Development of UVB LED Lighting System Based on UV Dose Calculation Algorithm to Meet Individual Daily UV Dose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
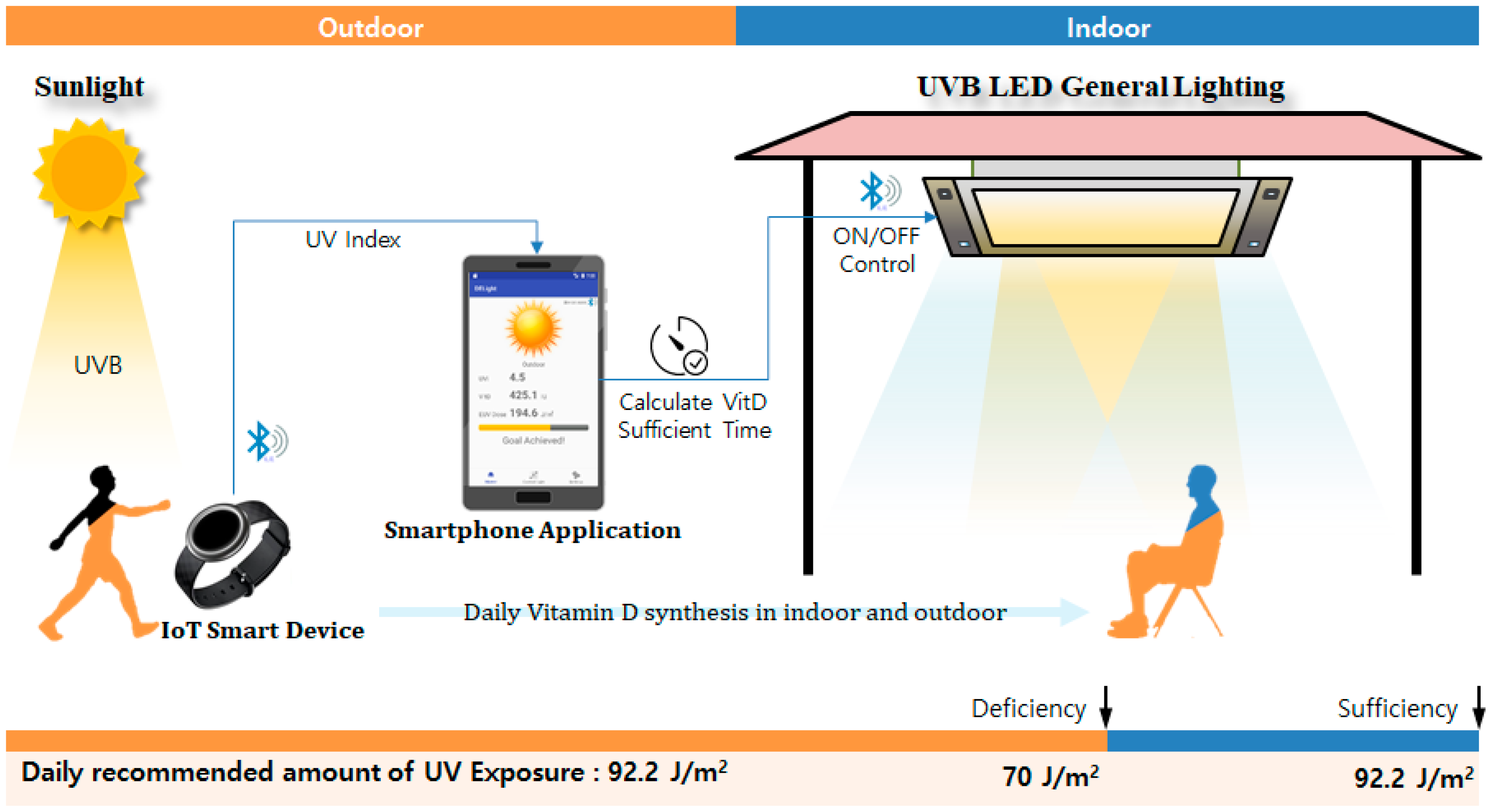
2. UVB LED General Lighting System
2.1. System Construction
2.2. IoT UV Measuring Device
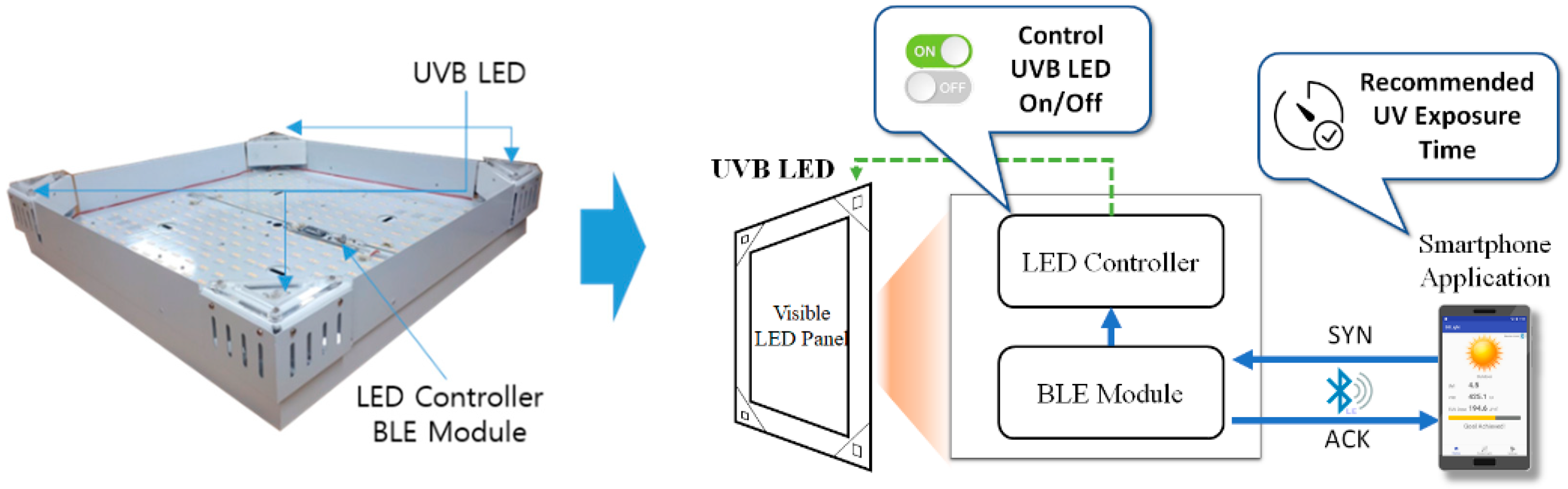
2.3. UVB LED General Lighting
2.4. Smartphone Application
3. UV Exposure Amount Calculation Algorithm
4. Experiment and Simulation
4.1. Performance Test for IoT UV Smart Device and UVB LED Lighting
4.2. Lighting System Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Rhee, H.J.; de Vries, E.; Coebergh, J.W. Regular sun exposure benefits health. Med. Hypoth. 2016, 97, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, E.S.; Chung, M.H.; Park, J.C. A study on applicability of light therapy using daylight. J. Korean Soc. Living Environ. Syst. 2016, 23, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, L.D. Sources and measurement of ultraviolet radiation. Methods 2002, 28, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Holick, M.F. Sunlight “D”ilemma: Risk of skin cancer or bone disease and muscle weakness. Lancet 2001, 357, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.H. Anti-aging effects of P7C3 in UVA-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. Asian J. Beauty Cosmetol. 2017, 15, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, Y.; Lorente, J. Contribution of UVA irradiance to the erythema and photoaging effects in solar and sunbed exposures. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 143, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Exposure to Artificial UV Radiation and Skin Cancer; IARC: Lyon, France, 2006; pp. 3–64. [Google Scholar]
- Biniek, K.; Levi, K.; Dauskardt, R.H. Solar UV radiation reduces the barrier function of human skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17111–17116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scragg, R.; Rahman, J.; Thornley, S. Association of sun and UV exposure with blood pressure and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 187, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsen, O. The relationship between ultraviolet radiation exposure and vitamin D status. Nutrients 2010, 2, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1678S–1688S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terenetskaya, I.; Orlova, T.; Kapinos, P. Adequate UV exposures for healthy life: In situ monitoring and model calculation of the vitamin-D- synthetic capacity of sunlight of the vitamin-D-synthetic capacity of sunlight. Chem. J. Mold. 2016, 7, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kecorius, S.; Tamayo, E.G.; Galvez, M.C.; Madueño, L.; Betito, G.; Gonzaga-Cayetano, M.; Vallar, E.; Wiedensohler, A. Activity pattern of School/University tenants and their family members in metro Manila–Philippines. Aeros. Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2412–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.; Rotter, A.; Malvestiti, A.; Silva, M. The role of glass as a barrier against the transmission of ultraviolet radiation: An experimental study. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2009, 25, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Oh, S.T.; Lim, J.H. Development of local area alert system against particulate matters and ultraviolet rays based on open IoT platform with P2P. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2018, 11, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lim, J.H. Development of a UV index sensor-based portable measurement device with the EUVB ratio of natural light. Sensors 2019, 19, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Wolfenden, L.L.; Ziegler, T.R.; Tian, J.; Luo, M.; Stecenko, A.A.; Chen, T.C.; Holick, M.F.; Tangpricha, V. Treatment of vitamin D deficiency with UV light in patients with malabsorption syndromes: A case series. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2007, 23, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Ahn, H.H.; Kye, Y.C. Targeted broadband UVB phototherapy forthe treatment of localized vitiligo. Ann. Dermatol. 2008, 20, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.T.; Park, D.H.; Lim, J.H. Designing safe general LED lighting that provides the UVB benefits of sunlight. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Solar UV Index: A Practical Guide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Organización Internacional de Normalización. ISO 8995-1: 2002 (CIE S 008/E: 2001) Lighting of Indoor Work Places; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, R.L.; Liley, J.B.; Björn, L.O. UV radiation: Balancing risks and benefits. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godar, D.E.; Pope, S.J.; Grant, W.B.; Holick, M.F. Solar UV doses of young americans and vitamin D 3 production. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiaratchy, S.; Papini, R. Initial management of a major burn: II—assessment and resuscitation. BMJ 2004, 329, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godar, D.E.; Pope, S.J.; Grant, W.B.; Holick, M.F. Solar UV doses of adult americans and vitamin D 3 production. Dermatoendocrinol 2011, 3, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare; The Korean Nutrition Society. Summary of 2015 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans (KDRIs). In Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015, 1st ed.; The Korean Nutrition Society: Sejong, Korea, 2015; p. 1053. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, S.J.; Holick, M.F.; Mackin, S.; Godar, D.E. Action spectrum conversion factors that change erythemally weighted to previtamin D3-weighted UV doses. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, S.J.; Godar, D.E. Solar UV geometric conversion factors: Horizontal plane to cylinder model. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R.; Eisman, J.; Garabedian, M.; Holick, M.; Kleinschmidt, J.; Suda, T.; Terenetskaya, I.; Webb, A. Action Spectrum for the Production of PreVitamin D in Human Skin; (CIE 174:2006); CIE: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp Systems; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.P. A Study on the Evaluation Criteria of Photobiological Safety for LED Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea, August 2017. [Google Scholar]






| Seasonal Conversion Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Item | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter |
| 30° N | ASCF | 0.742 | 1.11 | 1.061 | 0.91 |
| GCF | 0.593 | 0.593 | 0.655 | 0.655 | |
| 35° N | ASCF | 1.049 | 1.104 | 1.029 | 0.842 |
| GCF | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.655 | 0.655 | |
| 40° N | ASCF | 1.008 | 1.067 | 0.963 | 0.7 |
| GCF | 0.608 | 0.608 | 0.681 | 0.681 | |
| Experiment Cases | Age | AF | RVA (IU) | RVUD According to PBE (J/m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin Type II | Skin Type III | ||||||||
| 10% | 15% | 30% | 10% | 15% | 30% | ||||
| CASE 1 | 0–21 | 1 | 400 | 77 | 51 | 26 | 102 | 68 | 34 |
| CASE 2 | 22–40 | 0.83 | 400 | 92 | 61 | 31 | 123 | 82 | 41 |
| CASE 3 | 41–59 | 0.66 | 400 | 116 | 77 | 39 | 155 | 103 | 52 |
| CASE 4 | 60– | 0.49 | 600 | 234 | 156 | 78 | 312 | 208 | 104 |
| Outdoor Time (EUD) (J/m2) | Factors | Skin Type II (Unit: J/m2) | Skin Type III (Unit: J/m2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | CASE 3 | CASE 4 | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | CASE 3 | CASE 4 | ||
| RVUD | 51 | 61 | 77 | 156 | 68 | 82 | 103 | 208 | |
| 30 Min (157.38) | VUDout | 95.90 | 152.38 | ||||||
| tr (s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12,474 | 0 | 0 | 1482 | 23,248 | |
| VUDin | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 60.28 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7.16 | 112.34 | |
| Total EUD | 157.38 | 157.38 | 157.38 | 188.68 | 157.38 | 157.38 | 161.10 | 215.70 | |
| Met RVA | O | O | O | O + I | O | O | O + I | O + I | |
| 20 Min (91.40) | VUDout | 57.52 | 91.40 | ||||||
| tr (s) | 0 | 816 | 4093 | 20,417 | 2174 | 5057 | 9426 | 31,192 | |
| VUDin | 0.0 | 3.95 | 19.78 | 98.66 | 10.50 | 24.44 | 45.55 | 150.72 | |
| Total EUD | 91.40 | 93.45 | 101.67 | 142.62 | 96.85 | 104.09 | 115.05 | 169.66 | |
| Met RVA | O | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | |
| 10 Min (44.58) | VUDout | 28.06 | 44.58 | ||||||
| tr (s) | 4752 | 6915 | 10,191 | 26,516 | 8272 | 11,155 | 15,524 | 37,290 | |
| VUDin | 22.96 | 33.41 | 49.25 | 128.13 | 39.97 | 53.90 | 75.01 | 180.19 | |
| Total EUD | 56.50 | 61.93 | 70.15 | 111.11 | 65.33 | 72.57 | 83.53 | 138.14 | |
| Met RVA | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | O + I | |
| 0 Min (0) | VUDout | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| tr (s) | 10,559 | 12,721 | 15,998 | 32,322 | 14,078 | 16,962 | 21,331 | 43,096 | |
| VUDin | 51.02 | 61.47 | 77.30 | 156.18 | 68.03 | 81.96 | 103.07 | 208.25 | |
| Total EUD | 26.49 | 31.92 | 40.14 | 81.09 | 35.32 | 42.56 | 53.52 | 108.12 | |
| Met RVA | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, D.-H.; Oh, S.-T.; Lim, J.-H. Development of UVB LED Lighting System Based on UV Dose Calculation Algorithm to Meet Individual Daily UV Dose. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9122479
Park D-H, Oh S-T, Lim J-H. Development of UVB LED Lighting System Based on UV Dose Calculation Algorithm to Meet Individual Daily UV Dose. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(12):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9122479
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Dae-Hwan, Seung-Taek Oh, and Jae-Hyun Lim. 2019. "Development of UVB LED Lighting System Based on UV Dose Calculation Algorithm to Meet Individual Daily UV Dose" Applied Sciences 9, no. 12: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9122479
APA StylePark, D.-H., Oh, S.-T., & Lim, J.-H. (2019). Development of UVB LED Lighting System Based on UV Dose Calculation Algorithm to Meet Individual Daily UV Dose. Applied Sciences, 9(12), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9122479




