Accuracy and Inter-Unit Reliability of Ultra-Wide-Band Tracking System in Indoor Exercise
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
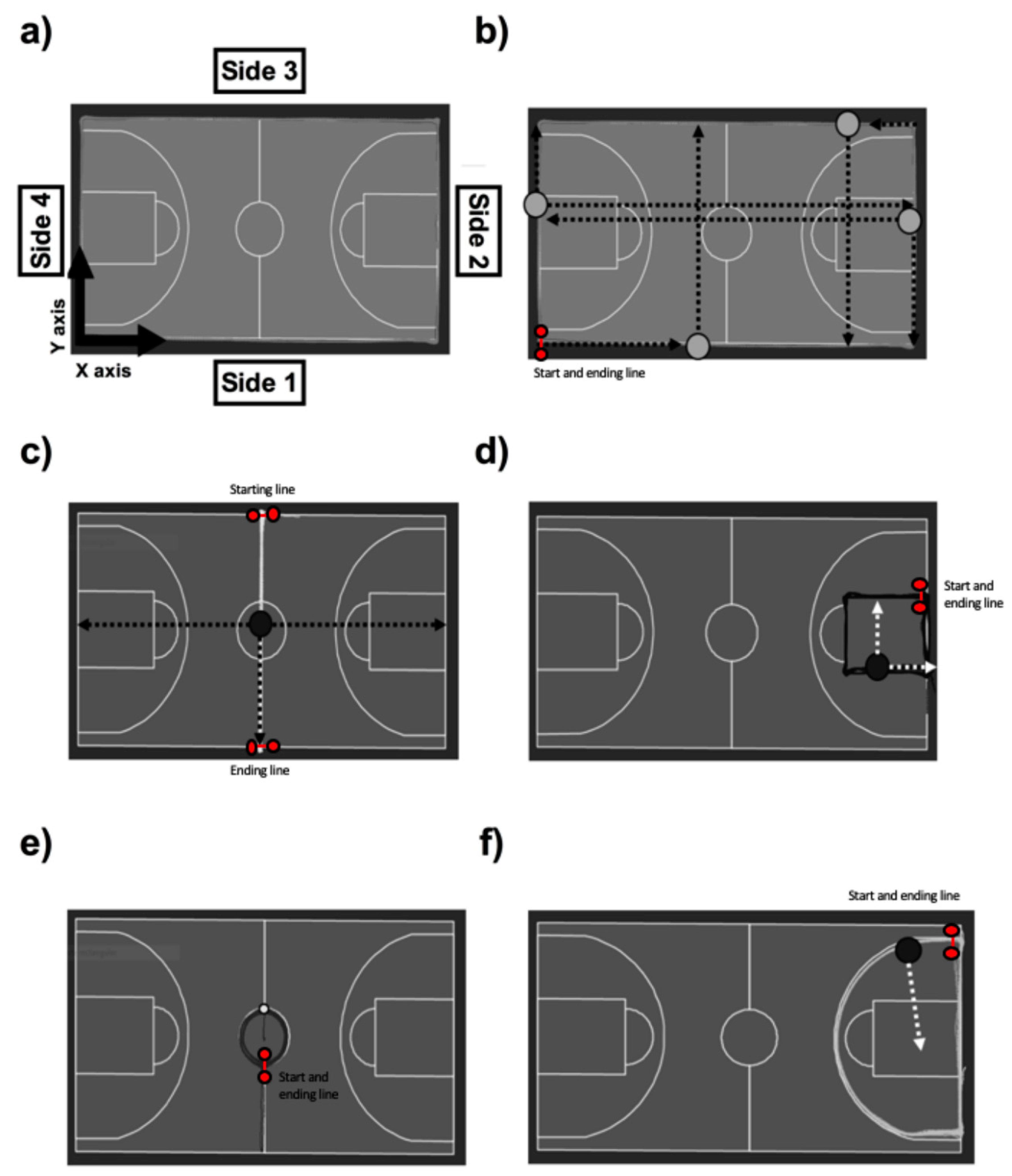
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
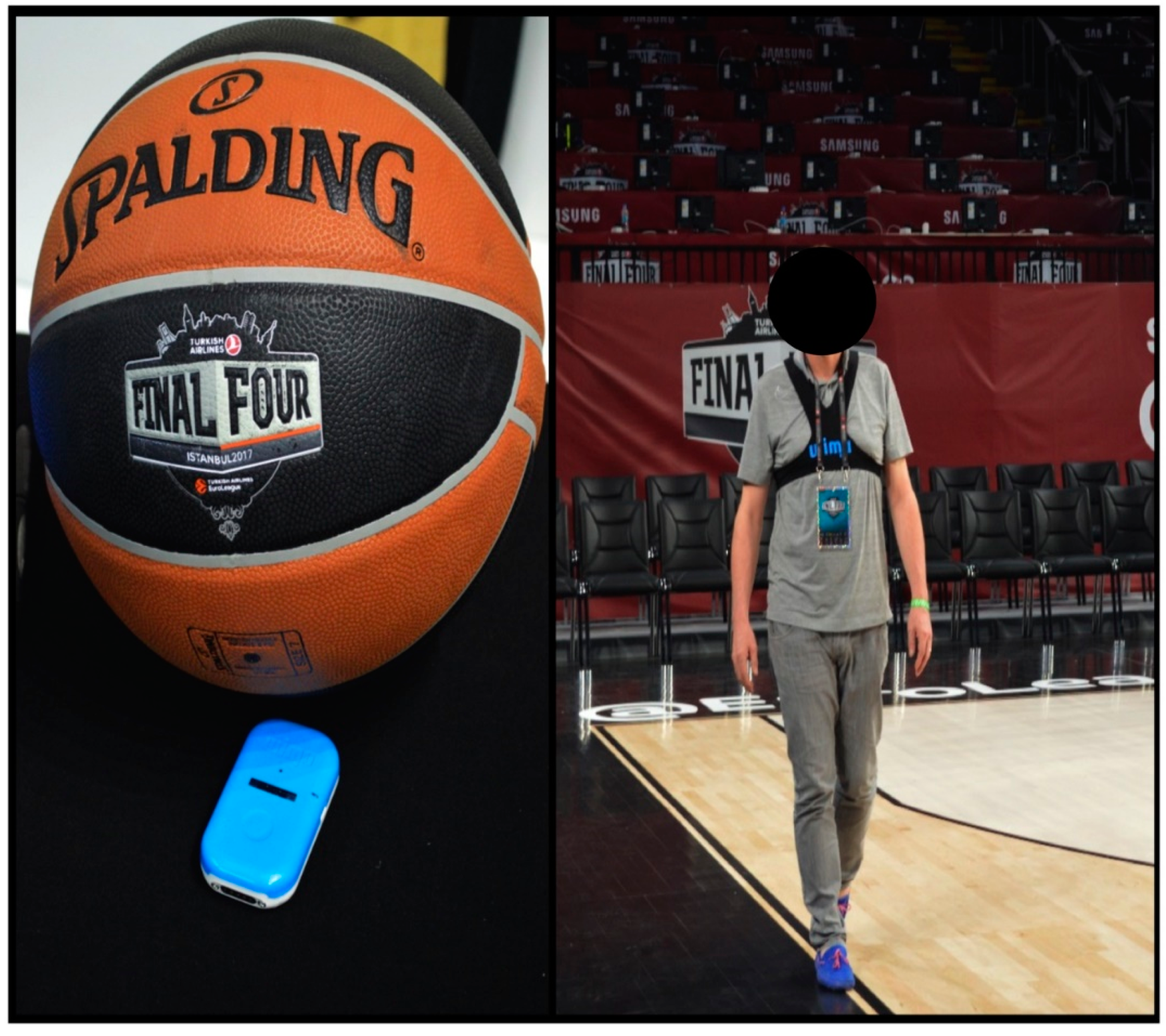
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Data Processing
- (b)
- Perimeter markings of court. (1) Baseline: 28 m with respect to the opposite baseline (coordinate x) and 0 m with respect to the displacement baseline (coordinate y). (2) Lateral line: 0 m with respect to the displacement lateral line (coordinate x) and 15 m with respect to the opposite lateral line (coordinate y).
- (c)
- Middle line court. 14 m with respect to the baseline (coordinate x) and 0 m with respect to the center line (coordinate y).
- (d)
- Exterior perimeter of the painted lines. (1) Baseline/front-line of the paint: 5.8 m with respect to the baseline or the front line of the paint (coordinate x) and 0 m with respect to the displacement line of the paint (coordinate y). (2) Lateral line of the paint: 0 m with respect to the displacement line of the paint (coordinate x) and 4.9 m with respect to the opposite lateral line of the paint.
- (e)
- Centre circle. 1.8 m with respect to the centroid of the center circle (coordinate x).
- (f)
- 6.75 m line. 6.75 m with respect to the centroid of the three-point line (coordinate x).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy
3.2. Inter-Unit Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Study Limits
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leser, R.; Baca, A.; Ogris, G. Local Positioning Systems in (Game) Sports. Sensors 2011, 11, 9778–9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbero-Álvarez, J.C.; Coutts, A.; Granda, J.; Barbero-Álvarez, V.; Castagna, C. The validity and reliability of a global positioning satellite system device to assess speed and repeated sprint ability (RSA) in athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M.; Allen, A.; Poon, T.K.; Modonutti, M.; Gregson, W.; Di Salvo, V. Integrating different tracking systems in football: multiple camera semi-automatic system, local position measurement and GPS technologies. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1844–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frencken, W.G.P.; Lemmink, K.A.P.M.; Delleman, N.J. Soccer-specific accuracy and validity of the local position measurement (LPM) system. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogris, G.; Leser, R.; Horsak, B.; Kornfeind, P.; Heller, M.; Baca, A. Accuracy of the LPM tracking system considering dynamic position changes. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leser, R.; Schleindlhuber, A.; Lyons, K.; Baca, A. Accuracy of an UWB-based position tracking system used for time-motion analyses in game sports. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 14, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.; Mason, B.; Perrat, B.; Smith, M.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V. The validity and reliability of a novel indoor player tracking system for use within wheelchair court sports. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valter, D.S.; Adam, C.; Barry, M.; Marco, C. Validation of Prozone®: A new video-based performance analysis system. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2006, 6, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barris, S.; Button, C. A review of vision-based motion analysis in sport. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carling, C.; Reilly, T.; Williams, A.M. Performance Assessment for Field Sports; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-415-42684-8. [Google Scholar]
- Buchheit, M.; Simpson, B.M. Player Tracking Technology: Half-Full or Half-Empty Glass? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastida Castillo, A.; Gómez Carmona, C.D.; De la Cruz Sánchez, E.; Pino Ortega, J. Accuracy, intra- and inter-unit reliability, and comparison between GPS and UWB-based position-tracking systems used for time–motion analyses in soccer. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.; Alvarez-Pastor, D.; Bradley, P.S. Evaluation of Research Using Computerised Tracking Systems (Amisco (R) and Prozone (R)) to Analyse Physical Performance in Elite Soccer: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.T.U.; Scott, T.J.; Kelly, V.G. The validity and reliability of global positioning systems in team sport: A brief review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, J.J.; Lovell, R.; Varley, M.C.; Coutts, A.J. Unpacking the Black Box: Applications and Considerations for Using GPS Devices in Sport. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, S2-18–S2-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutts, A.J.; Duffield, R. Validity and reliability of GPS devices for measuring movement demands of team sports. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldron, M.; Worsfold, P.; Twist, C.; Lamb, K. Concurrent validity and test–retest reliability of a global positioning system (GPS) and timing gates to assess sprint performance variables. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luteberget, L.S.; Spencer, M.; Gilgien, M. Validity of the Catapult ClearSky T6 Local Positioning System for Team Sports Specific Drills, in Indoor Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyan, T.; Shuttleworth, R.; Hedley, M.; Davids, K. Validity and reliability of a radio positioning system for tracking athletes in indoor and outdoor team sports. Behav. Res. Methods 2012, 44, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Begon, M.; Colloud, F.; Fohanno, V.; Bahuaud, P.; Monnet, T. Computation of the 3D kinematics in a global frame over a 40m-long pathway using a rolling motion analysis system. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, T.G.A.; de Ruiter, C.J.; van Niel, C.; van de Rhee, R.; Beek, P.J.; Savelsbergh, G.J.P. Measuring Acceleration and Deceleration in Soccer-Specific Movements Using a Local Position Measurement (LPM) System. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Kruk, E.; Reijne, M.M. Accuracy of human motion capture systems for sport applications; state of the art review. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittet, S.; Renaudin, V.; Merminod, B.; Kasser, M. UWB and MEMS Based Indoor Navigation. J. Navig. 2008, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sczyslo, S.; Schroeder, J.; Galler, S.; Kaiser, T. Hybrid localization using UWB and inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Hannover, Germany, 10–12 September 2008; IEEE: Hannover, Germany, 2008; pp. 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa, R.; Ebinuma, T. A Low-Cost Tightly Coupled GPS/INS for Small UAVs Augmented with Multiple GPS Antennas. Navigation 2009, 56, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, J. Sensor Fusion and Calibration of Inertial Sensors, Vision, Ultra-Wideband and GPS; Department of Electrical Engineering, Linköping University: Linköping, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hol, J.D.; Schon, T.B.; Gustafsson, F. Ultra-wideband calibration for indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Nanjing, China, 20–23 September 2010; IEEE: Nanjing, China, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bastida Castillo, A.; Gómez Carmona, C.D.; Pino Ortega, J.; de la Cruz Sánchez, E. Validity of an inertial system to measure sprint time and sport task time: A proposal for the integration of photocells in an inertial system. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castellano, J.; Casamichana, D.; Calleja-González, J.; San Román, J.; Ostojic, S.M. Reliability and Accuracy of 10 GPS Devices for Short-Distance Exercise. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duffield, R.; Reid, M.; Baker, J.; Spratford, W. Accuracy and reliability of GPS devices for measurement of movement patterns in confined spaces for court-based sports. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.J.; Jenkins, D.; Andrews, M.H.; Taaffe, D.R.; Glover, M.L. Validity and reliability of GPS for measuring distance travelled in field-based team sports. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Watsford, M.L.; Pine, M.J.; Spurrs, R.W.; Murphy, A.J.; Pruyn, E.C. The validity and reliability of 5-hz global positioning system units to measure team sport movement demands. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Watsford, M.L.; Kelly, S.J.; Pine, M.J.; Spurrs, R.W. Validity and interunit reliability of 10 Hz and 15 Hz GPS units for assessing athlete movement demands. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beato, M.; Bartolini, D.; Ghia, G.; Zamparo, P. Accuracy of a 10 Hz GPS Unit in Measuring Shuttle Velocity Performed at Different Speeds and Distances (5–20 M). J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Sachlikidis, A. Validity and reliability of intra-stroke kayak velocity and acceleration using a GPS-based accelerometer. Sports Biomech. 2010, 9, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Designed Travel | Device | Differences | Percentage of Differences | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | X | Y | ||
| Perimeter of court | 1 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 0.39% | 0.41% |
| 2 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 0.34% | 0.34% | |
| Center line of the court | 1 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 0.53% | 0.51% |
| 2 | 11 | 10.8 | 0.79% | 0.77% | |
| Perimeter of the paint | 1 | 0.3 | 4.4 | 0.05% | 0.76% |
| 2 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 0.57% | 0.62% | |
| 6.75 m line | 1 | 1.9 | - | 0.28% | - |
| 2 | 8.6 | - | 1.27% | - | |
| Center circle | 1 | 5 | 5.9 | 3.03% | 3.58% |
| 2 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 2.48% | 2.36% | |
| Mean ± SD | 5.2 ± 3.1 | 5.8 ± 2.3 | 0.97 ± 1 | 0.94 ± 1.14 | |
| LOA (L to U) | 2.1 to 8.3 | 3.5 to 8.2 | −0.03 to 1.98 | −0.21 to 2.08 | |
| Axis | Unit 1 (Mean ± SD) | Unit 2 (Mean ± SD) | ICC | 90% CI | % TEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 4.1 ± 2.9 | 6.4 ± 3.3 | 0.65 | −0.15 to 0.94 | 2 |
| y | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 5.9 ± 3.4 | 0.88 | 0.26 to 0.99 | 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bastida-Castillo, A.; Gómez-Carmona, C.D.; De la Cruz-Sánchez, E.; Reche-Royo, X.; Ibáñez, S.J.; Pino Ortega, J. Accuracy and Inter-Unit Reliability of Ultra-Wide-Band Tracking System in Indoor Exercise. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050939
Bastida-Castillo A, Gómez-Carmona CD, De la Cruz-Sánchez E, Reche-Royo X, Ibáñez SJ, Pino Ortega J. Accuracy and Inter-Unit Reliability of Ultra-Wide-Band Tracking System in Indoor Exercise. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(5):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050939
Chicago/Turabian StyleBastida-Castillo, Alejandro, Carlos David Gómez-Carmona, Ernesto De la Cruz-Sánchez, Xavier Reche-Royo, Sergio José Ibáñez, and José Pino Ortega. 2019. "Accuracy and Inter-Unit Reliability of Ultra-Wide-Band Tracking System in Indoor Exercise" Applied Sciences 9, no. 5: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050939
APA StyleBastida-Castillo, A., Gómez-Carmona, C. D., De la Cruz-Sánchez, E., Reche-Royo, X., Ibáñez, S. J., & Pino Ortega, J. (2019). Accuracy and Inter-Unit Reliability of Ultra-Wide-Band Tracking System in Indoor Exercise. Applied Sciences, 9(5), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9050939








