Shear Wave Elastography Measures of the Achilles Tendon: Influence of Time of Day, Leg Dominance and the Impact of an Acute 30-Minute Bout of Running
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Methods
2.3. Scanning Techniques
2.4. Conventional Ultrasound Technique
2.5. Shear Wave Elastography
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Time of Day
3.2. Leg Dominance
3.3. Acute Bout of Exercise
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joseph, M.F.; Lillie, K.R.; Bergeron, D.J.; Deneqar, C.R. Measuring Achilles Tendon Mechanical Properties: A Reliable, Non-invasive method. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2017–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, S.J.; Onambele, G.N.L. Influence of time of day on tendon compliance and estimations of voluntary activation levels. Muscle Nerve 2006, 33, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onambele-Pearson, N.L.G.; Pearson, S.J. Time-of-day effect on patella tendon stiffness alters vastus lateralis fascicle length but not the quadriceps force-angle relationship. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.M.; Scott, A. Mechanotherapy: How physical therapists’ prescription of exercise promotes tissue repair. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuite, D.J.; Renström, P.A.F.H.; O’Brien, M. The aging tendon. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2007, 7, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curwin, S. Rehabilitation after tendon injuries. In Tendon Injuries: Basic Science and Clinical Medicine; Maffulli, N., Renstrom, P., Leadbetter, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: London, UK, 2005; pp. 242–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer, M. Role of extracellular matrix in adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to mechanical loading. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 649–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H. Mechanobiology of tendon. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1563–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, S.P.; Narici, M.V.; Maganaris, C.N.; Kiaer, M. Human tendon behaviour and adaptation, in vivo. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obst, S.J.; Barrett, R.S.; Newsham-West, R. Immediate effect of exercise on achilles tendon properties: Systematic review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, K.E.; Graham-smith, P.; Pearson, S.J. Effect of Acute Tensile Loading on Gender-Specific Tendon Structural and Mechanical Properties. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, E.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T.; Kawakami, Y. Changes in ankle joint stiffness due to stretching: The role of tendon elongation of the gastrocnemius muscle. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2010, 10, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, C.I.; Degens, H.; Seynnes, O.R.; Maqanaris, C.N.; Jones, D.A. The acute effect of stretching on the passive stiffness of the human gastrocnemius muscle tendon unit. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubo, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Effects of transient muscle contractions and stretching on the tendon structures in vivo. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2002, 175, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.D.; Blazevich, A.J. Isometric contractions reduce plantar flexor moment, Achilles tendon stiffness, and neuromuscular activity but remove the subsequent effects of stretch. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kay, A.D.; Blazevich, A.J. Concentric muscle contractions before static stretching minimize, but do not remove, stretch-induced force deficits. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubo, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukunaga, T. Influence of static stretching on viscoelastic properties of human tendon structures in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Ikezoe, T.; Takeno, Y.; Ichihashi, N. Acute and prolonged effect of static stretching on the passive stiffness of the human gastrocnemius muscle tendon unit in vivo. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, D.Y.; Rubenson, J.; Carr, A.; Mattson, J.; Besier, T.; Chou, L.B. Influence of Stretching and Warm-Up on Achilles Tendon Material Properties. Foot Ankle Int. 2011, 32, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mademli, L.; Arampatzis, A.; Walsh, M. Effect of muscle fatigue on the compliance of the gastrocnemius medialis tendon and aponeurosis. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mademli, L.; Arampatzis, A. Mechanical and morphological properties of the triceps surae muscle-tendon unit in old and young adults and their interaction with a submaximal fatiguing contraction. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Umemura, Y. Viscoelasticity of the muscle-tendon unit is returned more rapidly than range of motion after stretching. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, D.J.; Trewartha, G.; McGuigan, M.P. The effects of a 30-min run on the mechanics of the human Achilles tendon. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltonen, J.; Cronin, N.J.; Avela, J.; Finni, T. In vivo mechanical response of human Achilles tendon to a single bout of hopping exercise. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosengarten, S.D.; Cook, J.L.; Bryant, A.L.; Cordy, J.T.; Daffy, J.; Docking, S.I. Australian football players’ Achilles tendons respond to game loads within 2 days: An ultrasound tissue characterisation (UTC) study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsgaard, M.; Aagaard, P. Structural Achilles tendon properties in athletes subjected to different exercise modes and in Achilles tendon rupture patients. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Docking, S.I.; Cook, J. Pathological tendons maintain sufficient aligned fibrillar structure on ultrasound tissue characterization (UTC). Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.L.; Purdam, C.R. Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced tendinopathy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, P.R. Principles of ultrasound elastography. Ultrasound 2012, 20, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, S.; Risson, J.; Kastler, A.; Barbier-Brion, B.; Siliman, G.; Runge, M.; Kastler, B. Biomechanical properties of the calcaneal tendon in vivo assessed by transient shear wave elastography. Skelet. Radiol. 2013, 42, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arda, K.; Ciledag, N.; Aktas, E.; Aribas, B.K.; Köse, K. Quantitative assessment of normal soft-tissue elasticity using shear-wave ultrasound elastography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, B.C.W.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lee, A.W.C.; Leung, V.Y.; Fu, S.N. Elastic modulus of muscle and tendon with shear wave ultrasound elastography: Variations with different technical settings. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Cui, L.; He, P.; Shen, W.W.; Qian, Y.J.; Wang, J.R. Shear wave elastographic characterization of normal and torn achilles tendons a pilot study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltz, C.D.; Haladik, J.A.; Divine, G.; Siegal, D.; van Holsbeeck, M.; Bey, M.J. ShearWave elastography: Repeatability for measurement of tendon stiffness. Skelet. Radiol. 2013, 42, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, N.; Hirata, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Yoshitake, Y. Validity of measurement of shear modulus by ultrasound shear wave elastography in human pennate muscle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Greenleaf, J.F.; An, K.N. Validation of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siu, W.; Chan, C.; Lam, C.; Lee, C.M.; Ying, M. Sonographic evaluation of the effect of long-term exercise on Achilles tendon stiffness using shear wave elastography. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Ying, M. Sonographic measurement of Achilles tendons in asymptomatic subjects. J. Ultrasound Med. 2006, 25, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Marzilger, R.; Schroll, A.; Arampatzis, A. Asymmetry of Achilles tendon mechanical and morphological properties between both legs. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.B.; Schuckman, B.E.; Docherty, C.L.; Schrader, J.; Poppy, W. Differences in ankle range of motion before and after exercise in 2 tape conditions. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, S.B.; Sekir, U.; Gur, H.; Akova, B. Eccentric/concentric training of ankle evertor and dorsiflexors in recreational athletes: Muscle latency and strength. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, e29–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-K.; Lien, Y.-H.; Lin, K.-H.; Shih, T.T.; Wang, T.G.; Wang, H.K. Relationships between three potentiation effects of plyometric training and performance. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, e80–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, C.; Webborn, N.; Watt, P.; Cercianani, M. Poor reproducibility of compression elastography in the Achilles tendon: Same day and consecutive day measurements. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, R.; Kongsgaard, M.; Hougs Kjaer, B.; Øhlenschlæger, T.; Kjær, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Heavy Slow Resistance Versus Eccentric Training as Treatment for Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianculescu, V.; Ciolovan, L.M.; Dunant, A.; Vielh, P.; Mazouni, C.; Delaloge, S.; Dromain, C.; Blidaru, A.; Balleyguier, C. Added value of Virtual Touch IQ shear wave elastography in the ultrasound assessment of breast lesions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, J.R.; Trahey, G.E.; Nightingale, K.R.; Palmeri, M.L. Acoustic radiation force elasticity imaging in diagnostic ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbon, W.W.; Cooper, J.R.; Radcliffe, G.S. Sonographic incidence of tendon microtears in athletes with chronic Achilles tendinosis. Br. J. Sports Med. 1999, 33, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Docking, S.I.; Daffy, J.; van Schie, H.T.M.; Cook, J.L. Tendon structure changes after maximal exercise in the Thoroughbred horse: Use of ultrasound tissue characterisation to detect in vivo tendon response. Vet. J. 2012, 194, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, C.I.; Marsh, R.L. Effects of exercise on the biomechanical, biochemical and structural properties of tendons. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002, 133, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.K.C.; Chu, K.L.; Lai, C. Sonographic evaluation of the immediate effects of eccentric heel drop exercise on Achilles tendon and gastrocnemius muscle stiffness using shear wave elastography. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chino, K.; Akagi, R.; Dohi, M.; Fukashiro, S.; Takahashi, H. Reliability and validity of quantifying absolute muscle hardness using ultrasound elastography. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Zhao, H.; Brault, J.S.; Chen, S.; An, K.N. Ultrasound elastography: The new frontier in direct measurement of muscle stiffness. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, C.; Watt, P.; Cercignani, M.; Webborn, N. Reproducibility of shear wave elastography measures of the Achilles tendon. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
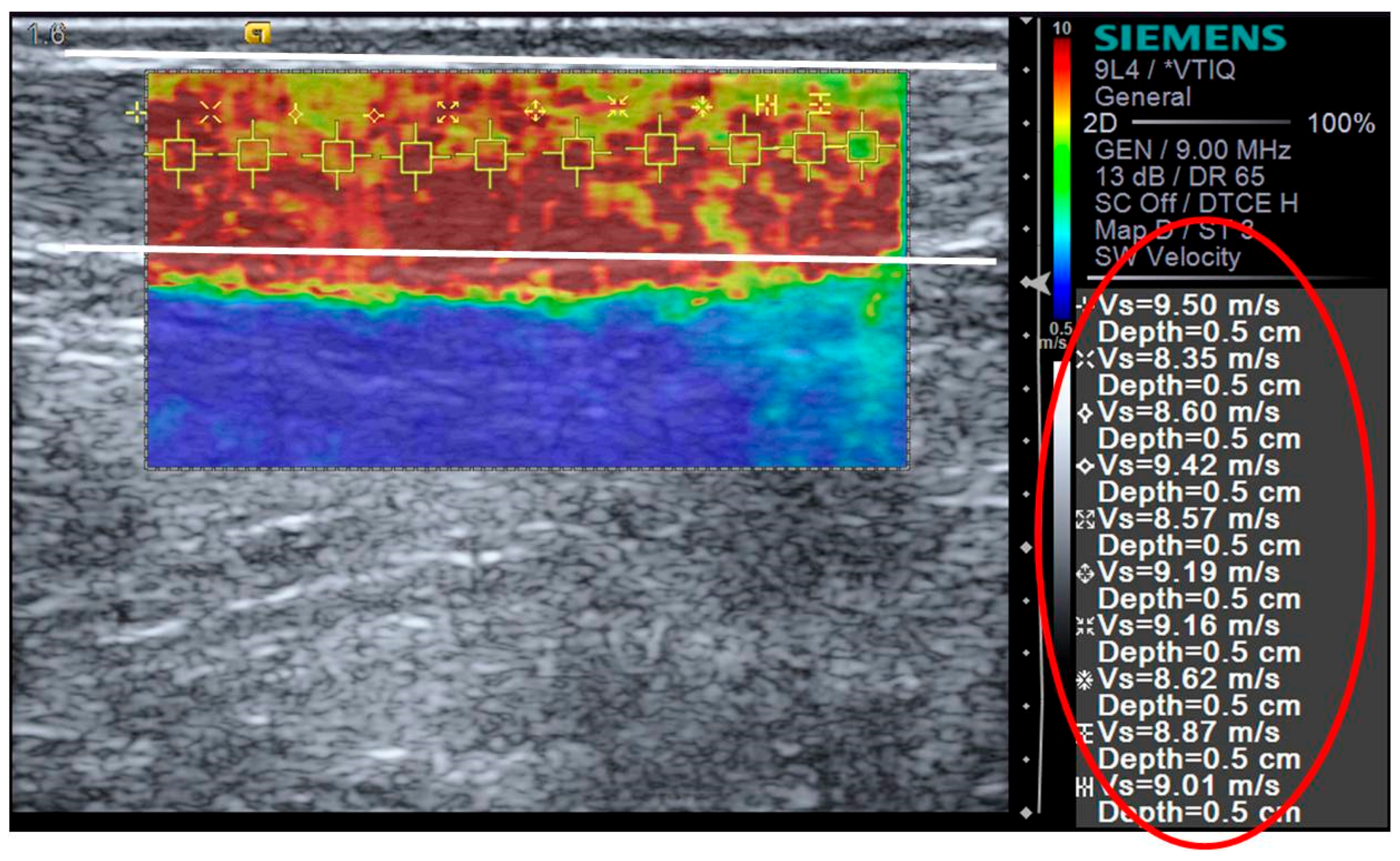
| PRE | POST | 6 h POST | 24 h POST | 48 h POST | 72 h POST | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUN AT Length (mm) | 44.3 ± 11.2 | 45.0 ± 11.2 | 44.8 ± 11.3 | 44.1 ± 11.1 | 44.3 ± 11.1 | 44.1 ± 10.8 |
| CONT AT Length (mm) | 29.9 ± 5.7 | 29.6 ± 6.2 | 30.0 ± 5.9 | 30.0 ± 5.6 | 30.2 ± 5.6 | 30.0 ± 5.2 |
| RUN Max AP (mm) | 4.37 ± 0.27 | 4.08 ± 0.19 | 4.58 ± 0.29 | 4.38 ± 0.26 | 4.45 ± 0.31 | 4.34 ± 0.28 |
| CONT Max AP (mm) | 4.66 ± 0.64 | 4.69 ± 0.63 | 4.63 ± 0.64 | 4.71 ± 0.61 | 4.63 ± 0.69 | 4.66 ± 0.63 |
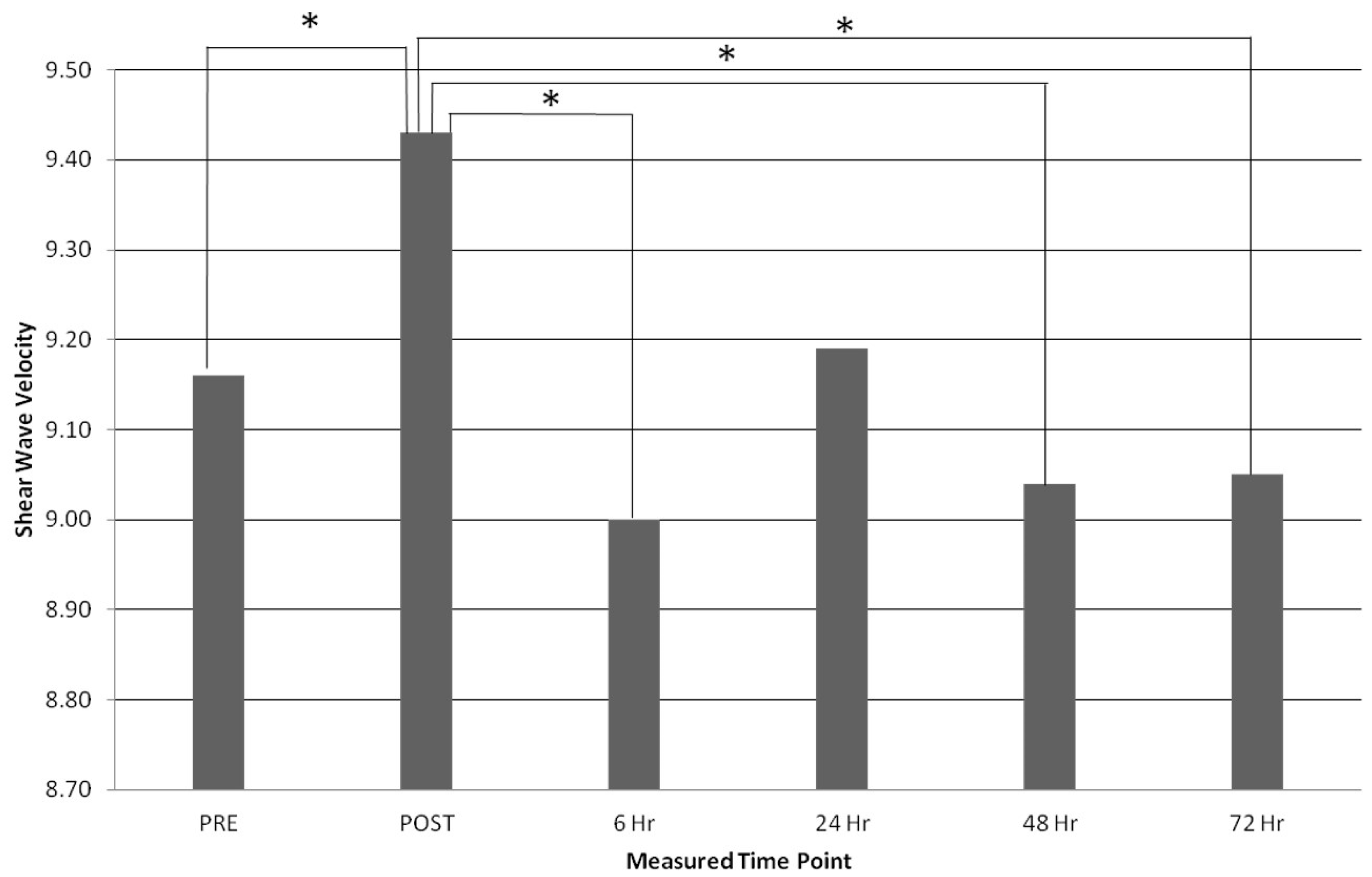
| RUN SWV (m/s) | 9.16 ± 0.39 | 9.43 ± 0.39 | 9.00 ± 0.42 | 9.19 ± 0.31 | 9.04 ± 0.36 | 9.05 ± 0.28 |
| CONT SWV (m/s) | 9.11 ± 0.23 | 9.08 ± 0.22 | 9.04 ± 0.26 | 9.05 ± 0.22 | 9.06 ± 0.21 | 9.09 ± 0.22 |
| Absolute Difference | % Difference | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Post | −0.29 mm | −6.64% | p = 0.000 ** |
| Pre-6 h | 0.21 mm | 4.81% | p = 0.042 * |
| Post-6 h | 0.50 mm | 12.25% | p = 0.000 ** |
| Post-24 h | 0.30 mm | 7.35% | p = 0.000 ** |
| Post-48 h | 0.37 mm | 9.07% | p = 0.000 ** |
| Post-72 h | 0.26 mm | 6.37% | p = 0.000 ** |
| Post-6 h–Post-24 h | −0.20 mm | −4.37% | p = 0.028 * |
| Absolute Difference | % Difference | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Post | −0.27 m/s | −2.95% | P = 0.037 * |
| Post-6 h | −0.43 m/s | −4.56% | P = 0.019 * |
| Post-48 h | −0.39 m/s | −4.14% | P = 0.015 * |
| Post-72 h | −0.38 m/s | −4.03% | P = 0.013 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Payne, C.; Watt, P.; Webborn, N. Shear Wave Elastography Measures of the Achilles Tendon: Influence of Time of Day, Leg Dominance and the Impact of an Acute 30-Minute Bout of Running. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071170
Payne C, Watt P, Webborn N. Shear Wave Elastography Measures of the Achilles Tendon: Influence of Time of Day, Leg Dominance and the Impact of an Acute 30-Minute Bout of Running. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(7):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071170
Chicago/Turabian StylePayne, Catherine, Peter Watt, and Nick Webborn. 2018. "Shear Wave Elastography Measures of the Achilles Tendon: Influence of Time of Day, Leg Dominance and the Impact of an Acute 30-Minute Bout of Running" Applied Sciences 8, no. 7: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071170
APA StylePayne, C., Watt, P., & Webborn, N. (2018). Shear Wave Elastography Measures of the Achilles Tendon: Influence of Time of Day, Leg Dominance and the Impact of an Acute 30-Minute Bout of Running. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071170






