Abstract
This review addresses the effects of the modifications with nanomaterials, particularly nanosilica, nanoclays, and nanoiron, on the mechanical performance and aging resistance of asphalt mixtures. The desire for high-performance and long-lasting asphalt pavements significantly pushed the modification of the conventional paving asphalt binders. To cope with such demand, the use of nanomaterials for the asphalt binder modification seems promising, as with a small amount of modification an important enhancement of the asphalt mixture mechanical performance can be attained. Several studies already evaluated the effects of the modifications with nanomaterials, mostly focusing on the asphalt binder properties and rheology, and the positive findings encouraged the study of modified asphalt mixtures. This review focuses on the effects attained in the mechanical properties of the asphalt mixtures, under fresh and aged conditions. Generally, the effects of each nanomaterial were evaluated with the current state-of-art tests for the characterization of mechanical performance of asphalt mixtures, such as, permanent deformation, stiffness modulus, fatigue resistance, indirect tensile strength, and Marshall stability. Aging indicators, as the aging sensitivity, were used to evaluate the effects in the asphalt mixture’s aging resistance. Finally, to present a better insight into the economic feasibility of the analyzed nanomaterials, a simple cost analysis is performed.
1. Introduction
The asphalt binder, i.e., the bitumen, is a material widely used for road construction worldwide. Generally, the bitumen is obtained from refining crude oil and its final properties are dependent on crude oil origin and refining processes. Bitumen can be described as a thermoplastic, viscous-elastic material that behaves as a solid at low/intermediate temperatures (under 25 °C) and as a semi-solid/liquid at higher temperatures (typically above 60 °C) [1,2]. This property allows its use in road construction, where firstly, the bitumen is heated to properly mix with the aggregates and, finally, after the compaction process and cooling to ambient temperature, the bitumen will act as the binder of the aggregates. Nevertheless, the bitumen temperature sensitivity causes several problems for the asphalt pavement in service. The permanent deformation and cracking mechanics are highly related to high and low service temperatures, respectively.
While in service, the asphalt pavement has to withstand a wide range of environmental conditions and traffic loads. In many cases, the conventional penetration grade bitumen no longer ensures the desired performance over the service life, and early conservation work or reconstruction may be needed. In addition, the bitumen is a material sensitive to aging, and its properties deteriorate over the service life. The aged bitumen becomes stiffer and more brittle, thus affecting the performance of the asphalt mixture [1]. Aging effect is particularly severe in surface layers that are exposed to environmental conditions such as UV radiation, moisture, oxygen, and larger temperature change [3]. Thus, the service life of the asphalt mixture is dependent of its aging resistance [4].
Over the years, several types of additives have been studied to modify the properties of the asphalt mixtures, generally, focusing on the improvement of mechanical performance. The additives studied more frequently were adhesion improvers, fibers, rubber, to use warm mix asphalt (WMA) technology, and a wide variety of polymers [5]. In the last one or two decades, following the developments in the field of nanotechnology, the study of nanomaterials broadened and its application as asphalt mixture additive was considered.
The definition of nanomaterial encompasses a wide variety of different materials, generally, designated according to their specific properties or structures (e.g. nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanowires, nanoplatelets, nanorods, and nanoporous). Nano is a unit prefix name, represented by the symbol n, which corresponds to the submultiple 10−9. Thus, the materials that have their dimensions in the nanoscale, generally 1 nm to 100 nm, are often designated as nanomaterials. The European Commission Recommendation (2011/696/EU) [6] provides a more concise definition for nanomaterial: “Natural, incidental or manufactured material containing particles, in an unbounded state or as an aggregate or as an agglomerate and where, for 50% or more of the particles in the number size distribution, one or more external dimensions is in the size range 1 nm to 100 nm”. Fairly similar description is provided by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) in ASTM E2456-06 2012 [7].
The nanoscale allows the material to behave differently than its macroscopic counterpart. Such behavior can be triggered by two effects: The surface to volume ratio (specific surface area) and spatial confinement [8]. The specific surface area increases as the particle size decreases, becoming significantly large in the nanoscale. For example, in the case of a single spherical particle the surface to volume ratio is 3 mm−1, 3 × 103 mm−1, and 3 × 106 mm−1, for the sphere radius of 1 mm, 1 µm, and 1 nm, respectively. Thus, considering the same volume unit, the use of nanoparticles instead of microparticles will allow a much larger available surface area. Nanomaterials can play a significant role in enhancing the performance of the existing materials by providing better resistance to traffic and environmental loads or mitigating incompatibility between some natural aggregates and asphalt binder, enabling more sustainable and durable pavement solutions [9].
The objective of this review is to analyze the effects of the modification with nanomaterials in the mechanical performance of the asphalt mixture. This review focuses on the modifications with nanosilica, nanoclay, and nanoiron. Firstly, the effects of the modifications in the properties and rheology of the modified bitumen are summarized, subsequently, the effects of the modifications in the mechanical performance of the asphalt mixture are analyzed as well as their contributions for aging resistance.
2. Nanomaterials
2.1. Type of Nanomaterials
Theoretically, any material can be synthetized in the nanometric scale, generically, by processing macroparticles of the respective material. The nanomaterials more studied for asphalt binder and asphalt mixture modification are types of nanosilica and of nanoclay.
Nanosilica is the term used to designate nanoparticles of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Silicon dioxide is an inorganic material produced mainly from silica precursors, e.g. synthetized from silica fume or chemically processed from rice husk ash [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. It has a molecular mass of 60.08 g/mol and the appearance of a white powder. Figure 1 presents a comparison of the volume taken by a sample of 2.50 g of nanosilica and 2.50 g of limestone filler (in the case of the filler, it is only the fraction under 63 µm). One can see that the nanoparticles occupy considerably more volume. Concerning the asphalt binder modification, the good dispersion ability and large surface area are its most interesting characteristics. Table 1 presents the properties of the nanosilica used by several researchers.

Figure 1.
Mass of 2.50 g of limestone filler under 0.063 mm (left) and nanosilica (right).

Table 1.
Properties of nanosilica used by several authors.
The clays are materials that can be found abundantly in nature. Although presenting some natural variability in their constitution, such ease of access made them known materials with many applications. Currently, there are few processes to extract nanoclay from a layered clay [26,27]. Montmorillonite, is a smectite clay material derived from bentonite ore [28], is the most common natural nanomineral used by industry [29]. Majority of the clays present a layered structure, which consists of a Silica tetrahedron connected to an alumina octahedron, coordinated by oxygen atoms or hydroxyl groups, with the overall thickness of a single layer approaching one nanometer [30]. The complete separation (exfoliation) of the nanoclay layers will result in a large surface area, up to 800 m2/g [9], as well as, very high aspect ratio, typically 100 to 1500 [31].
Generally, the natural nanoclays have hydrophilic properties. The hydrophilic behavior may cause difficulties to disperse the nanoclay homogeneously in the asphalt binder, which has organophilic properties [32]. To mitigate such a problem, the raw nanoclays can be modified by replacing the interlayer cations with quaternized ammonium or phosphonium cations, preferably with long alkyl chains, originating an organically modified or organophilic nanoclay [5], e.g. cloisite is an organically modified nanoclay which base is montmorillonite. Table 2 presents the properties of the nanoclay used by several researchers, where, in all the cases, the base of the studied nanoclays was montmorillonite. The dispersion of nanoclay in the asphalt matrix can create immiscible, intercalated, or exfoliated nanostructures [33]. In an intercalated structure, there is an expansion of the nanoclay interlayer spacing that is occupied by asphalt molecules. In an exfoliated structure, the layers of the nanoclay are exfoliated (completely separated) and the individual layers are distributed throughout the polymer matrix.

Table 2.
Properties of nanoclay used by several authors.
Iron nanoparticles are mostly Fe and iron oxides, such as FeO, Fe2O3, and Fe3O4. Generally, these materials are a red brown/black powder, depending of the percentage of iron oxides in its composition. The Fe nanoparticles are also commercially available in the form of zero-valent iron (ZVI), also designated zero-valent nanoiron (nZVI). ZVI can be found as a dry ferrous powder of non-valent chain presenting alkaline properties (pH from 11 to 12). Currently, ZVI has been successfully applied in groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment. Thus, the production of such nanoparticles streamlined over the last years [44,45,46,47,48]. Their properties such as reactivity and high specific surface may cause an important impact on the properties of the asphalt binder. Table 3 presents the properties of iron nanoparticles used by several researchers.

Table 3.
Properties of nanoiron used by several authors.
2.2. Modification of the Asphalt Binder with Nanomaterials
In the majority of the studies found in literature, the modification of asphalt mixtures with nanomaterials is initially done at the binder level, i.e., the asphalt binder is modified with the nanomaterials, and then, the modified binder is used to produce the asphalt mixture. The optimum dosage of nanomaterial in the asphalt binder will be dependent on the type of nanomaterial, type of asphalt binder, and the methodology used, i.e., type of testing selected. Generally, the nanomaterials are blended with asphalt binder in small percentages, around 2 to 6% by mass of asphalt binder [51]. In some cases, besides the nanomaterial, a polymer modification is also done, or the binder being modified is a polymer-modified binder (PMB). Generally, for the modification of the asphalt binder with nanomaterials in laboratory one out of two methods is used: The dry blending method or the solvent blending method [52,53,54,55]. A recent review addresses more in depth the details of the polymer modification with nanoclays [56,57].
The dry blending method consists of the use of high-speed stirring to disperse the nanomaterials in the asphalt binder matrix. In this method the asphalt binder is previously heated above the softening point temperature, generally, up to a temperature equal or near to the recommended asphalt mixture mixing temperature, the nanomaterial is added, and a shear mixing effect is applied for a specific time period. As it will be additive (nanomaterial) and neat asphalt binder dependent, several trials may be needed to determine the adequate combination of rotation speed and mixing time. In addition to the high-speed shear mixing, some authors also applied sonication. Table 4 presents the dry blending configuration used by several authors.

Table 4.
Dry blending configurations used by several authors.
The use of excessive rotational speed and prolonged mixing times can cause an undesired accelerated oxidation and consequent aging of the asphalt binder. The geometry of the mixing shaft head can also play an important role. The use of the most common shaft head geometries (such as blades, anchor, propeller, and Rushton) at high rotation speed can easily induce vortex effects that will potentiate the entrapment of air bubbles in the asphalt matrix. This effect, aggravated by the fact that the mixing occurs at high temperatures, may promote a significant premature oxidation of the asphalt. To mitigate this effect, the use of head geometries, such as the Jiffy head, that prevent vortex formation can be preferable. Other possibility to eliminate undesired oxidation could be to carry out the process of asphalt modification under controlled atmosphere conditions, for example using a nitrogen atmosphere furnace.
In the solvent blending method, the nanomaterial is initially dispersed in a compatible solvent (for example toluene or kerosene) that later will be mixed with the neat asphalt binder under medium to high temperature applying low speed stirring. The mixing process finishes when the evaporation of the solvent is complete. Some authors also applied sonication during the stirring time. The description of the solvent blending configurations can be found in the respective studies [65,66,67].
Due to several advantages, the dry blending method is the most widely used. Compared to the solvent blending method, the most important advantages of the dry blending method are that it is cheaper and easier to implement and does not require the use of high amount of solvents. For either method, the evaluation of the final modified binder properties will reveal if a homogeneous blend was achieved. To perform this evaluation, a procedure similar to the one stated by the CEN specification EN 13399—determination of storage stability of modified bitumen [68] or ASTM D5892-00 [69] can be used [63,70]. As the used dosages of nanomaterials are typically low, under 6% of the mass of asphalt binder, and the individual mass of the nanoparticles is very small, sedimentation problems were not reported.
There are some concerns regarding the safety of nanoparticles and the associated potential health risks. Because of their nanoscale dimensions, they can easily pass through biological systems, such as human skin and cell membranes and accumulate in undesirable locations up to toxic levels [71]. Grassian et al. [72] found that the inhalation of nano TiO2 at 8.8 mg/m3 concentration caused lung inflammation. Although some studies were already conducted, there is still a big uncertainty regarding the effects of engineered nanomaterials on environment and human health. Recently, due to the proliferation of nanotechnology in several industries, particularly food additives and packaging, more publications are addressing this topic [30,71,73,74,75]. The production of nanomaterials and the asphalt binder modification are important phases where exposure can be significant. The most likely routes for exposure are inhalation, ocular, and dermal adsorption [75]. Unless other information is given by the nanomaterials’ suppliers, the manipulation and handling of such materials should be assumed as a potential hazard, thus safety handling protocols should be implemented accordingly. Crucho [36] modified asphalt binder in laboratory using a fume hood cabinet and individual protections: Nitrile gloves at least 0.5 mm thick, mask for eye protection, breathing mask with particle-filter FFP3, and protection suit (Tychen C—category III).
3. Effect of the Modification with Nanomaterials in the Asphalt Binder
Some studies about the use of nanomaterials in asphalt binders have already been done, with special attention to nanosilica and nanoclays. Regarding the effects of the modification with nanomaterials in the properties of the asphalt binder, few recent reviews address this topic. Porto et al. [5] presented a review about the asphalt binder modification covering several types of modifiers, such as, polymers, chemical modifiers (including nanocomposite modifiers), and warm mix technology. The review of Martinho and Farinha [51] focused on the use of nanoclays. Li et al. [52] presented a review covering a wide range of nanomaterials, such as, nanocarbon, nanoclay, nanofiber, nanosilica, and nanotitanium. Wu and Tahri [76] presented a state-of-the-art about the use of carbon and graphene family nanomaterials in asphalt modification.
The following paragraphs present a brief description of the effects of the modifications with nanomaterials in the properties of the asphalt binder, as well as, some additional details found in literature.
In brief, the nanosilica-modified binder presented a decrease in penetration, increase in viscosity, and increase in softening point [10,18,25,27,77,78]. Regarding the rheological behavior, evaluated using the dynamic shear rheometer (DSR), the modified binders present higher complex modulus and lower phase angle [18,64,77,79]. Authors evaluating the binder fatigue with DSR tests, concluded that the nanosilica modifications showed superior fatigue resistance [22,80,81].
At the level of fundamental characterization, the nanoclay-modified binder presented a decrease in penetration, increase in softening point, and increase in viscosity [10,25,27,35,39,41,55,79,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89]. And consistently, regarding rheology, the nanoclay modified binders present an increase in complex shear modulus and decrease in phase angle [34,38,41,42,55,86,87,90]. The existing studies mostly focused on organically modified montmorillonite, due to the expectation of obtaining exfoliated structures in the modified binders and higher performance improvements. The raw nanoclays, in their hydrophilic natural form, may form only intercalated structures, although, some authors studying raw nanoclays [38,41,42,91,92] also obtained considerable performance improvements.
The type of nanoclay used in the modification has an important effect in results, i.e., in the modified binder performance. Although the overall trends were the same, the authors that studied more than one nanoclay type obtained different results, regardless of using the same control binder. A study [41] about the modification of 60/70 asphalt binder with nanoclays, sodium bentonite (BT) and organically modified sodium bentonite (OBT), revealed that both modifications caused reduction of the phase angle and increased viscosity, softening point, and complex shear modulus. The effects were correlated with the dosage of nanoclay introduced and, in all cases, the effects of the organically modified clay were stronger. The exfoliated structure of the organically modified nanoclay, that promotes a better dispersion in the asphalt matrix, can explain these effects. On the other hand, in another study [55], the authors studied the modification of a PG 64-28 with two organically modified nanoclays with similar structure (nanoclay A and nanoclay B) and observed different effects. For example, regarding viscosity, the modifications caused an increase of 41% and 112% with 2% of nanoclay A and 2% of nanoclay B, respectively, and regarding complex shear modulus, the modifications caused an increase of 66% and 184% with 2% of nanoclay A and 2% of nanoclay B, respectively. Jahromi and Khodaii [34] studied the effects of two organically modified nanoclays (Nanofil-15 and Cloisite-15A) on the properties of the 60/70 asphalt binder and, found the effects of the second stronger than those of the first. In the cases that authors studied the same dosage and nanomodification in different control binder, they reported that the effects in softer binders are stronger than those in harder binders [93,94].
Onochie et al. [79] studied the effects of the modifications with an organically modified nanoclay and nanosilica on the properties of a PG 58-28 asphalt binder. The results obtained by the authors were dependent of the type and dosage of the nanomaterial. For example, regarding viscosity, 2% nanoclay and 4% nanoclay increased the viscosity by 22% and 36%, respectively, and 2% nanosilica and 4% nanosilica increased the viscosity by 13% and 10%, respectively. Regarding complex shear modulus, 2% nanoclay and 4% nanoclay presented an increase of 19% and 40%, respectively, and 2% nanosilica and 4% nanosilica presented an increase of 21% and 35%, respectively.
A possible drawback of the modification of asphalt mixtures with nanomaterials is underperformance at low temperatures (PG low temperature). Onochie et al. [79] tested a PG 58-28 with 2% and 4% nanosilica modifications with bending beam rheometer (BBR) and found the modifications to present 6% and 14% higher creep stiffness and equal and 2% lower m-value, respectively. In the same study, the authors also evaluated the effects of 2% and 4% nanoclay modification, using the same control binder (PG 58-28) and an organically modified nanoclay (cloisite 30B), and found the modifications to present 8% and 14% higher creep stiffness and 2% and 4% lower m-value, respectively. Regarding nanoclays, other studies [38,55,90] reported similar underperformance of the modified binders in BBR or direct tensile test (DTT) at PG low temperature. However, in another study [41], the modifications of the 60/70 control binder with 5% nanoclay bentonite and 5% organically modified bentonite presented similar m-values but, 19% and 22% lower creep stiffness, respectively, indicating enhanced low temperature performance. On the one hand, the effects of the modifications with nanomaterials in the low temperature performance are not entirely understood and deserve further investigation. On the other hand, besides the worsening in low temperature performance, authors reported that the modified binders still passed the respective Superpave™ specification (maximum 300 MPa creep stiffness and minimum 0.300 m-value) presenting the same PG low temperature of the control binder. Thus, the use of such modifications in cold regions can be possible, but further investigation is recommended.
4. Effect of the Modification with Nanomaterials in the Mechanical Performance of Asphalt Mixtures
4.1. Nanosilica
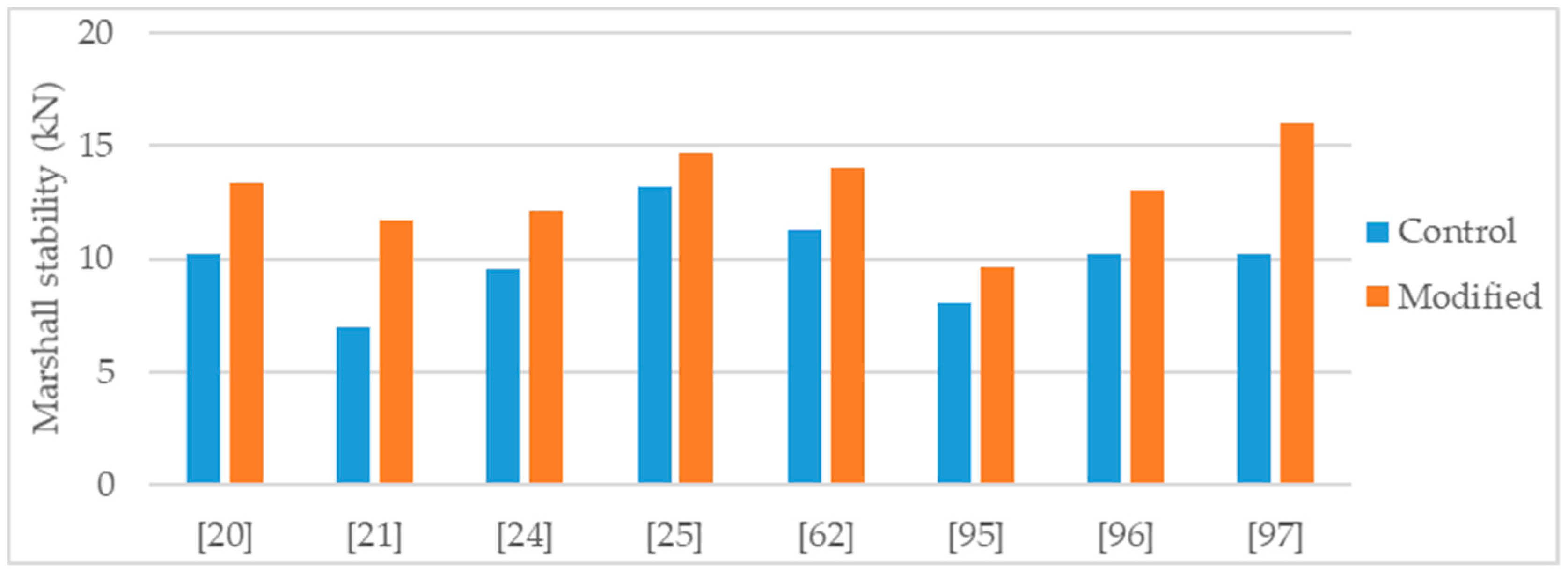
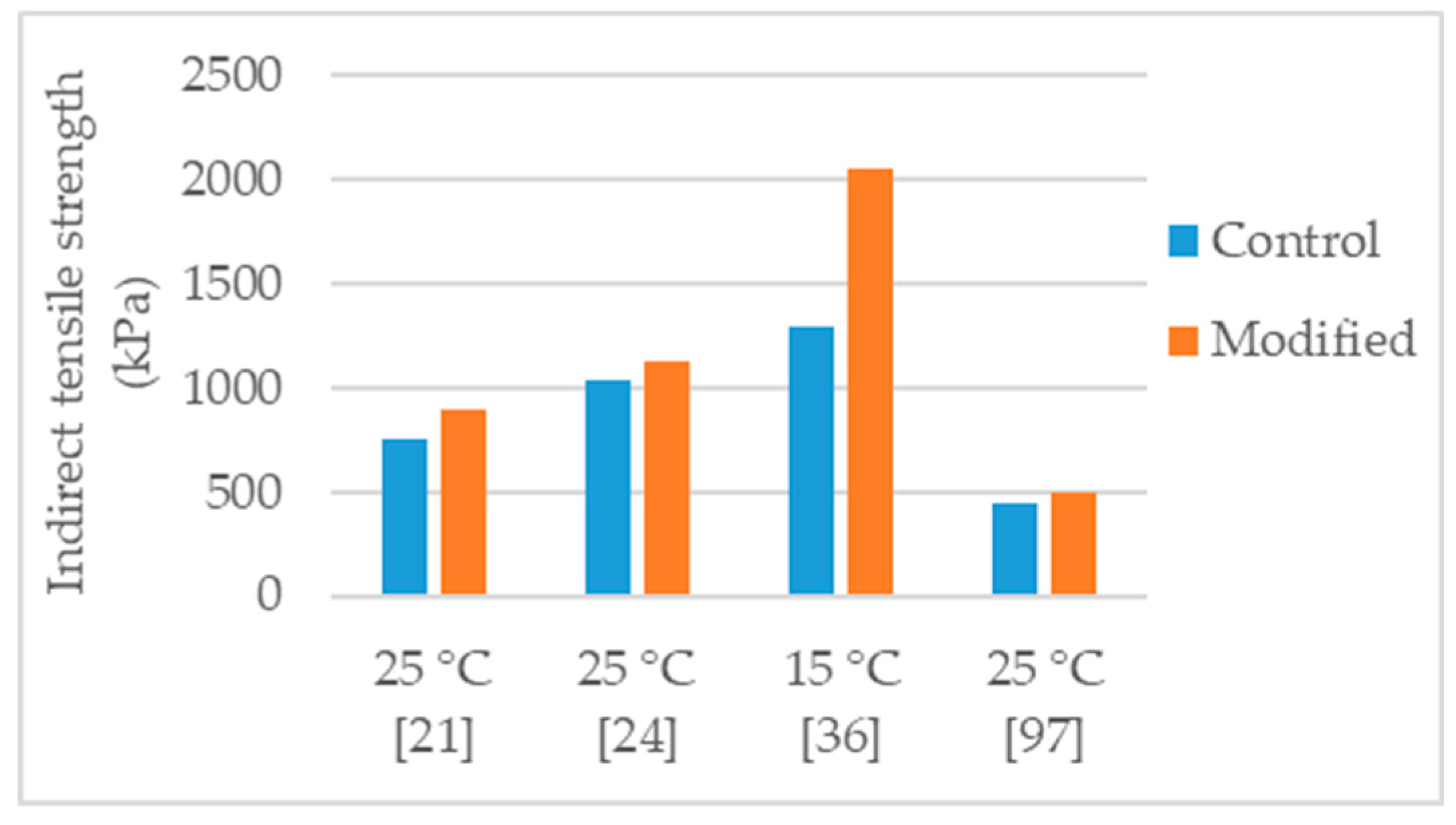
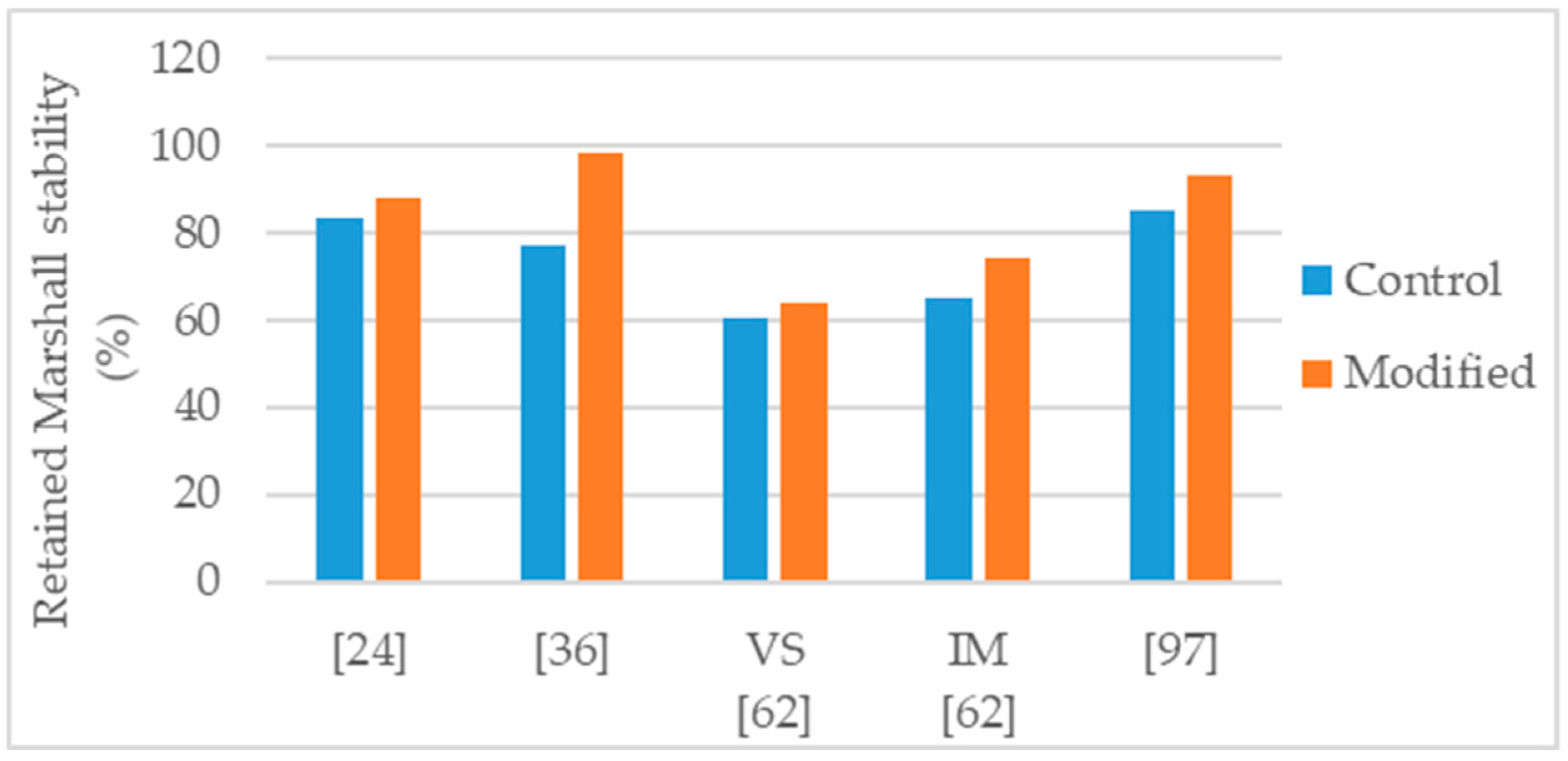
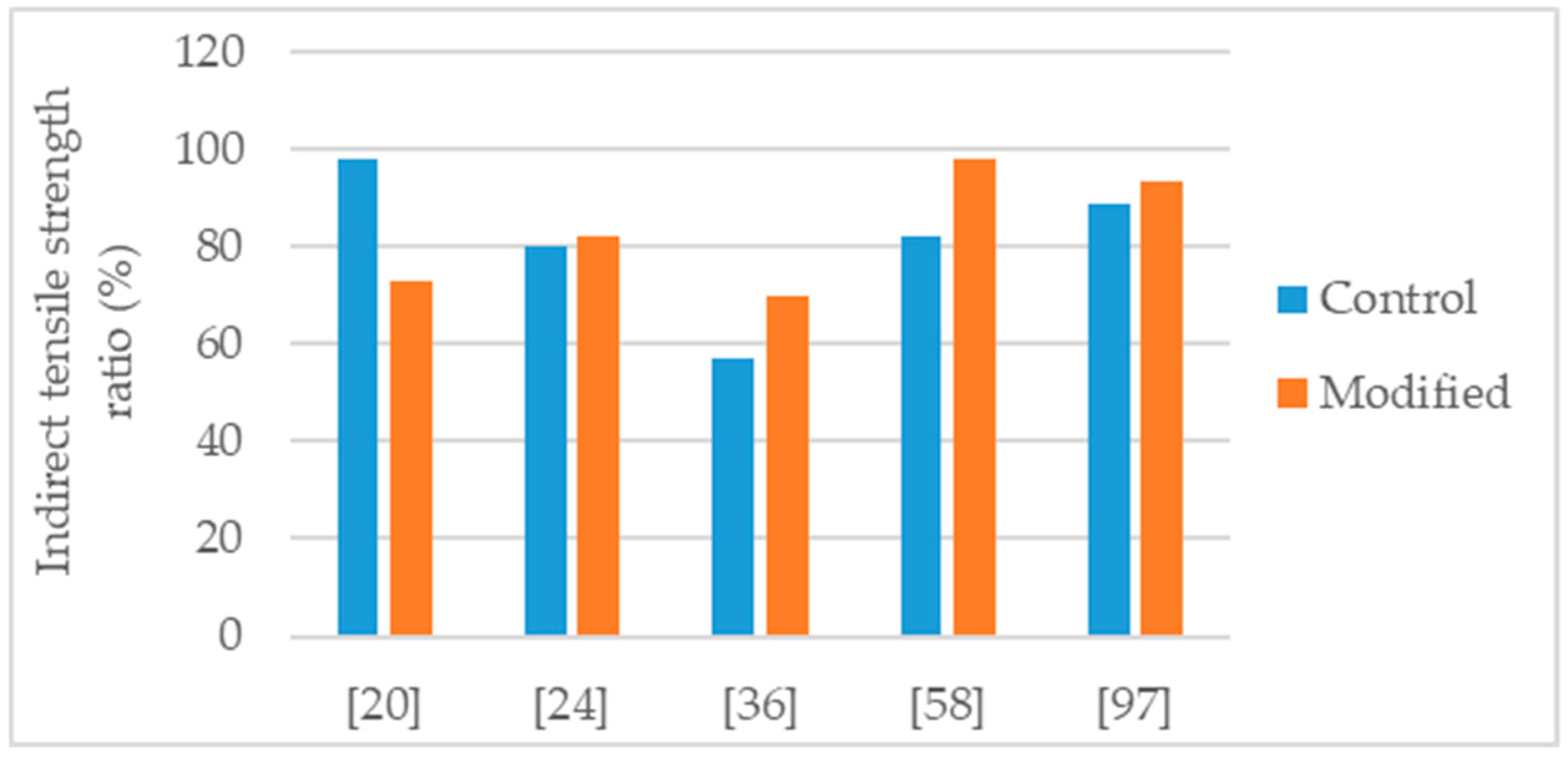
The authors that conducted studies about nanosilica modified asphalt mixtures, reported important improvements in the mechanical performance of the mixture. To evaluate the asphalt mixture performance, the mechanical tests most found in literature were Marshall stability, water sensitivity (using the indirect tensile strength ratio or the retained Marshall stability), permanent deformation, and stiffness. The Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 present the results found in several studies. “Control” refers to the mixtures with 0% of nanosilica and, “Modified” refers to the modification performed by each author.
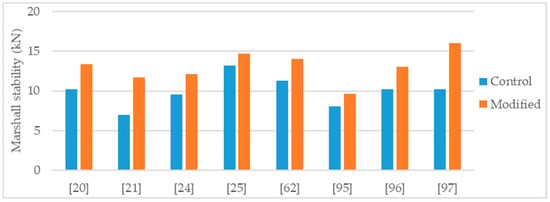
Figure 2.
Marshall stability of control and nanosilica modified asphalt mixtures.
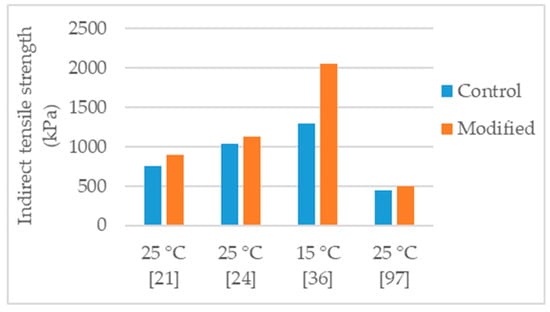
Figure 3.
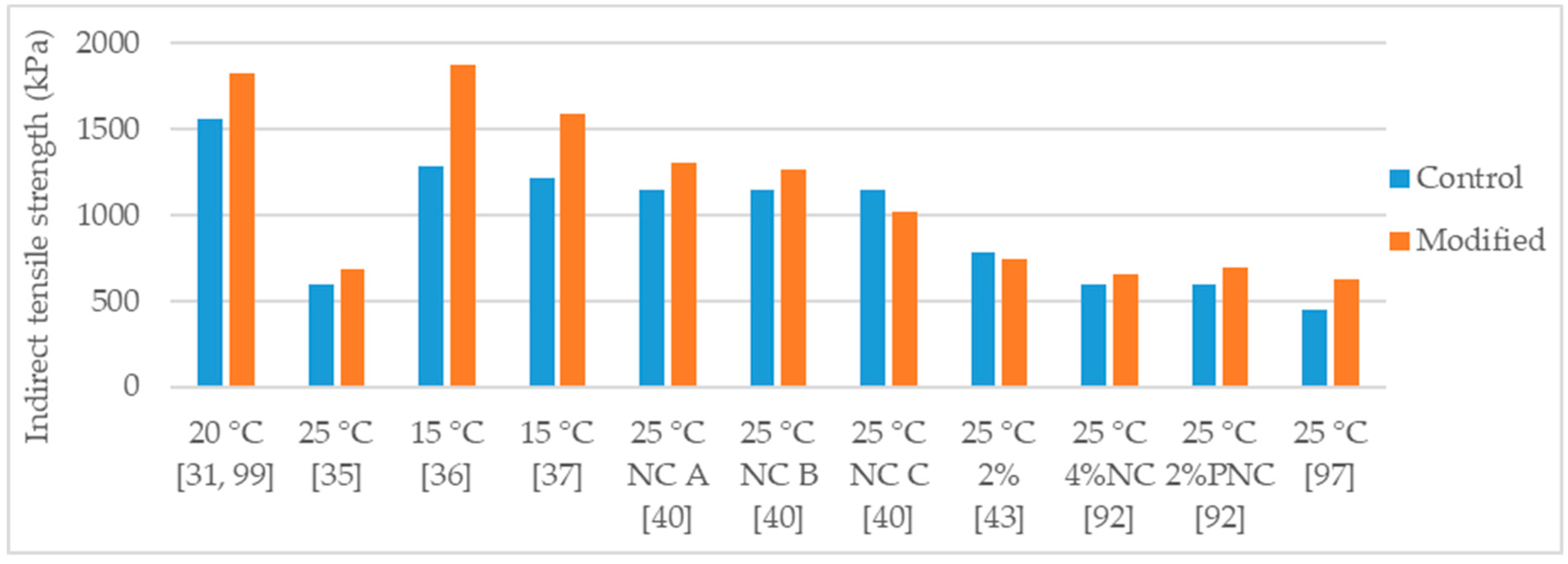
Indirect tensile strength of control and nanosilica modified asphalt mixtures.
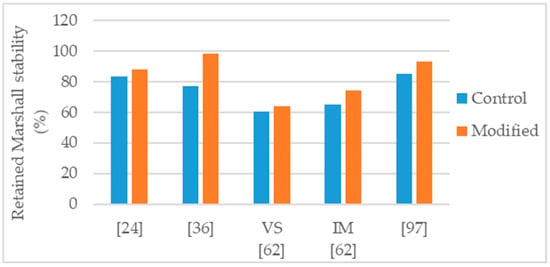
Figure 4.
Retained Marshall stability of control and nanosilica modified asphalt mixtures.
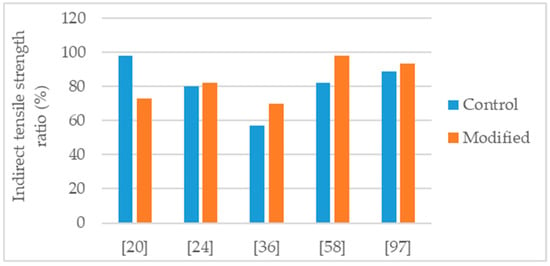
Figure 5.
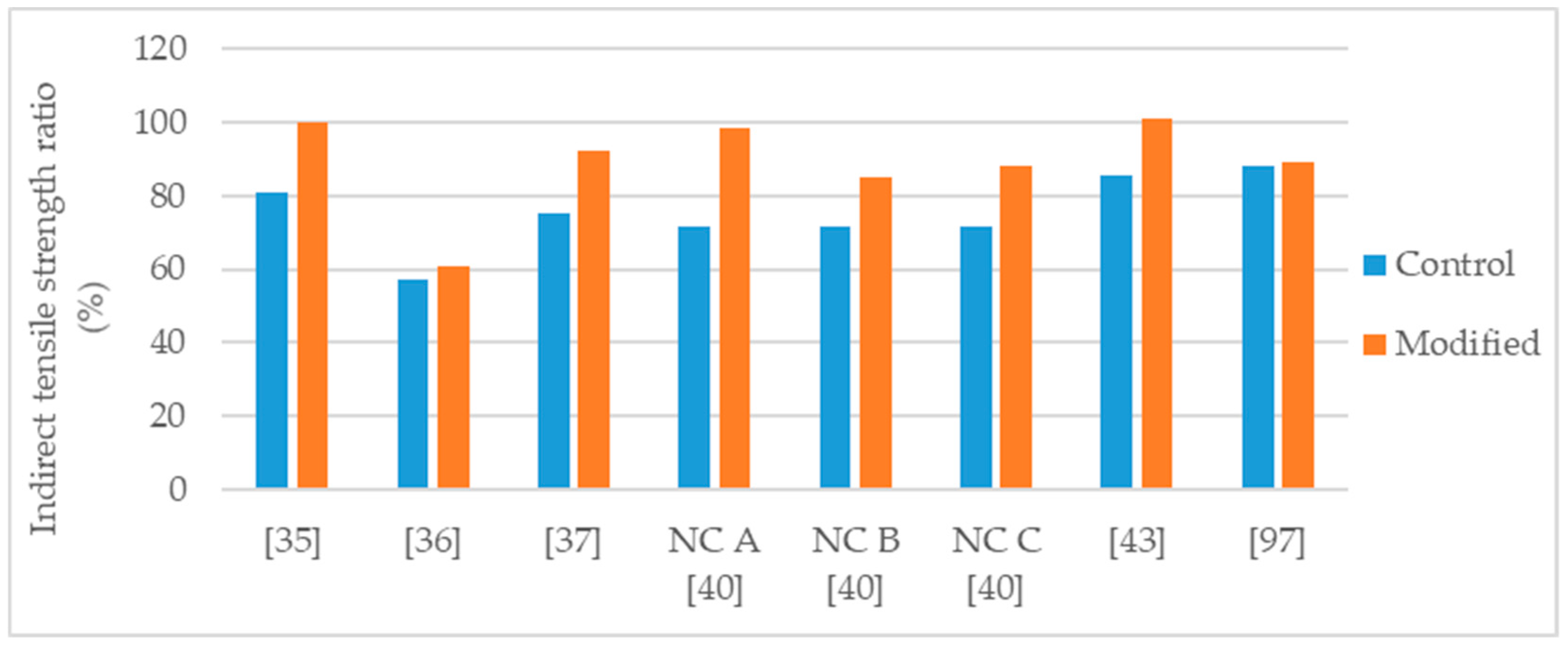
Indirect tensile strength ratio of control and nanosilica modified asphalt mixtures.
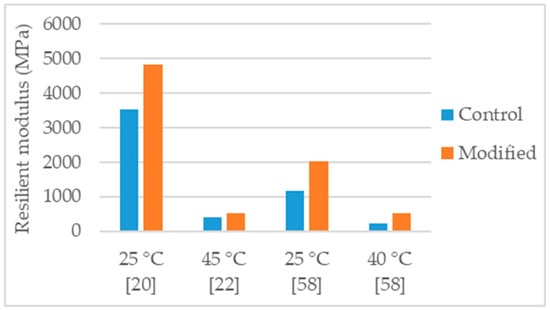
Figure 6.
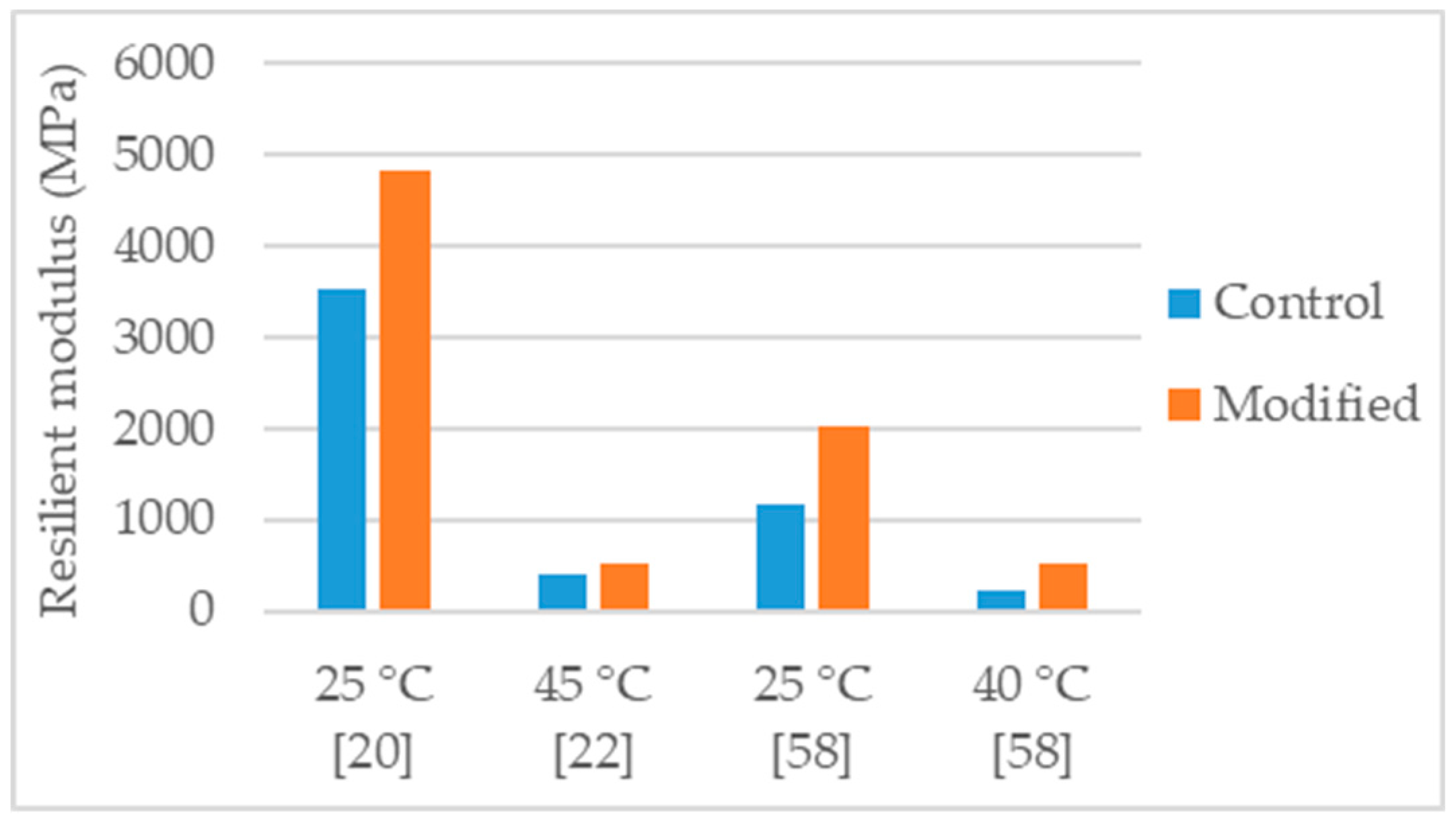
Resilient modulus of control and nanosilica modified asphalt mixtures.
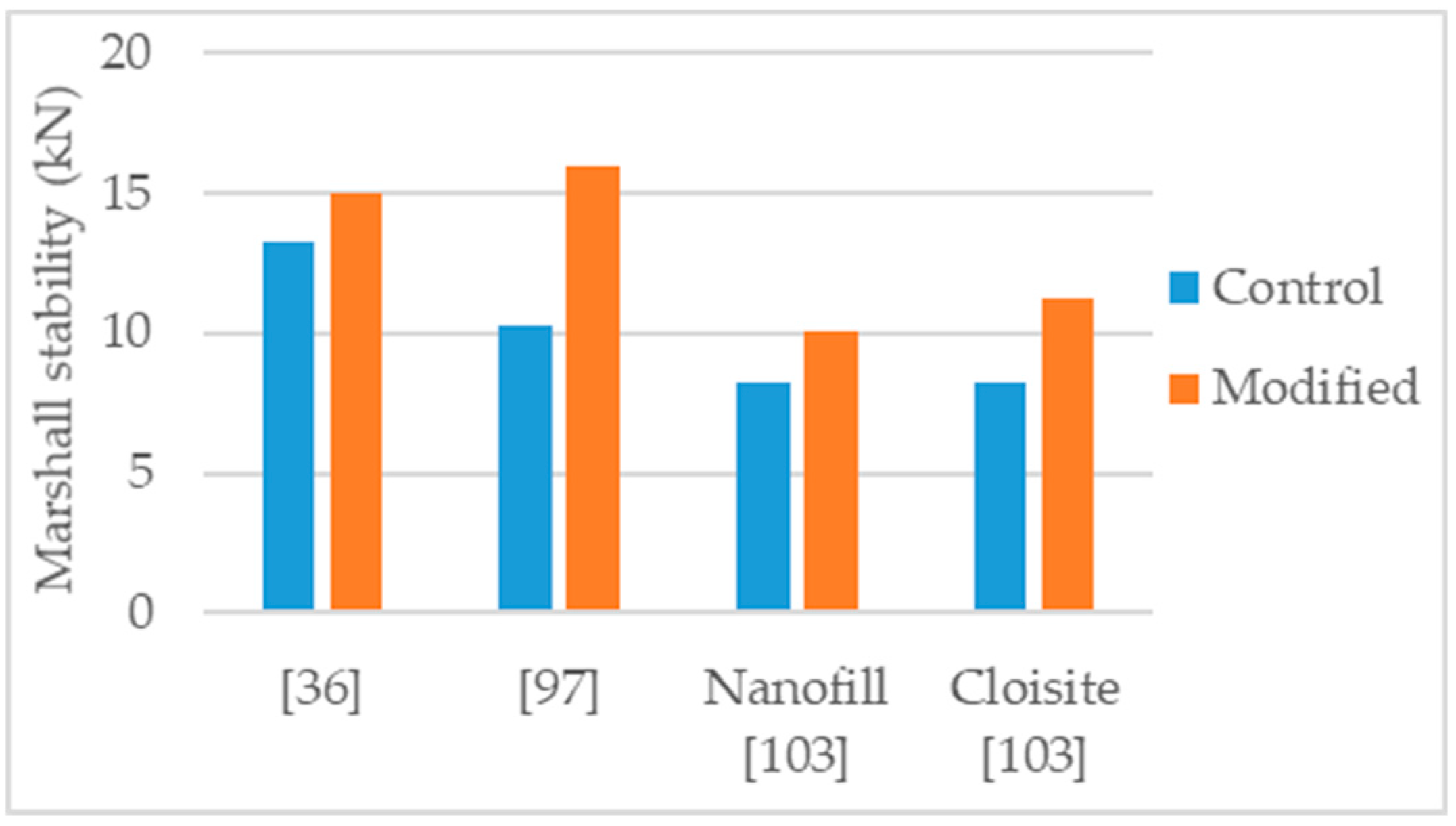
Burguete [95] studied an asphalt concrete, AC 14 Surf 35/50, using limestone filler, basalt aggregate, and considering two binder contents, 5.5% and 6.5%, with three nanosilica modifications, 2%, 4%, and 6%, respectively. From Marshall tests results the author observed, for both binder contents, that the peak of Marshall stability corresponded to the 4% nanosilica modification and, across the dosage range, a decrease of the Marshall flow related with the increase of the nanosilica dosage. The results of Burguete [95] presented in Figure 2 correspond to the 6.5% binder content mixture with 4% nanosilica modification, that caused an increase of 19% in Marshall stability.
Sun et al. [96] performed Marshall tests in cores from two test tracks, (1) using as binder a neat bitumen AH-70 (penetration grade 60/70) modified with 5% of styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS), and (2) using as binder the same neat bitumen (AH-70) modified with 5% styrene-butadiene-rubber (SBR), 0.5% nanosilica, and 1% polyethylene. The formula of the nanosilica-polymers modified mixture was determined through an orthogonal experiment. The authors concluded that a small amount of nanosilica could enhance significantly the performance of the polymer-modified binder. Regarding the Marshall stability results, with the nanosilica-polymers modification an increase of 28% was obtained (Figure 2).
Ghasemi et al. [21] studied a stone matrix asphalt (SMA), with aggregate maximum nominal size 19 mm and 6.3% binder content, modified with various percentages of nanosilica (0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%). The control binder used in the study was a 60/70 penetration grade bitumen modified with 5% SBS. The authors tested the asphalt mixtures for Marshall stability, indirect tensile strength, and indirect tensile stiffness modulus. The effects obtained in the tests increased according with the increase of nanosilica dosage. Thus, the mixture with 2% nanosilica had the most improved mechanical behavior. Regarding the 2% nanosilica modification, the Marshall stability increased 68% (Figure 2), indirect tensile strength increased 19% (Figure 3), and indirect tensile stiffness modulus increased 47%.
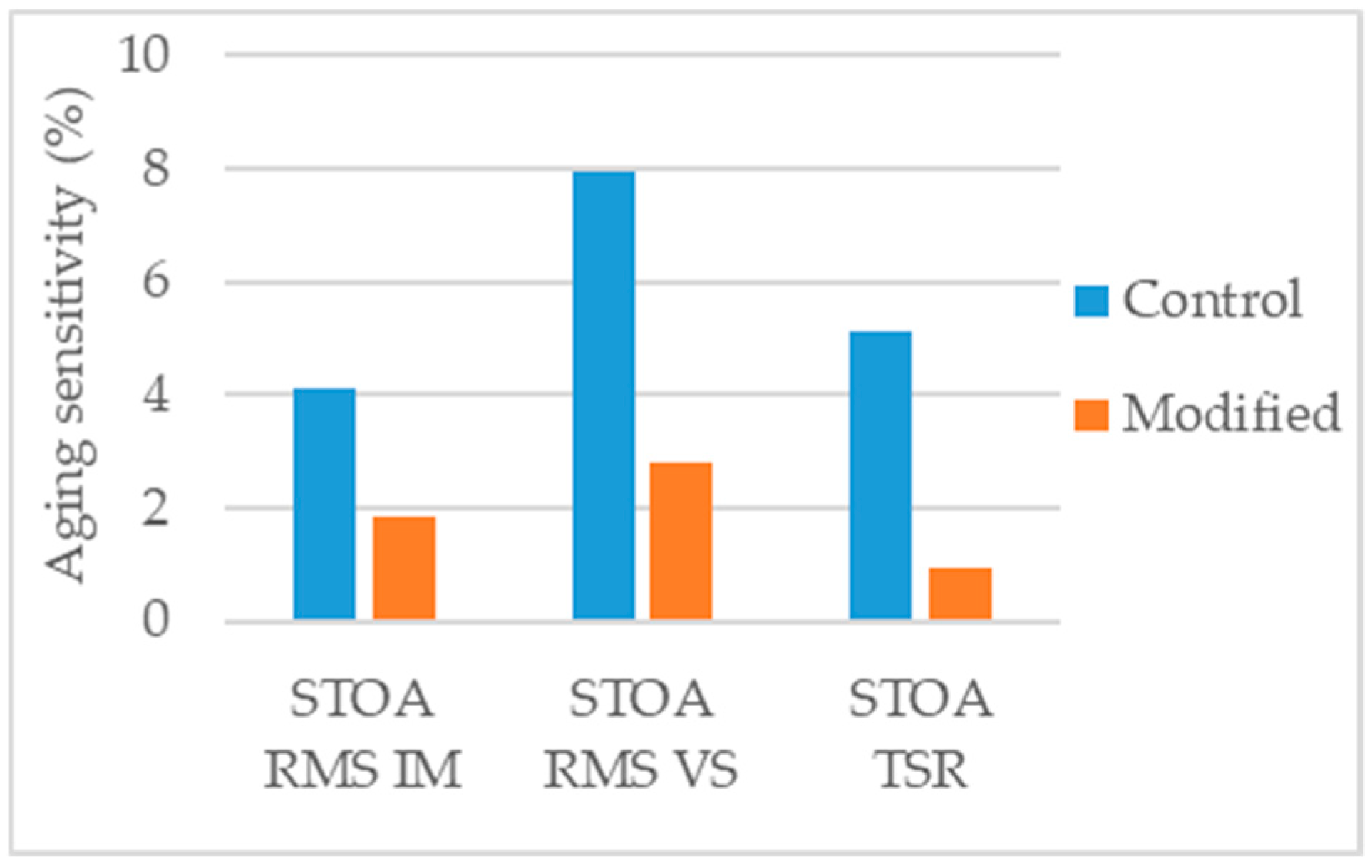
Guo et al. [62] studied an asphalt mixture modified with 3% silane silica (nanosilica modified with silane coupling agent). The neat binder was the Panjin 90 (penetration grade 70/100) and alkaline aggregates were used for the mixtures production. The modified mixture presented 24% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 2) and 26% increase in dynamic stability number (rutting test). To address water sensitivity, the authors performed Marshall tests in specimens conditioned for 48 h immersion (IM) and for 48 h vacuum saturation (VS) and determined the respective retained Marshall stability. With both conditioning methods, the modified mixture performed better than the control (Figure 4).
Yusoff et al. [58] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 19 mm) with PG 76 polymer-modified binder and modified with 2% and 4% nanosilica. For the mixture production, granitic aggregates were used, and the selected binder content was 7.5%. The effects obtained with the modifications were sensitive to the nanosilica dosage. Thus, the 4% modification had the highest effects in the mechanical performance. The authors evaluated water sensitivity using the tensile strength ratio and concluded that the 4% nanosilica modification enhanced significantly the behavior of the mixture, raising TSR from 82% to 98% (Figure 5). Regarding resilient modulus, the 4% modification lead to 74% and 142% of increase (Figure 6), at the temperatures of 25 °C and 40 °C, respectively. Testing for dynamic creep, a 42% reduction in permanent deformation was observed.
Hasaninia and Haddadi [20] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm) modified with 2%, 4%, 6%, and 8% nanosilica. The control binder was the 60/70. The optimum binder content (OBC) was calculated using the Marshal methodology, and the results showed a decrease in OBC proportional to the increase in nanosilica dosage. The OBC values were 5.5%, 5.3%, 5.2%, 5.0%, and 4.9% for the 0% (control mixture), 2%, 4%, 6%, and 8% nanosilica modified, respectively. Regarding the performance tests, the effects obtained with the modifications were sensitive to the nanosilica dosage thus, the 8% nanosilica modification had the highest effects. Concerning the 8% modification, the modified mixture presented 31% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 2), 37% increase in resilient modulus (Figure 6), 30% increase in indirect tensile strength, decrease in indirect tensile strength ratio from 98% to 73% (Figure 5), 71% increase in flow number (lower permanent deformation), and better fatigue resistance (18% increase in the strain for 105 cycles). As the authors produced the modified mixtures using the respective OBC, the decrease in water sensitivity (indirect tensile strength ratio) can be partially explained by the higher air void content of the nanosilica-modified mixtures (4.47% air void content in control mixture versus 5.93% air void content in 8% nanosilica modification).
Yao et al. [22] studied an asphalt mixture with PG 58-34 with acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (control binder) and modified with 4% and 6% nanosilica. The effects obtained were dependent of the nanosilica dosage. Thus, the 6% modification had the highest effects in the mechanical performance. Regarding the 6% modification, the authors reported 30% increase in the dynamic modulus, 34% reduction in permanent deformation (evaluated with the asphalt pavement analyzer rutting test) and 27% increase in resilient modulus (Figure 6).
Crucho et al. [25,36] studied an asphalt mixture (AC 14) with granitic aggregates, limestone filler, and 4.5% binder content. The selected binder was the 35/50 penetration grade (control binder) and the nanosilica dosage was 4%. The author concluded that the 4% nanosilica modification enhanced the mechanical performance of the mixture and reported the following effects: 11% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 2); improvement in retained Marshall stability from 77% to 98% (Figure 4); 59% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 3); improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 57% to 70% (Figure 5); better affinity aggregate-binder (more 10% of binder coverage); 34% reduction in permanent deformation; 4% and 18% average increase in stiffness modulus at the temperature of 20 °C and 30 °C, respectively; and better fatigue resistance (4% increase in the strain for 106 cycles).
Cai et al. [24] produced an asphalt mixture (AC 16) with limestone aggregates and 60/70 penetration grade bitumen and studied the modification with 1% nanosilica. The authors reported the following effects: 27% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 2); 14% reduction in permanent deformation; improvement in retained Marshall stability from 83% to 88% (Figure 4); 9% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 3); small improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 80% to 82% (Figure 5); 14% increase in stiffness modulus and better fatigue life (97% increase in number of cycles) in fatigue tests at 1000 µm/m controlled strain; 9% increase in flexural tensile strength and 25% increase in flexural strain in the three-point bending test.
Ezzat et al. [97] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 19 mm) modified with 7% nanosilica. The asphalt mixture was produced with limestone aggregates, limestone filler, 60/70 (control binder) and 5.5% binder content. The nanosilica modified mixture presented 56% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 2), increase in retained Marshall stability from 85% for control to 93% for nanosilica modified (Figure 4), 11% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 3), and increase in indirect tensile strength ratio from 88% for control to 93% for nanosilica modified (Figure 5).
Tanzadeh and Shahrezagamasaei [23] studied a porous asphalt mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm). For the mixture production, the authors used limestone aggregates, limestone filler, several combinations of additives (glass fiber, lime powder, polypropylene fiber, SBS and nanosilica), 60/70 asphalt binder and the binder contents 4.5%, 5.5%, and 6.0%. For the tested additives combinations, the introduction of 2% and 4% nanosilica modifications caused reduction in binder drain down, reduction in permanent deformation, and increase in indirect tensile strength. The effects of the nanosilica increased according with the dosage increase. In a following study, Tanzadeh et al. [98] evaluated the performance of a porous asphalt mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm), produced with limestone aggregates, limestone filler, lime (0.5% by weight of mixture), and 60/70 asphalt binder modified with 4.5% SBS. The binder contents of the asphalt mixture were 5% and 6%. The authors study the modification with 2% nanosilica alongside with 0.2% glass fiber and basalt fiber. The introduction of 2% nanosilica increased indirect tensile strength, improved the resistance to moisture sensitivity, and reduced abrasion (Cantabro test).
The use of silica nanoparticles to modify the asphalt mixture revealed to cause an overall improvement in its mechanical performance. Generally, the studies found in literature indicate higher Marshall stability, higher indirect tensile strength, enhanced water sensitivity (indicated by higher indirect tensile strength ratio and/or higher retained Marshall stability), higher stiffness (higher resilient modulus or stiffness modulus), lower permanent deformation, and better fatigue resistance.
4.2. Nanoclay
In the studies of asphalt mixtures modified with nanoclays, several improvements in the mechanical performance were identified. Generally, the effect reported by the authors were: Increase in Marshall stability, reduction in permanent deformation, lower water sensitivity (increase in indirect tensile strength ratio and/or retained Marshall stability), increase in stiffness modulus/resilient modulus, and better resistance to fatigue. Although the findings are generally consistent, the big variety of materials leads to different effects in mechanical performance. The nanoclay type, the modification of raw nanoclay with organo-modifiers, the nanoclay dosage and the original asphalt binder properties can have a strong influence in the results. The following paragraphs describe the most relevant studies found in the literature and their more important conclusions.
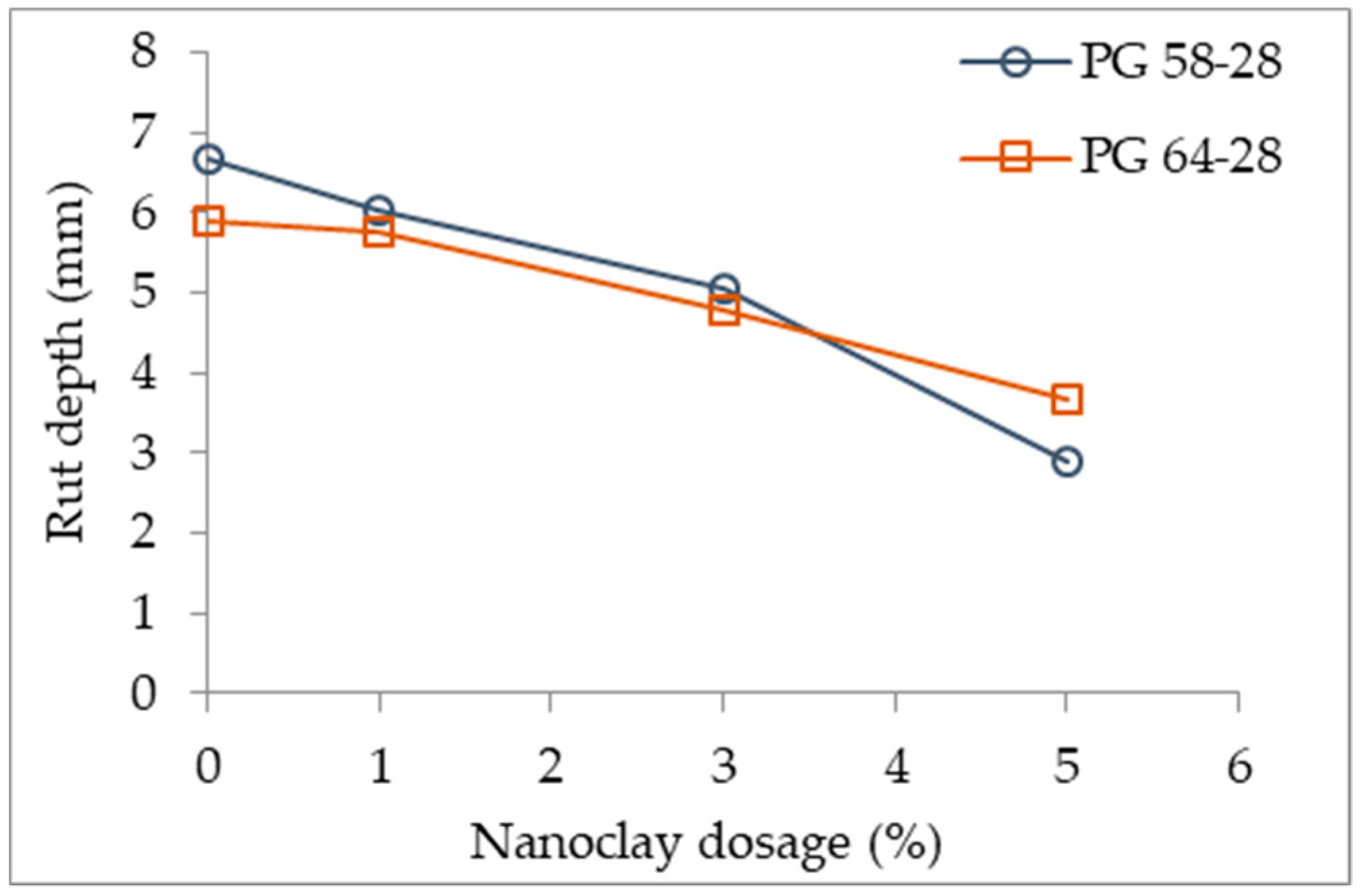
Gedafa et al. [94] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm) with 5.7% binder content, using two different binders, PG 58-28 and PG 64-28 (control binders), and modified with an organically modified nanoclay (cloisite) with the dosages of 1%, 3%, and 5%. The authors tested for permanent deformation using the asphalt pavement analyzer rut test (APA), and concluded that the resistance to permanent deformation increased with the nanoclay dosage (Figure 7). The effect of the modifications in the softer binder (PG 58-28) was stronger that in the harder binder (PG 64-28). The modifications with 5% nanoclay presented a reduction of 57% and 38% with the PG 58-28 and PG 64-28, respectively.
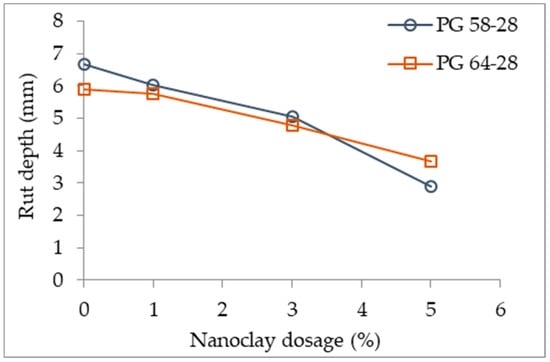
Figure 7.
Effect of nanoclay dosage on rut depth [94].
Iskender [40] studied the effects of three nanoclay modifications in the performance of a SMA mixture. The SMA mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm) was produced with 6.1% binder content and, basalt aggregates and asphalt binder 50/70 (control binder) were used. The author introduced the nanoclay as a partial substituent of the mineral filler, and not by previously blending with the asphalt binder. In this case, the nanoclay dosages were 2%, 3.5%, and 5% by mass of dry aggregates. The author modified raw bentonite clay with three organic modifiers, obtaining three organically modified clays: Nanoclay A—modified with dimethyl, dehydrogenated tallow, quaternary ammonium (NC A); nanoclay B—modified with methyl, tallow, bis 2 hydroxyethyl quaternary ammonium (NC B); and nanoclay C—modified with dimethyl, benzyl, hydrogenated tallow, quaternary ammonium (NC C). The author evaluated water sensitivity using the modified Lottman test at 25 °C, and observed: With nanoclay A the indirect tensile strength increased by 14%, 20%, and 3%; with nanoclay B the indirect tensile strength increased by 11%, 20%, and −2%; and with nanoclay C the indirect tensile strength decreased by 11%, 14%, and 17%, for 2%, 3.5%, and 5% dosages, respectively. The indirect tensile strength results corresponding to the 2% modifications are presented in Figure 8. Regarding the indirect tensile strength ratio, for all the nanoclays, the highest ratio corresponded to the 2% dosage (Figure 9). The ratio presented a trend of decrease with the increase in dosage, in such way, with 5% dosage all nanoclays performed worse that the control mixture. The author evaluated permanent deformation at 40 °C using the dynamic creep test, applying 100 kPa load for 21,600 pulses. The nanoclay A enhanced the resistance to permanent deformation, presenting a reduction of 9%, 10%, and 36% for 2%, 3.5%, and 5% dosages, respectively. The mixture modified with nanoclay B performed worse that the control mixture, presenting an increase in permanent deformation of 30%, 40%, and 51% for 2%, 3.5%, and 5% dosages, respectively. The behavior of the mixture modified with nanoclay C was more complex, presenting 12% increase with 2% dosage, 29% reduction with 3.5% dosage, and similar to control with 5% dosage.
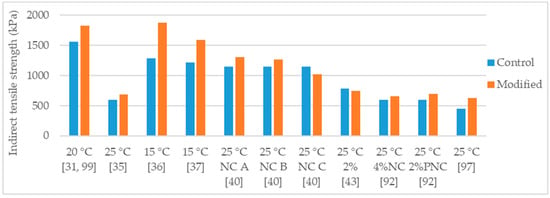
Figure 8.
Indirect tensile strength of control and nanoclay modified asphalt mixtures.
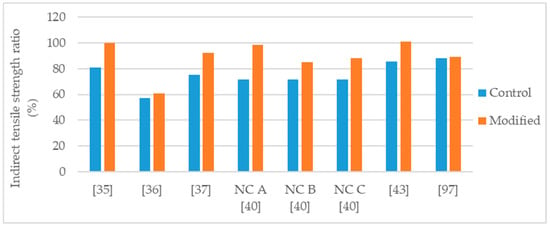
Figure 9.
Indirect tensile strength ratio of control and nanoclay modified asphalt mixtures.
Ghile [31] and van de Ven et al. [99] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 11.2 mm) with 5.7% binder content, modified with of 6% organically modified nanoclay (cloisite). For the mixture production, granitic aggregates and 40/60 asphalt binder (control binder) were used. The modified mixture presented 12% average increase in resilient modulus in the range from 5 °C to 35 °C (evaluated by the indirect tensile resilient modulus test). Regarding indirect tensile strength, the modified mixture presented 8%, 19%, 17%, 28%, and 39% increase for 5 °C, 12.5 °C, 20 °C, 27.5 °C, and 35 °C, respectively (Figure 8). The modification also enhanced the resistance to permanent deformation (50% increase in the flow number in dynamic creep tests at 60 °C and 200 KPa).
Ezzat et al. [97] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 19 mm) modified with 3% nanoclay (montmorillonite). The asphalt mixture was produced with limestone aggregates, limestone filler, 60/70 (control binder) and 5.5% binder content. The authors observed that the nanoclay modified mixture presented 55% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 10), decrease in retained Marshall stability (85% for control and 77% for nanoclay modified), 40% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 8), and similar indirect tensile ratio (Figure 9).
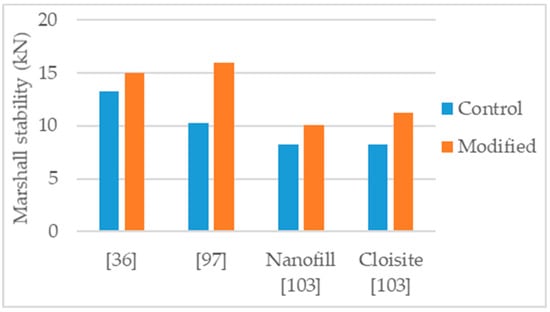
Figure 10.
Marshall stability of control and nanoclay modified asphalt mixtures.
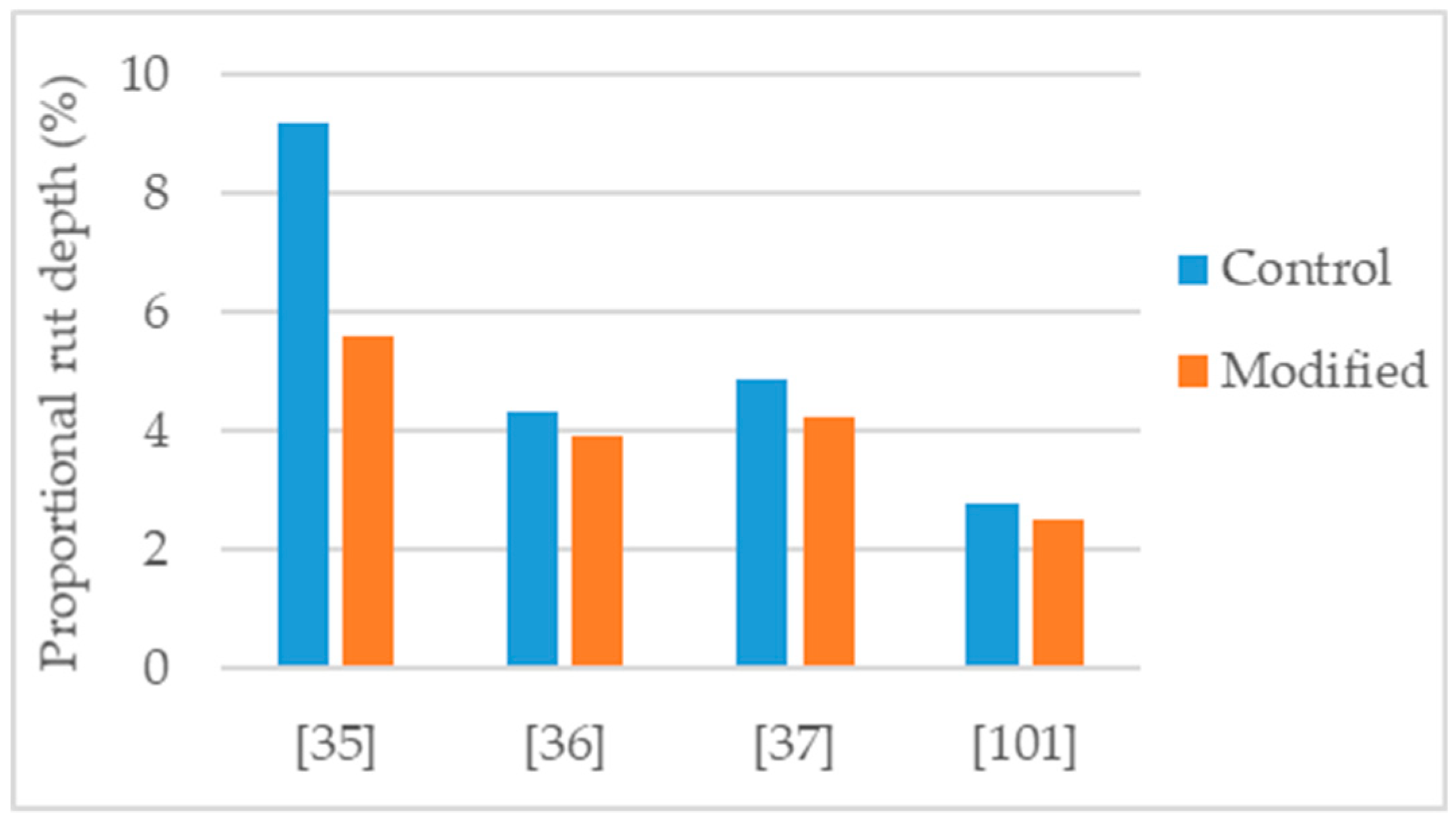
Crucho et al. [25,36,100] studied an asphalt mixture modified with 4% nanoclay hydrophilic bentonite. The mixture was an asphalt concrete (AC 14) using granitic aggregates, limestone filler, 35/50 asphalt binder, and 4.5% binder content. The modification had a positive effect in the properties of the asphalt mixture. The following effects were reported: 13% increase in Marshall stability (Figure 10); improvement in retained Marshall stability from 77% to 99%; 46% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 8); improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 57% to 61% (Figure 9); improvement in affinity aggregate-binder (from 40% to 67% of binder coverage); 10% reduction in permanent deformation (Figure 11); 7.2% reduction in stiffness modulus at 20 °C and 4.3% increase in stiffness modulus at 30 °C; and better fatigue resistance (7% increase in the strain for 106 cycles).
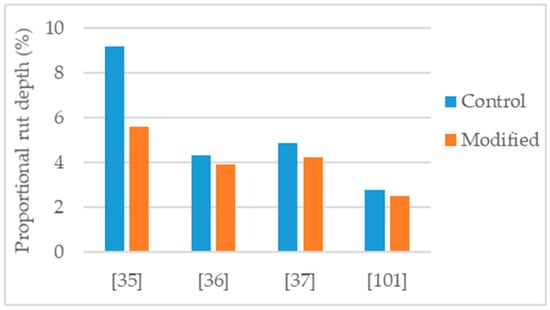
Figure 11.
Proportional rut depth of control and nanoclay modified asphalt mixtures.
De Melo and Trichês [35] studied the modification of a PG 58-22 asphalt binder with 3% organically modified montmorillonite. The asphalt mixture, NMAS 19 mm, had 4.35% binder content and, was produced with basaltic aggregates, and hydrated lime. The modified mixture presented: 15% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 8), improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 81% to 100% (Figure 9); 39% reduction in permanent deformation (Figure 11); 20% and 57% average increase in stiffness modulus at the temperature of 20 °C and 30 °C, respectively; and increase in fatigue resistance (22% increase in the strain for 106 cycles).
Blom et al. [101] studied an asphalt mixture (AC14) modified with 5% organically modified nanoclay (cloisite-15). For the mixture production, sandstone aggregates and 35/50 asphalt binder were used. The authors tested for permanent deformation using a wheel-tracking machine. After applying 50,000 cycles, the 5% nanoclay modified mixture presented 10% reduction in permanent deformation (Figure 11).
Goh et al. [43] studied the effects of the modification with 1% and 2% polysiloxane-modified montmorillonite in the indirect tensile strength of an asphalt mixture. The mixtures were produced with 5.2% binder content and the PG 58-28 was the control binder. On the one hand, in the indirect tensile strength of the unconditioned (dry) specimens, the modified mixtures presented 1% and 4% reduction for the 1% and 2% dosage (Figure 8), respectively. On the other hand, in the indirect tensile strength of the conditioned (wet) specimens (standard conditioning in water according to AASHTO T283-03), the modified mixtures presented 7% and 13% increase for the 1% and 2% dosage, respectively. This led to a progressive increase of the indirect tensile strength ratio with the increase in nanoclay dosage, 86%, 92%, and 101% for the 0%, 1%, and 2% dosage (Figure 9), respectively. The authors found the asphalt mixtures modified with polysiloxane-modified montmorillonite less susceptible to deicing solutions. These findings are in good agreement with another study [102], that reported the nanoclay to have a positive effect in mitigating stripping damage of asphalt mixtures exposed to non-chloride deicer solutions.
Jahromi et al. [103] studied the modification of an asphalt mixture, NMAS 12.5 mm, with two types of organically modified montmorillonite nanoclay, nanofil, and cloisite, with the dosages of 2%, 4%, and 7%. Limestone aggregates, limestone filler, and 60/70 control binder were used in the production of the mixtures. The authors concluded that the effects of the modifications increased according to the increase in the nanoclay dosage and the effects of cloisite were stronger than those of nanofil. Regarding the modifications with 7% nanoclay, the Marshall stability increased by 23% and 37% for the nanofill and cloisite (Figure 10), respectively. The increase in the nanoclays dosage lead to an increase in the optimum binder content, possibly explained by the large surface area of the nanoclays. The 7% modified mixtures presented 8% and 6% increase in indirect tensile strength at 25 °C, 40% and 18% increase in resilient modulus at 40 °C, and reduction in permanent deformations (37% and 83% increase in the flow number in dynamic creep tests at 60 °C and 300 KPa), for cloisite and nanofill, respectively.
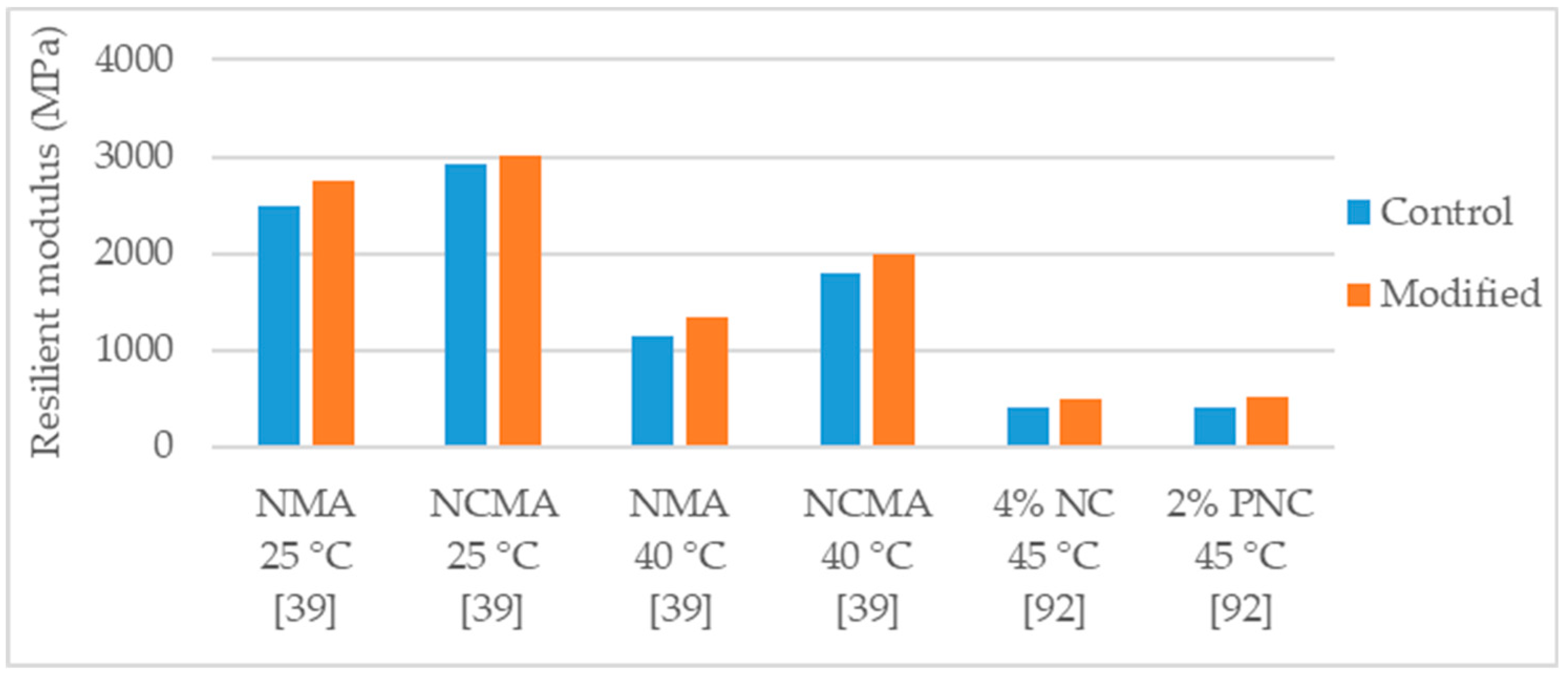
Golestani et al. [39] studied the effect of the modification with 1.5% organically modified montmorillonite (cloisite) in the properties of an asphalt mixture (NMAS 19 mm) with 4.8% binder content. For the production of the mixture the authors used limestone aggregates and considered two control binders, a neat PG 58-10 and a polymer modified binder (PG 58-10 modified with 6% SBS). Regarding the effects in the PG 58-10 binder (NMA), the modification lead to 10% increase in resilient modulus at 25 °C (Figure 12), 18% increase in resilient modulus at 40 °C (Figure 12), 26% reduction in permanent deformation, similar (0.5% increase) indirect tensile strength and improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 58% to 61%. Regarding the effects in the polymer modified binder (NCMA), the modification lead to 3% increase in resilient modulus at 25 °C (Figure 12), 12% increase in resilient modulus at 40 °C (Figure 12), 29% reduction in permanent deformation, similar (0.5% increase) indirect tensile strength, and improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 69% to 72%.
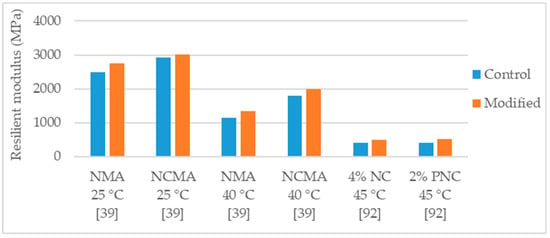
Figure 12.
Resilient modulus of control and nanoclay modified asphalt mixtures.
Yao et al. [92] evaluated the effects of the modifications with non-modified montmorillonite nanoclay (NC) and polymer-modified montmorillonite (PNC) in the performance of an asphalt mixture (NMAS 9.5 mm). The control binder was the PG 58-34 and were studied the dosages of 2% and 4%. The modification with NC presented stronger effects with the higher dosage (4%) while the modification with PNC, with exception of permanent deformation test, presented higher effects with the 2% dosage. With the 4% NC modification, the authors reported 9% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 8), 15% average increase in dynamic modulus, 25% increase in resilient modulus (Figure 12) and 59% reduction in permanent deformation (rut depth using APA rutting test). Regarding the 2% PNC modification, the modified mixture presented 16% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 8), 10% average increase in dynamic modulus, 29% increase in resilient modulus (Figure 12) and 34% reduction in permanent deformation (rut depth using APA rutting test). Only in the case of permanent deformation, the 4% PNC performed better than the 2% PNC, presenting 42% reduction in rut depth.
Crucho et al. [37] studied a stone mastic asphalt (SMA16) mixture modified with 4% nanoclay hydrophilic bentonite. The mixtures were produced with 6.0% binder content and using 35/50 asphalt binder (control binder), granitic aggregates, and limestone filler. The mixture with 4% nanoclay presented: 30% increase in indirect tensile strength (Figure 8); improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 75% to 92% (Figure 9); 13% reduction in permanent deformation (Figure 11); 6.6% reduction in stiffness modulus at 20 °C; and better fatigue resistance (14% increase in the strain for 106 cycles).
Ameri et al. [104] modified a SMA mixture (NMAS 9.5 mm) with 1%, 2%, 3%, and 4% cloisite-15A. For the mixture production, 6.7% binder content, limestone aggregates and limestone filer were used. In this study, two control binders were considered, the 60/70 asphalt binder and the 60/70 modified with 5% SBS. In both mixtures, 60/70 and 60/70 + SBS, the nanoclay modification enhanced the properties of the mixture, increasing the effect with the increase in dosage. Thus, the 4% dosage presented the highest gains in performance. Regarding the mixture with 60/70 control binder, the 4% modification presented 23% increase in Marshall stability, 9% increase in flow number (lower plastic deformation) and 61% reduction in permanent deformation. Regarding the mixture with 60/70 + SBS control binder, the 4% modification presented 11% increase in Marshall stability, 8% increase in flow number (lower plastic deformation), and 16% reduction in permanent deformation.
Generally, the asphalt mixtures modified with nanoclays revealed higher Marshall stability, enhanced water sensitivity (indicated by higher indirect tensile strength ratio and higher retained Marshall stability), lower permanent deformation, and better fatigue resistance. Regarding stiffness, the nanoclay modified mixtures presented higher values, particularly at higher temperatures. The effects obtained with the modifications were dependent on the type of nanoclay being used. The raw nanoclays tend to present stronger effects according to the increase in dosage, while some of the organically modified nanoclays present a peak in performance enhancement at a relatively low dosage and a further increase worsens the performance. Although the majority of the nanoclay modifications had the effect of increasing the indirect tensile strength, some of organic modifiers caused a reduction.
4.3. Nanoiron
Kordi and Shafabakhsh [49] evaluated the mechanical properties of a stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixture modified with 0.3%, 0.6%, 0.9%, and 1.2% of nano Fe2O3. The 60/70 asphalt binder was the control binder used in the study and, all the SMA were produced with 6.6% binder content. The authors tested for permanent deformation using the wheel-tracking test, for stiffness using the indirect tensile stiffness modulus (ITSM) and for fatigue using the indirect tensile fatigue test (ITFT). In all the tests, initially the performance improved, reaching peak with the 0.9% dosage, and then decreased for higher dosage. Regarding the 0.9% nano Fe2O3 modification; stiffness modulus increased by 28%, 14%, and 45%, at 5 °C, 15 °C, and 25 °C, respectively; fatigue life increased between 15% and 35%, depending on the temperature and stress level; and permanent deformation decreased by 48%, 35% and 18%, at 40 °C, 50 °C, and 60 °C, respectively.
Pirmohammad et al. [50] studied an asphalt mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm) modified with nano Fe2O3. The 60/70 asphalt binder (PG 64-22) was modified with the nanomaterial dosages of 0.1%, 0.4%, 0.8%, and 1.2%. The authors studied the fracture properties of the asphalt mixture by conducting semi-circular bending (SCB) tests. Regarding the nano Fe2O3 modification, the fracture resistance initially increases reaching the peak at 0.8% dosage (27% increase), and then decreases for higher dosage.
Crucho et al. [25,36] studied an asphalt concrete (AC 14) mixture modified with 4% nanoiron (zero-valent iron). For the mixture production was used granitic aggregates, limestone filler, 35/50 asphalt binder (control binder), and 4.5% mixture binder content. The modification had the following effects: 5% increase in Marshall stability; improvement in retained Marshall stability from 77% to 80%; 5% increase in indirect tensile strength; improvement in indirect tensile strength ratio from 57% to 82%; improvement in affinity aggregate-binder (from 40% to 70% of binder coverage); 20% reduction in permanent deformation; 7.3% and 1.5% reduction in stiffness modulus at 20 °C and 30 °C, respectively; and better fatigue resistance (4% increase in the strain for 106 cycles).
The authors studying the use of nanoiron to modify the asphalt mixture indicate several improvements in mechanical performance, such as, higher Marshall stability, higher indirect tensile strength, enhanced water sensitivity (indicated by higher indirect tensile strength ratio and higher retained Marshall stability), lower permanent deformation, better fatigue, and fracture resistance.
5. Aging Resistance
5.1. Asphalt Binder
The organic nature of the asphalt binder leads to a continuous non-reversible aging process. During the aging process, the chemical composition of the asphalt binder changes, generally, the asphaltenes content tend to increase, while resins and aromatics tend to decrease [1]. Regarding the properties of the binder, the aging process is most prominent in the form of hardening and brittleness. The aging of the asphalt mixtures is highly dependent on the aging of the asphalt binder thus, several methods were developed and standardized to simulate in laboratory the aging of the asphalt binder. Actually, the paving industry relies on such methods to establish criteria for the paving grade bitumen in Europe [105] and for the performance-graded asphalt binders in USA [106]. Also, due to its convenience, less time, and material consuming, researchers frequently only study aging at the binder level. The aging methods more frequently used are the rolling thin film oven test (RTFOT), thin film oven test (TFOT), and pressure aging vessel (PAV). The RTFOT is considered to be representative of the short-term aging (corresponding to the plant mixing and field compaction processes) and PAV is added to simulate long-term aging.
After the aging simulation, the properties of the aged binder can be compared with those of the unaged binder. Generally, researchers consider parameters such as retained penetration—RP (Equation (1)), increase in softening point—ISP (Equation (2)), viscosity aging index—VAI (Equation (3)), DSR rutting parameter (G*/sinδ), and DSR fatigue parameter (G*∙sinδ).
Regarding the properties of the asphalt binder, the aging process causes an increase in viscosity and softening point and a reduction in penetration value. From the rheology perspective, the aging process causes an increase in the complex modulus and a decrease in the phase angle.
Several authors highlight the positive contributions of nanomaterials to aging resistance. The presence of nanomaterials may play an important role in improving the asphalt mixture aging resistance by two mechanisms, first they may act as a barrier thus retarding the oxidation process and second as they can prevent the evaporation of light components of the asphalt [53].
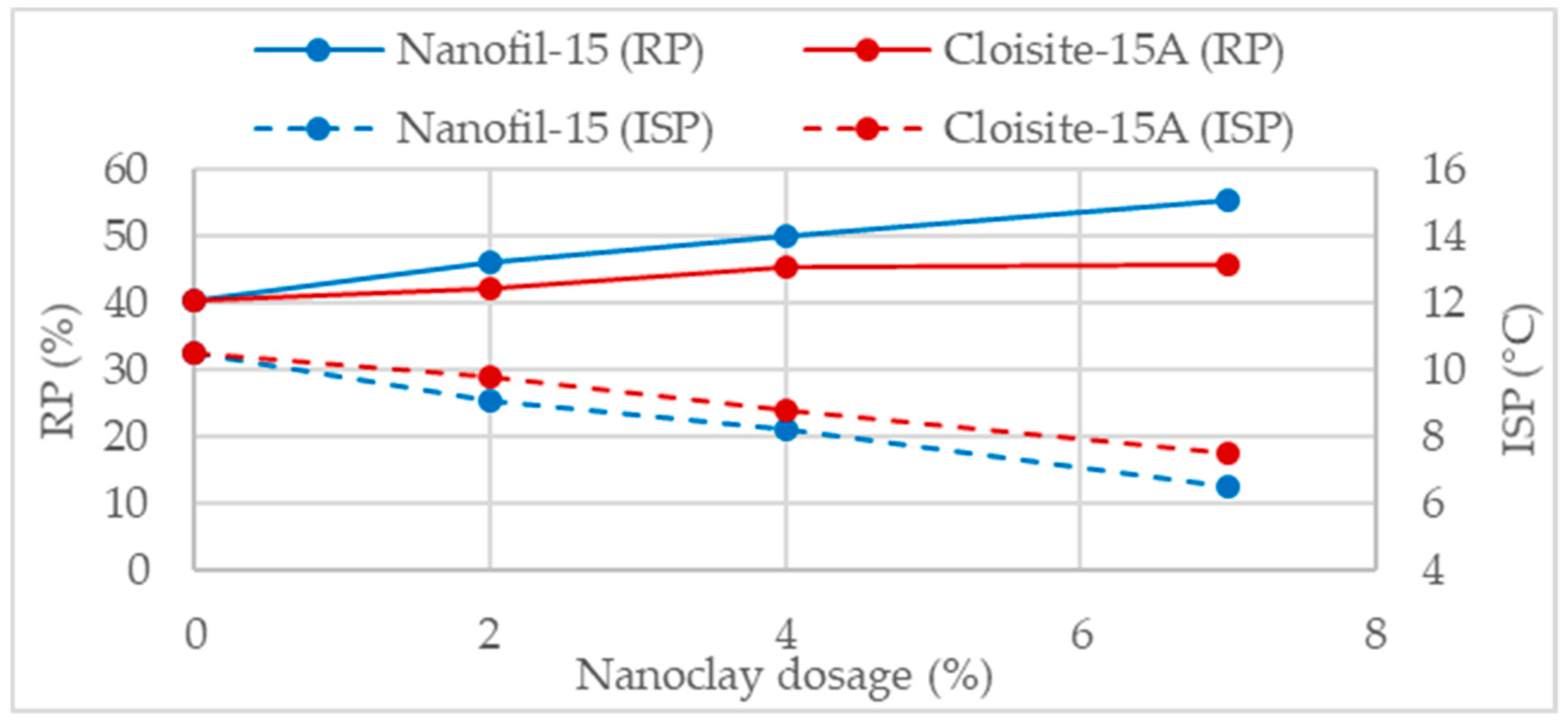
Jahromi and Khodaii [34] studied the 60/70 asphalt binder modification using two types of organically modified nanoclays, cloisite, and nanofil, with the dosages of 2%, 4%, and 7%. The modifications lead to higher RP and lower ISP values, indicating less effect of aging in the binder. The enhancement in aging resistance was increasing according to the increase in nanoclay dosage (Figure 13). Regardless of both nanoclays were organically modified, the obtained effects were dependent of the nanoclay type. According with both parameters, RP and ISP, the modifications with nanofil were more effective in enhancing aging resistance. Other studies concerning nanoclay modifications, reported similar trends, increase in RP and reduction in ISP and VAI [79,84,107,108,109,110].
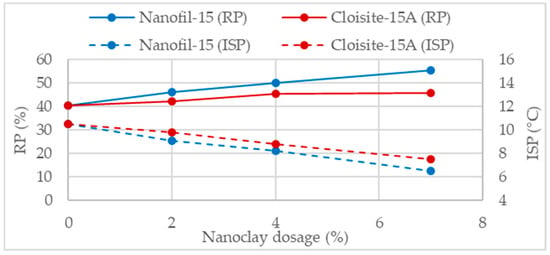
Figure 13.
Retained penetration and softening point increment of two nanomodified binders [34].
Ghile [31] and van de Ven et al. [99] studied the effects of organically modified nanoclays in the rheology of two asphalt binders. The authors selected 6% nanofill to modify the 70/100 asphalt binder and, 3% and 6% cloisite to modify the 40/60 asphalt binder. After short-term and long-term aging, in DSR testing the modified binders showed smaller variations (smaller increase in stiffness and smaller reduction of phase angle) when compared with the unaged modified binder, which means less aging effect. Then, the variation of the rutting parameter (G*/sinδ) was also smaller in the case of the modified binders. The modified binders also showed higher retained penetration and lower increment in softening point. Other studies [111,112] evaluating aging through the variation of rheological parameters, obtained similar conclusions. Ashish, Singh and Bohm [113] modified a 35/50 asphalt binder with 2%, 4%, and 6% of cloisite-30B (organically modified nanoclay). The authors evaluated fatigue of the PAV aged binders using the linear amplitude sweep (LAS) test and found the number of load cycles to failure increasing with the increasing of nanoclay dosage. Similar results were presented by Kavussi and Barghabany [114], that modified a PG 58-22 with 2% and 6% of cloisite-30B.
In addition to the traditional methods, that essentially reproduce well the aging caused by temperature and oxidation mechanisms, several researchers are developing alternative laboratory aging simulations to address other effects. Environmental conditions, such as, solar radiation, particularly the ultraviolet (UV), and moisture damage also have a significant role in the change of binder morphology during the aging process [115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128].
Zhang et al. [110] concluded that the modification of an 60/80 asphalt binder with 6% organically modified montmorillonite enhanced the resistance to UV aging. After UV aging, the modified binder presented lower VAI and SPI than the control binder. Other studies presented similar conclusions [129,130].
Crucho et al. [131] tested the recovered binders of TEAGE aged (under UV radiation and watering/drying cycles) [132] asphalt mixture specimens. The mixtures were modified with three nanomaterials independently, 4% nanosilica, 4% nanoiron, and 4% nanoclay bentonite (hydrophilic clay). The results obtained for RP were 55%, 76%, 55%, and 54% for the control, 4% nanosilica, 4% nanoiron, and 4% nanoclay, respectively. The results obtained for ISP were 14.5 °C, 12.2 °C, 14.3 °C, and 13.5 °C for the control, 4% nanosilica, 4% nanoiron, and 4% nanoclay, respectively. All the modifications presented lower ISP, although, the results of nanoiron modification are similar to those of control, indicating no enhancement in aging resistance. Regarding RP, the control, 4% nanoiron, and 4% nanoclay also presented very similar results. Other the other hand, 4% nanosilica modification presented a clear indication of enhanced aging resistance according both parameters.
5.2. Asphalt Mixtures
5.2.1. Methods
The evaluation of the asphalt mixture aging is complex and, currently, there is no test method to assess it directly. A possible approach is to characterize the asphalt mixture’s mechanical performance at early age (fresh mixture) and under aged conditions and then, determine the difference between them. Alternatively, some researchers compute the percent variation (principle similar to the VAI, Equation (3)) or the ratio between aged and fresh (principle similar to a retained performance, Equation (1)), commonly designating them as aging sensitivity and aging index, respectively. In this review, the effects of the nanomaterials in the aging resistance were analyzed by calculating the aging sensitivity (Equation (4)) of the evaluated mechanical performance parameters.
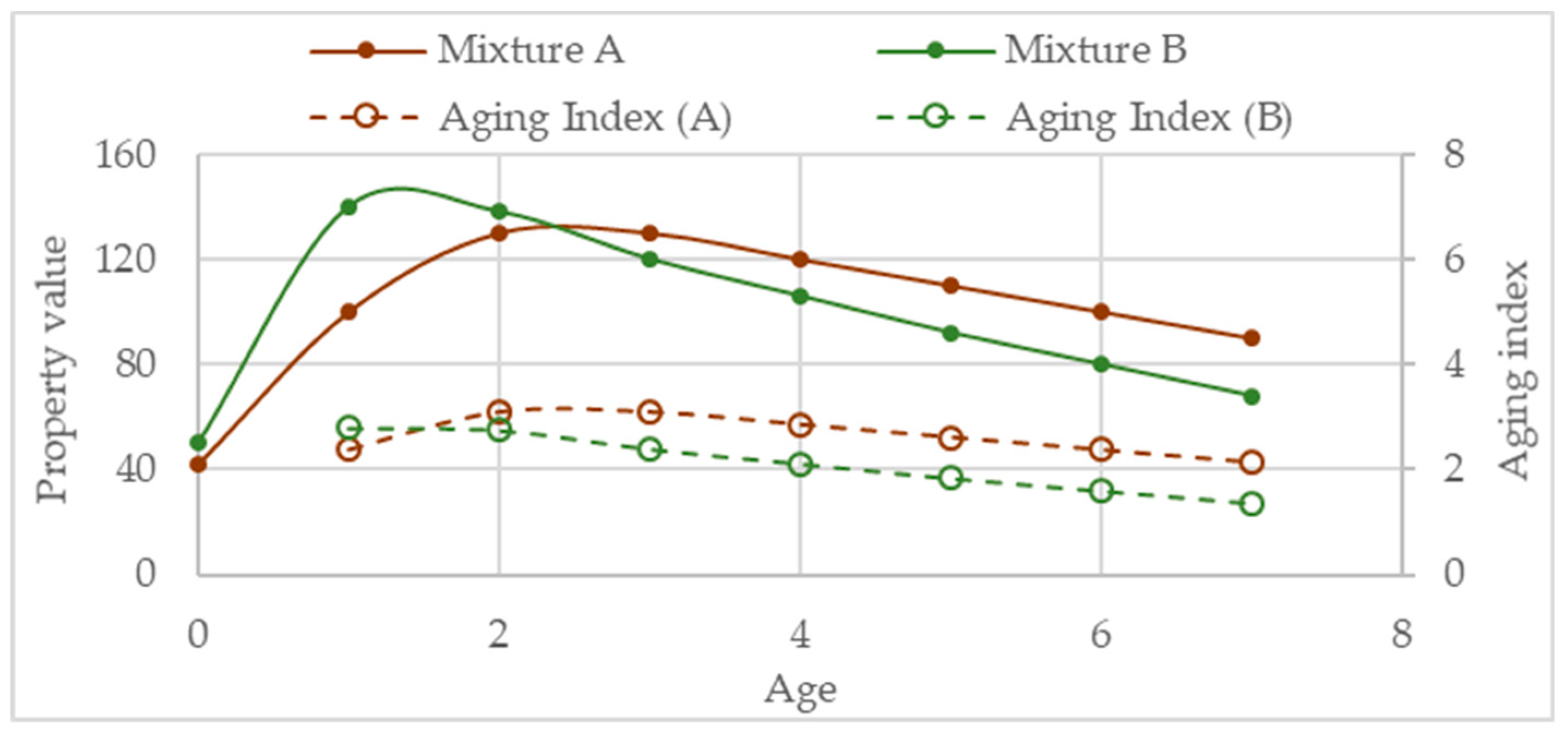
Apparently, the higher the absolute value of the selected indicator (difference aged-unaged, aging sensitivity, or aging index) the most aging sensitive is the mixture. A drawback of this approach is that in the case of a mechanical property which value increases with aging, e.g. stiffness or tensile strength, in some cases, a poor aging resistance performance may be wrongly understood as a good aging resistance. As example, Figure 14 presents the case of a mixture (mixture B) with higher aging sensitivity than the control mixture (mixture A) but presenting lower aging index in all evaluations after age one. Thus, to draw conclusions about aging resistance, one should have a good overview of the performance under aged conditions by conducting several performance tests. In this regard, due to the brittleness effect caused by aging, testing for fatigue resistance is particularly important. The production of aged specimens consumes a significant amount of time and resources, thus, generally, it is more practical to perform different tests than to simulate several aging times.
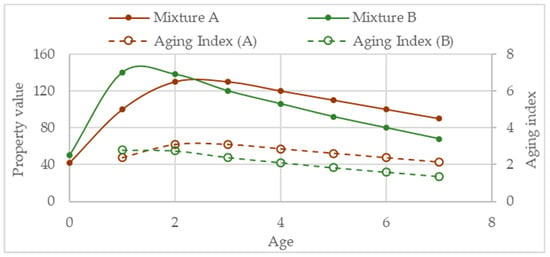
Figure 14.
Example of the evolution of aging index.
To obtain aged asphalt mixture specimens few laboratory aging methods were developed. Currently, the methods used more often worldwide by the researchers are the described by the specification AASHTO R30-02 [133], initially proposed by the Strategic Highway Research Program [134]. In brief, the specification presents two methods, the short-term oven aging (STOA) and the long-term oven aging (LTOA). The STOA consists in conditioning the loose asphalt mixture in a draft oven for four hours at 135 °C and, aims to simulate the aging caused the plant mixing and compaction processes. The LTOA consists in conditioning the compacted asphalt specimens for five days at 85 °C and, aims to reproduce the aging of the pavement in service for approximately five to ten years. Although STOA and LTOA are practical methods requiring only simple equipment, they do not simulate all the actions present during field aging, e.g. solar radiation and moisture damage. Thus, researchers proposed few alternative approaches to address aging simulation, such as the saturation aging tensile stiffness (SATS) developed by Choi [135], the Viennese Aging Procedure (VAPro) developed by Steiner et al. [136], and the Tecnico accelerated aging (TEAGE) developed by Crucho et al. [132].
5.2.2. Nanosilica
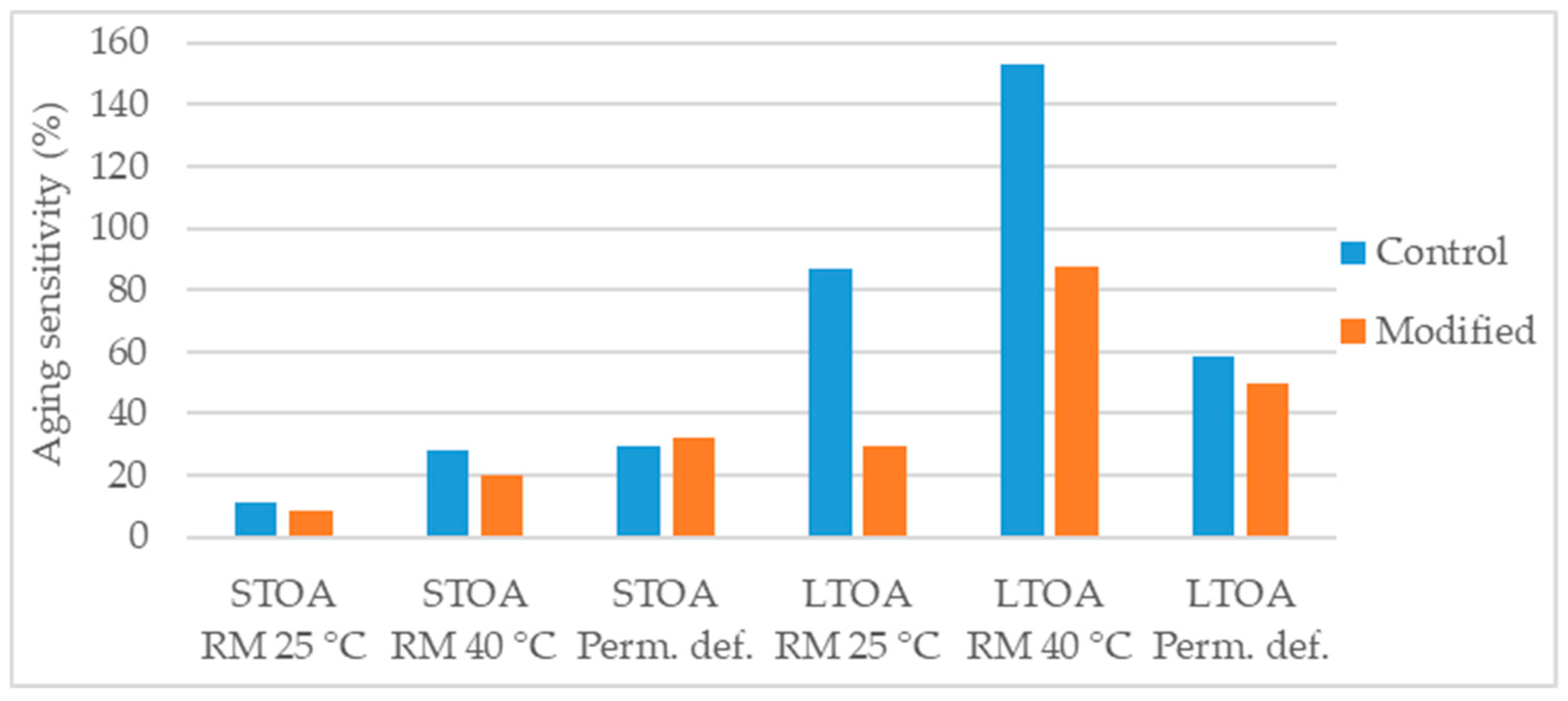
Yusoff et al. [58] aged the asphalt mixture using STOA and LTOA methods and, tested aged specimens for resilient modulus (RM) at 25 °C and 40 °C, and permanent deformation using the dynamic creep test. The authors found that the 4% nanosilica modification provided some aging resistance particularly at the long-term aging. Figure 15 presents the aging sensitivity of the parameters considered by the authors and under both aging methods.
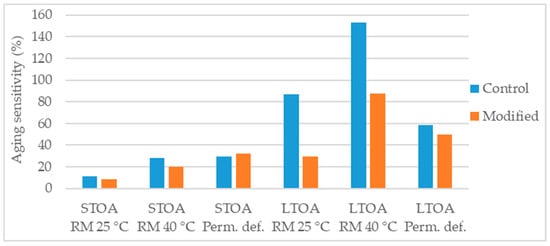
Figure 15.
Aging sensitivity of the parameters considered in the study [58].
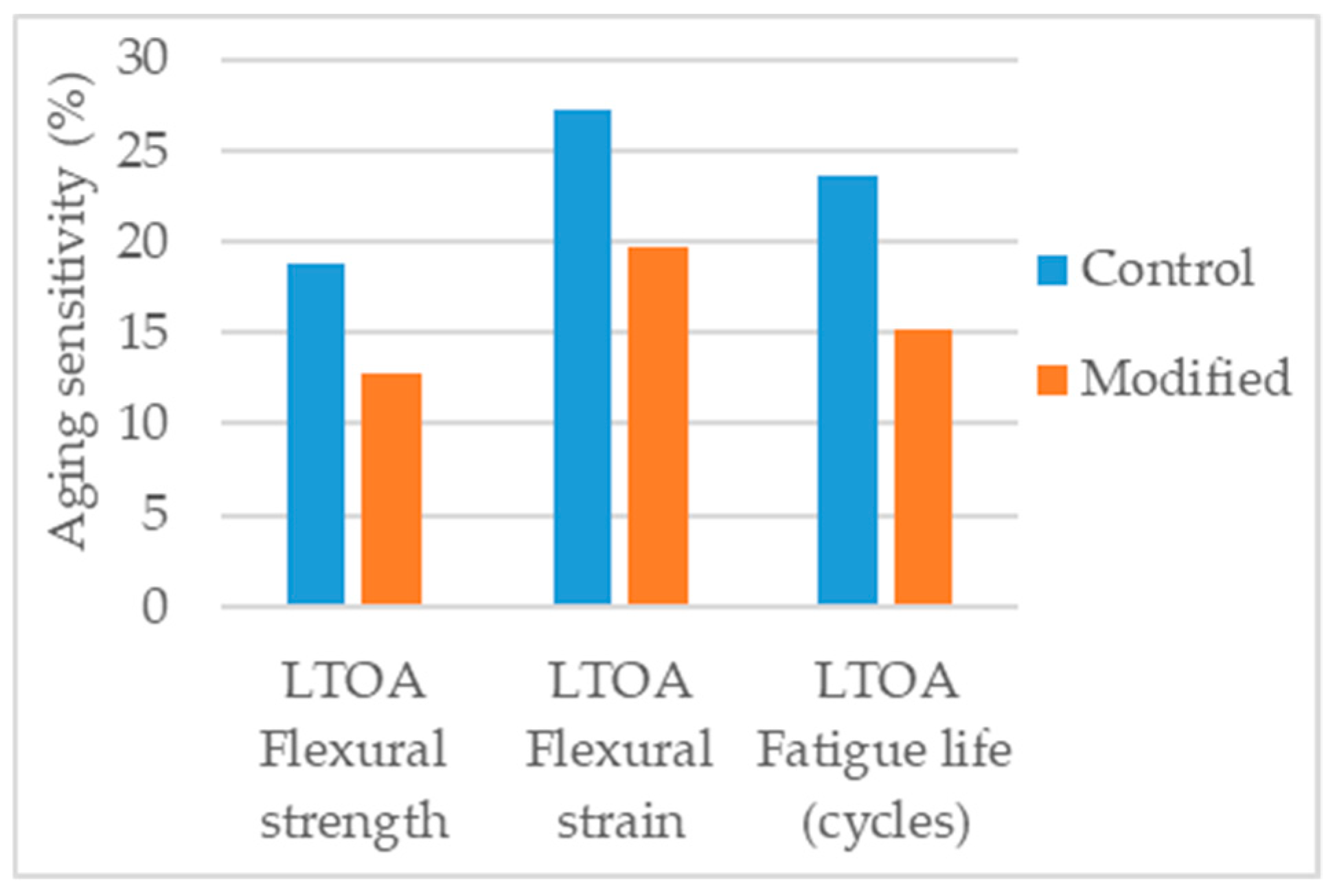
Cai et al. [24] produced LTOA aged specimens and conducted flexural tensile strength tests (three-point bending at −10 °C) and fatigue tests (four-point bending at 1000 µm/m constant strain). To study the effects of aging the authors compared the results of flexural strength, flexural strain, and fatigue life of the unaged and LTOA aged specimens and, concluded that the 1% nanosilica modification had a positive effect in aging resistance. Figure 16 presents the aging sensitivity of the parameters considered.
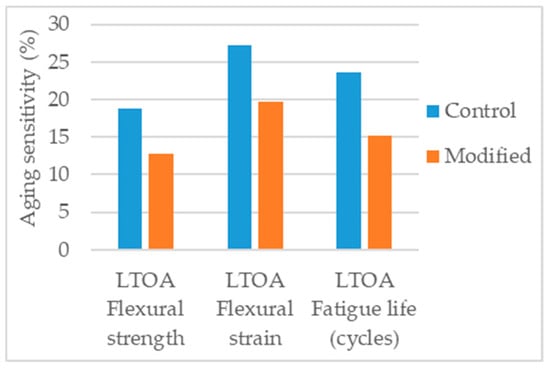
Figure 16.
Aging sensitivity of the parameters considered in the study [24].
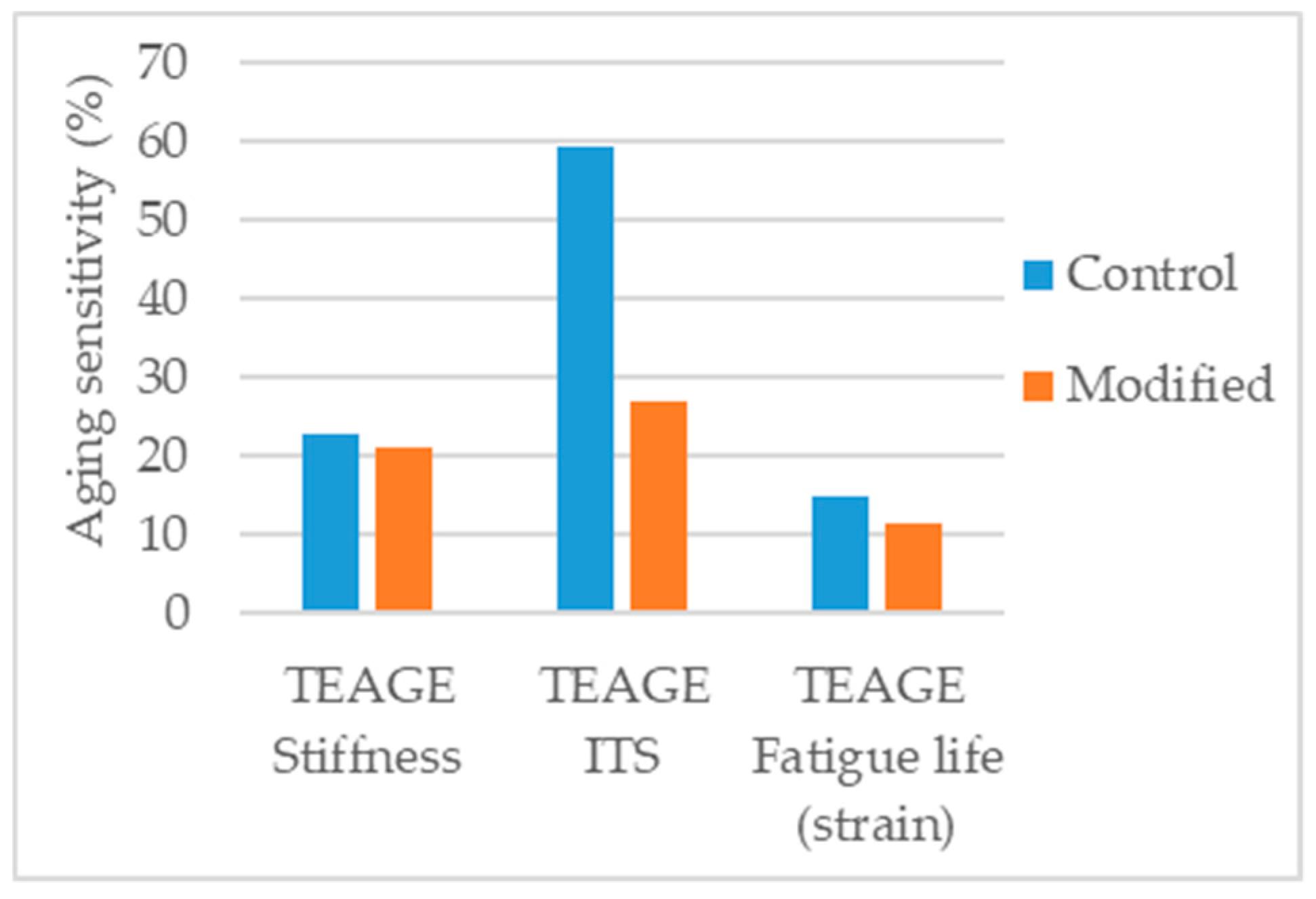
Crucho et al. [131] studied the effects of aging in the asphalt mixture using the TEAGE method [132], tuned to simulate seven years of field aging due to environmental conditions (UV radiation and precipitation) in the region of Lisbon. The aged mixtures were tested for indirect tensile strength (ITS), stiffness modulus, and fatigue, and the results were compared with those obtained under unaged conditions. The 4% nanosilica modified mixture presented lower aging sensitivity in all parameters, indicating an enhanced aging resistance (Figure 17).
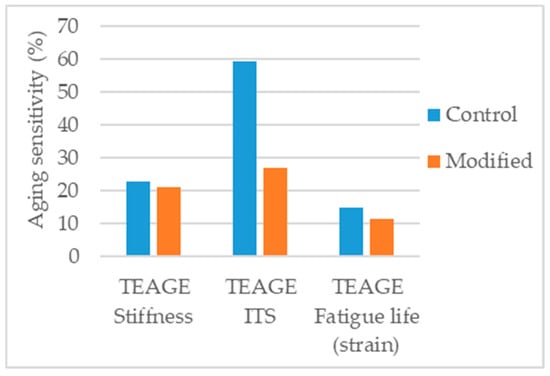
Figure 17.
Aging sensitivity of the parameters considered in the study [131].
Guo et al. [62] produced STOA aged specimens and compared their performance to that of unaged specimens. The authors evaluated the retained Marshall stability (RMS), using two conditioning methods: (1) 48 h immersion (IM) and (2) 48 h vacuum saturation (VS), and the tensile strength ratio (TSR). Analyzing the aging sensitivity of these parameters (Figure 18) it can be concluded that the modified mixture (3% silane silica) suffered less variation in these ratios. This indication is positive, although would be not sufficient to property conclude about aging resistance, as it would be possible that both specimens conditioned/unconditioned suffer intense aging thus maintaining approximately similar ratio under aged and unaged conditions. The analysis of Marshall stability or indirect tensile strength would be preferable.
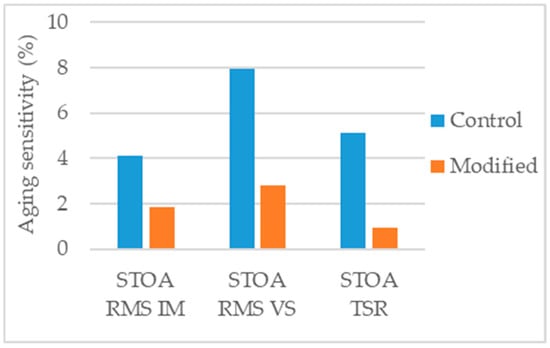
Figure 18.
Aging sensitivity of the parameters considered in the study [62].
Tanzadeh et al. [98] evaluated the abrasion of a porous asphalt mixture (NMAS 12.5 mm), under aged and unaged conditions, using the Cantabro test. The asphalt mixtures were produced with limestone aggregates, limestone filler, lime (0.5% by weight of mixture), and 60/70 asphalt binder modified with 4.5% SBS. The binder contents of the asphalt mixture were 5% and 6%. The authors used 0.2% glass fiber and 0.2 basalt fiber to modify the asphalt mixture and, following, studied the modification with 2% nanosilica. The specimens were conditioned for aging in a draft oven at 60 °C for seven days. In the mixture with 0.2% glass fiber, the modification with 2% nanosilica presented a reduction in Cantabro loss from 10.1% (control) to 4.4% (modified) and, from 7.7% (control) to 3.5% (modified), for binder content of 5% and 6%, respectively. In the mixture with 0.2% basalt fiber, the modification with 2% nanosilica presented a reduction in Cantabro loss from 10.7% to 5.5% and, from 8.9% to 4.7%, for binder content of 5% and 6%, respectively.
Under a variety of mechanical tests and aging methods, the asphalt mixtures modified with nanosilica presented systematically lower aging sensitivity if compared to the correspondent control mixture, indicating enhanced aging resistance.
5.2.3. Nanoclay
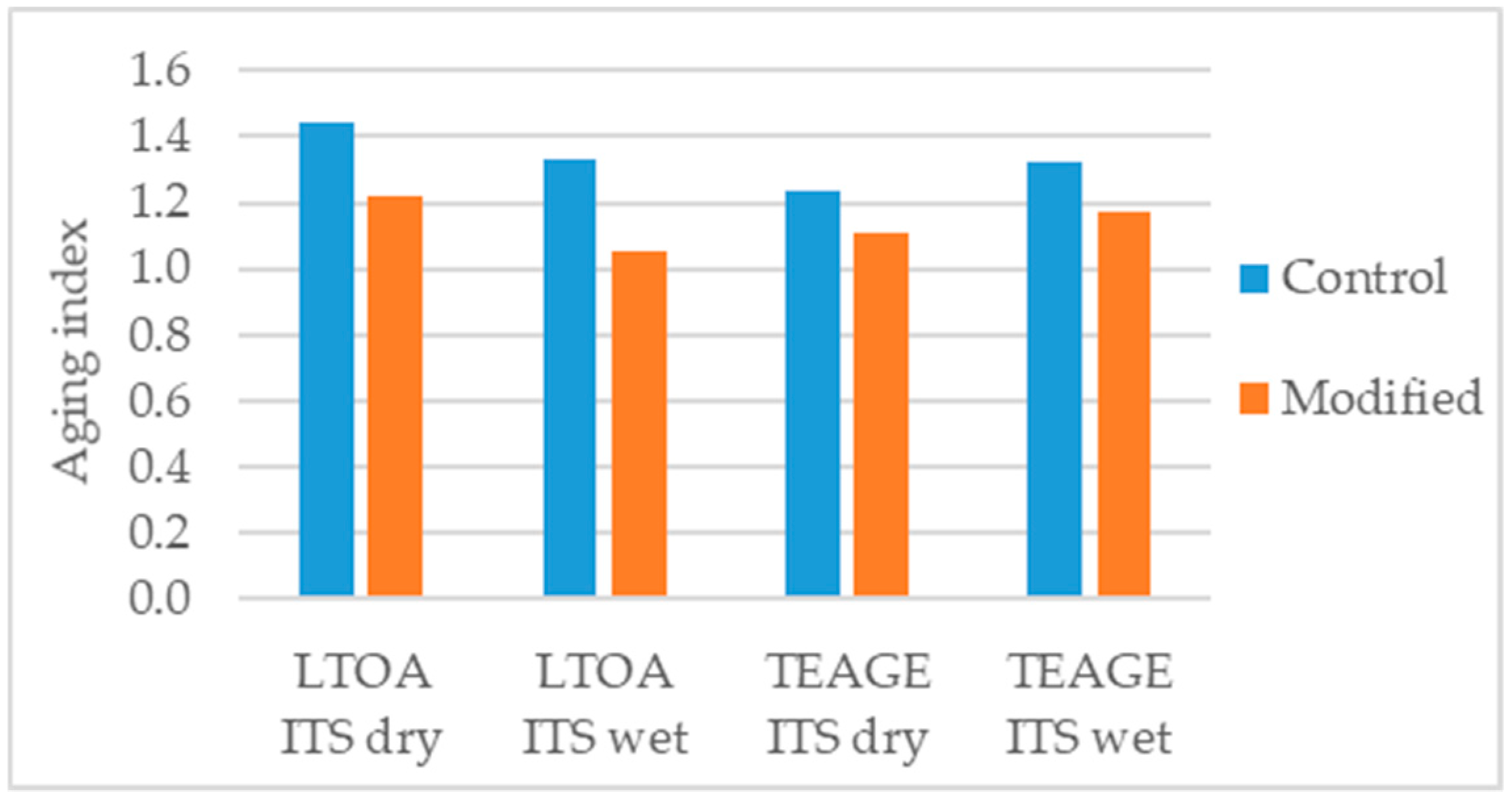
López-Montero et al. [100] studied the effects of aging in the indirect tensile strength (ITS), in dry and wet (water sensitivity conditioned) conditions, of the asphalt mixture using the LTOA and TEAGE methods. The TEAGE method [132] was used to simulate seven years of field aging in the region of Lisbon. The authors determined an aging index, ratio between aged, and unaged values, and concluded that for both conditions, dry and wet, and under both aging methods, LTOA and TEAGE, the modification with 4% nanoclay bentonite presented less aging (Figure 19).
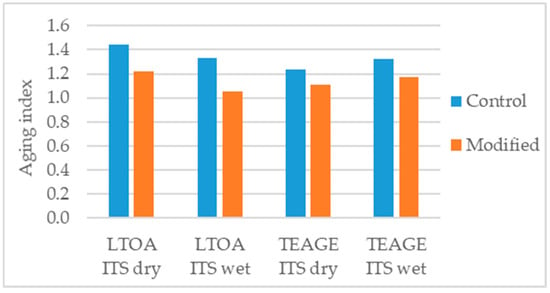
Figure 19.
Aging index of the parameters considered in the study [100].
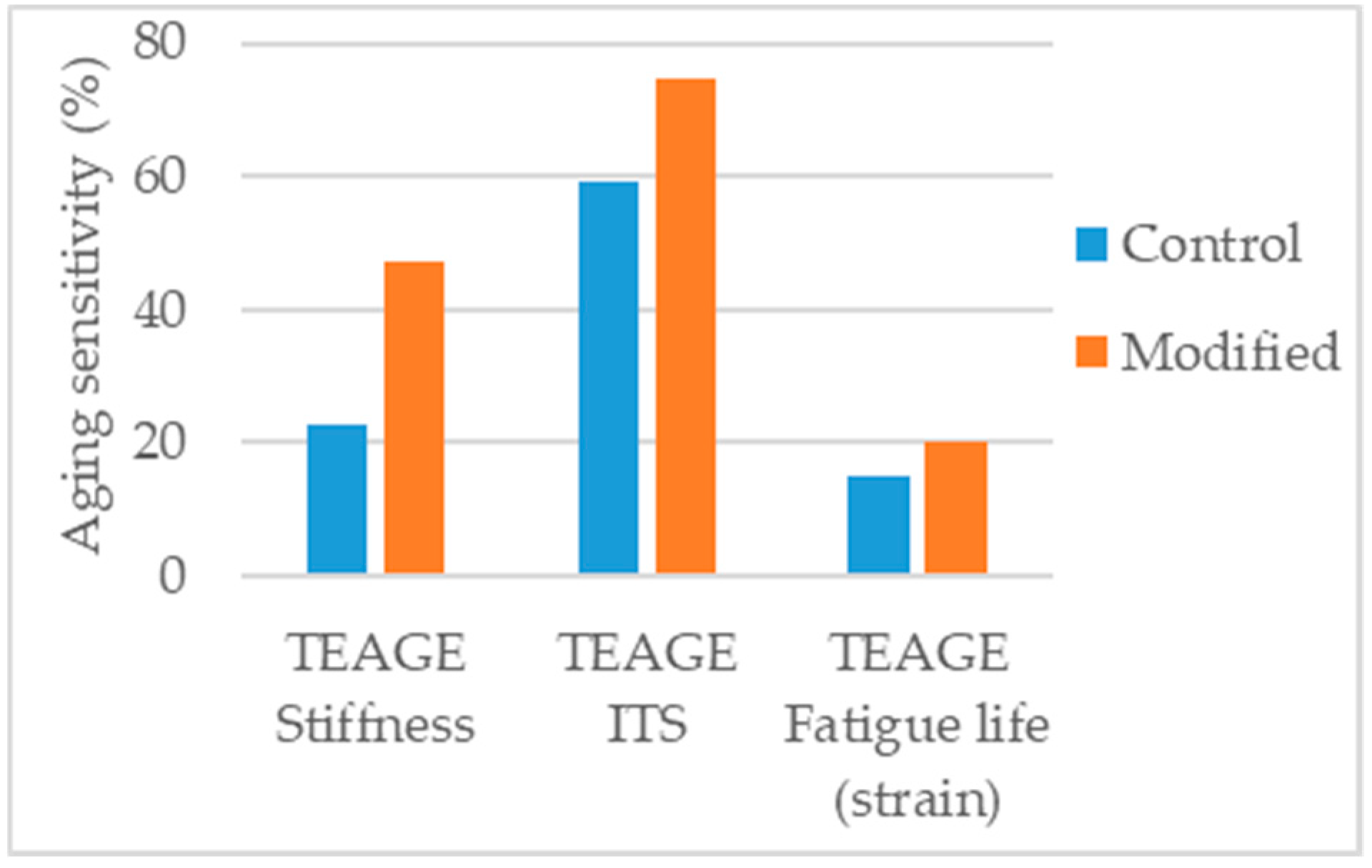
Crucho et al. [131] studied the effects of aging in an asphalt mixture modified with 4% nanoclay bentonite, using the TEAGE method, tuned to simulate seven years of field aging in the region of Lisbon. The aged mixtures were tested for indirect tensile strength, stiffness modulus and fatigue. The modified mixture presented lower aging sensitivity in indirect tensile strength and fatigue resistance, and higher in the case of stiffness modulus. Nevertheless, as fatigue resistance is the most critical parameter under aged conditions, the results are a positive indication of enhanced aging resistance (Figure 20).
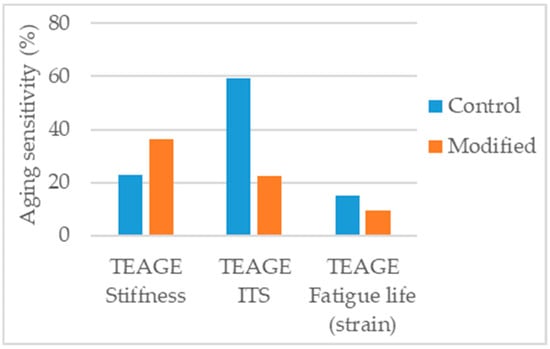
Figure 20.
Aging sensitivity of the parameters considered in the study [131].
The number of studies about the effects of nanoclay modification in the aging of asphalt mixtures is still limited. Nevertheless, the results found in literature gave a positive indication of enhanced aging resistance, as in most cases, the asphalt mixtures modified with nanoclay presented lower aging sensitivity if compared to the correspondent control mixture.
5.2.4. Nanoiron
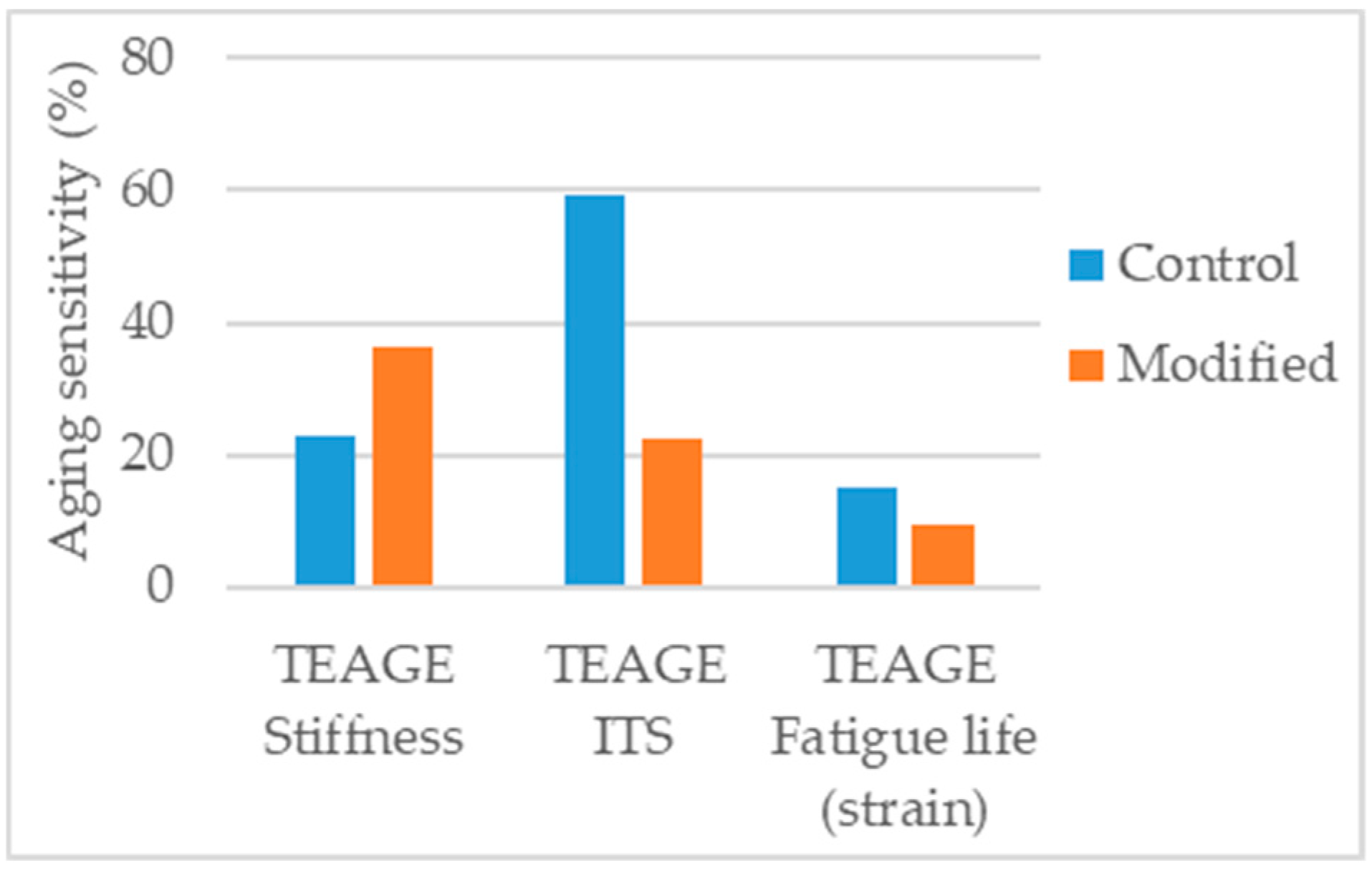
Crucho et al. [131] studied the effects of aging in an asphalt concrete mixture modified with 4% nanoiron. The TEAGE [132] method was used to simulate seven years of field aging in the region of Lisbon. The aged mixtures were tested for stiffness modulus, indirect tensile strength, and fatigue resistance. If compared with the control asphalt mixture the nanoiron-modified mixture presented higher aging sensitivity in all the parameters considered (Figure 21). Nevertheless, it is not possible to conclude immediately that nanoiron has a negative effect in the aging resistance of the asphalt mixture. As this is the only study found in literature addressing nanoiron-modified aged asphalt mixture, more studies are needed to validate these findings. Other studies [49,50] that determined the optimum nanoiron (Fe2O3) dosage using mechanical performance tests, indicated the optimum dosage to be 0.8% to 0.9% and, further increase in dosage worsened the performance. Although in the study of Crucho et al. [131] the used nanoparticles were different (zero-valent iron), this is a strong indication that the dosage considered (4%) is too high, beyond the optimum.
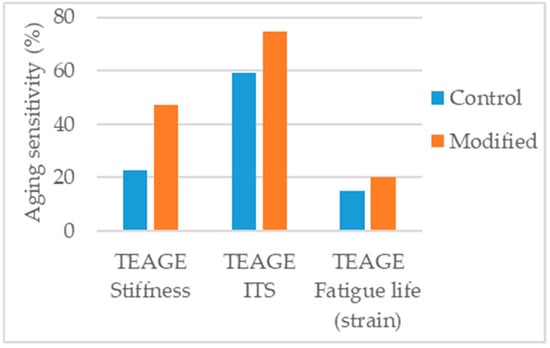
Figure 21.
Aging sensitivity of the parameters considered in the study [131].
6. Cost Evaluation
Asphalt pavement construction deals with large quantities of materials, in the range of tons, contrasting with the nanotechnology that synthetizes and manipulates few grams of a specific material. As the production of nanomaterials is oriented to deliver small quantities of highly controlled materials, i.e., purity levels ≥98%, the cost of these materials is relatively high compared to traditional paving materials. The costs are justified by the use of expensive equipment and technology involved, as well as, the fact that nanomaterials production is generally conducted by highly qualified personal. However, this cost has been decreasing over time and, the trend is for further decrease, pushed by an increasing demand and improvements in manufacturing technology.
Generally, due to the costs associated with their synthesis, the price of the nanomaterials are highly dependent on the particle’s size range and specific surface area. Products with high purity and narrow size range and high specific surface may demand higher processing efforts, thus having higher final costs.
The prices for nanosilica particles can vary from 80 €/kg to 1500 €/kg. The products with smaller size and narrow range (5 nm to 20 nm) and high specific surface (up to 690 m2/g) can cost between 1000 €/kg and 1500 €/kg. On the other side, particles with a wider size range (15 nm to 70 nm) and higher variation on specific surface area (130 m2/g to 600 m2/g) can cost between 80 €/kg to 150 €/kg. Further modifications of the nanosilica, for example with silane coupling agents, also brings an increase to the costs. Silane modified silica nanoparticles can cost between 180 €/kg to 450 €/kg.
Currently, the commercial price of nanoclays ranges from 100 €/kg to 250 €/kg, depending on the particle size and types of treatment/modification. Organically modified nanoclays are more expensive due to the additional surface treatment process. On the other side, raw nanoclays with natural hydrophilic behavior are cheaper.
The prices of nanoiron particles are in the range of 100 €/kg to 2600 €/kg. Costs are dependent on purity level and size range. Nanoparticles of Fe2O3 with average size 50 nm and purity around 98% cost can cost between 100 €/kg to 300 €/kg. The most expensive iron nanoparticles are 99.9% 5 nm Fe2O3. The zero-valent nanoiron (50 nm) can cost nearly 120 €/kg.
The framework provided by Martinho et al. [137] was considered to perform a simple cost analysis regarding the construction of a 5 cm thick asphalt concrete (AC14 surf 35/50) wearing course. Using conventional materials (unmodified asphalt binder) the estimated cost was 6.8 €/m2. Regarding the nanomodified binders, the cost where estimated using the costs of the respective raw materials but not accounting with the possible costs of technology implementation for industrial scale refinery- or plan-modification. Considering the available nanosilica with the lower cost, the asphalt mixture cost was estimated to be 21.0 €/m2, 44.7 €/m2 and 38.9 €/m2 for the modifications with 3% nanosilica, 8% nanosilica, and 3% silane-nanosilica, respectively. The cost for nanoclay modifications was estimated to be 25.4 €/m2 and 51.4 €/m2, when using 3% non-modified nanoclay and 3% organically modified nanoclay (modified with quaternary ammonium), respectively. The cost for nanoiron modifications were estimated in 12.1 €/m2 and 35.3 €/m2 for the modifications with 0.9% nano-Fe2O3 and 4% nano zero-valent iron.
The low dosage required by the nano-Fe2O3 modification indicated that it is competitive from the economic point of view. Regarding the group of the most studied nanomaterials, nanosilica, and nanoclays, the cost analysis suggests that nanosilica may be more promising as it had the lowest cost. Nevertheless, the three-fold increase in cost might be justified by the improvements obtained in mechanical performance and aging resistance. At current prices, for the nanomodifications to be cost effective, a significant improvement in durability has to be attained. It is expected that the production of nanoparticles in bulk quantity and the use of alternative sources will significantly reduce the costs. For example, rice husk, an abundant waste biomass with high content of silica was identified as a potential low-cost resource for the production of nanosilica particles [138].
7. Concluding Remarks
This review addressed the effects of the modifications with nanomaterials: Nanosilica, nanoclay, and nanoiron, on the mechanical properties of the asphalt mixtures. The studies about modification of asphalt binders with nanomaterials showed that if a correct dispersion of the nanomaterials in the asphalt matrix is attained, several properties can be improved. Regarding the properties of the asphalt binders, the modifications with nanomaterials brought a reduction in penetration value and an increase of viscosity and softening point, as well as, increase in complex modulus and a decrease in phase angle. The effects of the modifications are dependent on the type and dosage of the nanomaterial, as well as, on the properties of the original asphalt binder to be modified. The optimum nanomaterial dosage may be dependent on the mechanical property to be enhanced, as well as the cost of the modification. For example, softer binders attained higher gains in resistance to permanent deformation with the nanomaterials modification than harder binders.
The effects of the nanomaterial modifications in the properties of the asphalt mixtures conducted to similar trends than for binders, meaning that the consideration of the type of modification is connected to the goal in terms of performance achieved for the best cost. The review carried out allows for the following conclusions:
- For asphalt mixtures, the modifications with nanosilica present higher Marshall stability, higher indirect tensile strength, higher stiffness modulus, lower permanent deformation, enhanced fatigue resistance, and higher resistance to moisture damage. The studies found in literature covered the dosage range of 0.5% to 8%, and the effects of the modifications increase according with the increase in dosage. Nevertheless, the cost of the modification should be taken into account, as the use of high dosages can return not economical.
- The effects of the modifications with nanoclays were dependent of the type of nanoclay. Besides the particle size distribution and the specific surface area, the type of treatment, raw (hydrophilic) or organically modified (hydrophobic), can have particular importance in the obtained effects. Generally, the effects of nanoclays modifications are higher Marshall stability, lower permanent deformation, higher stiffness modulus at high temperatures, better fatigue resistance, and higher resistance to moisture damage. The studies found in literature covered the dosage range of 1% to 7% and, the effects of the modifications increase according with the increase in dosage. Nevertheless, in the case of some organically modified nanoclays, the performance enhancement peaked at relatively low dosages (e.g. 2%) and a further increase in dosage worsened the performance. As the cost of organically modified nanoclays can be roughly double the cost of raw nanoclay, the use of such modifications should be careful optimized to ensure maximum performance with lowest dosage possible.
- Currently, the modifications with nanoiron are not as explored as those with nanosilica and nanoclays, nevertheless, several studies reported important improvements in the mechanical performance of the modified asphalt mixture, such as, higher Marshall stability, higher indirect tensile strength, higher resistance to moisture damage, lower permanent deformation, enhanced fatigue resistance, and fracture resistance. The optimum dosage of nanoiron particles seems to be in the range of 0.8% to 0.9%, where the performance gains peak and, further increase in dosage worsens the performance. Comparatively to other nanomaterials, the lower optimum dosage of nanoiron particles can make them more competitive from economic point of view.
- Besides the improvements in mechanical performance, the nanomaterials also gave good indications regarding an enhanced aging resistance. The study of the properties of aged asphalt mixtures highlighted the full potential of the nanomaterials and this is a good inference regarding the necessary life cycle cost evaluation in order to achieve a good balance between direct construction costs, high for now due to the use of nanomaterials, and the long term effect on durability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and L.P.-S.; methodology, J.C., L.P.-S., J.N. and S.C.; validation, J.C. and L.P.-S.; formal analysis, J.N. and S.C.; investigation, J.C., J.N. and S.C.; resources, L.P.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; writing—review and editing, J.C. and L.P.-S.; supervision, L.P.-S., J.N. and S.C.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hunter, R.N.; Self, A.; Read, J. The Shell Bitumen Handbook, 6th ed.; Shell Bitumen by ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Carraher, C.E., Jr. Seymour/Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry, 6th ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Erkens, S.; Porot, L.; Glaser, R.; Glover, C.J. Aging of Bitumen and Asphalt Concrete: Comparing State of the Practice and Ongoing Developments in the United States and Europe. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 95th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolidis, P.; Liu, X.; Kasbergen, C.; Scarpas, T.A. Synthesis of Asphalt Binder Aging and the State-of-the-Art of Anti-aging Technologies. Transp. Res. Rec. 2017, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Teltayev, B.; Oliviero Rossi, C. Bitumen and Bitumen Modification: A Review on Latest Advances. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Commission. EC Commission Recommendation of 18 October 2011 on the definition of nanomaterial (2011/696/EU). Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L 275, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM E2456-06. Standard Terminology Relating to Nanotechnology; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Donegá, C.D.M. (Ed.) The Nanoscience Paradigm: “Size Matters!”. In Nanoparticles: Workhorses of Nanoscience; Spinger: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Steyn, W.J. Applications of Nanotechnology in Road Pavement Engineering. In Nanotechnology in Civil Infrastructure; Gopalakrishnan, K., Birgisson, B., Taylor, P., Attoh-Okine, N.O., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 48–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, H.; El-Badawy, S.; Gabr, A.; Zaki, E.-S. Evaluation of asphalt enhanced with locally made nanomaterials. Nanotechnologies Constr. 2016, 8, 42–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvakkumar, R.; Elango, V.; Rajendran, V.; Kannan, N. High-purity nano silica powder from rice husk using a simple chemical method. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2014, 9, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, T.H.; Yang, C.C. Synthesis and surface characteristics of nanosilica produced from alkali-extracted rice husk ash. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2011, 176, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana Costa, J.A.; Paranhos, C.M. Systematic evaluation of amorphous silica production from rice husk ashes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, B.; Gao, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. A recyclable method for production of pure silica from rice hull ash. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoohinkong, W.; Kitthawee, U. Low-Cost and Fast Production of Nano-Silica from Rice Husk Ash. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 979, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosa, A.A.; Saddam, B.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanosilica from Rice Husk with Applications to Polymer Composites. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 7, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Karnati, S.R.; Oldham, D.; Fini, E.H.; Zhang, L. Surface functionalization of silica nanoparticles to enhance aging resistance of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafabakhsh, G.H.; Ani, O.J. Experimental investigation of effect of Nano TiO2/SiO2 modified bitumen on the rutting and fatigue performance of asphalt mixtures containing steel slag aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaninia, M.; Haddadi, F. Studying Engineering Characteristics of Asphalt Binder and Mixture Modified by Nanosilica and Estimating Their Correlations. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaninia, M.; Haddadi, F. The characteristics of hot mixed asphalt modified by nanosilica. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Marandi, S.M.; Tahmooresi, M.; Kamali, R.J.; Taherzade, R. Modification of Stone Matrix Asphalt with Nano-SiO2. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; You, Z.; Li, L.; Lee, C.H.; Wingard, D.; Yap, Y.K.; Shi, X.; Goh, S.W. Rheological Properties and Chemical Bonding of Asphalt Modified with Nanosilica. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzadeh, J.; Shahrezagamasaei, R. Laboratory Assessment of Hybrid Fiber and Nano-silica on Reinforced Porous Asphalt Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shi, X.; Xue, J. Laboratory evaluation of composed modified asphalt binder and mixture containing nano-silica/rock asphalt/SBS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.; Neves, J.; Capitão, S.; Picado-Santos, L. Mechanical performance of asphalt concrete modified with nanoparticles: Nanosilica, zero-valent iron and nanoclay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-K. US 2010/0187474 A1–Pure Nanoclay and Process for Preparing Nanoclay; Patent Application Publication: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, H.; El-badawy, S.; Gabr, A.; Zaki, E.I.; Breakah, T. Evaluation of Asphalt Binders Modified with Nanoclay and Nanosilica. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolinski, M. Additives for Polyolefins, 2nd ed.; William Andrew Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, A.; Jung de Andrade, M.; Sánchez, F.A.L.; Takimi, A.S. Use of Natural and Modified Natural Nanostructured Materials. In Nanostructured Materials for Engineering Applications; Pérez Bergmann, C., Jung de Andrade, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, T.Z. Occurrence of Nanomaterials in the Environment. In Nanomaterials in the Environment; Brar, S.K., Zhang, T.C., Verma, M., Surampalli, R.Y., Tyagi, R.D., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VR, USA, 2015; pp. 179–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ghile, D.B. Effects of Nanoclay Modification on Rheology of Bitumen and on Performance of Asphalt Mixtures. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Mekelweg, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha Ray, S.; Okamoto, M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: A review from preparation to processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1539–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albdiry, M.T.; Yousif, B.F.; Ku, H.; Lau, K.T. A critical review on the manufacturing processes in relation to the properties of nanoclay/polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 47, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, S.G.; Khodaii, A. Effects of nanoclay on rheological properties of bitumen binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2894–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, J.V.S.; Trichês, G. Evaluation of properties and fatigue life estimation of asphalt mixture modified by organophilic nanoclay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.M.L. Development of an Accelerated Asphalt Concrete Aging Method and Utilization of Nano-Modifiers to Improve Durability of Asphalt Concrete. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Crucho, J.; Neves, J.; Capitão, S.; Picado-Santos, L. Experimental study about the effects of the modification with nanoclay on the properties of a SMA mixture. In Proceedings of the TEST&E 2019–2° Congress, Porto, Portugal, 19–21 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; You, Z.; Li, L.; Shi, X.; Goh, S.W.; Mills-beale, J.; Wingard, D. Performance of asphalt binder blended with non-modified and polymer-modified nanoclay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestani, B.; Nam, B.H.; Moghadas Nejad, F.; Fallah, S. Nanoclay application to asphalt concrete: Characterization of polymer and linear nanocomposite-modified asphalt binder and mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, E. Evaluation of mechanical properties of nano-clay modified asphalt mixtures. Measurement 2016, 93, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare-shahabadi, A.; Shokuhfar, A.; Ebrahimi-Nejad, S. Preparation and rheological characterization of asphalt binders reinforced with layered silicate nanoparticles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zeng, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, G. Preparation and properties of montmorillonite modified asphalts. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.W.; Akin, M.; You, Z.; Shi, X. Effect of deicing solutions on the tensile strength of micro- or nano-modified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tan, L.; Tsang, E.P. Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using Citrus maxima peels aqueous extracts. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tsang, E.P. Biosynthesized iron nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and its mechanism in the hexavalent chromium removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza, S.; Corea, M.; Gómez-Yáñez, C.; Cruz-Rivera, J.J.; Navarro-Clemente, M.E. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles preparation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C. Characterization of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced with tree leaf extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordi, Z.; Shafabakhsh, G. Evaluating mechanical properties of stone mastic asphalt modified with Nano Fe2O3. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmohammad, S.; Majd-Shokorlou, Y.; Amani, B. Experimental investigation of fracture properties of asphalt mixtures modified with Nano Fe2O3 and carbon nanotubes. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, F.C.G.; Farinha, J.P.S. An overview of the use of nanoclay modified bitumen in asphalt mixtures for enhanced flexible pavement performances. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.; You, Z.; Huang, J. Developments of nano materials and technologies on asphalt materials—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 143, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, R.; Liu, S.; Li, Y. Nanomaterials applied in asphalt modification: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tighe, S. A Review of Advances of Nanotechnology in Asphalt Mixtures. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 96, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Mills-Beale, J.; Foley, J.M.; Roy, S.; Odegard, G.M.; Dai, Q.; Goh, S.W. Nanoclay-modified asphalt materials: Preparation and characterization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Aryana, S.; Han, Y.; Jiao, Y. A Review of the Synthesis and Applications of Polymer–Nanoclay Composites. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, G.; Filippi, S.; Merusi, F.; Stastna, G. A review of the fundamentals of polymer-modified asphalts: Asphalt/polymer interactions and principles of compatibility. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 224, 72–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusoff, N.I.M.; Breem, A.A.S.; Alattug, H.N.M.; Hamim, A.; Ahmad, J. The effects of moisture susceptibility and ageing conditions on nano-silica/polymer-modified asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 72, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, E.; Baglieri, O.; Tsantilis, L.; Chiappinelli, G.; Aimonetto, I.B. Effect of sonication on high temperature properties of bituminous binders reinforced with nano-additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, J.V.S.; Trichês, G.; de Rosso, L.T. Experimental evaluation of the influence of reinforcement with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) on the properties and fatigue life of hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantilis, L.; Baglieri, O.; Santagata, E. Low-temperature properties of bituminous nanocomposites for road applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, M.; Dai, W.; Chen, S. Performance characteristics of silane silica modified asphalt. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, J.; Kamal, M.; Ahmad, N.; Hafeez, M.; Faizan ul Haq, M.; Aamara Asif, S.; Shabbir, F.; Bilal Ahmed Zaidi, S. Performance Evaluation of Carbon Black Nano-Particle Reinforced Asphalt Mixture. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, F.M.; Nazari, H.; Naderi, K.; Karimiyan Khosroshahi, F.; Hatefi Oskuei, M. Thermal and rheological properties of nanoparticle modified asphalt binder at low and intermediate temperature range. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Ahmad, N.; Nasir, M.; Jamal; Hafeez, M.; Rafi, J.; Zaidi, S.; Haroon, W. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) in Asphalt Binder: Homogeneous Dispersion and Performance Enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, M.; Arabani, M.; Haghi, A.K.; Mottaghitalab, V. Carbon nanotubes-modified asphalt binder: Preparation and characterization. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2015, 8, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, M.J.; Khattab, A.; Rizvi, H.R.; Zhang, P. The impact of carbon nano-fiber modification on asphalt binder rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standardization. EN 13399. Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Determination of Storage Stability of Modified Bitumen; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM D5892-00. Standard Specification for Type IV Polymer-Modified Asphalt Cement for Use in Pavement Construction; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Santagata, E.; Baglieri, O.; Tsantilis, L.; Chiappinelli, G. Storage Stability of Bituminous Binders Reinforced with Nano-Additives. In 8th RILEM International Symposium on Testing and Characterization of Sustainable and Innovative Bituminous Materials; Canestrari, F., Partl, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, K.T. Nanomaterials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grassian, V.H.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Pettibone, J.M.; Thorne, P.S. Inhalation exposure study of Titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a primary particle size of 2 to 5 nm. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. A Research Strategy for Environmental, Health, and Safety Aspects of Engineered Nanomaterials; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, A.; Luch, A. Genotoxicity of nanomaterials in vitro: Treasure or trash? Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2827–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramachandran, G.; Ostraat, M.; Evans, D.E.; Methner, M.M.; O’Shaughnessy, P.; D’Arcy, J.; Geraci, C.L.; Stevenson, E.; Maynard, A.; Rickabaugh, K. A strategy for assessing workplace exposures to nanomaterials. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2011, 8, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tahri, O. State-of-art carbon and graphene family nanomaterials for asphalt modification. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, E.; Hajikarimi, P.; Rahi, M.; Nejad, F.M. Physiochemical, Rheological, and Oxidative Aging Characteristics of Asphalt Binder in the Presence of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamali, D.I.; Yusoff, N.I.; Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Albrka, S.I. The Effects of Nano Silica Particles on the Physical Properties and Storage Stability of Polymer-Modified Bitumen. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2015, 5, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onochie, A.; Fini, E.; Yang, X.; Mills-Beale, J.; You, Z. Rheological Characterization of Nano-particle based Bio-modified Binder. Transp. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 92nd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi-Sevilla, A.; Montero, M.L.; Aguiar-Moya, J.P.; Loría, L.G. Influence of nanosilica and diatomite on the physicochemical and mechanical properties of binder at unaged and oxidized conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, H.; Naderi, K.; Moghadas Nejad, F. Improving aging resistance and fatigue performance of asphalt binders using inorganic nanoparticles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Pourjafar, S. Optimization of Asphalt Binder Modified with PP/SBS/Nanoclay Nanocomposite using Taguchi Method. Int. Sch. Sci. Res. Innov. 2012, 6, 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.E.; Zamhari, K.A.; Hainin, M.R.; Oluwasola, E.A.; Hassan, N.A.; Yusoff, N.I.M. Engineering properties of asphalt binders containing nanoclay and chemical warm-mix asphalt additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Tao, Y. Effect of Various Organomodified Montmorillonites on the Properties of Montmorillonite/Bitumen Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, E.; Baglieri, O.; Tsantilis, L.; Chiappinelli, G. Effects of Nano-sized Additives on the High-Temperature Properties of Bituminous Binders: A Comparative Study. In Multi-Scale Modeling and Characterization of Infrastructure Materials, RILEM 8; Kringos, N., Birgisson, B., Frost, D., Wang, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 297–309. [Google Scholar]
- Mills-Beale, J.; You, Z. Nanoclay-Modified Asphalt Binder Systems. In Nanotechnology in Civil Infrastructure; Gopalakrishnan, K., Birgisson, B., Taylor, P., Attoh-Okine, N.O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Siddig, E.A.A.; Feng, C.P.; Ming, L.Y. Effects of ethylene vinyl acetate and nanoclay additions on high-temperature performance of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestani, B.; Moghadas Nejad, F.; Sadeghpour Galooyak, S. Performance evaluation of linear and nonlinear nanocomposite modified asphalts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, G.; Kříž, P.; Filippi, S.; Stastna, J.; Biondi, D.; Zanzotto, L. Rheological properties of asphalt/SBS/clay blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 3512–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Katti, D.R.; Ghavibazoo, A.; Upadhyay, H.B.; Katti, K.S. Engineering physical properties of asphalt binders through nanoclay-asphalt interactions. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; You, Z.; Li, L.; Goh, S.W.; Lee, C.H.; Yap, Y.K.; Shi, X. Rheological properties and chemical analysis of nanoclay and carbon microfiber modified asphalt with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; You, Z.; Li, L.; Shi, X.; Hansen, M. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Mixtures Blended by Nonmodified Nanoclay and Polymer-Modified Nanoclay. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 92nd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw, S.A.; Kemmitt, T.; Waterland, M.; Brooke, S. Effect of blending conditions on nano-clay bitumen nanocomposite properties. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedafa, D.S.; Landrus, D.; Suleiman, N. Effect of Nanoclay on Binder Rheology and Rutting Resistance of HMA Mixes. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 96nd Annual, Washington, DC, USA, 8–12 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Burguete, L.M. Contribuition to the study of bituminous mixtures with nanomaterials (in Portuguese). Master’s Thesis, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Xin, X.; Ren, J. Asphalt modification using nano-materials and polymers composite considering high and low temperature performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, H.; El-Badawy, S.; Gabr, A.; Zaki, S.; Breakah, T. Predicted performance of hot mix asphalt modified with nano-montmorillonite and nano-silicon dioxide based on Egyptian conditions. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzadeh, R.; Tanzadeh, J.; honarmand, M.; Tahami, S.A. Experimental study on the effect of basalt and glass fibers on behavior of open-graded friction course asphalt modified with nano-silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, M.; Besamusca, J.; Molenaar, A. Nanoclay for binder modification of asphalt mixtures. In Proceedings of the 7th International RILEM Symposium ATCBM09–Advanced Testing and Characterization of Bituminous Materials, Rhodes, Greece, 27–29 May 2009; Loizos, A., Partl, M.N., Scarpas, T., Al-Qadi, I.L., Eds.; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Montero, T.; Crucho, J.; Picado-Santos, L.; Miró, R. Effect of nanomaterials on ageing and moisture damage using the indirect tensile strength test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, J.; de Kinder, B.; Meeusen, J.; Van den bergh, W. The influence of nanoclay on the durability properties of asphalt mixtures for top and base layers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 236, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X. Impact of nanoclay and carbon microfiber in combating the deterioration of asphalt concrete by non-chloride deicers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, S.G.; Andalibizade, B.; Vossough, S. Engineering properties of nanoclay modified asphalt concrete mixtures. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2010, 35, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Vamegh, M.; Molayem, M. Evaluation the effects of nanoclay on permanent deformation behavior of stone mastic asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standardization. EN 12591:2009. Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Specifications for Paving Grade Bitumens; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. AASHTO M320-10. Standard Specification for Performance-Graded Asphalt Binder; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Galooyak, S.S.; Dabir, B.; Nazarbeygi, A.E.; Moeini, A.; Berahman, B. The Effect of Nanoclay on Rheological Properties and Storage Stability of SBS-Modified Bitumen. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, L.M.J.; Muniandy, R.; Yunus, R.B.; Hasham, S.; Aburkaba, E. Effect of Short Term Aging on Organic Montmorillonite Nanoclay Modified Asphalt. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 5434–5442. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.Y.; Feng, P.C.; Zhang, H.L.; Wu, S.P. Effect of organo-montmorillonite on aging properties of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2636–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, C. Properties of Bitumen Containing Various Amounts of Organic Montmorillonite. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, P.K.; Singh, D.; Bohm, S. Investigation on influence of nanoclay addition on rheological performance of asphalt binder. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1007–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.E.; Zamhari, K.A.; Buhari, R.; Nayan, M.N.; Mohd Rosli, H. Short Term and Long Term Aging Effects of Asphalt Binder Modified with Montmorillonite. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 594–595, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, P.K.; Singh, D.; Bohm, S. Evaluation of rutting, fatigue and moisture damage performance of nanoclay modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavussi, A.; Barghabany, P. Investigating Fatigue Behavior of Nanoclay and Nano Hydrated Lime Modified Bitumen Using LAS Test. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Baaj, H.; Kringos, N.; Tighe, S. Coupling of oxidative ageing and moisture damage in asphalt mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrieu, F.; Farcas, F.; Mouillet, V. The influence of UV aging of a Styrene/Butadiene/Styrene modified bitumen: Comparison between laboratory and on site aging. Fuel 2007, 86, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, V.F.C.; Araújo, M.F.A.S.; Yoshida, M.I.; Ferraz, V.P.; Andrada, D.M.; Lameiras, F.S. Photodegradation of hot-mix asphalt. Fuel 2008, 87, 3254–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Zhao, D.; Chailleux, E.; Kane, M.; Gabet, T.; Petiteau, C.; Soares, J. Characterization of aging processes on the asphalt mixture surface. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2014, 15, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillet, V.; Farcas, F.; Chailleux, E.; Sauger, L. Evolution of bituminous mix behaviour submitted to UV rays in laboratory compared to field exposure. Mater. Struct. 2014, 47, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauste, R.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Understanding the bitumen ageing phenomenon: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá Araújo, M.D.F.A.; Lins, V.D.F.C.; Pasa, V.M.D.; Leite, L.F.M. Weathering aging of modified asphalt binders. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 115, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-G.; Bian, H.; Li, X.; Yu, J. FTIR analysis of UV aging on bitumen and its fractions. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-G.; Yu, J.-Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; Kuang, D.-L.; Xue, L.-H. Effect of ultraviolet aging on rheology, chemistry and morphology of ultraviolet absorber modified bitumen. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Pang, L.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J. Laboratory Study on Ultraviolet Radiation Aging of Bitumen. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y. Effect of ultraviolet aging on rheological properties of organic intercalated layered double hydroxides modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Delehei; Wang, J.; Feng, X. Effect of Ultraviolet Light Aging on Fatigue Properties of Asphalt. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 599, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wu, S.; Wen, J.; Chen, Z. The temperature effects in aging index of asphalt during UV aging process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, C.; Yu, J.; Shi, C.; Zhang, D. Influence of surface modification on physical and ultraviolet aging resistance of bitumen containing inorganic nanoparticles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Wu, S. Effect of montmorillonite organic modification on ultraviolet aging properties of SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Xue, L. Investigation of microstructures and ultraviolet aging properties of organo-montmorillonite/SBS modified bitumen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.M.L.; das Neves, J.M.C.; Capitão, S.D.; de Picado-Santos, L.G. Evaluation of the durability of asphalt concrete modified with nanomaterials using the TEAGE aging method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.; Picado-Santos, L.; Neves, J.; Capitão, S.; Al-Qadi, I.L. Tecnico accelerated ageing (TEAGE)—A new laboratory approach for bituminous mixture ageing simulation. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. AASHTO R30-02. Standard Practice for Mixture Conditioning of Hot Mix Asphaltl; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, C.A.; Abwahab, Y.; Cristi, M.E.; Sosnovske, D. Selection of Laboratory Aging Procedures for Asphalt-Aggregate Mixtures. In SHRP-A-383; Strategic Highway Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; p. 92. ISBN 0309057620. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.K. Development of the Saturation Ageing Tensile Stiffness (SATS) Test for High Modulus Base Materials; University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, D.; Hofko, B.; Hospodka, M.; Handle, F.; Grothe, H.; Füssl, J.; Eberhardsteiner, L.; Blab, R. Towards an optimised lab procedure for long-term oxidative ageing of asphalt mix specimen. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2016, 17, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, F.C.G.; Picado-Santos, L.G.; Capitão, S.D. Feasibility assessment of the use of recycled aggregates for asphalt mixtures. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargin, Ş.; Saltan, M.; Morova, N.; Serin, S.; Terzi, S. Evaluation of rice husk ash as filler in hot mix asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).