Auditory Localization in Low-Bitrate Compressed Ambisonic Scenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Human Auditory Localization
2.2. Binaural-Based Ambisonics
2.3. Auditory Localization in Ambisonics
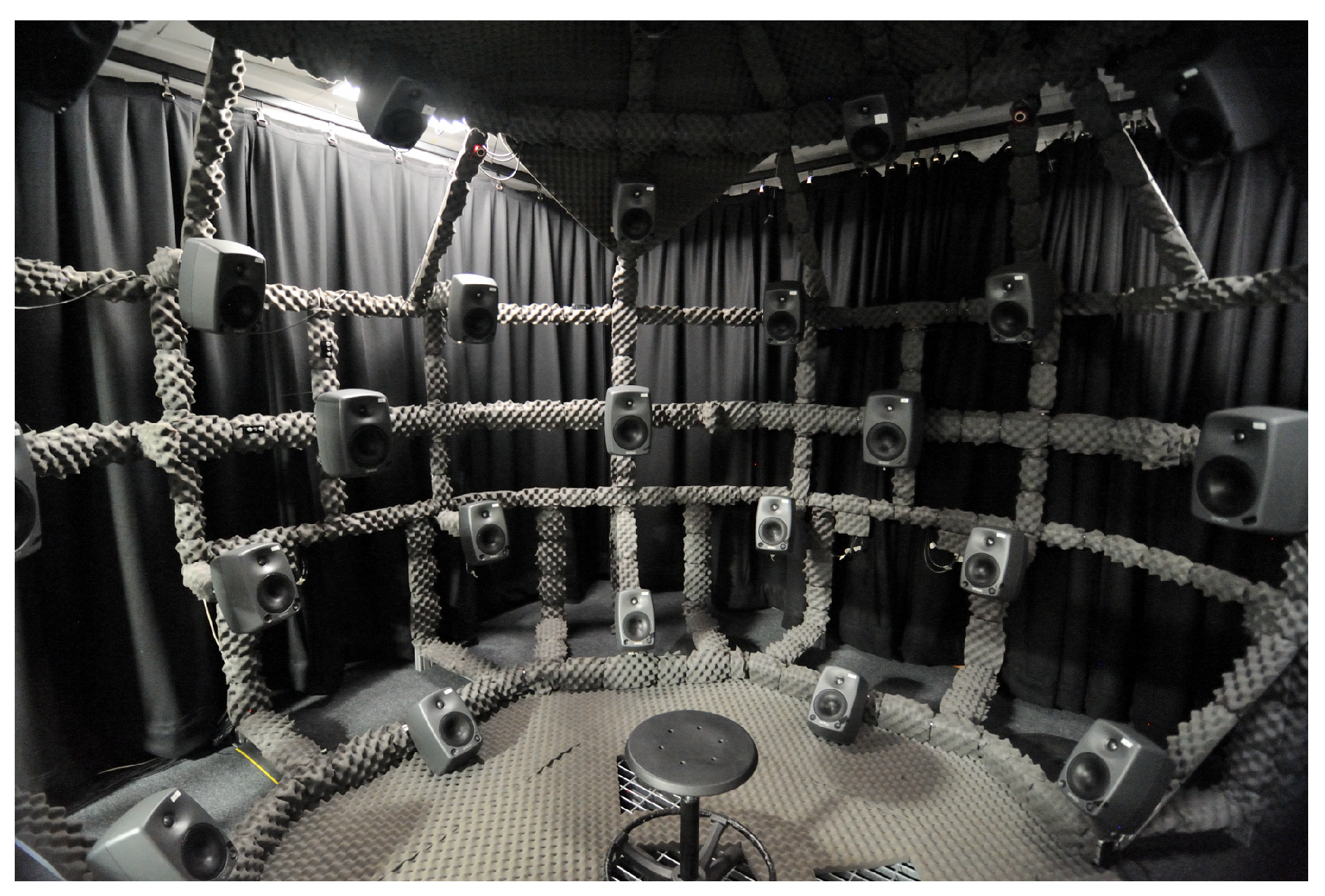
3. Methods
3.1. Test Stimuli
3.2. Spatial Audio Rendering
3.3. Participants
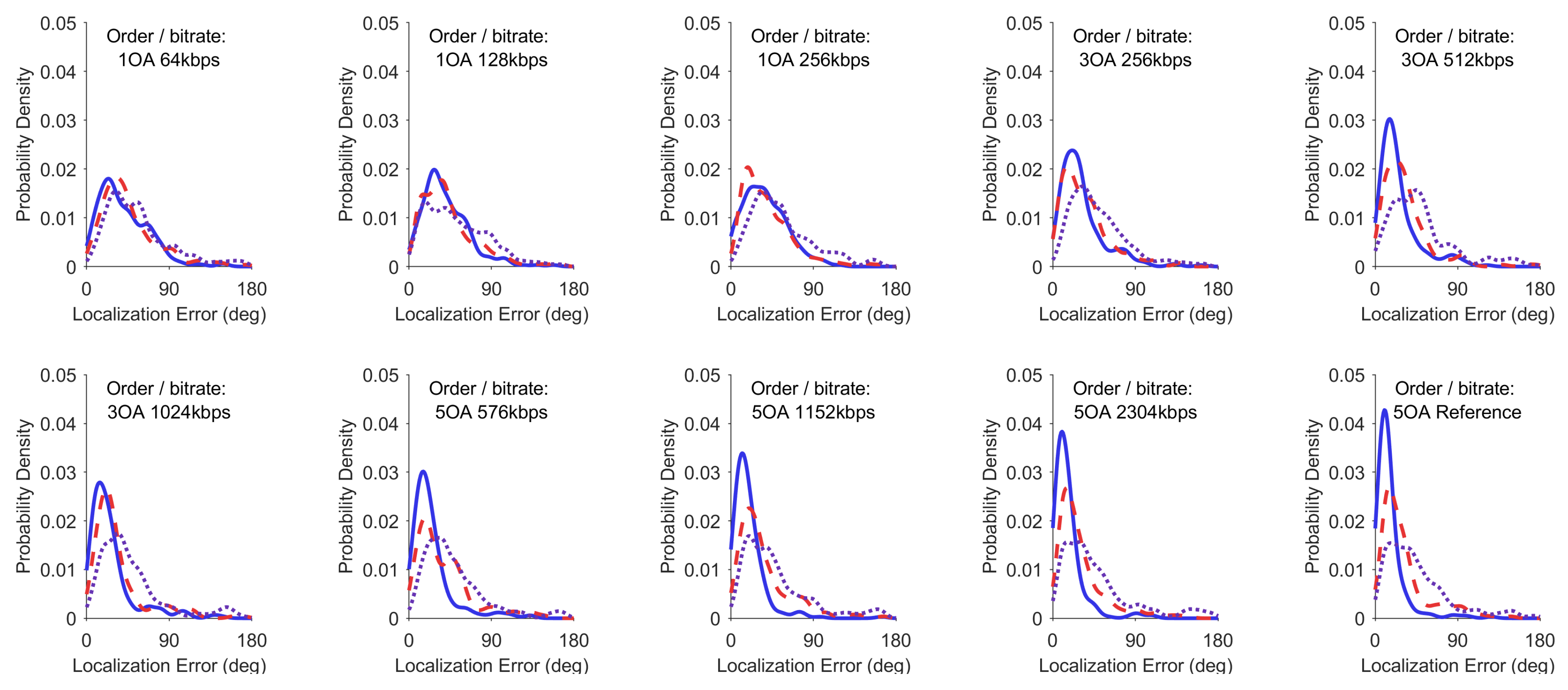
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPL | Sound Pressure Level |
| ITD | Interaural Time Difference |
| ILD | Interaural Level Difference |
| HRTF | Head-Related Transfer Function |
| HRIR | Head-Related Impulse Response |
| MAA | Minimum Audible Angle |
| HOA | Higher-Order Ambisonics |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| DAW | Digital Audio Workstation |
Appendix A


References
- Gerzon, M.A. Periphony: With-Height Sound Reproduction. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1973, 21, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Herre, J.; Hilpert, J.; Kuntz, A.; Plogsties, J. MPEG-H 3D Audio–The New Standard for Coding of Immersive Spatial Audio. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Sign. Proces. 2015, 9, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valin, J.M.; Maxwell, G.; Terriberry, T.B.; Vos, K. High-Quality, Low-Delay Music Coding in the Opus Codec. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.04845. [Google Scholar]
- Blauert, J.; Allen, J. Spatial Hearing: The Psychophysics of Human Sound Localization; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Letowski, T.; T Letowski, S. Auditory Spatial Perception: Auditory Localization; No. ARL-TR-6016; U.S. Army Research Laboratory: Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, A.W. On the Minimum Audible Angle. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1958, 30, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrott, D.R.; Saberi, K. Minimum audible angle thresholds for sources varying in both elevation and azimuth. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grantham, D.W.; Hornsby, B.W.; Erpenbeck, E.A. Auditory spatial resolution in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal planes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langendijk, E.H.; Kistler, D.J.; Wightman, F.L. Sound localization in the presence of one or two distracters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 109, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, F.L.; Kistler, D.J. Headphone simulation of free-field listening. I: stimulus synthesis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H. Fundamentals of binaural technology. Appl. Acoust. 1992, 36, 171–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begault, D.R.; Trejo, L.J. 3-D Sound for Virtual Reality and Multimedia; NASA/TM-2000-209606; NASA Ames Research Center: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 2000.
- Wightman, F.L.; Kistler, D.J. Resolution of front–back ambiguity in spatial hearing by listener and source movement. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 2841–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begault, D.R.; Wenzel, E.M.; Anderson, M.R. Direct comparison of the impact of head tracking, reverberation, and individualized head-related transfer functions on the spatial perception of a virtual speech source. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2001, 49, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pulkki, V. Virtual sound source positioning using vector base amplitude panning. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1997, 45, 456–466. [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout, A.J.; de Vries, D.; Vogel, P. Acoustic control by wave field synthesis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 2764–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotter, F.; Frank, M. Ambisonics: A Practical 3D Audio Theory for Recording, Studio Production, Sound Reinforcement, and Virtual Reality; Springer Topics in Signal Processing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, J.; Moreau, S.; Nicol, R. Further investigations of high-order ambisonics and wavefield synthesis for holophonic sound imaging. In Audio Engineering Society Convention 114; Audio Engineering Society: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, G. Auditory Scene Synthesis Using Virtual Acoustic Recording and Reproduction. PhD Thesis, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, T.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. Diffuse-field equalisation of binaural ambisonic rendering. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronlachner, M. Spatial transformations for the alteration of ambisonic recordings. Master’s Thesis, University of Music and Performing Arts, Graz, Institute of Electronic Music and Acoustics, Graz, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brettle, J.; Skoglund, J. Open-Source Spatial Audio Compression for VR Content. In Proceedings of the SMPTE 2016 Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25–27 October 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzel, M.; Allen, A.; Kelly, I.; Kammerl, J.; Gungormusler, A.; Yeh, H.; Boland, F. Efficient Encoding and Decoding of Binaural Sound with Resonance Audio. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Conference: 2019 AES International Conference on Immersive and Interactive Audio, York, UK, 27–29 March 2019; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, T.; Murphy, D.T.; Kearney, G. Interaural Level Difference Optimization of Binaural Ambisonic Rendering. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunschirm, M.; Schörkhuber, C.; Höldrich, R. Binaural rendering of Ambisonic signals by head-related impulse response time alignment and a diffuseness constraint. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 3616–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdak, P.; Goupell, M.J.; Laback, B. 3-D localization of virtual sound sources: Effects of visual environment, pointing method, and training. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2010, 72, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahu, H.; Carpentier, T.; Noisternig, M.; Warusfel, O. Comparison of different egocentric pointing methods for 3D sound localization experiments. Acta Acust. Acust. 2016, 102, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkey, R.H.; Good, M.D.; Ericson, M.A.; Brinkman, J.; Stewart, J.M. A pointing technique for rapidly collecting localization responses in auditory research. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1995, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, S.; Frank, M. Localization of 3D ambisonic recordings and ambisonic virtual sources. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Spatial Audio, (Detmold), Detmold, Germany, 10–13 November 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bertet, S.; Daniel, J.; Parizet, E.; Warusfel, O. Investigation on localisation accuracy for first and higher order ambisonics reproduced sound sources. Acta Acust. Acust. 2013, 99, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, P.; Davies, W.; Hirst, J.; Dunn, C. Localisation of elevated virtual sources in higher order ambisonic sound fields. In Proceedings of the Institute of Acoustics, Brighton, UK, 14–16 November 2012; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rudzki, T.; Gomez-Lanzaco, I.; Hening, P.; Skoglund, J.; McKenzie, T.; Stubbs, J.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. Perceptual Evaluation of Bitrate Compressed Ambisonic Scenes in Loudspeaker Based Reproduction. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Conference: 2019 AES International Conference on Immersive and Interactive Audio, York, UK, 27–29 March 2019; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thresh, L.; Armstrong, C.; Kearney, G. A Direct Comparison of Localization Performance When Using First, Third, and Fifth Ambisonics Order for Real Loudspeaker and Virtual Loudspeaker Rendering. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Convention 143, New York, NY, USA, 18–21 October 2017; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund, J.; Graczyk, M. Ambisonics in an Ogg Opus Container; RFC 8486; Internet Engineering Task Force: Fremont, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Narbutt, M.; O’Leary, S.; Allen, A.; Skoglund, J.; Hines, A. Streaming VR for immersion: Quality aspects of compressed spatial audio. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Virtual System & Multimedia (VSMM), Dublin, Ireland, 31 October–4 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narbutt, M.; Allen, A.; Skoglund, J.; Chinen, M.; Hines, A. AMBIQUAL—A full reference objective quality metric for ambisonic spatial audio. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2018 Tenth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Cagliari, Italy, 29 May–1 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cardozo, B.L. Adjusting the Method of Adjustment: SD vs DL. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1965, 37, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendijk, E.H. Collecting localization response with a virtual acoustic pointer. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzki, T.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. A DAW-Based Interactive Tool for Perceptual Spatial Audio Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Convention 145, New York, NY, USA, 17–20 October 2018; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Green, M.C.; Murphy, D. EigenScape: A database of spatial acoustic scene recordings. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, P.; Gauthier, P.A.; Langrenne, C.; Berry, A.; Garcia, A. A Fifty-Node Lebedev Grid And Its Applications To Ambisonics. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2016, 64, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Boland, F. On the distortion of binaural localization cues using headphones. In Proceedings of the IET Irish Signals and Systems Conference, Cork, Ireland, 23–24 June 2010; Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2010; pp. 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki, H.; Shinomoto, S. Kernel bandwidth optimization in spike rate estimation. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2010, 29, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, N.I.; Lewis, T.; Embleton, B.J. Statistical Analysis of Spherical Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdebout, T. On some validity-robust tests for the homogeneity of concentrations on spheres. J. Nonparametr. Stat. 2015, 27, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, R.; Tukey, J.W.; Larsen, W.A. Variations of box plots. Am. Stat. 1978, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Makous, J.C.; Middlebrooks, J.C. Two-dimensional sound localization by human listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 2188–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




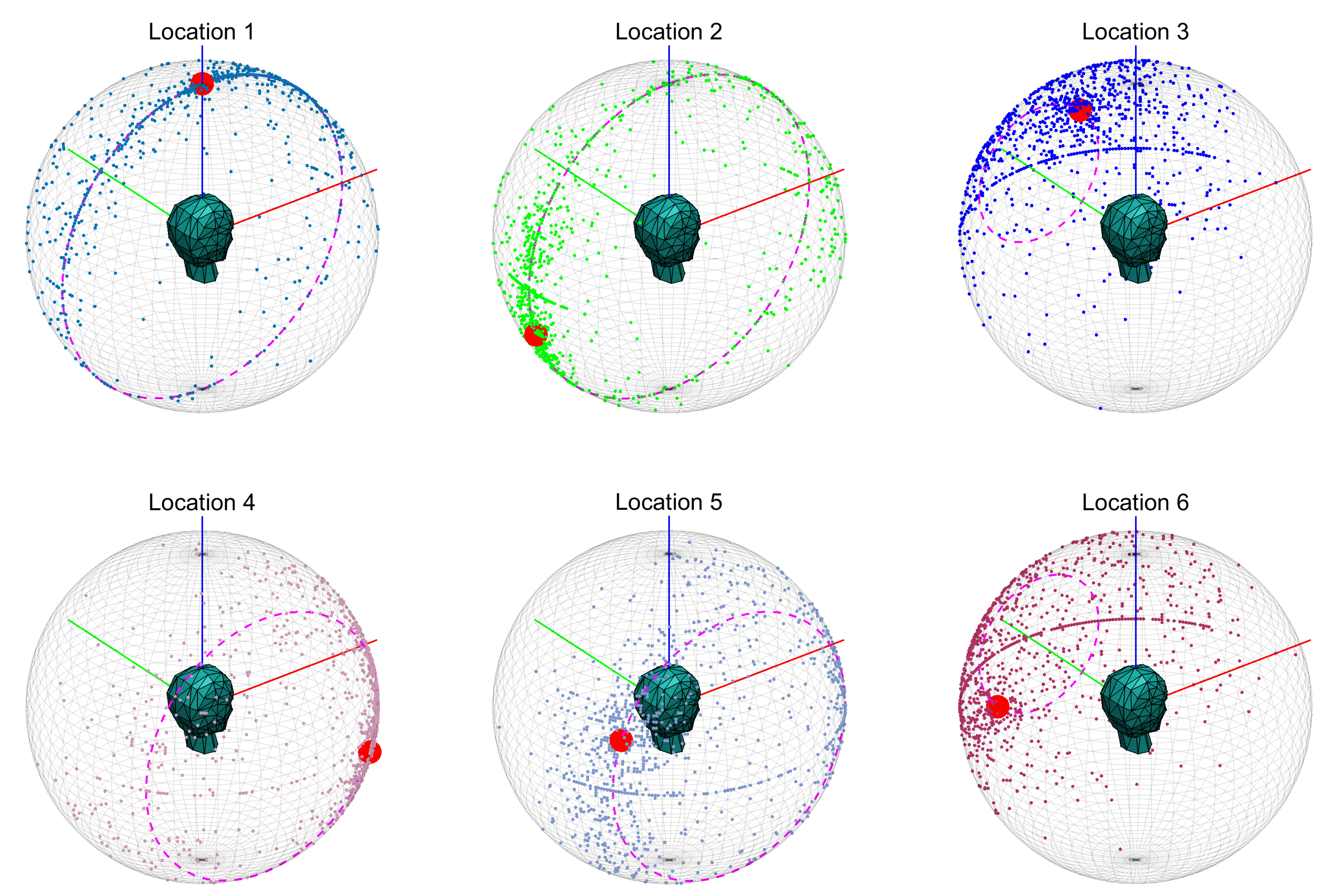


| Direction | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azimuth (°) | 0 | 180 | 72 | 324 | 216 | 108 |
| Elevation (°) | 90 | −18 | 18 | −18 | 18 | −18 |
| Bitrate per Channel | Total Bitrate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1OA | 3OA | 5OA | ||
| Compressed | 16 | 64 | 256 | 576 |
| Compressed | 32 | 128 | 512 | 1152 |
| Compressed | 64 | 256 | 1024 | 2304 |
| Uncompressed | 768 | 27,648 | ||
| Reproduction Method | Loudspeakers | Binaural (Individual HRTFs) | Binaural (Generic HRTFs) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content Type | Simple | Complex | Simple | Complex | Simple | Complex |
| Number of Participants | 21 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 19 | 19 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudzki, T.; Gomez-Lanzaco, I.; Stubbs, J.; Skoglund, J.; Murphy, D.T.; Kearney, G. Auditory Localization in Low-Bitrate Compressed Ambisonic Scenes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132618
Rudzki T, Gomez-Lanzaco I, Stubbs J, Skoglund J, Murphy DT, Kearney G. Auditory Localization in Low-Bitrate Compressed Ambisonic Scenes. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132618
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudzki, Tomasz, Ignacio Gomez-Lanzaco, Jessica Stubbs, Jan Skoglund, Damian T. Murphy, and Gavin Kearney. 2019. "Auditory Localization in Low-Bitrate Compressed Ambisonic Scenes" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132618
APA StyleRudzki, T., Gomez-Lanzaco, I., Stubbs, J., Skoglund, J., Murphy, D. T., & Kearney, G. (2019). Auditory Localization in Low-Bitrate Compressed Ambisonic Scenes. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132618





