Abstract
Resolution is crucially important for optical imaging, which defines the smallest spatial feature of object that can be delivered by light wave. However, due to the wave nature of light, optical imaging is of limited resolution, widely known as Rayleigh limit or Abbe limit. Nevertheless, this limit can be overcome by considering the loopholes in the derivation of the Rayleigh limit, such as light–matter interaction, structured illumination, and near-field interference. In contrast to the conventional single-photon interference, multi-photon amplitudes responsible for optical high-order interference could be designed to possess a reduced effective wavelength, enabling the breakthrough of the Rayleigh limit. In this review, we will present recently developed super-resolution imaging schemes based on optical high-order interference, and discuss future perspectives.
1. Introduction
Optical imaging is important for fundamental research and practical applications, prompting advances in our society. Resolution is essential in optical imaging, since it determines the smallest spatial feature of an object that can be acquired through optical imaging. Due to the wave nature of light, any imaging scheme, e.g., the widely used lens-assisted imaging scheme, is of limited resolution with a point-to-spot correlation between the object plane and image plane. The size of the image spot thus defines the resolution limit, which is formulated as Rayleigh Criterion (or Abbe diffraction limit) [1]. To break the Rayleigh limit for acquiring smaller spatial features of an object, extensive efforts have been made, leading to several milestone achievements that have already achieved a great success in many applications, such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) [2], structured illumination microscopy (SIM) [3], photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM) [4], and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) [5]. The above-mentioned methods are far-field super-resolution imaging methods, and on the other hand, methods employing near-field interference for achieving super-resolution have also been developed, such as scanning near-field optical microscopy (SNOM) [6] and superlens imaging [7]. Moreover, the surface polariton wave possesses a smaller wavelength in comparison with the excitation light, and therefore can be employed to achieve super-resolution [8]. Besides the well-known single-photon interference, optical interference indeed emerges for the unity of multiple photons, known as multi-photon or high-order interference [9,10,11]. By considering n-photon interference with photonic de Broglie wave [12], the diffraction resolution limit could be increased by a factor of n, reaching the Heisenberg limit (HL). The fundamental insights in optical high-order interference provide new routes for achieving super-resolution imaging.
The super-resolved n-photon interference was initially realized in the optical interferometers and the far-field diffraction setups, firstly with quantum entangled sources [13,14,15,16,17,18,19], and later with different classical sources such as thermal/pseudothermal light [20,21,22,23,24] and laser [25,26], and recently with dynamical phase control on the wavefront of spatially coherent light [27,28,29,30]. The super-resolved interference has been shown to be important for applications such as super-resolved phase measurement and high-resolution optical lithography. Recently, much effort has been devoted to realizing super-resolution in direct imaging schemes, and several practically achievable schemes have been developed in conventional lens-assisted imaging schemes, as well as in newly designed imaging schemes [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. These far-field super-resolution imaging methods could be quite useful in many applications such as biological imaging [33,37], laser radar [32] and nano imaging [38], and therefore attract a lot of interest.
In this paper, we give a review of the progress of the super-resolution imaging through optical high-order interference. The paper is organized as follows: we will first give a brief introduction to the Rayleigh resolution limit with a lens-assisted imaging scheme, then review the recently developed super-resolution imaging schemes based on optical high-order interference, and finally discuss future perspectives.
2. Rayleigh Resolution Limit
Lens-assisted imaging is the most widely used imaging scheme. A thin lens can be viewed as a thin static phase screen. It introduces a phase pattern on the wavefront that reverses the divergence of light wave originating from an object point, making light wave converge to a point on the observation plane as shown in Figure 1a. In this way, a point-to-point correlation between the object and the observation plane is built up, giving rise to direct imaging for the object. The point-to-point correlation is expressed as [45]
for coherent imaging, and
for incoherent imaging. Here, is the object aperture function, is the point-spread function of an imaging scheme.
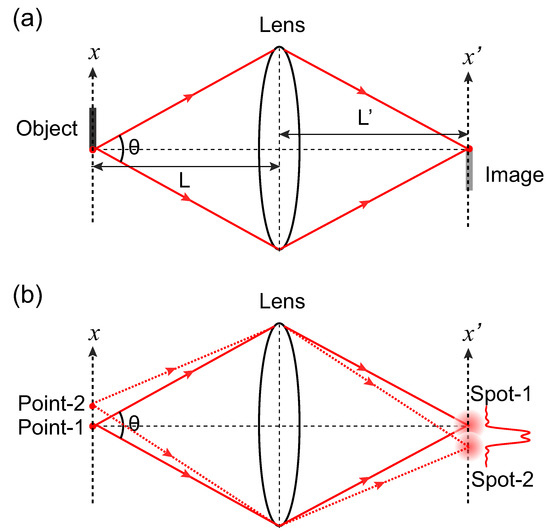
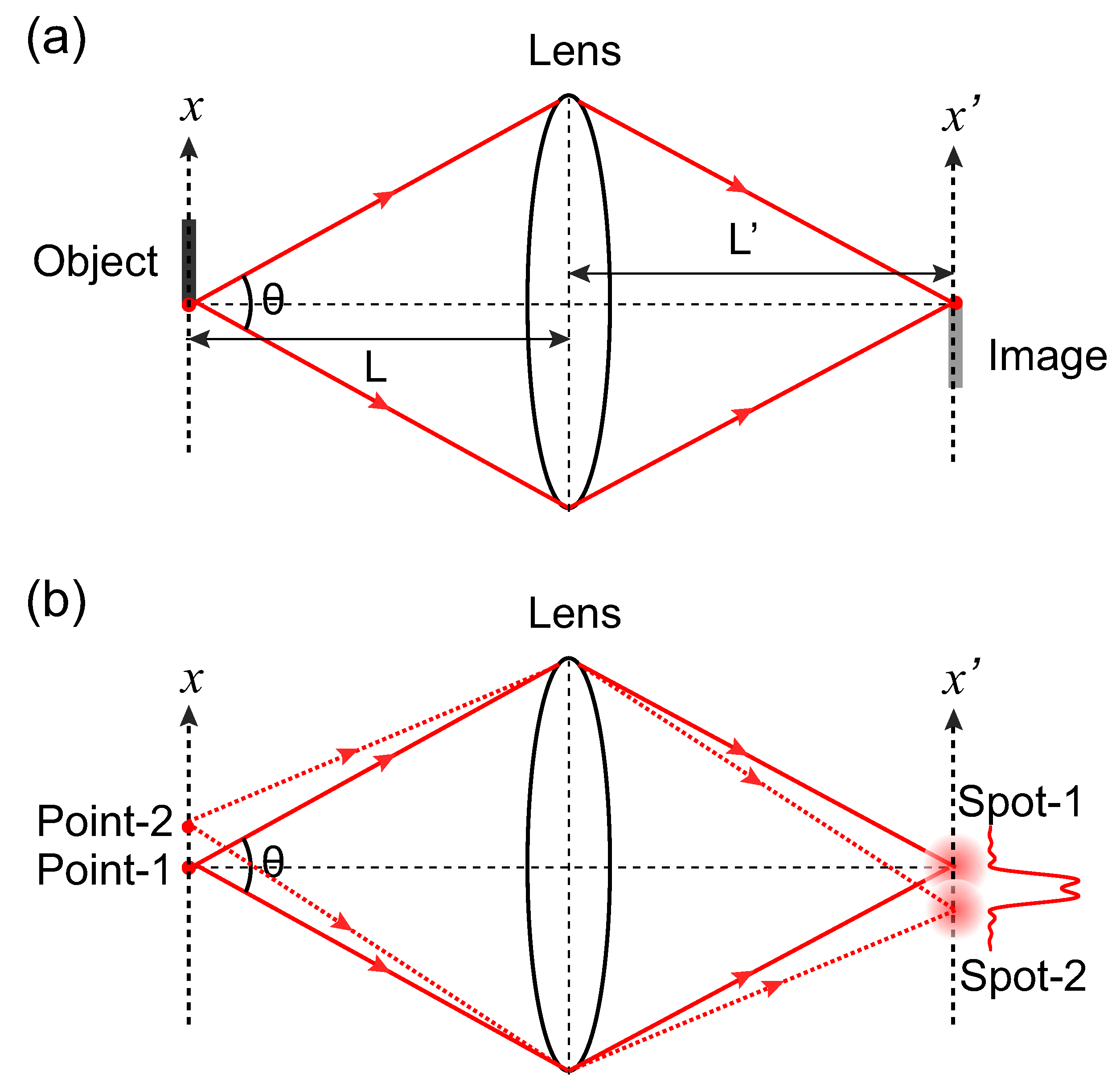
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of lens-assisted imaging system. The divergence of light wave originating from a point of the object is reversed by the lens, converging to a point on the image plane; (b) The point-to-point correlation between the object and the image plane is not ideal. The image spot is of finite size that is determined by the wavelength of the light wave and the numerical aperture of the imaging lens (refractive index n = 1 for air).
However, due to the wave nature of light, the imaging process is not ideal, but of limited resolution determined by the wavelength and the numerical aperture , i.e., the well-known Rayleigh limit [45]. Here, n is the refractive index of the environment dielectric material ( for air), and is the maximum cross angle for the diverging wave originating from the object point as shown in Figure 1a. Please note that the numerical aperture is expressed as in the paraxial approximation, where D is the diameter of the lens, and L is the distance from the object to the lens. Within the Rayleigh Criterion, better imaging resolution is achieved by employing light wave of shorter wavelength and scheme of larger numerical aperture.
The emergence of Rayleigh resolution limit can be understood by considering superposition of indistinguishable single-photon paths. The imaging process is in fact a result of constructive interference between alternative single-photon paths from the object point to the image point, since the phase differences caused by propagation with a single photon transmitting through different positions of the lens are compensated for by the static phase pattern of the lens. By scanning the lateral position on the image plane, the phase compensation process is gradually destroyed until complete destructive interference occurs. This leads to an image spot formed on the observation plane for an object point as illustrated in Figure 1b, and any two adjacent image spots with a separation smaller than the size of the image spot are thus indistinguishable. For a quantitative estimation on the resolution limit, we consider the one-dimensional (1D) geometry in the paraxial approximation for simplicity, in which the complete destructive interference occurs when the phase mismatch between the two single-photon paths shown in Figure 1b (solid lines) reaches . With a position shift on the image plane, with being the angular wavenumber of light while being the distance from the lens to the image plane, giving rise to an image spot of size . Therefore, two adjacent image spots of separation is not separable. By considering the magnification factor , the imaging resolution limit for the object is therefore derived as in the 1D case. The Rayleigh resolution limit in the 2D case can be explained with the same argument.
Next, we will review several recently developed schemes that surpass the Rayleigh resolution limit based on optical high-order interference effect.
3. Super-Resolution with Scanning Focused Beam
In 2009, Giovannetti et al. proposed that n-photon coincidence can be employed for realizing sub-Rayleigh quantum imaging in lens-assisted imaging schemes [31], giving rise to the standard quantum limit (SQL) resolution with an enhancement factor . Nevertheless, direct n-photon detection within the conventional lens-assisted imaging scheme does not guarantee the realization of SQL super-resolution imaging. The key is to employ proper illumination, such that the nth-order cumulant function for super-resolution is obtained. The nth-order cumulant function is the filtered/efficient nth-order correlation function with the contributions related to photons from different point sources of the object being eliminated [33]. To achieve this goal, entangled n-photon illumination and scanning focused-beam illumination are introduced, leading to coherent SQL super-resolution imaging
and incoherent SQL super-resolution imaging
respectively. Here, is the object aperture function, is the point-spread function in an imaging scheme. We see that the effective PSF of the nth-order cumulant function is nth power of the original PSF of conventional intensity imaging, leading to an enhancement factor of in the spatial resolution. Please note that with these two kinds of illumination mentioned above, there is no contributions to the nth-order correlation function that is related to n-photon paths originating from different positions of the object, i.e., the cross talk between different positions of the object is prohibited [42]. Therefore, the nth-order correlation function is exactly the nth-order cumulant function. From the result, we see that the SQL super-resolution is a result of constructive interference of n-photon paths when the n photons are from the same position of the object.
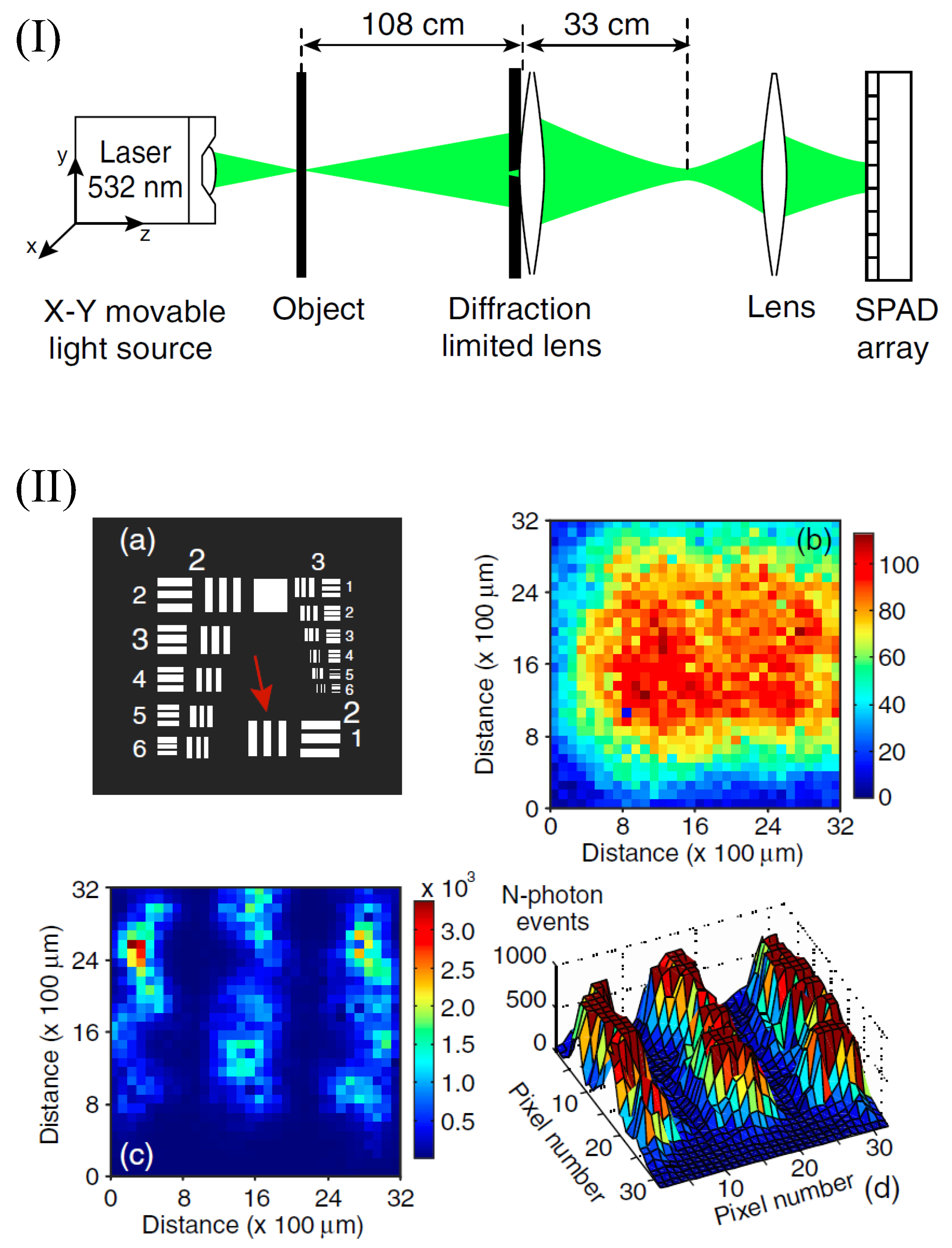
With the scanning-focused laser beam illumination, Guerrieri et al. have demonstrated the sub-Rayleigh imaging effect by taking n-photon detection [32]. In the experiment, a 532 nm laser mounted on an xy translation stage was used for providing scanning focused-beam illumination as shown in Figure 2I. The N-photon detection is done with a detector consisting of 32 × 32 single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) array [46]. By considering the Poisson statistics of photon counting process [47,48], the n-photon counting events within single frame of measurements was post-selected, such that the imaging resolution is improved by a factor of with being the maximum average single-photon counts at a single detecting point. The SQL resolution is approached at low average single-photon counts with much smaller than unity as shown in Figure 2II. This super-resolution imaging with scanning-focused-beam illumination is useful for high-resolution image transfer through laser radar.
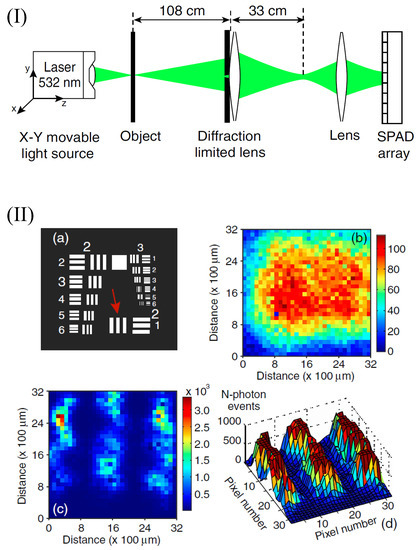
Figure 2.
(I): Schematic of the experimental setup for realizing SQL super-resolution imaging with scanning-focused-beam illumination. (II): Super-resolution image realized in the experiment for a scheme with Rayleigh resolution limit 1.86 mm. The triple-slit object with slit width 125 m is marked by the red arrow (a). The intensity image realized with conventional lens-assisted imaging scheme is presented in (b), and the super-resolution image realized with the n-photon detection (n = 23) is shown in (c) and (d), where (d) is the three-dimensional image of (c) by clipping the event counts at 800. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [32] of APS.
Besides the scanning-focused-beam illumination, the SQL super-resolution imaging can also be realized with wide-field illumination such as that with an entangled n-photon source [31], as will be shown in the following sections.
4. Super-Resolution via Bunching Effect
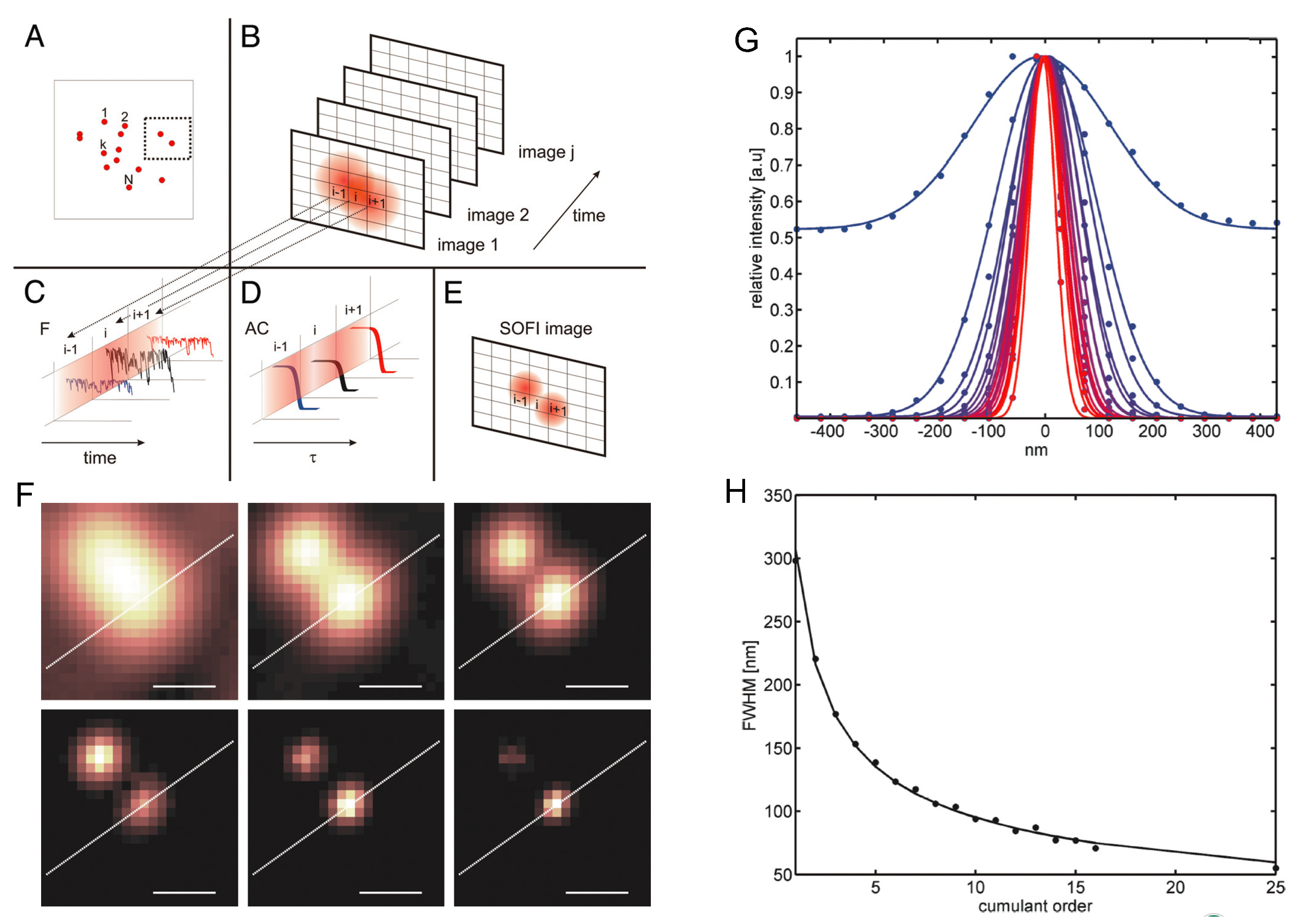
The Rayleigh resolution limit can be surpassed by considering the bunching effect of chaotic light [49,50]. The initial work in this direction was done by Dertinger et al., termed as super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI) [33]. SOFI is a fluorescent imaging scheme for object consisting of many fluorescent point emitters as illustrated in Figure 3A. In this case, the cross talk between different positions of the object is inevitable, and the nth-order cumulant function needs to be extracted out from the measured nth-order correlation function. Interestingly, by considering the emission fluctuation of single fluorescent emitter (Figure 3C) [51], the bunching effect of the fluorescent light provides the possibility to separate the nth-order cumulant function through computation with the measured lower order autocorrelation function (Figure 3D). Consequently, super-resolution is achieved in SOFI with the resolution reaching the SQL (Figure 3E). In this scenario, the obtained SQL image is an incoherent one as described in Equation (4). The experiment was done in an inverted wide-field microscope, and the sample was excited by a 470 nm LED array. The fluorescence light was recorded by an electron multiplying CCD (EMCCD) camera at a relatively low acquisition rate (10 Hz) that is limited mainly by the blinking behavior of the quantum dots used in the experiment. The results show that the imaging resolution increases with the increase of the order of autocorrelation measurement, demonstrating the -scaling of SQL super-resolution imaging as shown Figure 3F–H.
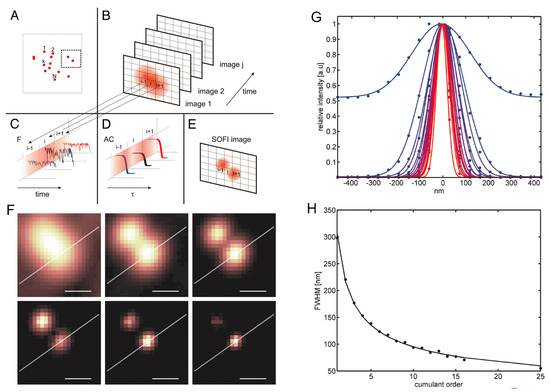
Figure 3.
Super-resolution fluorescence imaging through optical fluctuation. The object to be imaged consists of many independent fluorescent emitters (A); and the fluorescent intensity of the image spot fluctuates independently for different emitters (B,C). By taking advantage of the bunching effect of the optical fluctuation (D); super-resolution image can be realized (E). Super-resolution images demonstrated in experiment (F) clearly show that the imaging resolution increases with cumulant orders, confirmed by the one-dimensional Gaussian fit of the cross-sections (G). The reduced full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the fitted Gaussian curves upon the cumulant orders is plotted in (H). Scale bars in (F): 250 nm. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [33] of PNAS.
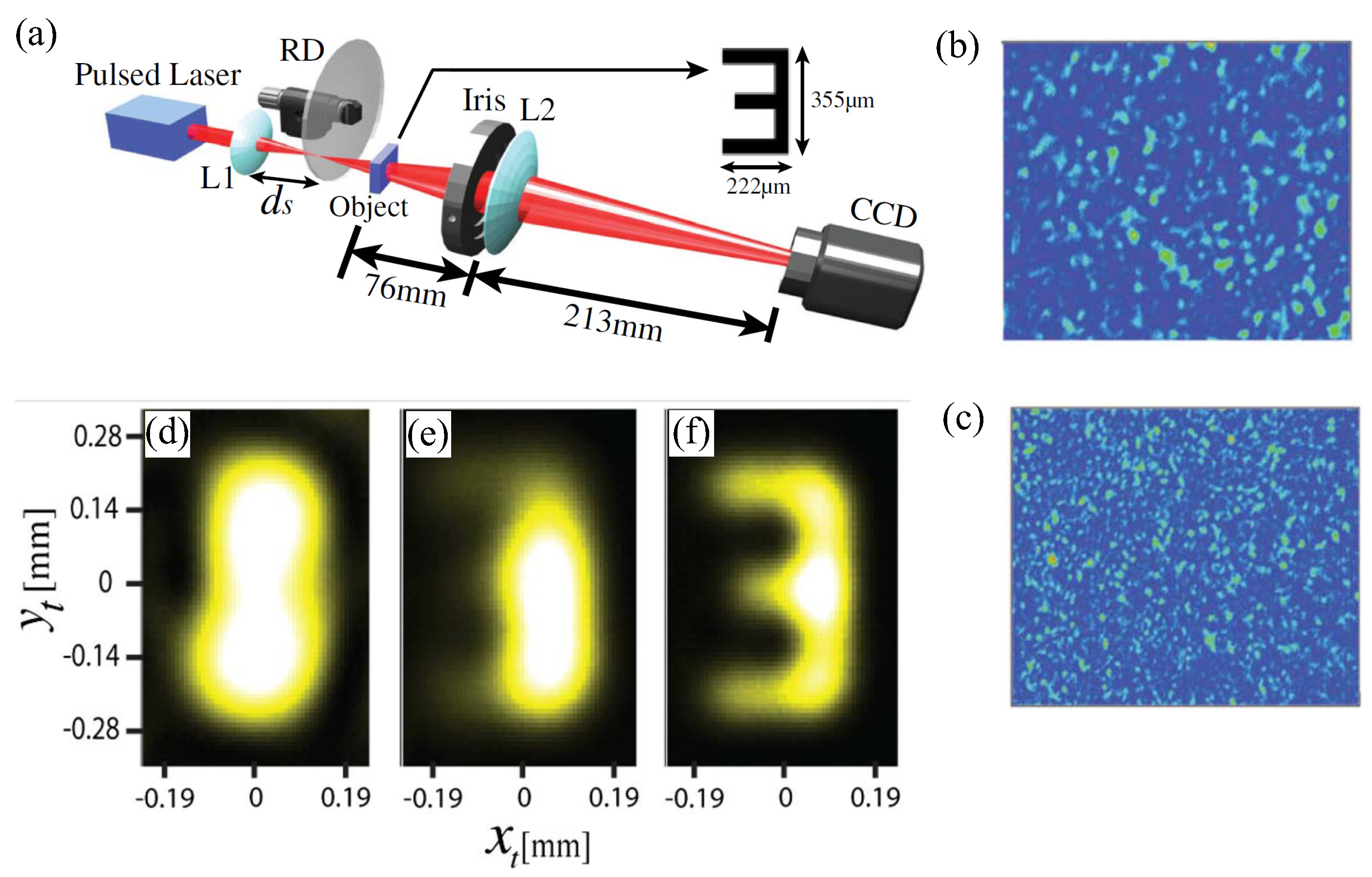
For non-fluorescent imaging, the SQL super-resolution imaging can be achieved by employing thermal/pseudothermal light for illumination. In fact, the working principle is similar to SOFI, since the thermal/pseudothermal source is constituted by many independent fluctuating point sources [52,53]. In the work reported by Oh et al. [34], the pseudothermal light is generated by focusing a 783 nm laser beam onto a rotating ground glass disk as shown in Figure 4a. A CCD camera was used to measure the second-order correlation function on the image plane. By calculating the second-order cumulant function, sub-Rayleigh imaging has been demonstrated with the resolution improved by a factor of ∼1.4. Notably, the resolution enhancement is limited by the spatial correlation length of the pseudothermal source [54], i.e., the size of single speckle of the light field employed for illuminating the object as shown in Figure 4b,c. The smaller the correlation length, the finer the imaging resolution, as shown in Figure 4e,f. In addition, other types of artificial fluctuating light source are also applicable for realizing the SQL super-resolution imaging [35].
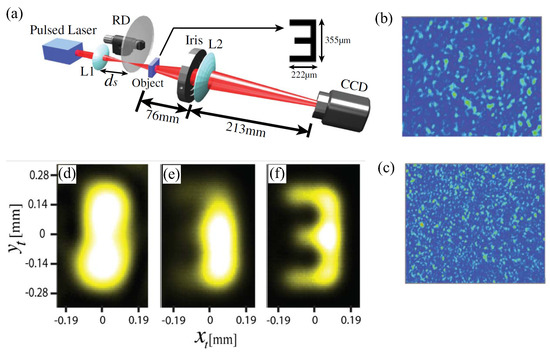
Figure 4.
Super-resolution imaging with pseudothermal light illumination. (a) represents the schematic of experimental setup with the pseudothermal light generated by launching a focused laser beam onto a rotating ground glass disk (RD). The spatial correlation length of the illumination pseudothermal source is controlled by varying the distance () between the lens and the RD, which is revealed by the instantaneous intensity image of the illumination speckle field on the object plane (b,c). Compared to the conventional intensity image (d), second-order correlation measurement leads to super-resolution image of the object, such as that shown in (e) with speckle illumination (b), and (f) with speckle illumination (c). The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [34] of OSA.
5. Super-Resolution via Quantum Antibunching Effect
Single-photon emitters have also been employed to realize the SQL super-resolution imaging. In 2012, Schwartz and Oron proposed that the nonclassical emission of fluorescent markers can be employed for realizing super-resolution imaging [36]. For the fluorophores used in bioimaging, photons are emitted one by one, leading to the antibunching effect [55,56]. By taking advantage of the antibunching effect, measurement of the nth-order antibunching signal gives rise to the enhanced resolution scaling as . Physically, the SQL super-resolution imaging through antibunching is resulted from the lack of the in-position n-photon constructive interference signal, in contrast to the case through classical bunching effect that is resulted from the excess of the in-position n-photon constructive interference signal. Similar to the bunching induced SQL imaging, the antibunching induced SQL imaging generates an incoherent image of the object.
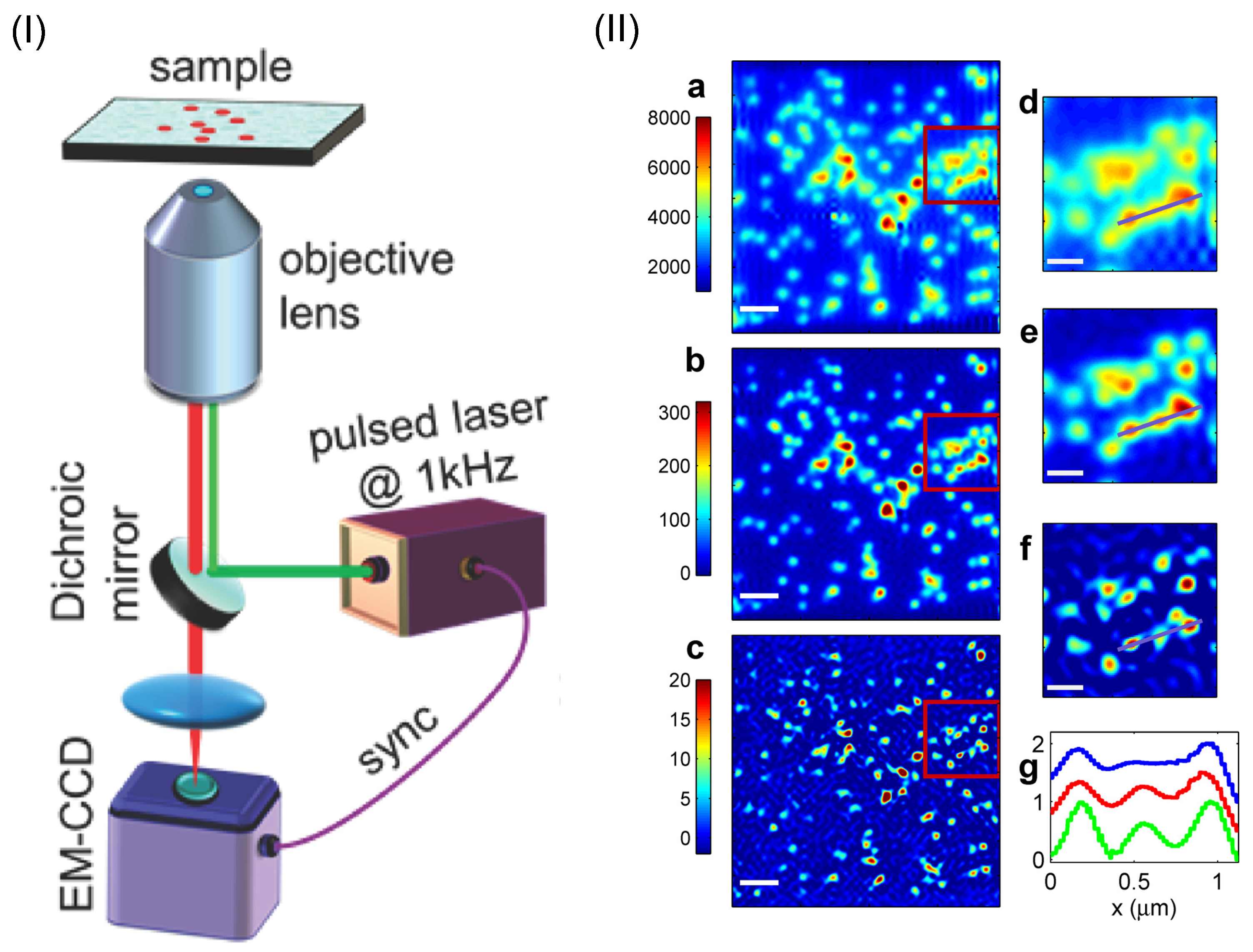
The antibunching induced super-resolution imaging has been realized in a standard wide-field epi-fluorescence microscope [37], as shown in Figure 5I. The non-Poisson emitter is CdSe/CdS/ZnS colloidal quantum dot excited by a pulse laser at 532 nm, and emits light photon with a wavelength at 617 nm. An EMCCD has been used for measuring the high-order correlation function [57] with a repetition rate at 1 kHz. By introducing two-photon and three-photon coincidence measurement, the fluorescence imaging resolution is increased by a factor of 1.3 and 1.5 as shown in Figure 5II-b and Figure 5II-c, respectively.
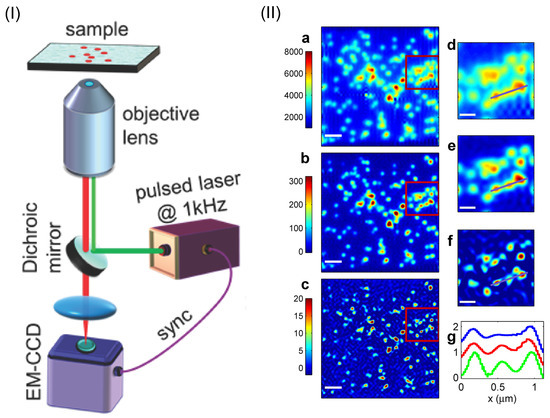
Figure 5.
(I): Schematic of the experimental setup for realizing super-resolution image based on antibunching effect of quantum single-photon emitters. The sample to be imaged consists of many independent single-photon emitters. Multi-photon coincidence counts are measured with an EMCCD camera. (II): Super-resolution images measured with second-order (b) and third-order (c) antibunching effect, which clearly show the resolution enhancement in comparison with the conventional intensity image (a). Scale bars in (a–c): 1 m. (d–f) are zoom-in images of the zones marked by red box in (a–c), while (g) shows the one-dimensional plot of the cross-sections marked by the solid line in (d–f). Scale bars in (d–f): 400 nm. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [37] of ACS.
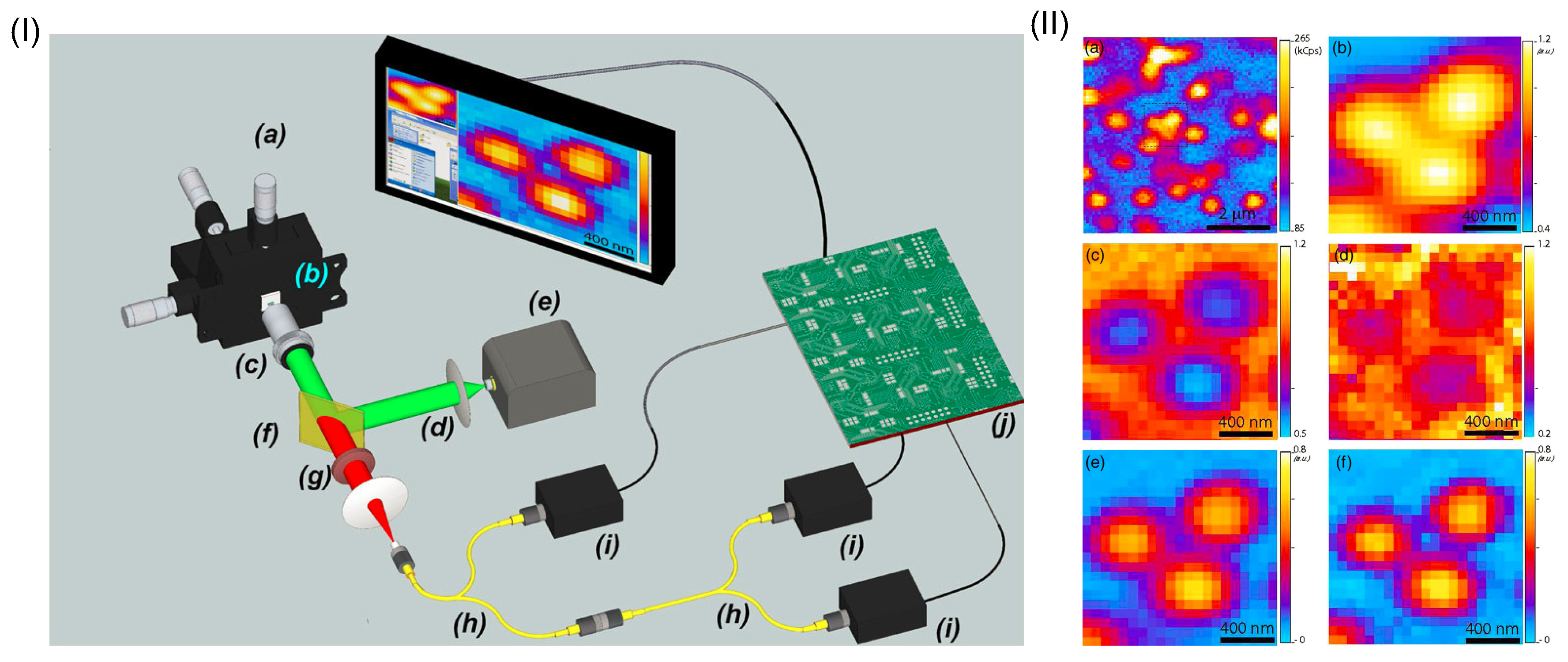
With antibunching emitters, Monticone et al. have demonstrated super-resolution fluorescence imaging in a confocal microscope [38]. The sample to be imaged is a diamond with clusters of NV centers, which are excited by a focused laser beam at 532 nm and emit fluorescent light within 640–800 nm. n-photon coincident measurement is taken with several single-photon detectors operating in Geiger mode [58], as shown in Figure 6I. By scanning the sample, SQL super-resolution imaging is obtained with two-photon and three-photon coincidence measurement as shown in Figure 6II. Moreover, with the prior knowledge of the number of the quantum emitters , better resolution can be reached by further calculating the higher-order cumulant function with the hitherto known Glauber higher-order (kth-order) correlation function when .
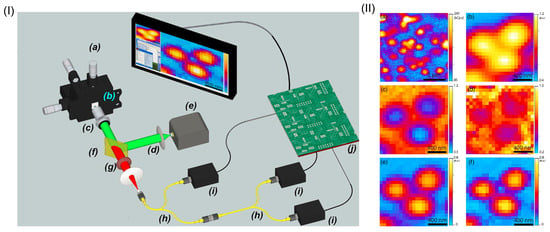
Figure 6.
(I): Schematic of super-resolution confocal microscope for fluorescence imaging. Multi-photon coincidence counts are measured by using single-photon detectors configured in the tree structure with fiber beam splitters. (II): Three partially overlapped NV centers in the conventional intensity image (a) is selected, which cannot be clearly distinguished as seen in the zoom-in image (b). The antibunching effect of NV emitters is seen by employing second-order (c) and third-order (d) correlation measurement. After processing numerical calculation, the second-order (e) and third-order (f) cumulant function gives rise to super-resolution image, revealing three clearly distinguishable NV centers. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [38] of APS.
6. Super-Resolution via Quantum Entanglement
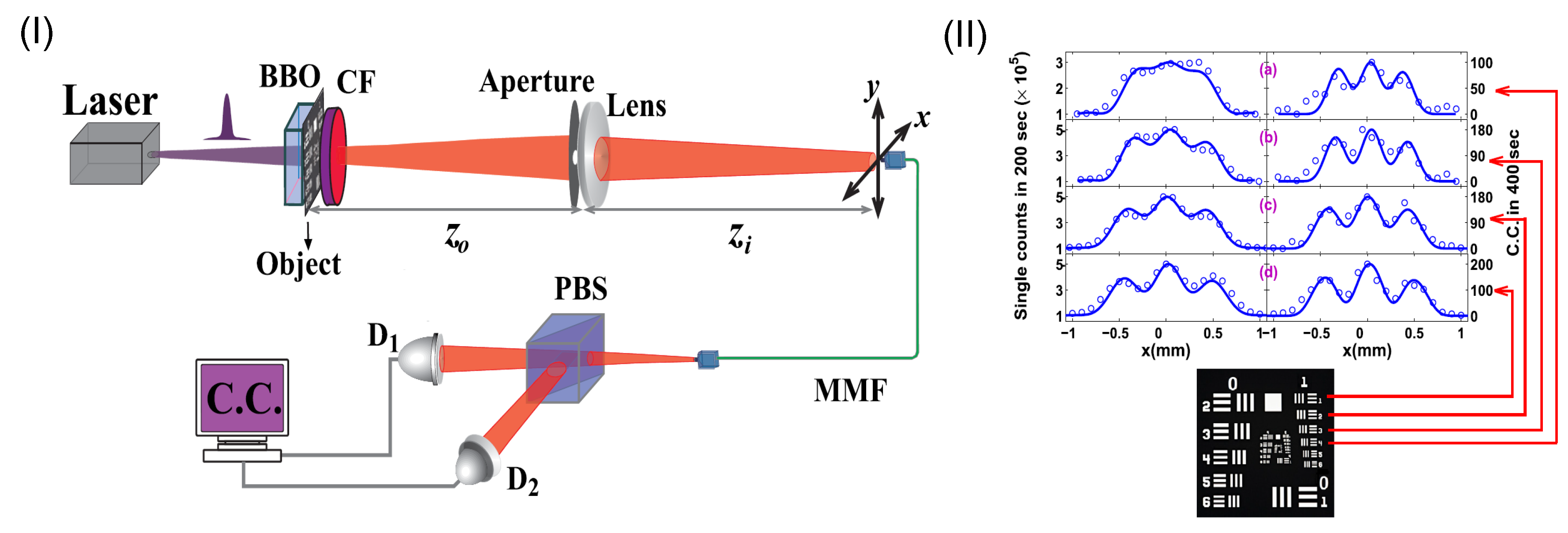
Position-entangled n-photon source can be used for realizing the coherent SQL super-resolution imaging, as initially proposed by Giovannetti et al. [31]. Currently, the most well-developed entangled source is entangled two-photon source [59]. By placing the object in proximity to the output plane of an entangled two-photon source, Xu et al. have experimentally demonstrated the SQL super-resolution imaging [39], as shown in Figure 7I. The entangled source was generated through the type-II parametric down conversion process (SPDC) [59], which was implemented with a betabarium-borate crystal pumped by a pulse laser with a center wavelength at 400 nm. The two-photon coincidence was measured by two single-photon detectors connected to a coincident circuit. The results show a times improved resolution for direct imaging for the objects as shown in Figure 7II. In this case, the realized SQL imaging is coherent, since the two-photon paths originating from different points of the object are coherent with respect to each other.
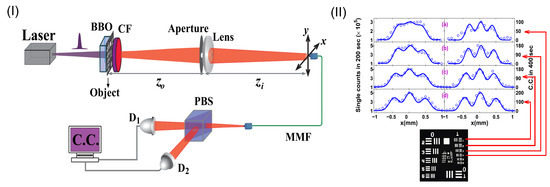
Figure 7.
(I): Schematic of experimental setup for realizing super-resolution imaging with entangled two-photon source illumination. The entangled two-photon source is generated by optical parametric down conversion with the betabarium-borate (BBO) crystal. (II): Super-resolution images (right column) in comparison with the conventional intensity images (left column). The object to be imaged is marked by the red lines in the figure. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [39] of AIP.
More interestingly, the entangled two-photon source can be employed to realize Heisenberg-resolution imaging. Super-resolution imaging at HL was initially discussed by Giovannetti et al. [31], which is based on synchronous-position n-photon interference (dependent on the sum coordinates of observation positions), but relies on a conceptual nonlinear n-photon transmitting screen. The Heisenberg-resolution imaging based on synchronous-position multi-photon interference can expressed as
for coherent imaging, and is expressed as
for the incoherent imaging. Here, is the object aperture function, is the nth-order effective point-spread function with an effective wavelength , giving rise to an n-time reduced FWHM in comparison to that of the for the conventional single-photon imaging. However, the nonlinear n-photon transmitting screen does not exist currently, and is quite difficult to be realized. Therefore, more feasible method needs to be explored.
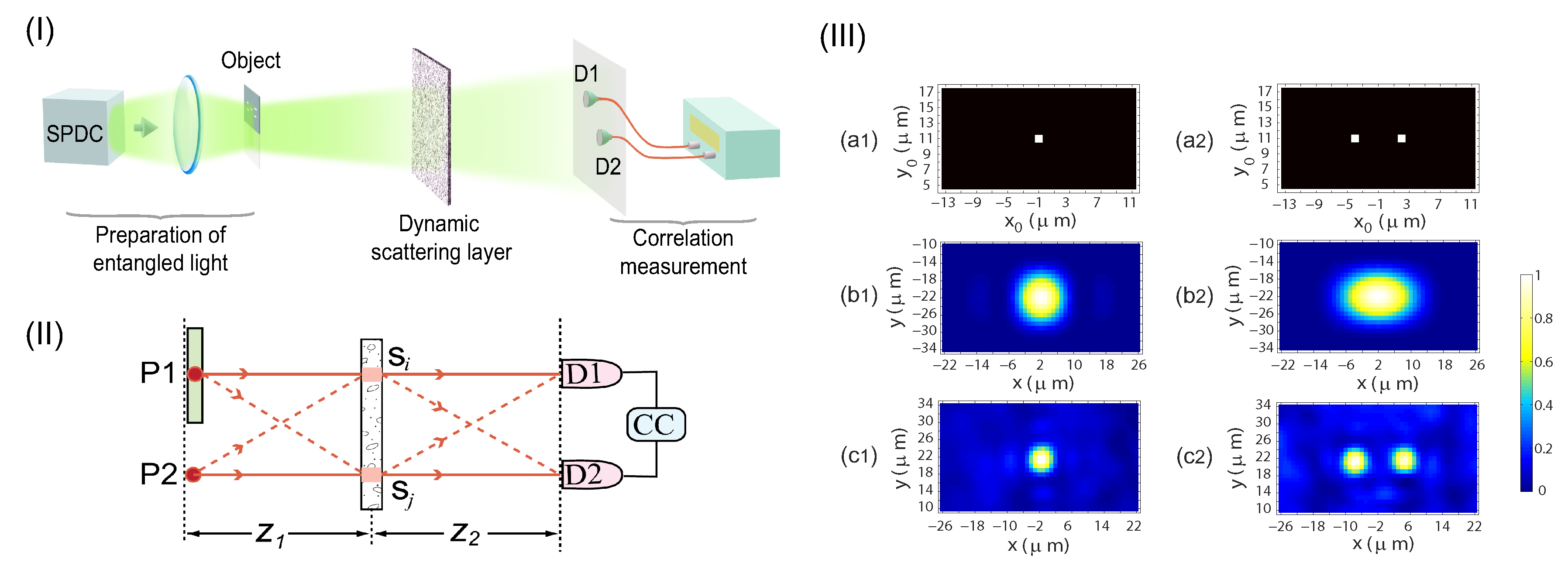
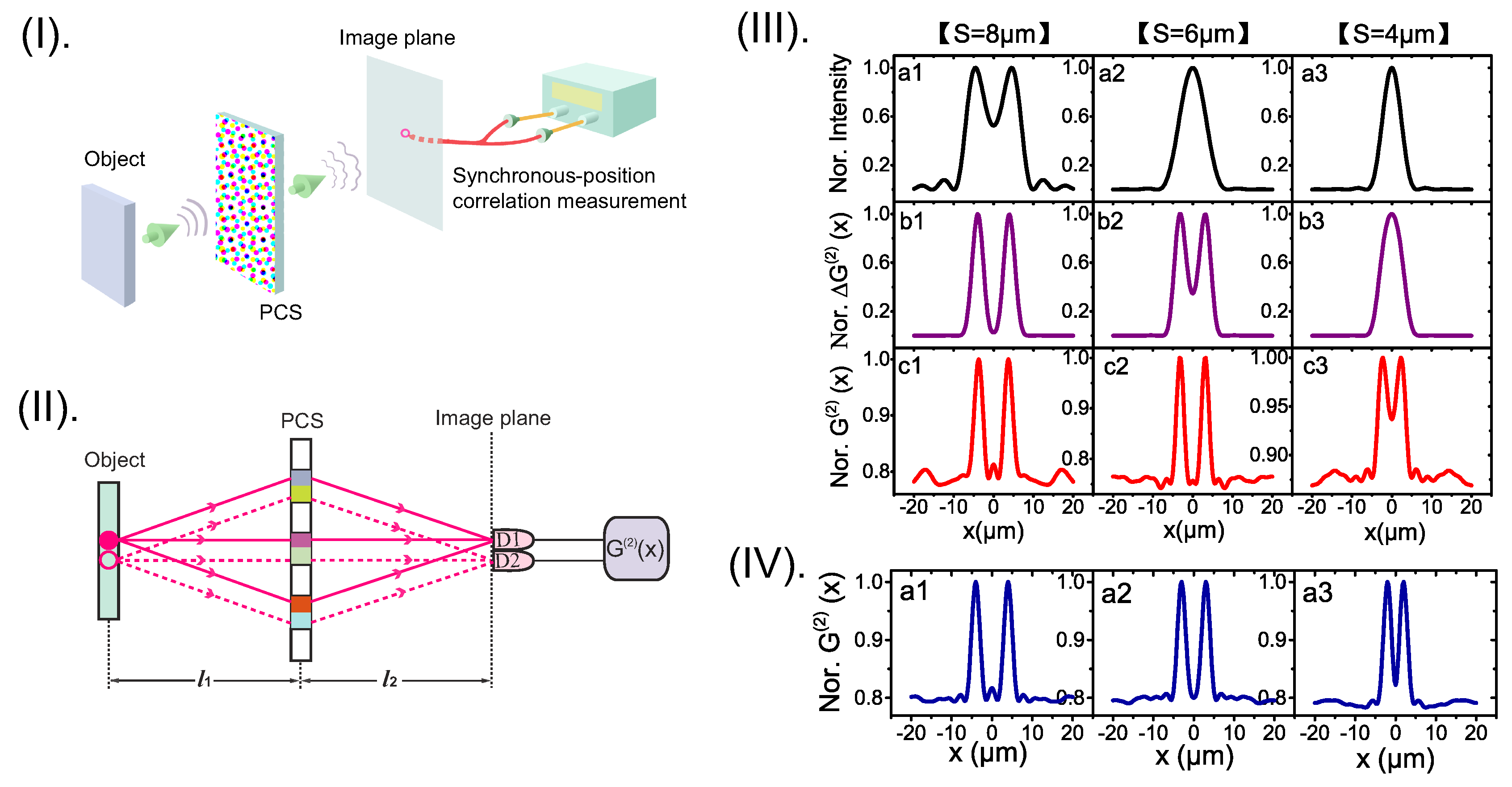
Besides the synchronous-position multi-photon interference [28,31], Hanbury Brown-Twiss type interference (dependent on the coordinate difference of the observation points) has recently been introduced for realizing Heisenberg-resolution imaging [40]. The proposed imaging scheme is shown in Figure 8I, which can be realized with current well-developed technology. In the scheme, the object is placed on the top half of the Fourier plane of an entangled two-photon source [57,59], while the bottom half of the Fourier plane is kept transparent. Instead of employing a lens for imaging, the super-resolution imaging process is assisted by a dynamic random scattering layer, although the random scattering is well known for destroying imaging process in conventional single-photon imaging systems. By taking two-photon coincidence measurement with the totally scrambled light through the scattering layer, a direct imaging of the object can be obtained on the image plane, and the imaging resolution can reach the HL as shown in Figure 8III. By analyzing the superposition of two-photon paths [27,60,61], it is found that constructive two-photon interference for imaging is employed naturally with the dynamic scattering layer, as shown in Figure 8II. In contrast to the synchronous-position Heisenberg-resolution imaging expressed in Equations (5) and (6), the Hanbury Brown-Twiss type two-photon interference leads to an imaging term expressed as
where with () being the coordinate on the image plane, and is the two-fold enhanced point-spread function (PSF). The two possible values of (=±1) is related to exchanging the positions of the two detectors (D1 and D2), which does not change the super-resolution imaging result in scheme.
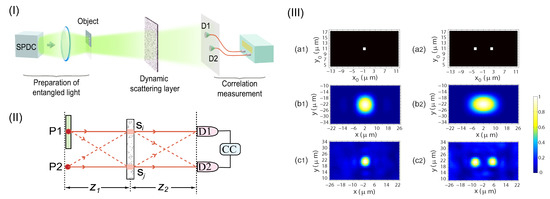
Figure 8.
(I): Schematic of the super-resolution imaging scheme assisted by a dynamic scattering layer. The object is placed on the top half of the Fourier plane of the output plane of the entangled source, while the bottom half of the Fourier plane is kept transparent. For achieving super-resolution image of an amplitude object, an additional dynamic scattering layer should be placed near the object, or directly on the bottom half of the Fourier plane. (II): Different but indistinguishable two-photon paths in the imaging scheme. Constructive two-photon interference employed by the scattering layer can be observed by scanning the two single-photon detectors D1 and D2. (III): HL super-resolution images (c1,c2) for single point object (a1) and two point objects (a2), respectively. The super-resolution effect is demonstrated by comparing with the intensity images (b1,b2) of the two objects obtained through conventional lens-assisted single-photon imaging. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [40] of AIP.
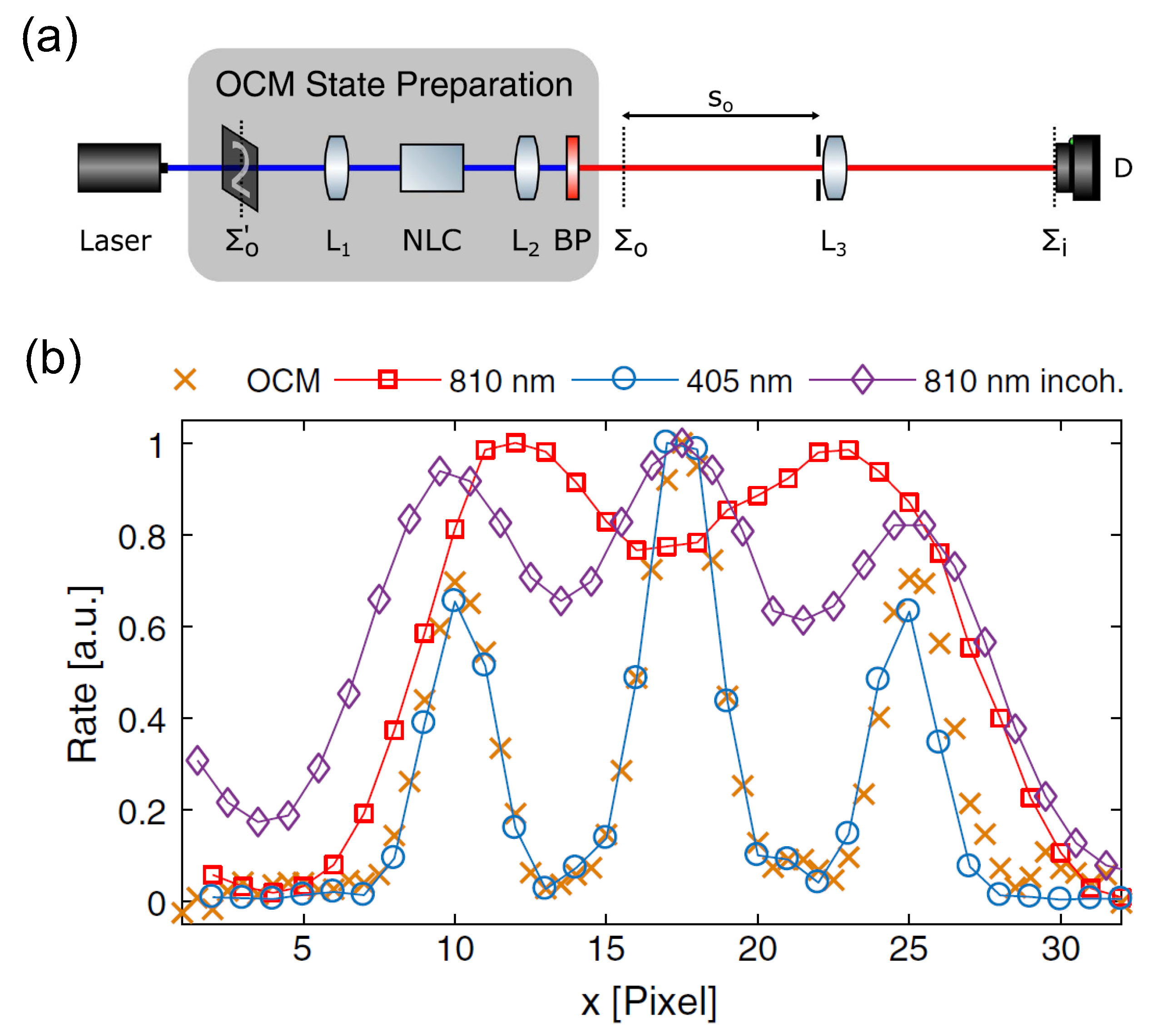
Recently, Unternhrer et al. have reported a synchronous-position Heisenberg-resolution imaging in a lens-assisted imaging scheme [41]. The object is first illuminated by a continuous-wave pump laser at 405 nm, such that its information is encoded into the complex amplitude of pump light as shown in Figure 9a. The transmitted pump light is then projected to the Fourier plane via a lens , where the pump light is down-converted to the entangled two-photon light through SPDC process. As a result, the Fourier image of the object encoded in the complex amplitude of pump light is transferred to the two-photon complex amplitude. Consequently, the image of the object can be obtained by employing two-photon coincidence measurement on the Fourier plane of the SPDC source [17], and the imaging resolution breaks the Rayleigh limit related to the SPDC photons by a factor of 2. In the experiment, the Fourier plane of the SPDC source is in fact imaged to the detection plane with an additional imaging lens , and the numerical aperture is limited by the aperture size of the lens . Nevertheless, the HL imaging resolution has been demonstrated in the scheme as shown in Figure 9b. The result has been explained by considering the optical centroid measurement state [62,63]. Notably, the super-resolution imaging here is related to the down-converted photons, but not to the directly illuminating light photons transmitted through the object. From this respect, it is different from the Heisenberg-resolution imaging discussed by Giovannetti et al. [31], which is related to the light directly illuminating the object.
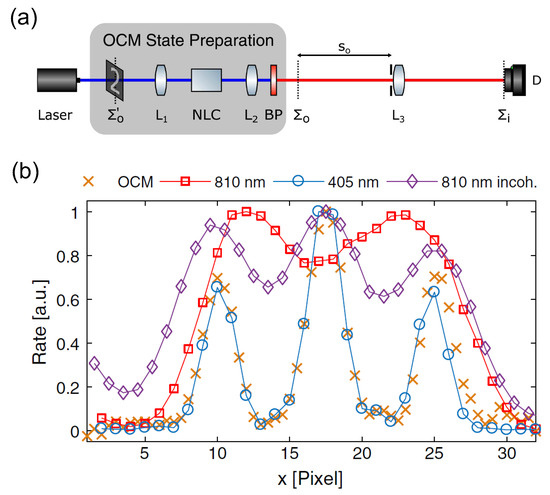
Figure 9.
(a): Schematic of the super-resolution imaging scheme by encoding the image of an object onto the optical centroid measurement state (OCM). The spatial information of the object is first encoded onto the pump light (), and a lens is used to project the pump light onto its focal plane, where parametric down conversion process transfers the Fourier information of the object into the two-photon amplitude of the generated entangled light. By employing an additional Fourier transform with lens , the OCM state of the object is built, i.e., subwavelength far-field interference of the Fourier image of the object. (b): HL super-resolution image realized through the OCM state of a triple-slit object with entangled light at 810 nm. The super-resolution effect is demonstrated by comparing with the conventional intensity images at wavelengths 810 nm and 405 nm. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [41] of OSA.
7. Super-Resolution via Dynamic Phase Control
In 2017, Hong and Zhang designed a dynamic phase screen to replace the imaging lens, and achieved direct n-photon imaging [42] as shown in Figure 10I. It has been shown that synchronous-position multi-photon interference plays a key role in the scheme, leading to super-resolution imaging for the object with the resolution reaching the HL. Importantly, the designed phase screen can be easily implemented with a commercial spatial light modulator [27], indicating the developed Heisenberg-resolution imaging is achievable with current well-developed technology. The phase screen is of specially designed dynamic phase structure, i.e., each point on the phase screen is loaded with a different complex amplitude that is a superposition of n correlated dynamic phase modes together with a lens-type static phase mode as detailed in Ref [42]. In the two-photon interference case, it was found that the synchronous-position two-photon interference pattern is mainly caused by the two-photon paths with the pair of photons transmitting through the same point of the phase screen as illustrated in Figure 10II. Therefore, the linear dynamic phase screen is of similar functionality as the conceptual nonlinear n-photon transmitting screen discussed by Giovannetti et al. [31], leading to the HL two-photon imaging. To realize the proposed n-photon Heisenberg-resolution imaging, the object should be illuminated by an entangled n-photon source or a scanning focused beam as shown in Figure 10III,IV, corresponding to coherent and incoherent Heisenberg-resolution imaging, respectively.
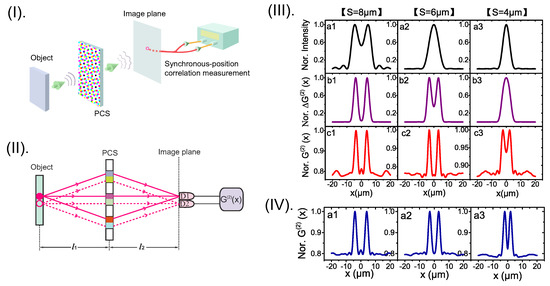
Figure 10.
(I): Schematic of the super-resolution imaging scheme with a phase-controlled screen (PCS). (II): Different but indistinguishable two-photon paths responsible for the super-resolution effect; (III): Coherent Heisenberg-resolution imaging with entangled two-photon illumination for double-slit objects of different separation S (c1–c3). The HL super-resolution effect is demonstrated by comparing with the conventional intensity imaging (a1–a3) and the SQL super-resolution imaging with thermal/pseudothermal light illumination (b1–b3). (IV): Incoherent Heisenberg-resolution imaging with scanning focused-beam illumination for double-slit objects of different separation S. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [42] of OSA.
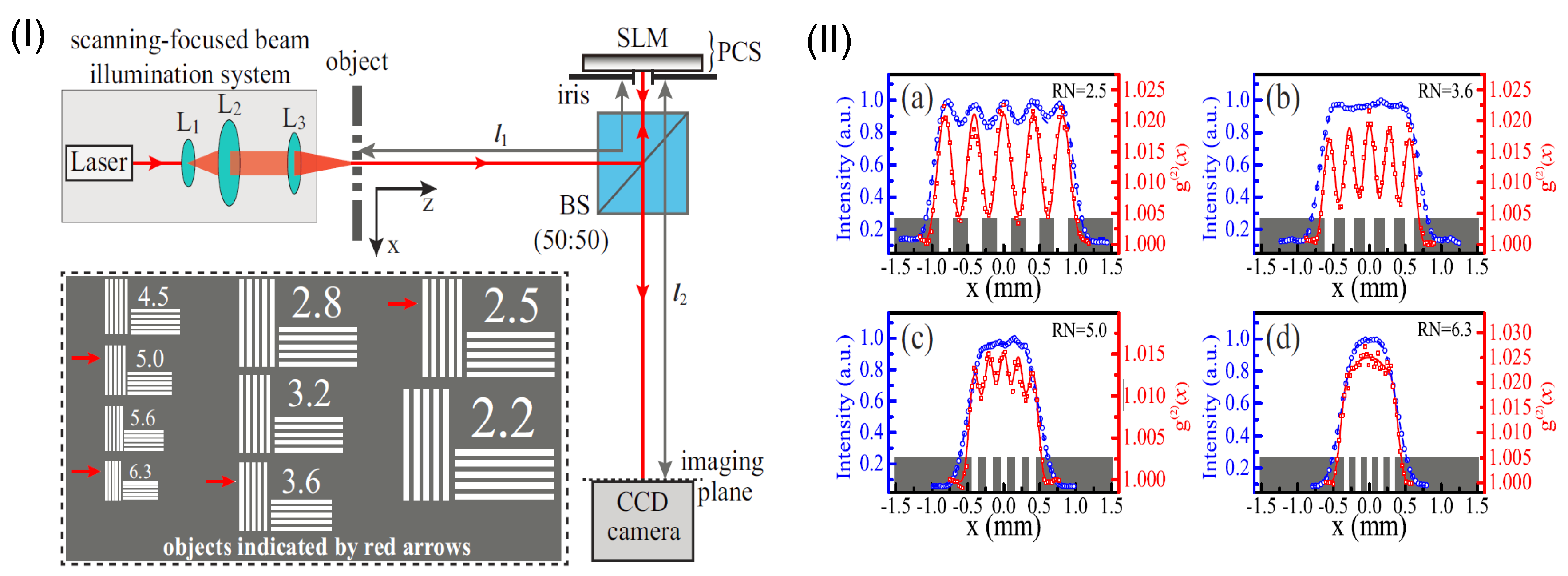
Recently, Li et al. have experimentally realized the Heisenberg-resolution imaging with scanning focused-beam illumination [43]. In the experiment, the dynamic phase screen was realized by using a reflection-type phase-only spatial light modulator (see Figure 11I). Both the laser and the pseudothermal light were introduced for illumination, and the synchronous-position two-photon correlation was measured by using a CCD camera. Both the PSF and the spatial resolution of the Heisenberg-resolution imaging system were characterized. The results with laser light are shown in Figure 11II, which demonstrate the HL super-resolved spatial resolution of the imaging system.
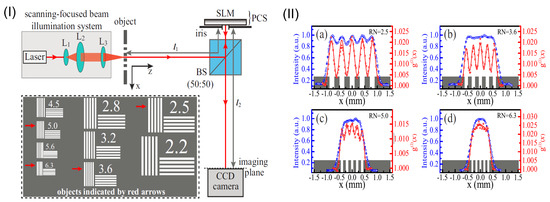
Figure 11.
(I): Schematic of experimental setup for realizing Heisenberg-resolution imaging with scanning focused-beam illumination. The phase-controlled screen (PCS) is realized by a phase-only spatial light modulator. The objects to be imaged are shown in the inset, indicated by the red arrows; (II): The HL super-resolution images (red circles) for different objects. The super-resolution effect is demonstrated by comparing with the conventional intensity images (blue circles). Please note that the object with a RN = 5.0 is with slit separation beyond the SQL. The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [43] of OSA.
8. Discussion and Perspectives
The super-resolution imaging based on optical high-order interference could be beneficial in many applications, such as biomedical imaging [33,37,64,65], laser radar [32], nano imaging [38] and astronomical imaging [9]. For comparison, a summary of the different super-resolution imaging schemes is listed in Table 1, showing the key difference between the imaging schemes, as well as the different conditions in different experiments. To improve the performance of the super-resolution imaging schemes, three main factors should be taken into consideration, i.e., the illuminating light field, the imaging element, and the detector. Besides the fundamental limit set by the SQL or HL, the imaging resolution is technically limited by the pixel size of the detector [33], as well as the spatial correlation length of the illuminating light field [42]. The image acquisition speed is limited by the speed of the detector, the properties of the illumination sources such as the scanning speed in the scanning-focused-beam illumination scheme, and the dynamic speed of the imaging element such as the refreshing rate of the spatial light modulator. Consequently, light sources of tailored properties, high-efficient and fast detectors, and fast spatial light modulators could be very helpful for prompting the application of the multi-photon super-resolution imaging. The optical high-order interference is not only useful for improving the imaging resolution of conventional lens-assisted imaging schemes, but also provides the possibility to design fundamentally new direct imaging schemes such as that realized with dynamic phase-controlled screen or scattering layer [40,42]. This result indicates the possibility to explore novel type of multi-photon imaging schemes that can break the limitations existed in conventional lens-assisted imaging scheme. These super-resolution multi-photon imaging schemes are important additions to the library of multi-photon imaging [66,67,68,69,70,71,72].

Table 1.
A summary of different super-resolution schemes based on optical high-order interference.
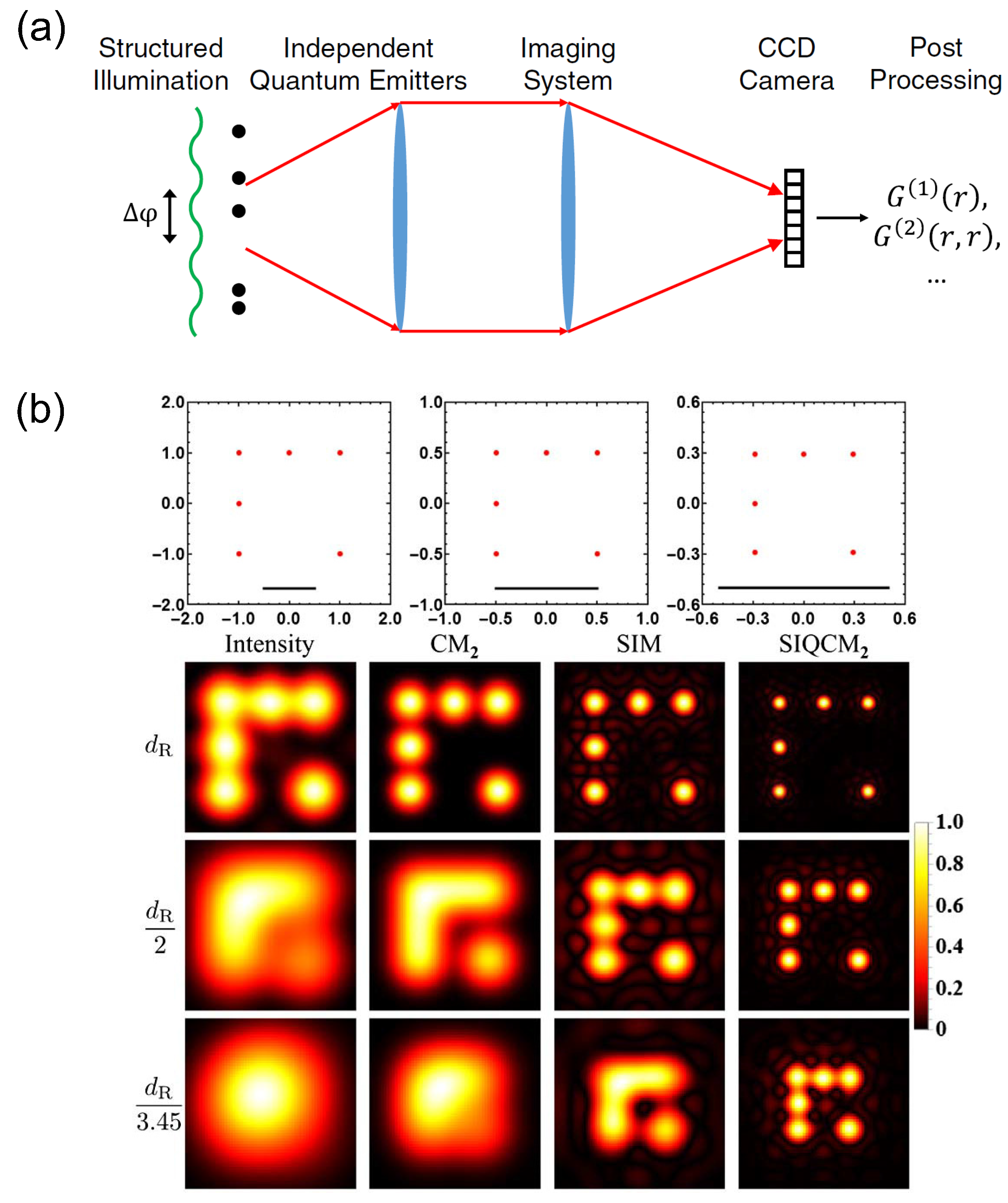
Similar to the conventional lens-assisted imaging schemes, the multi-photon imaging schemes are in fact of limited resolution, despite that it can break the Rayleigh limit and reach the SQL or HL. Therefore, a future direction would be to break these limits to reach higher imaging resolution. One possible way is building hybrid super-resolution imaging schemes, i.e., combining several super-resolution imaging methods together to gain further resolution improvement. This is indeed feasible as revealed by a recent theoretical work in Ref. [44]. In the work, Classen et al. developed a super-resolution imaging scheme by combining the SQL super-resolution imaging with antibunching fluorescent emitters [36] and the structured illumination [3] that is well known for achieving super-resolution in conventional single-photon imaging, as shown in Figure 12a. It has been shown that the imaging resolution in this scheme can surpass the -scaling for SQL, giving rise to a -scaling super-resolution imaging as shown in Figure 12b. Since novel super-resolution imaging schemes are being developed in recent years, we believe that many exciting super-resolution imaging schemes based on hybrid super-resolution imaging methods will be reported in the future.
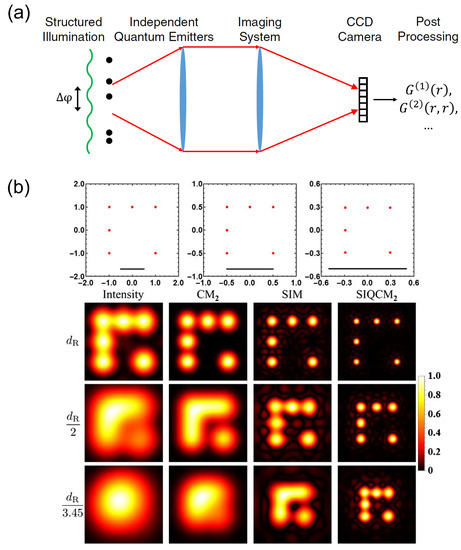
Figure 12.
(a) Schematic of the structured illumination quantum correlation microscopy (SIQC) for fluorescence imaging. The super-resolution effect is greatly enhanced by combining the structured illumination and the quantum antibunching correlation; (b) Super-resolution imaging with SIQC at the second-order correlation (column indicated by SIQCM). The enhanced super-resolution with SIQCM is clearly seen by comparing with the conventional intensity images (column indicated by intensity), the second-order cumulant super-resolution images (column indicated by CM), and the structured illumination induced super-resolution images (column indicated by SIM). The figure is reproduced with permissions from Ref. [44] of OSA.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to the writing, discussion, and revision of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11604150, 91750204, 61475077 and 11774182), the 973 program (2013CB328702), the 111 project (B07013) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SQL | Standard quantum limit |
| HL | Heisenberg limit |
| CCD | Charge-coupled device |
References
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 7th (expanded) ed.; Cambridge U. Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; Volume 890. [Google Scholar]
- Hell, S.W.; Wichmann, J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, M.G. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000, 198, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzig, E.; Patterson, G.H.; Sougrat, R.; Lindwasser, O.W.; Olenych, S.; Bonifacino, J.S.; Davidson, M.W.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Hess, H.F. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 2006, 313, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.J.; Bates, M.; Zhuang, X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courjon, D.; Bainier, C. Near field microscopy and near field optics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1994, 57, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendry, J.B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, S.; Inouye, Y.; Verma, P. Plasmonics for near-field nano-imaging and superlensing. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.H.; Twiss, R. A test of a new type of stellar interferometer on Sirius. Nature 1956, 178, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauber, R.J. The quantum theory of optical coherence. Phys. Rev. 1963, 130, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, H. Interference between independent photons. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1986, 58, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.; Björk, G.; Chuang, I.; Yamamoto, Y. Photonic de Broglie waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.; Monken, C.; Pádua, S. Measurement of the de Broglie wavelength of a multiphoton wave packet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boto, A.N.; Kok, P.; Abrams, D.S.; Braunstein, S.L.; Williams, C.P.; Dowling, J.P. Quantum interferometric optical lithography: exploiting entanglement to beat the diffraction limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edamatsu, K.; Shimizu, R.; Itoh, T. Measurement of the photonic de Broglie wavelength of entangled photon pairs generated by spontaneous parametric down-conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 213601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.W.; Lundeen, J.S.; Steinberg, A.M. Super-resolving phase measurements with a multiphoton entangled state. Nature 2004, 429, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, M.; Chekhova, M.V.; Shih, Y. Two-photon diffraction and quantum lithography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 013602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, P.; Pan, J.W.; Aspelmeyer, M.; Ursin, R.; Gasparoni, S.; Zeilinger, A. De Broglie wavelength of a non-local four-photon state. Nature 2004, 429, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afek, I.; Ambar, O.; Silberberg, Y. High-NOON states by mixing quantum and classical light. Science 2010, 328, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarcelli, G.; Valencia, A.; Shih, Y. Two-photon interference with thermal light. Europhys. Lett. 2004, 68, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cao, D.Z. Subwavelength coincidence interference with classical thermal light. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 041801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cao, D.Z.; Huang, F.; Li, H.G.; Sun, X.J.; Wang, K. Experimental observation of classical subwavelength interference with a pseudothermal light source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 173601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.Z.; Ge, G.J.; Wang, K. Two-photon subwavelength lithography with thermal light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 051105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.H.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, L.A. Two-photon interference with true thermal light. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 043805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe’er, A.; Dayan, B.; Vucelja, M.; Silberberg, Y.; Friesem, A.A. Quantum lithography by coherent control of classical light pulses. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 6600–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, G. Unified interpretation for second-order subwavelength interference based on Feynman’s path-integral theory. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 013822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Zhang, G. Subwavelength interference with an effective entangled source. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 043838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Zhang, G. Synchronous position two-photon interference of random-phase grating. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2015, 32, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Zhang, G. Super-resolved optical lithography with phase controlled source. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 053830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G. Active control on high-order coherence and statistic characterization on random phase fluctuation of two classical point sources. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, V.; Lloyd, S.; Maccone, L.; Shapiro, J.H. Sub-Rayleigh-diffraction-bound quantum imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 013827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrieri, F.; Maccone, L.; Wong, F.N.; Shapiro, J.H.; Tisa, S.; Zappa, F. Sub-Rayleigh imaging via N-photon detection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 163602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dertinger, T.; Colyer, R.; Iyer, G.; Weiss, S.; Enderlein, J. Fast, background-free, 3D super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22287–22292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.E.; Cho, Y.W.; Scarcelli, G.; Kim, Y.H. Sub-Rayleigh imaging via speckle illumination. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Lin, H.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, P. Sub-Rayleigh-diffraction imaging via modulating classical light. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 33506–33513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, O.; Oron, D. Improved resolution in fluorescence microscopy using quantum correlations. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 033812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, O.; Levitt, J.M.; Tenne, R.; Itzhakov, S.; Deutsch, Z.; Oron, D. Superresolution microscopy with quantum emitters. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5832–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, D.G.; Katamadze, K.; Traina, P.; Moreva, E.; Forneris, J.; Ruo-Berchera, I.; Olivero, P.; Degiovanni, I.; Brida, G.; Genovese, M. Beating the Abbe diffraction limit in confocal microscopy via nonclassical photon statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 143602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.Q.; Song, X.B.; Li, H.G.; Zhang, D.J.; Wang, H.B.; Xiong, J.; Wang, K. Experimental observation of sub-Rayleigh quantum imaging with a two-photon entangled source. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 171104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P. Two-photon imaging assisted by a thin dynamic scattering layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unternährer, M.; Bessire, B.; Gasparini, L.; Perenzoni, M.; Stefanov, A. Super-Resolution Quantum Imaging at the Heisenberg Limit. Optica 2018, 5, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Zhang, G. Heisenberg-resolution imaging through a phase-controlled screen. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 22789–22796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hong, P.; Zhang, G. Experimental realization of Heisenberg-limit resolution imaging through a phase-controlled screen with classical light. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 18950–18956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, A.; von Zanthier, J.; Scully, M.O.; Agarwal, G.S. Superresolution via structured illumination quantum correlation microscopy. Optica 2017, 4, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, G.; Brooker, G. Modern Classical Optics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrieri, F.; Tisa, S.; Tosi, A.; Zappa, F. Single-photon camera for high-sensitivity high-speed applications. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Cameras, and Systems for Industrial/Scientific Applications XI, International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Jose, CA, USA, 25 January 2010; Volume 7536, p. 753605. [Google Scholar]
- Arecchi, F.; Berné, A.; Bulamacchi, P. High-order fluctuations in a single-mode laser field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, M.; Jacobs, B.; Pittman, T.; Franson, J. Photon-number resolution using time-multiplexed single-photon detectors. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 68, 043814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiss, R.; Little, A.; Brown, R.H. Correlation between photons, in coherent beams of light, detected by a coincidence counting technique. Nature 1957, 180, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Mandel, L. Measurement of photon bunching in a thermal light beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantsuzov, P.; Kuno, M.; Janko, B.; Marcus, R.A. Universal emission intermittency in quantum dots, nanorods and nanowires. Nat. Phys. 2008, 4, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martienssen, W.; Spiller, E. Coherence and fluctuations in light beams. Am. J. Phys. 1964, 32, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G. Two-photon superbunching of thermal light via multiple two-photon path interference. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 013807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarcelli, G.; Valencia, A.; Shih, Y. Experimental study of the momentum correlation of a pseudothermal field in the photon-counting regime. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 051802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimble, H.J.; Dagenais, M.; Mandel, L. Photon antibunching in resonance fluorescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1977, 39, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, R.; Mandel, L. Observation of sub-Poissonian photon statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 51, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, M.P.; Tasca, D.S.; Izdebski, F.; Warburton, R.E.; Leach, J.; Agnew, M.; Buller, G.S.; Boyd, R.W.; Padgett, M.J. Imaging high-dimensional spatial entanglement with a camera. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Chen, L.K.; Li, W.; Huang, H.L.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Luo, Y.H.; Su, Z.E.; Wu, D.; Li, Z.D.; et al. Experimental ten-photon entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 210502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y. Entangled biphoton source-property and preparation. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2003, 66, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fano, U. Quantum theory of interference effects in the mixing of light from phase-independent sources. Am. J. Phys. 1961, 29, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L. Quantum effects in one-photon and two-photon interference. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 71, S274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M. Quantum imaging beyond the diffraction limit by optical centroid measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 253601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Chan, K.W.C.; Chang, H.J.; Boyd, R.W. Quantum spatial superresolution by optical centroid measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 083603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, K.C.; Chadd, E.H.; Liou, G.F.; Bergman, K.; Block, S.M. Characterization of photodamage to Escherichia coli in optical traps. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 2856–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Mancini, M.C.; Nie, S. Bioimaging: Second window for in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, G.; Genovese, M.; Berchera, I.R. Experimental realization of sub-shot-noise quantum imaging. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, G.B.; Borish, V.; Cole, G.D.; Ramelow, S.; Lapkiewicz, R.; Zeilinger, A. Quantum imaging with undetected photons. Nature 2014, 512, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, T.; Shih, Y.; Strekalov, D.; Sergienko, A. Optical imaging by means of two-photon quantum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 52, R3429–R3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, A.; Brambilla, E.; Bache, M.; Lugiato, L.A. Ghost imaging with thermal light: comparing entanglement and classicalcorrelation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 093602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.H. Computational ghost imaging. Phy. Rev. A 2008, 78, 061802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Bromberg, Y.; Silberberg, Y. Compressive ghost imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 131110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, F.; Magatti, D.; Lugiato, L.; Gatti, A. Differential ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 253603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).