Study of the Relationship between Urban Expansion and PM10 Concentration Using Multi-Temporal Spatial Datasets and the Machine Learning Technique: Case Study for Daegu, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
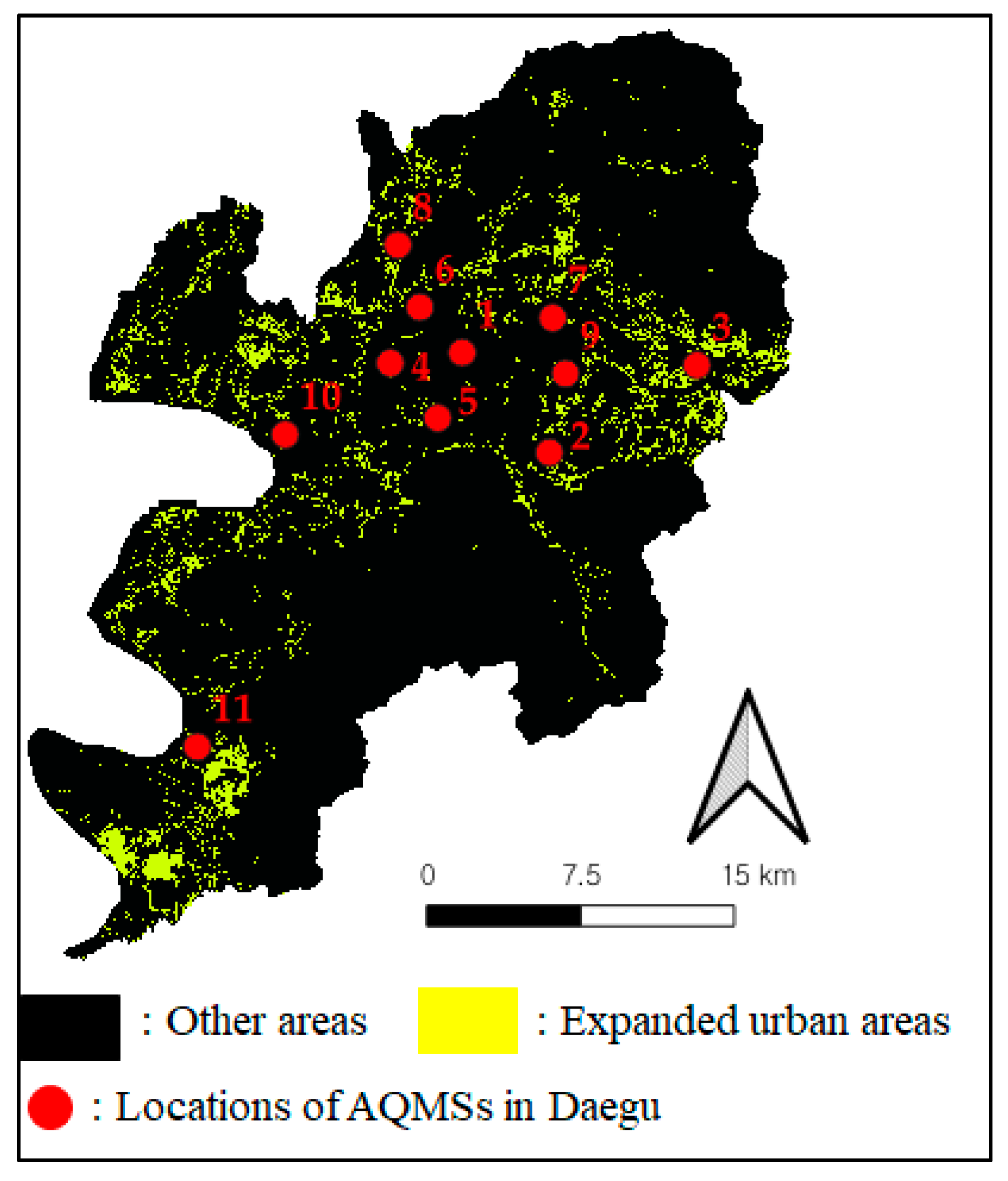
2. Study Area and Datasets
3. Methodology
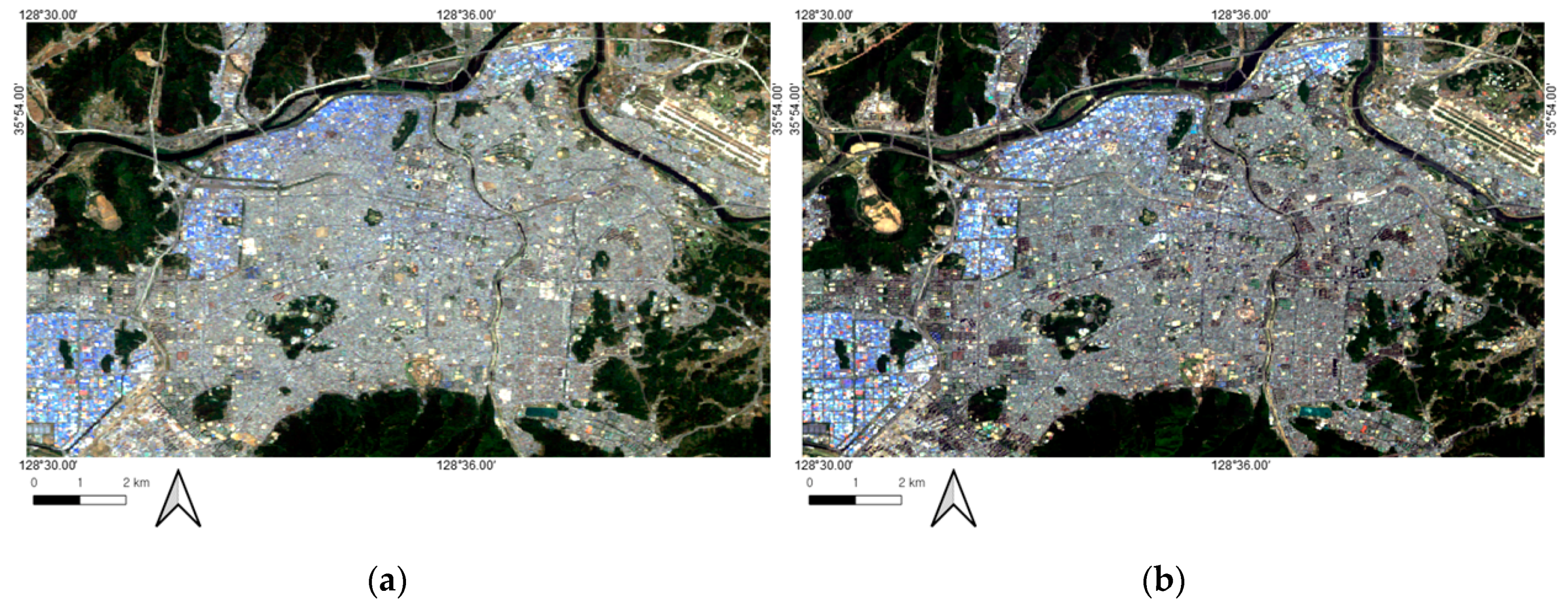
3.1. Generation of the Urban Maps by the SVM Technique
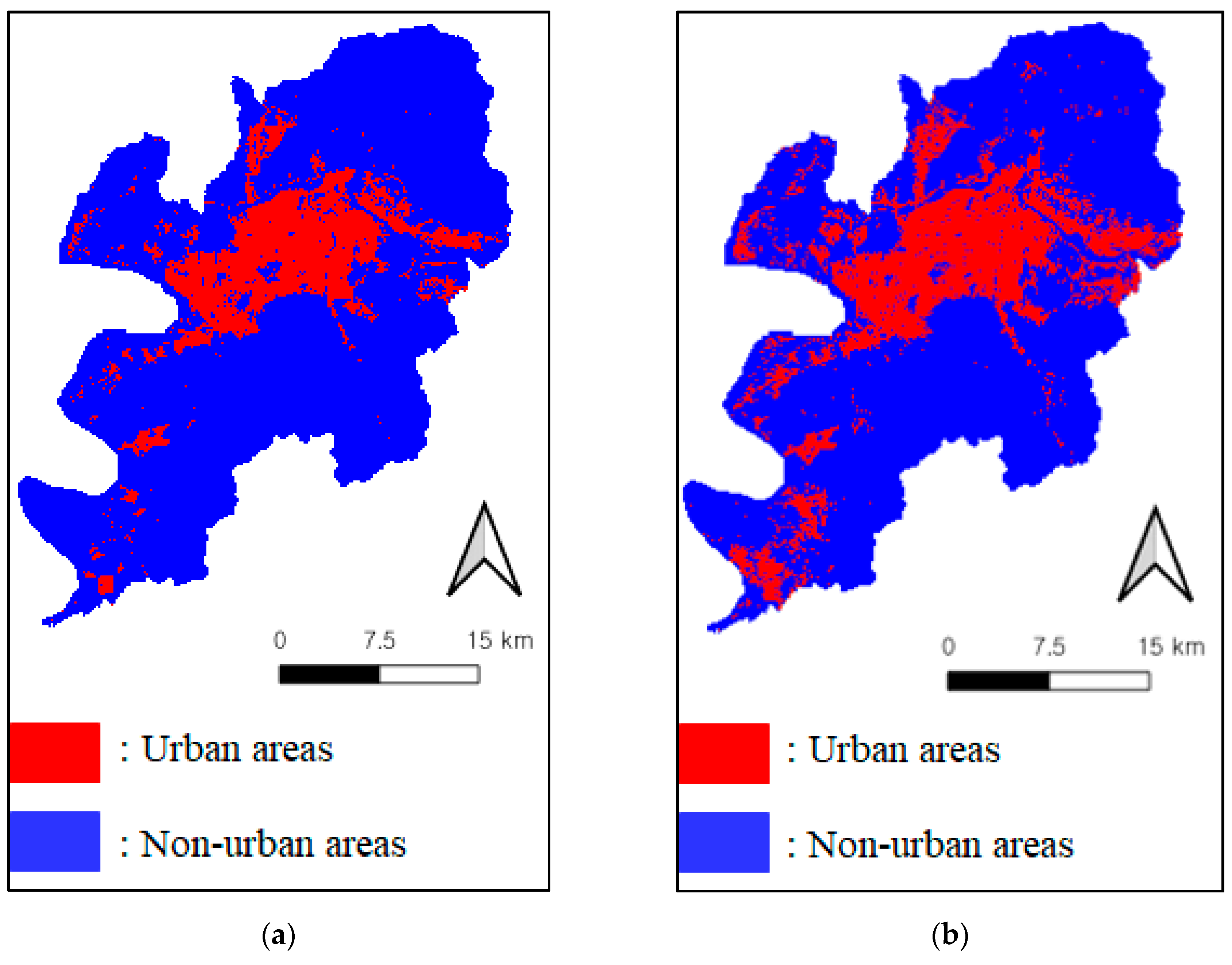
3.2. Detection of the Expaned Urban Areas in Daegu from 2007 to 2017
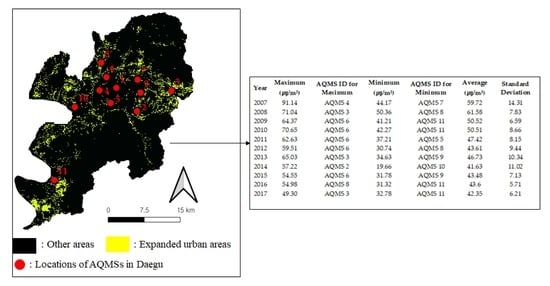
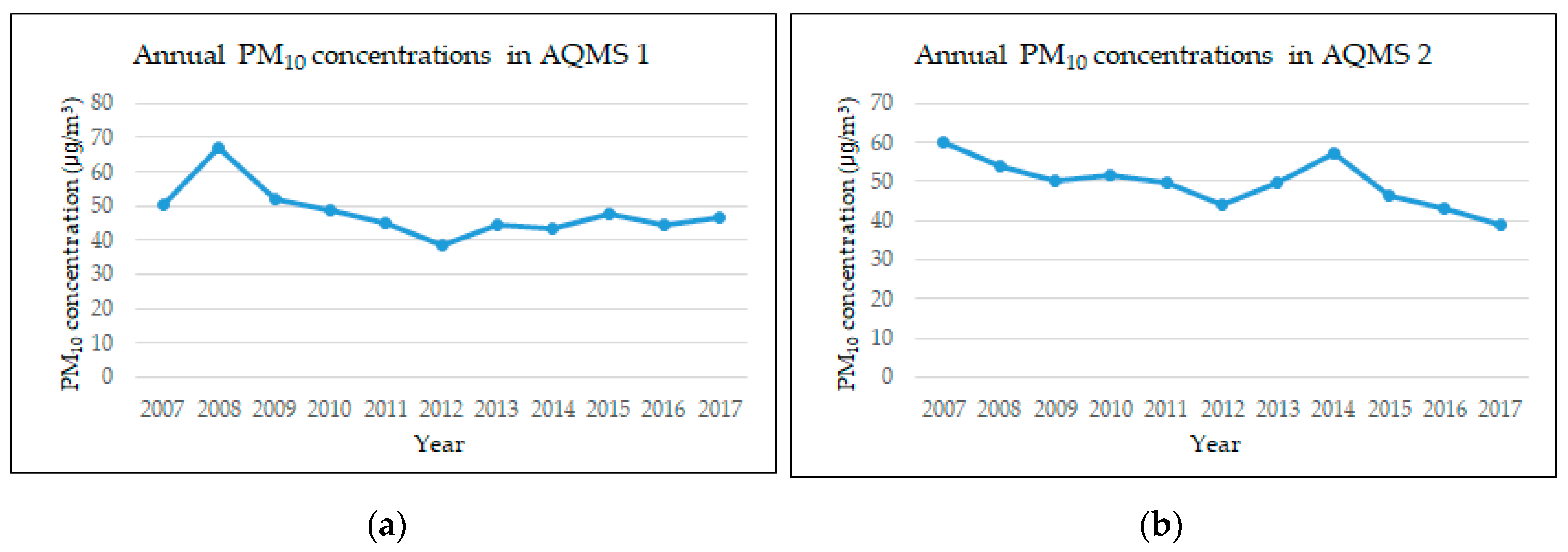
3.3. Calculation of the Statistics for the Annual PM10 Concentrations
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Accuracies of the Generated Urban Maps
4.2. Relationship between the Urban Expansions and the PM10 Concentrations in Daegu from 2007 to 2017
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merriam-Webster. Urban Sprawl. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/urban%20sprawl (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- Encyclopedia Britanica. Urban Sprawl. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/topic/urban-sprawl (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- Conserve Energy Future. What Is Urban Sprawl. Available online: https://www.conserve-energy-future.com/causes-and-effects-of-urban-sprawl.php (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- Kang, D.; Kim, J.-E. Fine, Ultrafine and Yellow Dust: Emerging Health Problems in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Particulate Matter (PM) Basics. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- Ghorani-Azam, A.; Riahi-Zanjani, B.; Balali-Mood, M. Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevision in Iran. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO) Working Group. Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide; World Health Organization: Bonn, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y. Monetary Valuation of PM10—Related Health Risks in Beijing China: The Necessity for PM10 Pollution Indemnity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9967–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourahmad, A.; Baghavand, A.; Shahraki, S.Z.; Givehchi, S. The Impact of Urban Sprawl up on Air Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2007, 1, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B. Urban Sprawl and Air Quality in Large US Cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.S.; Choi, M.J. Effects of Compact Urban Development on Air Pollution: Empirical Evidence from Korea. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5968–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, D.; Ma, Q. The relationship between urban form and air pollution depends on seasonality and city size. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15554–15567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daegu Metropolitan City. The Document for the Urban Planning Policy of Daegu. Available online: http://ebook.daegu.go.kr/Viewer/RBL5N2AFGRNW (accessed on 22 November 2018).
- Daegu Atmospheric Information System. PM10 Statistics. Available online: https://air.daegu.go.kr/open_content/ko/index.do (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). Landsat Missions. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/land-resources/nli/landsat (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- DicionaryCom. Machine Learning. Available online: https://www.dictionary.com/browse/machine-learning (assessed on 22 November 2018).
- Choung, Y.-J.; Jo, M.-H. Comparison between a Machine-learning-based Method and a Water-index-based Method for Shoreline Mapping Using a High-Resolution Satellite Image Acquired in Hwado Island, South Korea. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 8245204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.J.; Alavi, A.H.; Gandomi, A.H.; Walker, A.L. Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| (a) | |||
| Overall Accuracy | 97% | ||
| Producer’s Accuracy (Error of Omission) | User’s Accuracy (Error of Commission) | ||
| Urban areas | 94% | Urban areas | 100% |
| Non-urban areas | 100% | Non-urban areas | 94% |
| (b) | |||
| Overall Accuracy | 99% | ||
| Producer’s Accuracy (Error of Omission) | User’s Accuracy (Error of Commission) | ||
| Urban areas | 100% | Urban areas | 98% |
| Non-urban areas | 98% | Non-urban areas | 100% |
| (a) | |||||||||||||
| Total Areas of the Urban Areas in the First Urban Map (km2) | Total Areas of the Urban Areas in the Second Urban Map (km2) | Increase of the Expanded Urban Areas in Daegu from 2007 to 2017 (km2) | |||||||||||
| 148.08 | 203.35 | + 55.27 | |||||||||||
| (b) | |||||||||||||
| AQMS ID | Maximum (μg/m³) | Minimum (μg/m³) | Average (μg/m³) | Standard Deviation | Variation of Annual PM10 Concentration (2017 vs 2007) (μg/m³) | ||||||||
| AQMS 1 | 67.28 | 38.79 | 48.07 | 7.35 | −4.12 | ||||||||
| AQMS 2 | 60.21 | 38.80 | 49.61 | 6.30 | −21.41 | ||||||||
| AQMS 3 | 75.32 | 49.30 | 58.80 | 8.40 | −26.02 | ||||||||
| AQMS 4 | 91.14 | 41.99 | 55.85 | 13.79 | −42.28 | ||||||||
| AQMS 5 | 66.16 | 34.64 | 42.95 | 8.97 | +0.45 | ||||||||
| AQMS 6 | 70.65 | 45.23 | 59.54 | 8.34 | −19.29 | ||||||||
| AQMS 7 | 52.22 | 36.29 | 41.85 | 5.78 | −7.88 | ||||||||
| AQMS 8 | 56.75 | 32.78 | 47.61 | 9.72 | −22.75 | ||||||||
| AQMS 9 | 54.86 | 31.78 | 43.03 | 8.43 | −15.59 | ||||||||
| AQMS 10 | 68.53 | 19.66 | 43.78 | 11.85 | -12.81 | ||||||||
| AQMS 11 | 56.75 | 32.78 | 41.05 | 7.26 | −19.35 | ||||||||
| (c) | |||||||||||||
| Year | Maximum (μg/m³) | AQMS ID for Maximum | Minimum (μg/m³) | AQMS ID for Minimum | Average(μg/m³) | Standard Deviation | |||||||
| 2007 | 91.14 | AQMS 4 | 44.17 | AQMS 7 | 59.72 | 14.31 | |||||||
| 2008 | 71.04 | AQMS 3 | 50.36 | AQMS 8 | 61.58 | 7.83 | |||||||
| 2009 | 64.37 | AQMS 6 | 41.21 | AQMS 11 | 50.52 | 6.59 | |||||||
| 2010 | 70.65 | AQMS 6 | 42.27 | AQMS 11 | 50.51 | 8.66 | |||||||
| 2011 | 62.63 | AQMS 6 | 37.21 | AQMS 5 | 47.42 | 8.15 | |||||||
| 2012 | 59.51 | AQMS 6 | 30.74 | AQMS 8 | 43.61 | 9.44 | |||||||
| 2013 | 65.03 | AQMS 3 | 34.63 | AQMS 9 | 46.73 | 10.34 | |||||||
| 2014 | 57.22 | AQMS 2 | 19.66 | AQMS 10 | 41.63 | 11.02 | |||||||
| 2015 | 54.55 | AQMS 6 | 31.78 | AQMS 9 | 43.48 | 7.13 | |||||||
| 2016 | 54.98 | AQMS 8 | 31.32 | AQMS 11 | 43.6 | 5.71 | |||||||
| 2017 | 49.30 | AQMS 3 | 32.78 | AQMS 11 | 42.35 | 6.21 | |||||||
| (d) | |||||||||||||
| Year | Spring (μg/m³) | Summer (μg/m³) | Autumn (μg/m³) | Winter (μg/m³) | |||||||||
| 2007 | 81.58 | 41.55 | 48.47 | 64.32 | |||||||||
| 2008 | 73.63 | 52.11 | 55.88 | 64.10 | |||||||||
| 2009 | 51.74 | 42.37 | 45.51 | 62.87 | |||||||||
| 2010 | 57.39 | 39.86 | 50.21 | 58.59 | |||||||||
| 2011 | 59.77 | 37.59 | 42.20 | 50.59 | |||||||||
| 2012 | 50.63 | 33.98 | 41.76 | 48.14 | |||||||||
| 2013 | 52.92 | 38.99 | 39.90 | 55.02 | |||||||||
| 2014 | 50.01 | 33.82 | 35.30 | 47.49 | |||||||||
| 2015 | 50.51 | 34.59 | 31.14 | 57.61 | |||||||||
| 2016 | 53.33 | 32.71 | 40.02 | 48.49 | |||||||||
| 2017 | 50.47 | 33.55 | 39.69 | 45.55 | |||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choung, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-M. Study of the Relationship between Urban Expansion and PM10 Concentration Using Multi-Temporal Spatial Datasets and the Machine Learning Technique: Case Study for Daegu, South Korea. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061098
Choung Y-J, Kim J-M. Study of the Relationship between Urban Expansion and PM10 Concentration Using Multi-Temporal Spatial Datasets and the Machine Learning Technique: Case Study for Daegu, South Korea. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(6):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061098
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoung, Yun-Jae, and Jin-Man Kim. 2019. "Study of the Relationship between Urban Expansion and PM10 Concentration Using Multi-Temporal Spatial Datasets and the Machine Learning Technique: Case Study for Daegu, South Korea" Applied Sciences 9, no. 6: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061098
APA StyleChoung, Y.-J., & Kim, J.-M. (2019). Study of the Relationship between Urban Expansion and PM10 Concentration Using Multi-Temporal Spatial Datasets and the Machine Learning Technique: Case Study for Daegu, South Korea. Applied Sciences, 9(6), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061098