Effect of Rotating Cylinder on Mixing Performance in a Cylindrical Double-Ribbon Mixer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Mixing Indices and Subdomain Mixing Index (SMI)
3. Simulation Method
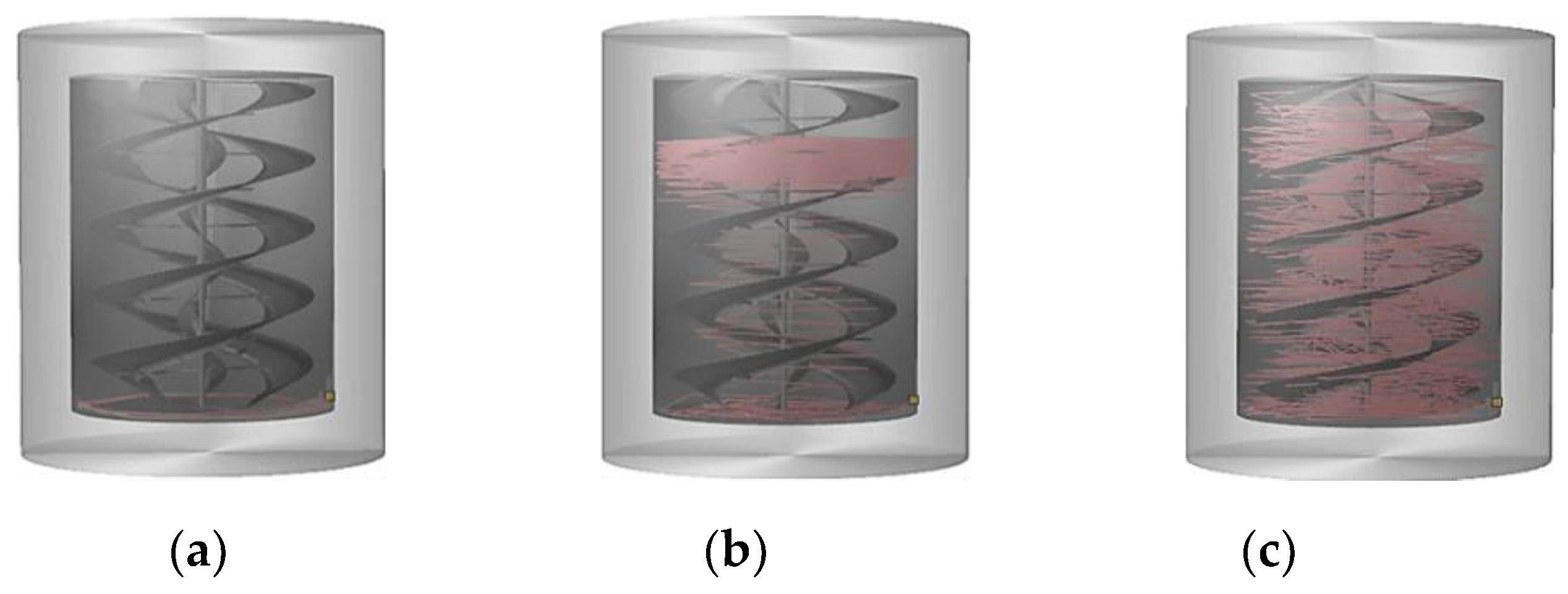
3.1. Model System
3.2. Computational Model
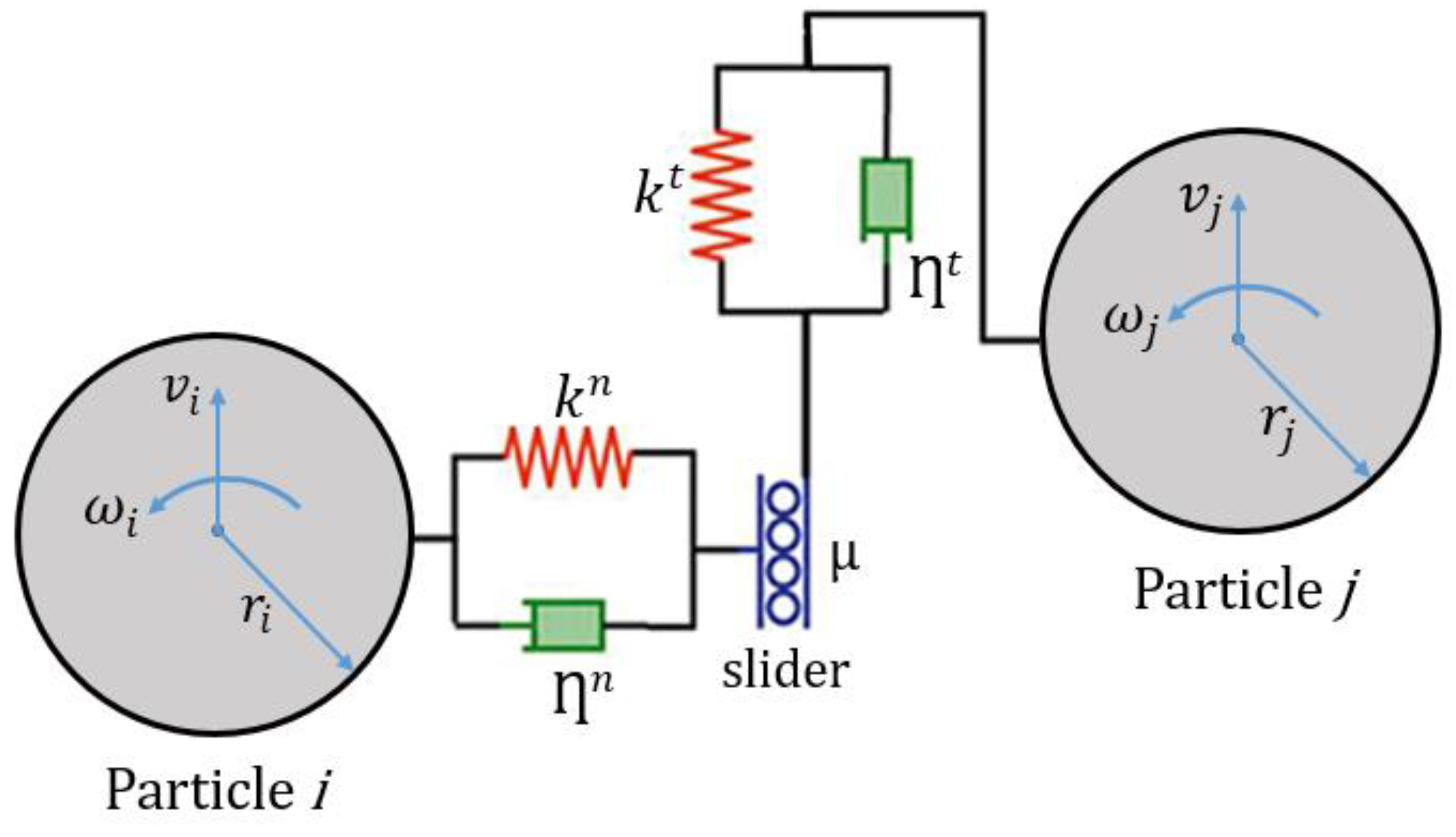
3.3. DEM
4. Results and Discussions
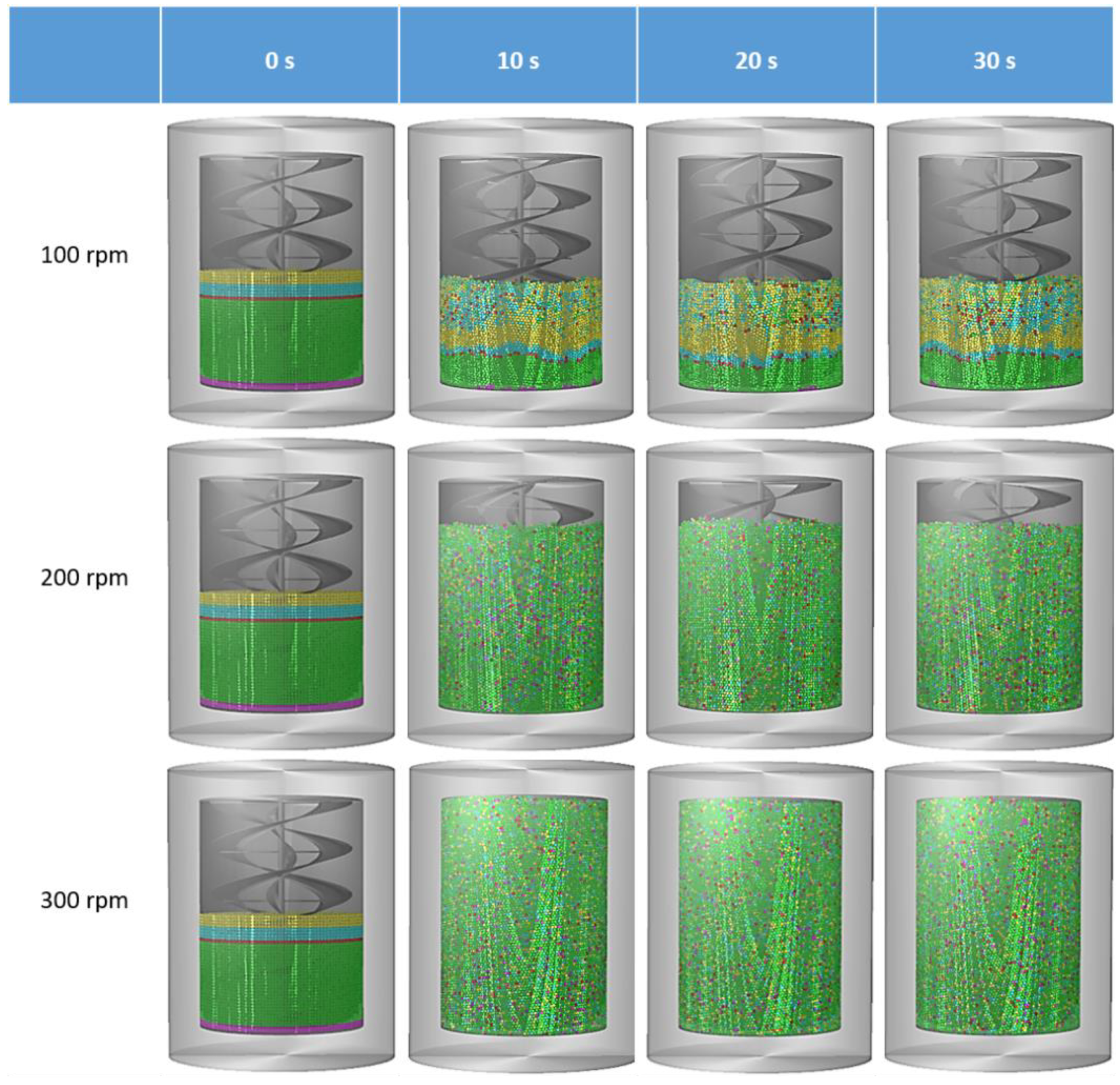
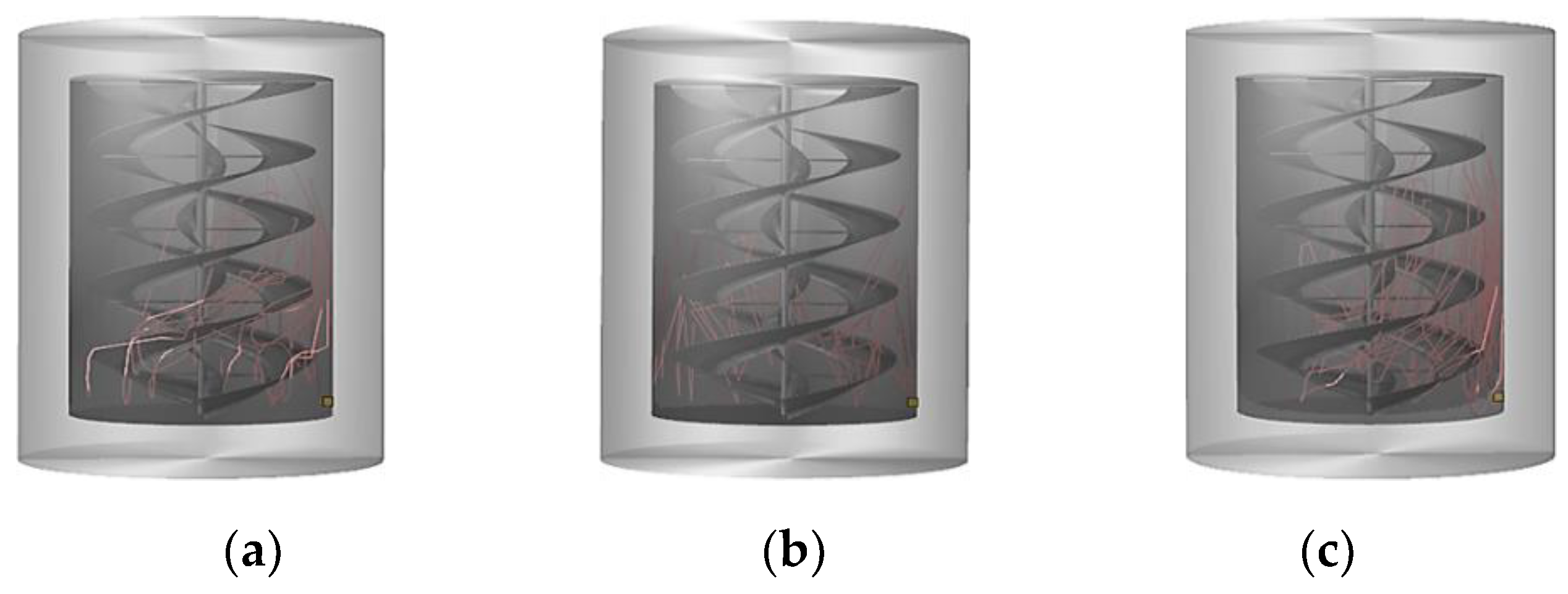
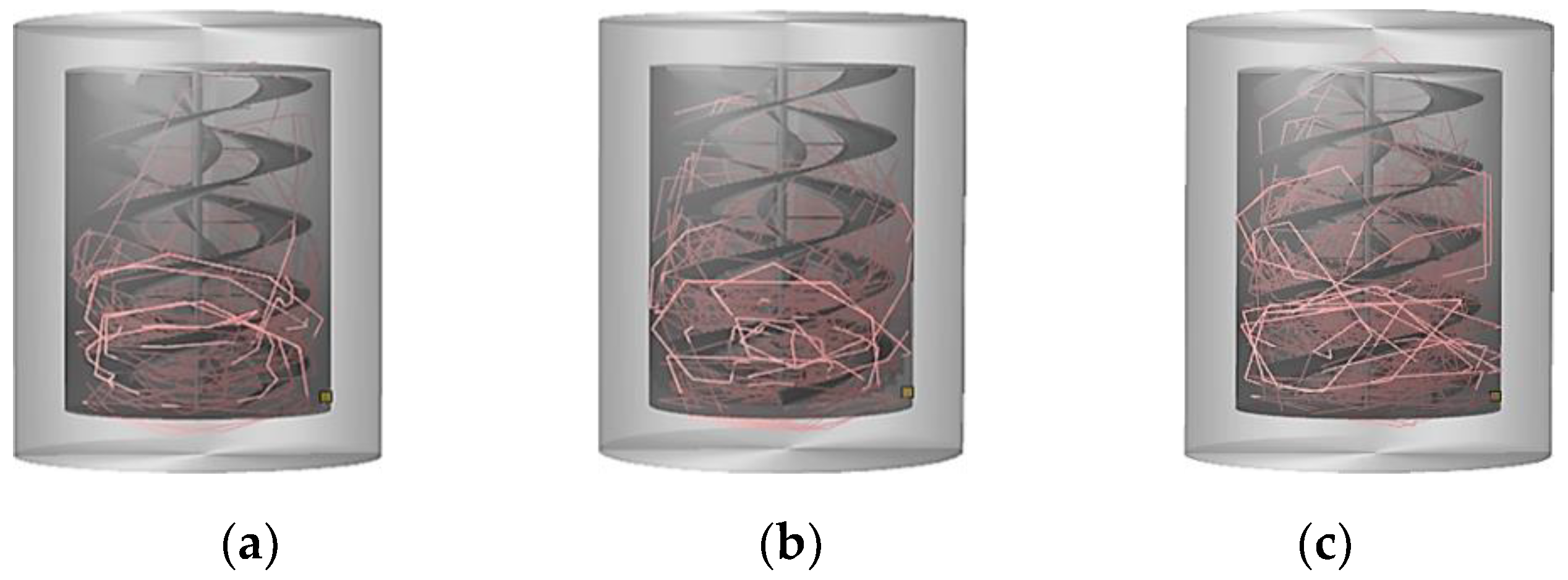
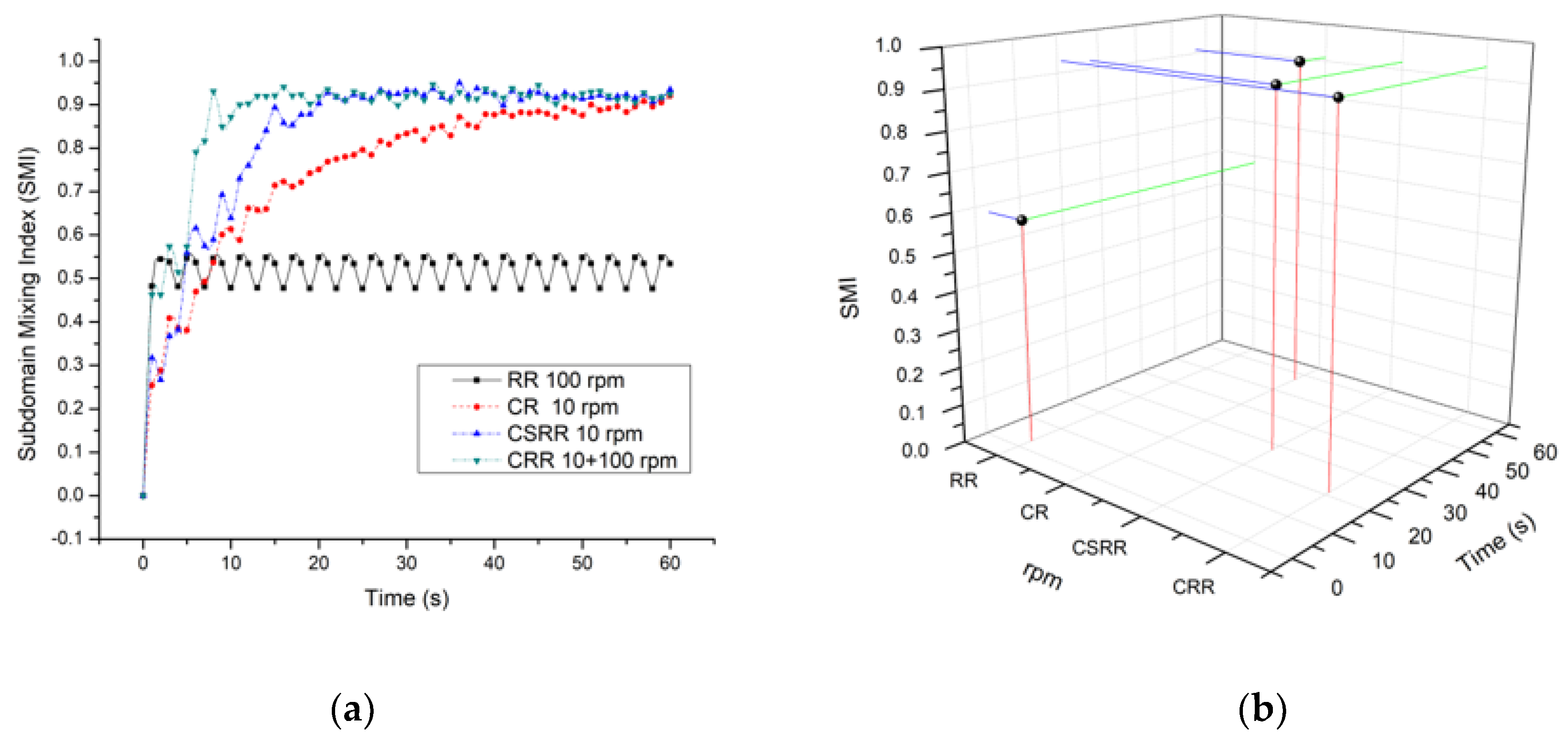
4.1. Effect of Ribbon Rotational (RR) Speed
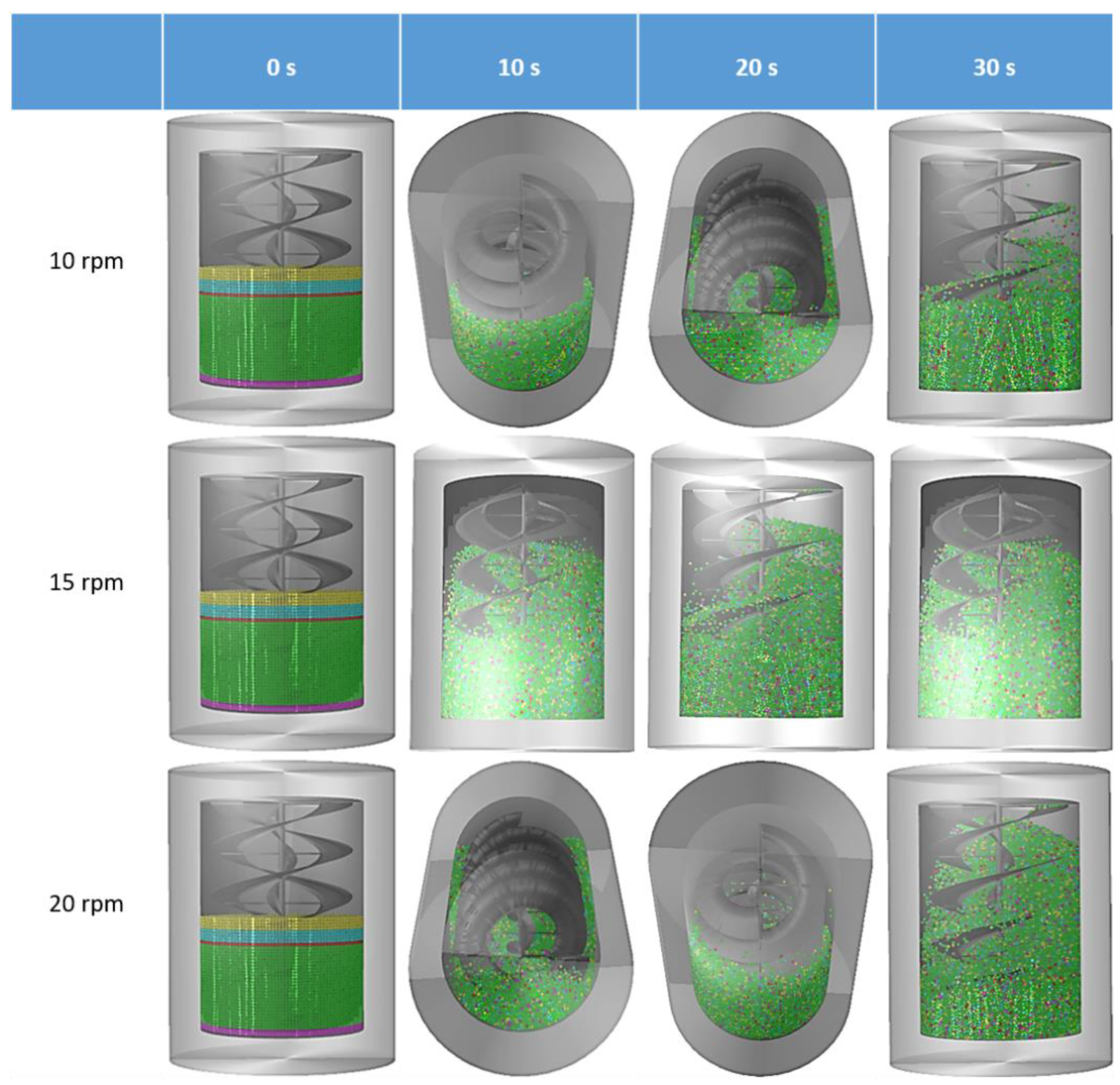
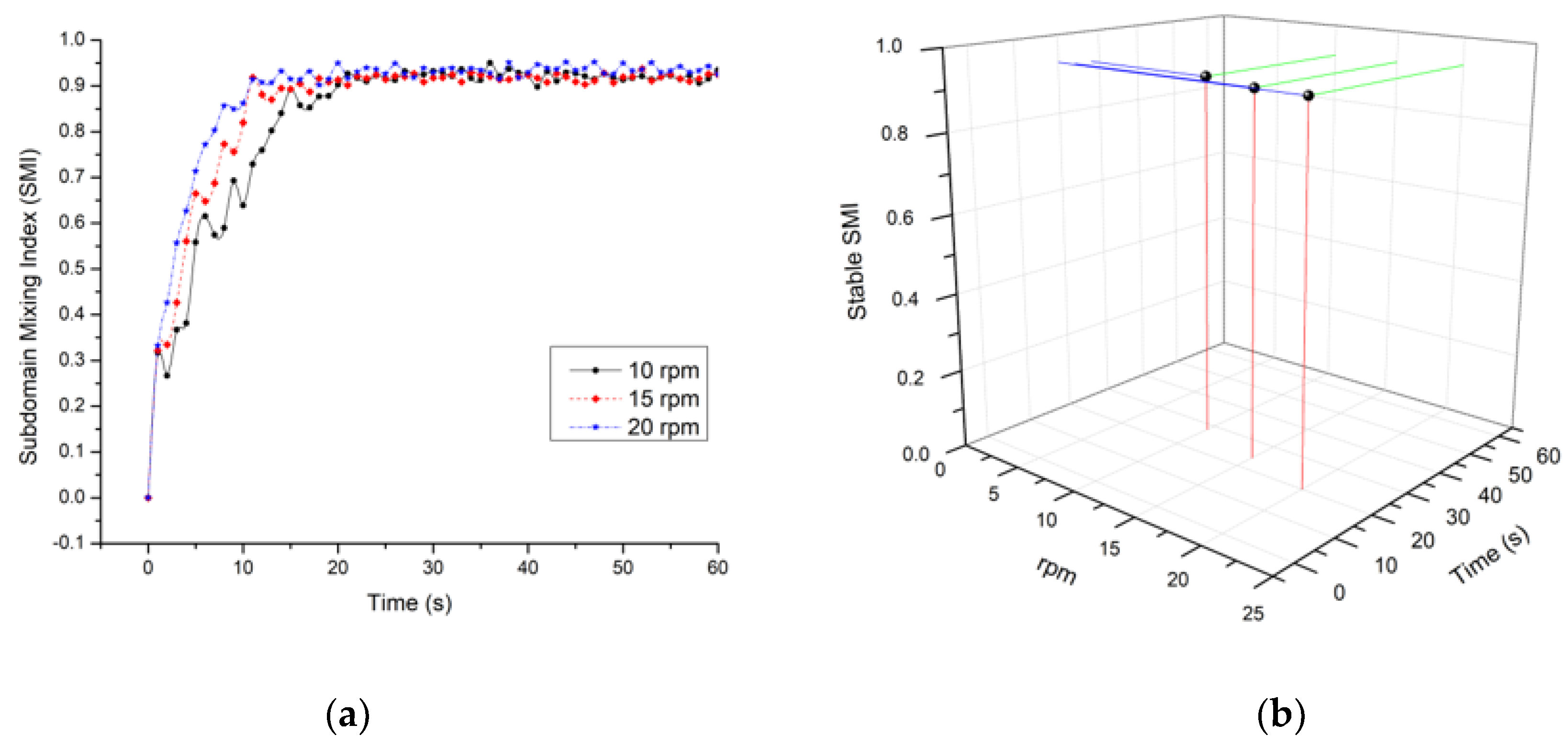
4.2. The Effect of Cylinder Rotational Speed
4.2.1. The Effect of Cylinder Rotational (CR) Speed without Ribbon
4.2.2. The Effect of Cylinder with Static Ribbon Rotational Speed (CSRR)
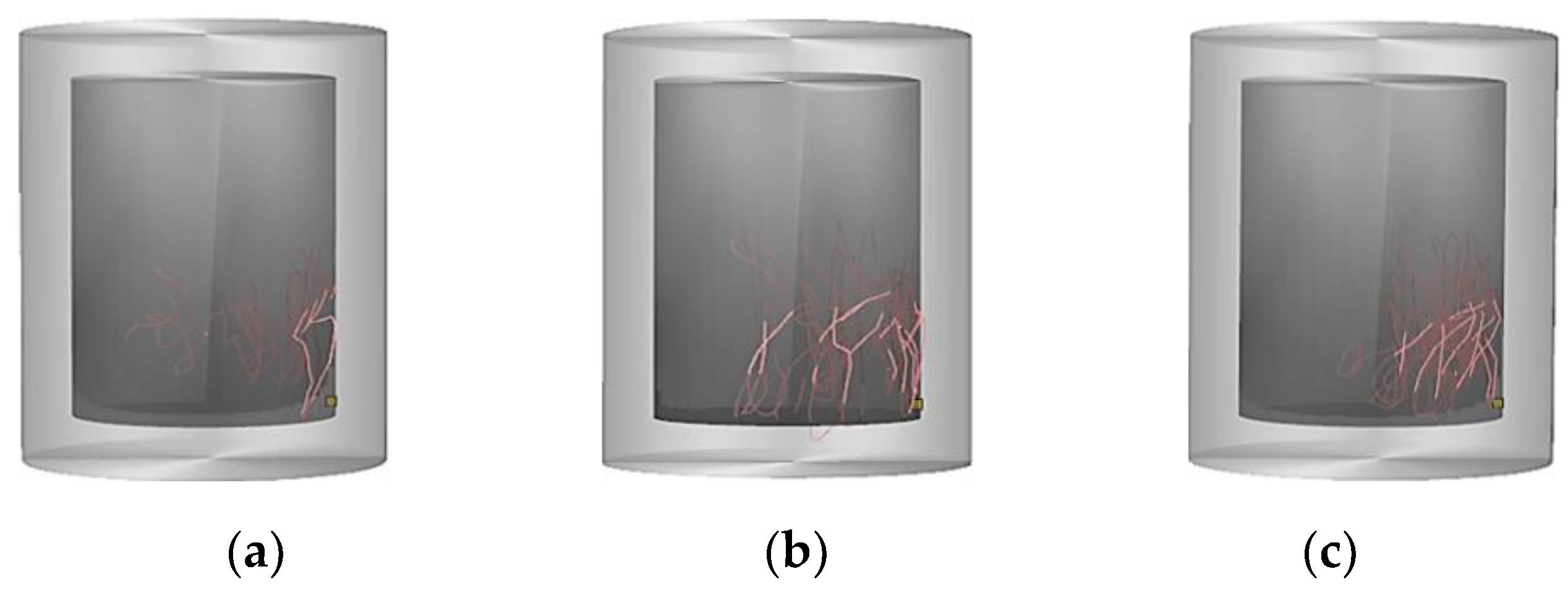
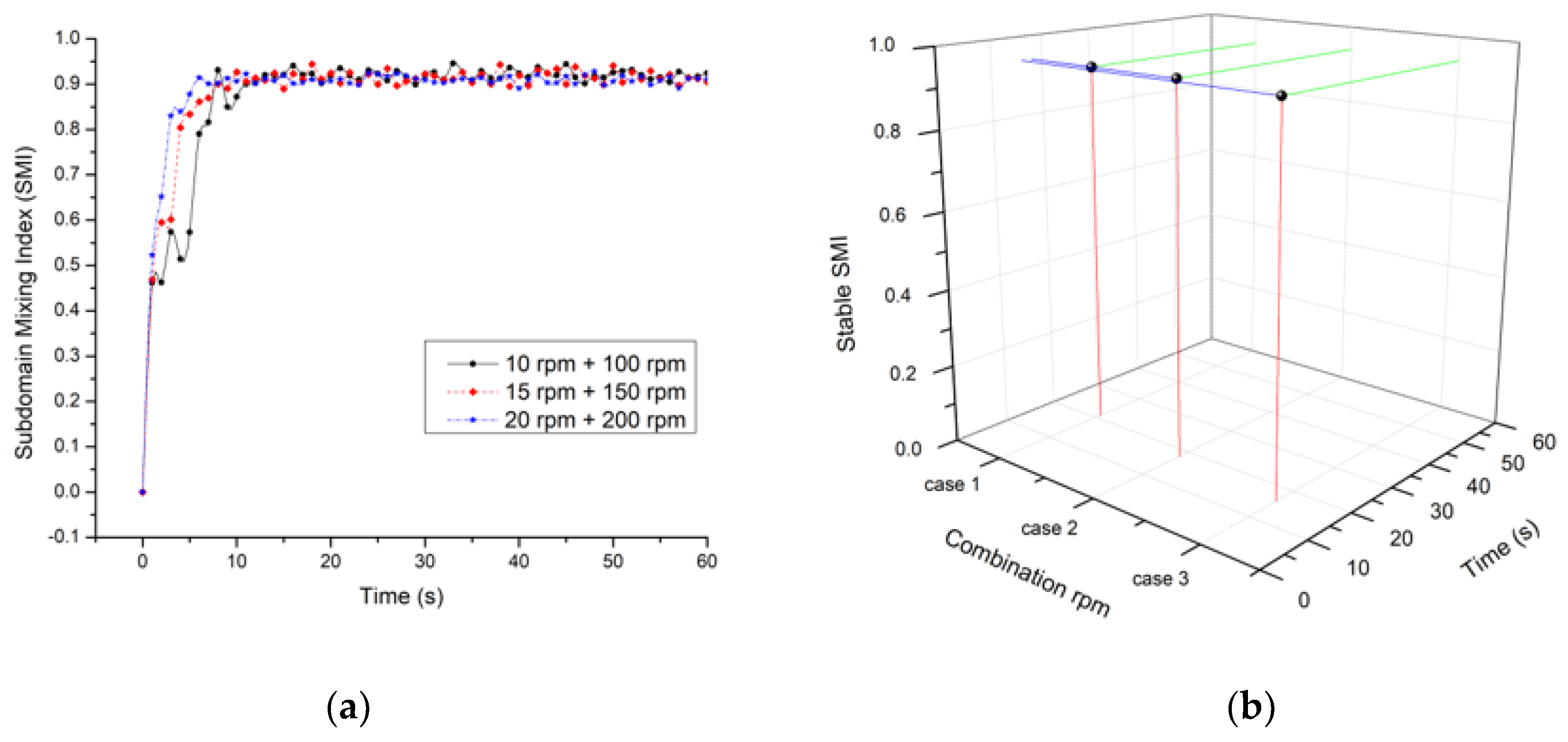
4.3. Effect of Combination (Cylinder + Ribbon) Rotational Speed
4.4. Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SMI | Subdomain-based mixing index |
| RR | Ribbon rotation |
| CR | Cylinder rotation |
| CSRR | Cylinder with static ribbon rotation |
| CRR | Cylinder and ribbon rotation |
References
- Thakur, R.K.; Vial, C.; Nigam, K.D.P.; Nauman, E.B.; Djelveh, G. Static Mixers in the Process Industries—A Review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2003, 81, 787–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, S.I.F.; Lee, T.J.; Menning, M.M. Effect of drug substance particle size on the characteristics of granulation manufactured in a high-shear mixer. AAPS PharmSciTech 2000, 1, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoornahad, H.; Koenders, E.A.B. Towards Simulation of Fresh Granular-Cement Paste Material Behavior. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 295, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radl, S.; Kalvoda, E.; Glasser, B.J.; Khinast, J.G. Mixing characteristics of wet granular matter in a bladed mixer. Power Technol. 2010, 200, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Dutta, P.; Shim, J. A non-sampling mixing index for multicomponent mixtures. Power Technol. 2017, 319, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnby, N.; Edwards, M.F.; Nienow, A.W. Mixing in the Process Industries, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 1992; 414p. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, B.F.C.; Bridgwater, J.; Parker, D.J. Motion in a particle bed agitated by a single blade. AIChE J. 2004, 46, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrsin, S. Simple theory of an idealized turbulent mixer. AIChE J. 1957, 3, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Heindel, T.J.; Wright, M.M. Numerical study of particle mixing in a lab-scale screw mixer using the discrete element method. Power Technol. 2017, 308, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alian, M.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Upreti, S.R. Analysis of the mixing of solid particles in a plowshare mixer via discrete element method (DEM). Power Technol. 2015, 274, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, H.; Kamla, Y.; Sahel, D. Performance of Helical Ribbon and Screw Impellers for Mixing Viscous Fluids in Cylindrical Reactors. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, X. Mixing Performance of a 3D Micro T-Mixer with Swirl-Inducing Inlets and Rectangular Constriction. Micromachines 2018, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liu, L.; Liao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zang, M.; Tan, Y. Discrete element analysis of the particle mixing performance in a ribbon mixer with a double U-shaped vessel. Granul. Matter 2019, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailova, O.; Mothersdale, T.; Rodgers, T.; Ren, Z.; Watson, S.; Lister, V.; Kowalski, A. Optimisation of mixing performance of helical ribbon mixers for high throughput applications using computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 132, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiuk, S. Power consumption, mixing time and attrition action for solid mixing in a ribbon mixer. Power Technol. 1987, 51, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Cleary, P.W. Flow and mixing performance in helical ribbon mixers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 84, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzio, F.J.; Llusa, M.; Goodridge, C.L.; Duong, N.-H.; Shen, E. Evaluating the mixing performance of a ribbon blender. Power Technol. 2008, 186, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiński, H.; Rzyski, E. Power requirements of helical ribbon mixers. Chem. Eng. J. 1980, 19, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, M.C.; Phillips, S.M. Supplemental Protein in Support of Muscle Mass and Health: Advantage Whey. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, A8–A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ellis, V.; Dhaliwal, S. Effects of whey protein isolate on body composition, lipids, insulin and glucose in overweight and obese individuals. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morifuji, M.; Koga, J.; Kawanaka, K.; Higuchi, M. Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Containing Dipeptides, Identified from Whey Protein Hydrolysates, Stimulate Glucose Uptake Rate in L6 Myotubes and Isolated Skeletal Muscles. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2009, 55, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basinskas, G.; Sakai, M. Numerical study of the mixing efficiency of a ribbon mixer using the discrete element method. Power Technol. 2016, 287, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Quoc, L.; Zhang, X.; Walton, O.R. A 3-D discrete-element method for dry granular flows of ellipsoidal particles. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 187, 483–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luding, S. Introduction to discrete element methods. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2008, 12, 785–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, S. Experimental and DEM studies on the transition of axial segregation in a truck mixer. Power Technol. 2017, 314, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, P.M.C. Developments in the theory of particle mixing. J. Appl. Chem. 1954, 4, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, P.M.C. The mixing of solid particles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1997, 75, S49–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, B.N.; Langston, P.A.; Matchett, A.J. A generalised mixing index in distinct element method simulation of vibrated particulate beds. Granul. Matter 2002, 4, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraj, M.S.; Radl, S.; Glasser, B.J.; Khinast, J.G. Effect of blade angle and particle size on powder mixing performance in a rectangular box. Power Technol. 2011, 211, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Ingredients | Percentage (%) | Weight (g) | Density (kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated fats | 10 | 100 | 917.2 |
| Salts (sugar, sodium, flavor, etc) | 10 | 100 | 1203.5 |
| Fibers | 3 | 30 | 1300.5 |
| Protein | 70 | 700 | 1319.5 |
| Carbohydrates | 7 | 70 | 1592.9 |
| Ingredients | Number of particles | Radius (mm) | Assigned color |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated fats | 8014 | 2 | Yellow |
| Salts (sugar, sodium, flavor, etc) | 8006 | 2 | Sky Blue |
| Fibers | 2007 | 2 | Red |
| Protein | 52140 | 2 | Green |
| Carbohydrates | 4119 | 2 | Pink |
| Ingredients | Value |
|---|---|
| Coefficient of restitution | 0.5 |
| Coefficient of static friction | 0.3 |
| Coefficient of dynamic friction | 0.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harish, V.V.N.; Cho, M.; Shim, J. Effect of Rotating Cylinder on Mixing Performance in a Cylindrical Double-Ribbon Mixer. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235179
Harish VVN, Cho M, Shim J. Effect of Rotating Cylinder on Mixing Performance in a Cylindrical Double-Ribbon Mixer. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(23):5179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235179
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarish, V.V.N., Migyung Cho, and Jaesool Shim. 2019. "Effect of Rotating Cylinder on Mixing Performance in a Cylindrical Double-Ribbon Mixer" Applied Sciences 9, no. 23: 5179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235179
APA StyleHarish, V. V. N., Cho, M., & Shim, J. (2019). Effect of Rotating Cylinder on Mixing Performance in a Cylindrical Double-Ribbon Mixer. Applied Sciences, 9(23), 5179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235179





