Regeneration of Activated Carbons Spent by Waste Water Treatment Using KOH Chemical Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Regenerated ACs
2.2. Characterization of Prepared ACs
2.3. Test for Adsorption of Toluene on the ACs
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellmann, P.; Greiner-perth, K.; Jacob, S.; Knoll, M.; Schäfer, M.; Stängle, M.; Ziegler, M.; Scheurer, M.; Köhler, H.R.; Triebskorn, R. Does Waste Water Treatment Plant Upgrading with Powdered Activated Carbon Result in Reduced Water and Sediment Toxicity of the Receiving Stream? Int. Water Wastewater Treat. 2017, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- San Miguel, G.; Lambert, S.D.; Graham, N.J.D. The regeneration of field-spent granular-activated carbons. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moona, N.; Murphy, K.R.; Bondelind, M.; Bergstedt, O.; Pettersson, T.J.R. Partial renewal of granular activated carbon biofilters for improved drinking water treatment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, E.; González, E.; González, J.F.; González-García, C.M.; Ramiro, A.; Gañan, J. Thermal regeneration of activated carbon saturated with p-nitrophenol. Carbon N. Y. 2004, 42, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagawan, D.; Poodari, S.; Ravi kumar, G.; Golla, S.; Anand, C.; Banda, K.S.; Himabindu, V.; Vidyavathi, S. Reactivation and recycling of spent carbon using solvent desorption followed by thermal treatment (TR). J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2014, 17, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, B.; Román, S.; Álvarez-Murillo, A.; Sabio, E.; González-García, C.M. Fundamental study on the thermal regeneration stages of exhausted activated carbons: Kinetics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Junior, O.P.; Vargas, A.M.M.; Da Silva, A.P.; Zou, X.; Asefa, T.; Almeida, V.C. Thermal regeneration study of high surface area activated carbon obtained from coconut shell: Characterization and application of response surface methodology. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Du, E. The Effects of Thermal Regeneration Conditions and Inorganic Compounds on the Characteristics of Activated Carbon Used in Power Plant. Energy Procedia 2012, 17, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalişkan, E.; Bermúdez, J.M.; Parra, J.B.; Menéndez, J.A.; Mahramanlioĝlu, M.; Ania, C.O. Low temperature regeneration of activated carbons using microwaves: Revising conventional wisdom. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, R.; Marco-Lozar, J.P.; Quijada, C.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Comparison among chemical, thermal, and electrochemical regeneration of phenol-saturated activated carbon. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 3366–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, P.M.; Beltrán, F.J.; Gómez-Serrano, V.; Jaramillo, J.; Rodríguez, E.M. Comparison between thermal and ozone regenerations of spent activated carbon exhausted with phenol. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagreev, A.; Rahman, H.; Bandosz, T.J. Thermal regeneration of a spent activated carbon previously used as hydrogen sulfide adsorbent. Carbon N. Y. 2001, 39, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapteijn, F.; Porre, H.; Moulijn, J.A. CO2 gasification of activated carbon catalyzed by earth alkaline elements. AIChE J. 1986, 32, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, F.; Sánchez Jiménez, C. Effect of regeneration treatment with liquid water at high pressure and temperature on the characteristics of three commercial activated carbons. Carbon N. Y. 1999, 37, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, L.; Essex, D.; Giess, P.; Graham, N.; Kaur, K.; Lambert, S.; Spencer, C. Improving the performance of granular activated carbon (GAC) via pre-regeneration acid treatment. Water Environ. J. 2005, 19, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-G.; Son, H.-J.; Jung, J.-M.; Ryu, D.-C.; Yoo, P.-J. Evaluation of Drinking Water Treatment Efficiency according to Regeneration Temperatures of Granular Activated Carbon (GAC). J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2015, 24, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, G.; Drikas, M. Chemical regeneration of granular activated carbon from an operating water treatment plant. Water Res. 1993, 27, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Lee, G.B.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, B.U.; Kim, H.; Kim, S. The effects of methane storage capacity using upgraded activated carbon by KOH. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.B.; Park, J.E.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Hong, B.U. Comparison of by-product gas composition by activations of activated carbon. Carbon Lett. 2019, 29, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, P. Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 479–495. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, L.J.R.; De Oliveira Matias, J.C.; Da Silva Catalão, J.P. Torrefaction of Biomass for Energy Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Manocha, S.M. Porous carbons. Sadhana 2003, 28, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, D.; Yan, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, T. The pore size distribution and its relationship with shale gas capacity in organic-rich mudstone of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations, Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 1, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Bogeat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Fernández-González, C.; Gómez-Serrano, V. Activated carbon surface chemistry: Changes upon impregnation with Al(III), Fe(III) and Zn(II)-metal oxide catalyst precursors from NO3− aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tu, L.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Coconut-based activated carbon fibers for efficient adsorption of various organic dyes. Rsc. Adv. 2018, 8, 42280–42291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsyuk, V.; Kalyva, M.; Papagelis, K.; Parthenios, J.; Tasis, D.; Siokou, A.; Kallitsis, I.; Galiotis, C. Chemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon N. Y. 2008, 46, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Abouelamaiem, D.; Mostazo-López, M.J.; He, G.; Patel, D.; Neville, T.P.; Parkin, I.P.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; Morallón, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Jorge, A.B.; et al. New insights into the electrochemical behaviour of porous carbon electrodes for supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage 2018, 19, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, A.; Podkościelny, P.; Hubicki, Z.; Barczak, M. Adsorption of phenolic compounds by activated carbon—A critical review. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.T.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Koo, S.; Jerng, D.-W.; Wongwises, S.; Ahn, H.S. Mesoporous graphene adsorbents for the removal of toluene and xylene at various concentrations and its reusability. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, G.B.; Park, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Hong, B. Removal and recycling of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) adsorbed on activated carbons using in situ vacuum systems. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 7827–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo-Ródenas, M.A.; Cazorla-Amoró, D.; Linares-Solano, A. Behaviour of activated carbons with different pore size distributions and surface oxygen groups for benzene and toluene adsorption at low concentrations. Carbon N. Y. 2005, 43, 1758–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, Y.C.; Chiang, P.C.; Huang, C.P. Effects of pore structure and temperature on VOC adsorption on activated carbon. Carbon N. Y. 2001, 39, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


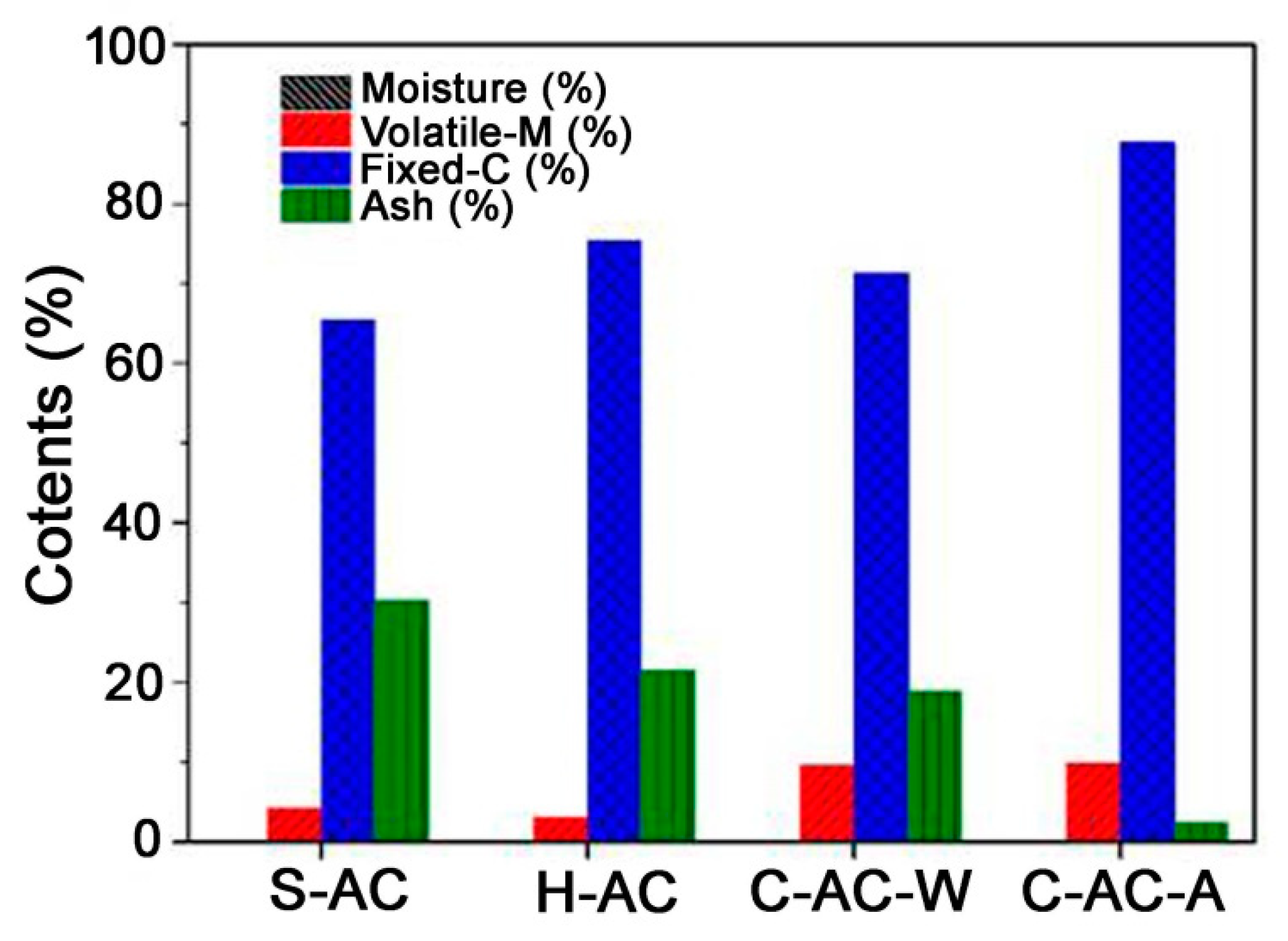

| S-AC | H-AC | C-AC-W | C-AC-A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 681 ± 20 | 709 ± 18 | 1383 ± 16 | 1612 ± 9 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.38 ± 0.06 | 0.40 ± 0.06 | 0.78 ± 0.04 | 0.85 ± 0.03 |
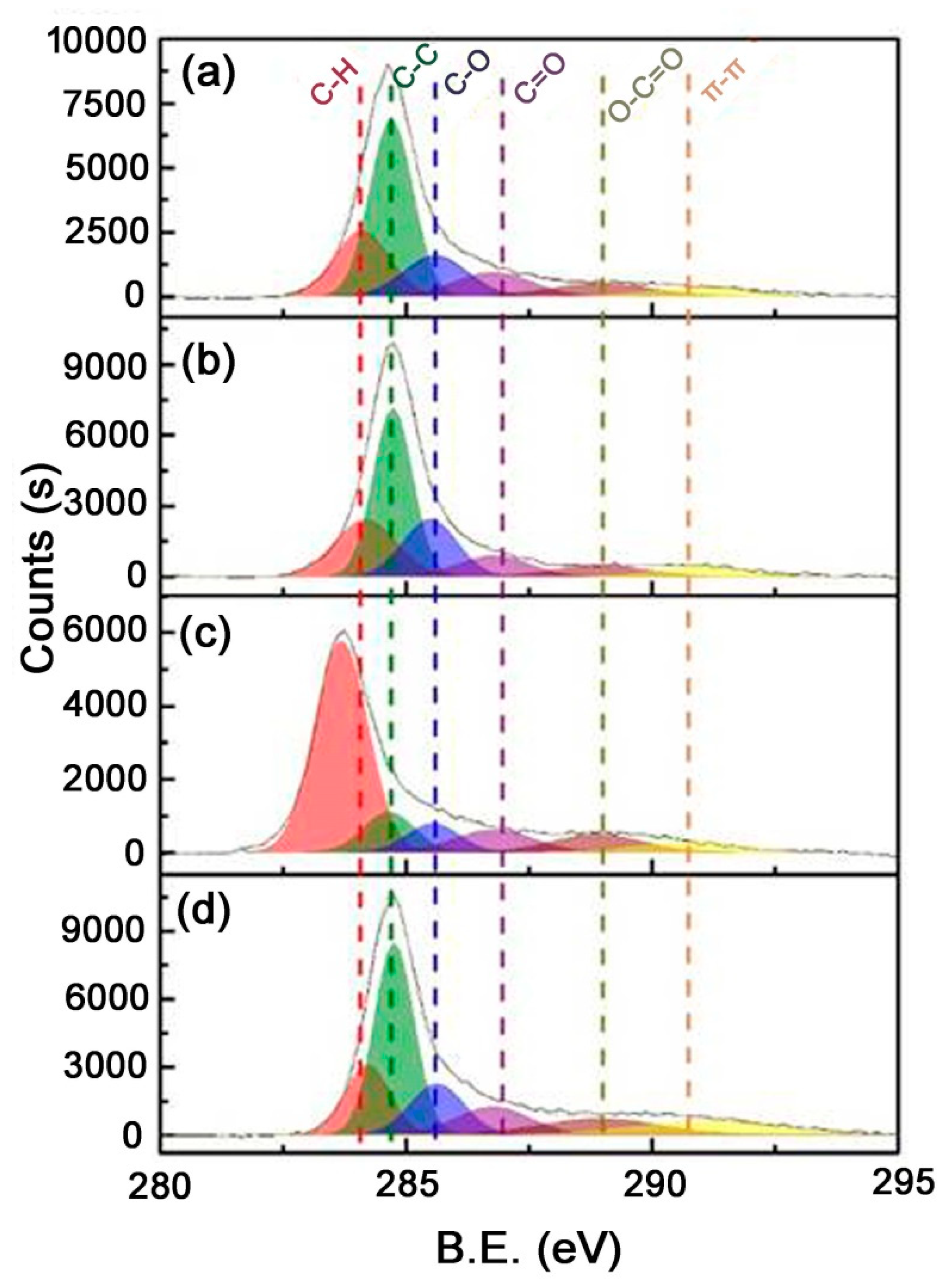
| Surface Concentration (from C 1 s Peak) of (% at.): | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.E. (eV) (Assign) | 283.6–284.2 | 284.6–284.8 | 285.5–285.6 | 286.7–286.8 | 288.8–289.0 | 290.6–291.1 |
| (C-H) | (C-C) | (C-O/C-O-C) | (C=O) | (O-C=O) | (π-π) | |
| S-AC | 20.14 | 42.70 | 14.46 | 10.39 | 7.41 | 4.89 |
| H-AC | 21.13 | 39.57 | 18.69 | 8.85 | 6.55 | 5.21 |
| C-AC-W | 58.51 | 10.69 | 7.86 | 9.32 | 8.42 | 5.21 |
| C-AC-A | 16.01 | 39.25 | 14.20 | 10.60 | 9.87 | 10.08 |
| Elemental Analysis (wt. %) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Carbon | Hydrogen | Sulfur | Oxygen | Total | |
| S-AC | N.D. | 69.98 | 0.38 | N.D. | 2.27 | 72.64 |
| H-AC | N.D. | 73.43 | 0.33 | N.D. | 0.84 | 74.60 |
| C-AC-W | N.D. | 71.30 | 0.34 | N.D. | 3.47 | 75.12 |
| C-AC-A | N.D. | 86.26 | 0.11 | N.D. | 2.30 | 88.68 |
| XRF Analysis Results (wt. %) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | Si | Fe | S | K | Al | Mn | Ti | P | Cu | Cr | |
| S-AC | 31.2 | 23.5 | 18.2 | 8.0 | 5.8 | 5.02 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 0.6 |
| H-AC | 29.1 | 29.2 | 12.6 | 9.4 | 6.9 | 6.27 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 0 | 0 |
| C-AC-W | 34.3 | 31.1 | 13.0 | 0.6 | 7.9 | 8.77 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C-AC-A | 3.7 | 21.2 | 44.2 | 4.8 | 16.0 | 1.6 | 0 | 6.0 | 2.6 | 0 | 0 |
| S-AC | H-AC | C-AC-W | C-AC-A | Commercial AC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toluene Capacity (g-toluene/g-AC) | 0.033 | 0.100 | 0.091 | 0.154 | 0.142 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.E.; Lee, G.B.; Hong, B.U.; Hwang, S.Y. Regeneration of Activated Carbons Spent by Waste Water Treatment Using KOH Chemical Activation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235132
Park JE, Lee GB, Hong BU, Hwang SY. Regeneration of Activated Carbons Spent by Waste Water Treatment Using KOH Chemical Activation. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(23):5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235132
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jung Eun, Gi Bbum Lee, Bum Ui Hong, and Sang Youp Hwang. 2019. "Regeneration of Activated Carbons Spent by Waste Water Treatment Using KOH Chemical Activation" Applied Sciences 9, no. 23: 5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235132
APA StylePark, J. E., Lee, G. B., Hong, B. U., & Hwang, S. Y. (2019). Regeneration of Activated Carbons Spent by Waste Water Treatment Using KOH Chemical Activation. Applied Sciences, 9(23), 5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235132




