Novel Phenotypic Elements of Type IV Collagenopathy Revealed by the Drosophila Model
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Myopathic Defects in Drosophila col4a1 Mutants
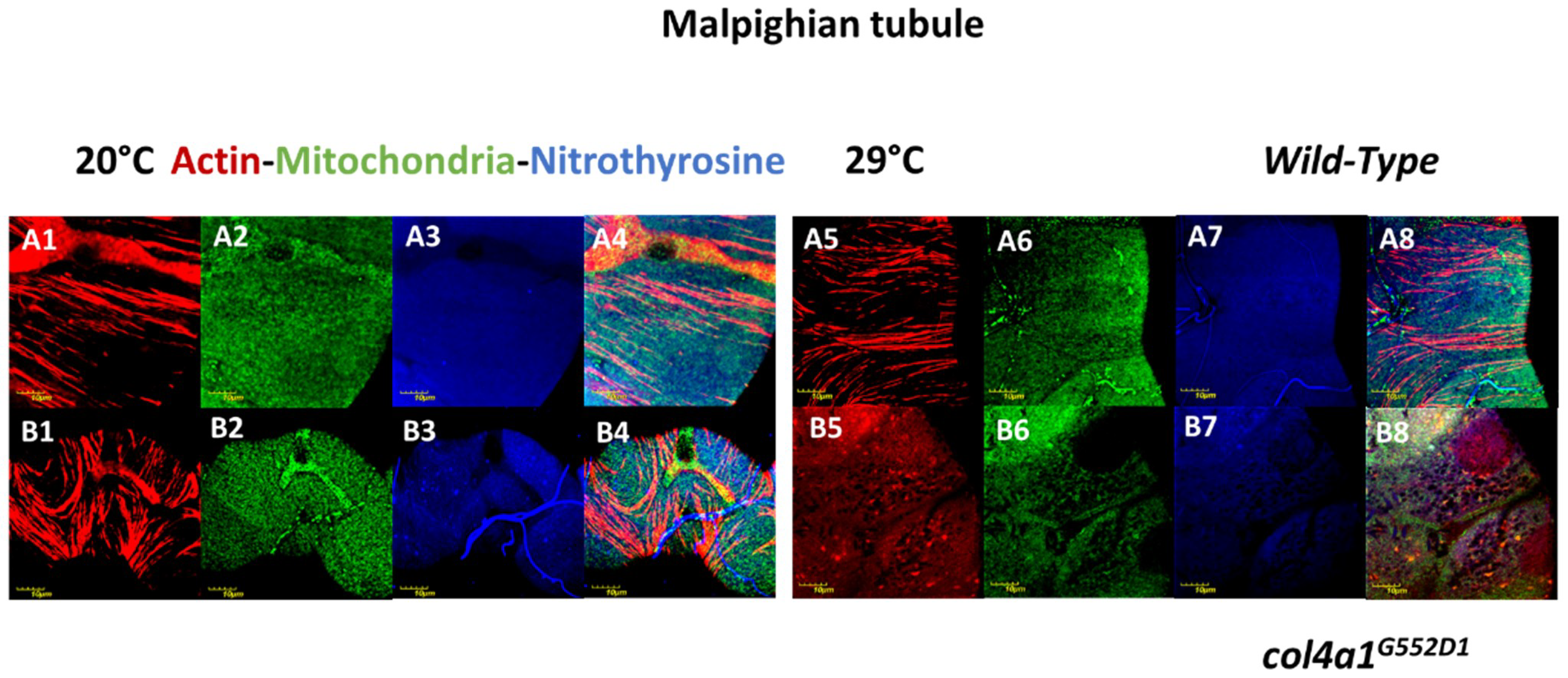
3. Compromised Excretory System in the Mutants
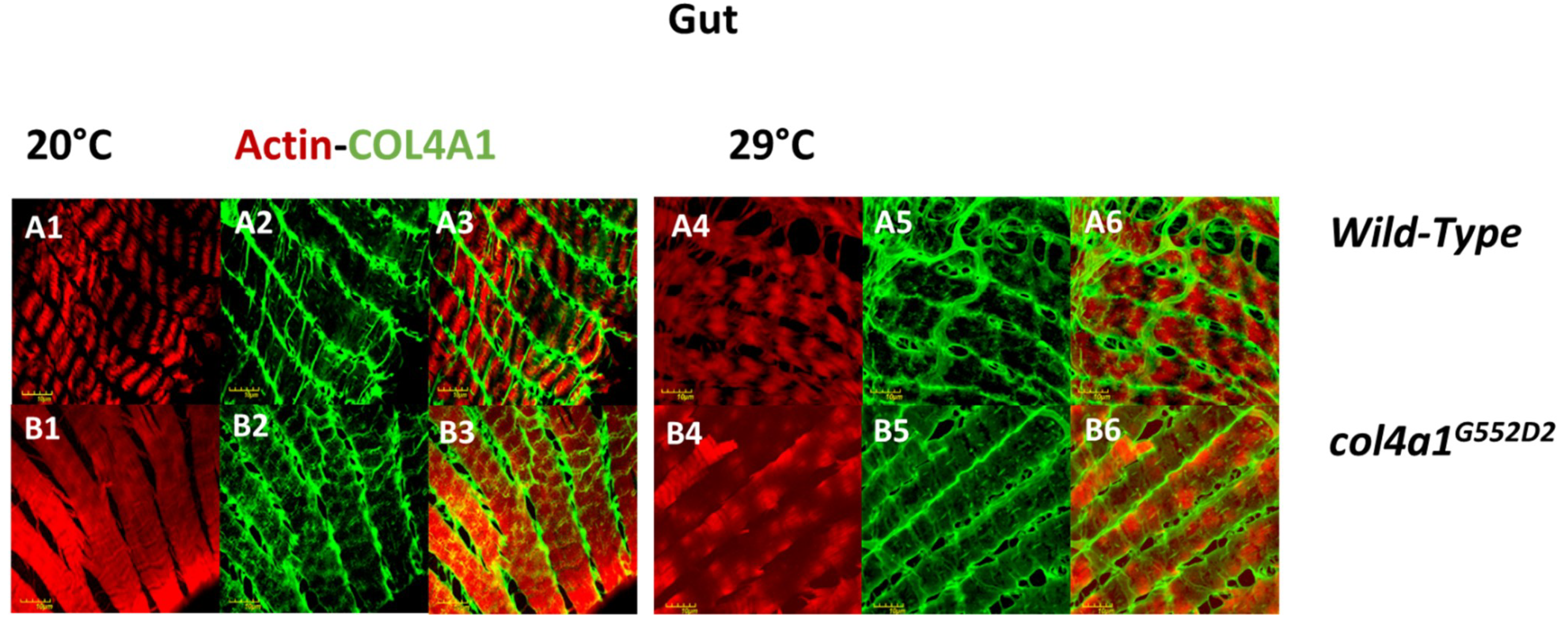
4. Intestinal Manifestation of col4a1 Mutations in Drosophila
5. Materials and Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pozzi, A.; Yurchenco, P.D.; Iozzo, R.V. The nature and biology of basement membranes. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenco, P.D.; Patton, B.L. Developmental and pathogenic mechanisms of basement membrane assembly. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, S.S.; Fässler, R. Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sado, Y.; Kagawa, M.; Naito, I.; Ueki, Y.; Seki, T.; Momota, R.; Oohashi, T.; Ninomiya, Y. Organization and expression of basement membrane collagen IV genes and their roles in human disorders. J. Biochem. 1998, 123, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtan, C.E. Alport syndrome. An inherited disorder of renal, ocular, and cochlear basement membranes. Medicine (Baltimore) 1999, 78, 338–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miosge, N. The ultrastructural composition of basement membranes in vivo. Histol. Histopathol. 2001, 16, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Mallebrera, C.; Brown, S.C.; Sewry, C.A.; Muntoni, F. Congenital muscular dystrophy: molecular and cellular aspects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagawa, M.; Toda, T. The genetic and molecular basis of muscular dystrophy: roles of cell-matrix linkage in the pathogenesis. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 51, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejas, V.; Hinkes, B.; Alkandari, F.; Al-Gazali, L.; Annexstad, E.; Aytac, M.B.; Barrow, M.; Bláhová, K.; Bockenhauer, D.; Cheong, H.I.; et al. Mutations in the human laminin beta2 (LAMB2) gene and the associated phenotypic spectrum. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alport, A.C. Hereditary Familial Congenital Haemorrhagic Nephritis. Br. Med. J. 1927, 1, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlajaniemi, T.; Tryggvason, K.; Myers, J.C.; Kurkinen, M.; Lebo, R.; Cheung, M.C.; Prockop, D.J.; Boyd, C.D. cDNA clones coding for the pro-alpha1(IV) chain of human type IV procollagen reveal an unusual homology of amino acid sequences in two halves of the carboxyl-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 7681–7687. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.D.; Weliky, K.; Toth-Fejel, S.; Deak, S.B.; Christiano, A.M.; Mackenzie, J.W.; Sandell, L.J.; Tryggvason, K.; Magenis, E. The single copy gene coding for human alpha 1 (IV) procollagen is located at the terminal end of the long arm of chromosome 13. Hum. Genet. 1986, 74, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazel, D.; Pollner, R.; Oberbäumer, I.; Kühn, K. Human basement membrane collagen (type IV). The amino acid sequence of the alpha 2(IV) chain and its comparison with the alpha 1(IV) chain reveals deletions in the alpha 1(IV) chain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 172, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkowski, R.J.; Langeveld, J.P.; Wieslander, J.; Hamilton, J.; Hudson, B.G. Localization of the Goodpasture epitope to a novel chain of basement membrane collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 7874–7877. [Google Scholar]
- Saus, J.; Wieslander, J.; Langeveld, J.P.; Quinones, S.; Hudson, B.G. Identification of the Goodpasture antigen as the alpha 3(IV) chain of collagen IV. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13374–13380. [Google Scholar]
- Hostikka, S.L.; Eddy, R.L.; Byers, M.G.; Höyhtyä, M.; Shows, T.B.; Tryggvason, K. Identification of a distinct type IV collagen alpha chain with restricted kidney distribution and assignment of its gene to the locus of X chromosome-linked Alport syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oohashi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Mattei, M.G.; Ninomiya, Y. Identification of a new collagen IV chain, alpha 6(IV), by cDNA isolation and assignment of the gene to chromosome Xq22, which is the same locus for COL4A5. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7520–7526. [Google Scholar]
- Antignac, C.; Zhou, J.; Sanak, M.; Cochat, P.; Roussel, B.; Deschênes, G.; Gros, F.; Knebelmann, B.; Hors-Cayla, M.C.; Tryggvason, K. Alport syndrome and diffuse leiomyomatosis: deletions in the 5′ end of the COL4A5 collagen gene. Kidney Int. 1992, 42, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antignac, C.; Knebelmann, B.; Drouot, L.; Gros, F.; Deschênes, G.; Hors-Cayla, M.C.; Zhou, J.; Tryggvason, K.; Grünfeld, J.P.; Broyer, M. Deletions in the COL4A5 collagen gene in X-linked Alport syndrome. Characterization of the pathological transcripts in nonrenal cells and correlation with disease expression. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmink, H.H.; Mochizuki, T.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Schröder, C.H.; Barrientos, A.; Monnens, L.A.; van Oost, B.A.; Brunner, H.G.; Reeders, S.T.; Smeets, H.J. Mutations in the type IV collagen alpha 3 (COL4A3) gene in autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994, 3, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmink, H.H.; Schröder, C.H.; Monnens, L.A.; Smeets, H.J. The clinical spectrum of type IV collagen mutations. Hum. Mutat. 1997, 9, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Shield, C.F.; Todd, P.; Hudson, B.G.; Neilson, E.G. Isoform switching of type IV collagen is developmentally arrested in X-linked Alport syndrome leading to increased susceptibility of renal basement membranes to endoproteolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, B.G.; Tryggvason, K.; Sundaramoorthy, M.; Neilson, E.G. Alport’s Syndrome, Goodpasture’s Syndrome, and Type IV Collagen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen-Valkony, I.; Kiss, M.; Csiha, J.; Kiss, A.; Bircher, U.; Szidonya, J.; Maróy, P.; Juhász, G.; Komonyi, O.; Csiszár, K.; et al. Drosophila basement membrane collagen col4a1 mutations cause severe myopathy. Matrix Biol. 2012, 31, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, M.; Kiss, A.A.; Radics, M.; Popovics, N.; Hermesz, E.; Csiszár, K.; Mink, M. Drosophila type IV collagen mutation associates with immune system activation and intestinal dysfunction. Matrix Biol. 2016, 49, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelemen-Valkony, I.; Kiss, M.; Csiszar, K.; Mink, M. Inherited Myopathies. In Myopathies: New Research; Washington, H.S., Jimenez, C.E.C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781622573721. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, A.A.; Popovics, N.; Szabó, G.; Csiszár, K.; Mink, M. Altered stress fibers and integrin expression in the Malpighian epithelium of Drosophila type IV collagen mutants. Data Brief 2016, 7, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, A.A.; Popovics, N.; Boldogkői, Z.; Csiszár, K.; Mink, M. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal Alkylated and Peroxynitrite Nitrated Proteins Localize to the Fused Mitochondria in Malpighian Epithelial Cells of Type IV Collagen Drosophila Mutants. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3502401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A.A.; Popovics, N.; Marton, K.; Boldogkoi, Z.; Csiszar, K.; Mink, M. Type IV collagen is essential for proper function of integrin-mediated adhesion in Drosophila muscle fibers. bioRxiv 2018, 318337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, L.M.; Barth, P.G.; Valk, J.; Njiokiktjien, C. Familial porencephalic white matter disease in two generations. Brain Dev. 1984, 6, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguglia, U.; Gambardella, A.; Breedveld, G.J.; Oliveri, R.L.; Le Piane, E.; Messina, D.; Quattrone, A.; Heutink, P. Suggestive evidence for linkage to chromosome 13qter for autosomal dominant type 1 porencephaly. Neurology 2004, 62, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, D.B.; Phalan, F.C.; Breedveld, G.J.; van Mil, S.E.; Smith, R.S.; Schimenti, J.C.; Aguglia, U.; van der Knaap, M.S.; Heutink, P.; John, S.W.M. Mutations in Col4a1 Cause Perinatal Cerebral Hemorrhage and Porencephaly. Science (80-.) 2005, 308, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisier, E.; Gribouval, O.; Alamowitch, S.; Mougenot, B.; Prost, C.; Verpont, M.C.; Marro, B.; Desmettre, T.; Cohen, S.Y.; Roullet, E.; et al. COL4A1 Mutations and Hereditary Angiopathy, Nephropathy, Aneurysms, and Muscle Cramps. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisier, E.; Chen, Z.; Gekeler, F.; Benhassine, S.; Dahan, K.; Marro, B.; Alamowitch, S.; Paques, M.; Ronco, P. Novel COL4A1 mutations associated with HANAC syndrome: a role for the triple helical CB3[IV] domain. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 2550–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenteno, J.C.; Crespí, J.; Buentello-Volante, B.; Buil, J.A.; Bassaganyas, F.; Vela-Segarra, J.I.; Diaz-Cascajosa, J.; Marieges, M.T. Next generation sequencing uncovers a missense mutation in COL4A1 as the cause of familial retinal arteriolar tortuosity. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-C.; Sonni, A.; Labelle-Dumais, C.; de Leau, M.; Kauffman, W.B.; Jeanne, M.; Biffi, A.; Greenberg, S.M.; Rosand, J.; Gould, D.B. COL4A1 mutations in patients with sporadic late-onset intracerebral hemorrhage. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoneda, Y.; Haginoya, K.; Kato, M.; Osaka, H.; Yokochi, K.; Arai, H.; Kakita, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Otsuki, Y.; Shimizu, S.; et al. Phenotypic Spectrum of COL4A1 Mutations: Porencephaly to Schizencephaly. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Matsuduka, A.; Okanari, K.; Miyahara, H.; Kato, M.; Miyatake, S.; Saitsu, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Tomoki, M.; Ihara, K. A severe pulmonary complication in a patient with COL4A1-related disorder: A case report. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 60, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, M.E.C.; Halley, D.J.J.; Smit, L.S.; Lequin, M.H.; Cobben, J.M.; de Coo, R.; van Harssel, J.; Sallevelt, S.; Woldringh, G.; van der Knaap, M.S.; et al. The expanding phenotype of COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations: clinical data on 13 newly identified families and a review of the literature. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labelle-Dumais, C.; Dilworth, D.J.; Harrington, E.P.; de Leau, M.; Lyons, D.; Kabaeva, Z.; Manzini, M.C.; Dobyns, W.B.; Walsh, C.A.; Michele, D.E.; et al. COL4A1 Mutations Cause Ocular Dysgenesis, Neuronal Localization Defects, and Myopathy in Mice and Walker-Warburg Syndrome in Humans. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Agtmael, T.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; McKie, L.; Brownstein, D.G.; Lee, A.W.; Cross, S.H.; Sado, Y.; Mullins, J.J.; Pöschl, E.; Jackson, I.J. Dominant mutations of Col4a1 result in basement membrane defects which lead to anterior segment dysgenesis and glomerulopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, D.B.; Marchant, J.K.; Savinova, O.V.; Smith, R.S.; John, S.W.M. Col4a1 mutation causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and genetically modifiable ocular dysgenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guiraud, S.; Migeon, T.; Ferry, A.; Chen, Z.; Ouchelouche, S.; Verpont, M.-C.; Sado, Y.; Allamand, V.; Ronco, P.; Plaisier, E. HANAC Col4a1 Mutation in Mice Leads to Skeletal Muscle Alterations due to a Primary Vascular Defect. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, D.S.; Labelle-Dumais, C.; Mao, M.; Jeanne, M.; Kauffman, W.B.; Allen, J.; Favor, J.; Gould, D.B. Allelic heterogeneity contributes to variability in ocular dysgenesis, myopathy and brain malformations caused by Col4a1 and Col4a2 mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Migeon, T.; Verpont, M.-C.; Zaidan, M.; Sado, Y.; Kerjaschki, D.; Ronco, P.; Plaisier, E. HANAC Syndrome Col4a1 Mutation Causes Neonate Glomerular Hyperpermeability and Adult Glomerulocystic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, R.; Schüpbach, T. Molecular analysis of the Drosophila EGF receptor homolog reveals that several genetically defined classes of alleles cluster in subdomains of the receptor protein. Genetics 1994, 137, 531–550. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, D.T.; Procunier, D. Temperature-sensitive mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. 3. Dominant lethals and semilethals on chromosome 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1969, 62, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.A.T.; Romero, M.F. Drosophila provides rapid modeling of renal development, function, and disease. Am. J. Physiol. 2010, 299, F1237–F1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OOta, S.; Saitou, N. Phylogenetic relationship of muscle tissues deduced from superimposition of gene trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, F.L.; Di Lorenzo, C. Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction: Assessment and Management. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S29–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, A.L.; Darris, C.E.; Chetyrkin, S.V.; Pedchenko, V.K.; Boudko, S.P.; Brown, K.L.; Gray Jerome, W.; Hudson, J.K.; Rokas, A.; Hudson, B.G. Collagen IV and basement membrane at the evolutionary dawn of metazoan tissues. eLife 2017, 6, e24176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, M.; Gould, D.B. Genotype-phenotype correlations in pathology caused by collagen type IV alpha 1 and 2 mutations. Matrix Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lewis, W.; Page-McCaw, A. Basement membrane mechanics shape development: Lessons from the fly. Matrix Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiss, A.A.; Somlyai-Popovics, N.; Tubak, V.; Boldogkői, Z.; Csiszár, K.; Mink, M. Novel Phenotypic Elements of Type IV Collagenopathy Revealed by the Drosophila Model. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102083
Kiss AA, Somlyai-Popovics N, Tubak V, Boldogkői Z, Csiszár K, Mink M. Novel Phenotypic Elements of Type IV Collagenopathy Revealed by the Drosophila Model. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(10):2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiss, András A., Nikoletta Somlyai-Popovics, Vilmos Tubak, Zsolt Boldogkői, Katalin Csiszár, and Mátyás Mink. 2019. "Novel Phenotypic Elements of Type IV Collagenopathy Revealed by the Drosophila Model" Applied Sciences 9, no. 10: 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102083
APA StyleKiss, A. A., Somlyai-Popovics, N., Tubak, V., Boldogkői, Z., Csiszár, K., & Mink, M. (2019). Novel Phenotypic Elements of Type IV Collagenopathy Revealed by the Drosophila Model. Applied Sciences, 9(10), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102083




