Effect of Plasma-Activated Water on the Microbial Decontamination and Food Quality of Thin Sheets of Bean Curd
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of PAW
2.2. PAW Treatment
2.3. Microbial Enumeration
2.4. Color Measurement
2.5. Textural Property Analysis
2.6. Determination of Total Isoflavones
2.7. Sensory Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of PAW Activation Time on Inactivation Effect of Microorganisms
3.2. Influence of Soaking Time on Inactivation Effect of Microorganisms
3.3. Influence of PAW Treatments on Color of Thin Sheets of Bean Curd
3.4. Influence of PAW on Textural Properties
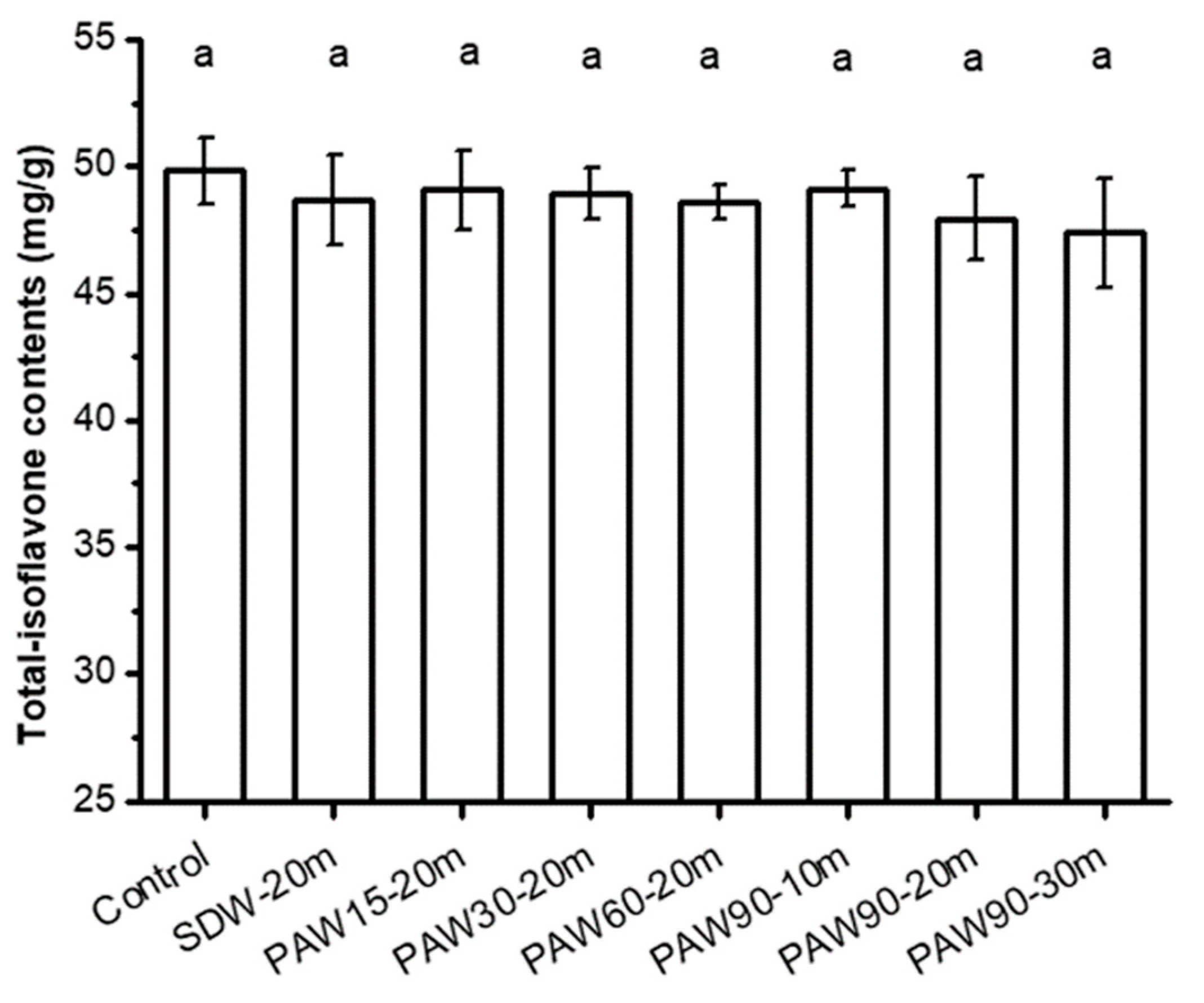
3.5. Influence of PAW on Total Isoflavone Content
3.6. Influence of PAW on Sensory Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, M.C.; Torre, M.; Marina, M.L.; Laborda, F. Composition and characterization of soyabean and related products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 37, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, H.; Uesugi, T.; Hirai, K.; Toda, T.; Nukaya, H.; Yokotsuka, K.; Tsuji, K. Preventive effects of the plant isoflavones, daidzin and genistin, on bone loss in ovariectomized rats fed a calcium-deficient diet. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Study on extending shelf life of tofu. Food Res. Dev. 2015, 36, 175–177. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Knorr, D.; Froehling, A.; Jaeger, H.; Reineke, K.; Schlueter, O.; Schoessler, K. Emerging technologies in food processing. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 203–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekezie, F.G.C.; Sun, D.W.; Cheng, J.H. A review on recent advances in cold plasma technology for the food industry: Current applications and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.T.; Shi, J.J.; Kong, M.G. Physical mechanisms of inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores using cold atmospheric plasmas. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2006, 34, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, E.; Ikawa, S.; Kitano, K.; Kuwabara, J.; Shiraki, K. Molecular mechanism of plasma sterilization in solution with the reduced pH method: Importance of permeation of HOO radicals into the cell membrane. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 295402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Muhammad, A.I.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Liu, D.; Ding, T. Bacterial spore inactivation induced by cold plasma. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.S.; Kang, C.D.; Niu, L.Y.; Zhao, D.B.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.H. Antibacterial activity and a membrane damage mechanism of plasma- activated water against Pseudomonas deceptionensis CM2. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Non-thermal plasma-activated water inactivation of food-borne pathogen on fresh produce. J. Hazard Mater. 2015, 300, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Lyu, C.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Inactivation of yeast on grapes by plasma-activated water and its effects on quality attributes. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Effect of plasma activated water on the postharvest quality of button mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.S.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, S.N.; Ma, Y.F.; Xu, C.Q.; Bai, Y.H. Effect of plasma-activated water on microbial quality and physicochemical characteristics of mung bean sprouts. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.D.; Feng, H.Q.; Ma, R.N.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. A study of oxidative stress induced by non-thermal plasma-activated water for bacterial damage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 141502. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, R.N.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, H.Q.; Liang, Y.D.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Assessment of the physicochemical properties and biological effects of water activated by non-thermal plasma above and beneath the water surface. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Bactericidal Effects against S.aureus and physicochemical properties of plasma activated water stored at different temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.Y.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, J.E.; Bin Song, K.; Oh, D.H.; Min, S.C. Cold plasma treatment for microbial safety and preservation of fresh lettuce. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puligundla, P.; Kim, J.W.; Mok, C. Effect of corona discharge plasma jet treatment on decontamination and sprouting of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) seeds. Food Control 2017, 71, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.M.H.; Pinto, I.S.S.; Soares, E.V.; Soares, H.M.V.M. (Un)suitability of the use of pH buffers in biological, biochemical and environmental studies and their interaction with metal ions—A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30989–31003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.B.; Chen, W.M.; Xiao, X.M. The generation and inactivation mechanism of oxidation-reduction potential of electrolyzed oxidizing water. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naitali, M.; Kamgang-Youbi, G.; Herry, J.M.; Bellon-Fontaine, M.N.; Brisset, J.L. Combined effects of long- living chemical species during microbial inactivation using atmospheric plasma- treated water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7662–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R. Impact of ultraviolet radiation treatments on the quality of freshly prepared tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) juice. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.S.; Liu, X.F.; Li, J.G.; Liu, S.N.; Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.H. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on the inactivation of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii and quality of apple juice. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, D.B.; Putnik, P.; Dragovic-Uzelac, V.; Pedisic, S.; Jambrak, A.R.; Herceg, Z. Effects of cold atmospheric gas phase plasma on anthocyanins and color in pomegranate juice. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasan, B.G.; Boyaci, I.H. Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on Inactivation of Escherichia coli and Physicochemical Properties of Apple, Orange, Tomato Juices, and Sour Cherry Nectar. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.; Jin, F.; Li, J.G.; Xu, Y.Y.; Dong, H.T.; Liu, Q.; Xing, P.; Zhu, G.L.; Xu, H.; Miao, Z.F. Dietary isoflavones or isoflavone-rich food intake and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huser, S.; Guth, S.; Joost, H.G.; Soukup, S.T.; Kohrle, J.; Kreienbrock, L.; Diel, P.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Eisenbrand, G.; Vollmer, G.; et al. Effects of isoflavones on breast tissue and the thyroid hormone system in humans: A comprehensive safety evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2703–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giolo, J.S.; Costa, J.G.; da Cunha-Junior, J.P.; Pajuaba, A.; Taketomi, E.A.; de Souza, A.V.; Caixeta, D.C.; Peixoto, L.G.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Everman, S.; et al. The effects of isoflavone supplementation plus combined exercise on lipid levels, and inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in postmenopausal women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.S.; Liu, X.F.; Li, J.G.; Ding, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.S.; Bai, Y.H. Influences of cold atmospheric plasma on microbial safety, physicochemical and sensorial qualities of meat products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| L* | a* | b* | ΔE* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 77.44 ± 0.24 b | 7.37 ± 0.04 a | 36.18 ± 0.80 a | - |
| SDW-30m | 77.96 ± 0.68 b | 7.13 ± 0.25 a | 33.98 ± 1.09 bc | 2.39 ± 1.04 b |
| PAW15-20m | 77.91 ± 0.53 b | 6.88 ± 0.23 b | 32.90 ± 0.89 cd | 3.52 ± 1.14 a |
| PAW30-20m | 77.90 ± 0.44 b | 6.80 ± 0.23 b | 32.40 ± 1.37 d | 3.86 ± 1.40 a |
| PAW60-20m | 78.95 ± 0.19 a | 6.72 ± 0.17 b | 32.88 ± 0.79 cd | 3.69 ± 0.77 a |
| PAW90-10m | 78.00 ± 0.89 b | 7.27 ± 0.29 a | 34.55 ± 0.92 b | 1.97 ± 0.85 b |
| PAW90-20m | 78.74 ± 0.26 a | 6.77 ± 0.20 b | 32.93 ± 0.84 cd | 3.55 ± 0.88 a |
| PAW90-30m | 78.71 ± 0.16 a | 6.76 ± 0.20 b | 32.70 ± 0.75 d | 3.76 ± 0.74 a |
| Springiness (g/s) | Cohesiveness | Chewiness (×1000) | Resilience | Hardness (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.43 ± 0.20 a | 0.93 ± 0.03 a | 16.05 ± 2.53 a | 0.85 ± 0.06 a | 12.19 ± 1.35 b |
| SDW-30m | 1.14 ± 0.43 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 16.13 ± 1.70 a | 0.89 ± 0.04 a | 14.96 ± 2.09 a |
| PAW15-20m | 1.19 ± 0.45 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 17.57 ± 2.21 a | 0.86 ± 0.03 a | 15.79 ± 1.64 a |
| PAW30-20m | 1.24 ± 0.58 a | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 16.60 ± 1.07 a | 0.85 ± 0.04 a | 14.30 ± 0.78 a |
| PAW60-20m | 1.03 ± 0.56 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 14.30 ± 2.01 a | 0.88 ± 0.03 a | 13.93 ± 1.10 a |
| PAW90-10m | 1.31 ± 0.56 a | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 14.58 ± 1.62 a | 0.85 ± 0.03 a | 11.98 ± 0.84 b |
| PAW90-20m | 1.56 ± 0.41 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 16.13 ± 1.98 a | 0.88 ± 0.03 a | 14.70 ± 1.28 a |
| PAW90-30m | 1.03 ± 0.54 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 14.43 ± 1.87 a | 0.89 ± 0.04 a | 14.86 ± 1.06 a |
| Appearance | Flavor | Brittleness | Overall Acceptance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5.08 ± 2.65 a | 7.84 ± 1.22 a | 6.82 ± 2.88 a | 6.15 ± 2.00 a |
| SDW-30m | 5.76 ± 2.35 a | 7.04 ± 1.86 a | 7.95 ± 0.80 a | 6.82 ± 1.44 a |
| PAW15-20m | 5.91 ± 1.91 a | 7.02 ± 1.15 a | 7.55 ± 1.20 a | 6.46 ± 1.58 a |
| PAW30-20m | 6.15 ± 2.25 a | 7.18 ± 1.15 a | 7.8 ± 1.86 a | 6.51 ± 2.20 a |
| PAW60-20m | 6.18 ± 2.25 a | 6.65 ± 1.97 a | 6.95 ± 2.30 a | 6.19 ± 1.99 a |
| PAW90-10m | 5.54 ± 2.79 a | 6.54 ± 1.46 a | 7.17 ± 1.54 a | 6.05 ± 2.13 a |
| PAW90-20m | 5.84 ± 2.20 a | 6.45 ± 1.61 a | 7.22 ± 1.44 a | 6.66 ± 1.58 a |
| PAW90-30m | 7.23 ± 1.97 a | 6.71 ± 1.75 a | 7.57 ± 1.82 a | 7.15 ± 1.71 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiang, Q.; Lyu, Y.; Shen, R. Effect of Plasma-Activated Water on the Microbial Decontamination and Food Quality of Thin Sheets of Bean Curd. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204223
Zhai Y, Liu S, Xiang Q, Lyu Y, Shen R. Effect of Plasma-Activated Water on the Microbial Decontamination and Food Quality of Thin Sheets of Bean Curd. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204223
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yafei, Shengnan Liu, Qisen Xiang, Ying Lyu, and Ruiling Shen. 2019. "Effect of Plasma-Activated Water on the Microbial Decontamination and Food Quality of Thin Sheets of Bean Curd" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204223
APA StyleZhai, Y., Liu, S., Xiang, Q., Lyu, Y., & Shen, R. (2019). Effect of Plasma-Activated Water on the Microbial Decontamination and Food Quality of Thin Sheets of Bean Curd. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204223




