Abstract
Person re-identification (re-ID) is a fundamental problem in the field of computer vision. The performance of deep learning-based person re-ID models suffers from a lack of training data. In this work, we introduce a novel image-specific data augmentation method on the feature map level to enforce feature diversity in the network. Furthermore, an attention assignment mechanism is proposed to enforce that the person re-ID classifier focuses on nearly all important regions of the input person image. To achieve this, a three-stage framework is proposed. First, a baseline classification network is trained for person re-ID. Second, an attention assignment network is proposed based on the baseline network, in which the attention module learns to suppress the response of the current detected regions and re-assign attentions to other important locations. By this means, multiple important regions for classification are highlighted by the attention map. Finally, the attention map is integrated in the attention-aware adversarial network (AAA-Net), which generates high-performance classification results with an adversarial training strategy. We evaluate the proposed method on two large-scale benchmark datasets, including Market1501 and DukeMTMC-reID. Experimental results show that our algorithm performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods.
1. Introduction
Person re-identification (re-ID) is a fundamental problem in computer vision, which aims to re-identify a person of interest in other cameras. In recent years, person re-ID has achieved increasing attention due to its wide applications and great potentials, such as criminal investigation and security enhancement.
Although recent deep learning-based person re-ID networks achieve favorable performance, most of them still suffer from a lack of training samples. Training images in most datasets are collected from manually-cropped person images. Therefore, it is time consuming to create a large-scale database. To tackle this problem, the methods of [1,2,3,4] propose to learn robust and discriminative features from limited training samples in a deep neural network. As implemented by most methods, common data augmentation methods, e.g., randomly cropping, flipping, and color jittering, are not sufficient to achieve high-quality results. One approach to augment training samples is to generate multiple images based on each occluded image by random erasure [5,6]. Although the performance is improved by this method, it aggravates the memory and storage requirements. The method [7] enriches the data on the feature map level. As a result, the learned object detector is robust to different conditions, i.e., occlusion, deformation, illumination, etc. Inspired by [7], we perform data augmentation on the level of feature maps by erasing (occluding) different spatial regions of the feature maps.
Existing person re-ID methods face various intrinsic difficulties, such as occlusion, illumination, image resolution, and noisy background, to name a few. Many methods [8,9,10,11] address these problems by representing the input person image with discriminative feature maps and matching them in a task-specific metric space. However, the performance of most of these methods may fall short due to limited training samples, e.g., training images are not sufficient to cover the complex conditions of real scenes. As a result, training models easily over-fit the training datasets. The recently-proposed image generation models, the generative adversarial networks (GANs) [8], provide powerful tools to handle this problem by generating more realistic style images. Many methods benefit from the high-performance GAN model [12,13]. The work in [5,6] generated adversarially-occluded samples based on a proposed re-ID model and used these samples to further improve the performance of the model. The work in [10,11,14,15] extracted numbers of discriminative characteristics, based on which end-to-end deep neural networks were trained. However, explicitly generating training samples and enlarging the datasets increase the burden on memory resources. It is feasible and efficient to enrich features on the feature map level when training networks.
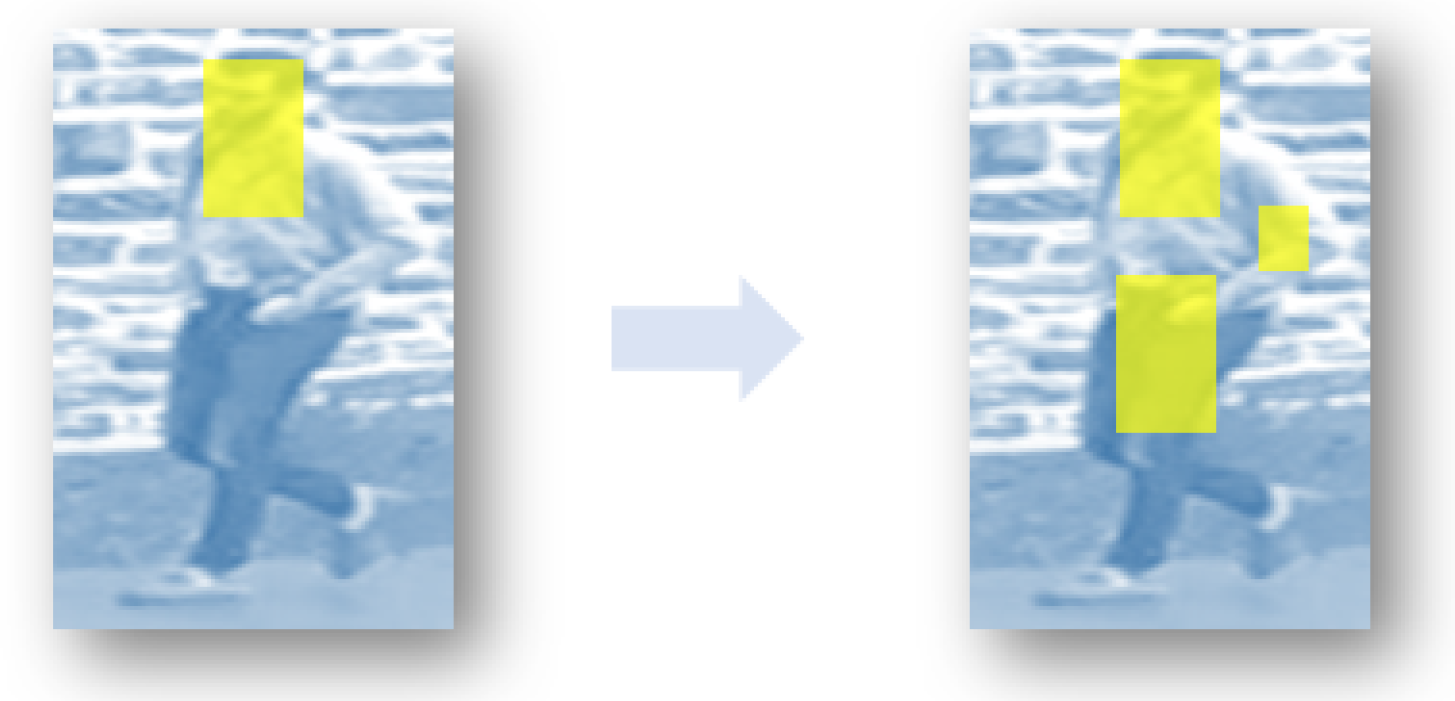
To this end, we propose a novel attention-aware adversarial network (AAA-Net) for person re-ID. Instead of explicitly enlarging the size of datasets, AAA-Net generates multiple occluded samples from each input on the feature map level. Specifically, the feature maps are blocked spatially, and a series of occluded feature maps is generated. Actually, this is an image-specific data augmentation method, which diversifies the features and provides sufficient training samples according to the input. Furthermore, an attention assignment mechanism is proposed to enforce attentions to be assigned to more important regions, as Figure 1, and thus, regions are served as convincing samples for the final classification results. Training the proposed framework consists of three stages. First, a baseline (BL) classifier for person re-ID is trained. Second, an attention assignment network is designed. According to the initial predicted attention map, as well as the set of occluded feature maps, attentions are further re-assigned to the rest of the interesting locations, besides the original focused area. This process is implemented in an adversarial strategy. As a result, an updated attention map is generated in the attention assignment network. Finally, an attention-aware adversarial network is proposed. Based on the attention map, an adversarial training strategy is employed to explore the determined feature maps and classify the input person image accurately.
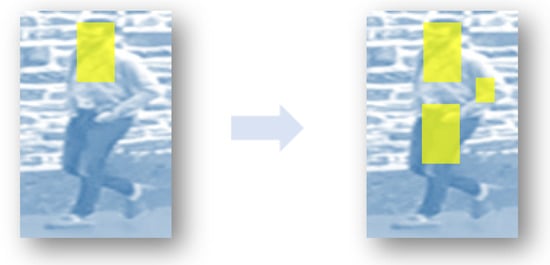
Figure 1.
Our result can focus on more important regions on feature maps.
The main contributions of this work are:
- We propose an attention-aware adversarial network for person re-ID, in which data augmentation is implemented on the feature map level.
- An attention assignment mechanism is proposed to re-assign attentions to more important regions.
- The proposed method is evaluated on two large benchmark datasets and achieves promising results.
2. Related Work
2.1. Person Re-ID
Two main technical components of person re-ID methods are feature extraction and metric learning. Existing methods focus on extracting robust and representative features of person images, based on which intra-class images are matched in a learned metric space. The work in [8,9,15,16] represented the input images with feature vectors, which are able to depict their global characteristics. However, these methods fail to capture local detailed information and lead to inferior matching and detection performance. In order to solve this problem, many work proposed to explore local features. The work [17] extracted the local features of key points. The work in [18] detected human pose in a local learning module for person re-ID. In [19], images were first divided into several patches. Then, all image patches were input into a a long short-term memory (LSTM) network in sequence to generate ensembled features, which consist of all local information.
Except for exploring discriminative feature representing methods, it is also crucial to learn a robust metric space, in which the distance of intra-class person images is small, and the distance between inter-class person images is large. This is implemented by elaborately designed loss functions, such as the contrastive loss [20], the triplet loss [21,22,23], the quadruplet loss [24], etc.
In recent years, convolutional neural network (CNN)-based architectures have demonstrated powerful ability for person re-ID. The work in [25] captured the relationship of person images in multi-views with a novel cross-input neighborhood layer. The work in [17] utilized human pose estimation methods to facilitate the person re-ID task. The work in [26] combined CNN and the dictionary learning technique for low-resolution person re-ID. The work in [27] integrated sparse reconstruction learning in a unified CNN framework to solve the partial person re-ID problem. The work in [22] proposed to detect discriminative regions in person images by training a comparative attention network (CAN), which is able to recognize which regions are determined to identify a person. Inspired by this work, our method employs an attention guidance module in the network to assign attentions on the spatial regions of feature maps, which are crucial to recognize a person.
2.2. Data Augmentation
The size of the database is crucial for training a robust model. However, it is time consuming and expensive to collect human-labeled samples and create a large-scale database. Most methods employ various data augmentation techniques to expand the dataset. Commonly-used data augmentation methods incorporate image resizing, color jittering, and horizontal or vertical flipping, to name a few. Different from these hard sample generation methods, the work in [28] proposed to occlude parts of the input image with a rectangular box. The occluded position and the size of the box are randomly selected from a range. The recent work [5] occluded a relatively complete part of the human body instead of small and scattered regions. All these methods generate multiple samples from one single image and expand the database to several times the size of the original database. Although these data augmentation strategies help to train robust models and avoid over-fitting to some extent, they require heavy computation and storage resources.
Instead of explicitly expanding the size of the database, we propose a novel data augmentation method on the feature map level. Specifically, occlusions are applied on the extracted representative feature maps of the input person image. This strategy enforces feature diversity in an online manner. By this means, attentions are assigned to different parts of the feature maps, and thus, the entire person is homogeneously highlighted in the adversarial network.
3. Method
In this work, a three-stage framework is proposed for person re-ID. First, a baseline classification network is trained. Second, an attention-assignment network is proposed to predict an attention map, which enforces the model to focus on more important target regions. Finally, an attention-aware adversarial network is designed to generate a high-performance classifier for person re-ID. In this section, each main component of the proposed framework is elaborated.
3.1. Baseline Network
As a foundation, we first trained a baseline network for person re-ID. The person re-ID task can be regarded as a classification problem, and the each person serves as a specific class. Denote the training set as , where is the person image, and is the ground truth class label. T contains N labeled images of C persons. The goal of the person re-ID task is to find a mapping function , which maps the input person image to its classification score vector . As a result, the class with the highest possibility is the corresponding category of the input person image.
The baseline network is based on the classical resnet-50 classification network [4]. Given the input person image, the convolutional modules of the resnet-50 network extract the representative feature maps. Subsequently, the feature maps are fed to a fully-connected layer to generate the classification vector. Finally, a classification loss function is employed to train the baseline classification network. The stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimization method is utilized to minimize the loss function.
3.2. Attention Assignment Network
Based on the baseline classification network, the proposed attention assignment network is trained. The procedure is shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 The training strategy of the attention assignment network. |
| Input: Nperson images; Whiledo 1: The feature maps of the middle layer are divided equally into 16 with a square grid; 2: Each grid in the feature maps is occluded and reproduced in sequence; 3: These 16 groups of feature maps are entered together into the classification network; 4: Select the feature maps with the lowest classification probability to guide the generation of feature maps of the attention assignment mechanism; 5: Update the parameters of the attention assignment mechanism; 6: ; end Retain the weight of the overall network structure |
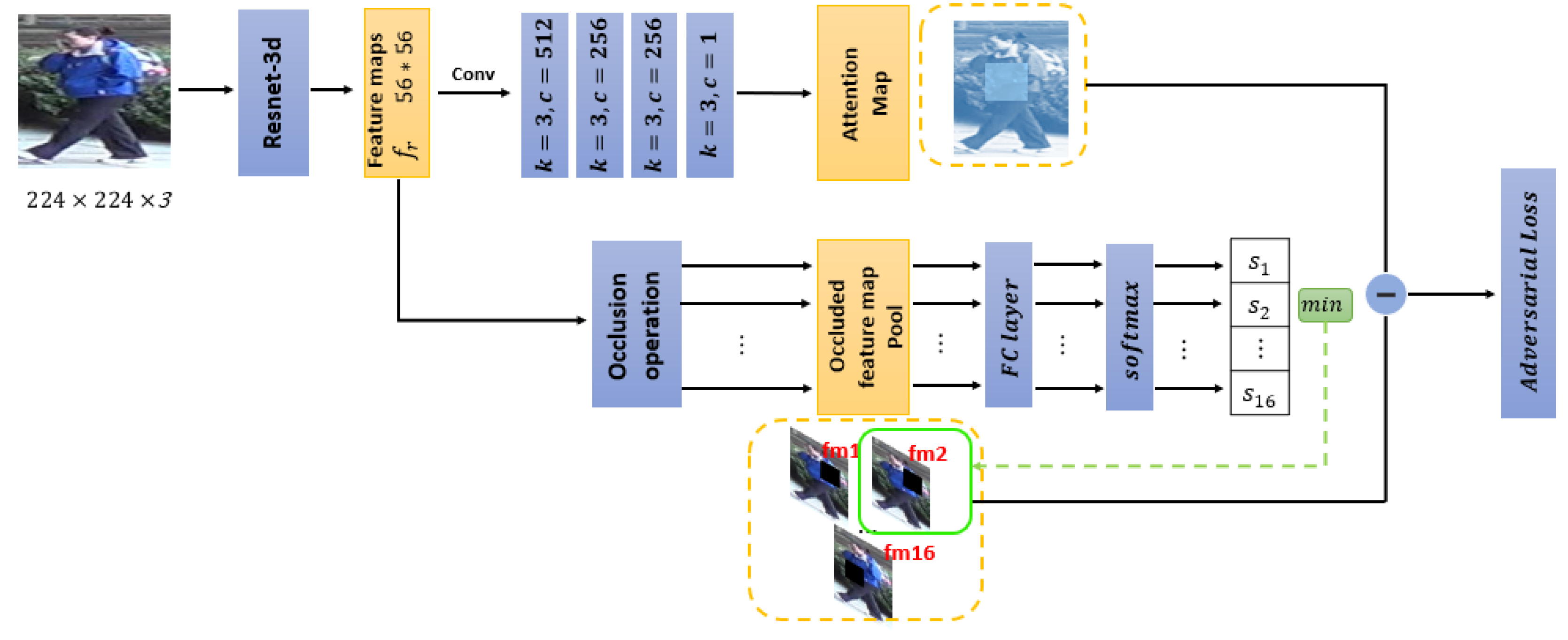
The attention assignment network aims to guide the attentions to be assigned to nearly all parts of the target objects. Concretely, besides the regions that contribute to the final result most, other important regions are further focused on according to the attention assignment mechanism. This is implemented in an adversarial manner. In detail, the occlusion sample with the lowest classification prediction probability is selected as a template in each iterative training process. This allows the attention map to fit the feature response range, which means that some areas of the image that are important to the classification get high values in the attention map. The framework of the attention assignment network is demonstrated in Figure 2. The architecture can be regarded as two branches. Given an input person image, the convolutional modules in the baseline network are employed to extract representative feature maps, denoted as . For one branch, the feature maps are input into several stacked convolutional layers to generate an attention map, which indicates the interesting important regions in the person image for detection and recognition. For the other branch, the feature maps are regularly occluded by 16 non-overlapped rectangular boxes, respectively. As a result, 16 groups of feature maps with occluded area are generated. Each group of occluded feature maps is fed into a fully-connected layer, and the corresponding classification scores are output after a operation. The occluded feature maps obtaining the lowest classification accuracy are picked out as a difficult sample. Subsequently, both the attention map and the difficult sample are input to the adversarial loss,
The first term is the data term, which enforces the attentions assigned to other important area, and has the following form:
The second term is the regularization term, which prevents the network from over-fitting. Meanwhile, it can also maintain the structure of the original feature maps,
During the training phase, the attention assignment network is fine-tuned by the common layers of the baseline network, including the convolution modules of the resnet-50 network and the fully-connected layer. These parameters are fixed in the backward stage. The rest of the parameters are initialized randomly. As a result, an attention map generation mechanism is learned in this network. The attention map is able to re-assign attentions to the area except for the most import region that contributes most to the final result. Therefore, nearly all parts of the target person are highlighted under this attention assignment mechanism.
Figure 2.
The attention assignment network. fm1 represents that the first part of the feature map is occluded, and s1 represents the classification probability of fm1. An occlusion feature map with the lowest classification probability is selected to guide the generation of the attention map according to the adversarial loss.
3.3. Attention-Aware Adversarial Network
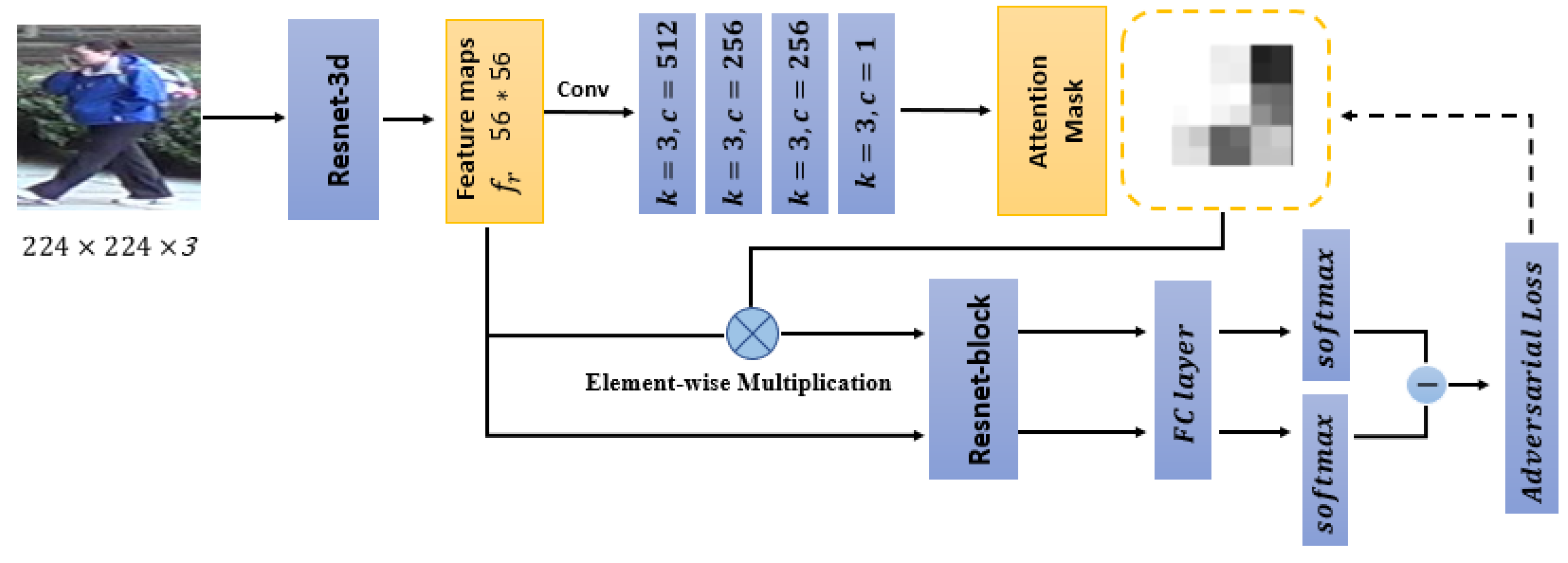
Established on the attention assignment network, the generated attention map is further integrated with the representative feature maps of the input person image, aiming to assign more attentions to the interesting regions besides the most important one. The framework of the attention-aware adversarial network for final person re-ID is illustrated in Figure 3. This is also a two-stream network, in which the common convolution modules are fine-tuned by the parameters of the attention assignment network pre-trained in Section 3.2. For one stream, the attention map is generated from the input person image. Attributed to the pre-trained network in Section 3.2, instead of only highlighting the most attentive regions, the attention map is able to assign attentions to nearly all target regions of the input person image. For the other stream, the attention map is integrated with the representative feature maps of the person image by an element-wise multiplication operation. The generated feature maps are known as attention-aware feature maps and are occluded by the attention mask. Together with the original representative feature maps, the occluded attention-aware feature maps are entered into the subsequent classification network. Not only will we update the parameters of the attention mask again by the switchable gradient update mechanism, but also we will update the entire baseline synchronously. The switchable gradient update mechanism is realized by the parameter of , which is detailed in Section 4.3.
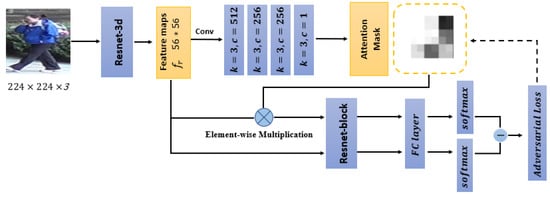
Figure 3.
The attention-aware adversarial network.
We focus on the feature maps to produce occlusions and might simply abide by the identical strategy to generate occlusions on feature maps with a square mask. Nevertheless, we consider that there may be multiple regions in the feature maps, for instance both the satchel and the T-shirt have equally significant effects when the classifier makes decisions. Consequently, we make use of a flexible policy to solve this weakness. The implementation details are as follows.
We use the raw feature maps and occluded feature maps as the inputs for the rest of the CNN network. These feature maps are used to calculate the predicted probability of classification. In this stage, the two parts of our network are jointly optimized. The loss function of the model on these samples is computed by the cross-entropy. The procedure is shown in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2 The training strategy of the attention-aware adversarial network. |
| Input: Nperson images; Whiledo 1: The feature maps obtained by the pre-training attention assignment mechanism are used as 0-1 attention mask; 2: The feature maps of the middle layer multiplied by the 0-1 mask as occluded feature maps; 3: The occluded feature maps are entered into the classification network along with the original feature maps to obtain , which is the classification probability of the original feature maps, and , which is the classification of occluded feature maps 4: Update parameters of the entire network by combining and with adversarial loss; 5: ; end |
The entire adversarial loss function is formulated as follows:
where are the constants, which are obtained by heuristic methods, respectively, and are the same as the pre-training adversarial loss function (1) in which represents a regularization term and represents . , and are the classification probability before occluding the feature maps, the classification probability after occluding the feature maps, and an empirical constant, respectively. and determine whether the parameters of the entire network are updated.
We use the decentralized training methods. More specially, we take turns to train a number of occluded samples and unabridged samples. The optimized approach is the same as the above, in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2.
4. Experimental Results
In this section, we conduct experiments to analyze the main components of the proposed method and evaluate the performance of our method with the state-of-the-art algorithms.
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
We evaluated the proposed method and the state-of-the-art algorithms on two large-scale benchmarks, Market1501 [29] and DukeMTMC-reID [30,31].
Market1501 incorporates 12,936 training images and 19,732 test images, with 1501 identities captured with six cameras, and 32,668 bounding boxes are generated by the DPM-detector.Then, 751 identities were used for training and 750 identities for testing.
DukeMTMC-reID has the same format as Mrarket1501, with 16,522 images for training and 19,889 images for testing. DukeMTMC-reID contains 1404 identities, of which 702 identities were used for training and the rest for testing. Manually-annotated pedestrian bounding boxes were provided as the ground truth.
Two common evaluation metrics, Rank-1 and mean average precision (mAP), were employed to evaluate the performance of the re-ID models.
4.2. Implementation Details
All input person images were uniformly resized to . The baseline network in Section 3.1 was based on the classical resnet-50 classification network. The learning rate was set to 0.001 and was decayed by 0.1 every two epochs. The baseline network achieved convergence after 10 epochs. Then, the parameters of the baseline network were used to fine-tune the attention assignment network in Section 3.2. The learning rate was 0.0001 and was decayed by 0.1 every three epochs. The attention assignment network converged after 10 epochs. Finally, in order to train the attention-aware adversarial network in Section 3.3, the parameters were fine-tuned by the attention assignment network. The learning rate was 0.0001 and was decayed by 0.1 every three epochs. The network converged after 10 epochs. For the three networks, the SGD optimization method was employed to minimize the training losses.
As for the hyper-parameters, , and were set to 0.3, 1.7, and 0.04, respectively. The dropout rates for the datasets Market1501 and DukeMTMC-reID were 0.5 and 0.6, respectively.
4.3. Analysis of the Parameters
The hyper-parameters and were used to adjust the importance of the two terms in the loss function Equation (4). According to the quantitative experiments in Table 1, we empirically gave the constraint that . In our work, and were set to 0.3 and 1.7, respectively.

Table 1.
Influence of different parameters , on the DukeMTMC-reID dataset. mAP, mean average precision.
Since we aimed to enforce the prediction results of the two feature maps before/after integrating with the attention map to be similar, the threshold , which was used to control the updating process, needs to be selected carefully. According to the experiments in Table 2, was set as 0.04.

Table 2.
The influence of on the DukeMTMC-reID dataset with the BL + Euclidean, BL + XQDA, and BL + KISSME.
4.4. Location of Generating Occluded Feature Maps
In this section, we analyze which convolutional layer is suitable for generating occluded feature maps. Consider that feature maps output by lower level convolutional layers incorporate more detailed information, such as color or texture. Feature maps generated by higher level convolutional layers indicate more semantic information. Therefore, we conducted extensive experiments to find which level of convolutional layer was able to provide appropriate feature maps to benefit the subsequent prediction results. In our experiments, four networks were evaluated, in which the occlusion operation were inserted after the second, third, fourth, and fifth convolutional modules of the resnet-50 network. The quantitative results are shown in Table 3. According to the experiments, the resnet-3D network was a more rational structure.

Table 3.
Performance of inserting the occlusion operation in different locations of the network. “Baseline” represents the baseline network.
4.5. Influence of the Attention Assignment Network
As elaborated in Section 3.2, the attention map predicted in this stage not only focused on the interesting regions that contributed most to the final results, but also the other important regions that indicated the unique features of the person. In the next stage, the parameters of the attention assignment network were employed to fine-tune the attention-aware adversarial network. As a result, the attention map in the attention-aware adversarial network inherited the ability to highlight nearly all attentive regions of the target person.
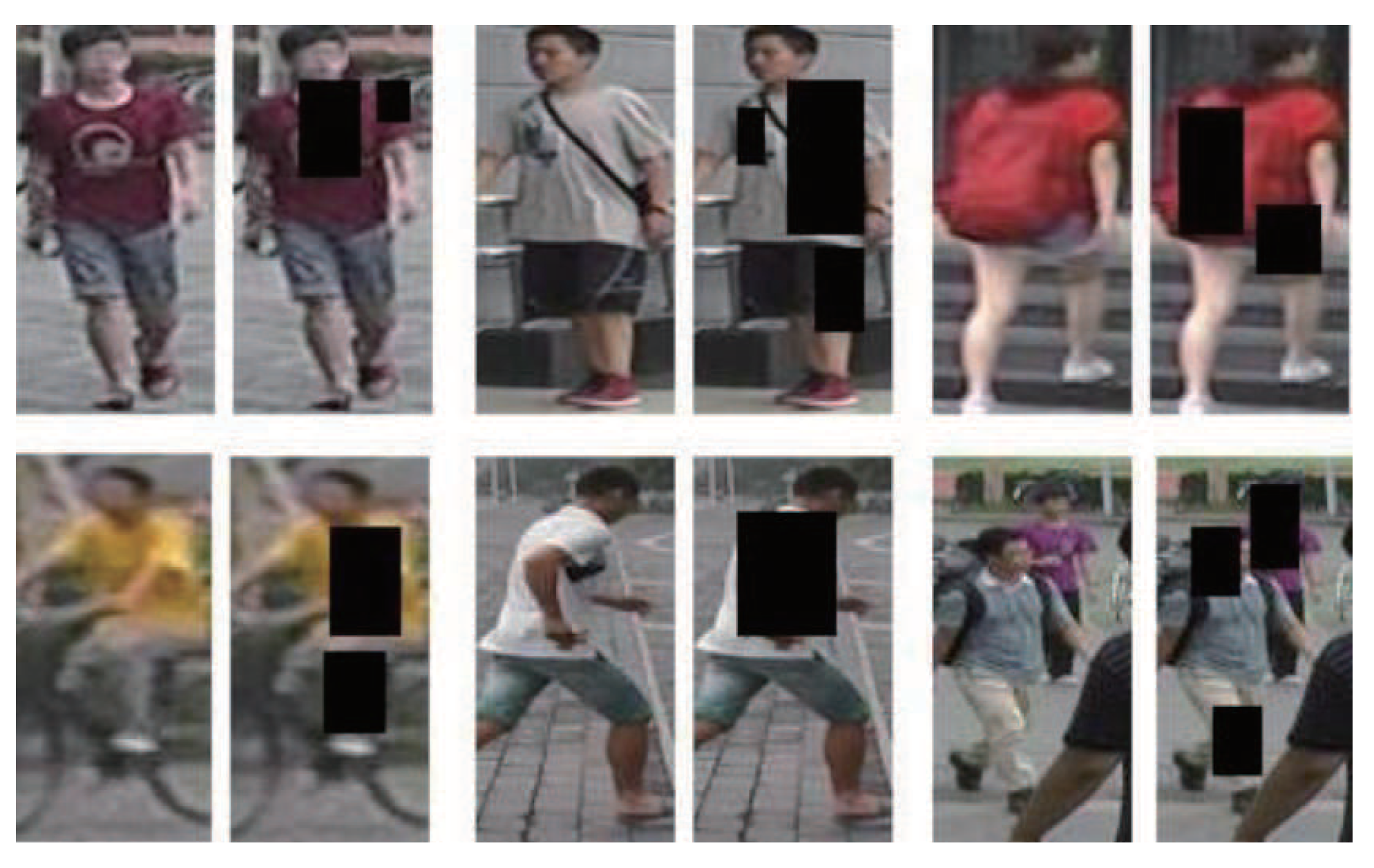
In this section, we experimentally analyze if the attention map trained in the attention-aware adversarial network was able to capture as many important regions as possible. Namely, we did not fine-tune the attention-aware adversarial network with the parameters of the attention assignment network; instead, we simply occluded one-third of the feature map regions with the highest response. As shown in Table 4, fine-tuning the attention-aware adversarial network with the pre-trained network was able to achieve more favorable performance. The visual occlusion results of the attention map generated in the attention-aware adversarial network are illustrated in Figure 4. According to the results, the occlusion samples presented diversity. Multiple parts of important regions were occluded for the adversarial process. Therefore, the attention-aware adversarial network with fine-tuning operation outperformed the one without fine-tuning and improved the performance of the baseline network by a large margin. As shown in Table 5, the attention-aware adversarial network also outperformed the network with random erasing.

Table 4.
Performance of training the attention-aware adversarial network with or without fine-tuning.

Figure 4.
Occlusion examples generated by the attention map in the attention-aware adversarial network with the fine-tuning operation. The black mask represents the occluded area.

Table 5.
Performance of the attention-aware adversarial network and random erasing on the baseline network.
4.6. Evaluation with the State-of-the-Art Algorithms
We evaluated the proposed method with the state-of-the-art methods on two large-scale benchmarks. On the Market1501 dataset, 10 recent works, BOW [29], WARCA [32], SCSP [33], DNS [34], gated [20], PS [35], CCAFA [36], CA [37], spindle [17], and GAN [30], were evaluated with our baseline and the proposed AAA-Net. The evaluation results are shown in Table 6. On the DukeMTMC-reID dataset, five state-of-the-art methods, GAN [30], OIM [38], ACRN [39], PAN [40], and APR [41], were compared with our baseline and the proposed network. The performances are demonstrated in Table 7. According to the quantitative results, our AAA-Net improved the Rank-1 by and the mAP by on the DukeMTMC-reID dataset, respectively. On the Market1501 dataset, the AAA-Net improved the Rank-1 by and the mAP by , respectively. Furthermore, our proposed method outperformed other state-of-the-art algorithms by a large margin.

Table 6.
Performance of our method and the state-of-the-art algorithms, BOW [29], WARCA [32], SCSP [33], DNS [34], gated [20], PS [35], CCAFA [36], CA [37], spindle [17], and GAN [30], on the Market1501 dataset. Two metrics, Rank-1 and mAP, are evaluated.

Table 7.
Performance of our method and the state-of-the-art algorithms, GAN [30], OIM [38], ACRN [39], PAN [40], and APR [41], on the DukeMTMC-reID dataset. Two metrics, Rank-1 and mAP, are evaluated.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we introduced an attention-aware adversarial network (AAA-Net) for person re-ID. A novel data augmentation method was proposed to enforce the data diversity on the feature map level. Based on the augmented feature maps, an attention map was generated in an attention assignment network to assign attentions to nearly all important regions of the person image. Subsequently, an attention-aware adversarial network was trained to classify the input hard samples accurately according to the attention map in an adversarial manner. Extensive experimental results on two large-scale benchmarks demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed framework. In the future, we will enhance the representation of the mask feature or use a recurrent training framework.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. and H.W.; methodology, A.S.; software, J.C.; validation, H.W.; formal analysis, A.S.; investigation, J.W. and X.L.; resources, J.W.; data curation, J.C.; writing, original draft preparation, J.W.; writing, review and editing, H.T.; visualization, H.T.; supervision, X.L.; project administration, H.W.; funding acquisition, X.L.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers for their valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Adversarially Occluded Samples for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5098–5107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, J.; Chen, Z.; Lai, J.; Wang, G. Occluded Person Re-identification. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.02792. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, A. A-fast-rcnn: Hard positive generation via adversary for object detection. In Proceedings of the the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 July 2017; pp. 3039–3048. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Chang, X.; Liu, L.; Hauptmann, A.G.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, N. Discriminative Dictionary Learning With Ranking Metric Embedded for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence—IJCAI 2017, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 964–970. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Liu, L.; Shao, L. Fast Person Re-identification via Cross-Camera Semantic Binary Transformation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5330–5339. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, K. Learning Deep Context-Aware Features over Body and Latent Parts for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7398–7407. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, J. Deeply-Learned Part-Aligned Representations for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision—ICCV 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3239–3248. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zheng, L.; Kang, G.; Yang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J. Image-Image Domain Adaptation with Preserved Self-Similarity and Domain-Dissimilarity for Person Re-identification. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1711.07027. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person Transfer GAN to Bridge Domain Gap for Person Re-Identification. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1711.08565. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, Q. Deep Representation Learning with Part Loss for Person Re-Identification. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1707.00798. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Deng, W.; Wang, S. SVDNet for Pedestrian Retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision—ICCV 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3820–3828. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Person Re-Identification by Deep Joint Learning of Multi-Loss Classification. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence—IJCAI 2017, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 2194–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Tian, M.; Sun, S.; Shao, J.; Yan, J.; Yi, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spindle Net: Person Re-identification with Human Body Region Guided Feature Decomposition and Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 907–915. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. GLAD: Global-Local-Alignment Descriptor for Pedestrian Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Multimedia Conference—MM 2017, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 420–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y. Pose Invariant Embedding for Deep Person Re-identification. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1701.07732. [Google Scholar]
- Varior, R.R.; Haloi, M.; Wang, G. Gated Siamese Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Human Re-identification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016—14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 791–808. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1503.03832. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Feng, J.; Qi, M.; Jiang, J.; Yan, S. End-to-End Comparative Attention Networks for Person Re-identification. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.04404. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Person Re-identification by Multi-Channel Parts-Based CNN with Improved Triplet Loss Function. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1335–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K. Beyond Triplet Loss: A Deep Quadruplet Network for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1320–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Mignon, A.; Jurie, F. PCCA: A new approach for distance learning from sparse pairwise constraints. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2666–2672. [Google Scholar]
- Kai Li, Z.D. Discriminative Semi-coupled Projective Dictionary Learning for Low-Resolution Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LO, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Liang, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Z. Deep Spatial Feature Reconstruction for Partial Person Re-identification: Alignment-Free Approach. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1801.00881. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Kang, G.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Random Erasing Data Augmentation. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.04896. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable Person Re-identification: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Unlabeled Samples Generated by GAN Improve the Person Re-identification Baseline in vitro. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance Measures and a Data Set for Multi-Target, Multi-Camera Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision workshop on Benchmarking Multi-Target Tracking, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, C.; Fleuret, F. Scalable Metric Learning via Weighted Approximate Rank Component Analysis. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016—14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 875–890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, B.; Zheng, N. Similarity Learning with Spatial Constraints for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1268–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S. Learning a Discriminative Null Space for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1239–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, N. Point to Set Similarity Based Deep Feature Learning for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5028–5037. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, W.S.; Lai, J.H. Person Re-Identification by Camera Correlation Aware Feature Augmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Ren, L.; Lu, J.; Feng, J.; Zhou, J. Consistent-Aware Deep Learning for Person Re-identification in a Camera Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3396–3405. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Lin, L.; Wang, X. End-to-End Deep Learning for Person Search. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1604.01850. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, A.; Stiefelhagen, R. Person Re-identification by Deep Learning Attribute-Complementary Information. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1435–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Pedestrian Alignment Network for Large-scale Person Re-identification. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1707.00408. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. Improving Person Re-identification by Attribute and Identity Learning. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1703.07220. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).