Simultaneous PAN Carbonization and Ceramic Sintering for Fabricating Carbon Fiber-Ceramic Composite Heaters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Fabrication
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Component Analysis
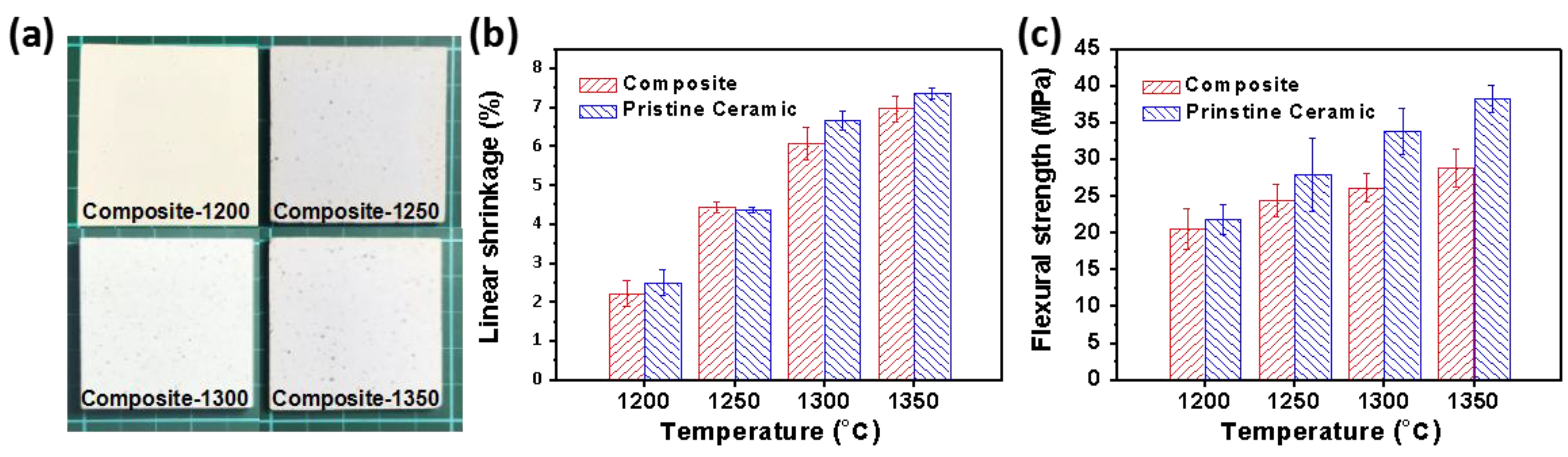
3.2. Physical Parameters of the Composites
3.3. Micromorphology of the Composites
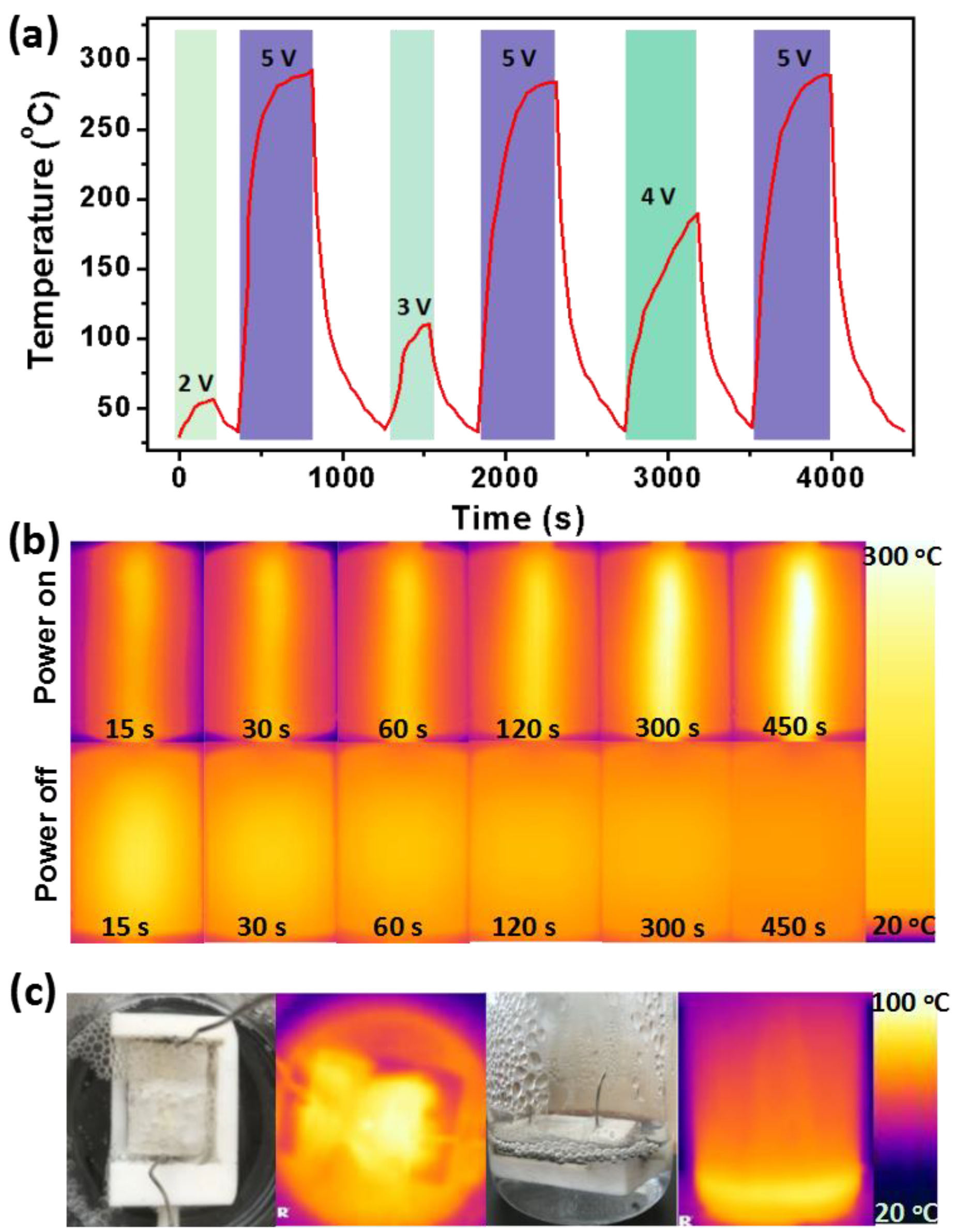
3.4. Evaluation of Electro-Thermal Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Liang, X.; Yin, Z.; Xia, K.; Wang, H.; Jian, M.; Zhang, Y. Weft-knitted fabric for a highly stretchable and low-voltage wearable heater. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1700193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-S.; Jeon, S.K.; Nahm, S.H. The manufacture of a transparent film heater by spinning multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2011, 49, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; He, W.; Wang, K.; Ran, Y.; Ye, C. Thermal response of transparent silver nanowire/pedot: Pss film heaters. Small 2014, 10, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Baima, M.; Andrew, T.L. Transforming commercial textiles and threads into sewable and weavable electric heaters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32299–32307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Cheng, F.; Ou, Y.; Lin, M.; Su, L.; Chen, S.; Yao, X.; Liu, D. A flexible and transparent thin film heater based on a carbon fiber/heat-resistant cellulose composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 153, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ke, K.-C.; Yang, S.-Y. Application of graphene–polymer composite heaters in gas-assisted micro hot embossing. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6336–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Islam, M.; Mahmood, N.; Achour, A.; Hameed, A.; Khatri, N. Catalytic growth of multi-walled carbon nanotubes using nife2o4 nanoparticles and incorporation into epoxy matrix for enhanced mechanical properties. J. Ploym. Eng. 2016, 36, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhai, H.; Wang, T.; Jin, Q.; Sun, J. Highly stretchable and conductive copper nanowire based fibers with hierarchical structure for wearable heaters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32925–32933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampuch, R. Ceramic Materials: An Introduction to Their Properties; Elsevier Science & Technology: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Dana, K.; Das, S.; Das, S.K. Effect of substitution of fly ash for quartz in triaxial kaolin–quartz–feldspar system. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 3169–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabi, A.; Guerfa, F.; Harabi, E.; Benhassine, M.-T.; Foughali, L.; Zaiou, S. Preparation and characterization of new dental porcelains, using k-feldspar and quartz raw materials. Effect of b 2 o 3 additions on sintering and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 65, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Schreuer, J.; Hildmann, B. Structure and properties of mullite—A review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jones, F.; James, P. Continuous fibre reinforced mullite matrix composites by sol–gel processing: Part i fabrication and microstructures. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 3361–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jones, F.; James, P. Continuous fiber reinforced mullite matrix composites by sol–gel processing: Part ii properties and fracture behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 3629–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yin, X.; Fan, X.; Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. Mechanical and electromagnetic shielding properties of carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites. Carbon 2015, 95, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrburger, P.; Donnet, J.; Ubbelohde, A.; Johnson, J.; Richardson, M.; Scott, R. Interface in composite materials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1980, 294, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Liu, W. Mechanical and oxidation resistance properties of 3d carbon fiber-reinforced mullite matrix composites prepared by sol–gel process. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 7203–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadzadeh, T. Formation of mullite from precursor powders: Sintering, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. 2003, 355, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, K. Interface engineering in mullite fiber/mullite matrix composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanlı, A.G.; Windle, A.H. Carbon fibres from cellulosic precursors: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4236–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Ismail, A. Post spinning and pyrolysis processes of polyacrylonitrile (pan)-based carbon fiber and activated carbon fiber: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2012, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Y.; Lee, W.E. Microstructural evolution in triaxial porcelain. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 3121–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ece, O.I.; Nakagawa, Z.-E. Bending strength of porcelains. Ceram. Int. 2002, 28, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Márquez, J.; Rincón, J.M.; Romero, M. Effect of firing temperature on sintering of porcelain stoneware tiles. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Márquez, J.; Rincón, J.M.; Romero, M. Mullite development on firing in porcelain stoneware bodies. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Ganguli, D.; Roy, S.K.; Kumar, S. Chemical Analysis of Ceramic and Allied Materials; Indian Institute of Ceramics: Andhra Pradesh, Indian, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- BS EN ISO 10545-3:2018 Ceramic Tiles. Determination of Water Absorption, Apparent Porosity, Apparent Relative Density and Bulk Density; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lerdprom, W.; Grasso, S.; Jayaseelan, D.D.; Reece, M.J.; Lee, W.E. Densification behaviour and physico-mechanical properties of porcelains prepared using spark plasma sintering. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2017, 116, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lan, G.; Tuan, W. Microstructural evolution of mullite during the sintering of kaolin powder compacts. Ceram. Int. 2000, 26, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.A.; Niño, C.J.; Contreras, J.E.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, F.; Perales, J.L.; Aguilar-Martínez, J.; Puente-Ornelas, R.; Banda, M.L. Influence of incorporation of fired porcelain scrap as partial replacement of quartz on properties of an electrical porcelain. J. Clean. Prod. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štubňa, I.; Chmelík, F.; Trník, A.; Šín, P. Acoustic emission study of quartz porcelain during heating up to 1150 °C. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 6919–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, L.; Pimenta, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M. Raman spectroscopy in graphene. Phys. Rep. 2009, 473, 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambach, M.; Möller, H.; Neumann, T.; Volkmer, D. Carbon fibre reinforced cement-based composites as smart floor heating materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 90, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacan, I.; Erzurumluoğlu, L. The effect of carbonization temperature on the structure and properties of carbon fibers prepared from poly (m-phenylene isophthalamide) precursor. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1629–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakali, G.; Perraki, T.; Tsivilis, S.; Badogiannis, E. Thermal treatment of kaolin: The effect of mineralogy on the pozzolanic activity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 20, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, A.E.; Perananthan, S.; Ferraris, J.P. Carbonized electrospun nanofiber sheets for thermophones. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 31192–31201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.H.; Park, S.B.; Ayrilmis, N.; Oh, S.W.; Kim, N.H. Effect of carbonization temperature on electrical resistivity and physical properties of wood and wood-based composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 46, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Tang, B.; Lu, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Simultaneous PAN Carbonization and Ceramic Sintering for Fabricating Carbon Fiber-Ceramic Composite Heaters. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224945
Li D, Tang B, Lu X, Li Q, Chen W, Dong X, Wang J, Wang X. Simultaneous PAN Carbonization and Ceramic Sintering for Fabricating Carbon Fiber-Ceramic Composite Heaters. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224945
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Daiqi, Bin Tang, Xi Lu, Quanxiang Li, Wu Chen, Xiongwei Dong, Jinfeng Wang, and Xungai Wang. 2019. "Simultaneous PAN Carbonization and Ceramic Sintering for Fabricating Carbon Fiber-Ceramic Composite Heaters" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224945
APA StyleLi, D., Tang, B., Lu, X., Li, Q., Chen, W., Dong, X., Wang, J., & Wang, X. (2019). Simultaneous PAN Carbonization and Ceramic Sintering for Fabricating Carbon Fiber-Ceramic Composite Heaters. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224945








