Quantification of the PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Protein Corona. Influence on Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) Synthesis
2.2. Characterization of AuNP
2.3. BSA-FITC Conjugation
2.4. Colloidal Stability in Biological Media
2.5. Protein Corona Formation and Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Stability Studies
3.3. Protein Corona Quantification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Versiani, A.F.; Andrade, L.M.; Martins, E.M.N.; Scalzo, S.; Geraldo, J.M.; Chaves, C.R.; Ferreira, D.C.; Ladeira, M.; Guatimosim, S.; Ladeira, L.O. Gold nanoparticles and their applications in biomedicine. Future Virol. 2016, 11, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, P.N.; Sangeetha, K.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Barhoum, A. Nanomaterials History, Classification, Unique Properties, Production and Market. In Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architectural Nanostructures: Current Prospects and Future Trends; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 341–384. [Google Scholar]
- Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H. Recent Biomedical Applications of Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. Talanta 2018, 184, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle size and surface properties determine the protein corona with possible implications for biological impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fetz, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; et al. Rapid formation of plasma protein corona critically affects nanoparticle pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, S.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Pitek, A.S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J. Reversible versus Irreversible Binding of Transferrin to Polystyrene Nanoparticles: Soft and Hard Corona. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2532–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagliani, R.; Gatto, F.; Bardi, G. Protein adsorption: A feasible method for nanoparticle functionalization? Materials 2019, 12, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshafiee, V.; Mahmoudi, M.; Lou, K.; Cheng, J.; Kraft, M.L. Protein corona significantly reduces active targeting yield. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz-Chalot, A.; Villiers, C.; Pourchez, J.; Boudard, D.; Martini, M.; Marche, P.N.; Cottier, M.; Forest, V. Impact of silica nanoparticle surface chemistry on protein corona formation and consequential interactions with biological cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, A.; Pitek, A.S.; Monopoli, M.P.; Prapainop, K.; Bombelli, F.B.; Hristov, D.R.; Kelly, P.M.; Aberg, C.; Mahon, E.; Dawson, K.A. Transferrin-functionalized nanoparticles lose their targeting capabilities when a biomolecule corona adsorbs on the surface. Nat. Nano 2013, 8, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Pitek, A.S.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Formation and characterization of the nanoparticle-protein corona. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1025, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Carril, M.; Parak, W.J. Techniques for the experimental investigation of the protein corona. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduru, N.V.; Molina, R.M.; Swami, A.; Damiani, F.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Lin, P.; Andreozzi, P.; Donaghey, T.C.; Demokritou, P.; Krol, S.; et al. Protein corona: Implications for nanoparticle interactions with pulmonary cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Liu, R.; Deng, Z.; Ge, G.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. Quantitative study of protein coronas on gold nanoparticles with different surface modifications. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkey, C.D.; Olsen, J.B.; Guo, H.; Emili, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry Determine Serum Protein Adsorption and Macrophage Uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastus, N.G.; Comenge, J.; Puntes, V. Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Size focusing versus ostwald ripening. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11098–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hühn, J.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Soliman, M.G.; Pfeiffer, C.; Valdeperez, D.; Masood, A.; Chakraborty, I.; Zhu, L.; Gallego, M.; Yue, Z.; et al. Selected Standard Protocols for the Synthesis, Phase Transfer, and Characterization of Inorganic Colloidal Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 399–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, R.; Hadjidemetriou, M.; Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Kostarelos, K. In vivo formation of protein corona on gold nanoparticles. the effect of their size and shape. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossmann, R.; Fahrländer, E.; Hummel, M.; Mulac, D.; Brockmeyer, J.; Langer, K. Comparative examination of adsorption of serum proteins on HSA- and PLGA-based nanoparticles using SDS-PAGE and LC-MS. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, E.; Araban, V.; Pelaz, B.; Alvarez, A.; Taboada, P.; Mahmoudi, M.; del Pino, P. Photothermal effects on protein adsorption dynamics of PEGylated gold nanorods. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahme, K.; Chen, L.; Hobbs, R.G.; Morris, M.A.; O’Driscoll, C.; Holmes, J.D. PEGylated gold nanoparticles: Polymer quantification as a function of PEG lengths and nanoparticle dimensions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6085–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, L.M.; Naletova, I.; Consiglio, G.; Satriano, C. A hybrid nanoplatform of graphene oxide/nanogold for plasmonic sensing and cellular applications at the nanobiointerface. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, L.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Pazos-Perez, N. Surface Modifications of Nanoparticles for Stability in Biological Fluids. Materials 2018, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Rahme, K.; Corbalan, J.J.; Faulkner, C.; Holmes, J.D.; Tajber, L.; Medina, C.; Radomski, M.W. Pegylation increases platelet biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piella, J.; Bastús, N.G.; Puntes, V. Size-dependent protein-nanoparticle interactions in citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles: The emergence of the protein corona. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.D.; Kreyling, W.G.; Pfeiffer, C.; Schäffler, M.; Sarioglu, H.; Ristig, S.; Hirn, S.; Haberl, N.; Thalhammer, S.; Hauck, S.M.; et al. Colloidal Stability and Surface Chemistry Are Key Factors for the Composition of the Protein Corona of Inorganic Gold Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Riviere, J.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Gold and silver nanoparticle interactions with human proteins: Impact and implications in biocorona formation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, J.; Jin, W.; Wei, Z.; Ho, C.-T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Q. Formation of Nanocomplexes between Carboxymethyl Inulin and Bovine Serum Albumin via pH-Induced Electrostatic Interaction. Molecules 2019, 24, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gref, R.; Lück, M.; Quellec, P.; Marchand, M.; Dellacherie, E.; Harnisch, S.; Blunk, T.; Müller, R.H. “Stealth” corona-core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): Influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2000, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
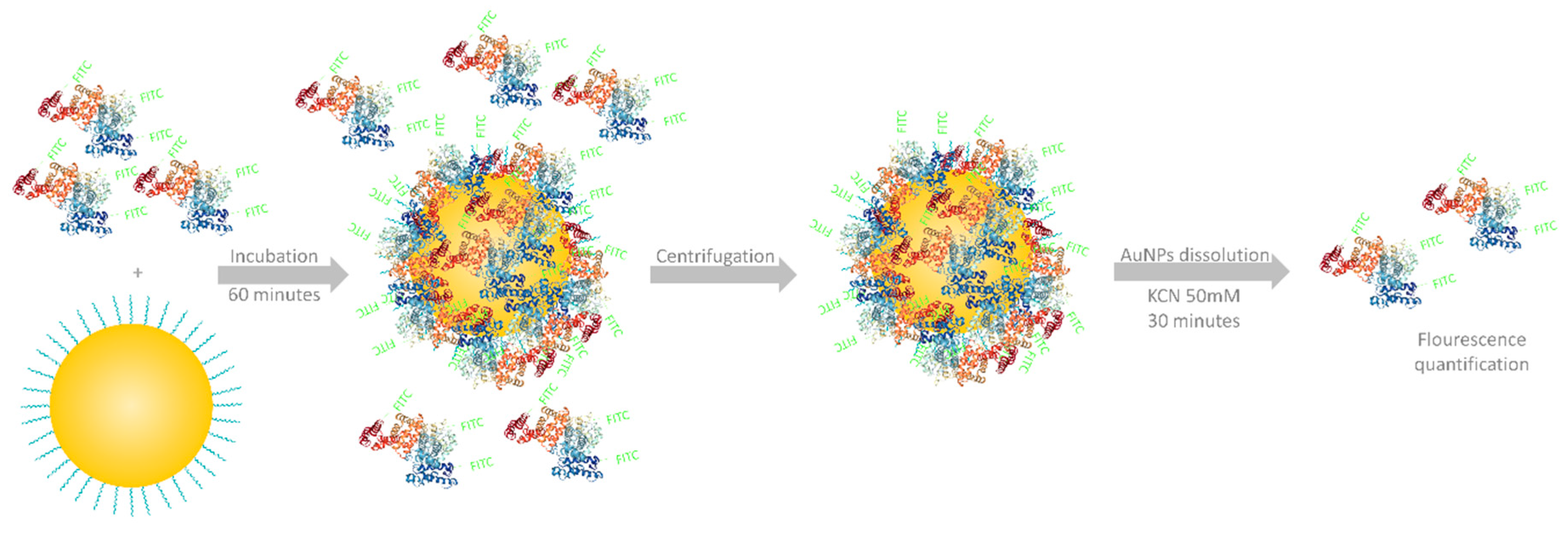
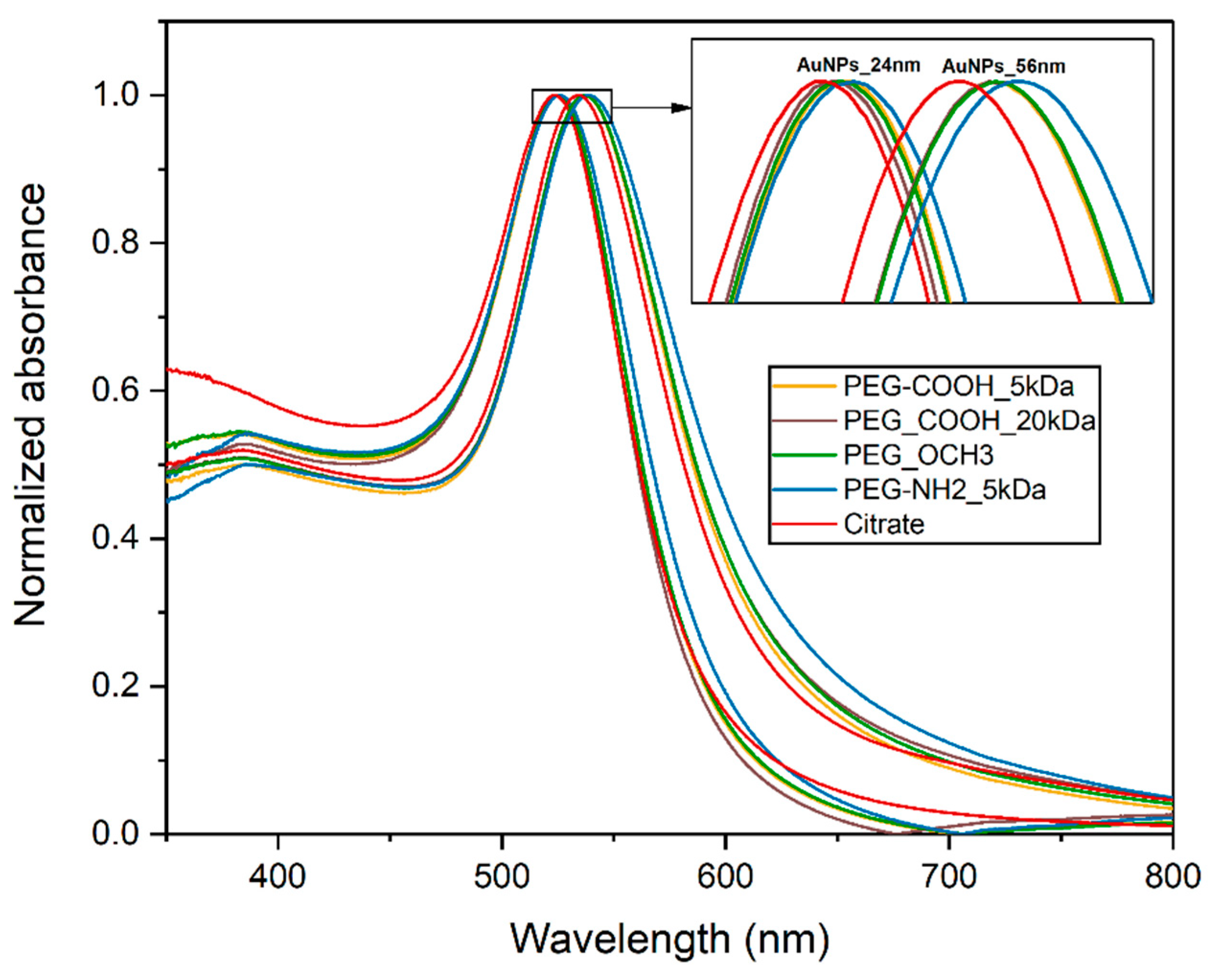




| Nanoparticle | Ligand | λspr (nm) | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNP 24 nm | citrate | 523.5 | 30.4 | −34.3 |
| PEG-COOH 5 kDa | 525 | 31.2 | −30.4 | |
| PEG-COOH 20 kDa | 524.5 | 30.9 | −32.3 | |
| PEG-OCH3 | 525 | 32.3 | −2.7 | |
| PEG-NH2 | 526 | 35.8 | 28.2 | |
| AuNP 56 nm | citrate | 534 | 64.2 | −32.4 |
| PEG-COOH 5 kDa | 537 | 66.3 | −30.4 | |
| PEG-COOH 20 kDa | 536.5 | 66.7 | −31.2 | |
| PEG-OCH3 | 537 | 65.8 | 1.3 | |
| PEG-NH2 | 539 | 69.2 | 30.2 |
| Nanoparticle | PEG Ligand | % Recovery | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ng | 50 ng | 100 ng | ||
| AuNP 24 nm | PEG-COOH 5 kDa | 98.1 | 98.1 | 101.1 |
| PEG-COOH 20 kDa | 98.2 | 98.2 | 99.2 | |
| PEG-OCH3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 98.5 | |
| PEG-NH2 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 98.4 | |
| AuNP 56 nm | PEG-COOH 5 kDa | 97.2 | 99.7 | 98.2 |
| PEG-COOH 20 kDa | 98.4 | 102.4 | 99.4 | |
| PEG-OCH3 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 98.2 | |
| PEG-NH2 | 96.4 | 98.6 | 100.3 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicoară, R.; Ilieș, M.; Uifălean, A.; Iuga, C.A.; Loghin, F. Quantification of the PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Protein Corona. Influence on Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224789
Nicoară R, Ilieș M, Uifălean A, Iuga CA, Loghin F. Quantification of the PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Protein Corona. Influence on Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224789
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicoară, Raul, Maria Ilieș, Alina Uifălean, Cristina Adela Iuga, and Felicia Loghin. 2019. "Quantification of the PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Protein Corona. Influence on Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224789
APA StyleNicoară, R., Ilieș, M., Uifălean, A., Iuga, C. A., & Loghin, F. (2019). Quantification of the PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Protein Corona. Influence on Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224789






