Joining of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy to 6061 Aluminum Alloy with Sn-Zn Filler Metals Containing Trace Rare Earth Elements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
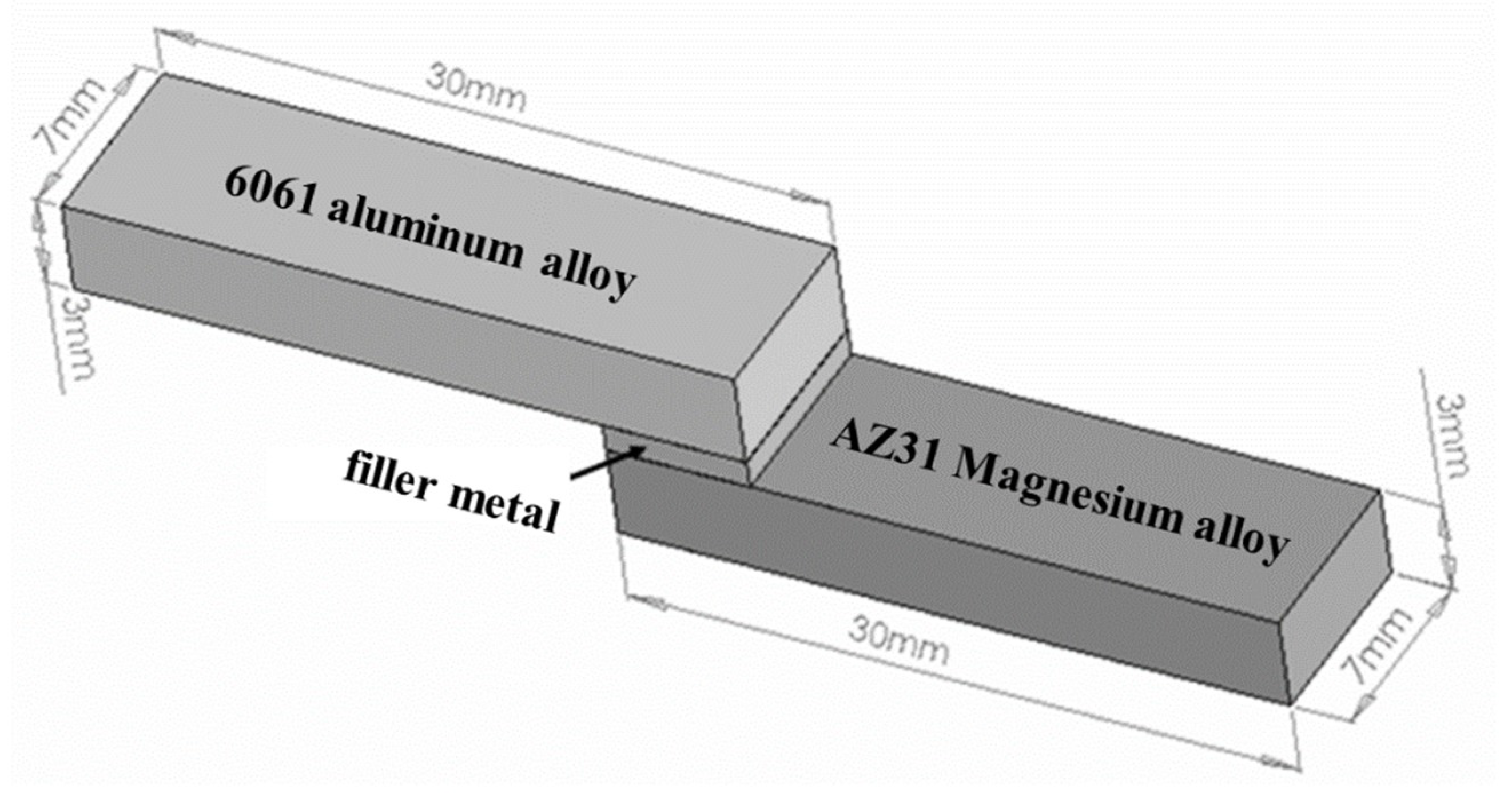
2. Experimental Section
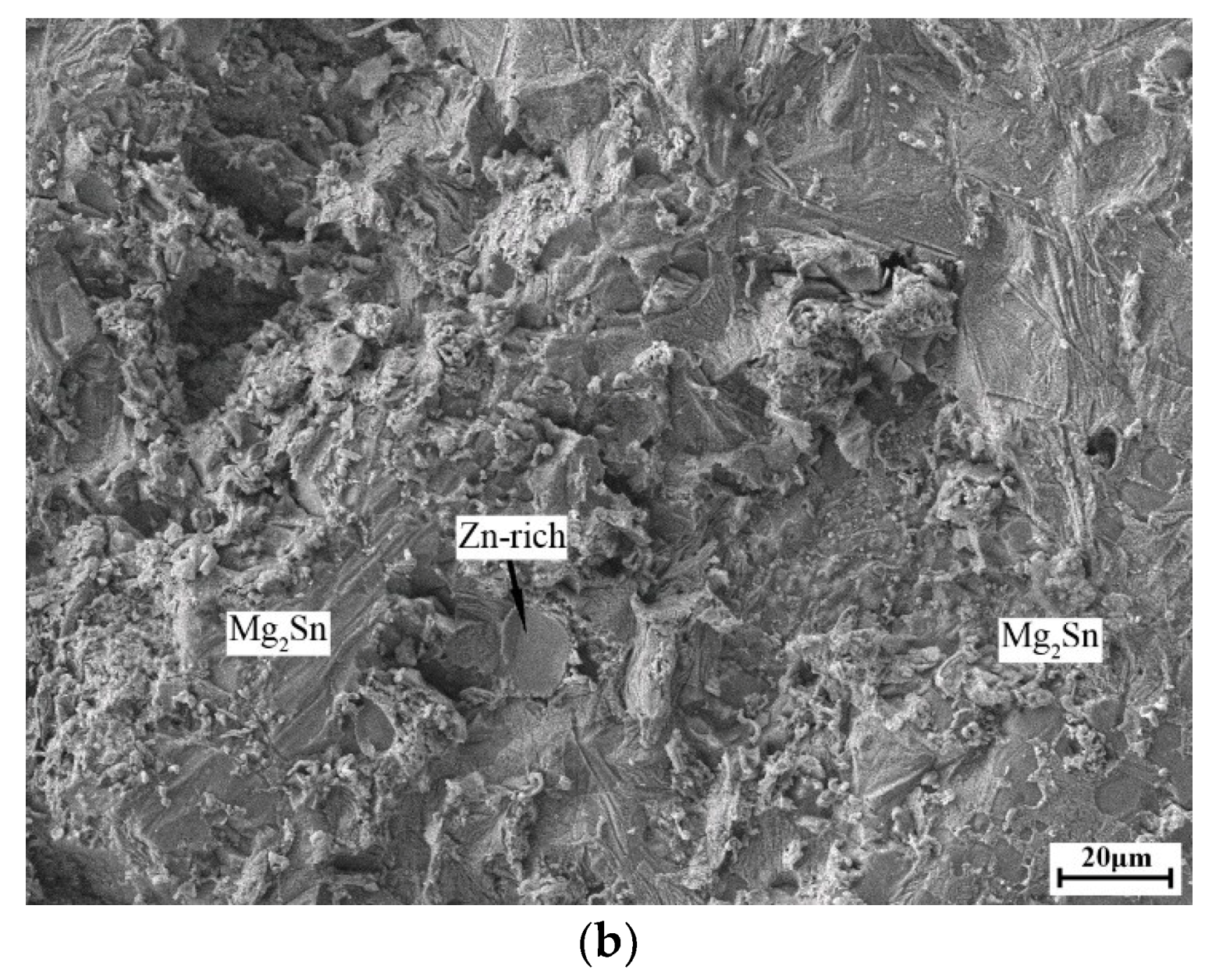
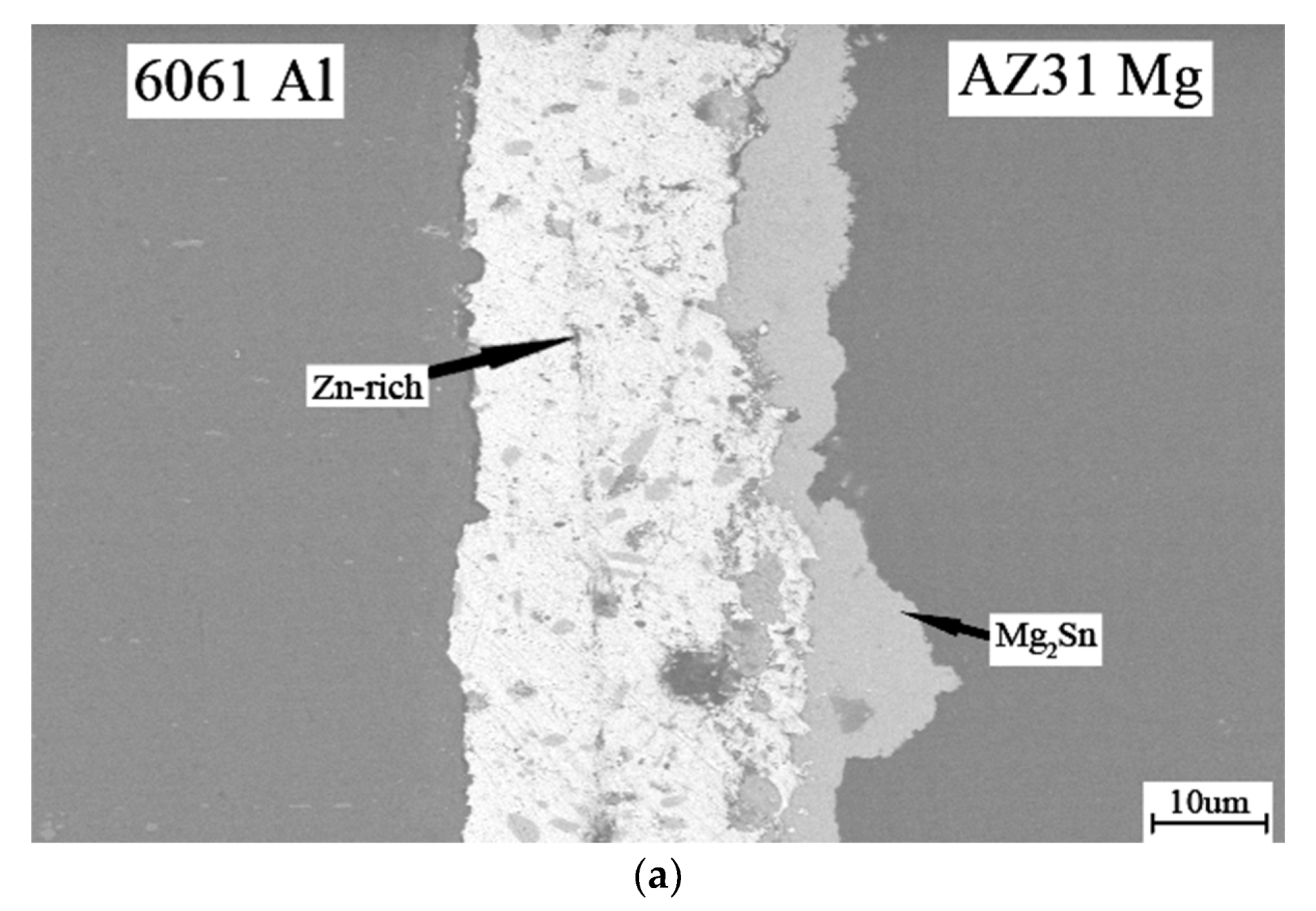
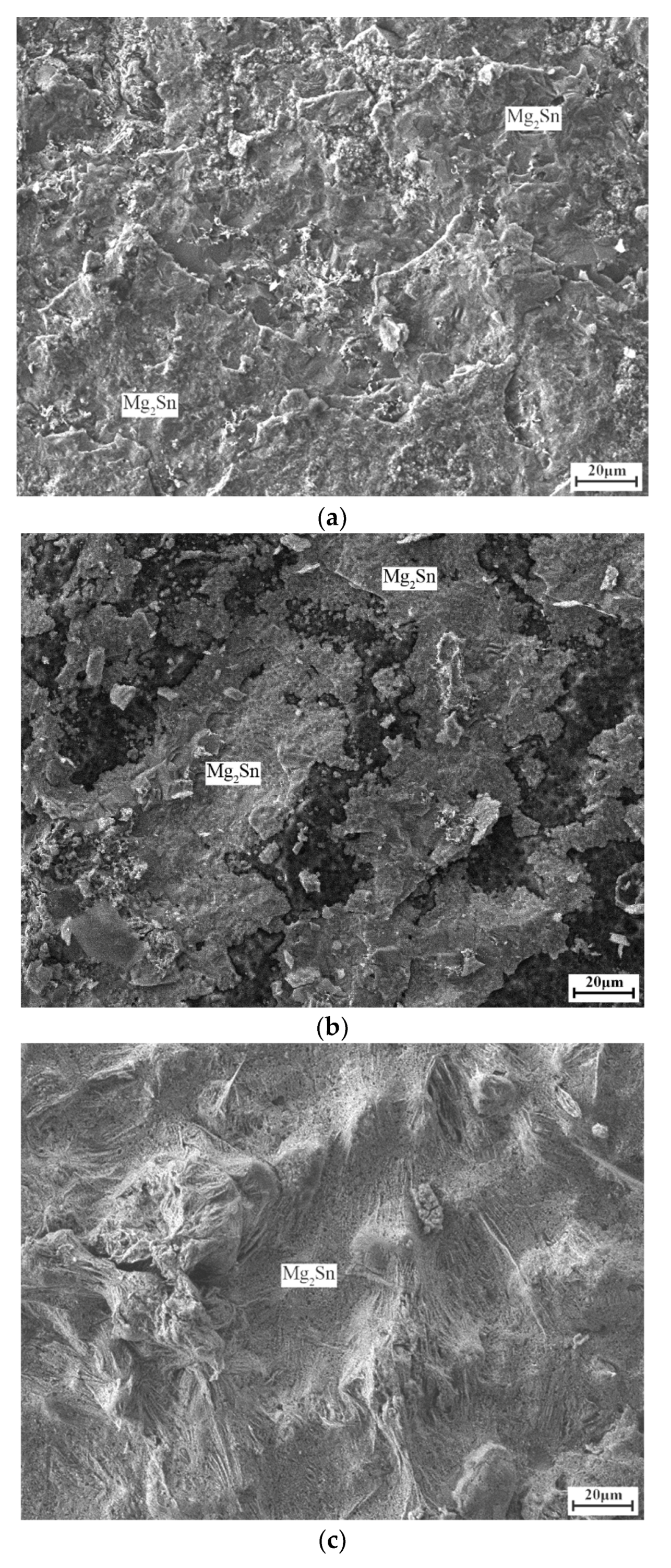
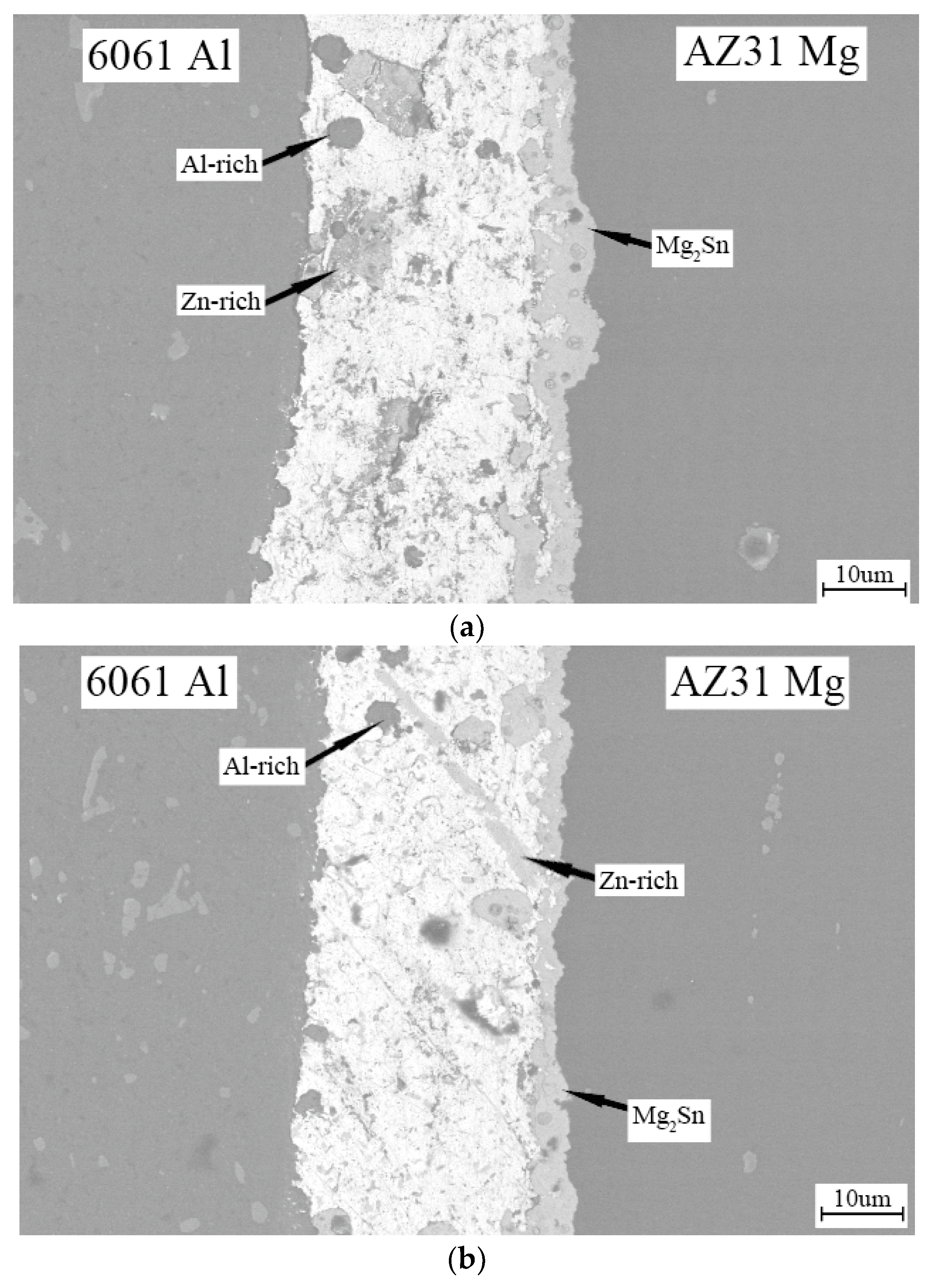
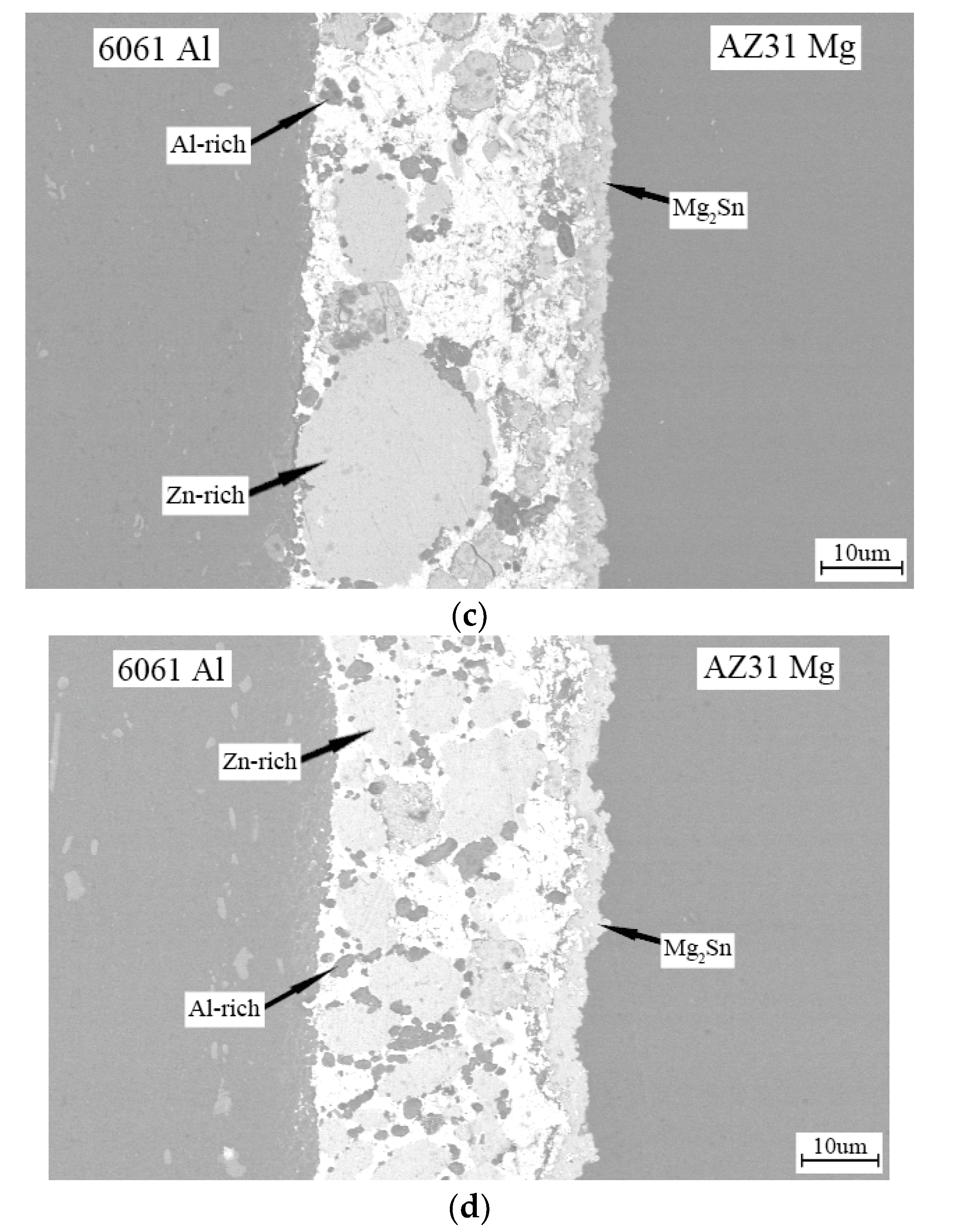
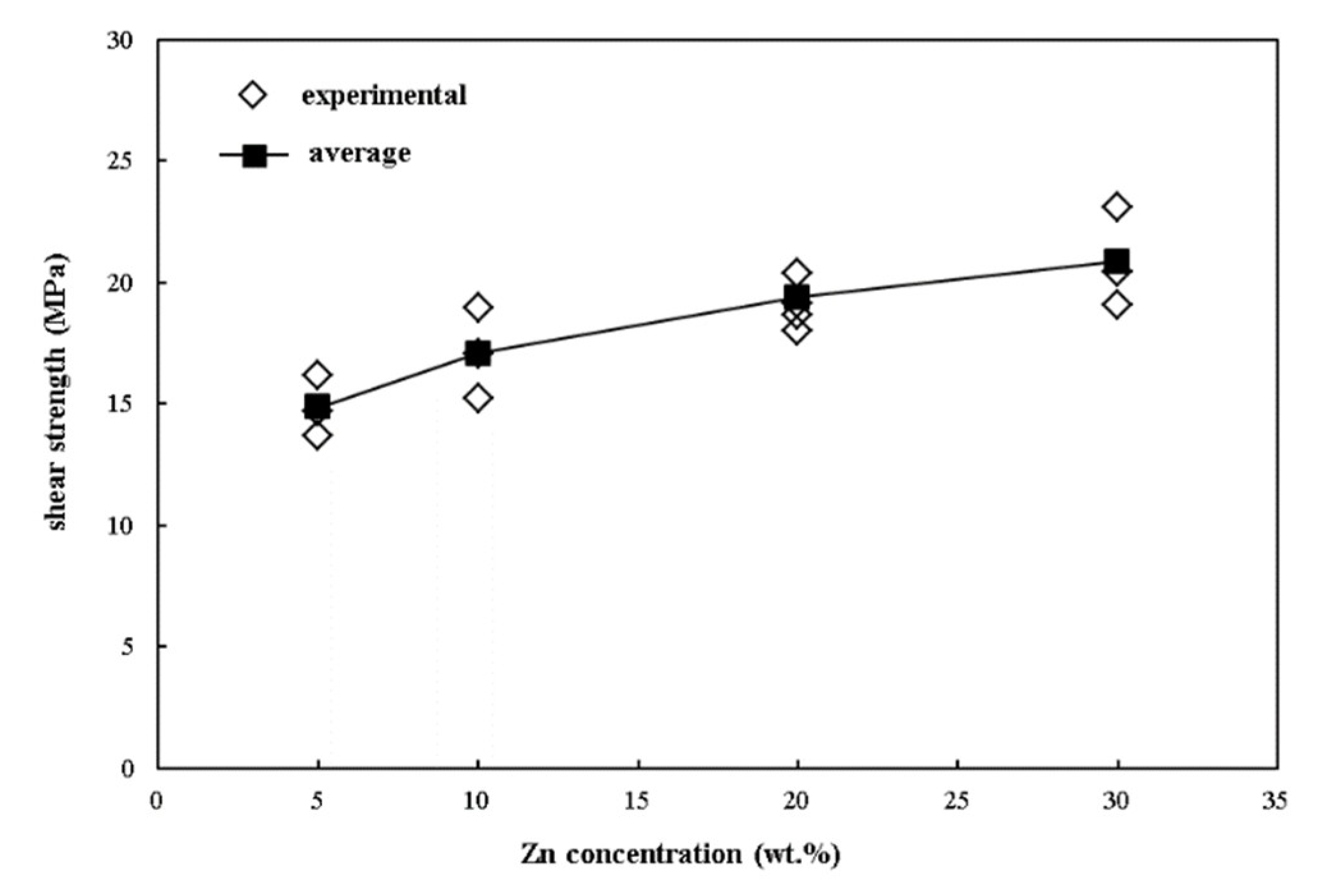
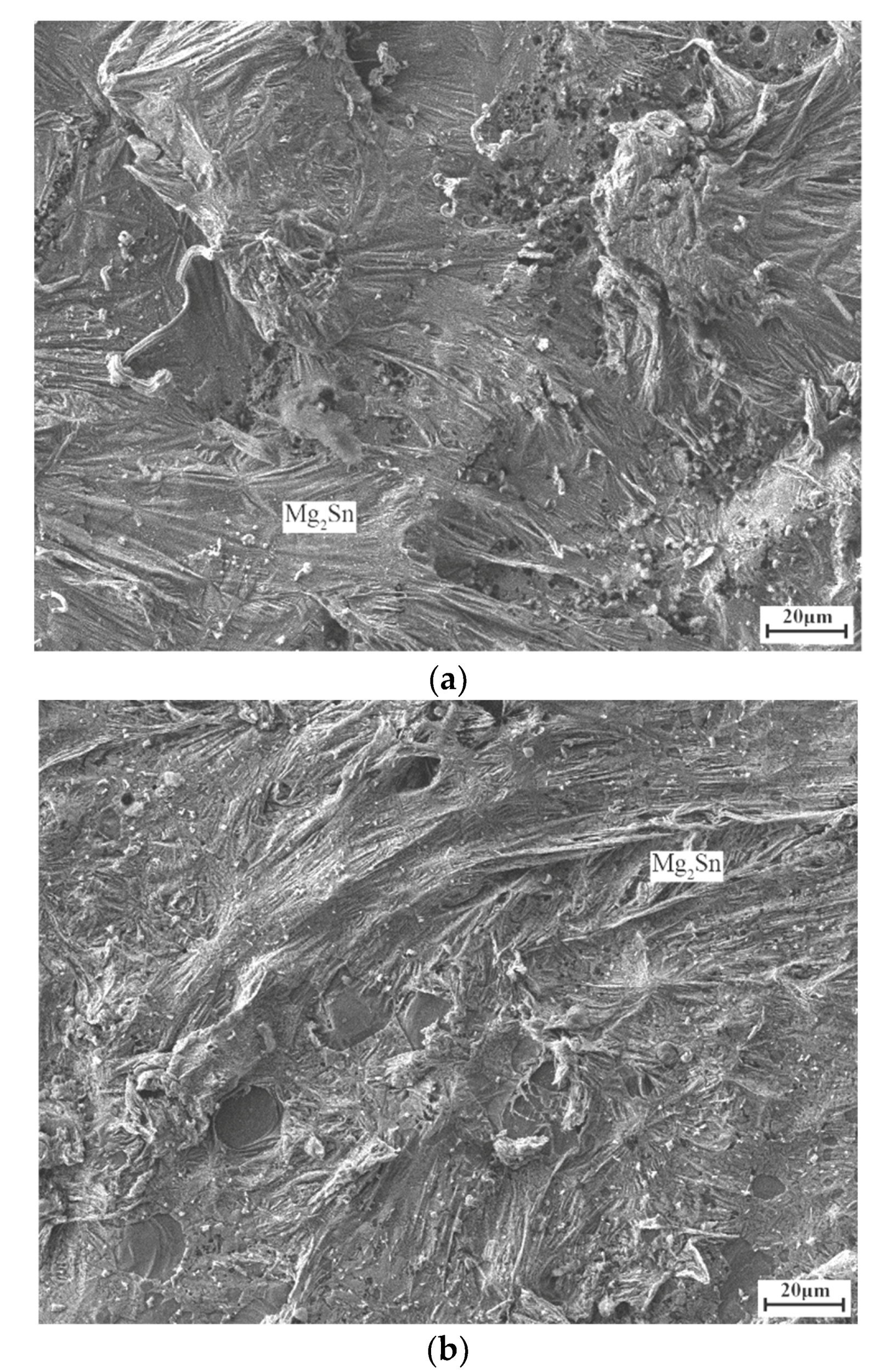
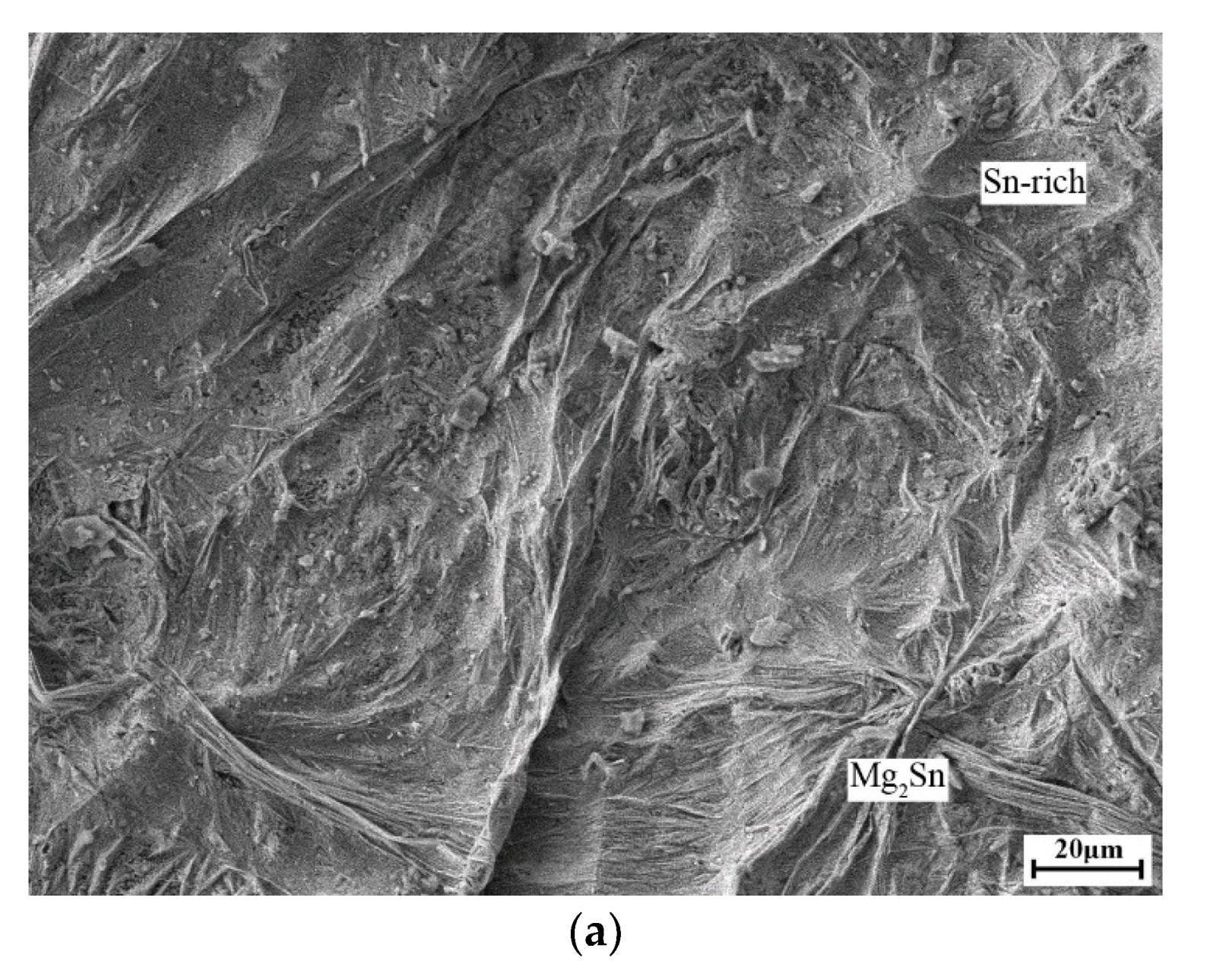
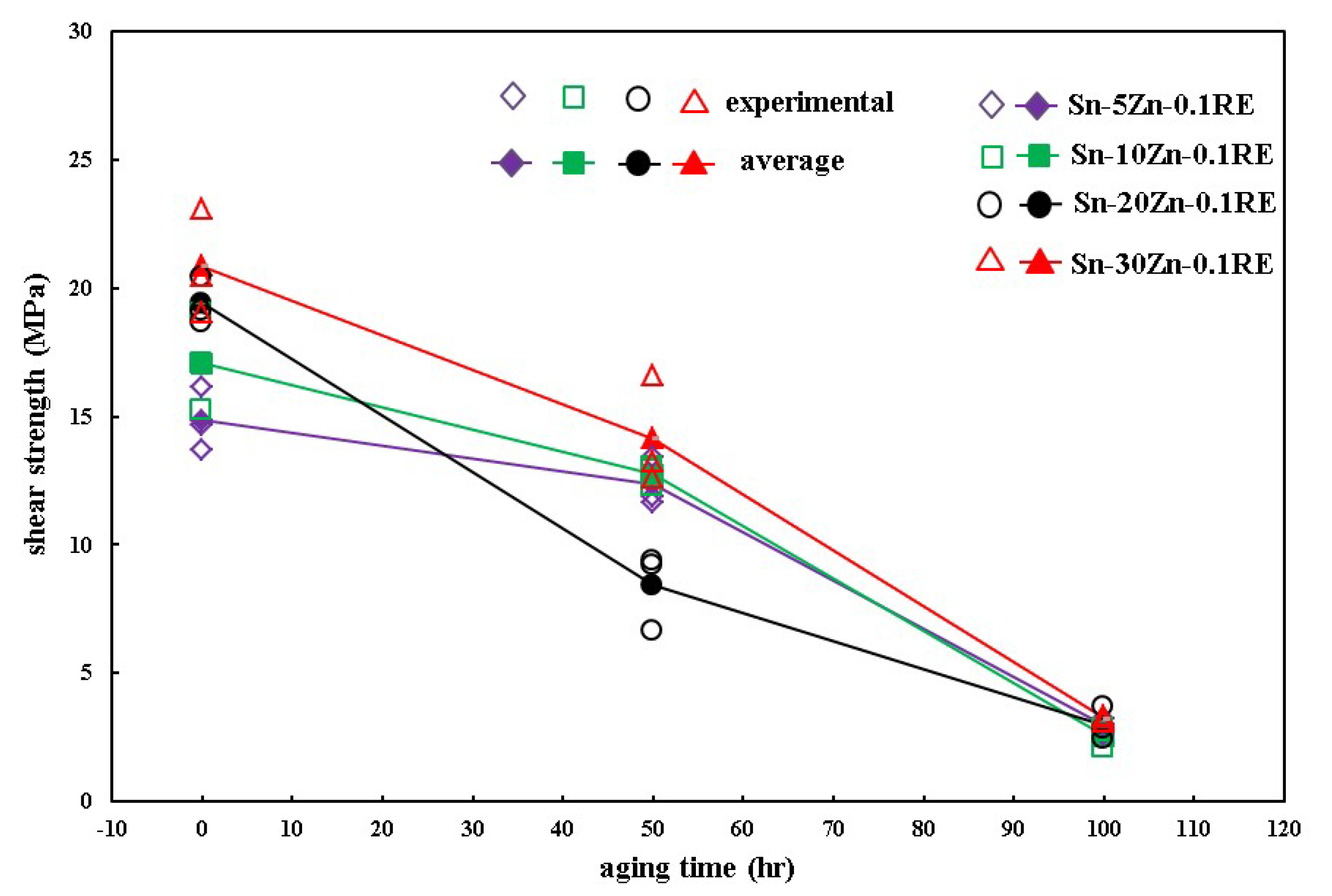
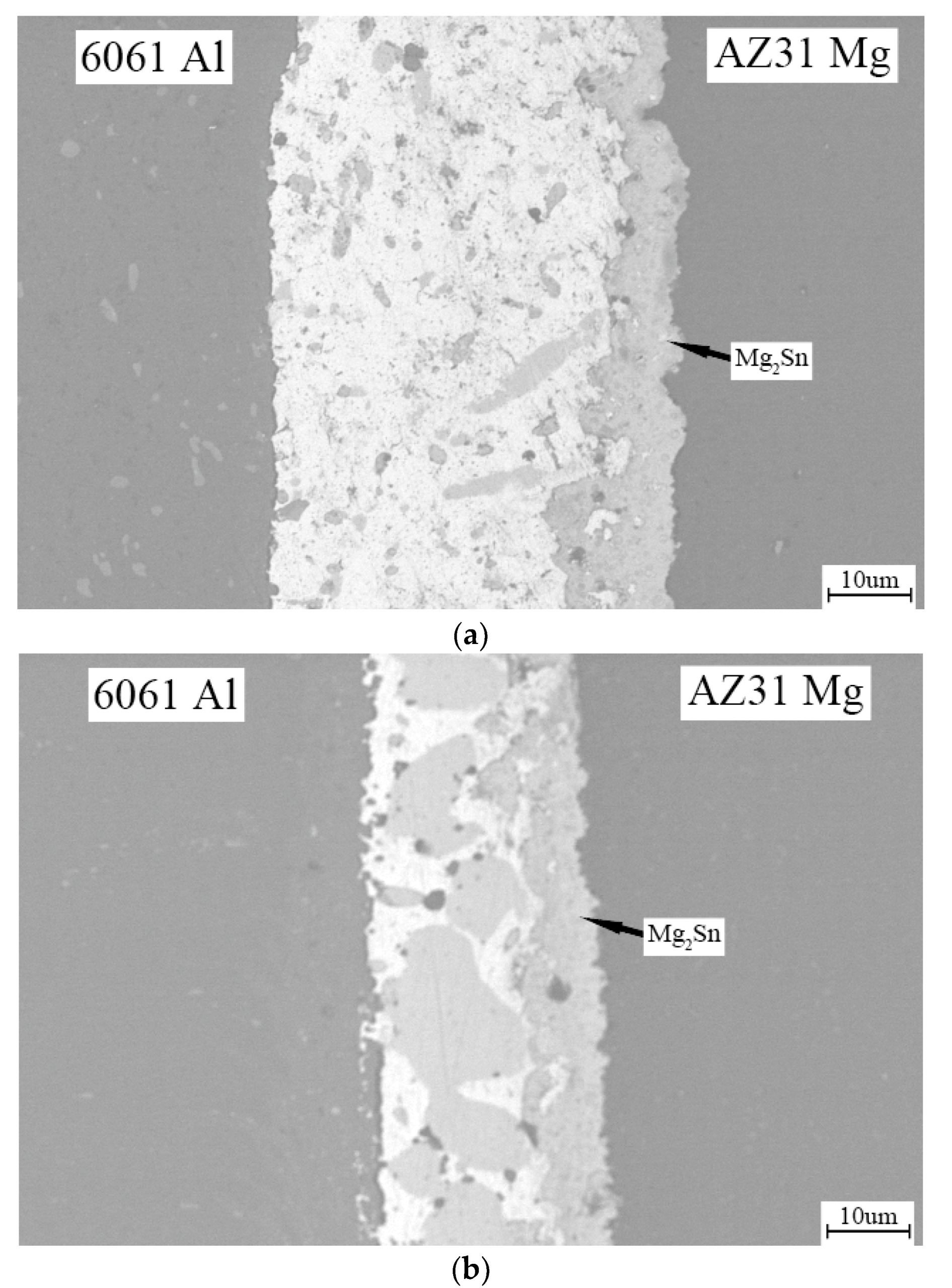
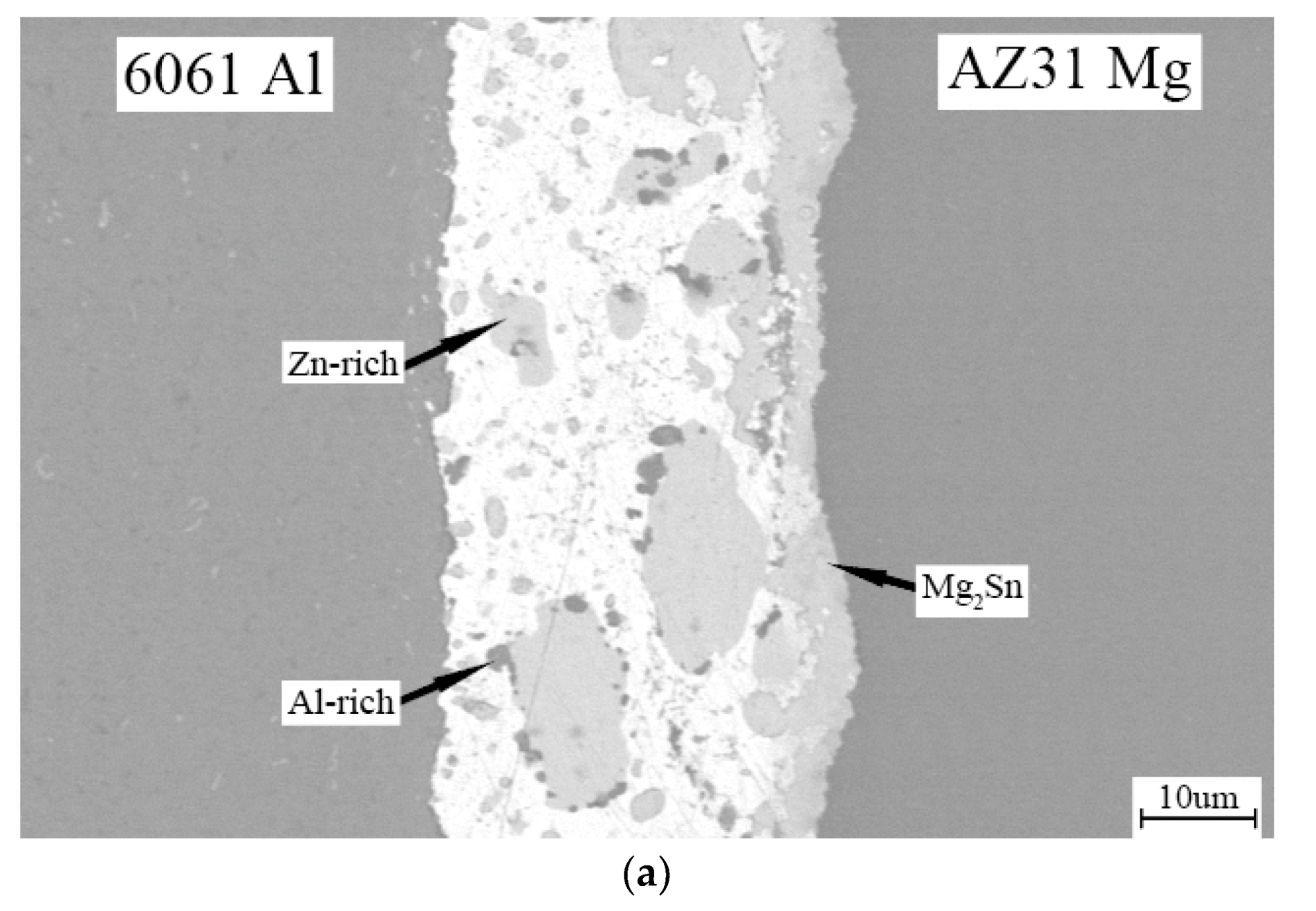
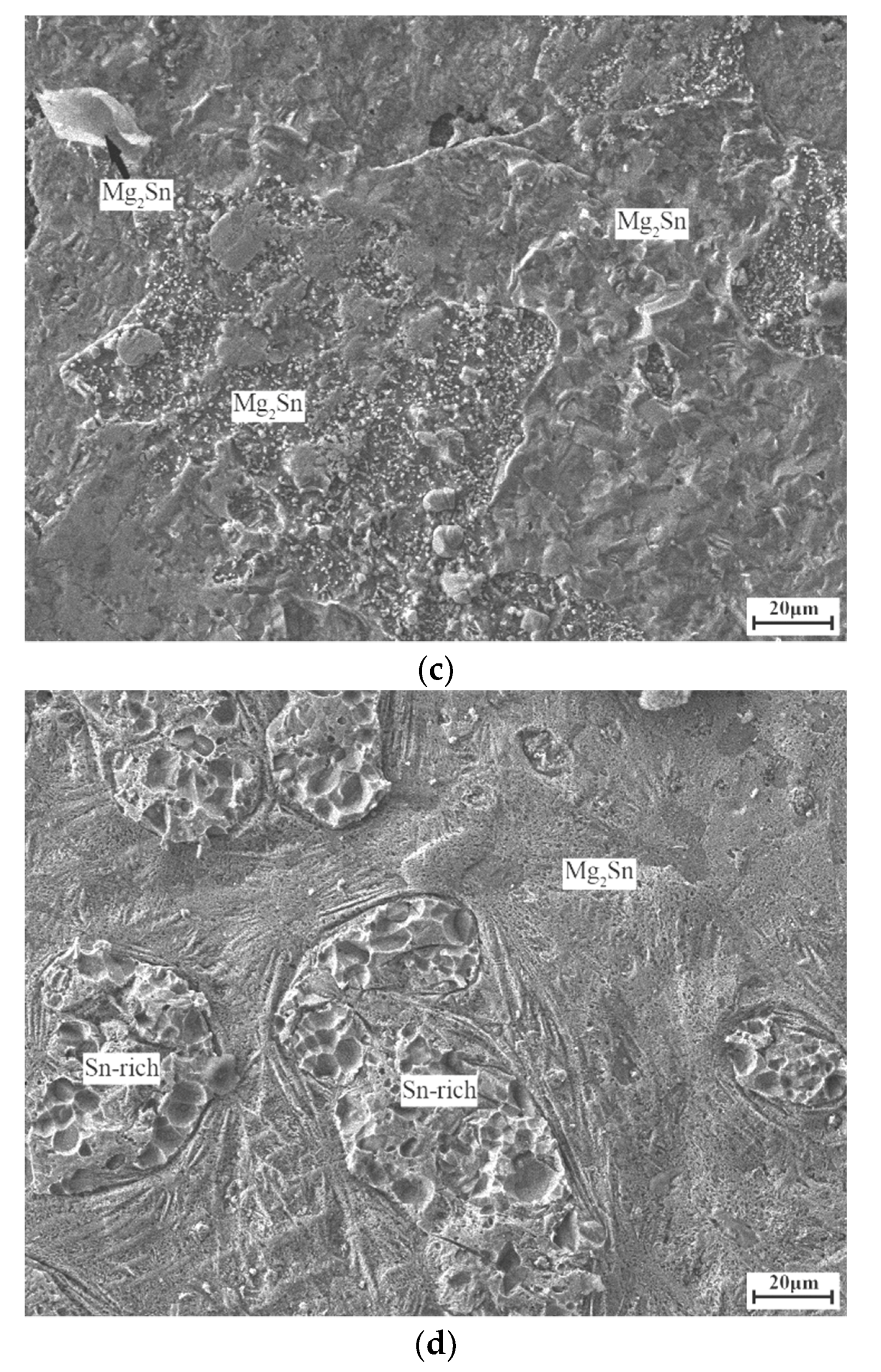
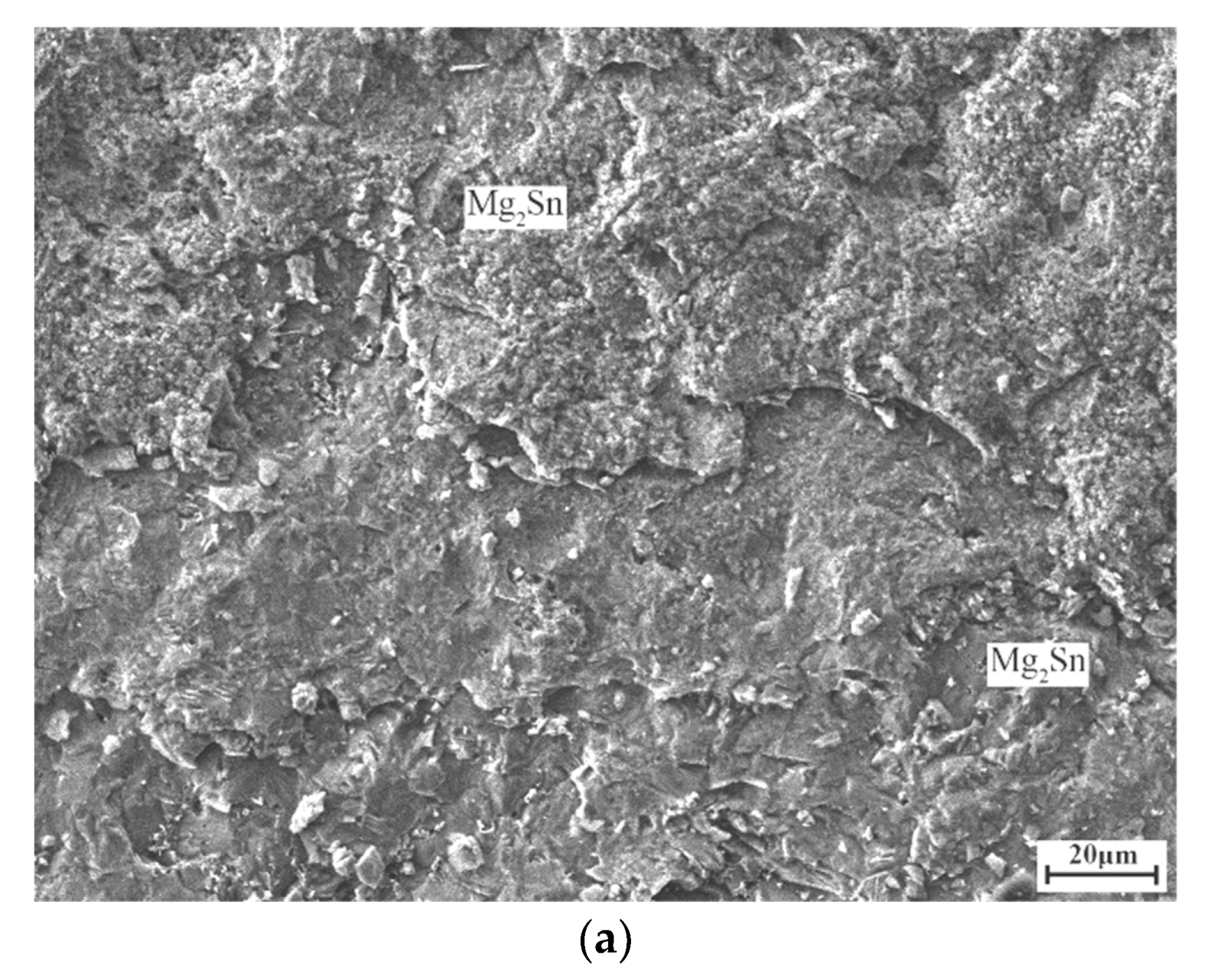
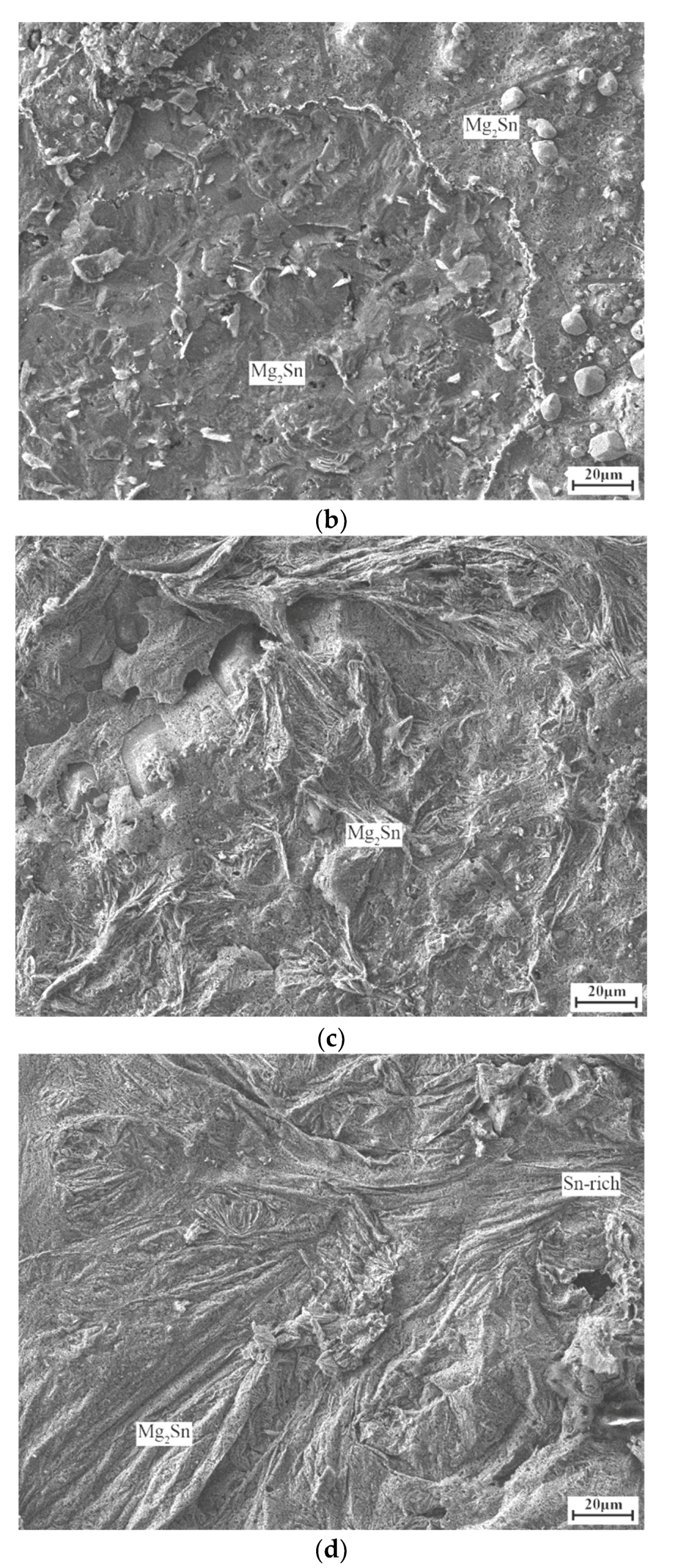
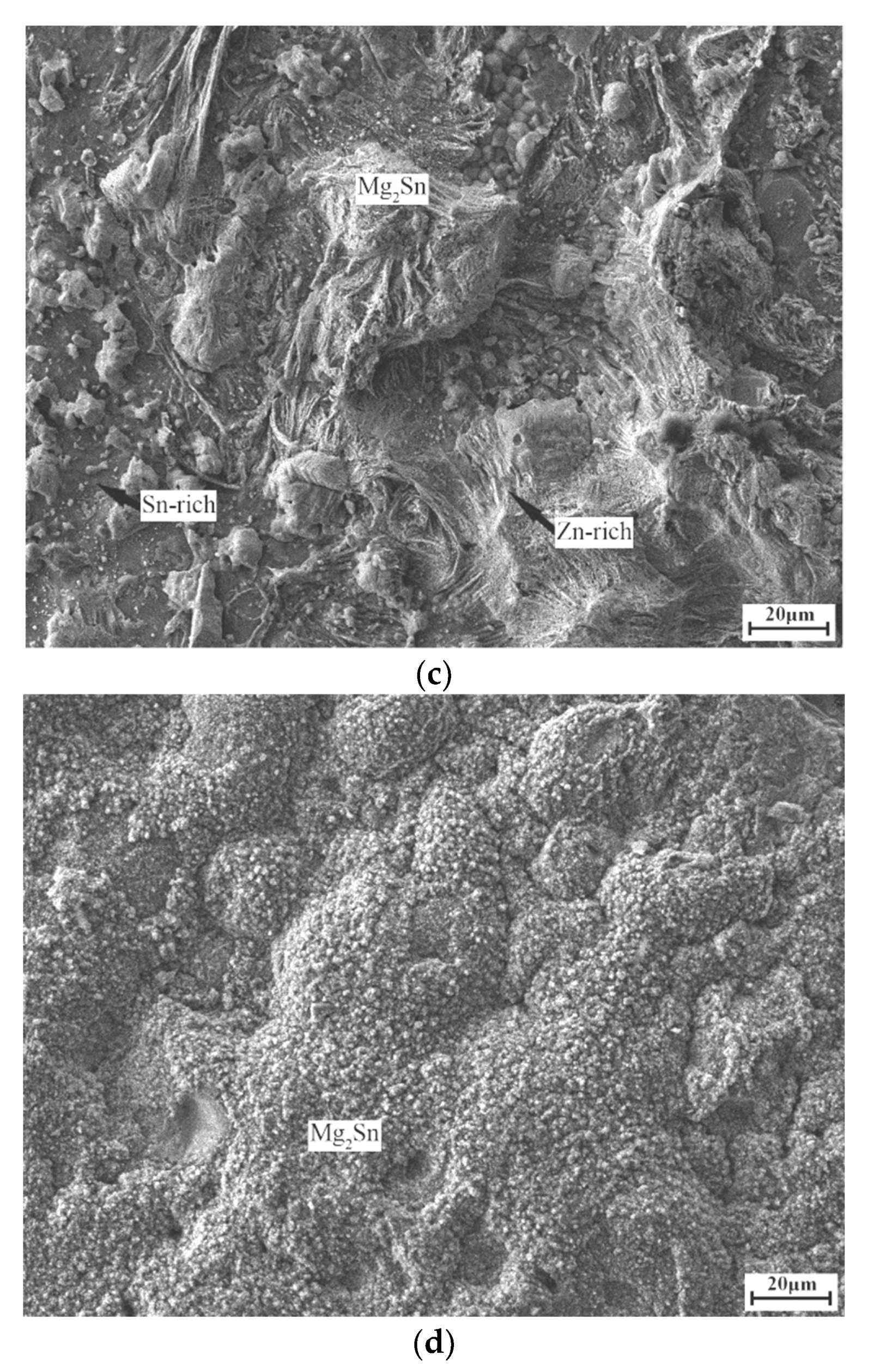
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamang, S.; Aravindan, S. An investigation on joining of Al6061-T6 to AZ31B by microwave hybrid heating using active braze alloy as an interlayer. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrisutthekul, R.; Miyashita, Y.; Mutoh, Y. Dissimilar material laser welding between magnesium alloy AZ31B and aluminum alloy A5052-O. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. An investigation on diffusion bonding of aluminum and magnesium using a Ni interlayer. Mater. Lett. 2012, 83, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Liang, W.; Zhao, X.G.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.P.; Liu, F.C. Bonding of Mg and Al with Mg-Al eutectic alloy and its application in aluminum coating on magnesium. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 471, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Li, Z.W.; Li, J.P.; Ma, Z.P.; Yan, J.C. Control Al/Mg intermetallic compound formation during ultrasonic-assisted soldering Mg to Al. Ultrason. Sonochem 2018, 46, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Ren, D.; Liu, F. A Review of dissimilar welding techniques for magnesium alloys to aluminum alloys. Materials 2014, 7, 3735–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adisa, S.B.; Loginova, I.; Khalil, A.; Solonin, A. Effect of Laser Welding Process Parameters and Filler Metals on the Weldability and the Mechanical Properties of AA7020 Aluminium Alloy. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, D.M.; Humpston, G.; Sangha, S.P.S. A New Low-Melting-Point Aluminum Braze. Weld. Res. Suppl. 1996, 8, 243s–250s. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, L.C.; Chiang, M.J.; Lin, W.H.; Cheng, M.D.; Chuang, T.H. Effect of zinc additions on the microstructure and melting temperature of Al-Si-Cu filler metals. Mater. Charact. 2002, 48, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjan, L.; Blugan, G.; Boretius, M.; De La Pierre, S.; Ferraris, M.; Casalegno, V.; Rizzo, S.; Graule, T.; Kuebler, J. Fracture behavior of soldered Al2O3 ceramic to A356 aluminum alloy and resistance of the joint to low temperature exposure. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjan, L.; Boretius, M.; Blugan, G.; Gili, F.; Mangherini, D.; Lizarralde, X.; Ferraris, M.; Graule, T.; Igartua, A.; Mendoza, G.; et al. Ceramic protection plates brazed to aluminum brake discs. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15739–15746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, L.M. Study on low temperature brazing of magnesium alloy to aluminum alloy using Sn-xZn solders. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.A.; Wu, B.Y.; Alam, M.O.; Chan, Y.C.; Jillek, W. Investigations on microhardness of Sn–Zn based lead-free solder alloys as replacement of Sn-Pb solder. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 392, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.R.; Osório, W.R.; Peixoto, L.C.; Garcia, A. Mechanical properties of Sn-Zn lead-free solder alloys based on the microstructure array. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.L.; Yu, D.Q.; Law, C.M.T.; Wang, L. Properties of lead-free solder alloy with rare earth element additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2004, R44, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.L.; Law, C.M.T.; Yu, D.Q.; Wang, L. The Wettability and Microstructure of Sn-Zn-RE Alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 22, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.A.; Chawla, N. Oxidation behavior of rare-earth-containing Pb-free solders. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.L.; Yu, D.Q.; Law, C.M.T.; Wang, L. The Properties of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder alloys doped with trace rare earth elements. J. Electron. Mater. 2002, 31, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, J.; Han, J.H.; Guo, Y.H.; He, C.W. Microstructures and properties of SnZn-xEr lead-free solders. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleňák, R.; Kostolný, I. Study of direct bonding ceramics with metal using Sn2La solder. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleňák, R.; Šebo, P.; Provazník, M.; Koleňáková, M.; Ulrich, K. Shear strength and wettability of active Sn3.5Ag4Ti(Ce,Ga) solder on Al2O3 ceramics. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Chuang, T.H.; Yang, C.L. Low temperature bonding of alumina/alumina and alumina/copper in air using Sn3.5Ag4Ti(Ce,Ga) Filler. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillen, F.; Pickart-Castillo, D.; Rass, I.J.; Lugscheider, E. Solder alloy and soldering processes for flux–free soldering of difficult-to-wet materials. Weld. Cut. 2000, 52, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Chun, D.W.; Kim, G.W.; Chen, R.K. Universal solder for direct bonding and packaging of optical devices. Mater. Lett. 2015, 152, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.G.; Mavoori, H.; Jin, S. Bonding nature of rare-earth-containing lead-free solders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.W. Active solder joining of metals, ceramics and composites. Weld. J. 2001, 10, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.Y.; Tsao, L.C.; Chiang, M.J.; Tung, C.N.; Pan, G.H.; Chuang, T.H. Active soldering of indium tin oxide (ITO) with Cu in air using an Sn3.5Ag4Ti(Ce,Ga) filler. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 2, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y. Active Soldering of ZnS-SiO2 Sputtering targets to copper backing plates using an Sn56Bi4Ti(Ce, Ga) filler. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2006, 21, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C. Direct Active Soldering of Micro–arc Oxidized Ti/Ti Joints in air using Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu4Ti(RE) filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.X.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, Z.L.; Wu, Z.Z. Influence of active element Ti on interfacial reaction and soldering strength between Sn3.5Ag4Ti(Ce, Ga) alloy filler and Si substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.X.; Liu, M.R.; Wang, X.Q.; Yan, B.H.; Li, G.Y. Effect of active element Ti on interfacial microstructure and bonding strength of SiO2/SiO2 joins soldered using Sn3.5Ag4Ti(Ce, Ga) alloy filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y. Joining of Magnesium Alloys and Aluminum Alloys Using Sn-Zn Aolders. Master’s Thesis, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Yunlin County, Taiwan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Murray, J.L.; Bennett, L.H.; Baker, H. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams; American Society for Metal: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]











| Alloy | Chemical Composition (wt.%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Al | Zn | Cr | Cu | Si | Mn | |
| AZ31 magnesium alloy | Bal. | 3 | 1 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 0.2 | |
| 6061 aluminum alloy | 1.1 | Bal. | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.61 | 0.01 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Wu, A.-B. Joining of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy to 6061 Aluminum Alloy with Sn-Zn Filler Metals Containing Trace Rare Earth Elements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132655
Chang S-Y, Lee J-Y, Huang Y-H, Wu A-B. Joining of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy to 6061 Aluminum Alloy with Sn-Zn Filler Metals Containing Trace Rare Earth Elements. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132655
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Shih-Ying, Jun-Yen Lee, Yan-Hua Huang, and An-Ban Wu. 2019. "Joining of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy to 6061 Aluminum Alloy with Sn-Zn Filler Metals Containing Trace Rare Earth Elements" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132655
APA StyleChang, S.-Y., Lee, J.-Y., Huang, Y.-H., & Wu, A.-B. (2019). Joining of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy to 6061 Aluminum Alloy with Sn-Zn Filler Metals Containing Trace Rare Earth Elements. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132655




