Effect of Fiber Weave Structure in Printed Circuit Boards on Signal Transmission Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dielectric Constant Fluctuations of Different Types of Fiber Weaves
3.2. Impact of the Fiber Weave Effect on Impedance Fluctuations
3.2.1. Effect of the Fiber Weave Effect on Single-Ended Impedance Lines
3.2.2. Effect of the Fiber Weave Effect on Differential Lines
= {0.3*εG*(H1 + H2) + Dk*[H − 0.3*(H1 + H2)]}/H.
3.3. Effects of Trace Direction on Impedance Fluctuation
3.4. Methods to Improve Fiber Weave Effects
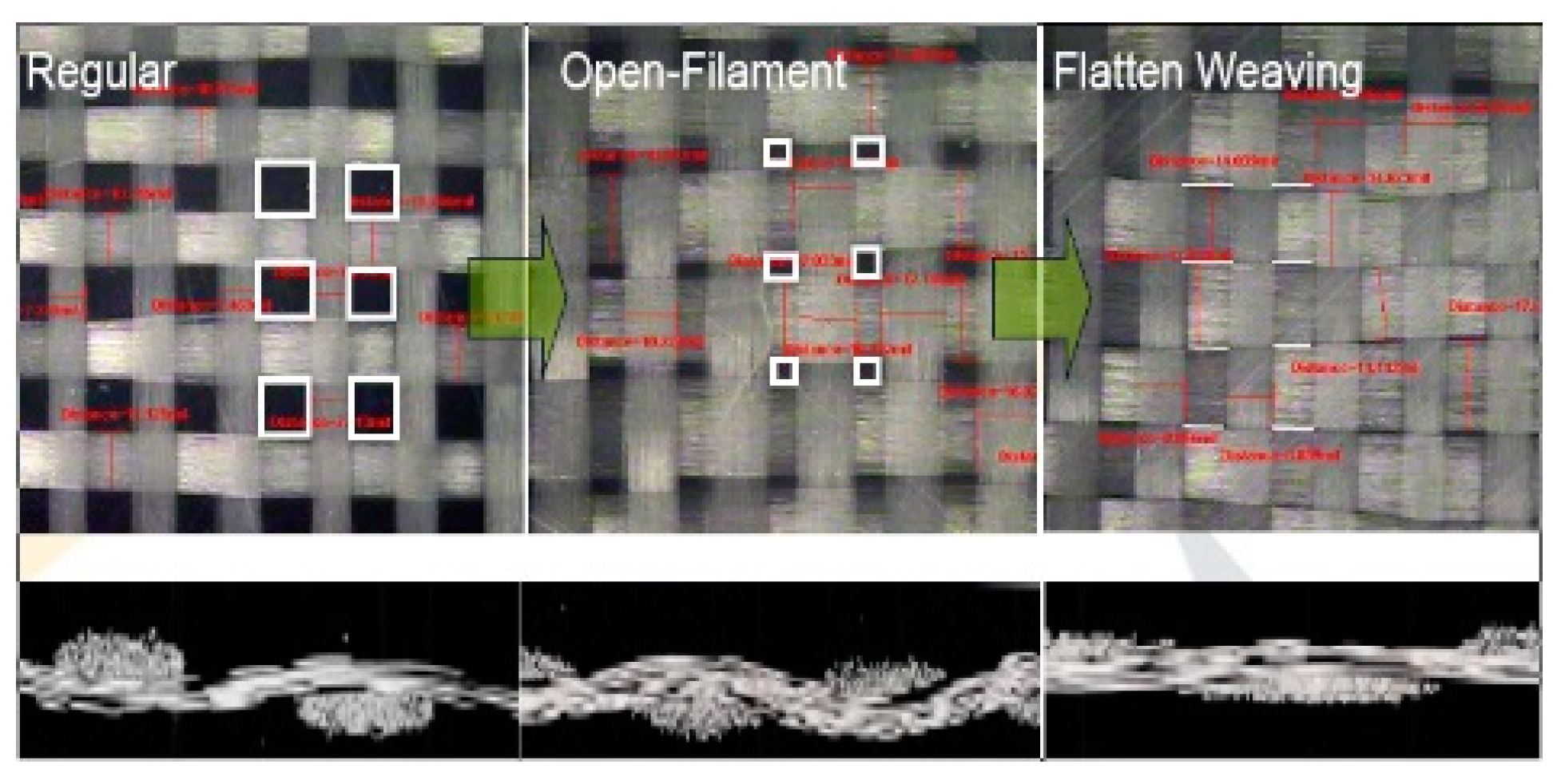
3.4.1. Flattened Fiber Weaves
3.4.2. NE-Glass Fiber Weaves
3.4.3. Making Traces and Fiber Weave Bundles with an Angle
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudek, R.; Goldman, P.; Kuhn, J. Advanced Glass Reinforcement Technology for Improved Signal Integrity. Printed Circuit Design & Fab. 2008, pp. 40–42. Available online: https://www.pcdandf.com/pcdesign/index.php/articles-by-subject/210-signal-integrity/3378-advanced-glass-reinforcement-technology-for-improved-signal-integrity (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Scott, M.; Chris, H. The impact of PCB laminate weave on the electrical performance of differential signaling at multi-Gigabit data rates. In Proceedings of the Design Conference, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 31 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.Q. PCB used layer insulation film and high function glass cloth Printed Circuit Information. Circuit Inf. 2011, 12, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Avendano, V.; Champac, V.; Figureas, J. Signal integrity verification using high speed monitors. In Proceedings of the European Test Symposium, Corsica, France, 23–26 May 2004; pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Loyer, J.; Kuuze, R.K.; Ye, X.N. Fiber Wave Effect: Fiber Weave Effect: Practical Impact Analysis and Mitigation Strategies. In Proceedings of the Design Conference, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 29 January–1 February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sharawi, M.S. Practical Issues in High Speed PCB Design. Potentials IEEE 2004, 23, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Zhuo, N.Z.; Xing, H.D.; Wang, H.B. The Research of the Low Dielectric Properties of Fiberglass and the Application of Fiberglass in High Frequency Printed circuit Board. Fiber Glass 2016, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bucur, D. Fiber Weave Effect—A performance-limiting factor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications, Bucharest, Romania, 29–31 May 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Schutt-Aine, J.E.; Cangellaris, A.C. Statistical analysis of fiber weave effect over differential microstrips on printed circuit boards. Signal Power Integr. 2014, 40, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Luevano, G.R.; Shin, J.; Michalka, T. Practical Investigations of Fiber Weave Effects on High-speed Interfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Electronic Components & Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 28–31 May 2013; pp. 2041–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Shlepnev, Y.; Nwachukwu, C. Modelling Jitter Induced by Fibre Weave Effect in PCB Dielectrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Raleigh, NC, USA, 4–8 August 2014; pp. 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Zheng, M. Design Consideration for 10 Gbps Signal Transmission Channel in Copper Backplane System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science & Its Applications, Santander, Spain, 20–23 June 2011; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar]















| Style | Measurement Results (mil) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | |
| 1035 | 0.82 | 8.8 | 14.2 | 0.78 | 12.4 | 13.7 |
| 1080 | 1.6 | 8.2 | 17.0 | 1.1 | 12.1 | 22.4 |
| 1078 | 1.4 | 14.2 | 16.2 | 1.0 | 17.6 | 17.8 |
| 3313 | 1.9 | 13.1 | 16.2 | 1.5 | 11.0 | 16.3 |
| 2116 | 2.2 | 14.1 | 17.2 | 2.0 | 15.5 | 17.3 |
| W/S (mil) | Differential Skew (ps/in) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1035 | 1080 | 3313 | 2116 | 1078 | ||||||
| Weft | Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | Warp | |
| 4/4 | 4.7 | 3.5 | 7.2 | 5.1 | 6.3 | 3.1 | 6.4 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 1.9 |
| 4/8 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 6.5 | 5.1 | 6.5 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 3.6 | 2.2 | 1.6 |
| 5/5 | 4.3 | 2.3 | 6.6 | 4.7 | 7.3 | 5.6 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 2.0 |
| 5/9 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 5.0 | 4.7 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| 6/6 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 5.2 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 2.3 | 1.5 |
| 6/8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 4.3 | 3.5 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| 7/7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 4.0 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.7 |
| 7/9 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 3.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 8/8 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| 8/10 | 1.87 | 1.47 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Fiber Weave Style | Warp Direction | Weft Direction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Dk | ∆Z0/Ω | ∆Dk | ∆Z0/Ω | |
| Conventional fiber weave | 0.58 | 3.80 | 0.44 | 2.73 |
| Flattened fiber weave | 0.25 | 1.56 | 0.18 | 1.11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Yao, R.; Wang, H.; Geng, K.; Li, J. Effect of Fiber Weave Structure in Printed Circuit Boards on Signal Transmission Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020353
Chen B, Yao R, Wang H, Geng K, Li J. Effect of Fiber Weave Structure in Printed Circuit Boards on Signal Transmission Characteristics. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020353
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bei, Ruohe Yao, Hongfei Wang, Kuiwei Geng, and Juan Li. 2019. "Effect of Fiber Weave Structure in Printed Circuit Boards on Signal Transmission Characteristics" Applied Sciences 9, no. 2: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020353
APA StyleChen, B., Yao, R., Wang, H., Geng, K., & Li, J. (2019). Effect of Fiber Weave Structure in Printed Circuit Boards on Signal Transmission Characteristics. Applied Sciences, 9(2), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020353





