Recent Advances in Femtosecond Laser-Induced Surface Structuring for Oil–Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Femtosecond Laser-Induced Self-Organized Periodic Surface Structures (LIPSS)
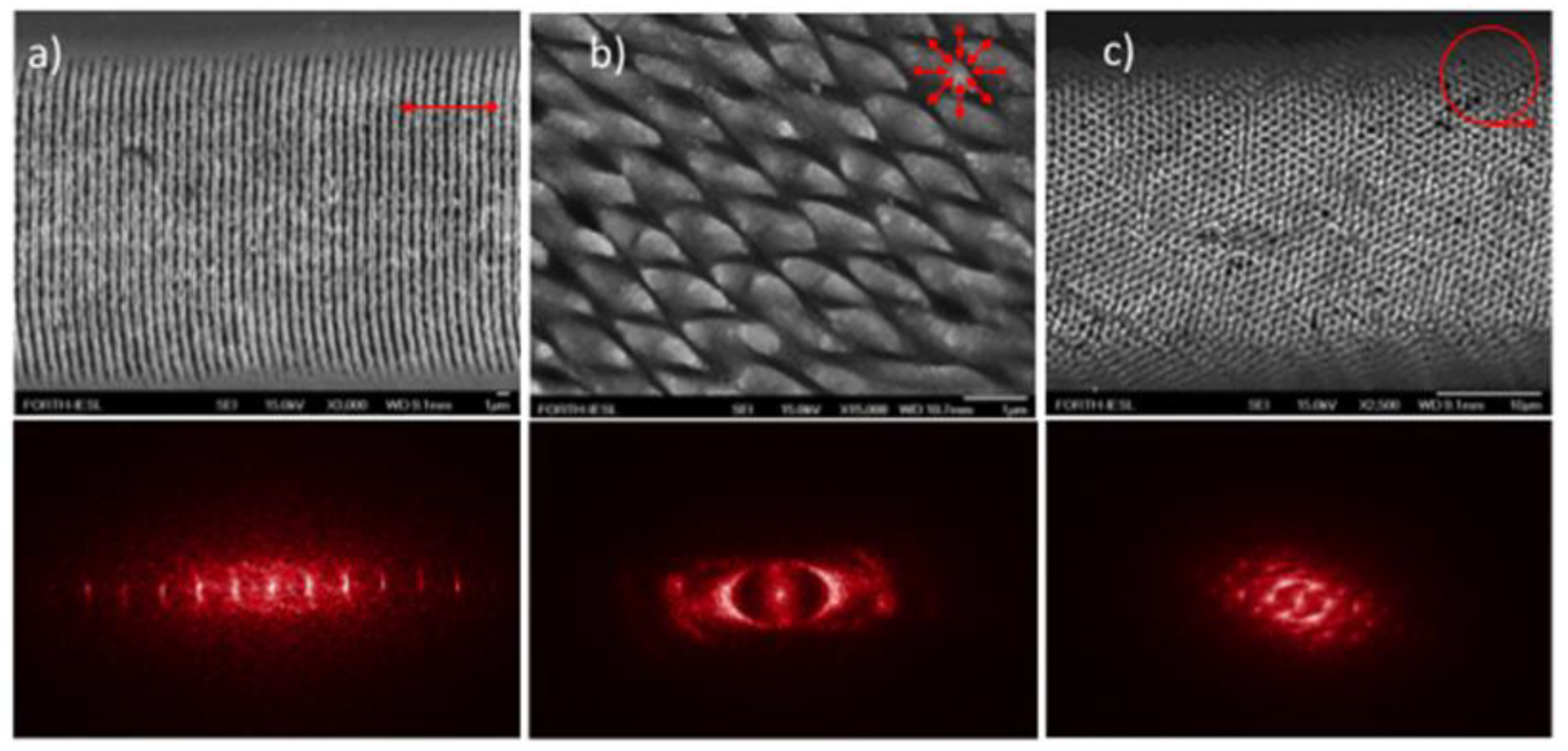
2.1. Laser-Induced Surface Ripples
2.2. Microgrooves
2.3. Conical Spikes or Columnar Structures
3. Wettability Control
4. Oil–Water Separation Mechanism
5. Oil–Water Separation via FS Laser Structuring
5.1. FS Laser-Structured Meshes
5.2. FS Laser Fabrication of Arrays of Micro-Through Holes
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyaji, G.; Miyazaki, K. Origin of periodicity in nanostructuring on thin film surfaces ablated with femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 16265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakis, E. Nanomaterials by ultrafast laser processing of surfaces. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2012, 4, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser blackening of platinum. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 053516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, S.; Gimpel, T.; Baumann, A.L.; Guenther, K.-M.; Schade, W. Laser Processed Black Silicon for Photovoltaic Applications. Energy Procedia 2012, 27, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygletou, M.; Petridis, C.; Kymakis, E.; Stratakis, E. Advanced Photonic Processes for Photovoltaic and Energy Storage Systems. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Feng, G.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, B.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Strong infrared absorber: Surface-microstructured Au film replicated from black silicon. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 20462. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Metal colorization with femtosecond laser pulses. In High-Power Laser Ablation VII; Phipps, C.R., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 7005, p. 70051T. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Colorizing metals with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Dai, Q.; Wu, L.; Lan, S.; Gopal, A.V.; Trofimov, V.A.; Lysak, T.M. Selective appearance of several laser-induced periodic surface structure patterns on a metal surface using structural colors produced by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7625–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Fan, P.; Gong, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zhong, M. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser with Tunable Water Adhesion: From Lotus Leaf to Rose Petal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9858–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratakis, E.; Ranella, A.; Fotakis, C. Biomimetic micro/nanostructured functional surfaces for microfluidic and tissue engineering applications. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 013411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ngo, C.-V.; Singh, S.C.; Yang, J.; Xin, W.; Yu, Z.; Guo, C. Bioinspired Hierarchical Surfaces Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser and Hydrothermal Method for Water Harvesting. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3562–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Metal pumps liquid uphill. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 2007–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradisanos, I.; Fotakis, C.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Stratakis, E. Gradient induced liquid motion on laser structured black Si surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 111603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, T.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W.J.; Fan, S.; Duan, X.M. Controllable wettability of metallic surfaces via micro-nano structure fabricated by femtosecond laser. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Subdiffraction-Limited Plasmonic Lithography and Innovative Manufacturing Technology 2019, Chengdu, China, 26–29 June 2019; Volume 10842. [Google Scholar]
- Allahyari, E.; Ausanio, G.; Vecchione, A.; Amoruso, S.; Oscurato, S.L.; Salvatore, M.; Fittipaldi, R.; Bruzzese, R.; Nivas, J.; Maddalena, P. Laser surface texturing of copper and variation of the wetting response with the laser pulse fluence. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 470, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z.K.; Zheng, H.Y.; Thwe, A.M.; Lam, Y.C. Investigation on polycarbonate surface wetting property with femtosecond laser irradiation and ultrasonic treatment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 115, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Murillo, D.; García-Girón, A.; Romano, J.M.; Cardoso, J.T.; Cordovilla, F.; Walker, M.; Dimov, S.S.; Ocaña, J.L. Wettability modification of laser-fabricated hierarchical surface structures in Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, M.; Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Hou, X. A femtosecond laser-induced superhygrophobic surface: Beyond superhydrophobicity and repelling various complex liquids. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6650–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser structuring of titanium implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7272–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranella, A.; Barberoglou, M.; Bakogianni, S.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Tuning cell adhesion by controlling the roughness and wettability of 3D micro/nano silicon structures. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Kourgiantaki, A.; Athanassakis, I.; Efstathopoulos, P.; Fotakis, C.; Ranella, A.; Stratakis, E.; Gravanis, A.; Simitzi, C. Laser fabricated discontinuous anisotropic microconical substrates as a new model scaffold to control the directionality of neuronal network outgrowth. Biomaterials 2015, 67, 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Buividas, R.; Stoddart, P.R.; Juodkazis, S. Laser fabricated ripple substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Ann. Phys. 2012, 524, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Koter, R.; Hartelt, M.; Spaltmann, D.; Pentzien, S.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Tribological performance of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on titanium and a high toughness bearing steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 336, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignano, C.; Scarati, D.; Gaudiuso, C.; Di Mundo, R.; Ancona, A.; Carbone, G. Soft matter laser micro-texturing for friction reduction: An experimental investigation. Tribol. Int. 2019, 136, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser nanostructuring of metals. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Baba, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ganeev, R.A.; Kuroda, H.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Xu, Z.; Liang, G.; et al. Fabrication of two-dimensional periodic nanostructures by two-beam interference of femtosecond pulses. Nanoeng. Adv. Polym. Sci 2005, 72, 125429–125433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Yong, J.; Du, G.; Si, J.; Yun, F.; Hou, X. Bioinspired wetting surface via laser microfabrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6777–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulas, E.; Manousaki, A.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Biomimetic surface structuring using cylindrical vector femtosecond laser beams. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Calderon, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Dias, A.; Gómez-Aranzadi, M.; Olazoila, S.M. Femtosecond laser manufacturing of highly hydrophobic hierarchical structures fabricated by combining surface microstructures and LIPSS. In Proceedings of the Lasers in Manufacturing Conference, Munich, Germany, 15–22 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, X. A Review of Femtosecond-Laser-Induced Underwater Superoleophobic Surfaces. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1870033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, G.; Gaudiuso, C.; Cinquino, M.; Di Mundo, R.; Mirenghi, L.; Di Franco, C.; Scamarcio, G.; Lugarà, P.M.; Ancona, A. 1-D and 2-D surface structuring of steel by bursts of femtosecond laser pulses. In Proceedings of the Laser-Based Micro-and Nanoprocessing XIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2019; Volume 10906. [Google Scholar]
- Tanvir Ahmmed, K.M.; Grambow, C.; Kietzig, A.M. Fabrication of micro/nano structures on metals by femtosecond laser micromachining. Micromachines 2014, 5, 1219–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsibidis, G.D.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. From ripples to spikes: A hydrodynamical mechanism to interpret femtosecond laser-induced self-assembled structures. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2015, 92, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Kirner, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Laser-induced Periodic Surface Structures (LIPSS)—A Scientific Evergreen. In CLEO: Science and Innovations; Optical Society of America: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum, M. Semiconductor surface damage produced by Ruby lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1965, 36, 3688–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Chu, J.; Huang, W. Femtosecond laser color marking stainless steel surface with different wavelengths. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2014, 118, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Hou, X. Femtosecond laser controlled wettability of solid surfaces. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8897–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräf, S.; Müller, F.A. Polarisation-dependent generation of fs-laser induced periodic surface structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 331, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsibidis, G.D.; Skoulas, E.; Stratakis, E. Ripple formation on nickel irradiated with radially polarized femtosecond beams. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, U.; Kirner, S.V.; Emonts, C.; Comanns, P.; Skoulas, E.; Mimidis, A.; Mescheder, H.; Winands, K.; Krüger, J.; Stratakis, E.; et al. Mimicking lizard-like surface structures upon ultrashort laser pulse irradiation of inorganic materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakis, E.; Zorba, V.; Barberoglou, M.; Fotakis, C.; Shafeev, G.A. Laser writing of nanostructures on bulk Al via its ablation in liquids. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Gupta, M.C. Self-organized micro/nano structures in metal surfaces by ultrafast laser irradiation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Gupta, M.C.; Kolasinski, K.W. Formation of nano-textured conical microstructures in titanium metal surface by femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2008, 90, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Farooq, U.; Du, G.; Hou, X. Bioinspired underwater superoleophobic surface with ultralow oil-adhesion achieved by femtosecond laser microfabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8790–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, V.; Stratakis, E.; Barberoglou, M.; Spanakis, E.; Tzanetakis, P.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Fotakis, C. Biomimetic artificial surfaces quantitatively reproduce the water repellency of a lotus leaf. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4049–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhash Latthe, S.; Basavraj Gurav, A.; Shridhar Maruti, C.; Shrikant Vhatkar, R. Recent Progress in Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surfaces: A Review. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 2, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, A. Recent Progress in Preparation and Anti-Icing Applications of Superhydrophobic Coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Ke, Z.; Du, C.Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Z. Review: Porous Metal Filters and Membranes for Oil–Water Separation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Wetting on hydrophobic rough surfaces: To be heterogeneous or not to be? Langmuir 2003, 19, 8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Zulfiqar, U.; Hussain, S.Z.; Zaheer, U.; Hussain, I.; Husain, S.W.; Subhani, T. Fabrication of superhydrophobic filter paper and foam for oil–water separation based on silica nanoparticles from sodium silicate. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Hussain, S.Z.; Awais, M.; Khan, M.M.J.; Hussain, I.; Husain, S.W.; Subhani, T. In-situ synthesis of bi-modal hydrophobic silica nanoparticles for oil-water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 508, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, M.; Zang, D.; Gao, Z.; Wang, C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic cotton for application in the field of water/oil separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Shi, Z.; Ou, J.; Wang, F.; Xue, M.; Li, W.; Qiao, G.; Guan, X.; Zhang, J. Durable superhydrophobic cotton fabric for oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 533, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Huo, J.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Bian, H.; Li, W.; Wei, Y.; Dai, Y.; Hou, X. Green, Biodegradable, Underwater Superoleophobic Wood Sheet for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, L.; Hu, W.; Li, D.; Zha, F.; Lei, Z. Facile fabrication of underwater superoleophobic TiO2 coated mesh for highly efficient oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 489, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Magnetic, durable, and superhydrophobic polyurethane@Fe3O4@SiO2@fluoropolymer sponges for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4936–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Rational design of materials interface at nanoscale towards intelligent oil-water separation. Nanoscale Horiz. 2018, 3, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Liang, S.; Jin, Y.; et al. Facile fabrication of robust superhydrophobic porous materials and their application in oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23252–23260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Han, D.-D.; Jiao, Z.-Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.-B.; Wu, X.-H.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Sun, H.-B. Laser-structured Janus wire mesh for efficient oil–water separation. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17933–17938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Chu, D.; Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, J.-A.; He, J. Femtosecond laser induced robust periodic nanoripple structured mesh for highly efficient oil–water separation. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14229–14235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Fang, Y.; Chen, F.; Huo, J.; Yang, Q.; Bian, H.; Du, G.; Hou, X. Femtosecond laser ablated durable superhydrophobic PTFE films with micro-through-holes for oil/water separation: Separating oil from water and corrosive solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Peng, Q. A highly efficient, stable, durable, and recyclable filter fabricated by femtosecond laser drilling of a titanium foil for oil-water separation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, H.; Ren, F.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, B.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; et al. Multifunctional ultrathin aluminum foil: Oil/water separation and particle filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 18832–18840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Englezos, P. Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4821–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Singh, S.C.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, F.; Guo, C. How To Obtain Six Different Superwettabilities on a Same Microstructured Pattern: Relationship between Various Superwettabilities in Different Solid/Liquid/Gas Systems. Langmuir 2019, 35, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Huo, J.; Hou, X. Remarkably simple achievement of superhydrophobicity, superhydrophilicity, underwater superoleophobicity, underwater superoleophilicity, underwater superaerophobicity, and underwater superaerophilicity on femtosecond laser ablated PDMS surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25249–25257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Material | Laser Structures | Fabrication Parameters | Chemical Treatment | Wettability Characteristic | Oil Separated | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS Laser-Structured Meshes | ||||||
| Janus mesh (side 1) | LISR | 580 mW, 7.39 × 106 mJ/cm2 | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane | Superhydrophobic–superoleophilic | Bean oil, n-heptane, methyl benzene | [66] |
| Janus mesh (side 2) | - | - | Graphene oxide | superhydrophilic–underwater superoleophobic | Perchloromethane, trichloromethane. | |
| Stainless steel | LISR | λ = 1030 nm, 250 FS, 75 kHz | - | superhydrophilic–underwater superoleophobic | Edible oil, diesel, crude oil, hexadecane, 1,2-dichloroethane. | [67] |
| FS Laser-Fabricated Arrays of Micro-Through Holes | ||||||
| PTFE | - | λ = 800 nm, 50 FS, 1 kHz, | - | superhydrophobic–superoleophilic | petroleum ether, acid/base (HCl and KOH) solution, | [68] |
| Titanium | - | λ = 800 nm, 50 FS, 1 kHz, 3.1–15.5 J/cm2 | - | Superhydrophilic underwater–superoleophobic | petroleum ether, heptane, hexane, gasoline, crude oil, soybean, silicon oil | [69] |
| Aluminum | - | λ = 800 nm,104 FS, 1 kHz, 4–5 pulses/hole | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane (PFDTES) | superhydrophilic underwater–superoleophobic superhydrophobic–superoleophilic | Octane, 1,2-dichloroethane | [70] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alnaser, A.S.; Khan, S.A.; Ganeev, R.A.; Stratakis, E. Recent Advances in Femtosecond Laser-Induced Surface Structuring for Oil–Water Separation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081554
Alnaser AS, Khan SA, Ganeev RA, Stratakis E. Recent Advances in Femtosecond Laser-Induced Surface Structuring for Oil–Water Separation. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(8):1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081554
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlnaser, Ali Sami, Sharjeel Ahmed Khan, Rashid Ashirovich Ganeev, and Emmanuel Stratakis. 2019. "Recent Advances in Femtosecond Laser-Induced Surface Structuring for Oil–Water Separation" Applied Sciences 9, no. 8: 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081554
APA StyleAlnaser, A. S., Khan, S. A., Ganeev, R. A., & Stratakis, E. (2019). Recent Advances in Femtosecond Laser-Induced Surface Structuring for Oil–Water Separation. Applied Sciences, 9(8), 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081554







