Latency-Optimal Virtual Network Functions Resource Allocation for 5G Backhaul Transport Network Slicing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To optimize the transport network latency and improve load-balance, a pair-decision resource allocation model for backhaul transport NS is introduced on account of mapping virtual nodes and links in a coordinated way. Here, the mapping objects are substrate network resources and SCs of E2E slices (i.e., including VNUs and their interconnections), and the problem model encloses the formulation of ILP, whose resolution yields the optimal path for VNFs and virtual links mapping and traffic routing.
- For further improving extreme QoS (such as 5G ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC)), the above resource allocation problem is formulated to minimize the transport network latency with considering the transmission time and propagation time, subject to the network capacity and link bandwidth constraints. In addition, in order to improve the network resource utilization and load balance, a node importance metric is employed to analyze the DCs’ availability and priority in the substrate network.
2. Related Work
2.1. NFV and SDN
2.2. VNF Placement and Virtual Network Embedding
2.3. Network Slicing and Resource Allocation
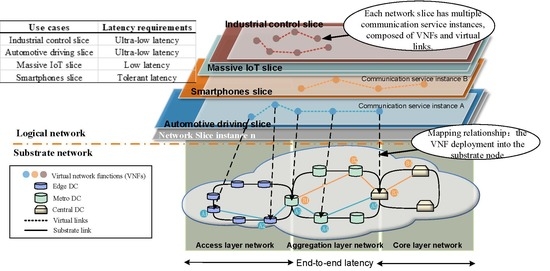
3. System Model
3.1. VNF Resources Allocation Process
3.2. NS Resource of Substrate and Logical Network
3.3. Substrate Node Importance Metric
3.4. Pair-Decision Resource Mapping Relations
3.5. Latency Performance
4. Problem Statement and Algorithm Framework
4.1. Problem Formulation
4.2. Algorithm Framework
5. Numerical Results and Performance Analysis
5.1. Simulation Setup
5.2. Numerical Results
5.2.1. Transport Network Latency
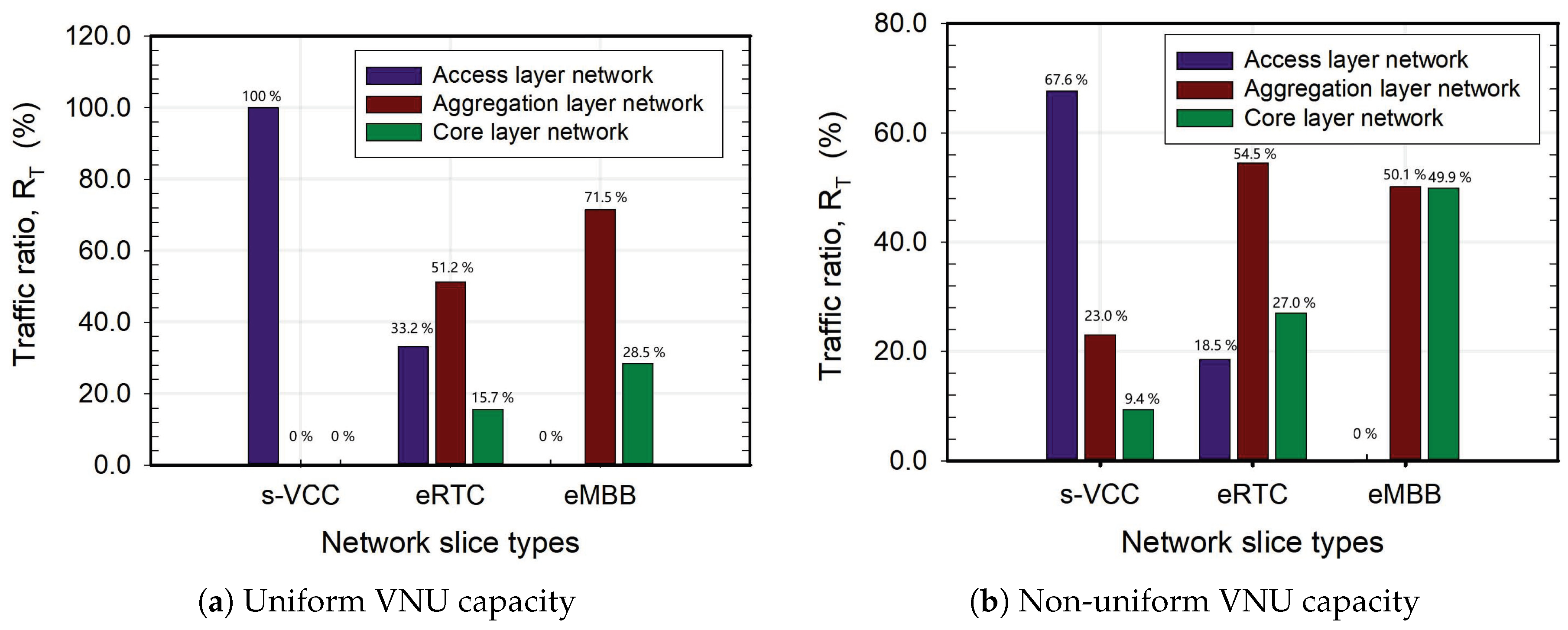
5.2.2. Transport Network Traffic Distribution
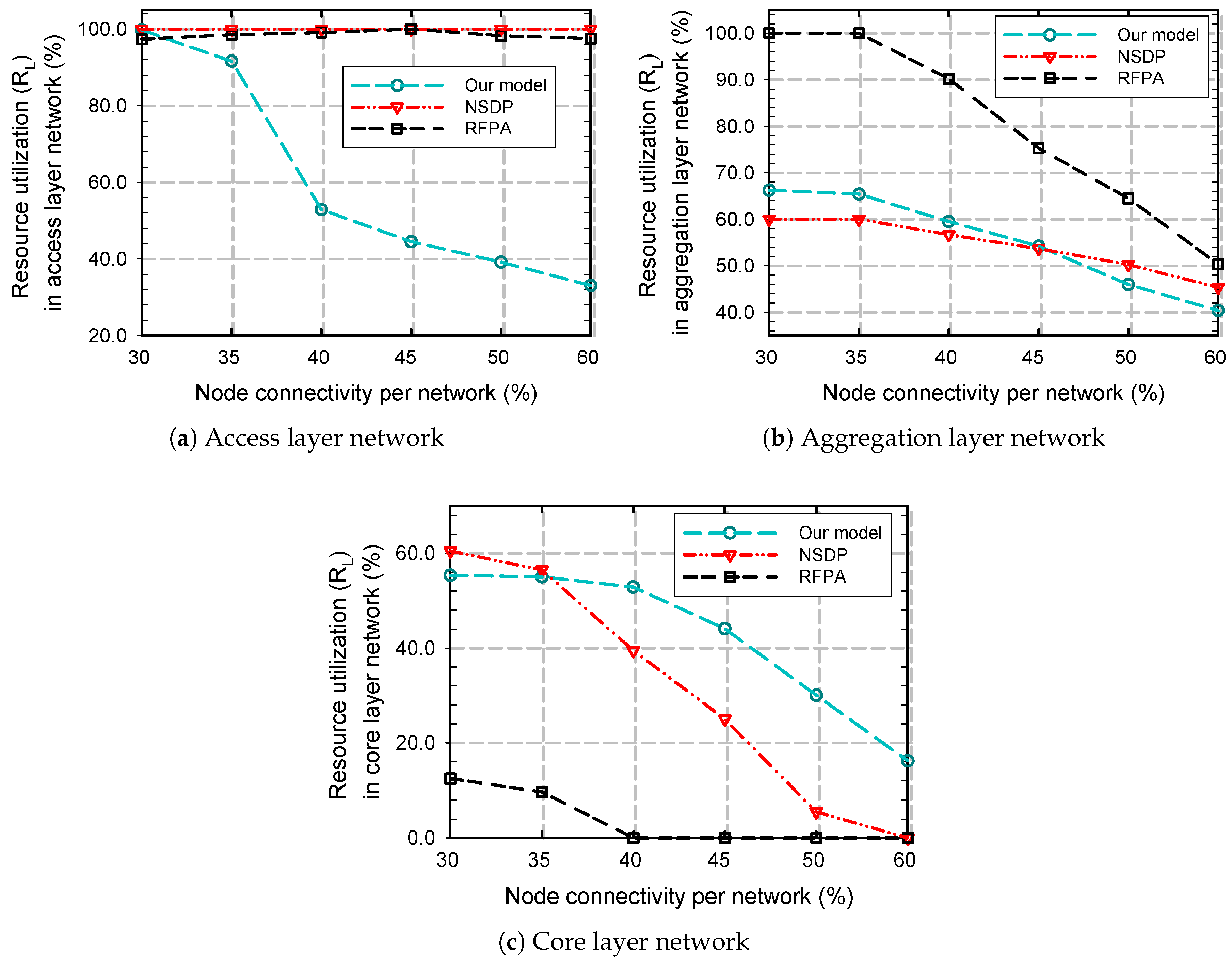
5.2.3. Substrate Link Load
5.2.4. Serviceability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alliance, N. 5G white paper. In Next Generation Mobile Networks, White Paper; NGMN: Frankfurt, Germany, 17 February 2015; pp. 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Timalsina, S.K.; Bhusal, R.; Moh, S. NFC and its application to mobile payment: Overview and comparison. In Proceedings of the 2012 8th International Conference on Information Science and Digital Content Technology (ICIDT2012), Jeju, Korea, 26–28 July 2012; Volume 1, pp. 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Pateromichelakis, E.; Samdanis, K.; Wei, Q.; Spapis, P. Slice-Tailored Joint Path Selection and Scheduling in mm-Wave Small Cell Dense Networks. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017—2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, N.; Chu, X.; Long, K.; Aghvami, A.; Leung, V.C.M. Network Slicing Based 5G and Future Mobile Networks: Mobility, Resource Management, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, A.; Botero, J.F.; Beck, M.T.; de Meer, H.; Hesselbach, X. Virtual Network Embedding: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1888–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, F.; Matta, I.; Ishakian, V. Slice embedding solutions for distributed service architectures. ACM Comput. Surv. 2013, 46, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, F.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Ahmed, R.; Boutaba, R.; Duarte, O.C.M.B. Orchestrating Virtualized Network Functions. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2016, 13, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, R.; Bradai, A.; Harutyunyan, D.; Rasheed, T.; Ahmed, T. Scheduling Wireless Virtual Networks Functions. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2016, 13, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Tarik, T.; Konstantinos, S.; Adlen, K.; Hannu, F. Network Slicing and Softwarization: A Survey on Principles, Enabling Technologies, and Solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2429–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Assi, C.; Shaban, K.; Khabbaz, M.J. A Reliability-Aware Network Service Chain Provisioning with Delay Guarantees in NFV-Enabled Enterprise Datacenter Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2017, 14, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Hasan, M.; Padhy, S.; Evchenko, K.; Piramanayagam, L.; Mohan, S.; Bobba, R.B. End-to-End Network Delay Guarantees for Real-Time Systems Using SDN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS), Paris, France, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tse, C.K.; Lau, F.C.M. Optimizing Performance of Communication Networks: An Application of Network Science. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hong, B.; Choi, W. Scale-Free Wireless Networks with Limited Degree Information. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2012, 1, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, A.; Bauschert, T.; Koster, A.M.C.A.; Reddy, V.S. Optimisation Models for Robust and Survivable Network Slice Design: A Comparative Analysis. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017—2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, F.; Dhahri, S.; Jukan, A. VNF placement with replication for load balancing in NFV networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatras, B.; Kwong, U.S.T.; Bihannic, N. NFV enabling network slicing for 5G. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th Conference on Innovations in Clouds, Internet and Networks (ICIN), Paris, France, 7–9 March 2017; pp. 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Feng, G.; Tan, W.; Ni, R.; Qin, S.; Wang, G. Protocol Function Block Mapping of Software Defined Protocol for 5G Mobile Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2018, 17, 1651–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Zhou, C.; Trivisonno, R.; Guerzoni, R.; Kaloxylos, A.; Soldani, D.; Hecker, A. On end to end network slicing for 5G communication systems. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2017, 28, e3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richart, M.; Baliosian, J.; Serrat, J.; Gorricho, J. Resource Slicing in Virtual Wireless Networks: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2016, 13, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mijumbi, R.; Serrat, J.; Gorricho, J.; Bouten, N.; Turck, F.D.; Boutaba, R. Network Function Virtualization: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 236–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, R.; Gibb, G.; Yap, K.K.; Appenzeller, G.; Casado, M.; McKeown, N.; Parulkar, G.M. Can the production network be the testbed? In Proceedings of the 9th USENIX Conference on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–6 October 2010; Volume 10, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Li, L.E.; Vanbever, L.; Rexford, J. Softcell: Scalable and flexible cellular core network architecture. In Proceedings of the Ninth ACM Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2013; pp. 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Sama, M.R.; An, X.; Wei, Q.; Beker, S. Reshaping the mobile core network via function decomposition and network slicing for the 5G Era. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Doha, Qatar, 3–6 April 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwin, G.; Sidharth, S.; Tamal, D.; Aniruddha, K. Strategies for VNF placements in large provider networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 19–23 March 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Carpio, F.; Bziuk, W.; Jukan, A. Replication of Virtual Network Functions: Optimizing link utilization and resource costs. In Proceedings of the 2017 40th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 22–26 May 2017; pp. 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijumbi, R.; Hasija, S.; Davy, S.; Davy, A.; Jennings, B.; Boutaba, R. Topology-Aware Prediction of Virtual Network Function Resource Requirements. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2017, 14, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khebbache, S.; Hadji, M.; Zeghlache, D. Scalable and cost-efficient algorithms for VNF chaining and placement problem. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th Conference on Innovations in Clouds, Internet and Networks (ICIN), Paris, France, 7–9 March 2017; pp. 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaznavi, M.; Khan, A.; Shahriar, N.; Alsubhi, K.; Ahmed, R.; Boutaba, R. Elastic virtual network function placement. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 4th International Conference on Cloud Networking (CloudNet), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 5–7 October 2015; pp. 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleg, A.; Ahmed, T.; Mosbah, M.; Riggio, R.; Boutaba, R. Delay-aware VNF placement and chaining based on a flexible resource allocation approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), Tokyo, Japan, 26–30 November 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.F.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Ahmed, R.; Boutaba, R. On orchestrating virtual network functions. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), Barcelona, Spain, 9–13 November 2015; pp. 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Duong, T.Q.; Nguyen, D.N.; Tran, L. Energy efficiency maximization for heterogeneous networks: A joint linear precoder design and small-cell switching-off approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 December 2016; pp. 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Tuan, H.D.; Duong, T.Q.; Dobre, O.A.; Poor, H.V. Downlink Beamforming for Energy-Efficient Heterogeneous Networks With Massive MIMO and Small Cells. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 3386–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Tuan, H.D.; Duong, T.Q. Energy-Efficient Signalling in QoS Constrained Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 7958–7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L. Resource allocation for energy efficiency in 5G wireless networks. EAI Endorsed Trans. Ind. Netw. Intell. Syst. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.N.; Tuan, H.D.; Duong, T.Q.; Poor, H.V. Multi-cell Massive MIMO Beamforming in Assuring QoS for Large Numbers of Users. arXiv, 2017arXiv:1712.03548.
- Long, D.N.; Tuan, H.D.; Duong, T.Q.; Poor, H.V. Beamforming and power allocation for energy-efficient massive MIMO. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, London, UK, 23–25 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Duong, T.Q.; Ngo, H.Q.; Tourki, K. Energy Efficiency in Cell-Free Massive MIMO with Zero-Forcing Precoding Design. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwak, J.; Moon, J.; Lee, H.; Le, L.B. Dynamic network slicing and resource allocation for heterogeneous wireless services. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Tang, J.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Feng, G.; Wang, G.; Tan, W. Robust Network Slicing in Software-Defined 5G Networks. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017—2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Mada, B.; Corici, M.; Nakao, A.; Flinck, H. PERMIT: Network Slicing for Personalized 5G Mobile Telecommunications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Wen, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; Shen, Y. A Service-Oriented Deployment Policy of End-to-End Network Slicing Based on Complex Network Theory. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 19691–19701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Mobile Communications Corporation; Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.; Deutsche Telekom AG; Volkswagen. 5G Service-Guaranteed Network Slicing White Paper. In Proceedings of the 2017 Mobile World Conference (MWC 2017), Barcelona, Spain, 27 February–2 March 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.; Brunstrom, A.; Grinnemo, K.; Taheri, J. SDN/NFV-Based Mobile Packet Core Network Architectures: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1567–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Rahman, M.R.; Boutaba, R. ViNEYard: Virtual Network Embedding Algorithms With Coordinated Node and Link Mapping. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2012, 20, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tversky, A.; Gati, I. Similarity, separability, and the triangle inequality. Psychol. Rev. 1982, 89, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddef, D.; Rinaldi, G. Branch-and-cut algorithms for the capacitated VRP. In The Vehicle Routing Problem; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 53–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, N.; Lee, J.; Vu, D.; Paek, J.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Chung, K.; Keum, C. Adaptive Resource Balancing for Serviceability Maximization in Fog Radio Access Networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14548–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreolo, M.S.; Nadal, L.; Fabrega, J.M. Towards advanced high capacity and highly scalable software defined optical transmission. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Girona, Spain, 2–6 July 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preyss, N.; Burg, A. Experimental signal-quality characterization of a high-capacity mmWave link for backhaul applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Rio de Janerio, Brazil, 10–13 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Grigoreva, E.; Wosinska, L.; Machuca, C.M. Enhancing the survivability and power savings of 5G transport networks based on DWDM rings. IEEE/OSA J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2017, 9, D74–D85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.E.; Trivedi, K.S.; Tomek, L.A.; Ackaret, J. Availability analysis of blade server systems. IBM Syst. J. 2008, 47, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Cases | Applications | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced mobile broadband access in dense areas (eMBB) | Hologram, high-definition (HD) video, user mobile broadband in a stadium | High traffic volume, high throughput |
| Small-volume, critical communications (s-VCC) | Robotic control, industry control | High reliability, ms latency, small traffic volume |
| High-volume, critical communications (h-VCC) | e-Health, virtual reality (VR) | High reliability, ms latency, high traffic volume |
| Extreme real-time communications (eRTC) | Autonomous driving, driving assistant, automotive factory | Sub-ms latency, mobility, high traffic volume |
| Massive Internet of Things (mIoT) | Smart wearables, meters, sensors | Massive connection, low power |
| Parameters | Values (Units) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of nodes in substrate networks | Access layer network | 10 nodes | |
| Aggregation layer network | 5 nodes | ||
| Core layer network | 3 nodes | ||
| Network capacity in substrate networks, | Access layer network | 40 Gbps | |
| Aggregation layer network | 80 Gbps | ||
| Core layer network | 80 Gbps | ||
| Maximum length of links in substrate networks, | Access layer network | 20 km | |
| Aggregation layer network | 50 km | ||
| Core layer network | 100 km | ||
| Node connectivity in substrate networks | (0.3, 0.4) | ||
| Bandwidth of each substrate link, | m/s | ||
| VNU capacity of substrate network nodes | Uniform condition | 5 VNUs per substrate node | |
| Access layer network | 3 VNUs | ||
| Non-uniform condition | Aggregation layer network | 5 VNUs | |
| Core layer network | 10 VNUs | ||
| NS types | 3 types, s-VCC, eRTC and eMBB | ||
| Types of VNUs | 8 | ||
| Maximum total traffic demands of NSs, | s-VCC | 500 MB | |
| eRTC | 6 GB | ||
| eMBB | 9 GB | ||
| Latency threshold (LT), | s-VCC | 30 ms | |
| eRTC | 80 ms | ||
| eMBB | 150 ms | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Zi, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhou, F.; Yu, P.; Qiu, X. Latency-Optimal Virtual Network Functions Resource Allocation for 5G Backhaul Transport Network Slicing. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040701
Li W, Zi Y, Feng L, Zhou F, Yu P, Qiu X. Latency-Optimal Virtual Network Functions Resource Allocation for 5G Backhaul Transport Network Slicing. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(4):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenjing, Yueqi Zi, Lei Feng, Fanqing Zhou, Peng Yu, and Xuesong Qiu. 2019. "Latency-Optimal Virtual Network Functions Resource Allocation for 5G Backhaul Transport Network Slicing" Applied Sciences 9, no. 4: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040701
APA StyleLi, W., Zi, Y., Feng, L., Zhou, F., Yu, P., & Qiu, X. (2019). Latency-Optimal Virtual Network Functions Resource Allocation for 5G Backhaul Transport Network Slicing. Applied Sciences, 9(4), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040701