Motion Capture Research: 3D Human Pose Recovery Based on RGB Video Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motion Capture
1.2. Human Pose Recovery
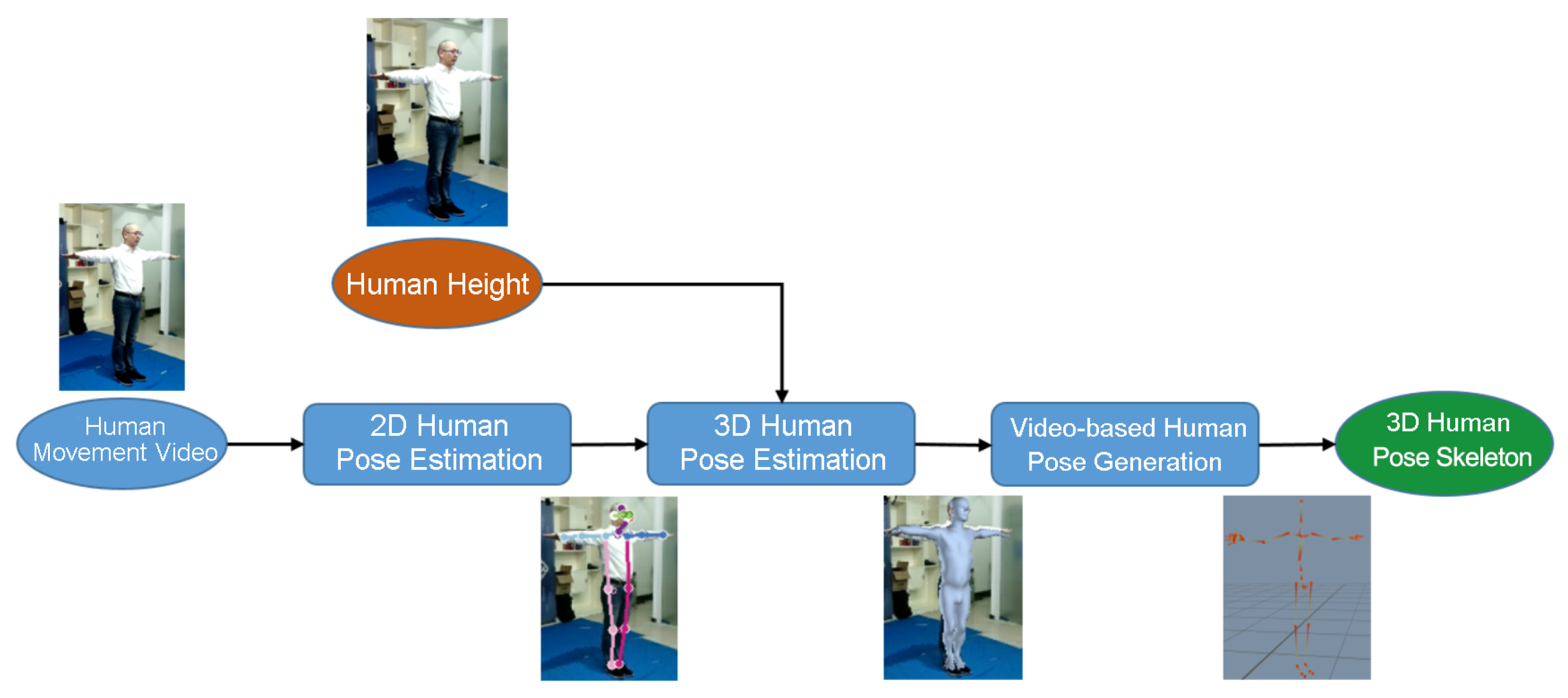
1.3. Overview
- The end-to-end method for 3D human pose estimation based on a single image is combined with 2D/3D skeleton point constraints and human height constraints to generate the 3D human model with higher precision. Meanwhile, the traditional method of manually defining rules is replaced by GAN constraints, which is used to generate a more human-like 3D human model;
- Combining the correlation of video sequences, a 3D human pose recovery method based on video streams is proposed, which uses the correlation between videos for smoothing to generate a more stable 3D human pose;
- Using two Kinect devices and iPi Soft series software to build a platform for motion capture experiments, an approach of using RGB-D video sequences is compared with the proposed approach of using RGB video sequences to verify the effectiveness of the proposed solution. In addition, experimental datasets are available to the public for related academic research.
2. Proposed Method
2.1. 3D Human Pose Estimation Based on a Single Frame Image
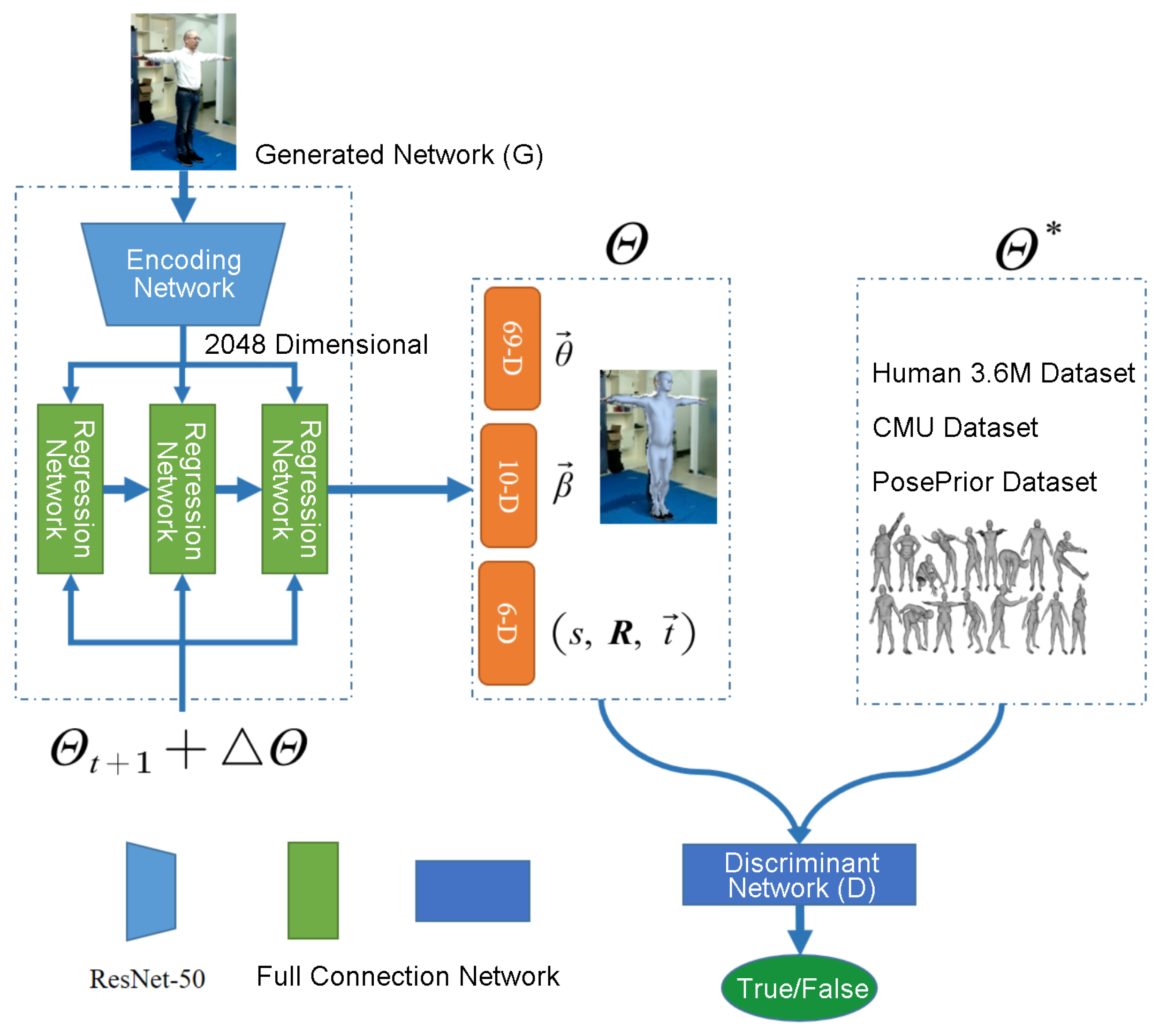
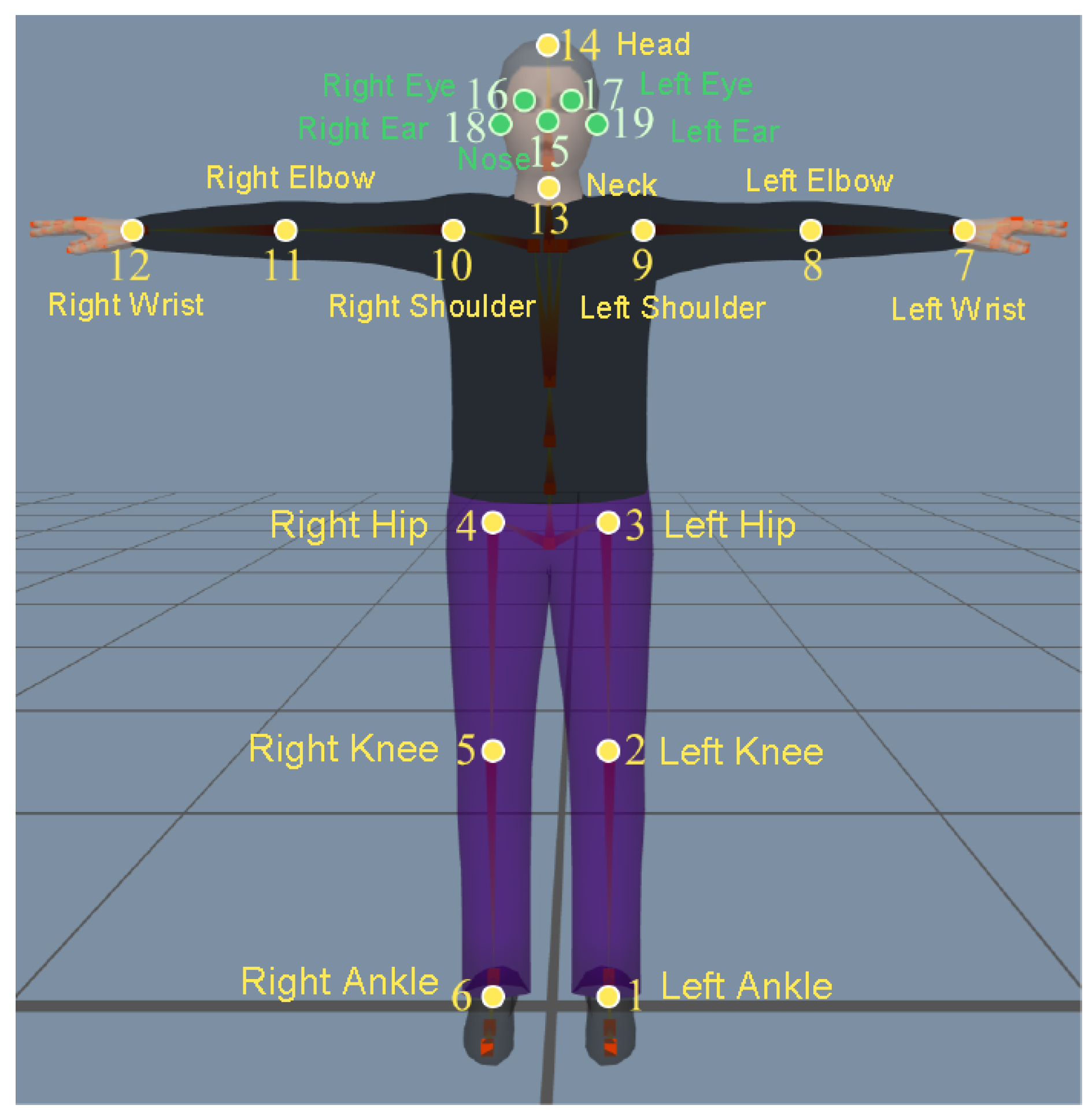
2.1.1. SMPL Model
2.1.2. End-to-End Network Structure
2.1.3. Model Pre-Training Process
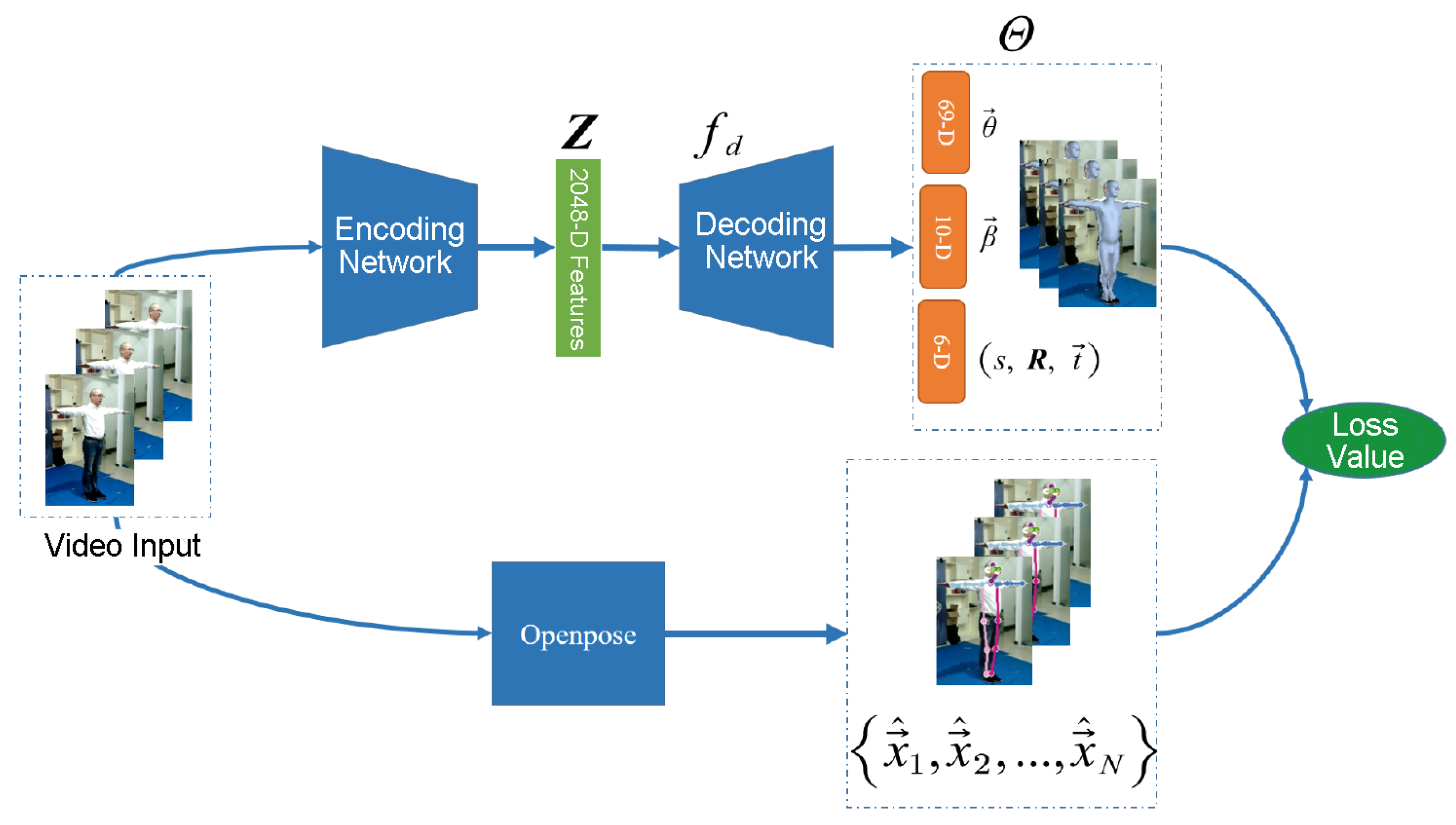
2.2. Human-Body Pose Generation Based on Video Streams
2.3. Results and Analysis
2.3.1. Effect of Different Constraints on the 3D Human Pose Perception Accuracy
2.3.2. Validation of Human Pose Perception Based on Video Sequences
3. Experiment Implementation and Result Discussion
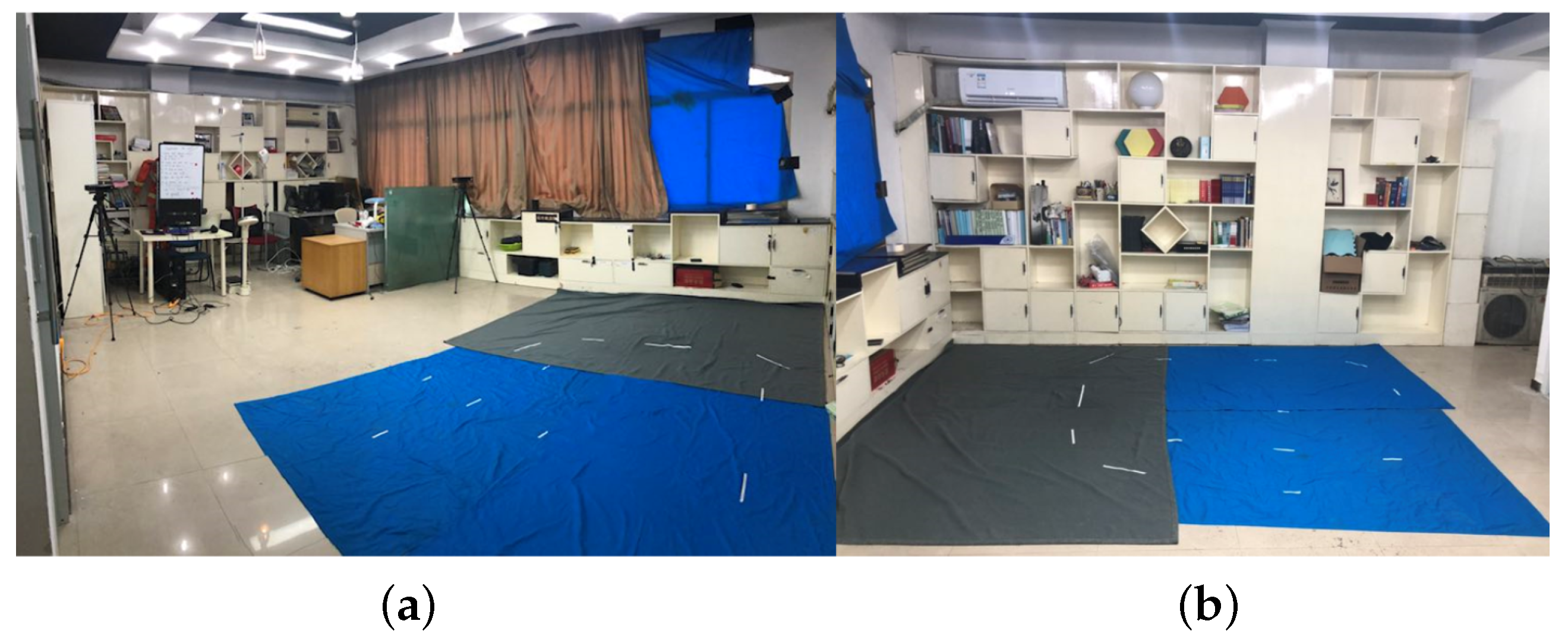
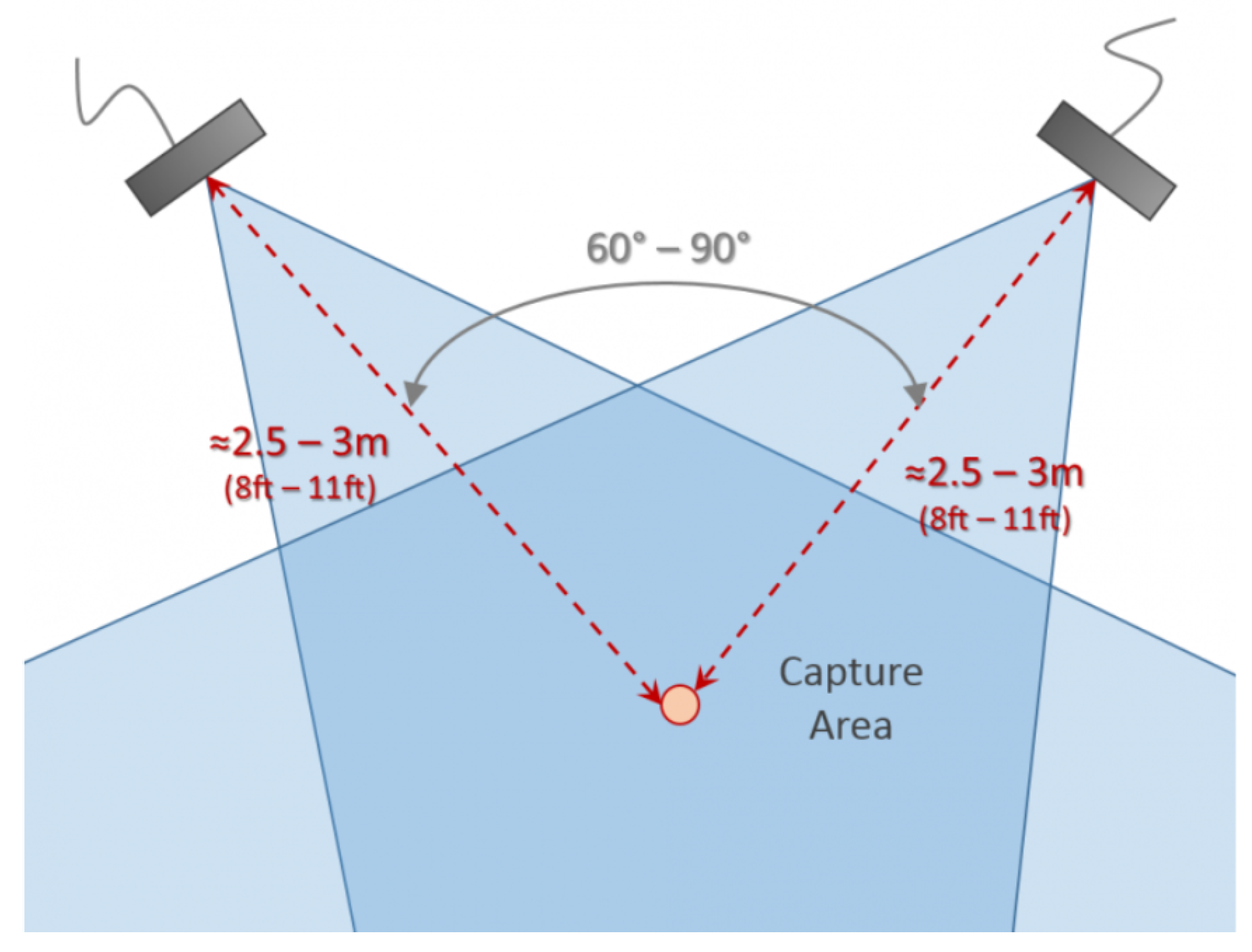
3.1. Experimental Setup and Environment
3.2. Types of Tasks
3.3. Results and Discussion
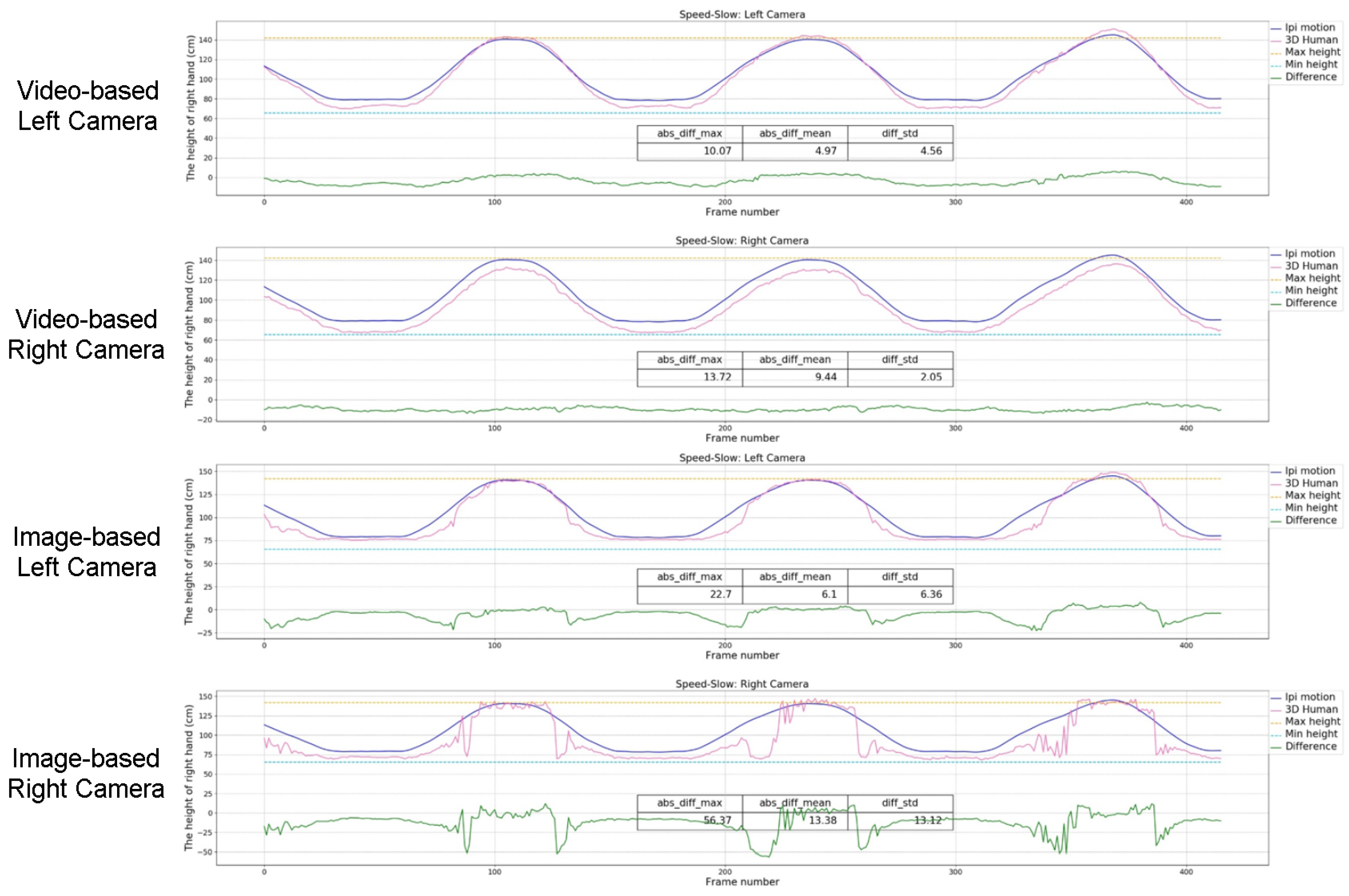
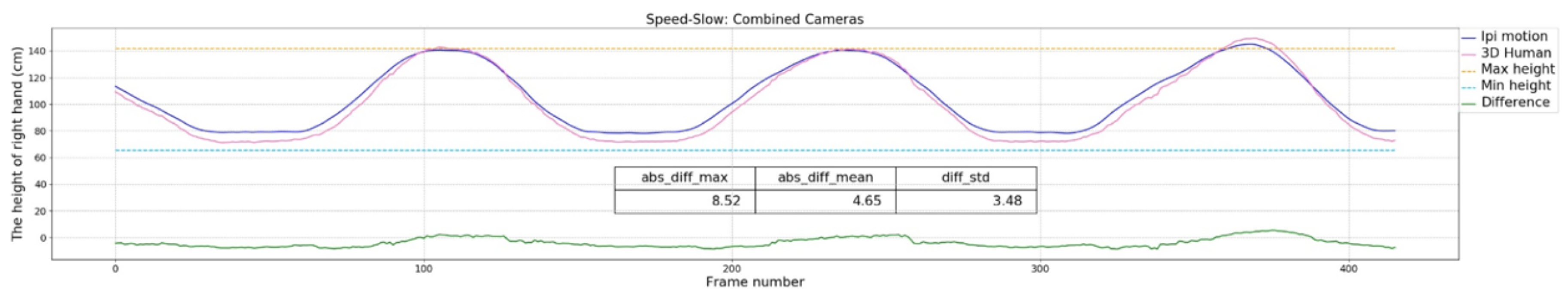
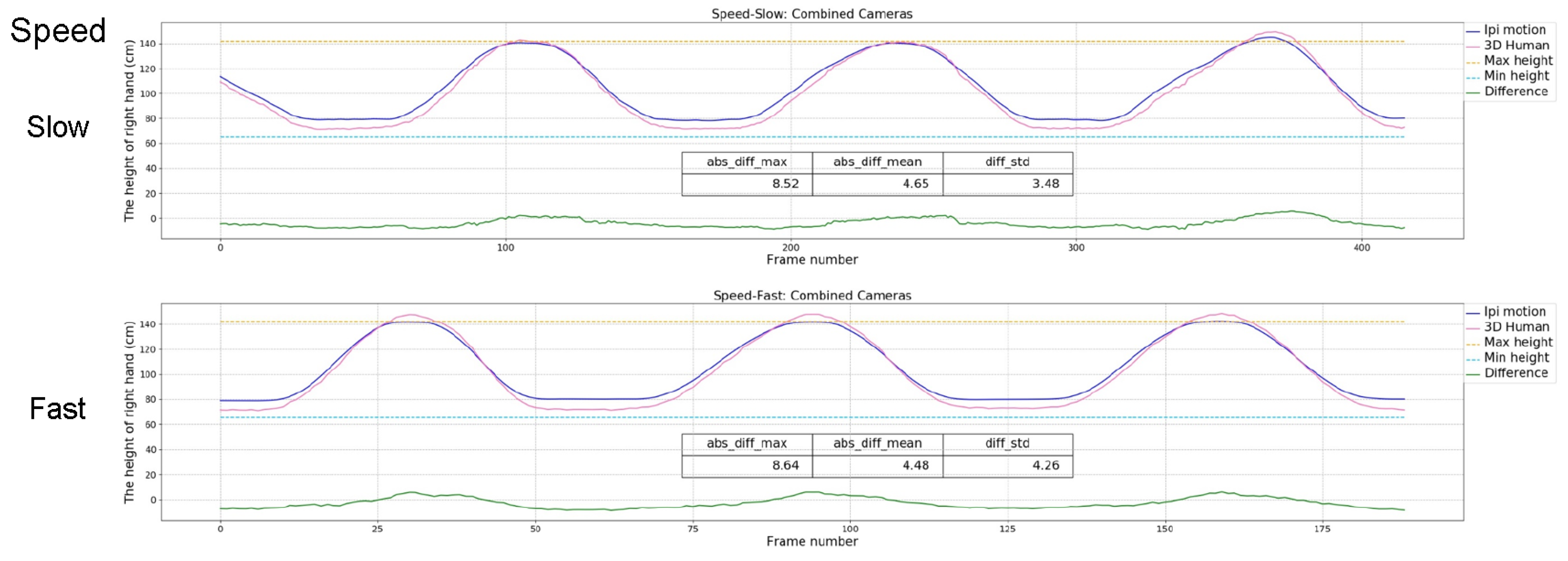
3.3.1. Speed of the Movements
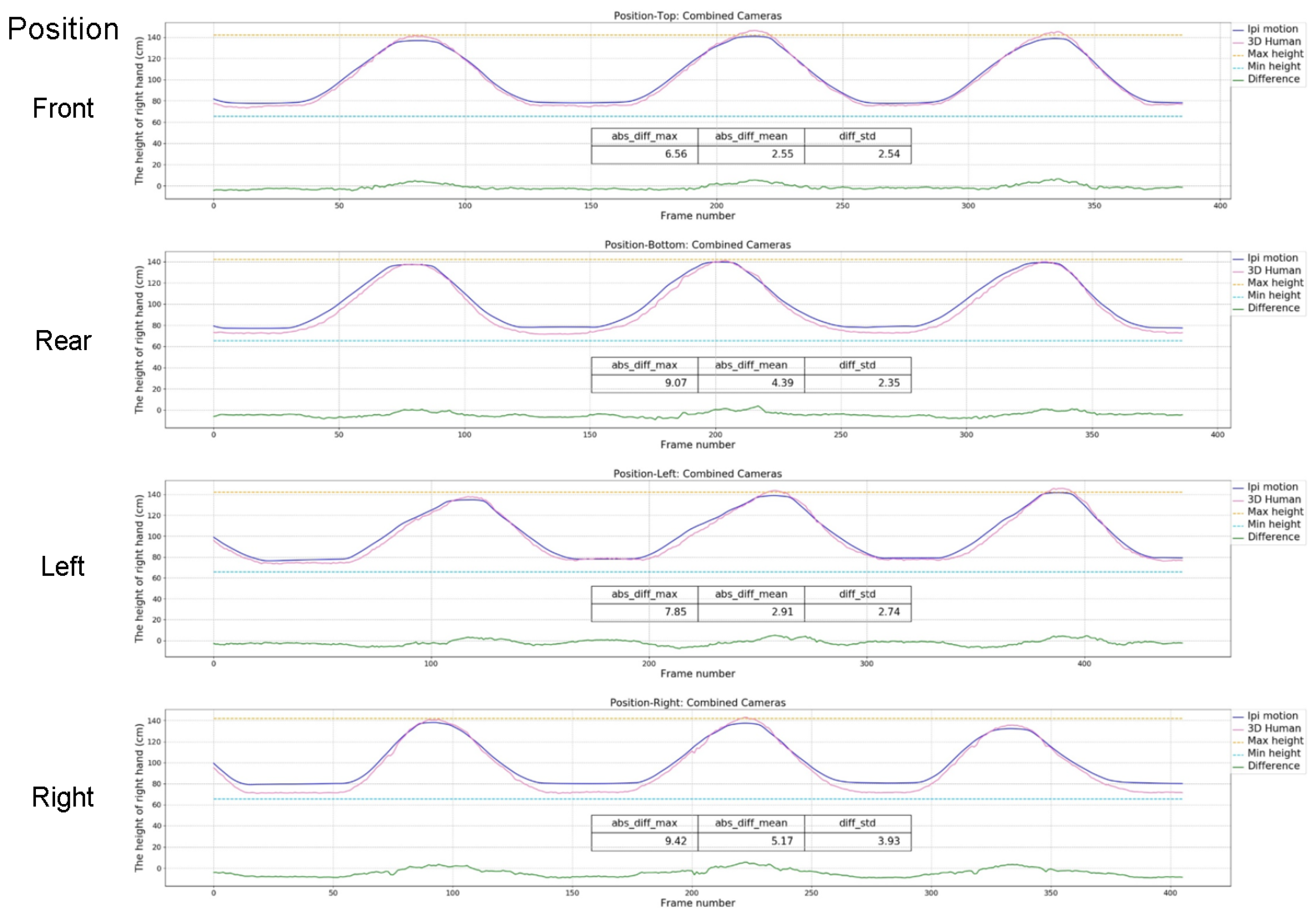
3.3.2. Position of the Subject
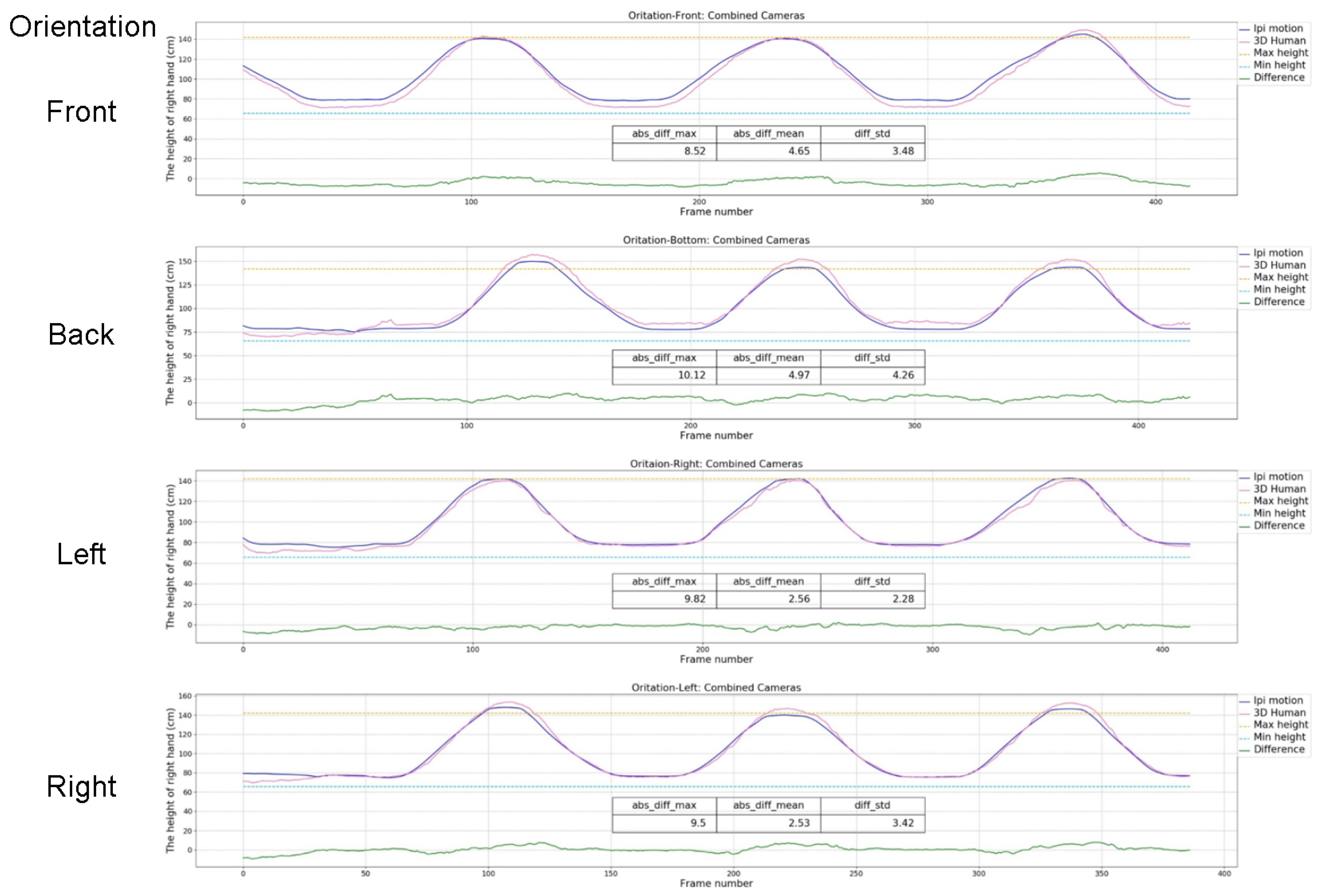
3.3.3. Orientation of the Subject
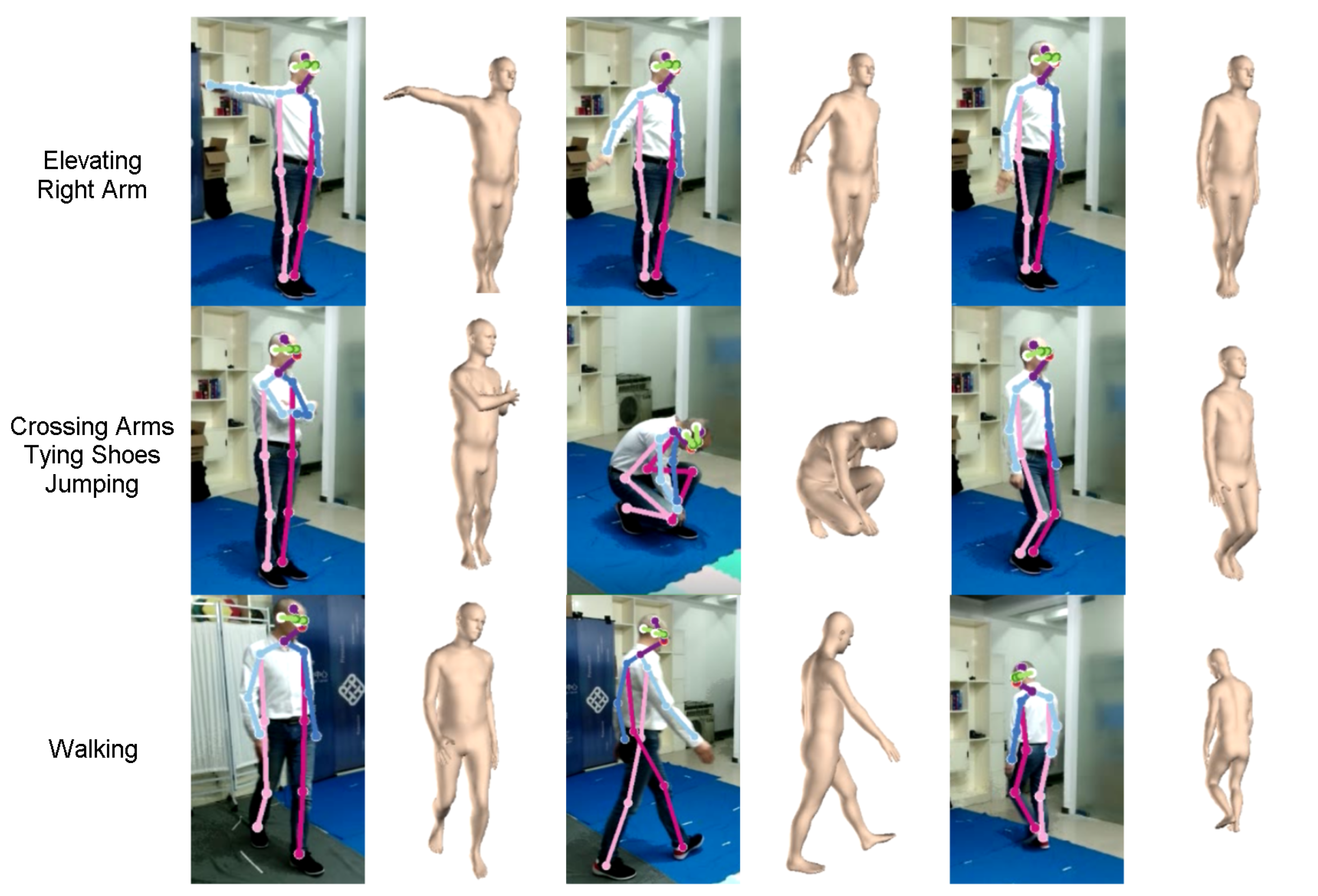
3.3.4. Complexity of the Movements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | three dimensional |
| SMPL | skinned multi-person linear |
| GAN | generative adversarial network |
| SGD | stochastic gradient descent |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| MARG | magnetic, angular rate and gravity |
| LSP | Leeds Sports Poses |
| MPII | Motion Picture Industry Institute |
| MS COCO | Microsoft COCO |
| Human3.6M | 3.6 Million accurate 3D Human poses |
| MPI-INF-3DHP | Max Planck Institute-Informatics-3D Human Pose |
| CMU | Carnegie Mellon University |
| BVH | Biovision Hierarchy |
References
- Skals, S.L.; Rasmussen, K.P.; Bendtsen, K.M.; Andersen, M.S. Validation of musculoskeletal models driven by dual Microsoft Kinect Sensor data. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on 3d Analysis of Human Movement, Lausanne, Switzerland, 14–17 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, G.; Facoetti, G.; Regazzoni, D.; Rizzi, C. A full virtual approach to design and test lower limb prosthesis. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2013, 8, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Gavrila, D.M. Multi-view 3D Human Pose Estimation in Complex Environment. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 96, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhayek, A.; Aguiar, E.D.; Jain, A.; Tompson, J.; Theobalt, C. Efficient ConvNet-based marker-less motion capture in general scenes with a low number of cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hasler, N.; Rosenhahn, B.; Thormählen, T.; Michael, W.; Gall, J.; Seidel, H.; Informatik, M. Markerless motion capture with unsynchronized moving cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yuille, A. Articulated Pose Estimation by a Graphical Model with Image Dependent Pairwise Relations. Eprint Arxiv 2014, 27, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yuille, A.L.; Gao, W. Robust Estimation of 3D Human Poses from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. Monocular 3D pose estimation and tracking by detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Sridhar, S.; Sotnychenko, O.; Rhodin, H.; Shafiei, M.; Seidel, H.P.; Xu, W.; Casas, D.; Theobalt, C. VNect: Real-time 3D Human Pose Estimation with a Single RGB Camera. Acm Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.B.; Kanazawa, A.; Malik, J.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. SFV: Reinforcement Learning of Physical Skills from Videos; SIGGRAPH Asia 2018 Technical Papers; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Romero, J.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. SMPL: A skinned multi-person linear model. Acm Trans. Graph. 2015, 34, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Bing, X.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Regazzoni, D.; De Vecchi, G.; Rizzi, C. RGB cams vs RGB-D sensors: Low cost motion capture technologies performances and limitations. J. Manuf. Syst. 2014, 33, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, M.T.; Smith, C.L.; Nash, M.R. Open-ended measurement of whole-body movement: A feasibility study. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2018, 14, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.U.; Achar, M.; Lee, S.H.; Penamora, F.A. Empirical assessment of a RGB-D sensor on motion capture and action recognition for construction worker monitoring. Vis. Eng. 2013, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillao, A. Modern Functional Evaluation Methods for Muscle Strength and Gait Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cappozzo, A.; Croce, U.D.; Leardini, A.; Chiari, L. Human movement analysis using stereophotogrammetry: Part 1: theoretical background. Gait Posture 2005, 21, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevilacqua, F.; Naugle, L.; Dobrian, C. Music control from 3D motion capture of dance. In Proceedings of the CHI 2001 for the NIME Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 1–2 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adesida, Y.; Papi, E.; Mcgregor, A.H. Exploring the Role of Wearable Technology in Sport Kinematics and Kinetics: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawsalyan, S.; Janarthanan, T.; Thiruthanikan, N.; Shahintha, R.; Silva, P. Upper limb analysis using wearable sensors for cricket. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Second International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Coimbatore, India, 22–24 February 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, A.; Conway, R.; Meagher, D.; Olaighin, G. Direct measurement of human movement by accelerometry. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 1364–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, A.; Din, S.D.; Barry, G.; Mathers, J.C.; Rochester, L. Instrumenting gait with an accelerometer: A system and algorithm examination. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 37, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannini, A.; Sabatini, A.M. Machine Learning Methods for Classifying Human Physical Activity from On-Body Accelerometers. Sensors 2010, 10, 1154–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillao, A.; Tedesco, S.; Barton, J.; Oflynn, B. Indirect measurement of ground reaction forces and moments by means of wearable inertial sensors: A systematic review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Ramakrishna, V.; Kanade, T.; Sheikh, Y. Convolutional Pose Machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.08008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Hossain, R.; Romero, J.; Little, J.J. A Simple Yet Effective Baseline for 3d Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2659–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakos, G.; Zhou, X.; Derpanis, K.G.; Daniilidis, K. Coarse-to-Fine Volumetric Prediction for Single-Image 3D Human Pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1263–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Bogo, F.; Kanazawa, A.; Lassner, C.; Gehler, P.V.; Romero, J.; Black, M.J. Keep It SMPL: Automatic Estimation of 3D Human Pose and Shape from a Single Image. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 561–578. [Google Scholar]
- Alldieck, T.; Magnor, M.A.; Xu, W.; Theobalt, C.; Ponsmoll, G. Video Based Reconstruction of 3D People Models. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8387–8397. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, A.; Black, M.J.; Jacobs, D.W.; Malik, J. End-to-End Recovery of Human Shape and Pose. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7122–7131. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bogo, F.; Romero, J.; Loper, M.; Black, M.J. FAUST: Dataset and evaluation for 3D mesh registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Robinette, K.M.; Blackwell, S.; Daanen, H.; Boehmer, M.; Fleming, S. Civilian American and European Surface Anthropometry Resource (CAESAR); Final Report; Technical Report; Sytronics Inc.: Dayton, OH, USA, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Black, M.J. MoSh: motion and shape capture from sparse markers. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2014, 33, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Deep Kinematic Pose Regression. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, H.F.; Harley, A.W.; Seto, W.; Fragkiadaki, K. Adversarial Inverse Graphics Networks: Learning 2D-to-3D Lifting and Image-to-Image Translation from Unpaired Supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4364–4372. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Wen, J.; Liu, R.; Long, L.; Dai, J.; Gong, Z. Unsupervised Representation Learning with Long-Term Dynamics for Skeleton Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 2644–2651. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.S.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Li, S.Z. Face Alignment Across Large Poses: A 3D Solution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Agrawal, P.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Malik, J. Human Pose Estimation with Iterative Error Feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.; Everingham, M. Clustered Pose and Nonlinear Appearance Models for Human Pose Estimation; University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2010; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Pishchulin, L.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. 2D Human Pose Estimation: New Benchmark and State of the Art Analysis. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 Junauary 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.; Papava, D.; Olaru, V.; Sminchisescu, C. Human3. 6m: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, D.; Rhodin, H.; Casas, D.; Fua, P.; Sotnychenko, O.; Xu, W.; Theobalt, C. Monocular 3D Human Pose Estimation in the Wild Using Improved CNN Supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3d Vision, Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; Volume 271, pp. 506–516. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, I.; Black, M.J. Pose-conditioned joint angle limits for 3D human pose reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1446–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the Operating Systems Design and Implementation, Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent. In Proceedings of COMPSTAT’2010; Physica-Verlag HD: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, K.; Asmara, R.A. 3D Skeleton model derived from Kinect Depth Sensor Camera and its application to walking style quality evaluations. Int. J. Adv. Res. Artif. Intell. 2013, 2, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Constraint Types | Dataset | Training Sample | Key Point | Converted Key Point | Loss Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Constraint | LSP | 1000 | 14 | 14 | |
| LSP-extended | 10,000 | 14 | 14 | ||
| MPII | 20,000 | 16 | 14 | ||
| MS COCO | 79,344 | 17 | 14 + 5 | ||
| 3D Constraint | Human3.6M | 312,188 | 24 | 14 | , |
| MPI-INF-3DHP | 147,221 | 28 | 14 | ||
| iPi Dataset | 20,955 | 65 | 14 | , | |
| Discriminant Constraint | Human3.6M | 1,559,985 | - | - | |
| CMU | 3,934,267 | - | - | ||
| PosePrior | 181,968 | - | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Motion Capture Research: 3D Human Pose Recovery Based on RGB Video Sequences. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173613
Min X, Sun S, Wang H, Zhang X, Li C, Zhang X. Motion Capture Research: 3D Human Pose Recovery Based on RGB Video Sequences. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(17):3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173613
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Xin, Shouqian Sun, Honglie Wang, Xurui Zhang, Chao Li, and Xianfu Zhang. 2019. "Motion Capture Research: 3D Human Pose Recovery Based on RGB Video Sequences" Applied Sciences 9, no. 17: 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173613
APA StyleMin, X., Sun, S., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Li, C., & Zhang, X. (2019). Motion Capture Research: 3D Human Pose Recovery Based on RGB Video Sequences. Applied Sciences, 9(17), 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173613





