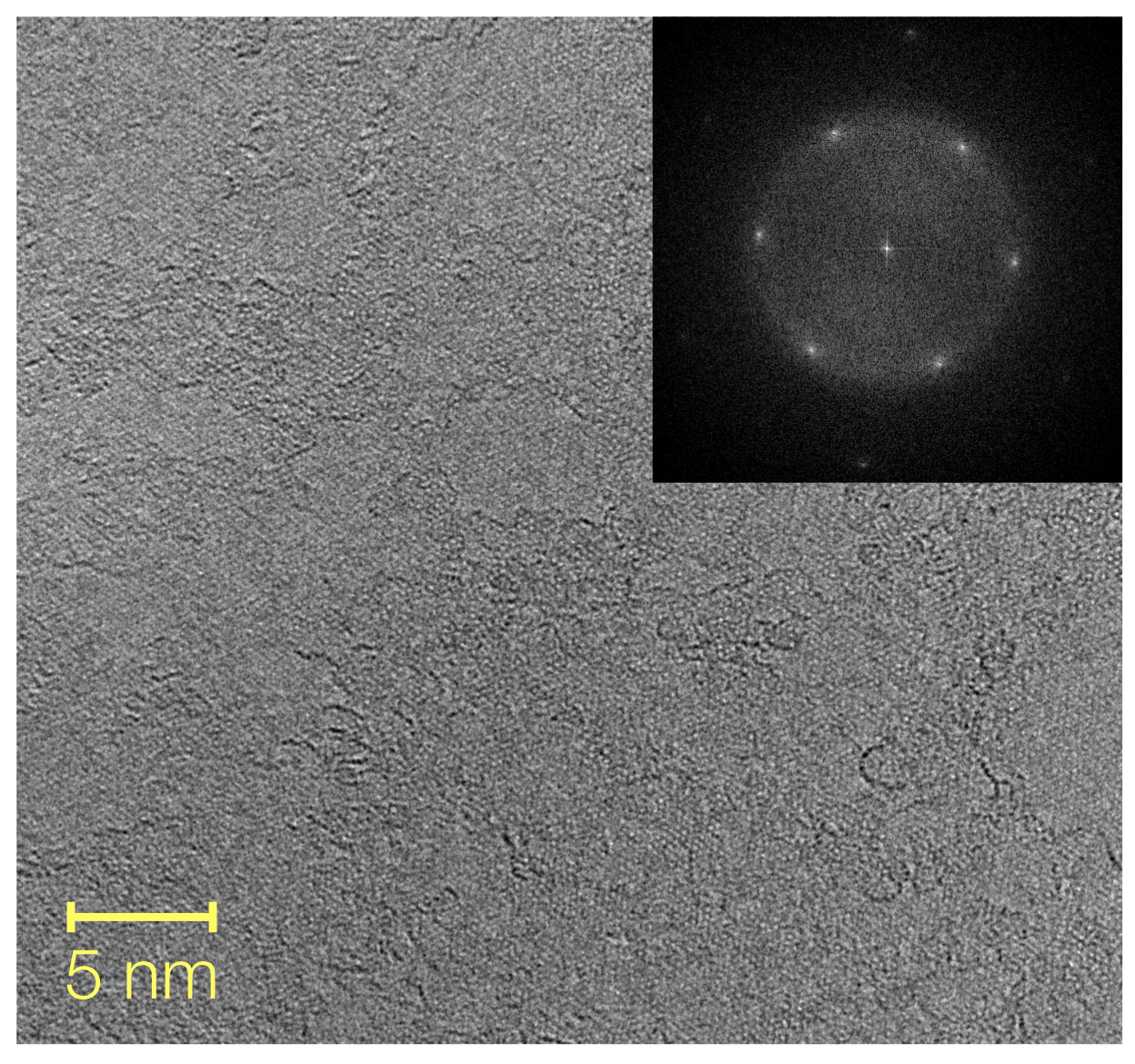
2.2.1. Carbon Nanomembranes
2.2.2. Single Layer Graphene
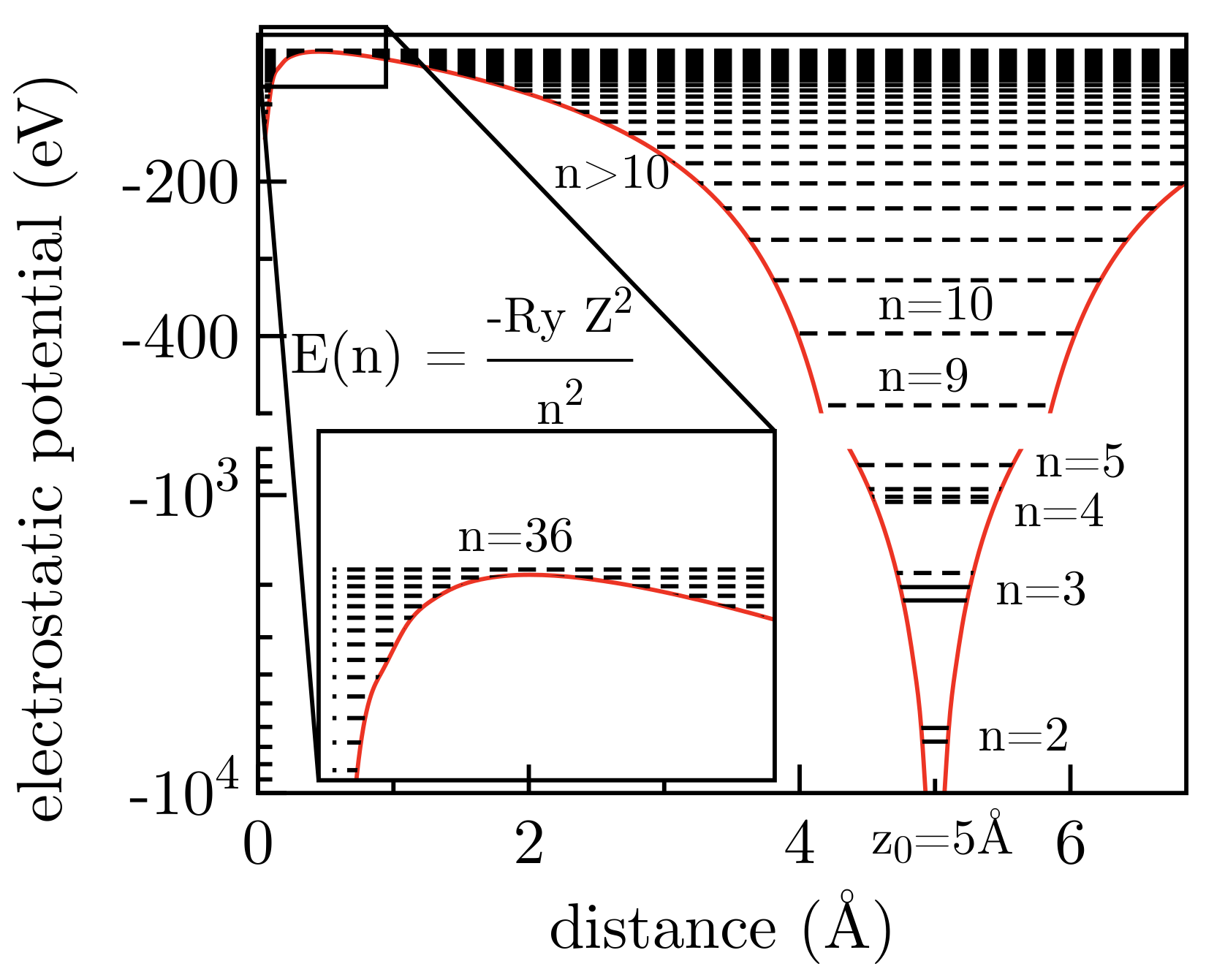
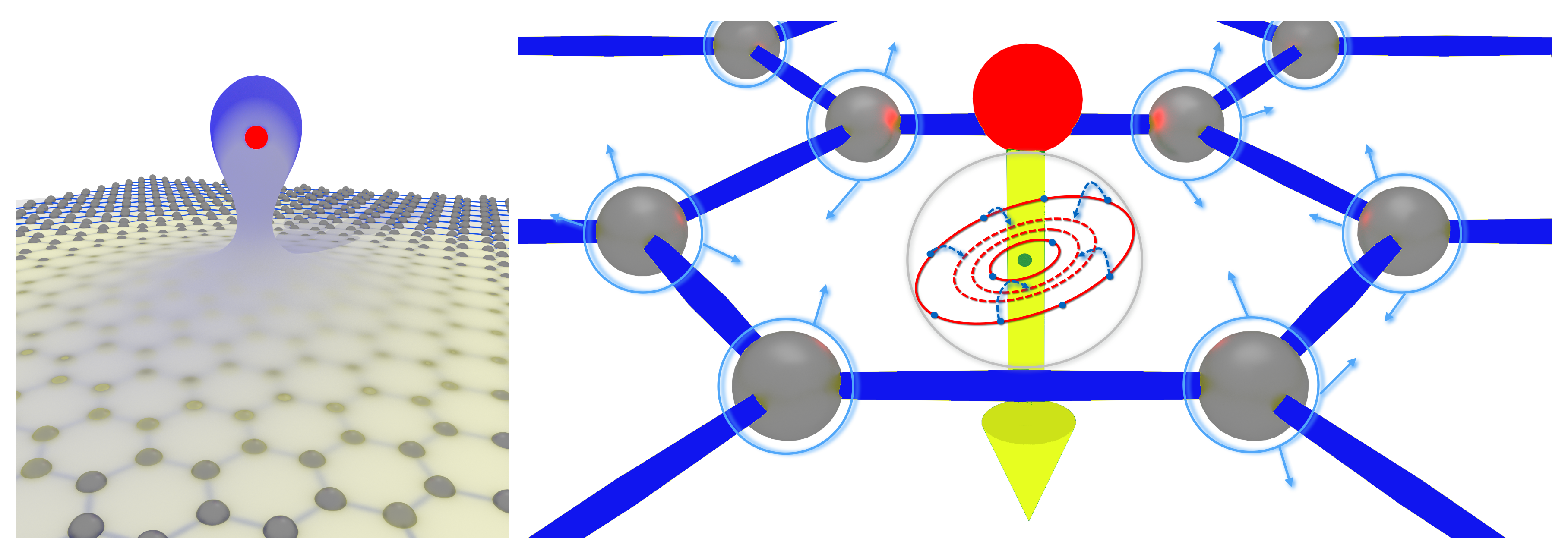
3. Discussion on Ion Interaction with 2D Materials
3.1. Single Layer Graphene
3.2. Carbon Nanomembranes
3.3. 2D Materials on Substrates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, S.; Brédy, R.; Bernard, J.; Désesquelles, J.; Chen, L. Very Fast Hollow-Atom Decay Processes in Xe30+ − C60 Collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 183401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, E.; Wilhelm, R.A.; Pétuya, R.; Smejkal, V.; Kozubek, R.; Hierzenberger, A.; Bayer, B.C.; Aldazabal, I.; Kazansky, A.K.; Libisch, F.; et al. Ultrafast electronic response of graphene to a strong and localized electric field. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ernst, P.; Kozubek, R.; Madauß, L.; Sonntag, J.; Lorke, A.; Schleberger, M. Irradiation of graphene field effect transistors with highly charged ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. 2016, 382, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebli, M.; Kiouche, A.; El-Said, A.S.; Bahlouli, H. On the formation of surface nanostructures induced by slow highly charged ions. Phys. Plasmas 2017, 24, 072115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, W.; Du, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, T. Potential effect on the interaction of highly charged ion with graphene. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2017, 407, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgdörfer, J.; Lerner, P.; Meyer, F.W. Above-surface neutralization of highly charged ions: The classical over-the-barrier model. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnau, A.; Aumayr, F.; Echenique, P.; Grether, M.; Heiland, W.; Limburg, J.; Morgenstern, R.; Roncin, P.; Schippers, S.; Schuch, R.; et al. Interaction of slow multicharged ions with solid surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 1997, 27, 113–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrée, J.J.; Casali, F.; Thumm, U. Extended classical over-barrier model for collisions of highly charged ions with conducting and insulating surfaces. Phys. Rev. A 1998, 57, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lake, R.E.; Pomeroy, J.M.; Grube, H.; Sosolik, C.E. Charge State Dependent Energy Deposition by Ion Impact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 063202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, R.E.; Sosolik, C.E.; Pomeroy, J.M. Classical over-the-barrier model for neutralization of highly charged ions above thin dielectric films. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.D. Charge States and Charge-Changing Cross Sections of Fast Heavy Ions Penetrating through Gaseous and Solid Media. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1972, 44, 465–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, R.; Cocke, C.L.; Ullrich, J.; Hagmann, S.; Stoeckli, M.; Schmidt-Boecking, H. Charge-state equilibration length of a highly charged ion inside a carbon solid. Phys. Rev. A 1994, 50, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, M.; Sataka, M.; Kawatsura, K.; Takahiro, K.; Komaki, K.; Shibata, H.; Sugai, H.; Nishio, K. Equilibrium and non-equilibrium charge-state distributions of 2 MeV/u sulfur ions passing through carbon foils. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2015, 354, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamour, E.; Fainstein, P.D.; Galassi, M.; Prigent, C.; Ramirez, C.A.; Rivarola, R.D.; Rozet, J.P.; Trassinelli, M.; Vernhet, D. Improvement of the ETACHA Code towards low velocities and many-electron ions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 635, 032022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farimani, A.B.; Min, K.; Aluru, N.R. DNA Base Detection Using a Single-Layer MoS 2. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7914–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy-Mayhew, J.D.; Bozym, D.J.; Punckt, C.; Aksay, I.A. Functionalized Graphene as a Catalytic Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kepaptsoglou, D.; Hardcastle, T.P.; Seabourne, C.R.; Bangert, U.; Zan, R.; Amani, J.A.; Hofsäss, H.; Nicholls, R.J.; Brydson, R.M.D.; Scott, A.J.; et al. Electronic Structure Modification of Ion Implanted Graphene: The Spectroscopic Signatures of p- and n-Type Doping. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11398–11407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritter, R.; Wilhelm, R.A.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Heller, R.; Mücklich, A.; Werner, U.; Vieker, H.; Beyer, A.; Facsko, S.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Aumayr, F. Fabrication of nanopores in 1 nm thick carbon nanomembranes with slow highly charged ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 063112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, R.A.; Gruber, E.; Ritter, R.; Heller, R.; Facsko, S.; Aumayr, F. Charge Exchange and Energy Loss of Slow Highly Charged Ions in 1 nm Thick Carbon Nanomembranes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 153201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, R.A.; Gruber, E.; Ritter, R.; Heller, R.; Beyer, A.; Turchanin, A.; Klingner, N.; Hübner, R.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Vieker, H.; et al. Threshold and efficiency for perforation of 1 nm thick carbon nanomembranes with slow highly charged ions. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, R.A.; Möller, W. Charge-state-dependent energy loss of slow ions. II. Statistical atom model. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 052709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, R.; Gruber, E.; Smejkal, V.; Facsko, S.; Aumayr, F. Charge-state-dependent energy loss of slow ions. I. Experimental results on the transmission of highly charged ions. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 052708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, R.A.; Gruber, E.; Schwestka, J.; Kozubek, R.; Madeira, T.I.; Marques, J.P.; Kobus, J.; Krasheninnikov, A.V.; Schleberger, M.; Aumayr, F. Interatomic Coulombic Decay: The Mechanism for Rapid Deexcitation of Hollow Atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwestka, J.; Melinc, D.; Heller, R.; Niggas, A.; Leonhartsberger, L.; Winter, H.; Facsko, S.; Aumayr, F.; Wilhelm, R. A versatile ion beam spectrometer for studies of ion interaction with 2D materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Niehaus, A. A classical model for multiple-electron capture in slow collisions of highly charged ions with atoms. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Phys. 1986, 19, 2925–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, J.P.; Giardino, G.; Borsoni, G.; Froment, M.; Eddrief, M.; Sébenne, C.; Bardin, S.; Schneider, D.; Jin, J.; Khemliche, H.; et al. Decay of hollow atoms above and below a surface. Phys. Rev. A 1996, 54, 4136–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemell, C.; Stöckl, J.; Burgdörfer, J.; Betz, G.; Winter, H.; Aumayr, F. Multicharged Ion Impact on Clean Au(111): Suppression of Kinetic Electron Emission in Glancing Angle Scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H. Collisions of atoms and ions with surfaces under grazing incidence. Phys. Rep. 2002, 367, 387–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolterfoht, N.; Arnau, A.; Grether, M.; Köhrbrück, R.; Spieler, A.; Page, R.; Saal, A.; Thomaschewski, J.; Bleck-Neuhaus, J. Multiple-cascade model for the filling of hollow Ne atoms moving below an Al surface. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 52, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducrée, J.; Andrä, H.J.; Thumm, U. Neutralization of hyperthermal multiply charged ions at surfaces: Comparison between the extended dynamical overbarrier model and experiment. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 60, 3029–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.; Aumayr, F. Hollow atoms. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1999, 32, R39–R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschornack, G.; Musiol, G.; Wagner, W. Dirac Fock Slater X-ray Energy Shifts and Electron Binding Energy Changes for All Ion Ground States in Elements Up to Uranium, zfk–574 ed.; Inst. für Kernforschung: Dresden, Germany, 1986; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, R.; Facsko, S.; Wilhelm, R.A.; Möller, W. Defect Mediated Desorption of the KBr(001) Surface Induced by Single Highly Charged Ion Impact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 096102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tona, M.; Watanabe, H.; Takahashi, S.; Fujita, Y.; Abe, T.; Jian, S.; Nakamura, N.; Yoshiyasu, N.; Yamada, C.; Sakurai, M.; et al. Observation of HCI-induced nanostructures with a scanning probe microscope. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 58, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Said, A.S.; Heller, R.; Meissl, W.; Ritter, R.; Facsko, S.; Lemell, C.; Solleder, B.; Gebeshuber, I.C.; Betz, G.; Toulemonde, M.; et al. Creation of Nanohillocks on CaF2 Surfaces by Single Slow Highly Charged Ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 237601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Said, A.S.; Wilhelm, R.A.; Heller, R.; Sorokin, M.; Facsko, S.; Aumayr, F. Tuning the Fabrication of Nanostructures by Low-Energy Highly Charged Ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumayr, F.; Varga, P.; Winter, H. Potential sputtering: Desorption from insulator surfaces by impact of slow multicharged ions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 192, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumayr, F.; Winter, H. Potential sputtering. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, R.A.; Heller, R.; Facsko, S. Slow highly charged ion induced nanopit formation on the KCl(001) surface. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2016, 115, 43001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, N. The penetration of atomic particles through matter. Math. Fys. Medd. Dan. Vid. Selsk. 1948, 18, 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hattass, M.; Schenkel, T.; Hamza, A.V.; Barnes, A.V.; Newman, M.W.; McDonald, J.W.; Niedermayr, T.R.; Machicoane, G.A.; Schneider, D.H. Charge Equilibration Time of Slow, Highly Charged Ions in Solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4795–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkerts, L.; Schippers, S.; Zehner, D.M.; Meyer, F.W. Time Scales for Charge Equilibration of Oq+ (3 < q < 8) Ions during Surface-Channeling Interactions with Au(110). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 2204–2207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winecki, S.; Cocke, C.L.; Fry, D.; Stöckli, M.P. Neutralization and equilibration of highly charged argon ions at grazing incidence on a graphite surface. Phys. Rev. A 1996, 53, 4228–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkel, T.; Briere, M.A.; Schmidt-Böcking, H.; Bethge, K.; Schneider, D.H. Electronic Sputtering of Thin Conductors by Neutralization of Slow Highly Charged Ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2481–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winecki, S.; Stöckli, M.P.; Cocke, C.L. Energy loss of highly charged argon ions at grazing incidence on a graphite surface. Phys. Rev. A 1997, 55, 4310–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smejkal, V.; Gruber, E.; Wilhelm, R.; Brandl, L.; Heller, R.; Facsko, S.; Aumayr, F. A setup for transmission measurements of low energy multiply charged ions through free-standing few atomic layer films. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2016, 382, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchanin, A.; Käfer, D.; El-Desawy, M.; Wöll, C.; Witte, G.; Gölzhäuser, A. Molecular Mechanisms of Electron-Induced Cross-Linking in Aromatic SAMs. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7342–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchanin, A.; Beyer, A.; Nottbohm, C.T.; Zhang, X.; Stosch, R.; Sologubenko, A.; Mayer, J.; Hinze, P.; Weimann, T.; Gölzhäuser, A. One Nanometer Thin Carbon Nanosheets with Tunable Conductivity and Stiffness. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biersack, J. The effect of high charge states on the stopping and ranges of ions in solids. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1993, 80–81, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insepov, Z.; Hassanein, A.; Swenson, D.; Terasawa, M. Computer simulation of surface modification with ion beams. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2005, 241, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neidhart, T.; Pichler, F.; Aumayr, F.; Winter, H.; Schmid, M.; Varga, P. Potential Sputtering of Lithium Fluoride by Slow Multicharged Ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 5280–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Kumamoto, A.; Kim, S.; Chen, X.; Hou, B.; Chiashi, S.; Einarsson, E.; Ikuhara, Y.; Maruyama, S. Self-Limiting Chemical Vapor Deposition Growth of Monolayer Graphene from Ethanol. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 10755–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algara-Siller, G.; Lehtinen, O.; Turchanin, A.; Kaiser, U. Dry-cleaning of graphene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 153115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Abajo, F.J.; Echenique, P.M. Wake potential in the vicinity of a surface. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 2663–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakhmedov, M. Auger and X-ray spectra formed at highly charged ion neutralization near the metal surface. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1995, 98, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez Muiño, R.; Salin, A.; Stolterfoht, N.; Arnau, A.; Echenique, P.M. Auger and radiative filling rates of highly charged ions below metal surfaces. Phys. Rev. A 1998, 57, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeri, P.; Quinet, P.; Zitane, N.; Vaeck, N. Calculation of Auger rates for complex hollow-atom configurations. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2001, 34, 4125–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederbaum, L.S.; Zobeley, J.; Tarantelli, F. Giant Intermolecular Decay and Fragmentation of Clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 4778–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, T. Interatomic and intermolecular Coulombic decay: The coming of age story. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2015, 48, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrwall, G.; Tchaplyguine, M.; Lundwall, M.; Feifel, R.; Bergersen, H.; Rander, T.; Lindblad, A.; Schulz, J.; Peredkov, S.; Barth, S.; et al. Femtosecond Interatomic Coulombic Decay in Free Neon Clusters: Large Lifetime Differences between Surface and Bulk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 173401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averbukh, V.; Cederbaum, L.S. Ab initio calculation of interatomic decay rates by a combination of the Fano ansatz, Green’s-function methods, and the Stieltjes imaging technique. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 204107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averbukh, V.; Cederbaum, L.S. Interatomic Electronic Decay in Endohedral Fullerenes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 053401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insepov, Z.; Ainabayev, A.; Kirkpatrick, S.; Walsh, M.; Vyatkin, A.F. Nanometer size hole fabrication in 2d ultrathin films with cluster ion beams. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 075014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopster, J.; Kozubek, R.; Krämer, J.; Sokolovsky, V.; Schleberger, M. Ultra-thin MoS2 irradiated with highly charged ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2013, 317, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopster, J.; Kozubek, R.; Ban-d’Etat, B.; Guillous, S.; Lebius, H.; Schleberger, M. Damage in graphene due to electronic excitation induced by highly charged ions. 2D Mater. 2014, 1, 011011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, H.; Sun, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Wang, T.; et al. Raman spectroscopy of graphene irradiated with highly charged ions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 306, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, J.; Yao, H.; Zhai, P.; Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Hu, P.; Duan, J.; Mo, D.; Hou, M.; et al. Comparative study of irradiation effects in graphite and graphene induced by swift heavy ions and highly charged ions. Carbon N. Y. 2016, 100, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochedowski, O.; Lehtinen, O.; Kaiser, U.; Turchanin, A.; Ban-d’Etat, B.; Lebius, H.; Karlušić, M.; Jakšić, M.; Schleberger, M. Nanostructuring graphene by dense electronic excitation. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 465302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aumayr, F.; Facsko, S.; El-Said, A.; Trautmann, C.; Schleberger, M. Single ion induced surface nanostructures: A comparison between slow highly charged and swift heavy ions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 393001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Grygiel, C.; Dufour, C.; Sun, J.R.; Wang, Z.G.; Zhao, Y.T.; Xiao, G.Q.; Cheng, R.; Zhou, X.M.; Ren, J.R.; et al. Energy deposition by heavy ions: Additivity of kinetic and potential energy contributions in hillock formation on CaF2. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilhelm, R.A.; Gruber, E.; Schwestka, J.; Heller, R.; Fascko, S.; Aumayr, F. Neutralization Dynamics of Slow Highly Charged Ions in 2D Materials. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071050
Wilhelm RA, Gruber E, Schwestka J, Heller R, Fascko S, Aumayr F. Neutralization Dynamics of Slow Highly Charged Ions in 2D Materials. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(7):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071050
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilhelm, Richard A., Elisabeth Gruber, Janine Schwestka, René Heller, Stefan Fascko, and Friedrich Aumayr. 2018. "Neutralization Dynamics of Slow Highly Charged Ions in 2D Materials" Applied Sciences 8, no. 7: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071050
APA StyleWilhelm, R. A., Gruber, E., Schwestka, J., Heller, R., Fascko, S., & Aumayr, F. (2018). Neutralization Dynamics of Slow Highly Charged Ions in 2D Materials. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071050




