Obtaining Various Shapes of Machined Surface Using a Tool with a Multi-Insert Cutting Edge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- profile cutters with a shaped cutting edge,
- profile cutters with multiple folding plates, and
- multi-edge cutters.
2. Methods and Materials
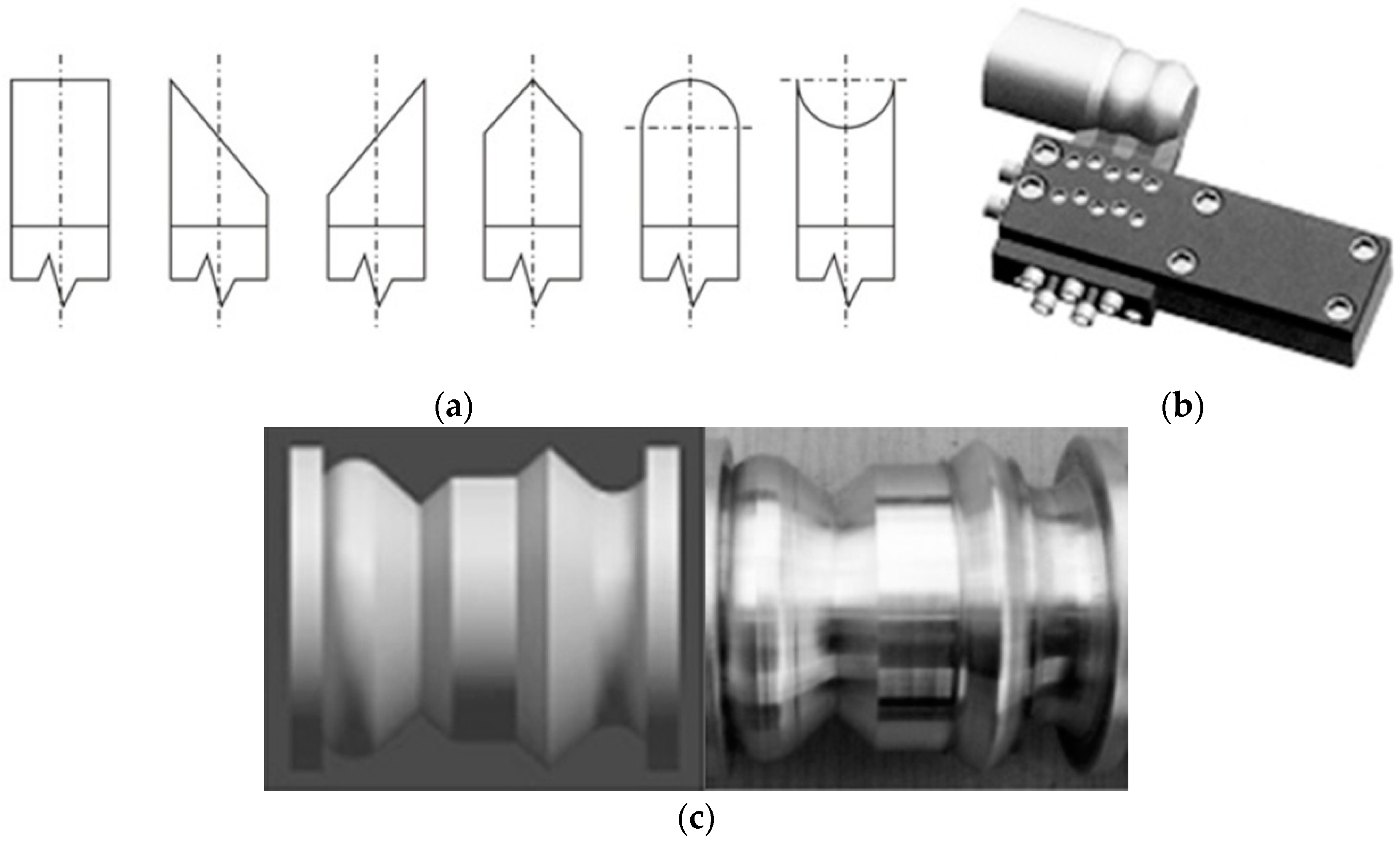
2.1. Universal Form Tool with a Multi-Insert Profile
2.2. Principle of the Build Outline of the Multi-Insert Form Tool
2.3. Computer-Aided Selection of the Outline of the Cutting Edge
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Universal Form Tool for Turning
3.2. Universal Form Tool for Milling
4. Summary and Conclusions
- An addition to an array of GKF tools, this tool permits the replacement of a few fixed geometric tools with a multi-insert- cutting edge tool. The feature may be particularly important for flexible production in small series. The use of this tool type can reduce the cost of tool manufacturing required in traditional form tool designs.
- A special feature of the proposed tools is the ability to obtain many different profiles using a small number of single inserts with other profiles. A working prototype was tested under practical working conditions, in both turning and milling.
- The given equation allows for prediction of the number of different profiles using several components of a multi-insert tool.
- Virtual modeling of the tool was extensively used during the design process of the tool. These CAD models entail the opportunity for virtual analysis of the model prior to physical testing. This feature is especially important in the case of GKF tools, where it is possible to change the form of tools and adjust or replace single edges after visualizing the resulting surface profile without any need for physical tests.
- The Tool_Shape software can generate an outline and provide the settings for single inserts for the proposed tool solutions for both turning and milling.
- An example of machining using the presented innovative tool is presented with a multi-insert cutting edge. These tools can be used both for turning and milling. It is possible to use these tools in both the woodworking and machining of aluminum alloys.
- In the cutting process using these tools, the range of the cutting speed effect on the wear of individual edges and the influence of cutting speed on the surface roughness could be found.
- In turning, profile diameters along the turning axis are key in determining contact segments during machining. Offsets perpendicular to the axis of symmetry affect profile dimensions and can double the tool shape error. To increase the rake angle, it is advisable to cut above the axis.
- In milling, shape errors still need to be investigated in future research. Definition of the contact points of machined material with compound multi-insert cutting edges is a problem. In case the tool’s stiffness is insufficient, vibrations may occur resulting in poor surface quality. A multi-insert tool is particularly suitable for use in the furniture industry and can produce complex shapes by moving single inserts.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| n | Number of single edges |
| i | Number of surface profiles |
| N | Number of different machined surface profiles |
| b | Single edge width |
| x1, y1 | Coordinates of the left control point |
| x2, y2 | Coordinates of the right control point |
| d | Vertical distance between neighboring edges control points |
| y’ | Control point y coordinate after offset is applied |
| γn | Rake angle |
| αn | Clearance angle |
| rε | Nose radius |
| kr/ | Primary main cutting angle |
| kr// | Secondary main cutting angle |
| vc | Cutting speed |
| f | Feed rate |
| ft | Feed rate |
References
- Nayak, P.K.; Shunmugam, M.S. CAD simulation and generation machining of discrete ring-involute spherical segment gear pair. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2012, 226, 1832–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkena, B.; Biermann, D. Cutting edge geometries. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 63, 631–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.V.; Filippova, E.O.; Chazov, P.A. Cutting-force components in turning by tools with no cutting tip. Russ. Eng. Res. 2016, 36, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omirou, S.L.; Rossides, S.; Lontos, A. A new CNC turning canned cycle for revolved parts with free-form profile. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 60, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.Y.; Ma, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Duan, X.Y.; Sun, P.P.; Yan, R. Total differential methods based universal post processing algorithm considering geometric error for multi-axis NC machine tool. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 70, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Tang, K. Optimization of machining strip width using effective cutting shape of flat-end cutter for five-axis free-form surface machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 94, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, N.A.; Altintas, Y. Open architecture modular tool kit for motion and machining process control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2000, 5, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Erol, N.A. Open architecture modular tool kit for motion and machining process control. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1998, 47, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boryczko, A. Measurement of relative tool displacement to the workpiece for the assessment of influences of machining errors on surface profiles. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2002, 31, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, D. Design method for screw forming cutter based on tooth profile composed of discrete points. J. Mech. Des. Trans. ASME 2015, 137, 085002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbikain, G.; López De Lacalle, L.N.; Campa, F.J.; Fernández, A.; Elías, A. Stability prediction in straight turning of a flexible workpiece by collocation method. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2012, 54–55, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A.D.; Mishkin, S.V. Calculation of cut-in profile cutters using KOMPAS 3D V8 graphic software. Russ. Eng. Res. 2007, 27, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.V. Cut-layer cross section in oblique turning by a single-edge tool with a curved rear surface. Russ. Eng. Res. 2015, 35, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Nieslony, P.; Wojciechowski, S.; Michalski, M.; Legutko, S. The influence of the cooling conditions on the cutting tool wear and the chip formation mechanism. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 24, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieslony, P.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Wojciechowski, S.; Chudy, R.; Zak, K.; Maruda, R.W. Surface quality and topographic inspection of variable compliance part after precise turning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, J.; Whitehouse, D.J. An investigation into the possibility of using surface profiles for machine tool surveillance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1984, 22, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Tandon, P. Mathematical modeling of a generic multi-profile form milling cutter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2013, 227, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuts, V.V.; Malneva, Y.A.; Skantsev, V.M. Development and testing of profile shafts processing method with constructive feed cutters. Procedia Eng. 2016, 150, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Shan, Y.X.; Bai, Y.F. Method for design of integral shaped milling cutter profile. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 328–330, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, S.; Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Niesłony, P. Application of signal to noise ratio and grey relational analysis to minimize forces and vibrations during precise ball end milling. Precis. Eng. 2018, 51, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolczyk, G.M.; Nieslony, P.; Maruda, R.W.; Wojciechowski, S. Dry cutting effect in turning of a duplex stainless steel as a key factor in clean production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3343–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, T.; Latos, H.; Paczkowski, T.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Szynka, T. Innovative tools for oblique cutting. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 22, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, T.; Latos, H.; Paczkowski, T.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Szynka, T. Using CAD CAM system for manufacturing of innovative cutting tool. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 22, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecik, K.; Ciecielag, K.; Zaleski, K. Damage detection of composite milling process by recurrence plots and quantifications analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguy, S.; Campa, F.J.; de Lacalla, L.N.L.; Arnaud, L.; Dessein, G.; Aramendi, G. Toolpath dependent stability lobes for the milling of thin-walled parts. Int. J. Mach. Mach. Mater. 2008, 4, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.; Dhar, R.N. Prediction of surface roughness in hard turning under high pressure coolant using Artificial Neural Network. Measurement 2016, 92, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Wan, Z. On the processing and morphological aspects of metal fibers based on low-speed multi-tooth dry cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 66, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.J.; Fong, Z.H. Design of form milling cutters with multiple inserts for screw rotors. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolny, K.; Kapłonek, W. Analysis of flatness deviations for austenitic stainless steel workpieces after efficient surface machining. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2014, 14, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapłonek, W.; Nadolny, K.; Krolczyk, G.M. The use of focus-variation microscopy for the assessment of active surfaces of a new generation of coated abrasive tools. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2016, 16, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, T. Analyse of possibility of form tools manufacturing using wire cutting EDM. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 656, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.W.; Hiziroglu, S.; Chan, C.T.M. Measurement of the surface roughness of wood based materials used in furniture manufacture. Measurement 2013, 46, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Rodríguez, A.; Fernández-Abia, A.I.; Barreiro, J.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Cryogenic and minimum quantity lubrication for an eco-efficiency turning of AISI 304. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polvorosa, R.; Suárez, A.; de Lacalle, L.N.L.; Cerrillo, I.; Wretland, A.; Veiga, F. Tool wear on nickel alloys with different coolant pressures: Comparison of Alloy 718 and Waspaloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 26, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, A.; Fernández-Valdivielso, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Sustainability analysis of lubricant oils for minimum quantity lubrication based on their tribo-rheological performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, A.; Lukic, L.; Ivanovic, S.; Pavlovic, A. Optimisation of tool path for wood machining on CNC machines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 231, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-W.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.-L.; Wang, X.-F. Design of formed milling cutter for screw of oil extraction progressing cavity pump based on non-instantaneous envelope method. Beijing Gongye Daxue Xuebao/J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2013, 39, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Olgun, U.; Budak, E. Machining of difficult-to-cut-alloys using rotary turning tools. Procedia CIRP 2013, 8, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajczyk, T. Form Tool. Patent PL No 216160, 31 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sandvik Coromant. Available online: https://www.sandvik.coromant.com/pl-pl/products/coroplex_mt/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Sandvik Coromant. Available online: https://www.sandvik.coromant.com/en-gb/campaigns/primeturning/pages/default.aspx?internal_camplink=primeturning&internal_camplink_type=highlight (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Latos, H. Geometric and Kinematic Flexibility of Cutting Tools; Publishing House of the Technical and Agricultural Academy: Bydgoszcz, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mikołajczyk, T. Form Cutter. Patent PL No 216166, 31 March 2014. [Google Scholar]






| Number of Inserts, n | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Surfaces, i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 2 | - | 2 | 6 | 12 | 20 | 30 | 42 | 56 | |
| 3 | - | - | 6 | 24 | 60 | 120 | 210 | 336 | |
| 4 | - | - | - | 24 | 120 | 360 | 840 | 1680 | |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | 120 | 720 | 2520 | 6720 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikolajczyk, T.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Pruncu, C.I.; Patra, K.; Latos, H.; Krolczyk, G.; Mia, M.; Klodowski, A.; Gupta, M.K. Obtaining Various Shapes of Machined Surface Using a Tool with a Multi-Insert Cutting Edge. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050880
Mikolajczyk T, Pimenov DY, Pruncu CI, Patra K, Latos H, Krolczyk G, Mia M, Klodowski A, Gupta MK. Obtaining Various Shapes of Machined Surface Using a Tool with a Multi-Insert Cutting Edge. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(5):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050880
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikolajczyk, Tadeusz, Danil Yurievich Pimenov, Catalin Iulian Pruncu, Karali Patra, Hubert Latos, Grzegorz Krolczyk, Mozammel Mia, Adam Klodowski, and Munish Kumar Gupta. 2019. "Obtaining Various Shapes of Machined Surface Using a Tool with a Multi-Insert Cutting Edge" Applied Sciences 9, no. 5: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050880
APA StyleMikolajczyk, T., Pimenov, D. Y., Pruncu, C. I., Patra, K., Latos, H., Krolczyk, G., Mia, M., Klodowski, A., & Gupta, M. K. (2019). Obtaining Various Shapes of Machined Surface Using a Tool with a Multi-Insert Cutting Edge. Applied Sciences, 9(5), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050880











