An Electric Load Simulator for Engine Camless Valvetrains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Design
2.1. System Configurations
2.2. Performance Requirements
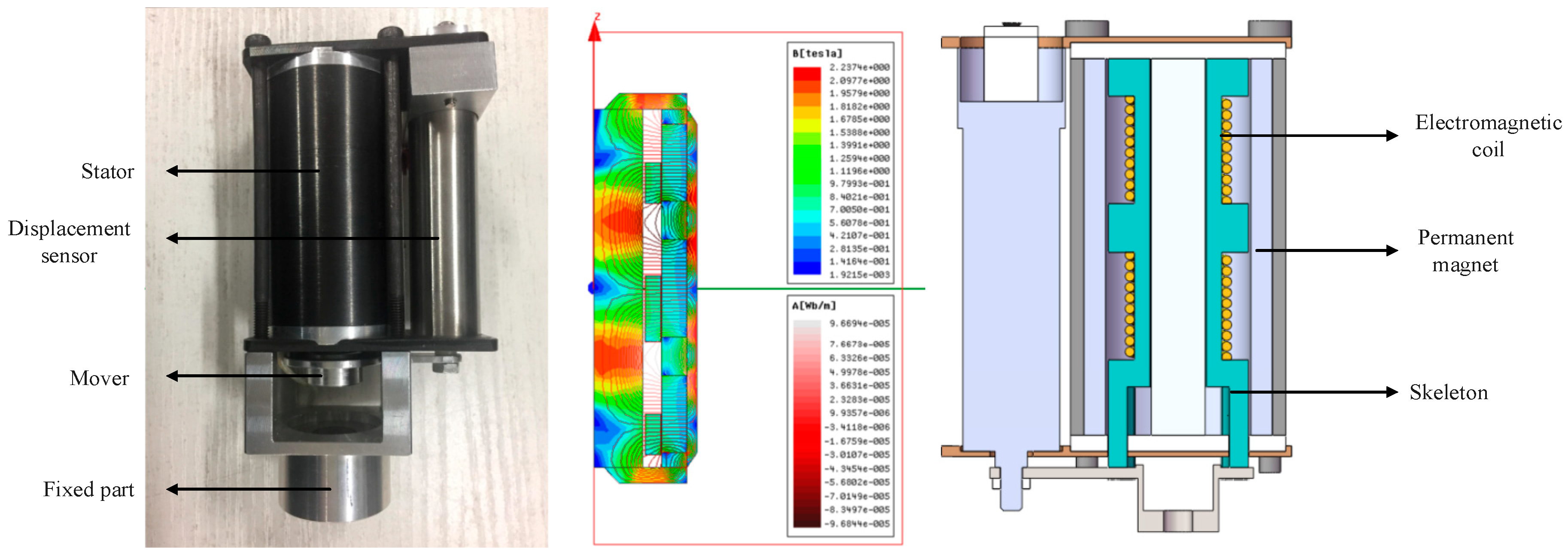
2.3. Electromagnetic Actuator Design
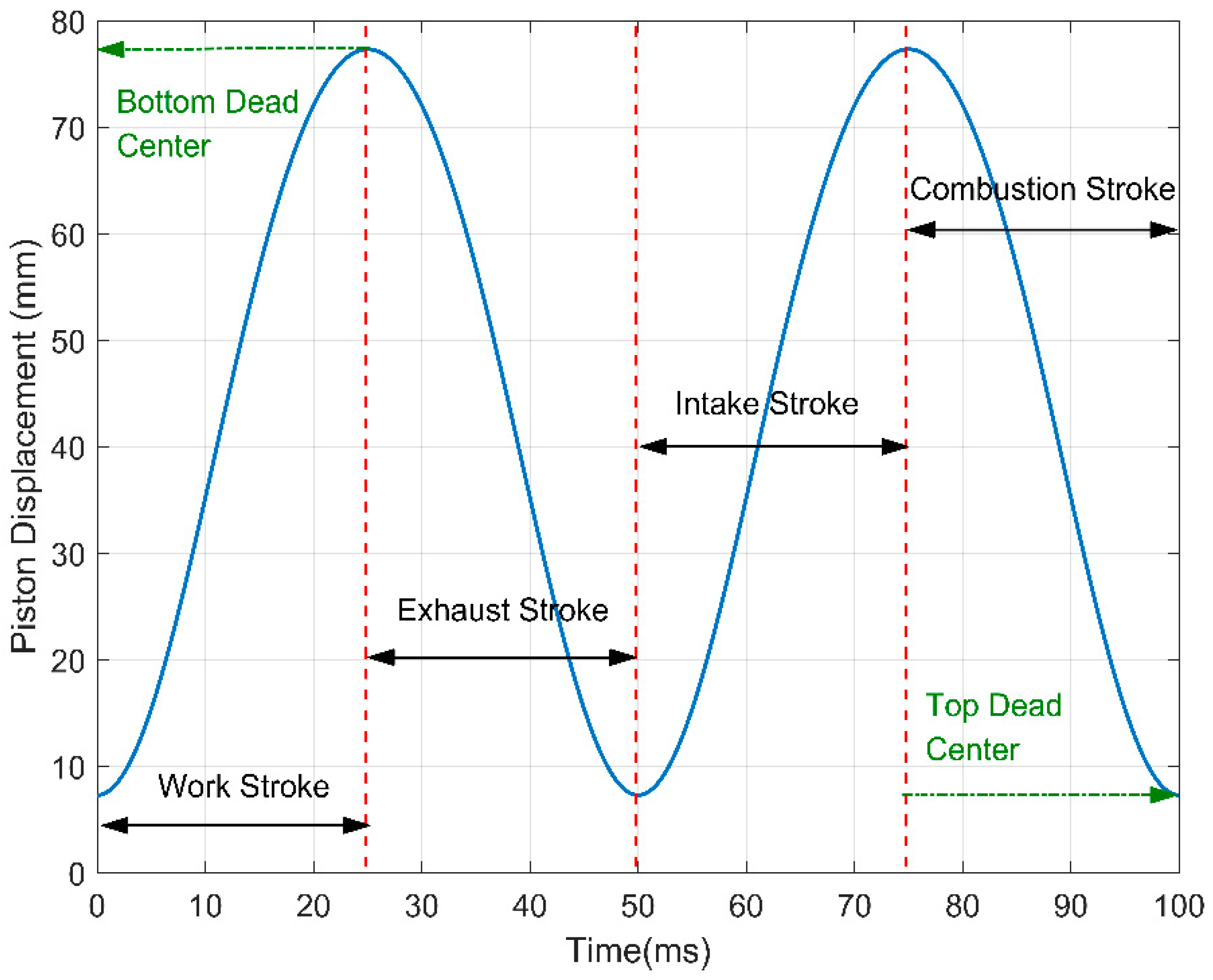
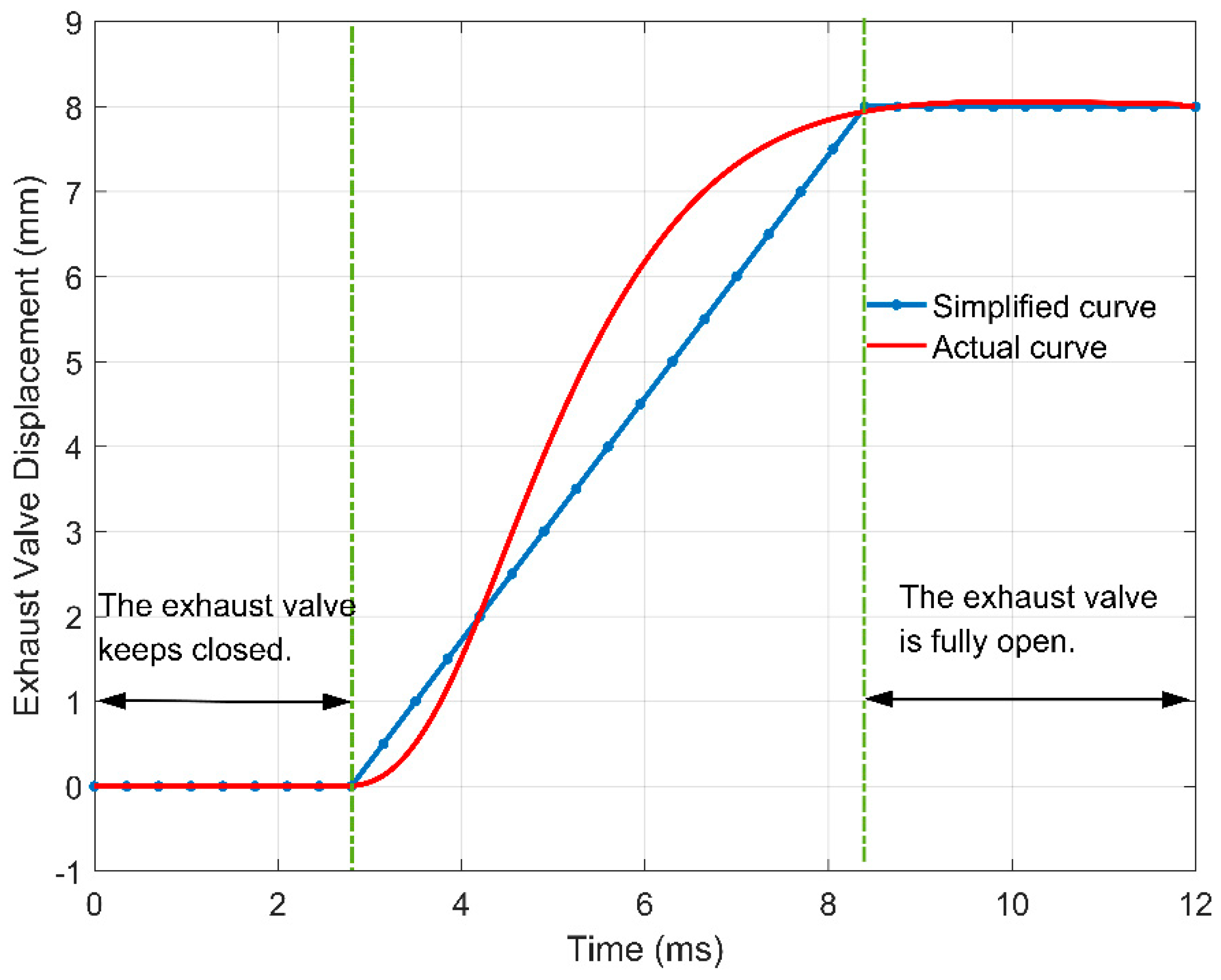
3. Load Characteristics of the Exhaust Valve
3.1. 1D Gas-Dynamic Simulation
3.2. 3D Numerical Simulation
4. Development and Validation of the System Model
4.1. Mathematical Model of the System
4.2. Model Validation
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Simulation Results
5.2. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, K.P.; Han, D.; Kim, W.T. Development of Continuously Variable Valve Lift Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Chang, S. Improvement of valve seating performance of engine’s electromagnetic valvetrain. Mechatronics 2011, 21, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Seethaler, R.J. Compensating combustion forces for automotive electromagnetic valves. Mechatronics 2010, 20, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chladny, R.R.; Koch, C.R. Flatness-Based Tracking of an Electromechanical Variable Valve Timing Actuator with Disturbance Observer Feedforward Compensation. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2008, 16, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernus, C.; Van Der Staay, F.; Janssen, H.; Neumeister, J.; Vogt, B.; Donee, L.; Estlimbaum, I.; Nicole, E.; Maerky, C. Modeling of Exhaust Valve Opening in a Camless Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Haskara, I.; Kokotovic, V.V.; Mianzo, L.A. Control of an electro-mechanical valve actuator for a camless engine. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2004, 14, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.; Peterson, K.; Stefanopoulou, A.G. Iterative Learning Control for Soft Landing of Electromechanical Valve Actuator in Camless Engines. Control Syst. Technol. IEEE Trans. 2003, 11, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.S.; Stefanopoulou, A.G. Extremum seeking control for soft landing of an electromechanical valve actuator. Automatica 2004, 40, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Krstic, N.; Chaturvedi, J. Parameter Identification for Electrohydraulic Valvetrain Systems. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2011, 133, 064502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bao, R.; Han, H. Robust Hybrid Control Based on PD and Novel CMAC with Improved Architecture and Learning Scheme for Electric Load Simulator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5271–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shen, G.; Zhu, W.; Yang, C.; Yao, J. Robust force control with a feed-forward inverse model controller for electro-hydraulic control loading systems of flight simulators. Mechatronics 2016, 38, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Q. A KCMAC-PD controller with reduced memory and optimized mapping for the torque control of electric load simulator. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.Q.; Ahn, K.K. Force control for hydraulic load simulator using self-tuning grey predictor—fuzzy PID. Mechatronics 2009, 19, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cho, H.S. A fuzzy controller for an aero-load simulator using phase plane method. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2001, 9, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S. High performance torque controller design for electric load simulator. In Proceedings of the 2011 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Beijing, China, 21–23 June 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Huang, Y. Experiment and study of electric loading simulator for linear rudder. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2008 7th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Chongqing, China, 25–27 June 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Jiao, Z.; Yao, J.; Shang, Y. Compound Velocity Synchronizing Control Strategy for Electro-Hydraulic Load Simulator and Its Engineering Application. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basic, G. Hardware-In-The-Loop Simulation of Mechanical Loads for Mechatronics System Design. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2003; doi:10393/26323. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jiao, Z.; Quan, L. Adaptive velocity synchronization compound control of electro-hydraulic load simulator. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaru, R.; Arcire, A.; Petrescu, C.; Mihai, M. A novel vibration actuator based on active magnetic spring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 264, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Son, J.; Lee, J. A High-Speed Sliding-Mode Observer for the Sensor-less Speed Control of a PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4069–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.; Levesley, M. Self-sensing applications for electromagnetic actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 116, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, R.; Munjal, M.; Mukherjee, N. Evaluation of Engine Acoustic Source Characteristics Using AVL BOOST Software; Mechanical Engineering: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Baburic, M.; Željko, B.; Neven, D. A New Approach to CFD Research: Combining AVL’s Fire Code with User Combustion Model. In Proceedings of the International Conference Information Technology Interfaces, Cavtat, Croatia, 24–27 June 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesan, W.; Mingyan, W.; Ben, G.; Zhe, W.; Di, W.; Yanlin, L. Analysis and Design of a Speed Controller for Electric Load Simulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7413–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercorelli, P.; Werner, N. An Adaptive Resonance Regulator Design for Motion Control of Intake Valves in Camless Engine Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascetta, L.; Rocco, P.; Magnani, G. Force Ripple Compensation in Linear Motors Based on Closed-Loop Position-Dependent Identification. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 15, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical load simulator | Simple structure; no extra torque | Unable to track aerodynamic loads | Small loop experiment |
| Electro-hydraulic load simulator | High operating frequency; strong capability of output | Complex structure; low energy efficiency | Large loop experiment |
| Electric load simulator | Strong tracking ability; high resolution | Poor load accuracy | Small and medium load laboratory |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Force constant | 7.8 | |
| Resistance of coil winding | 0.91 | |
| Inductance of coil winding | 0.43 | |
| The total mass of the mover Mechanical stroke | 64.6 g 10 mm |
| Region | Value |
|---|---|
| Cylinder pressure | 6.3 bar |
| Cylinder temperature | 1646.5 K |
| Exhaust pressure | 1.0 bar |
| Exhaust temperature | 775.0 K |
| Crank angle | 115° |
| Type | Single Cylinder, Four-Stroke |
|---|---|
| Bore | 80 mm |
| Stroke | 70 mm |
| Cylinder volume | 352 mL |
| Compression ratio | 10.63:1 |
| Valve lift | 8 mm |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Z. An Electric Load Simulator for Engine Camless Valvetrains. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081591
Zhang L, Liu L, Zhu X, Xu Z. An Electric Load Simulator for Engine Camless Valvetrains. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(8):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081591
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lingling, Liang Liu, Xiangbin Zhu, and Zhaoping Xu. 2019. "An Electric Load Simulator for Engine Camless Valvetrains" Applied Sciences 9, no. 8: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081591
APA StyleZhang, L., Liu, L., Zhu, X., & Xu, Z. (2019). An Electric Load Simulator for Engine Camless Valvetrains. Applied Sciences, 9(8), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081591





