A Study of Colormaps in Network Visualization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Color Models in Visualization
2.2. Colormaps and Evaluation Studies
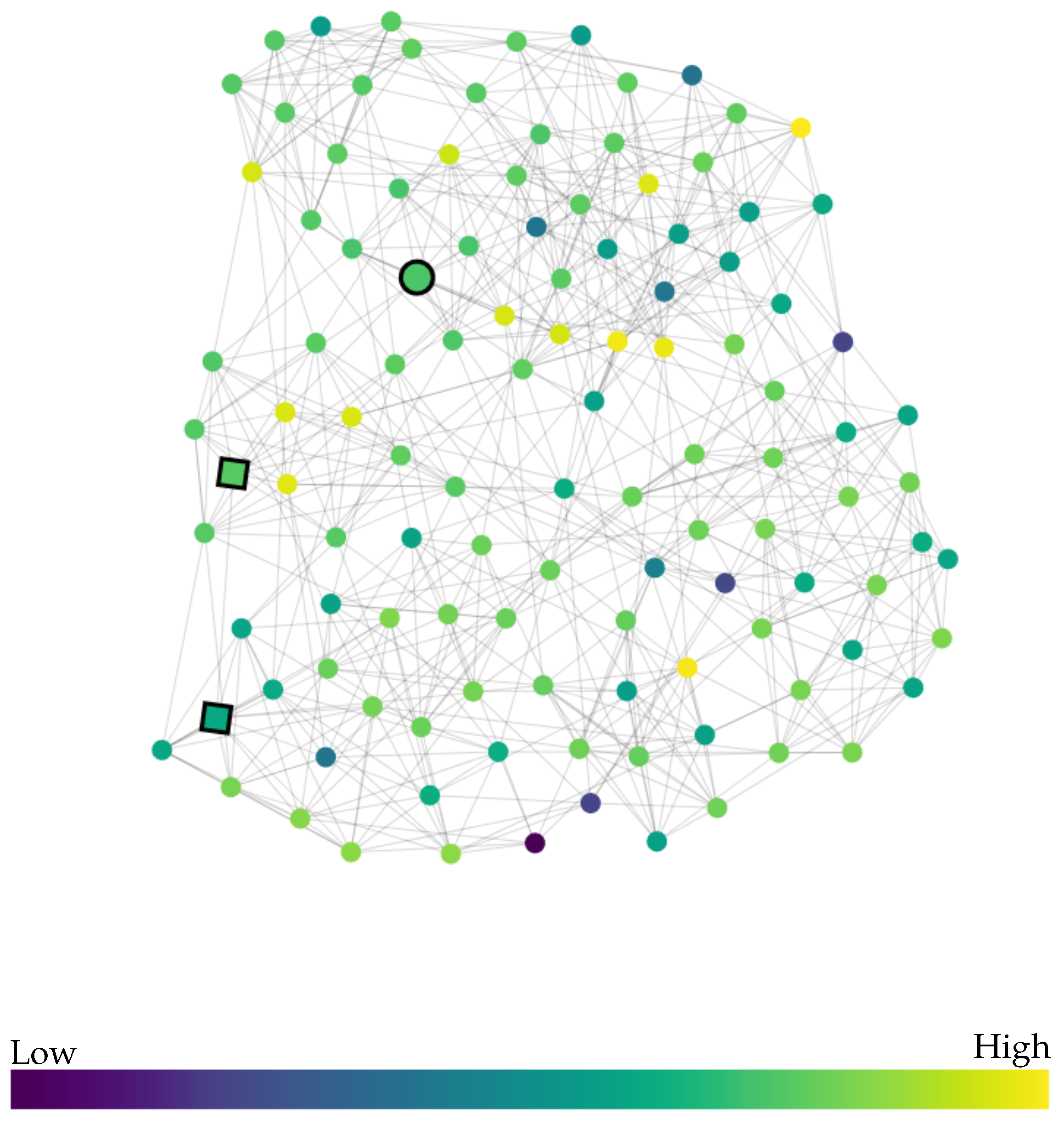
3. User Study
3.1. Experimental Design
3.1.1. Node Attributes
- PageRank: This is a ranking of the nodes in the node-link diagram based on the structure of incoming links. It is determined by counting the number of links to a node to get a rough estimate of how important that node is a network. It is assumed that more important nodes are more likely to receive a greater numbers of links;
- Random: As a non-structural node attribute, we assigned random values in for each node with a uniform distribution.
3.1.2. Task
3.1.3. Datasets
- Karate: this dataset, which has 34 nodes and 78 links, is the well-known and popularly used Zachary karate club network [38]. It was used for training;
- Lesmis: this network, which has 77 nodes and 254 links, is constructed based on co-occurrences of characters in Les Misérables [39];
- Football: this is a network of an American football game from 2000 [40] with 115 nodes and 613 links;
- Jazz: this is a collaboration network between jazz musicians [41] with 198 nodes and 2742 links.
3.1.4. Colormaps
3.1.5. Participants
3.2. Procedure
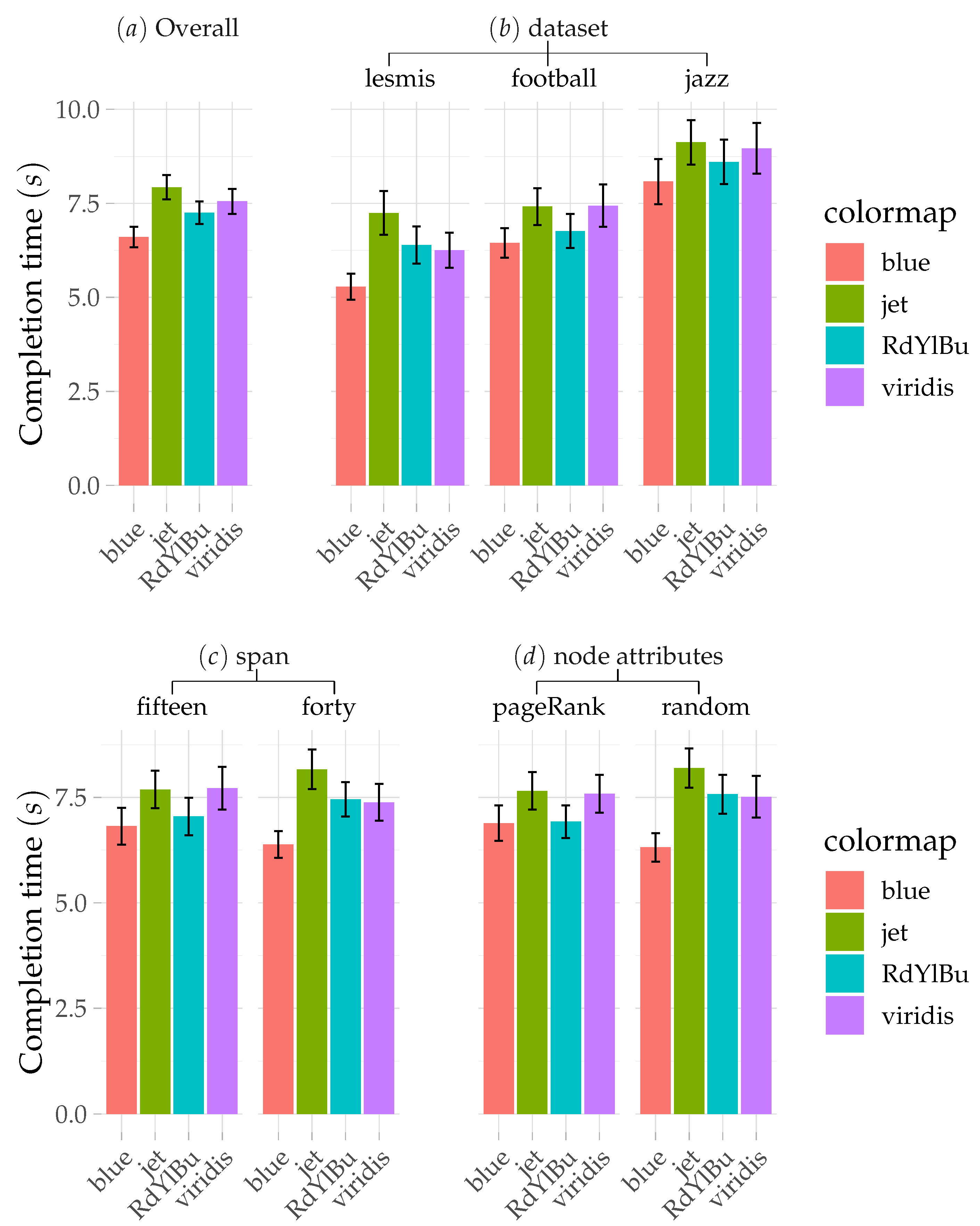
4. Results
4.1. Task Completion Time
4.2. Correctness Rate
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szafir, D.A. Modeling Color Difference for Visualization Design. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 24, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Hansen, C.D. A Survey of Colormaps in Visualization. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munzner, T. Visualization Analysis and Design. In AK Peters Visualization Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tominski, C.; Fuchs, G.; Schumann, H. Task-driven color coding. In Proceedings of the 2008 12th International Conference Information Visualisation, London, UK, 9–11 July 2008; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Viégas, F.B.; Donath, J. Social network visualization: Can we go beyond the graph. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Social Networks (CSCW), Chicago, IL, USA, 6–10 November 2004; Volume 4, pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alper, B.; Bach, B.; Henry Riche, N.; Isenberg, T.; Fekete, J.D. Weighted graph comparison techniques for brain connectivity analysis. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Paris, France, 27 April–2 May 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 483–492. [Google Scholar]
- Jourdan, F.; Melançon, G. Tool for metabolic and regulatory pathways visual analysis. In Proceedings of the Visualization and Data Analysis 2003, International Society for Optics and Photonics, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 21–23 January 2003; Volume 5009, pp. 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Barsky, A.; Gardy, J.L.; Hancock, R.E.; Munzner, T. Cerebral: A Cytoscape plugin for layout of and interaction with biological networks using subcellular localization annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1040–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Qu, H. A Survey on Graph Visualization. Ph.D. Thesis, Clear Water Bay, Hong Kong, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- L’Eclairage, C.I.D. CIE Recommendations on Uniform Color Spaces, Color-Difference Equations, and Metric Color Terms. Color Res. Appl. 1977, 2, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.; Smith, K.J. CIE94-a new colour-difference formula. J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1995, 111, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.R.; Cui, G.; Rigg, B. The development of the CIE 2000 colour-difference formula: CIEDE2000. Color Res. Appl. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, R.M.; Cui, G.; Li, C. Uniform colour spaces based on CIECAM02 colour apperance model. Color Res. Appl. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, G.; Howes, D.; Boring, E. Elements of Psychophysics; Holt, Rinehart and Winston: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke, K.; Flatla, D.R.; Brooks, C. Enabling designers to foresee which colors users cannot see. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 2693–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, R.C.; Silverstein, L.D. Size matters: Improved color-difference estimation for small visual targets. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2010, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.; Szafir, D.A.; Setlur, V. An engineering model for color difference as a function of size. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 3–7 November 2014; Volume 2014, pp. 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Brychtová, A.; Çöltekin, A. The effect of spatial distance on the discriminability of colors in maps. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 44, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, G.D. Colored Illustrations of the Brain: Some Conceptual and Contextual Issues. Neuroscientist 2010, 16, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafir, D.A.; Stone, M.; Gleicher, M. Adapting color difference for design. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 3–7 November 2014; Volume 2014, pp. 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Schloss, K.B.; Lessard, L.; Walmsley, C.S.; Foley, K. Color inference in visual communication: The meaning of colors in recycling. Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, K.B.; Gramazio, C.C.; Silverman, A.T.; Parker, M.L.; Wang, A.S. Mapping Color to Meaning in Colormap Data Visualizations. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 25, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujack, R.; Turton, T.L.; Samsel, F.; Ware, C.; Rogers, D.H.; Ahrens, J. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: A Theoretical Framework for the Assessment of Continuous Colormaps. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 24, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Heer, J. Somewhere Over the Rainbow: An Empirical Assessment of Quantitative Colormaps. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems—CHI’18, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–26 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, C.A. Color use guidelines for mapping. Vis. Mod. Cartogr. 1994, 2, 123–148. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.; Santos, B.S.; Madeira, J. Using color in visualization: A survey. Comput. Graph. 2011, 35, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, L.D.; Rogowitz, B.E.; Treinish, L.A. A rule-based tool for assisting colormap selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization’95, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28 October 1995; pp. 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Jacomy, M. I Want Hue. 2015. Available online: http://tools.medialab.sciences-po.fr/iwanthue/ (accessed on 18 July 2019).
- Gramazio, C.C.; Laidlaw, D.H.; Schloss, K.B. Colorgorical: Creating discriminable and preferable color palettes for information visualization. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016, 23, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrower, M.; Brewer, C.A. ColorBrewer.org: An Online Tool for Selecting Colour Schemes for Maps. Cartogr. J. 2003, 40, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheingans, P.L. Task-based color scale design. In Proceedings of the 28th AIPR Workshop: 3D Visualization for Data Exploration and Decision Making, Washington, DC, USA, 5 May 2000; Volume 3905, pp. 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mittelstädt, S.; Jäckle, D.; Stoffel, F.; Keim, D.A. Colorcat: Guided design of colormaps for combined analysis tasks. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Conference on Visualization (EuroVis)-Short Papers, Zurich, Switzerland, 4–8 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, W.S.; McGill, R. Graphical Perception: Theory, Experimentation, and Application to the Development of Graphical Methods. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1984, 79, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEachren, A.M.; Roth, R.E.; O’Brien, J.; Li, B.; Swingley, D.; Gahegan, M. Visual semiotics & uncertainty visualization: An empirical study. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2012, 18, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar]
- Zacks, J.; Tversky, B. Bars and lines: A study of graphic communication. Mem. Cogn. 1999, 27, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Fortuna, J.; Kulkarni, C.; Stone, M.; Heer, J. Selecting Semantically-Resonant Colors for Data Visualization. Comput. Graph. Forum 2013, 32, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.A.; MacEachren, A.M.; Pickle, L.W.; Herrmann, D. Mapping Mortality: Evaluating Color Schemes for Choropleth Maps. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1997, 87, 411–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachary, W.W. An Information Flow Model for Conflict and Fission in Small Groups. J. Anthropol. Res. 1977, 33, 452–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, D. The Stanford GraphBase: A Platform for Combinatorial Computing; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleiser, P.M.; Danon, L. Community structure in jazz. Adv. Complex Syst. 2003, 6, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Efficient and High Quality Force-Directed Graph Drawing. Math. J. 2005, 10, 37–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, H.; Faith, J.; Vickers, P. A Survey of Two-dimensional Graph Layout Techniques for Information Visualization. Inf. Vis. 2013, 12, 324–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creel, D.J. Visual and Auditory Anomalies Associated with Albinism; University of Utah Health Sciences Center: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Walt, S.; Smith, N. A Better Default Colormap for Matplotlib. In Proceedings of the Python in Science (SciPy) Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 6–12 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Satyanarayan, A.; Moritz, D.; Wongsuphasawat, K.; Heer, J. Vega-Lite: A Grammar of Interactive Graphics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 23, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, D.; Taylor, R., II. Rainbow Color Map (Still) Considered Harmful. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2007, 27, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, A.; Bartlein, P.J. The end of the rainbow? Color schemes for improved data graphics. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2004, 85, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethel, E.W.; Childs, H.; Hansen, C. High Performance Visualization: Enabling Extreme-Scale Scientific Insight, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]


| Category | Author | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluation | Szafir, D.A. [1] | Modeling color difference perceptions for three common mark types: points, bars, and lines. |
| Brychtová, A. and Çöltekin, A. [18] | Examine the effect of the spatial gap in discriminability of color hue and value between map symbols. | |
| Schloss, K.B. et al. [22] | Investigated how inferred color-quantity mappings for colormap data visualizations were influenced by the background color. | |
| Liu, Y. and Heer, J. [24] | A comparative analysis of different colormap types, with a focus on comparing single- and multi-hue schemes. | |
| Brewer, C.A et al. [37] | Evaluating specific combinations of colors on maps, for selecting colors for choropleth maps of mortality data. | |
| Recommendations and colormap generating tools | Tominski, C. et al. [4] | Describe a color coding approach that accounts for the different tasks users might pursue when analyzing data. |
| Bergman, L.D. et al. [27] | An interactive approach for guiding the user’s selection of colormaps in visualization. | |
| Gramazio, C.C. et al. [29] | A web-based tool for creating discriminable and aesthetically preferable categorical color palettes. | |
| Mittelstädt, S. et al. [32] | Proposed a methodology and tool to design colormaps for combined analysis tasks. | |
| Rheingans, P.L. [31] | General guideline for different types of colormaps and their characteristics. | |
| Borland, D. and Taylor Ii, R. [48] | Explains the characteristics that make the rainbow color map a poor choice. | |
| Light, A. and Bartlein, P.J. [49] | Explains the drawbacks of rainbow colormap and guidelines to use other colormaps. | |
| Brewer, C.A. [25] | Guidelines to the use of color to directly represent data that occur at locations in the graphic. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karim, R.M.; Kwon, O.-H.; Park, C.; Lee, K. A Study of Colormaps in Network Visualization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204228
Karim RM, Kwon O-H, Park C, Lee K. A Study of Colormaps in Network Visualization. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204228
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarim, Raja Mubashar, Oh-Hyun Kwon, Chanhee Park, and Kyungwon Lee. 2019. "A Study of Colormaps in Network Visualization" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204228
APA StyleKarim, R. M., Kwon, O.-H., Park, C., & Lee, K. (2019). A Study of Colormaps in Network Visualization. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204228





