Temporal Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities and Responses to Land-Use Change in the Loess Plateau, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Soil Enzyme Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Available Nutrients and Water Content
3.2. Temporal Variation in Soil Enzyme Activities after Afforestation
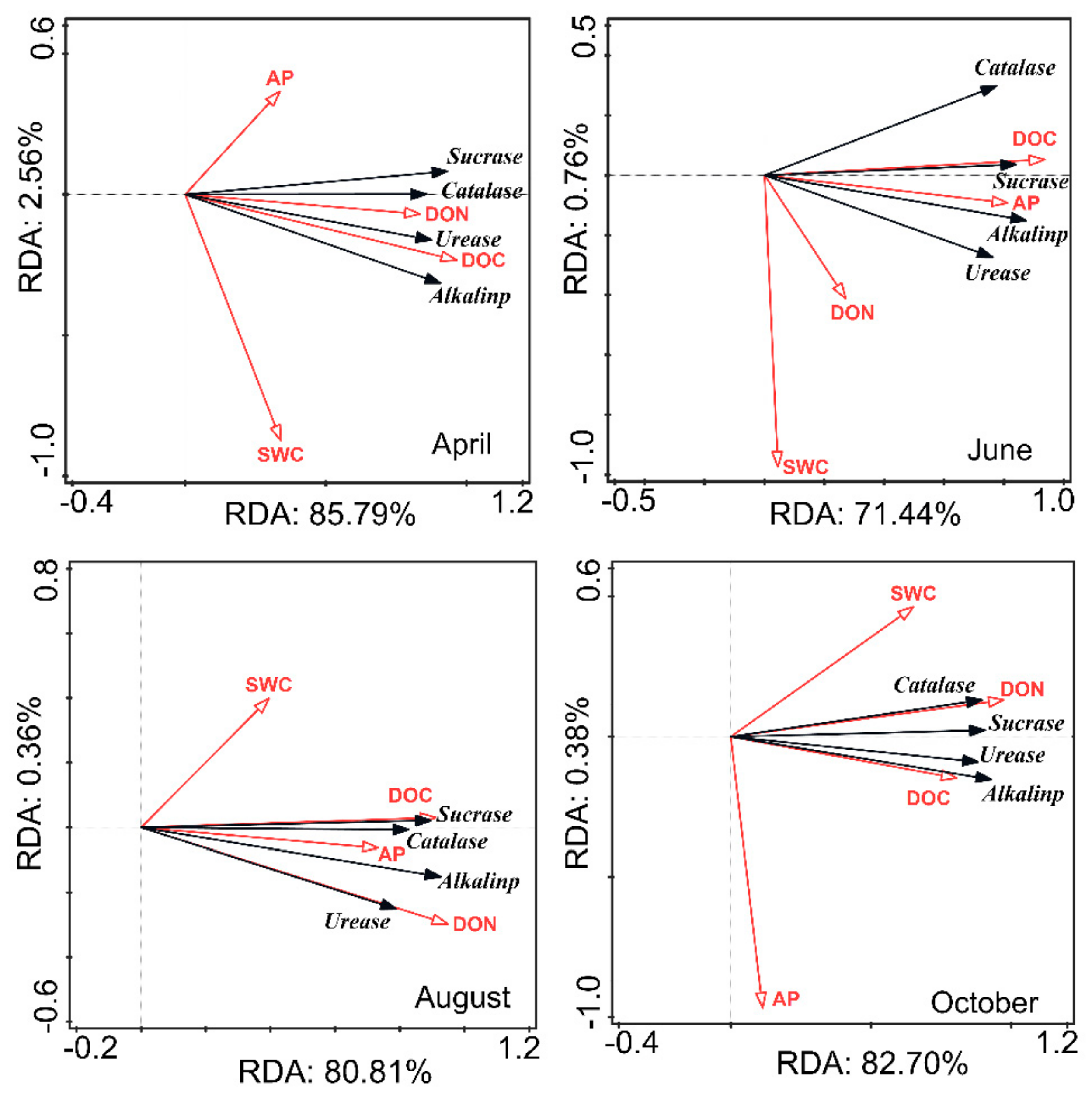
3.3. Relationship between Soil Properties and Soil Enzyme Activities in CK Lands
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laganière, J.; Angers, D.A.; Paré, D. Carbon accumulation in agricultural soils after afforestation: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.; Garcia-Fayos, P.; Hu, S.; Jiao, J. The effect of Robinia pseudoacacia afforestation on soil and vegetation properties in the Loess Plateau (China): A chronosequence approach. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 375, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, J.C.F.; Dáttilo, W.; Izzo, T.J. Efficiency of different planted forests in recovering biodiversity and ecological interactions in Brazilian Amazon. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 339, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Tong, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Linkages of C:N:P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, B.A. Enzyme activities as a component of soil biodiversity: A review. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gispert, M.; Emran, M.; Pardini, G.; Doni, S.; Ceccanti, B. The impact of land management and abandonment on soil enzymatic activity, glomalin content and aggregate stability. Geoderma 2013, 202, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, M.D.; Mcmahon, S.K.; Schimel, J.P. Seasonal variation in enzyme activities and temperature sensitivities in Arctic tundra soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; Šnajdr, J.; Merhautová, V.; Dobiášová, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Valášková, V. Responses of the extracellular enzyme activities in hardwood forest to soil temperature and seasonality and the potential effects of climate change. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 56, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.M.; Weiss, M.S.; Goodale, C.L.; Adams, M.B.; Fernandez, I.J.; German, D.P.; Allison, S.D. Temperature sensitivity of soil enzyme kinetics under N-fertilization in two temperate forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, B.; Kilpeläinen, P.; Kitunen, V.; Smolander, A. Potential activities of enzymes involved in N, C, P and S cycling in boreal forest soil under different tree species. Pedobiologia 2014, 57, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Aanderud, Z.; Lennon, J.; Fierer, N. Temporal variability in soil microbial communities across land-use types. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, R.M.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Wallenius, K.; Simpanen, S.; Alakukku, L.; Pietola, L. Temporal and soil depth-related variation in soil enzyme activities and in root growth of red clover (Trifolium pratense) and timothy (Phleum pratense) in the field. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 30, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Kang, D.; Wu, J.P.; Zhao, F.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Temporal variation in soil enzyme activities after afforestation in the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2016, 282, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activities as indicators of soil quality. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.-B.; Song, Z.-L. A comparison of soil qualities of different revegetation types in the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2011, 347, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Ma, K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J. The relationships between land use and soil conditions in the hilly area of the loess plateau in northern Shaanxi, China. Catena 2000, 39, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shangguan, Z.; Yao, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Dang, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, B. Ecological Effects of Soil Conservation in Loess Plateau. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Sun, P.; Zhao, F.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Soil C, N, P and Its Stratification Ratio Affected by Artificial Vegetation in Subsoil, Loess Plateau China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Soil stoichiometry and carbon storage in long-term afforestation soil affected by understory vegetation diversity. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, B.; Qin, S.; Fa, K. Fine-root distribution, production, decomposition, and effect on soil organic carbon of three revegetation shrub species in northwest China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 359, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Gao, S.-Y.; Xu, H.-Y.; Liu, L.-Y. Growth of Caragana korshinskii using runoff-collecting microcatchments under semiarid condition. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Jia, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T. Distribution, biomass, and dynamics of roots in a revegetated stand of Caragana korshinskii in the Tengger Desert, northwestern China. J. Plant Res. 2009, 122, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Soil conservation and sustainable agriculture on the Loess Plateau: Challenges and prospects. Ambio 1999, 28, 663–668. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Tam, C.; Chen, X. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Bennett, J. Nitrogen mineralization: Challenges of a changing paradigm. Ecology 2004, 85, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.L.; Bowman, W.D. Links between plant litter chemistry, species diversity, and below-ground ecosystem function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19780–19785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ma, Y.; Jin, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Fu, S.; Chen, H.Y.H. Soil enzyme activities increase following restoration of degraded subtropical forests. Geoderma 2019, 351, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Roldan, A.; Hernandez, T. Ability of different plant species to promote microbiological processes in semiarid soil. Geoderma 2005, 124, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Jiang, S.; Ying, Z.; Zhang, F.; Han, X. Spatial variability of soil nutrients and microbiological properties after the establishment of leguminous shrub Caragana microphylla Lam. plantation on sand dune in the Horqin Sandy Land of Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Drought decreases soil enzyme activity in a Mediterranean Quercus ilex L. forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Kiely, G. Modeling the change in soil organic carbon of grassland in response to climate change: Effects of measured versus modelled carbon pools for initializing the Rothamsted Carbon model. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criquet, S.; Tagger, S.; Vogt, G.; Petit, J.L. Endoglucanase and β-glycosidase activities in an evergreen oak litter: Annual variation and regulating factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bao, W.; Pang, X.; Wu, N.; Zhou, G. Changes of Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Restoration Ages of Spruce Forests on the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2005, 10, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Nannipieri, P.; Giagnoni, L.; Renella, G.; Puglisi, E.; Ceccanti, B.; Masciandaro, G.; Fornasier, F.; Moscatelli, M.C.; Marinari, S. Soil enzymology: Classical and molecular approaches. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Zhu, B. A meta-analysis of soil extracellular enzyme activities in response to global change. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Deng, J.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics along a revegetation chronosequence in the soils of abandoned land and Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajwa, H.A.; Dell, C.J.; Rice, C.W. Changes in enzyme activities and microbial biomass of tallgrass prairie soil as related to burning and nitrogen fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
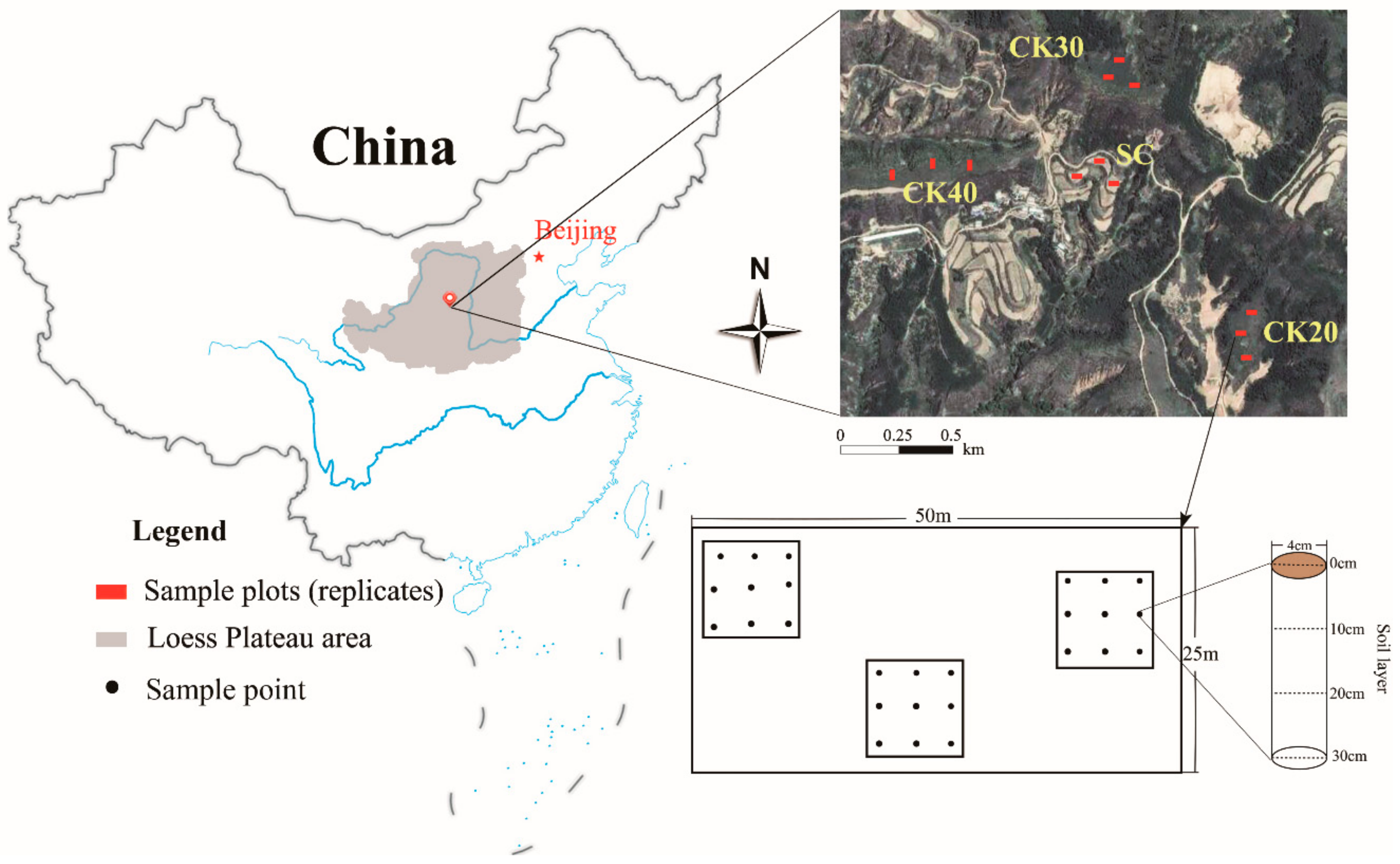
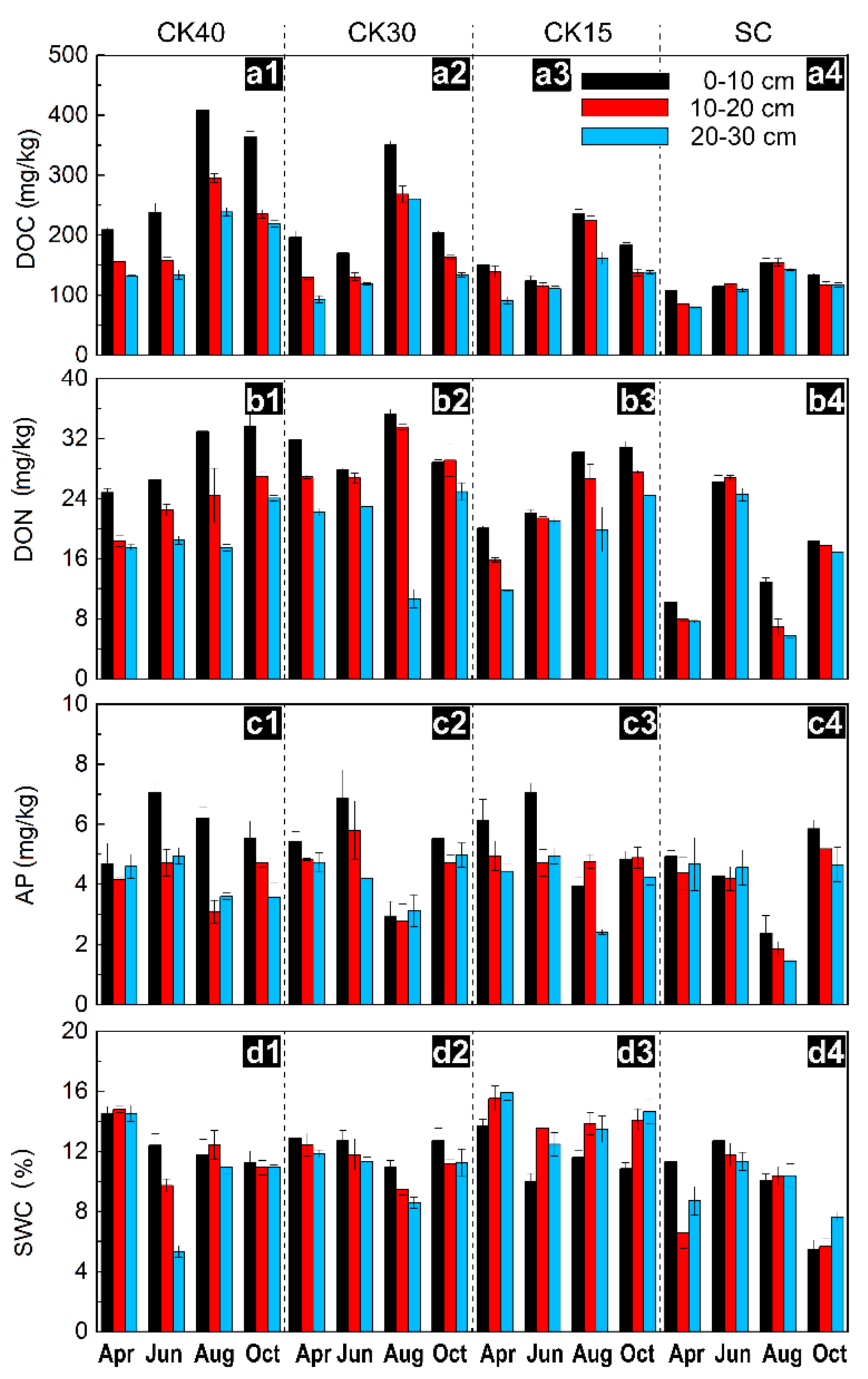
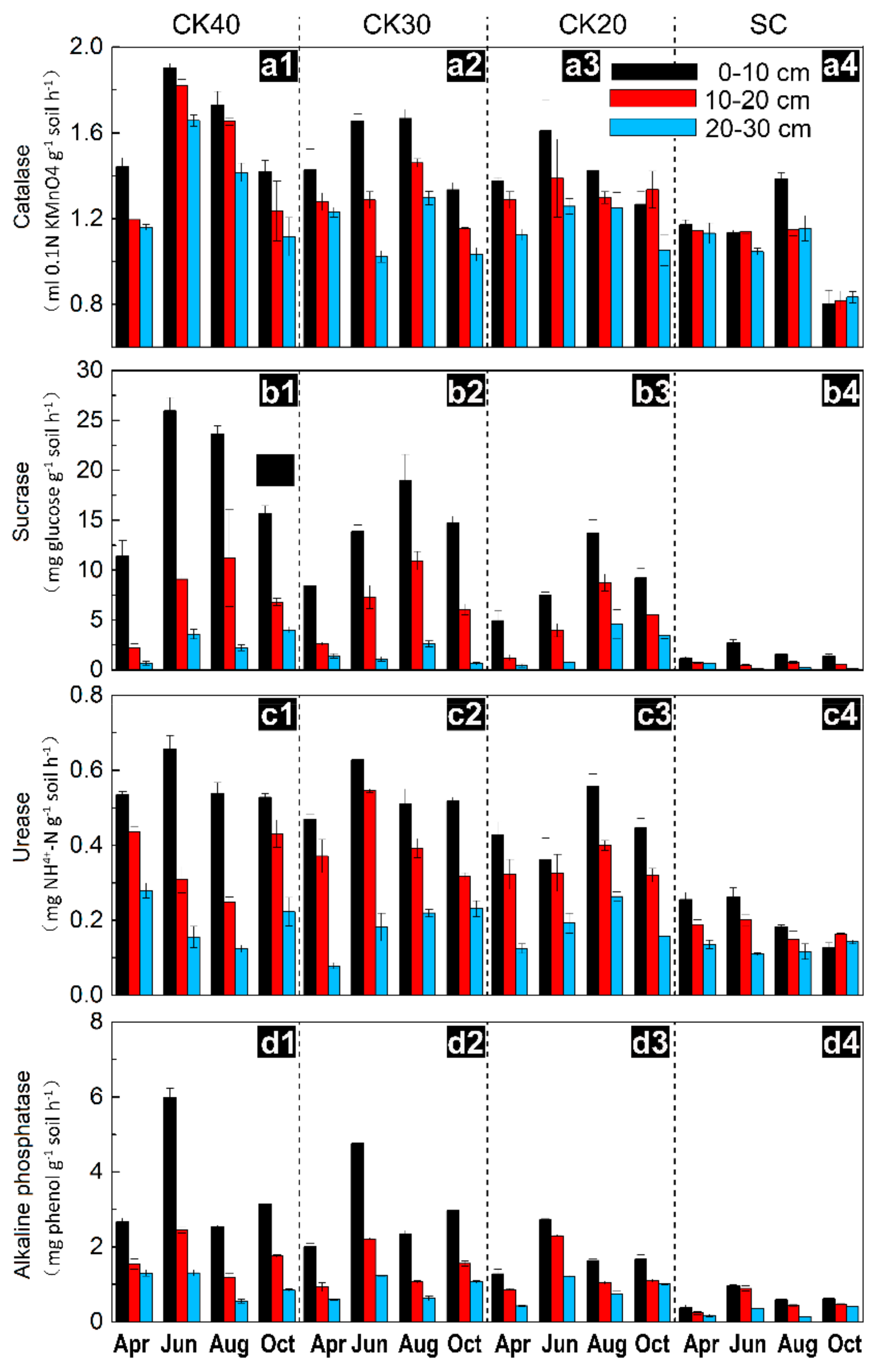
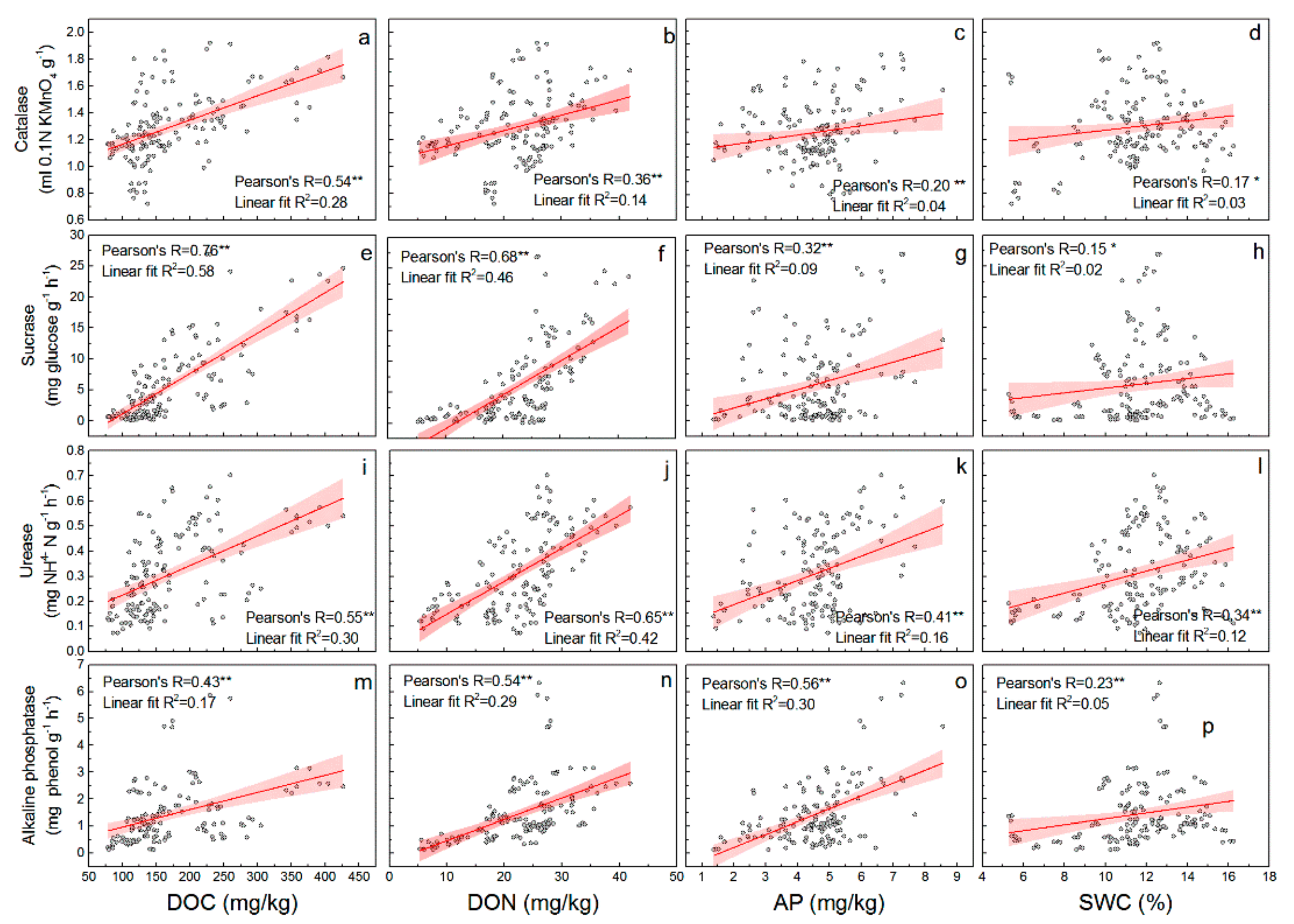
| Sample Sites | CK20 | CK30 | CK40 | SC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | 36°52′ N 109°21′ E | 36°53′ N 109°21′ E | 36°52′ N 109°21′ E | 36°52′ N 109°21′ E |
| Slope aspect (°) | 18 | 15 | 10 | 15 |
| Slope degree (°) | NbyW10 | SbyW60 | NbyE12 | SbyW50 |
| Elevation (m) | 1258 | 1260 | 1318 | 1263 |
| pH | 8.30 ± 0.13 | 8.41 ± 0.10 | 8.33 ± 0.06 | 8.48 ± 0.17 |
| SBD (g/cm3) | 1.04 ± 0.02 | 1.12 ± 0.03 | 1.15 ± 0.02 | 1.17 ± 0.03 |
| SOC (g/kg) | 3.94 ± 0.46 | 3.73 ± 0.41 | 2.73 ± 0.24 | 1.39 ± 0.22 |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.46 ± 0.06 | 0.44 ± 0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.05 |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 0.54 ± 0.02 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.03 |
| FRB (kg/hm2) | 1518 ± 47.12 | 2448 ± 40.38 | 2605 ± 32.74 | - |
| LB (kg/hm2) | 1233 ± 23.65 | 990 ± 8.77 | 719 ± 10.09 | - |
| Gleason SR | 2.17 ± 0.04 | 3.22 ± 0.03 | 3.50 ± 0.13 | - |
| CD (%) | 71.12 ± 3.82 | 78.22 ± 1.32 | 80.44 ± 2.96 | 40.29 ± 4.05 |
| AGB (kg/hm2) | 11023 ± 271.21 | 15130 ± 103.12 | 14500 ± 341.21 | 900 ± 23.25 |
| Source | Df | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F value | Pr > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOC | Model | 79 | 776313.47 | 9826.75 | 130.46 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 4820.66 | 75.32 | |||
| Total | 143 | 781134.13 | ||||
| DON | Model | 79 | 20312.92 | 257.13 | 108.86 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 151.16 | 2.36 | |||
| Total | 143 | 20464.08 | ||||
| AP | Model | 79 | 224.20 | 2.84 | 8.52 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 21.32 | 0.33 | |||
| Total | 143 | 245.52 | ||||
| SWC | Model | 79 | 869.46 | 11.01 | 3717.37 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 0.19 | 0.01 | |||
| Total | 143 | 869.65 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F value | Pr > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase | Model | 79 | 8.70 | 0.11 | 25.64 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 0.27 | 0.00 | |||
| Total | 143 | 8.97 | ||||
| Sucrase | Model | 79 | 5645.89 | 71.47 | 49.65 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 92.13 | 1.44 | |||
| Total | 143 | 5738.02 | ||||
| Urease | Model | 79 | 3.57 | 0.05 | 65.90 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 0.04 | 0.00 | |||
| Total | 143 | 3.62 | ||||
| Alkaline phosphatase | Model | 79 | 187.66 | 2.38 | 304.84 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 64 | 0.50 | 0.01 | |||
| Total | 143 | 188.16 |
| Enzyme | Growing Season | Stand Age | Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.18 * | 0.30 ** | 0.28 ** |
| Catalase | 0.25 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.23 * |
| Sucrase | 0.16 * | 0.40 ** | 0.32 ** |
| Urease | 0.09 NS | 0.34 ** | 0.48 ** |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 0.17 * | 0.40 ** | 0.32 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.; Chong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Yang, G. Temporal Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities and Responses to Land-Use Change in the Loess Plateau, China. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153129
Deng J, Chong Y, Zhang D, Ren C, Zhao F, Zhang X, Han X, Yang G. Temporal Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities and Responses to Land-Use Change in the Loess Plateau, China. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153129
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Jian, Yujie Chong, Dan Zhang, Chengjie Ren, Fazhu Zhao, Xiaoxi Zhang, Xinhui Han, and Gaihe Yang. 2019. "Temporal Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities and Responses to Land-Use Change in the Loess Plateau, China" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153129
APA StyleDeng, J., Chong, Y., Zhang, D., Ren, C., Zhao, F., Zhang, X., Han, X., & Yang, G. (2019). Temporal Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities and Responses to Land-Use Change in the Loess Plateau, China. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153129








