Effect of Height and Geometry of Stepped Spillway on Inception Point Location
Abstract
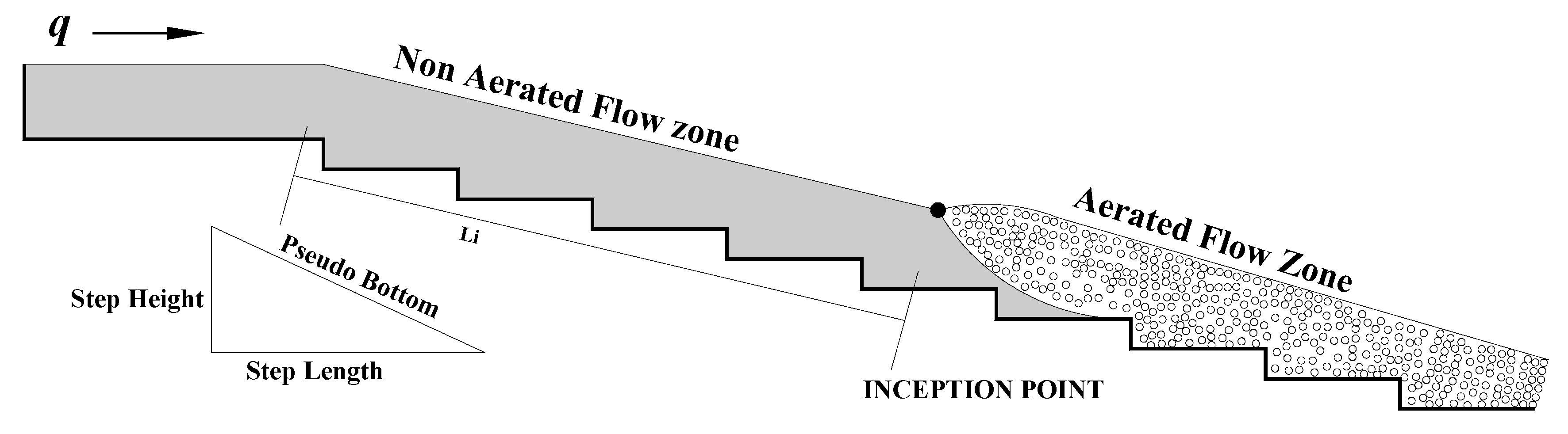
1. Introduction
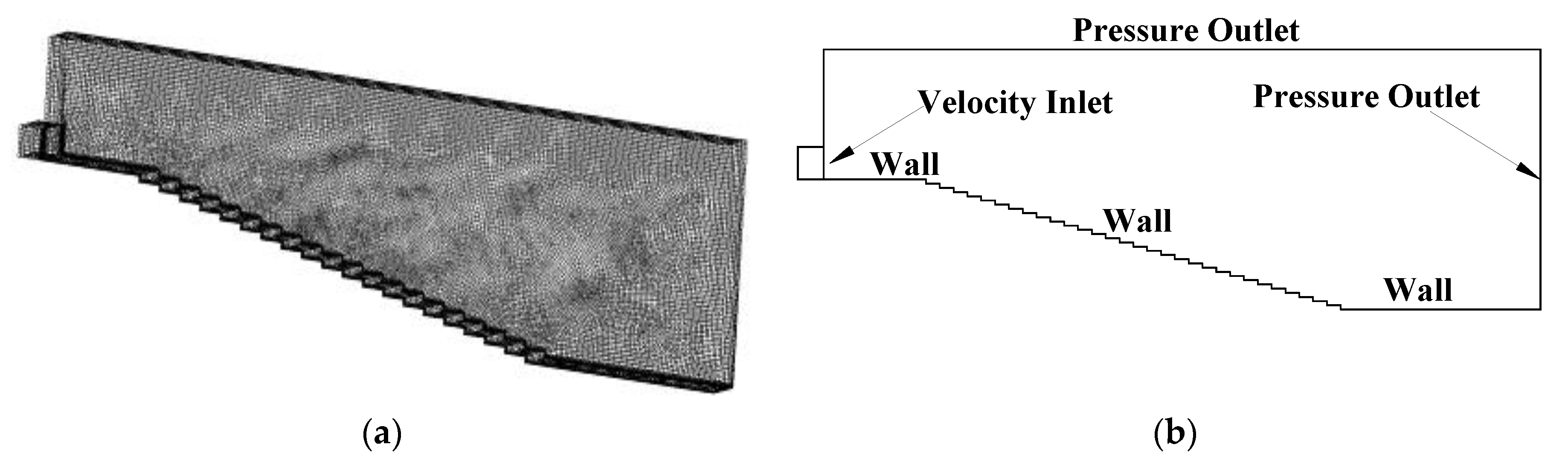
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VOF (Volume of Fluid)
2.2. Realizable k-ε Model
3. Results and Discussions
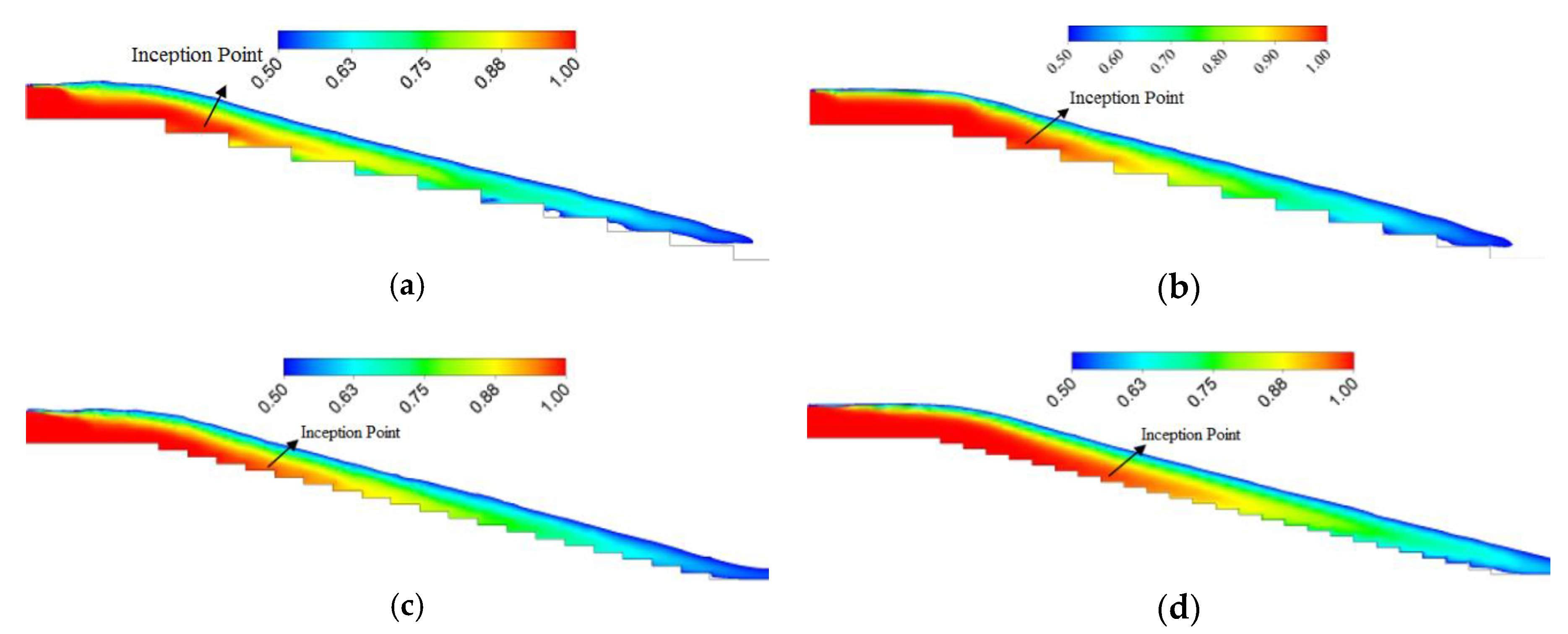
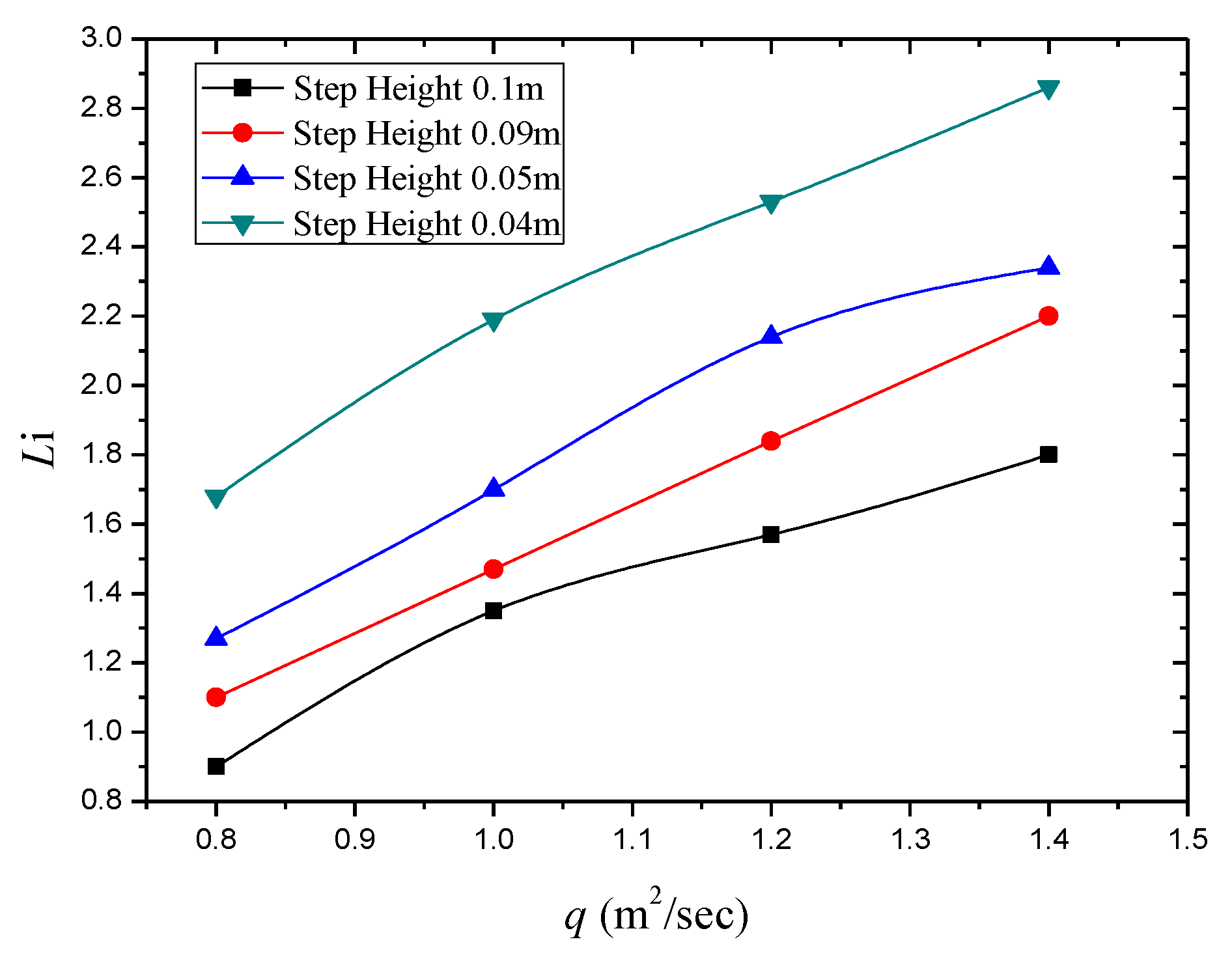
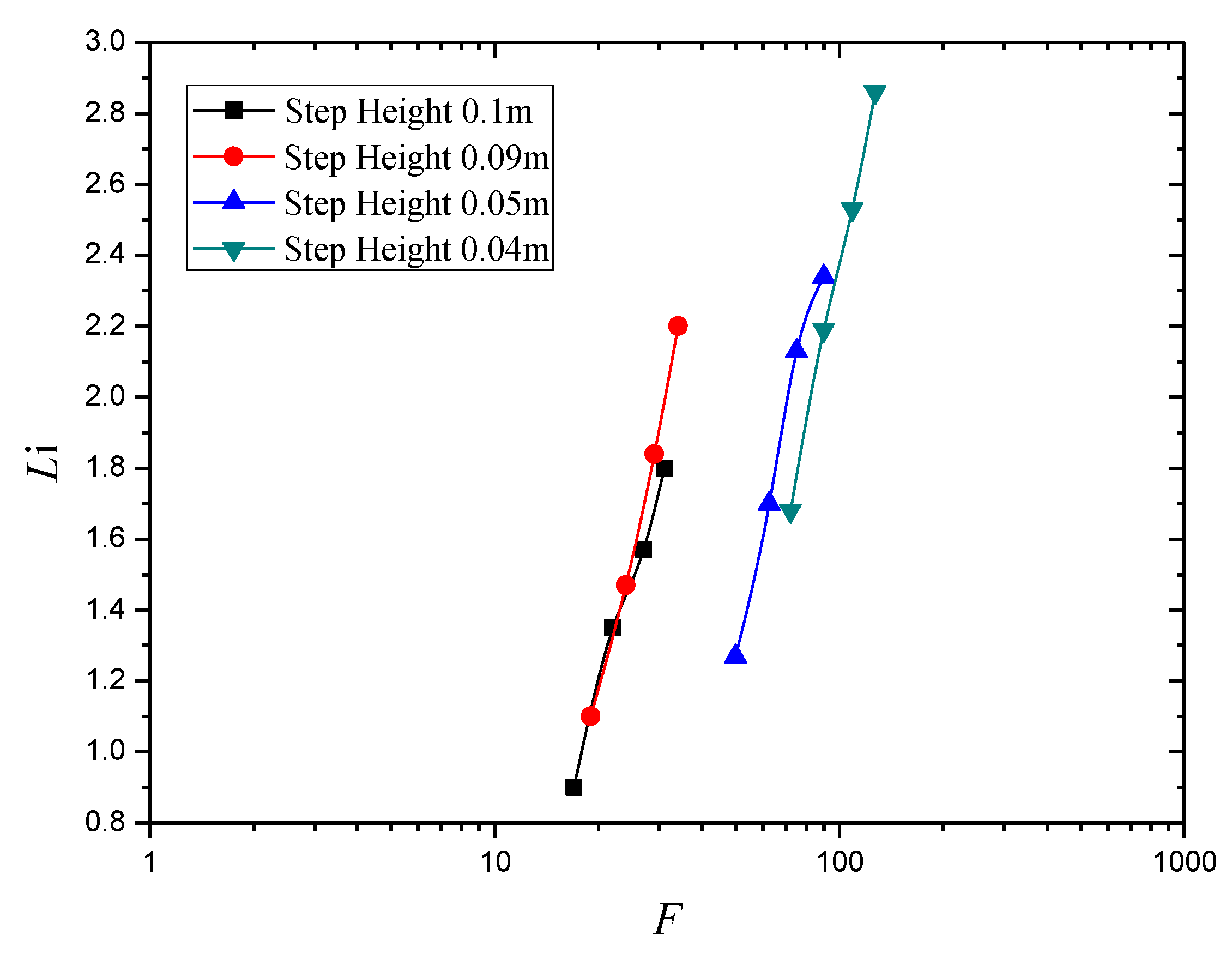
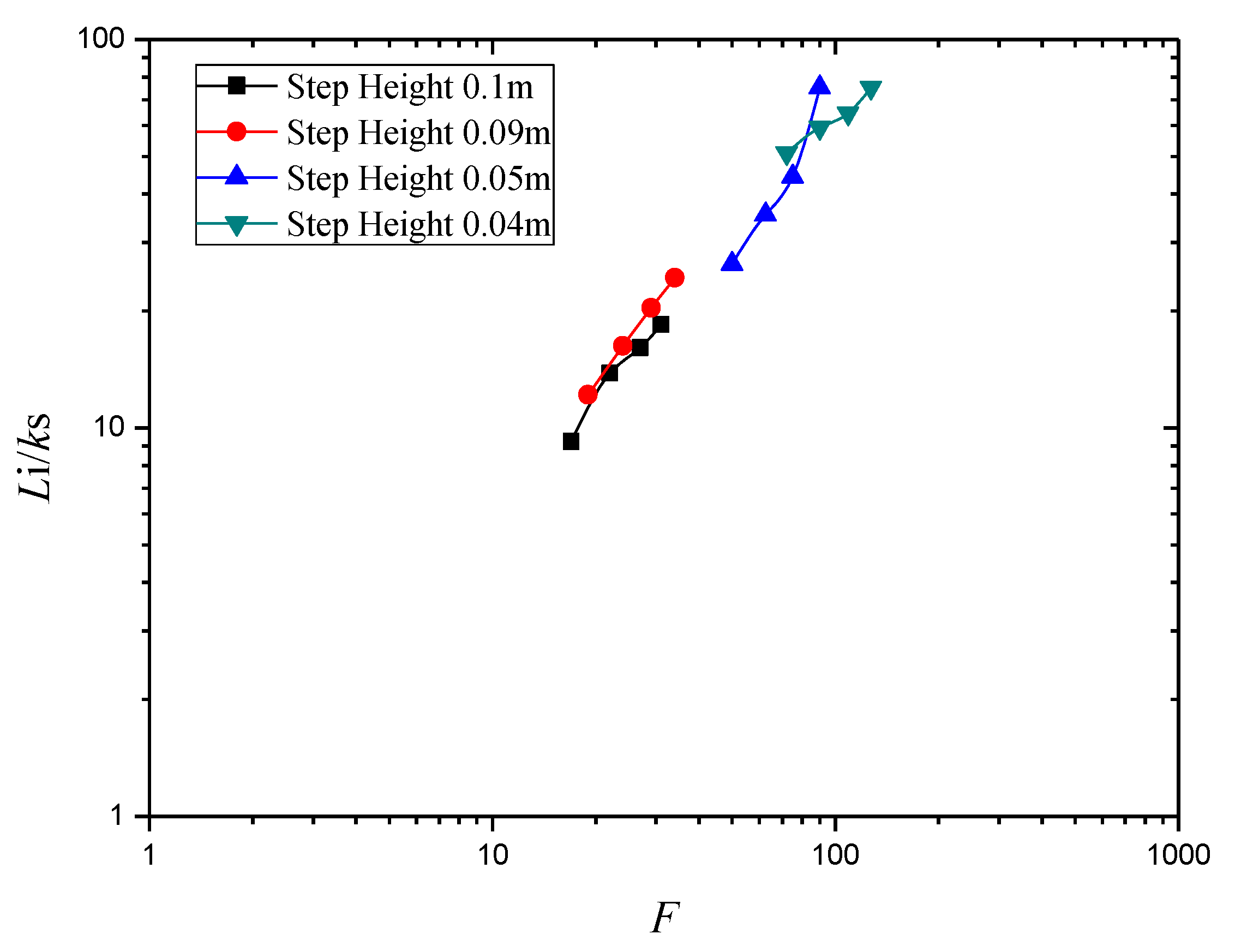
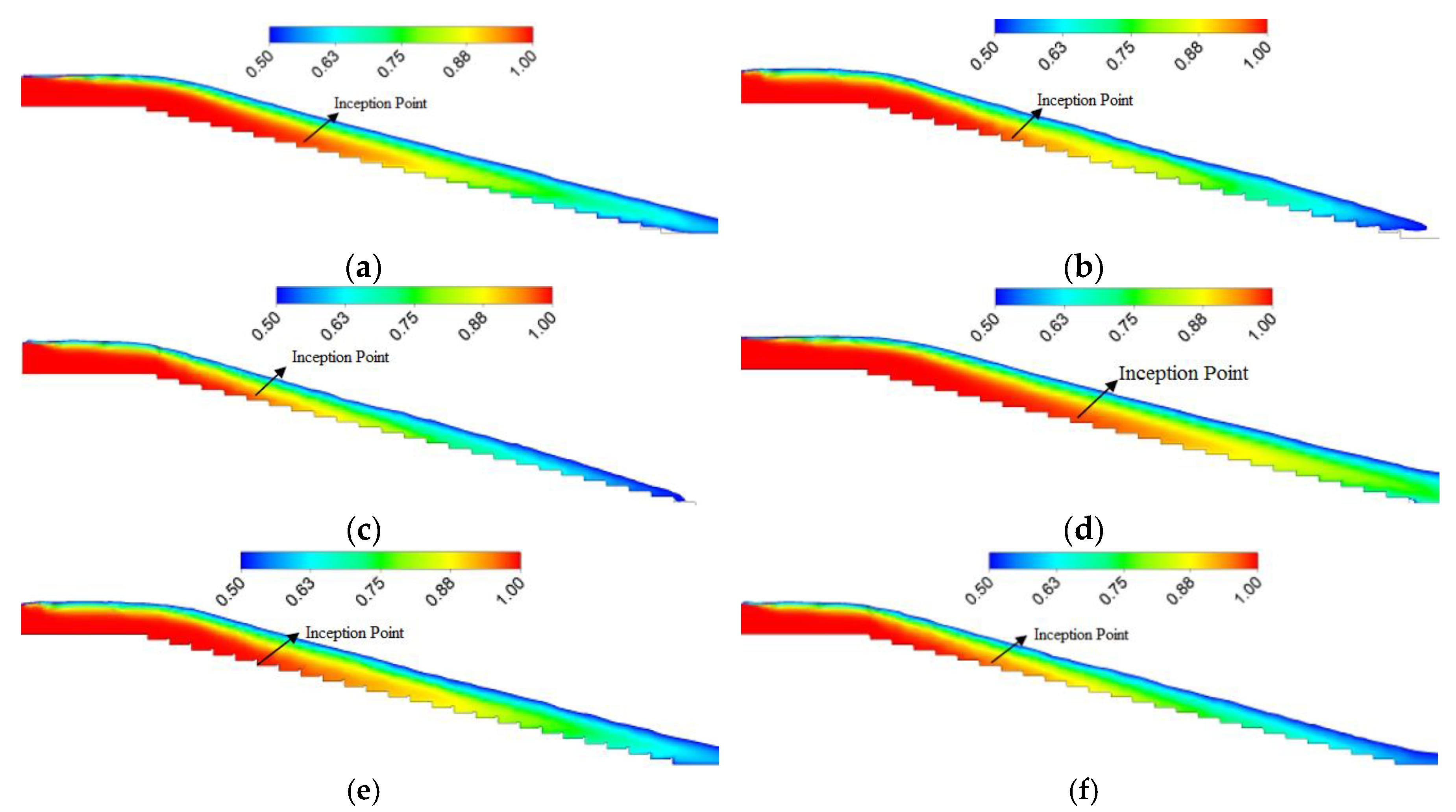
3.1. Effect of Step Height on Inception Length Using Flat Stepped Spillways
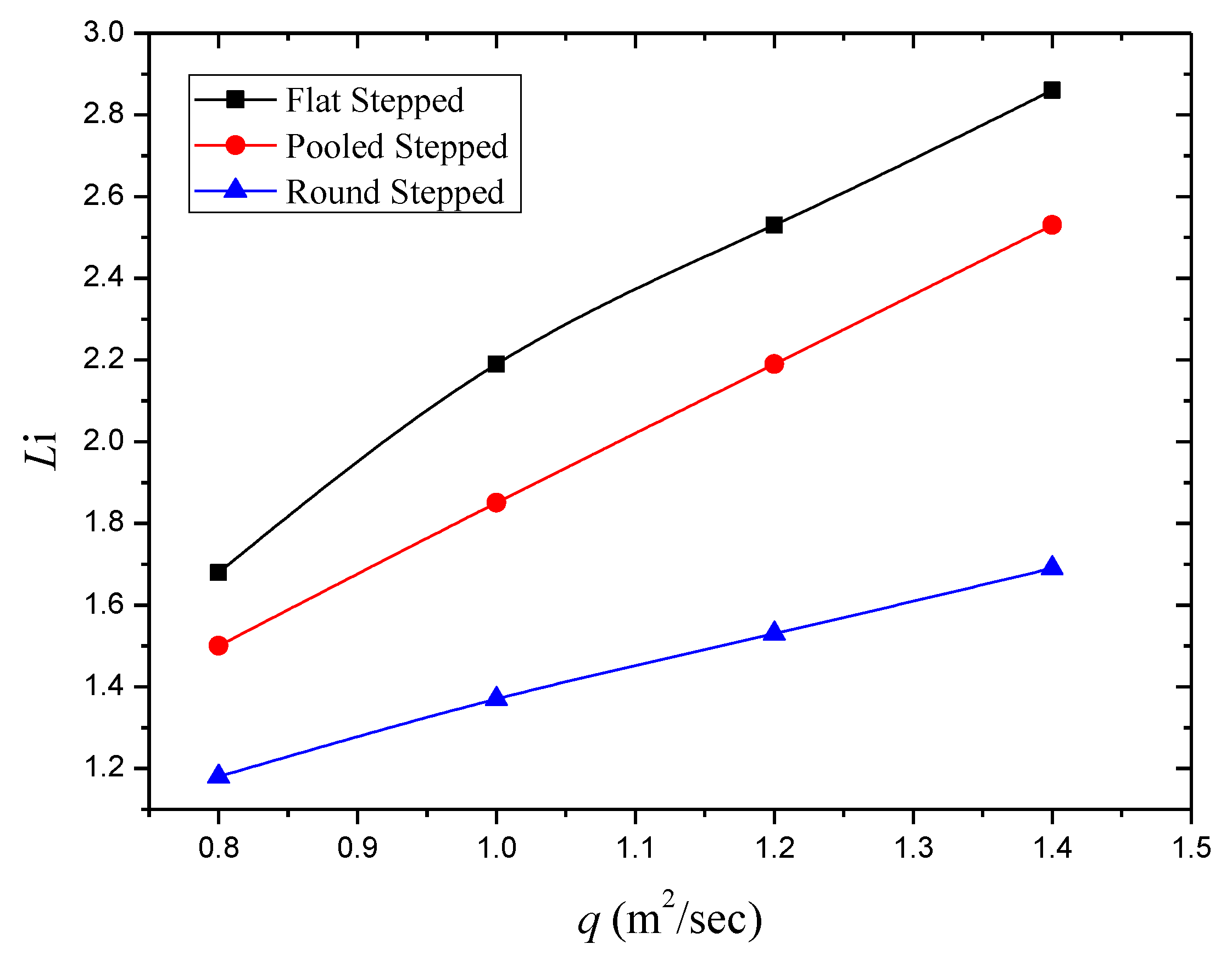
3.2. Effect of Step Geometry on Inception Length Using Different Step Shapes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| model constant (max [0.43,]) | |
| 1.9 (model constant) | |
| 1.44 (model constant) | |
| 1.0 (model constant) | |
| F | Froude surface roughness |
| generation of k due to buoyancy (kg/(ms3)) | |
| generation of k due to fluid Shear (kg/ms3) | |
| g | gravitational acceleration (m/s2) |
| h | step height (m) |
| hp | height of Pool (m) |
| k | turbulent kinetic energy (m2/s2) |
| ks | roughness height, ks = hcosθ (m) |
| l | step length (m) |
| Li | distance of inception point location from spillway crest (m) |
| normalized distance from spillway crest to Inception Point | |
| M1-M6 | number of stepped spillway models |
| N | number of steps |
| S | modulus of mean rate of tensor |
| source term of kinetic energy (kg/ms3) | |
| source term of dissipation rate (kg/ms4) | |
| mean rate of deformation | |
| P | pressure in (N/m2) |
| q | unit discharge (m2/sec) |
| W | width of the step (m) |
| effect of compressibility on turbulence (kg/ms3) | |
| turbulent Prandtl number | |
| turbulent Prandtl number | |
| velocity in direction (m/s) | |
| velocity in direction (m/s) | |
| volume fraction of air (%) | |
| volume fraction of water (%) | |
| turbulent dissipation rate (m2/s3) | |
| θ | spillway slope () |
| molecular dynamic viscosity (kg/ms) | |
| turbulent dynamic viscosity (kg/ms) | |
| cell density (kg/m3) | |
| density of air (kg/m3) | |
| density of water (kg/m3) | |
| t | time (s) |
| kinematic viscosity (m2/s) | |
| angular velocity |
References
- Chanson, H. Stepped Spillway Flows and Air Entrainment. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1993, 20, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H.; Yasuda, Y.; Ohtsu, I. Flow Resistance in Skimming Flow: A Critical Review. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Hydraulics of Stepped Spillways, Zurich, Switzerland, 22–24 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, I.R.; Ackers, P.; Loveless, J. General Method for Critical Point on Spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Hydraulics of skimming flows over stepped channels and spillways. J. Hydraul. Res. 1994, 32, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, S.; Chanson, H. Energy dissipation, flow resistance and gas-liquid interfacial area in skimming flows on moderate-slope stepped spillways. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2009, 9, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, R.M.; Hager, W.H. Two-Phase Flow Characteristics of Stepped Spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2003, 129, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, A.; Juny, M.S.; Dolz, J. Characterization of the Nonaerated Flow Region in a Stepped Spillway by PIV. J. Fluid Eng. 2006, 128, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Characteristics of skimming flow over stepped spillways: Discussion. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2000, 125, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, M.R.; Rajaratnam, N. Characteristics of Skimming Flow over Stepped Spillways. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Prediction of the transition nappe/skimming flow on a stepped channel. J. Hydraul. Res. 1996, 34, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juny, M.S.; Dolz, J. Experimental study of transition and skimming flows on stepped spillways in RCC dams: Qualitative analysis and pressure measurements. J. Hydraul. Res. 2010, 43, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, I.; Matos, J. Skimming Flow in the Nonaerated Region of Stepped Spillways over Embankment Dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, I.; Renna, F.; Matos, J.; Bombardelli, F. Skimming, Nonaerated Flow on Stepped Spillways over Roller Compacted Concrete Dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.; Frizell, K.H. Air Concentration and Velocity Measurements on Self-Aerated Flow Down Stepped Chutes. In Proceedings of the 2000 Joint Conference on Water Resource Engineering and Water Resources Planning & Management, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 30 July–2 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsu, I.; Yasuda, Y.; Takahasi, M. Flow Characteristics of Skimming Flows in Stepped Channels. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaily, D.K.K.E.; Lami, M.K.A. Study of Conveniency of Using Stepped Spillway in Roller Compacted Concrete Dams (RCCD). Eng. Technol. J. 2009, 27, 2964–2977. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C. Energy Dissipation on Flat-Sloped Stepped Spillways: Part 2. Downstream of the Inception Point. ASABE 2010, 53, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Air Bubble Entrainment in Free-Surface Turbulent Shear Flows; Academic Press: London, UK, 1997; p. 401. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.F.; Chanson, H. Hydraulics of the Developing Flow Region of Stepped Spillways. I: Physical Modeling and Boundary Layer Development. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. The Hydraulics of Stepped Chutes and Spillways; CRC Press/Balkema: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2002; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Alghazali, M.O.S.; Jasmin, S.M. Location of Air Inception Point for Different Configuration of Stepped Spillway. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2014, 5, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.-H.; Zhang, B.; Ma, F. Inception point of air entrainment over stepped spillways. J. Hydrodyn. 2013, 25, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, H.K.; Doering, J.C. Effect of rounding edges of stepped spillways on the flow characteristics. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 39, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, S.; Chanson, H. Air Entrainment and Energy Dissipation on Porous Pooled Stepped Spillways. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Hydraulic Design of Low-Head Structures (IWLHS), Aachen, Germany, 20–22 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Munta, S.; Otun, J.A. Study of Inception Point Length over Stepped Spillway Models. NIJOTECH Niger. J. Technol. 2014, 33, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Dai, G.; Liu, H. Volume of Fluid Model for Turbulence Numerical Simulation of Stepped Spillway over Flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, I.N.; Teimouri, M. An Investigation of Flow Energy Dissipation in Simple Stepped Spillways by NumerJical Model. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 47, 544–553. [Google Scholar]
- Eghbalzadeh, A.; Javan, M. Comparison of Mixture and VOF Models for Numerical Simulation of Air–entrainment in Skimming Flow over Stepped Spillways. J. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaie, A.; Moradinejad, A.; Haghiabi, A.H. Numerical Modelling of Flow Pattern in Spillway Approach Channel. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.D.; Hu, X.Q.; Huai, W.X.; Amador, A. Numerical simulation and analysis of water flow over stepped spillways. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmamar, S.; Kettab, A.; Thirriot, C. Numerical simulation of turbulent flow upstream of the inception point in a Stepped Channel. In Proceedings of the 30th IAHR Congress, Thessaloniki, Greece, 24–29 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.J.; Luo, L.; Zhao, W.Q.; Li, R. Two-phase flow simulation of aeration on stepped spillway. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2004, 14, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Lee, J.H.W. Numerical Simulation of Skimming Flow over Mild Stepped Channel. J. Hydrodyn. 2006, 18, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardelli, F.A.; Meireles, I.; Matos, J. Laboratory measurements and multi-block numerical simulations of the mean flow and turbulence in the non-aerated skimming flow region of steep stepped spillways. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2010, 11, 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbara, M.; Chatila, J.; Awwad, R. Computational simulation of flow over stepped spillways. J. Comput. Struct. 2005, 83, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L. Numerical simulation of air-water two-phase flow over stepped spillways. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2006, 49, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfaraz, M.; Attari, J.; Pfister, M. Numerical Computation of Inception Point Location for Steeply Sloping Stepped Spillways. In Proceedings of the 9th International Congress on Civil Engineering, Isfahan, Iran, 8–10 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.L.; Zhang, J.M. Comparison of Different Turbulence Models for Numerical Simulation of Pressure Distribution in V-Shaped Stepped Spillway. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 3537026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Zhang, J.M. Numerical Investigation on the Hydraulic Properties of the Skimming Flow over Pooled Stepped Spillway. Water 2018, 14, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.J.; Gulliver, J.S.; Zhu, D.T. Application of Displacement Height and Surface Roughness Length to Determination Boundary Layer Development Length over Stepped Spillway. Water 2014, 6, 3888–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubicic, R.; Zindovic, B.; Vojt, P.; Pavlovic, D.; Kapor, R.; Savic, L. Hydraulic Jumps in Adverse-Slope Stilling Basins for Stepped Spillways. Water 2018, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Liu, B.; Raza, A. Numerical Prediction and Risk Analysis of Hydraluic Cavitation Damage in a High-Speed-Flow Spillway. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 1817307. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. Volume of Fluid (VOF) Method for the Dynamics of Free Boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 39, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kositgittiwong, D.; Chinnarasri, C.; Julien, P.Y. Numerical simulation of flow velocity profiles along a stepped spillway. J. Process Mech. Eng. 2013, 227, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.H.; Liou, W.W.; Shabbir, A.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. A New k-ε Eddy Viscosity Model for High Reynolds-Number Turbulent Flows-Model Development and Validation. Comput. Fluids 1994, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
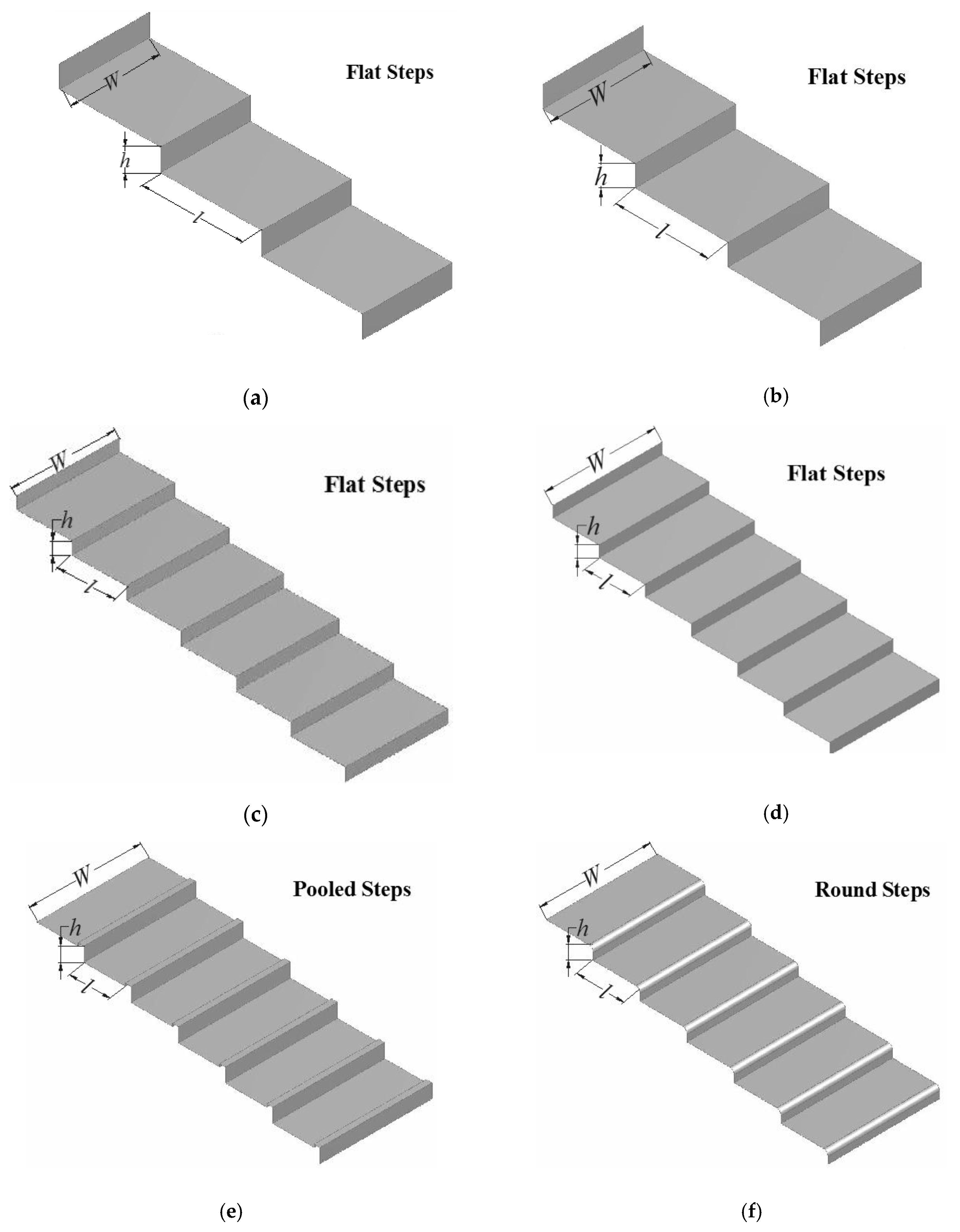
| Model | Step Geometry | Step Height(m) | Step Length(m) | Slope° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Flat | 0.10 | 0.45 | 12.52° |
| M2 | Flat | 0.09 | 0.37 | 13.67° |
| M3 | Flat | 0.05 | 0.21 | 13.39° |
| M4 | Flat | 0.04 | 0.17 | 13.24° |
| M5 | Pooled (hp = 0.01 m) | 0.04 | 0.15 | 14.93° |
| M6 | Round | 0.04 | 0.16 | 14.03° |
| Unit Discharge q (m2/s) | Step Height (m) | Number of Steps N | Froude Surface Roughness F | Inception Point Length Li (m) | Surface Roughness ks (m) | Li/ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.80 | 0.10 | 9 | 17.0 | 0.90 | 0.097 | 9.23 |
| 1.00 | 0.10 | 9 | 22.0 | 1.35 | 0.097 | 13.84 |
| 1.20 | 0.10 | 9 | 27.0 | 1.57 | 0.097 | 16.10 |
| 1.40 | 0.10 | 9 | 31.0 | 1.80 | 0.097 | 18.46 |
| 0.80 | 0.09 | 11 | 19.0 | 1.10 | 0.090 | 12.17 |
| 1.00 | 0.09 | 11 | 24.0 | 1.47 | 0.090 | 16.26 |
| 1.20 | 0.09 | 11 | 29.0 | 1.84 | 0.090 | 20.35 |
| 1.40 | 0.09 | 11 | 34.0 | 2.20 | 0.090 | 24.34 |
| 0.80 | 0.05 | 19 | 50.0 | 1.27 | 0.048 | 26.45 |
| 1.00 | 0.05 | 19 | 62.5 | 1.70 | 0.048 | 35.41 |
| 1.20 | 0.05 | 19 | 75.0 | 2.14 | 0.048 | 44.38 |
| 1.40 | 0.05 | 19 | 90.0 | 2.34 | 0.048 | 75.26 |
| 0.80 | 0.04 | 24 | 72.0 | 1.68 | 0.038 | 51.08 |
| 1.00 | 0.04 | 24 | 90.0 | 2.19 | 0.038 | 59.30 |
| 1.20 | 0.04 | 24 | 109.0 | 2.53 | 0.038 | 64.55 |
| 1.40 | 0.04 | 24 | 127.0 | 2.86 | 0.038 | 75.26 |
| Discharge q (m2/s) | Step Geometry | Number of Steps N | Li (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | Flat | 24 | 1.68 |
| 1.0 | Flat | 24 | 2.19 |
| 1.2 | Flat | 24 | 2.53 |
| 1.4 | Flat | 24 | 2.86 |
| 0.8 | Pooled | 24 | 1.50 |
| 1.0 | Pooled | 24 | 1.85 |
| 1.2 | Pooled | 24 | 2.19 |
| 1.4 | Pooled | 24 | 2.53 |
| 0.8 | Round | 24 | 1.18 |
| 1.0 | Round | 24 | 1.37 |
| 1.2 | Round | 24 | 1.53 |
| 1.4 | Round | 24 | 1.69 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, W.; Raza, A.; Chen, X. Effect of Height and Geometry of Stepped Spillway on Inception Point Location. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102091
Wan W, Raza A, Chen X. Effect of Height and Geometry of Stepped Spillway on Inception Point Location. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(10):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102091
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Wuyi, Awais Raza, and Xiaoyi Chen. 2019. "Effect of Height and Geometry of Stepped Spillway on Inception Point Location" Applied Sciences 9, no. 10: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102091
APA StyleWan, W., Raza, A., & Chen, X. (2019). Effect of Height and Geometry of Stepped Spillway on Inception Point Location. Applied Sciences, 9(10), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102091






