Interaural Level Difference Optimization of Binaural Ambisonic Rendering
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Binaural Rendering of Ambisonic Signals
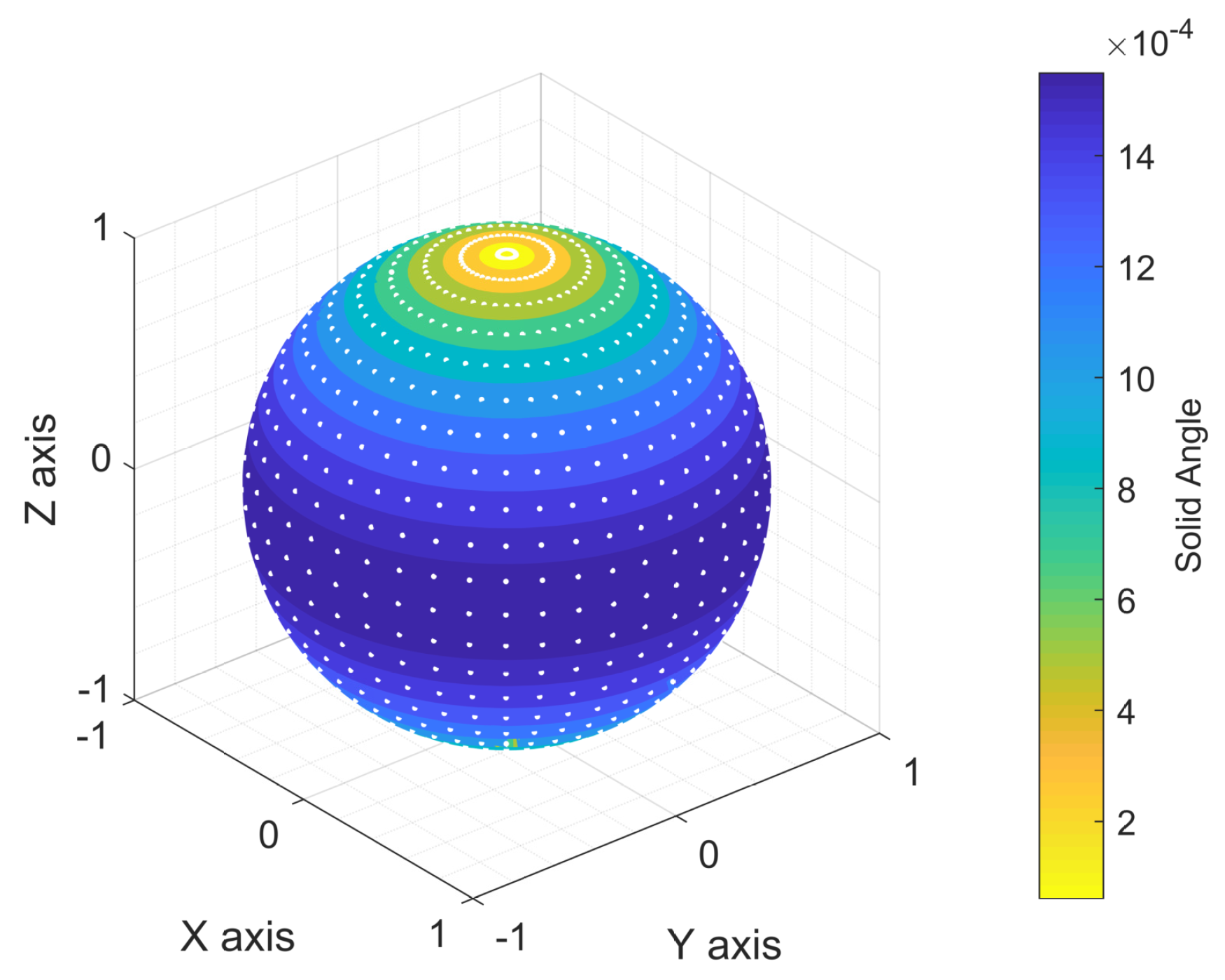
2.2. ILD Estimation
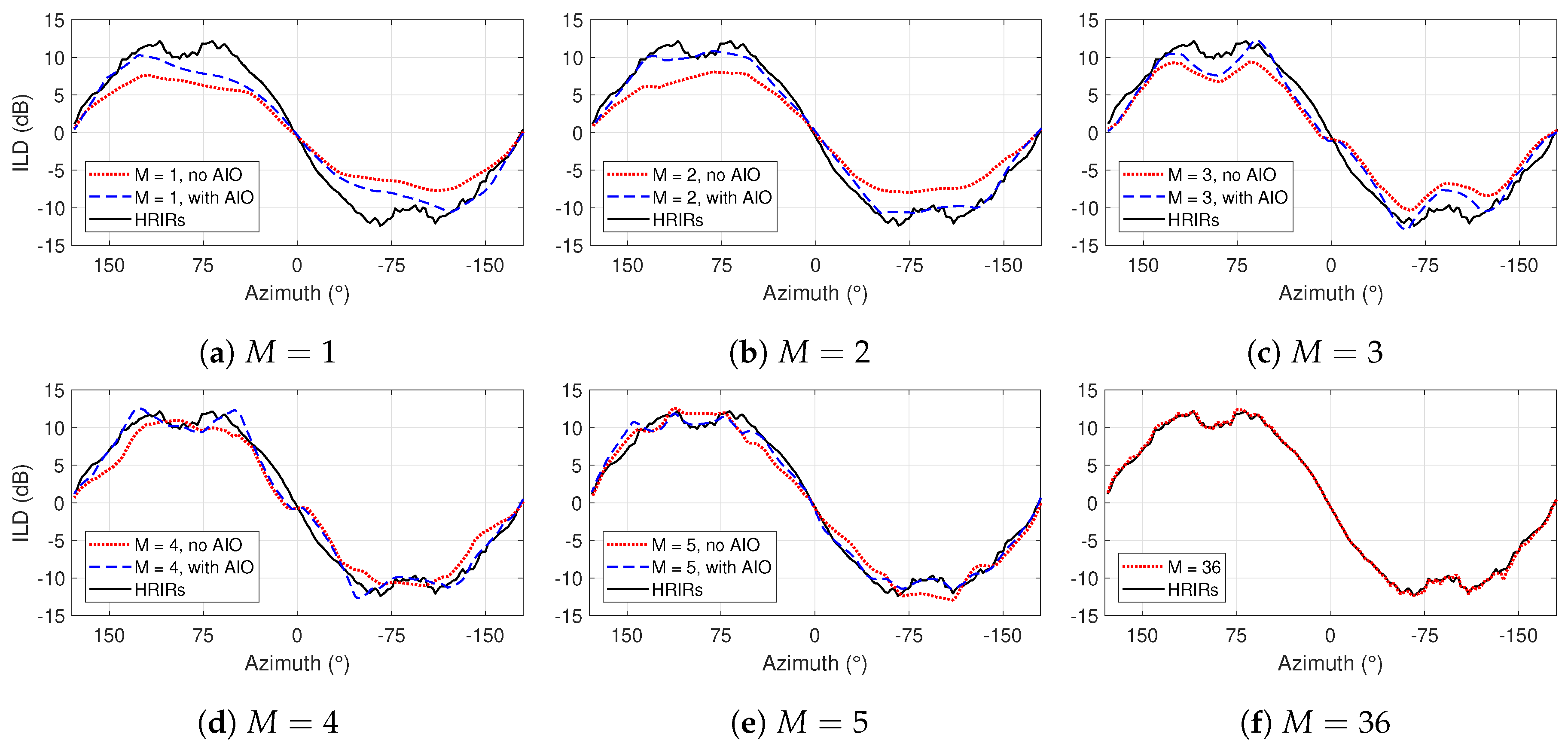
2.3. Ambisonic ILD Optimization
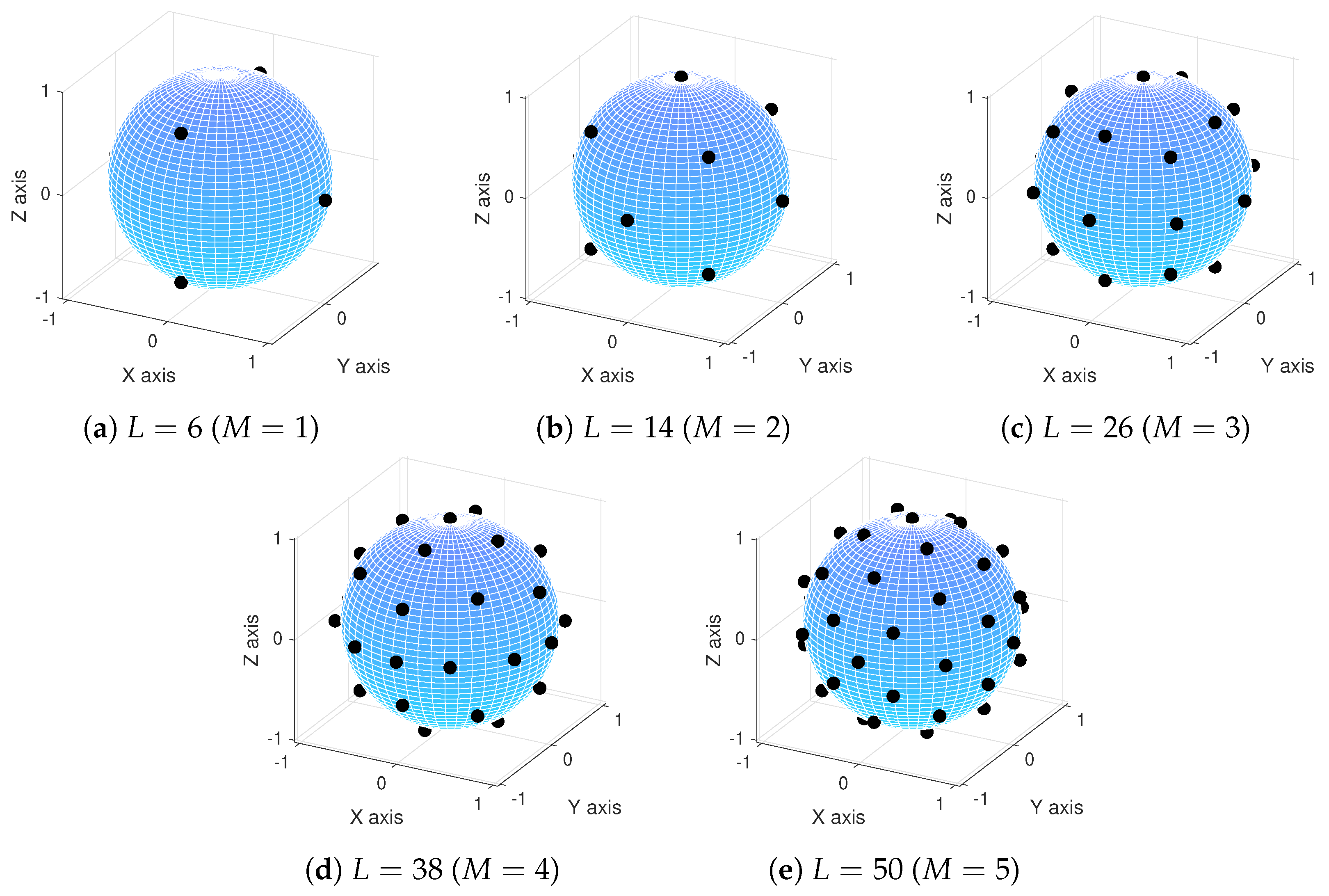
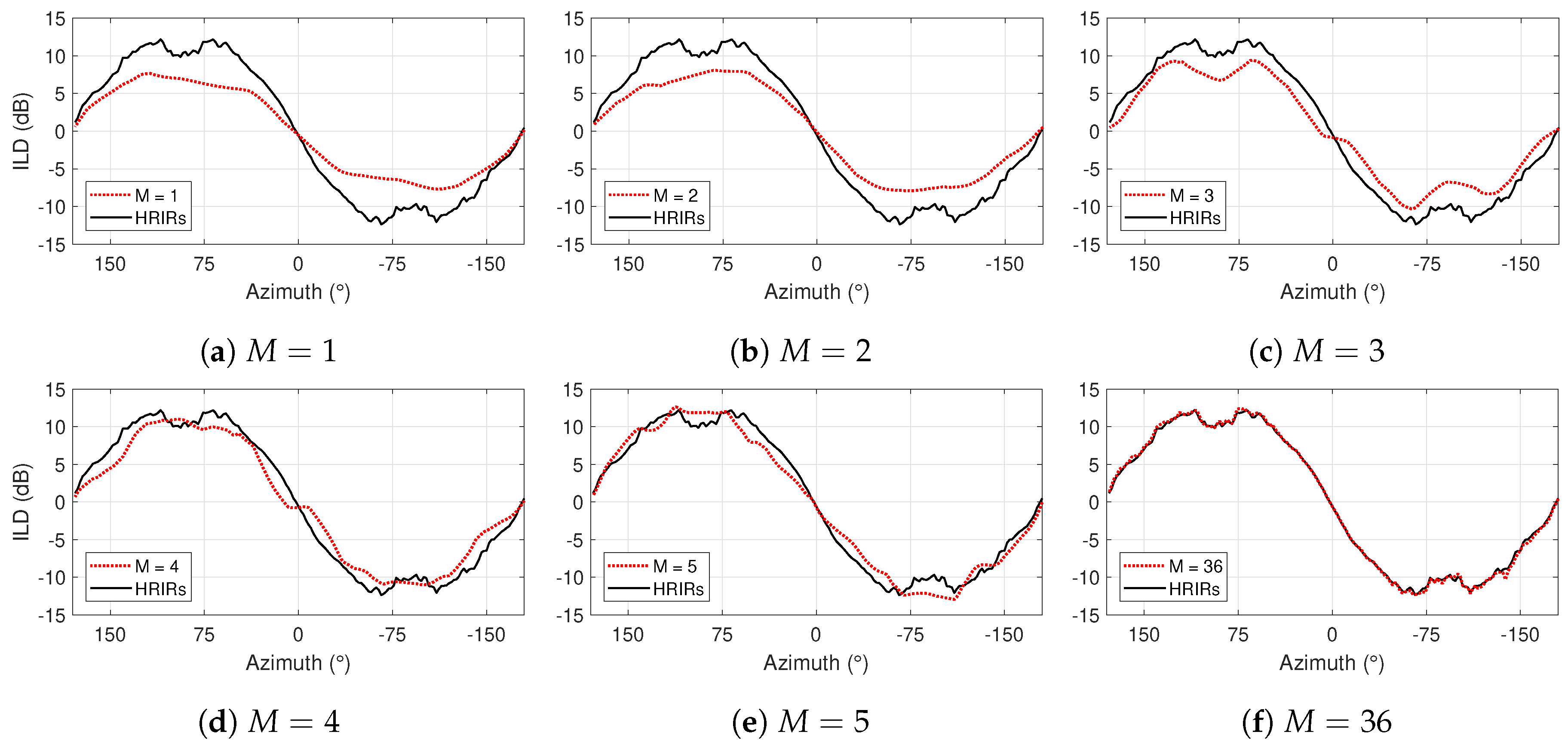
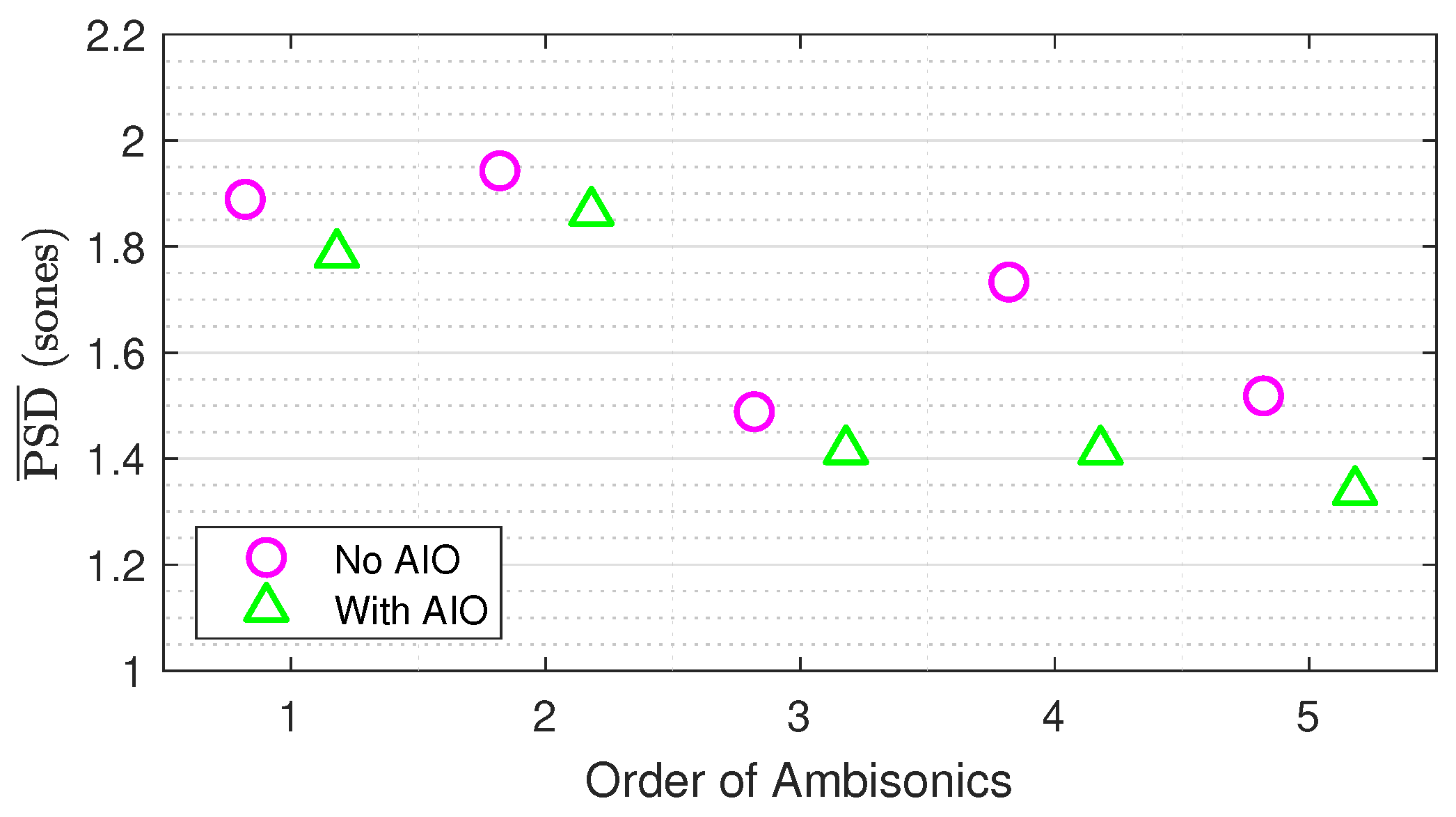
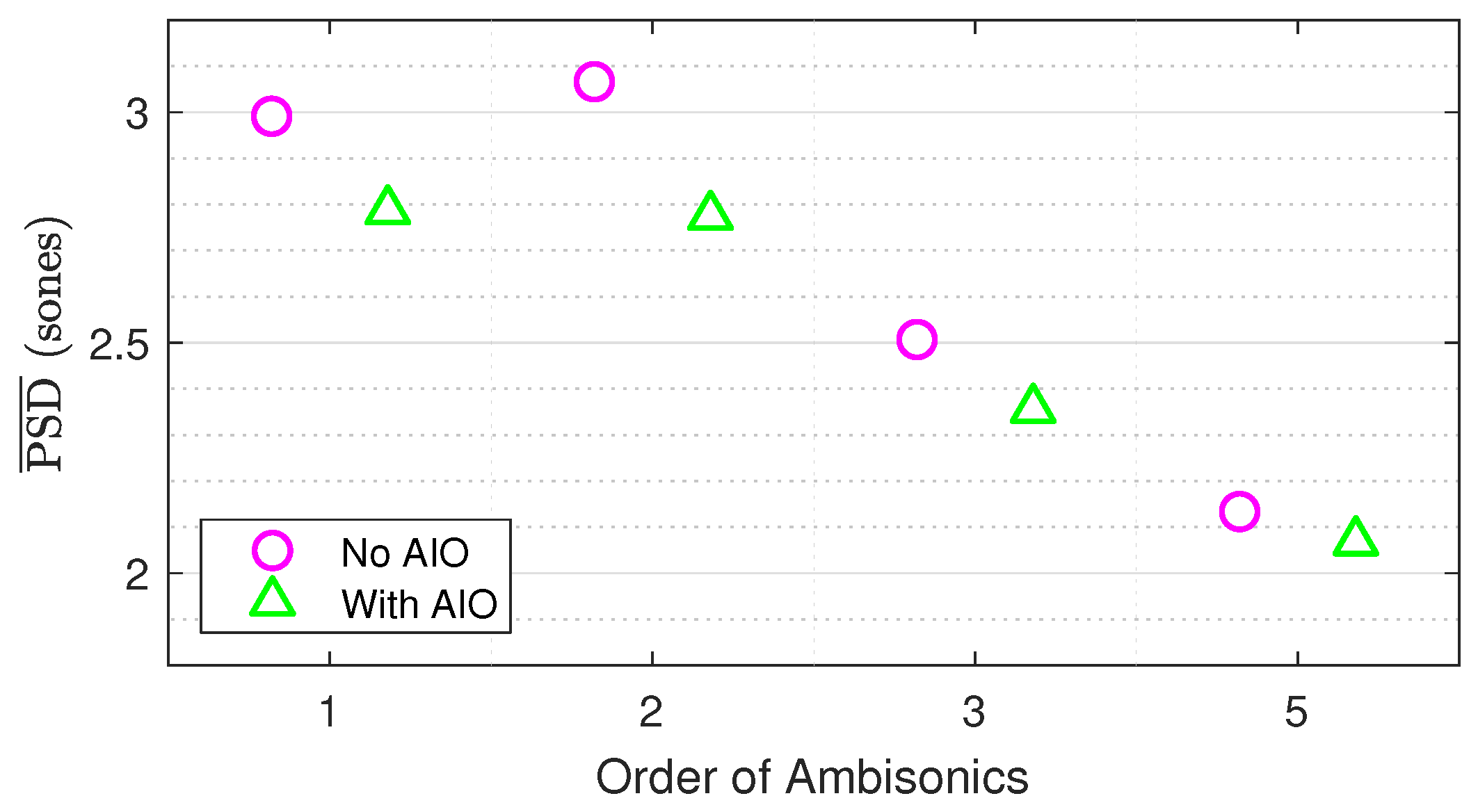
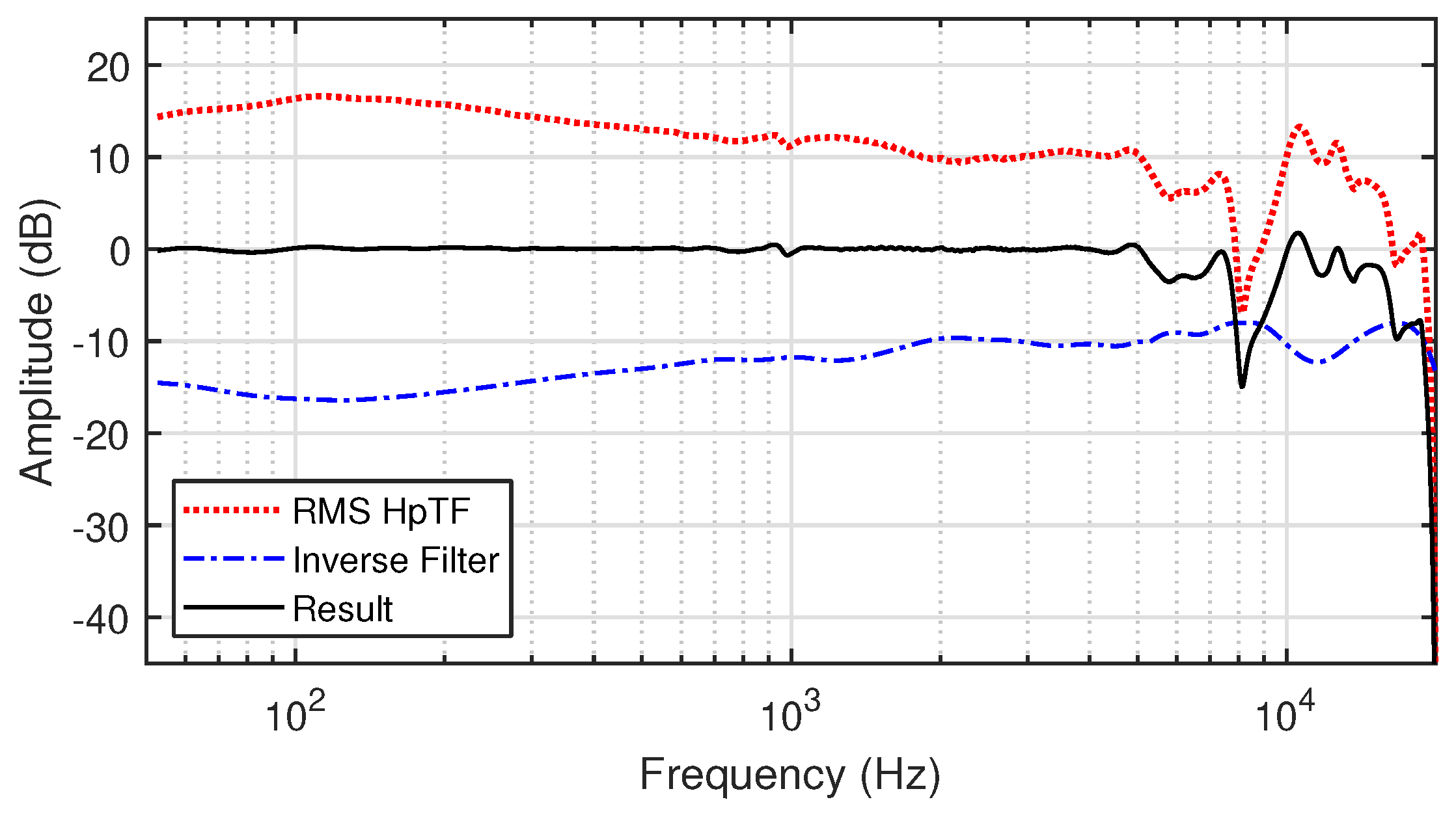
3. Objective Evaluation
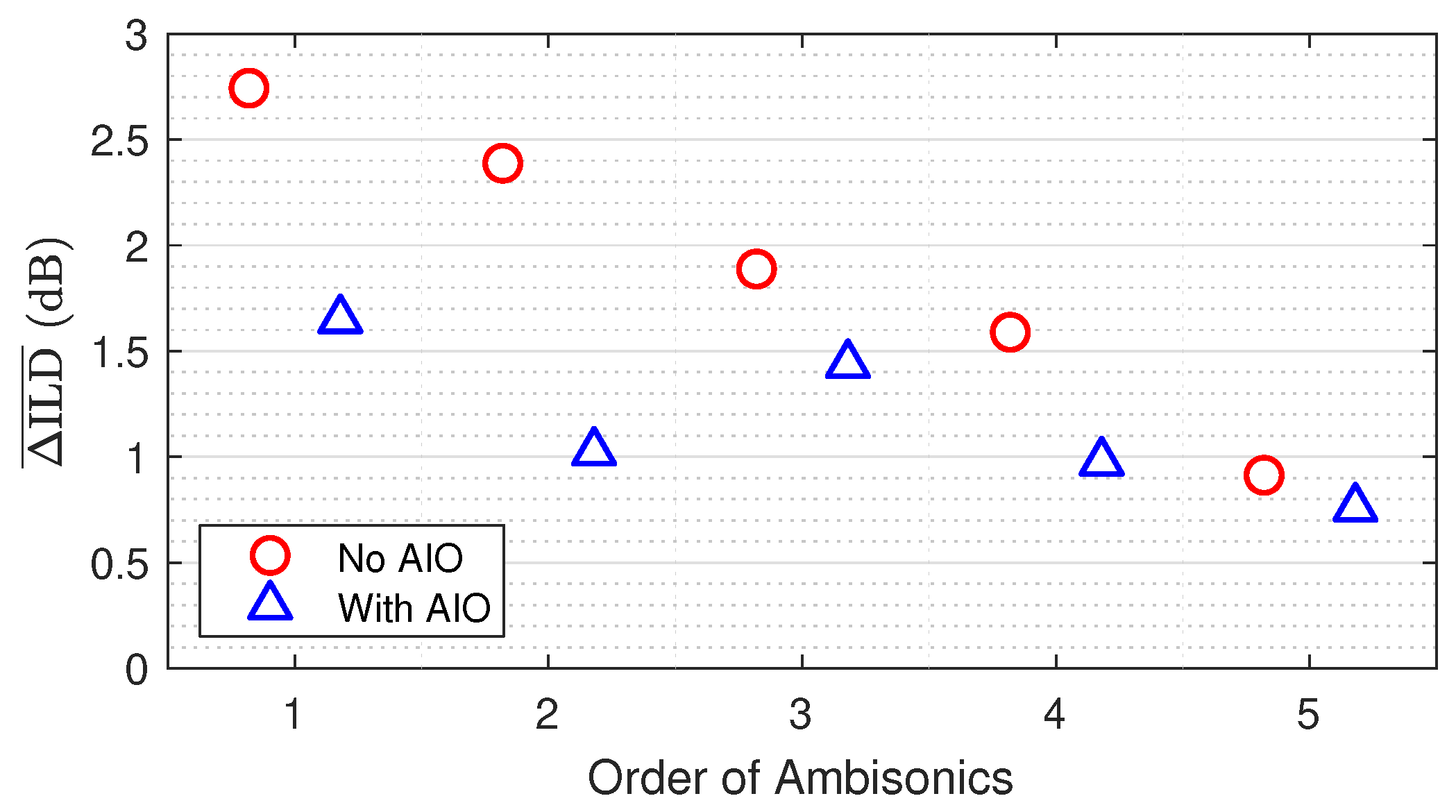
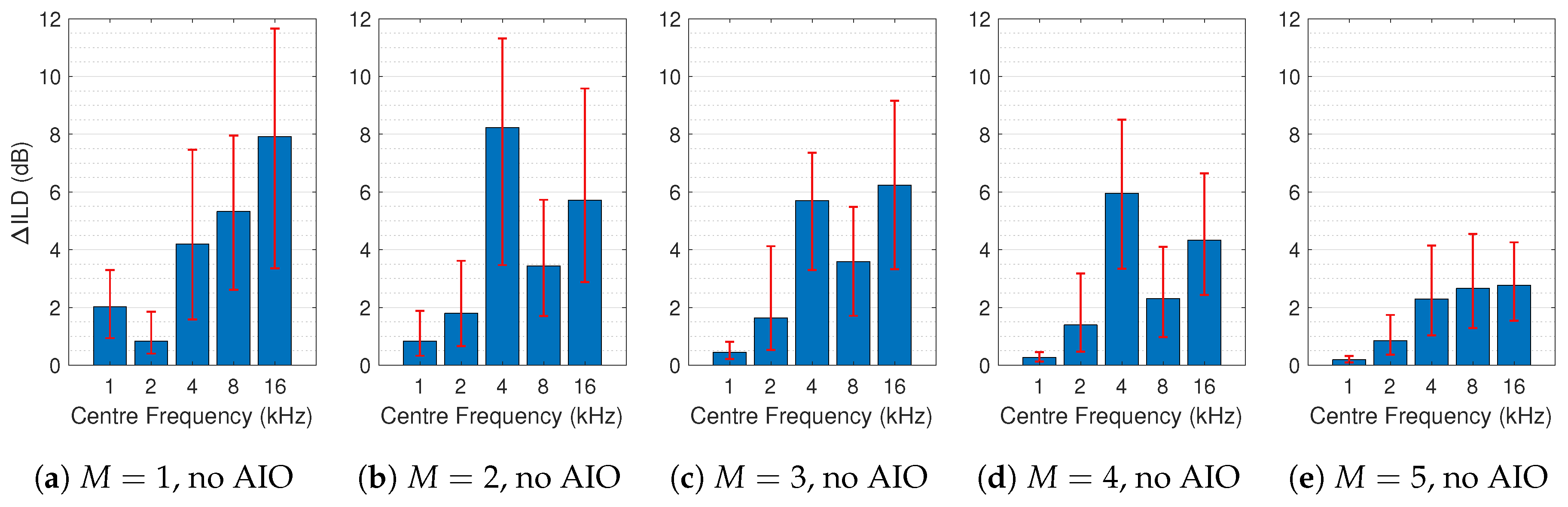
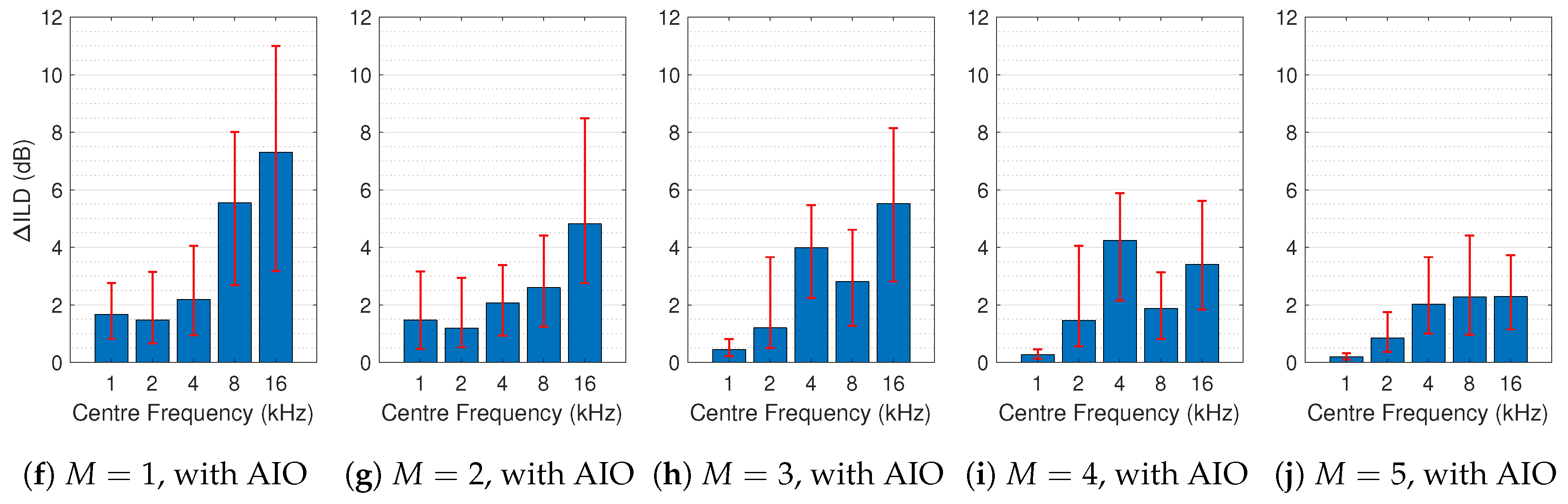
3.1. Change in ILD
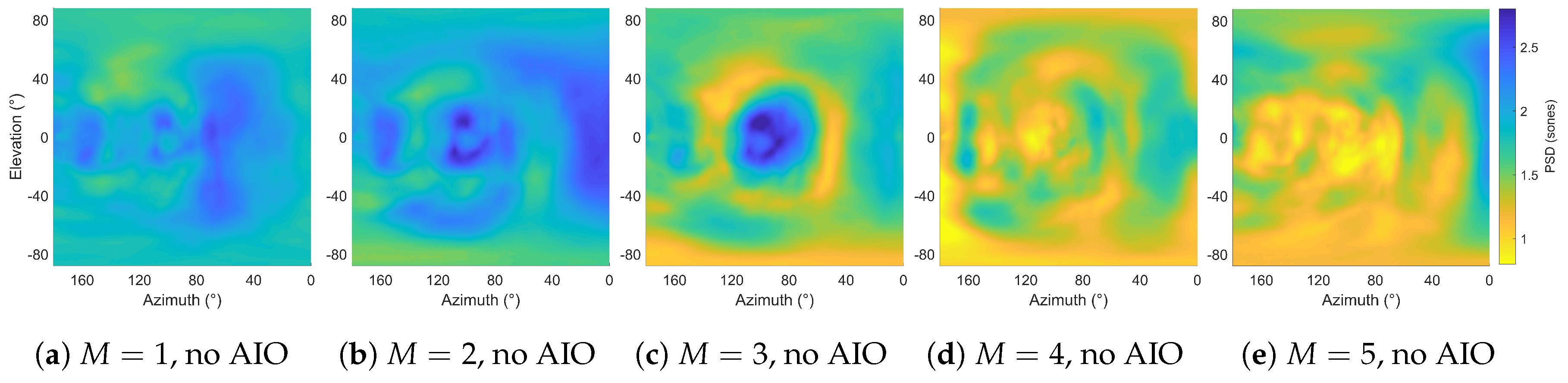
3.2. Spectral Difference
3.3. Generalizability
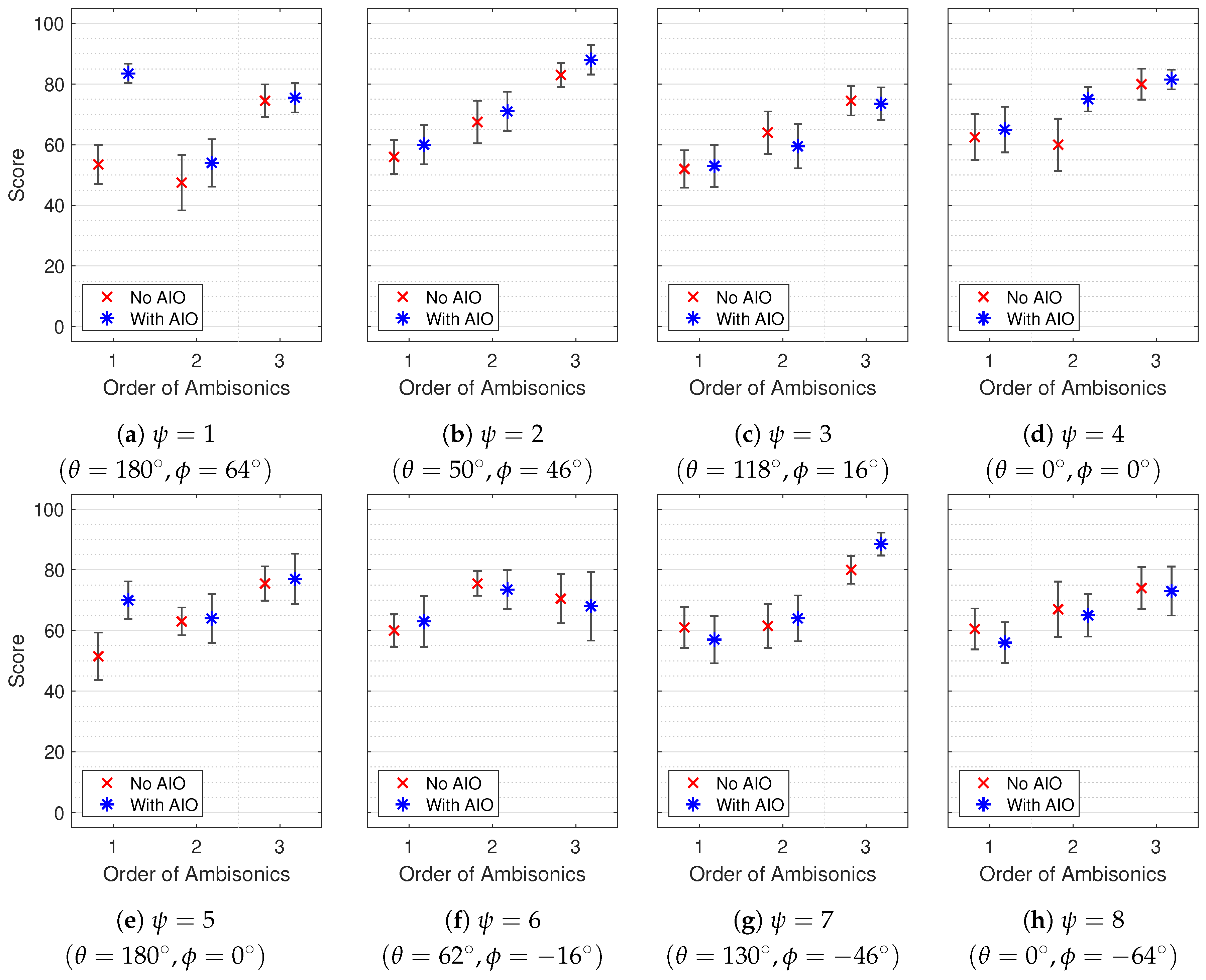
4. Perceptual Evaluation
4.1. Test Methodologies
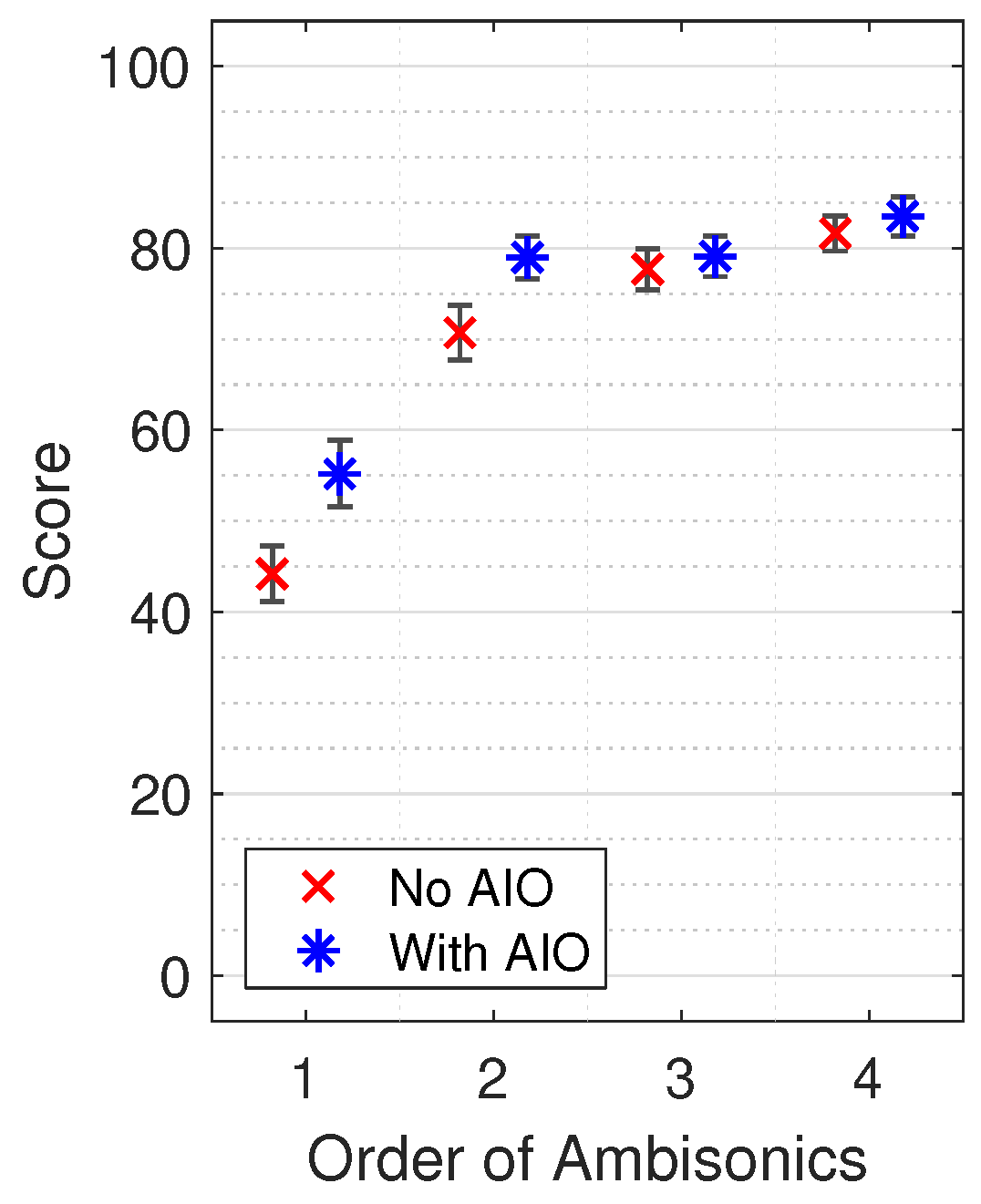
4.1.1. Simple Scenes
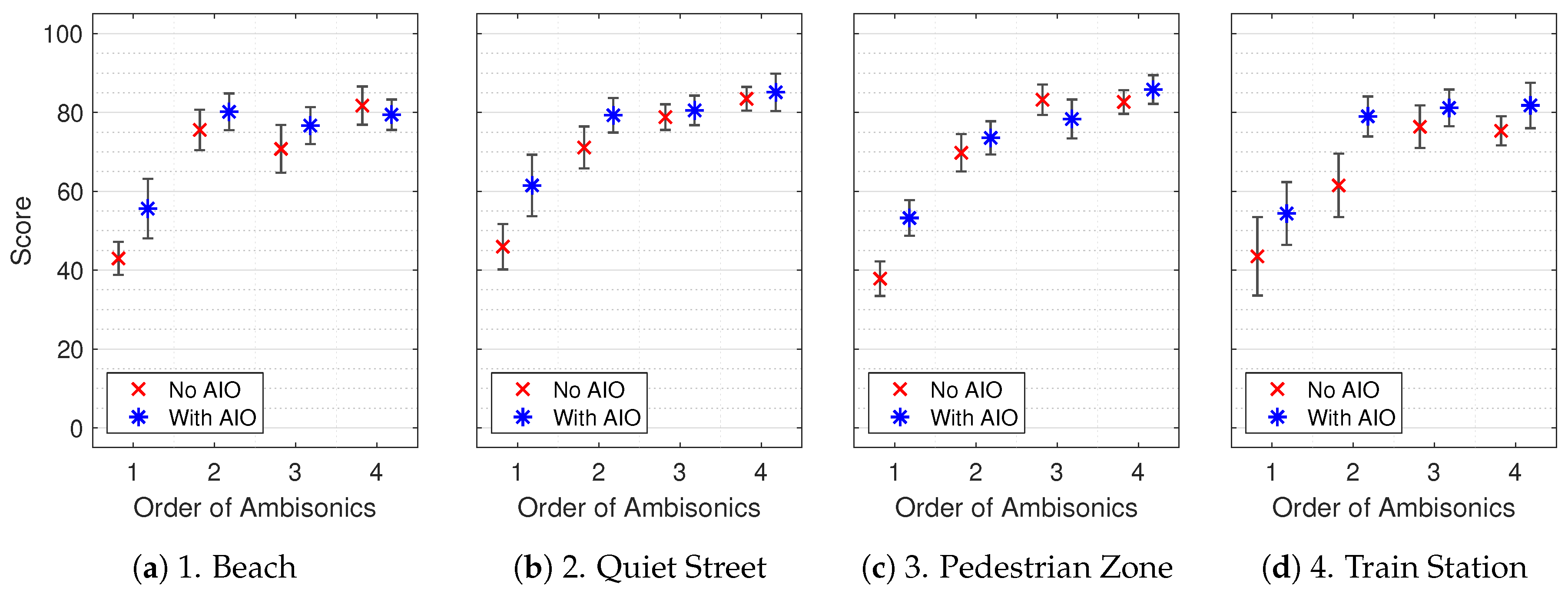
4.1.2. Complex Scenes
- Beach (waves breaking against the shore)
- Quiet Street (a single car drives past with birdsong)
- Pedestrian Zone (pedestrians walking around and talking)
- Train Station (travel announcement on the station platform)
4.2. Results
4.2.1. Simple Scenes
4.2.2. Complex Scenes
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blauert, J. Spatial Hearing: The Psychophysics of Human Sound Localization; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lindau, A.; Weinzierl, S. Assessing the plausibility of virtual acoustic environments. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2012, 98, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, F.; Lindau, A.; Weinzierl, S. On the authenticity of individual dynamic binaural synthesis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 1784–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, E.; Arruda, M.; Kistler, D.; Wightman, F.L. Localization using nonindividualized head-related transfer functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 94, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, H.; Sørensen, M.F.; Jensen, C.B.; Hammershøi, D. Binaural technique: Do we need individual recordings? J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1996, 44, 451–469. [Google Scholar]
- Lindau, A.; Maempel, H.; Weinzierl, S. Minimum BRIR grid resolution for dynamic binaural synthesis. In Proceedings of the Acoustics 08 Paris, Paris, France, 30 June–4 July 2008; pp. 3851–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Gerzon, M.A. Periphony: With-height sound reproduction. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1973, 21, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gerzon, M.A. Criteria for evaluating surround-sound systems. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1977, 25, 400–408. [Google Scholar]
- Malham, D.; Myatt, A. 3-D sound spatialization using Ambisonic techniques. Comput. Music J. 1995, 19, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, M. The Design of Encoding Functions for Stereophonic and Polyphonic Sound Systems. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1996, 44, 948–963. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, S.; Daniel, J.; Bertet, S. 3D Sound Field Recording With Higher Order Ambisonics-Objective Measurements and Validation of a 4th Order Spherical Microphone. In Proceedings of the 120th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Paris, France, 20–23 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bertet, S.; Daniel, J.; Parizet, E.; Warusfel, O. Investigation on localisation accuracy for first and higher order Ambisonics reproduced sound sources. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2013, 99, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jot, J.M.; Larcher, V.; Pernaux, J.M. A comparative study of 3-D audio encoding and rendering techniques. In Proceedings of the AES 16th International Conference: Spatial Sound Reproduction, Rovaniemi, Finland, 10–12 April 1999; pp. 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, J.; Rault, J.B.; Polack, J.D. Ambisonics encoding of other audio formats for multiple listening conditions. In Proceedings of the 105th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–29 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bamford, J.S.; Vanderkooy, J. Ambisonic Sound for Us. In Proceedings of the 99th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 6–9 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Malham, D.G. Higher order Ambisonic systems for the spatialisation of sound. Proc. ICMC 1999, 1999, 484–487. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, T. Binaural Ambisonic decoding with enhanced lateral localization. In Proceedings of the 134th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Rome, Italy, 4–7 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.N.; Collins, T.; Jančovič, P. Timbral and spatial fidelity improvement in ambisonics. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jot, J.M.; Wardle, S.; Larcher, V. Approaches to binaural synthesis. In Proceedings of the 105th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–29 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Noisternig, M.; Sontacchi, A.; Musil, T.; Höldrich, R. A 3D ambisonic based binaural sound reproduction system. In Proceedings of the AES 24th International Conference on Multichannel Audio, Banff, AB, Canada, 26–28 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Avni, A.; Ahrens, J.; Geier, M.; Spors, S.; Wierstorf, H.; Rafaely, B. Spatial perception of sound fields recorded by spherical microphone arrays with varying spatial resolution. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 2711–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernschütz, B.; Vázquez Giner, A.; Pörschmann, C.; Arend, J. Binaural reproduction of plane waves with reduced modal order. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, F.; Weinzierl, S. Comparison of head-related transfer functions pre-processing techniques for spherical harmonics decomposition. In Proceedings of the AES Conference on Audio for Virtual and Augmented Reality, Redmond, WA, USA, 20–22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hur, Z.; Brinkmann, F.; Sheaffer, J.; Weinzierl, S.; Rafaely, B. Spectral equalization in binaural signals represented by order-truncated spherical harmonics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.J.; Angus, J.A.S.; Tew, A.I. Analyzing head-related transfer function measurements using surface spherical harmonics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.G.; Pollow, M.; Wefers, F.; Fels, J. Spherical harmonics based HRTF datasets: Implementation and evaluation for real-time auralization. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunschirm, M.; Schörkhuber, C.; Höldrich, R. Binaural rendering of Ambisonic signals by HRIR time alignment and a diffuseness constraint. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 3616–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schörkhuber, C.; Zaunschirm, M.; Höldrich, R. Binaural rendering of Ambisonic signals via Magnitude Least Squares. In Proceedings of the DAGA 2018: 44. Deutsche Jahrestagung für Akustik, Munich, Germany, 19–22 March 2018; pp. 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, V.I. Quadratures on a sphere. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1976, 16, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotkin, D.N.; Duraiswami, R.; Grassi, E.; Gumerov, N.A. Fast head-related transfer function measurement via reciprocity. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 2202–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdak, P.; Balazs, P.; Laback, B. Multiple exponential sweep method for fast measurement of head-related transfer functions. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2007, 55, 623–636. [Google Scholar]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I. Handbook of Mathematical Functions, 10th ed.; Dover Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, A.J.; Lee, R.; Benjamin, E.M. Is my decoder ambisonic? In Proceedings of the 125th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–5 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gerzon, M.A.; Barton, G.J. Ambisonic decoders for HDTV. In Proceedings of the 92nd Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Vienna, Austria, 24–27 March 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, J. Représentation de Champs Acoustiques, Application à la Transmission et à la Reproduction De Scènes Sonores Complexes Dans un Contexte Multimédia. Ph.D. Thesis, l’Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, F.J. Multirate Signal Processing for Communication Systems; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte, P.; Gauthier, P.A.; Langrenne, C.; Berry, A.; Garcia, A. A fifty-node Lebedev grid and its applications to Ambisonics. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2016, 64, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thresh, L.; Armstrong, C.; Kearney, G. A direct comparison of localisation performance when using first, third and fifth order Ambisonics for real loudspeaker and virtual loudspeaker rendering. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Convention 143, New York, NY, USA, 18–20 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Burkardt, J. SPHERE_LEBEDEV_RULE—Quadrature Rules for the Unit Sphere. Available online: http://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/datasets/sphere_lebedev_rule/sphere_lebedev_rule.html (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Bernschütz, B. A spherical far field HRIR/HRTF compilation of the Neumann KU 100. In Proceedings of the Fortschritte der Akustik—AIA-DAGA 2013, Merano, Italy, 18–21 March 2013; pp. 592–595. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Ozawa, K.; Iwaya, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Aso, K. Estimation of interaural level difference based on anthropometry and its effect on sound localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterom, A.V.; Strackee, J. The solid angle of a plane triangle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1983, BME-30, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.; McKenzie, T.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. A perceptual spectral difference model for binaural signals. In Proceedings of the AES 145th Convention, New York, NY, USA, 17–20 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 226:2003. Normal Equal-Loudness-Level Contours; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, R.H.; Sloane, N.J.A. McLaren’s Improved Snub Cube and Other New Spherical Designs in Three Dimensions. Discret. Comput. Geom. 1996, 15, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotter, F.; Frank, M.; Sontacchi, A. The virtual T-Design Ambisonics-rig using VBAP. In Proceedings of the 1st EAA-EuroRegio, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 15–18 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, C.; Thresh, L.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. A perceptual evaluation of individual and non-individual HRTFs: A case study of the SADIE II database. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 389. Acoustics-Reference Zero for the Calibration of Audiometric Equipment; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. Simultaneous measurement of impulse response and distortion with a swept-sine technique. In Proceedings of the 108th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Paris, France, 19–22 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkeby, O.; Nelson, P.A. Digital filter design for inversion problems in sound reproduction. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1999, 47, 583–595. [Google Scholar]
- Schärer, Z.; Lindau, A. Evaluation of equalization methods for binaural signals. In Proceedings of the 126th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Munich, Germany, 7–10 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hatziantoniou, P.D.; Mourjopoulos, J.N. Generalized fractional-octave smoothing of audio and acoustic responses. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2000, 48, 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Bücklein, R. The audibility of frequency response irregularities. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1981, 29, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-R-BS.1534-3. Method for the Subjective Assessment of Intermediate Quality Level of Audio Systems; BS Series Broadcasting Service (Sound); International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Assembly: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lindau, A.; Erbes, V.; Lepa, S.; Maempel, H.J.; Brinkman, F.; Weinzierl, S. A spatial audio quality inventory (SAQI). Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Murphy, D. EigenScape: A database of spatial acoustic scene recordings. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgill, R.; Tukey, J.W.; Larsen, W.A. Variations of Box Plots. Am. Stat. 1978, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, T.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. Directional bias equalisation of first-order binaural Ambisonic rendering. In Proceedings of the AES Conference on Audio for Virtual and Augmented Reality, Redmond, WA, USA, 20–22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, T.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. Diffuse-field equalisation of binaural ambisonic rendering. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| () | 180 | 50 | 118 | 0 | 180 | 62 | 130 | 0 |
| () | 64 | 46 | 16 | 0 | 0 | −16 | −46 | −64 |
| M | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| h | 1 * | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h () | 1 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| h () | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| h () | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| M | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McKenzie, T.; Murphy, D.T.; Kearney, G. Interaural Level Difference Optimization of Binaural Ambisonic Rendering. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061226
McKenzie T, Murphy DT, Kearney G. Interaural Level Difference Optimization of Binaural Ambisonic Rendering. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(6):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061226
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcKenzie, Thomas, Damian T. Murphy, and Gavin Kearney. 2019. "Interaural Level Difference Optimization of Binaural Ambisonic Rendering" Applied Sciences 9, no. 6: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061226
APA StyleMcKenzie, T., Murphy, D. T., & Kearney, G. (2019). Interaural Level Difference Optimization of Binaural Ambisonic Rendering. Applied Sciences, 9(6), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061226





