Abstract
We propose the treatment of barley straw with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate [EMIMAcO] ionic liquids (ILs) and subsequent precipitation with antisolvent mixtures, thus allowing the separation of the sugar-rich fractions (cellulose and hemicellulose) from the lignin fraction. For this purpose, different concentration ranges of acetone:water antisolvent mixtures were studied. In all cases, a high recovery percentage and a high and effective separation of fractions was achieved for 1:1 acetone:water. The fractionated lignocellulosic compounds were studied by using infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance characterization techniques. This method allows the possibility of reusing IL, confirming the versatility of the established method. The fraction rich in cellulose and hemicellulose was subjected to acid hydrolysis (0.2 mol/L H2SO4) for 5 h at 140 °C, obtaining a yield of total reducing sugars of approximately 80%, much higher than those obtained in non-pretreated samples.
1. Introduction
The exponential growth of the global population and industrial activity in the last century has compromised the sustainability of life on Earth. The European Commission has set a long-term goal to develop a competitive, resource-efficient and low-carbon economy by 2050 [1]. The bioeconomy will play an important role (2.4 billon € market value in 2015). While fossil resources are the major source of energy and chemicals, biomass will eventually be the most prominent source. Cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin are the most abundant biopolymers on Earth [2]. These biopolymers are the major components of the plant cell wall, where they are present in a dense ordered matrix and are known as lignocellulose [3,4]. Biomass lignocellulosic used as a feedstock may contain also minor components like proteins and other nitrogen containing materials, non-structural material and inorganic material (ashes) structural or extractable [5]. Cellulose is a linear polymer of glucose units with β-(1→4) links that form a cellulose chain [6,7,8], and cellulose chains form fibers via H-bonds. Cellulose can be present in a crystalline or amorphous structure, which determines its resistance to hydrolysis [9,10]. In contrast to cellulose, the chemical composition of hemicelluloses differs between lignocellulose sources [3]. Lignin is a complex heterogeneous branched polymer that consists of 4-phenylpropane units linked by ether and carbon–carbon alkyl–aryl and aryl–aryl linkages [11]. Various linkages can also exist between lignin and cellulose or hemicelluloses in so-called ‘lignin-carbohydrate complexes’. Lignocellulosic biomass conversion requires, almost unavoidably, a pretreatment step, which can be physical, chemical, biochemical, biological or a combination thereof. Pretreatment can reduce the particle size, improve the porosity, alter the cellulose crystallinity and fractionate the lignocellulose [10,12,13,14,15,16,17]. The presence of lignin is considered to be a major barrier to achieving efficient cellulosic bioconversion because of its negative interaction with the biocatalyst during enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation [18,19]. Lignin acts as a cement around cellulose fibrils, and it is difficult to separate the two components. Typically, harsh conditions are used, causing chemical and structural changes [20]. Once lignin is isolated as a solid (technical lignin), the resulting material is even more recalcitrant than its native state. One of the more interesting lignocellulosic residues are barley wastes. These residues are the second largest biomass feedstock in Europe [21,22]. The estimated amounts of environmental sustainable of barley straw in the European Union for 2030 are 25 million tons [23].
Ionic liquids (ILs) are effective in solubilizing crystalline cellulose and lignocellulosic biomass [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32], and dissolved cellulose can be regenerated by precipitation with antisolvents. Interestingly, regenerated cellulose shows lower crystallinity and enhanced subsequent hydrolysis rates [33,34]. ILs can also deconstruct and fractionate lignocellulose. Once lignocellulosic biomass is dissolved, it can be fractionated into its principal components by the addition of antisolvents, which leads to the selective precipitation of lignin, cellulose or hemicellulose [35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. There is a plethora of studies of IL dissolution of lignocellulosic biomass, where ionic liquids of the imidazolium type are the best solvents [33,42,43,44,45,46,47]. Among them 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate [EMIMAcO] is the most popular, because of his physical properties (low boiling point and viscosity) and chemical properties, absence of halogen as an anion, is not corrosive and practically no reactive with the biomass [30,48,49,50,51,52,53,54].
In this work, we studied the dissolution of barley straw in [EMIMAcO] and subsequent precipitation with different concentrations of water:acetone mixtures to improve the fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass. This combination may be interesting because the presence of water favors the precipitation of all the main components of biomass (cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin), while acetone does not favor the precipitation of lignin, according to the literature [55].
2. Materials and Methods
All chemicals were of reagent grade and purchased from Meck Milipore Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany), except xylan (from beechwood), which was purchased from TCI-Europe, N. V. (Zwijndrecht, Belgium) and used without any further purification. The lignocellulosic biomass (barley straw) used was provided and characterized by the Biofuels Unit of CIEMAT.
Analysis of Barley Straw. The methods of characterization of barley straw are procedures adapted from the standard methods for the analysis of biomass published by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL; Colorado, USA) [56]. Determinations of extractives were made in quadruplicate, and component analysis of the collected samples was performed in triplicate. The average values for dried samples are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Composition analysis (wt.%) of samples of barley straw dried at 105 °C.
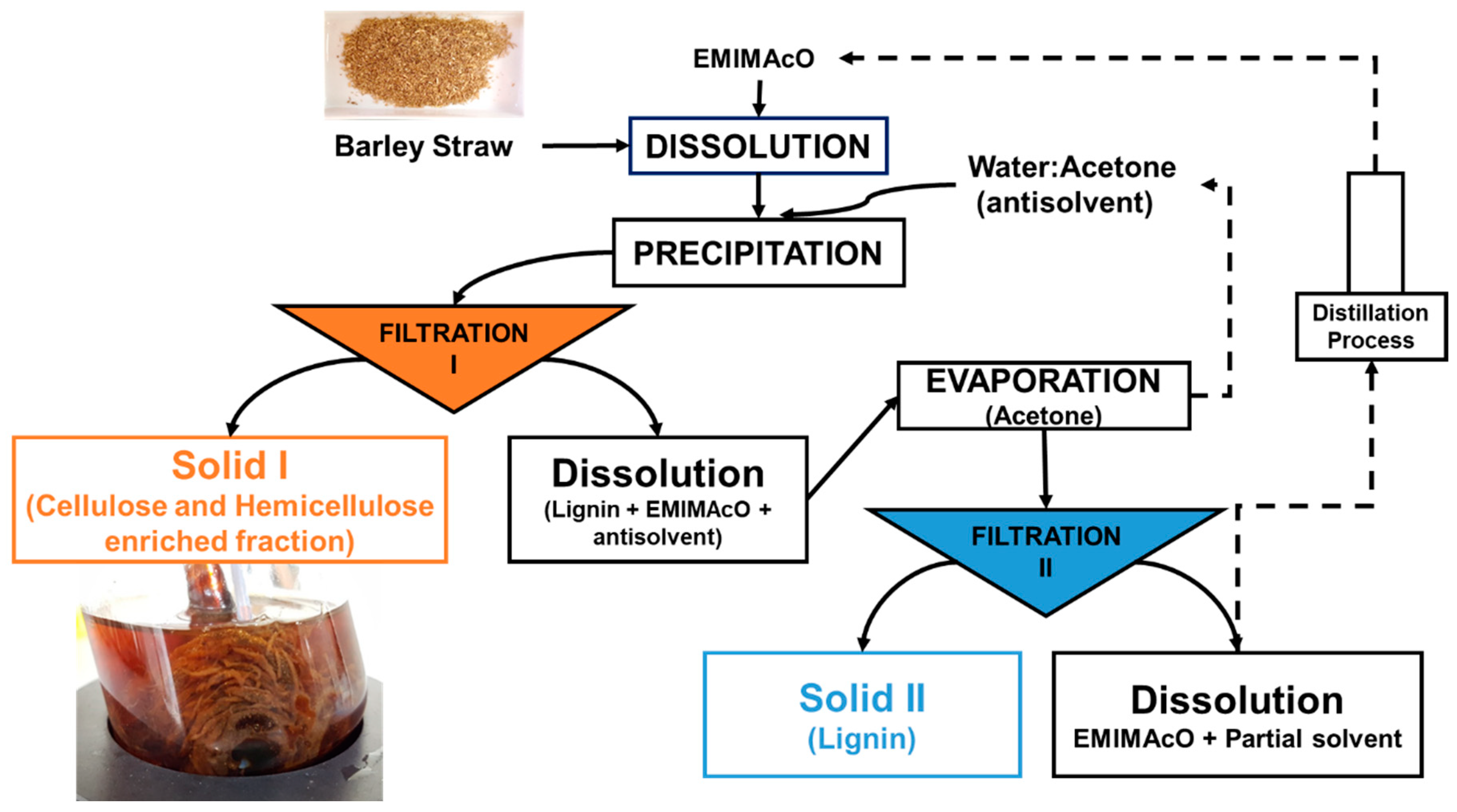
Dissolution and Precipitation. A total of 0.50 g of barley straw was dissolved in 9.50 g of ionic liquid (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate, [EMIMAcO]) at 105 °C in a Mettler-Toledo Easy Max 102® reactor equipped with mechanical stirring at atmospheric pressure [34,47,57,58]. Complete visual dissolution was observed at 3.5 h, and then the carbohydrate-rich material was precipitated by the addition of an antisolvent (25 mL). The antisolvents tested were water, acetone and mixtures thereof. The obtained Solid I was separated by vacuum filtration with a nylon membrane (20 µL) such that the lignin dissolved in the ionic liquid (IL) was not retained in the filter. The filtered solid, which was rich in carbohydrates, was washed several times with distilled water to remove the remaining IL. Solid II (carbohydrate-free lignin) was recovered by evaporation of acetone, vacuum filtration with a nylon membrane (0.2 µL) and washing with distilled water (Figure 1).
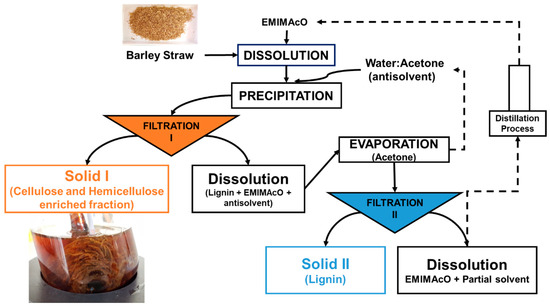
Figure 1.
The scheme of the process of dissolution of barley straw in [EMIMAcO] and subsequent precipitation with a water:acetone antisolvent mixture.
The scheme of the dissolution process of barley straw in the ionic liquid [EMIMAcO] and subsequent precipitation with mixtures of water:acetone is shown in Figure 1, which shows the methods used to obtain the two types of solids. Solid I (rich in cellulose and hemicellulose) was obtained after Filtration I, and Solid II (rich in lignin) was obtained after Filtration II from the liquid obtained in the first filtration after the evaporation of acetone.
Hydrolysis. Hydrolysis reactions were carried out batchwise in a magnetically stirred 100 mL thermostatic Teflon-lined steel Berghof reactor equipped with a pressure addition funnel [33,34,57]. In a typical run, 0.5 g of barley straw and 40 mL of water were mixed in the reactor, the suspension was heated to the reaction temperature (140 °C), and 10 mL of H2SO4 (0.2 mol/L) was added to the reactor. These are the optimal conditions obtained from previous works [33,57]. The reaction time was measured from this moment; the reaction was stopped at 5 h, and the suspension was quickly cooled. Aliquots were periodically taken from the reactor. The solution was filtered off and washed with distilled water, and finally, the solid was dried at 80 °C overnight. The amount of solid isolated was determined by weighing. The liquid was analyzed by HPLC (Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, California, USA) HPLC 1200 and 1260 series). The chromatographic separations were carried out in a Hi-PLEX H column at 60 °C using 0.6 mL/min sulfuric acid aqueous solution (0.01 M) as the mobile phase and in a Hi-Plex Pb column at 90 °C using 0.6 mL/min water solution for HPLC as the mobile phase and a refractive index detector. This method avoids the analysis of sugars (glucose and xylose) and the secondary products (5-hydroxy-methylfurfural, furfural and levulinic acid). Identification and quantification of the components was performed by comparison of retention times and using internal calibration curves by pattern compounds.
FTIR. Infrared spectra of the solids were recoded with a Jasco FT/IR-6300 spectrophotometer with KBr pellets made of 5% sample. A total of 180 cumulative scans were performed with a resolution of 4 cm−1 in the frequency range of 4000–800 cm−1 in absorption mode.
NMR.1H Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were obtained in DMSO-d6 and were recorded using a Bruker Advance at 300 MHz referenced to DMSO at 2.50 ppm.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM). SEM micrographs of untreated barley straw and barley straw pretreated with IL were collected with a Hitachi S-3000 N instrument. The samples were treated with increasing concentrations of ethanol to fix the structure and to dehydrate the samples. The samples were metallized in a Balzers SCD 004 gold sputter coater and were sputter-coated with a thin layer of gold.
X-ray diffraction (XRD). XRD profiles of samples were recorded with an X’Pert Pro PANalitical diffractometer equipped with a CuKα radiation source (λ = 0.15418 nm) and X’Celerator detector based on real-time multiple-strip (RTMS) detection. The samples were ground and placed on a stainless steel plate. The diffraction patterns were recorded in steps over a range of Bragg angles (2ϴ) between 4° and 90° at a scanning rate of 0.02° per step and an accumulation time of 50 s. Diffractograms were analyzed with X’Pert HighScore Plus software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Water:Acetone Ratio
The barley straw dissolved in [EMIMAcO] was reconstructed by the addition of an antisolvent. The antisolvents employed were mixtures of water:acetone (W:A) with different mass ratios: 1:0, 2:1, 1.5:1, 1:1, 1:1.5, 1:2 and 0:1. The solid precipitated after the addition of the solvent was labeled “Solid I”, and a second solid was obtained after the evaporation of acetone, labeled “Solid II”. To evaluate the fractionation ability of the antisolvent employed, the mass of each solid was measured and compared with the theoretical amount that corresponds in Solid I to the sum of cellulose and hemicellulose and in Solid II to lignin. In addition, the recovered in each solid and total biomass was calculated by comparing the sum of the masses recovered in the two filtrations and the sum of cellulose, lignin and hemicellulose present in the biomass added at the beginning of the experiment. The results obtained from precipitation with the different antisolvents are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Mass balance of matter based on dry barley straw after precipitating the biomass with different water:acetone antisolvent mixtures. The barley straw samples were dissolved in [EMIMAcO]) at 105 °C for 3.5 h.
The total recovered biomass was high, approximately 90%, in all cases, respect the sum of hemicellulose + cellulose + lignin present in the starting barley straw. In Solid II the recovery is between 70 and 80% while in Solid II is 10–17%, depending on the mixture of antisolvent employed. This effect was also observed in the % expected which depends also on the mixture employed. When pure solvent (water or acetone) was employed, only Solid I was obtained, which implies no separation of components by selective precipitation. However, the properties of the obtained solid were quite different depending on the pure solvent employed. When water was used as an antisolvent, Solid I was easy to manipulate, wash and filter, but in the case of acetone, the solid obtained was very difficult to handle, wash and filter. However, when the antisolvent was a mixture of water:acetone, the presence of two solids (Solid I and Solid II) was observed (Table 2). In all cases, the amount of Solid I was higher than the theoretical sum of cellulose and hemicellulose (>100%), and the amount of Solid II was lower than the theoretical amount of lignin (<100%). The values of mass recovered indicate that in Solid I, some lignin was incorporated with the cellulose and hemicellulose. However, these amounts changed with the W:A ratio The most interesting results were obtained for the ratio 1:1, where both Solid I and Solid II were close to 100%. Based on these results, the optimal antisolvent used was the W:A = 1:1 mixture. However, these mass balance calculations do not guarantee that Solid I is a cellulose- and hemicellulose-rich phase and Solid II is lignin or a lignin-rich phase. For this reason, we proceeded to analyze each of the solids obtained.
3.2. FTIR Analysis
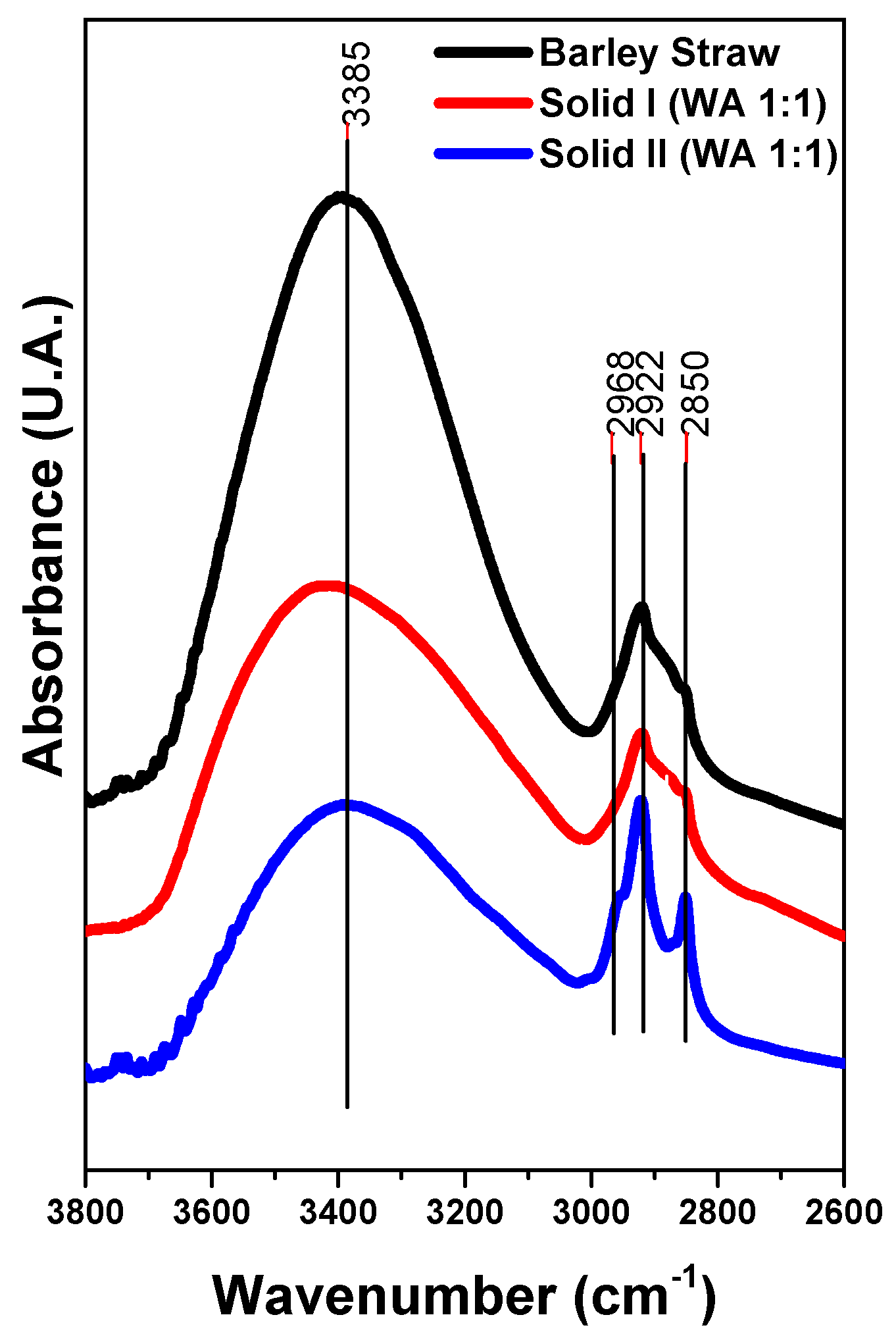
FTIR spectroscopy has been extensively employed to study the functional groups of cellulose, xylan-like hemicellulose and lignin in the literature. Changes in the composition of Solid I and Solid II were monitored using FTIR. The spectra of Solid I and Solid II are very different. Figure 2 demonstrates that the IR spectra of the raw barley straw, Solid I and Solid II show a broad and intense band in the region of 3800–2600 cm−1, which is associated with OH groups and their interactions with water molecules via H-bridging bonds [59]. In addition, a set of overlapping peaks appears between 3000 and 2800 cm−1 due to the stretching vibration modes of C-H bonds. The relative intensity of these peaks increases in Solid II with respect to the spectra of raw barley straw and Solid I, indicating an enrichment of lignin, the component containing a greater proportion of C-H bonds than O-H groups.
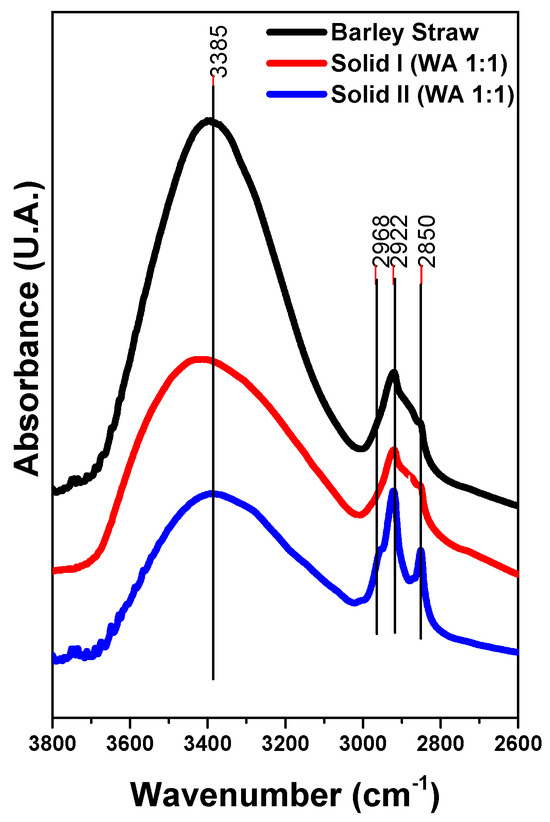
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of Solid I, Solid II and raw barley straw.
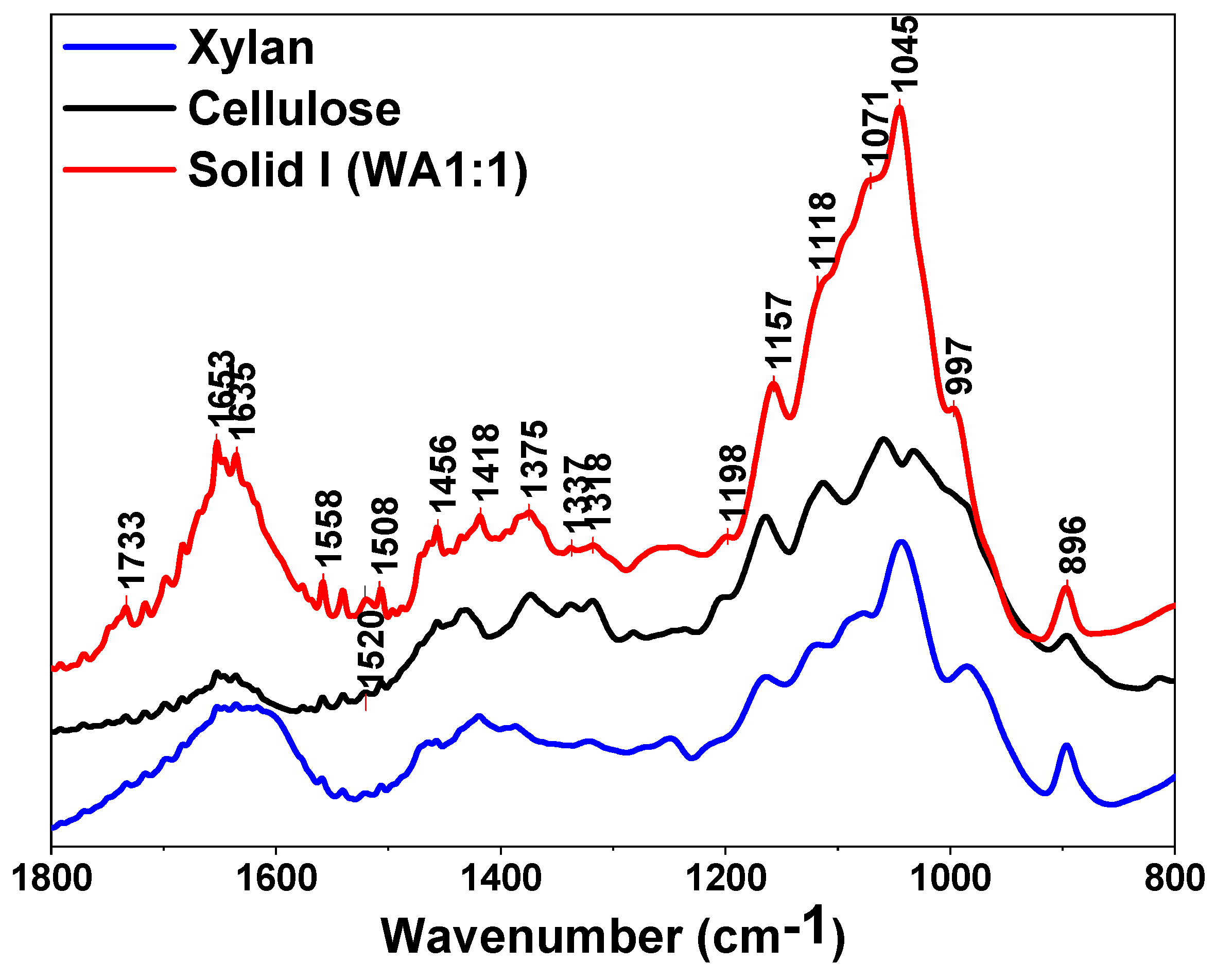
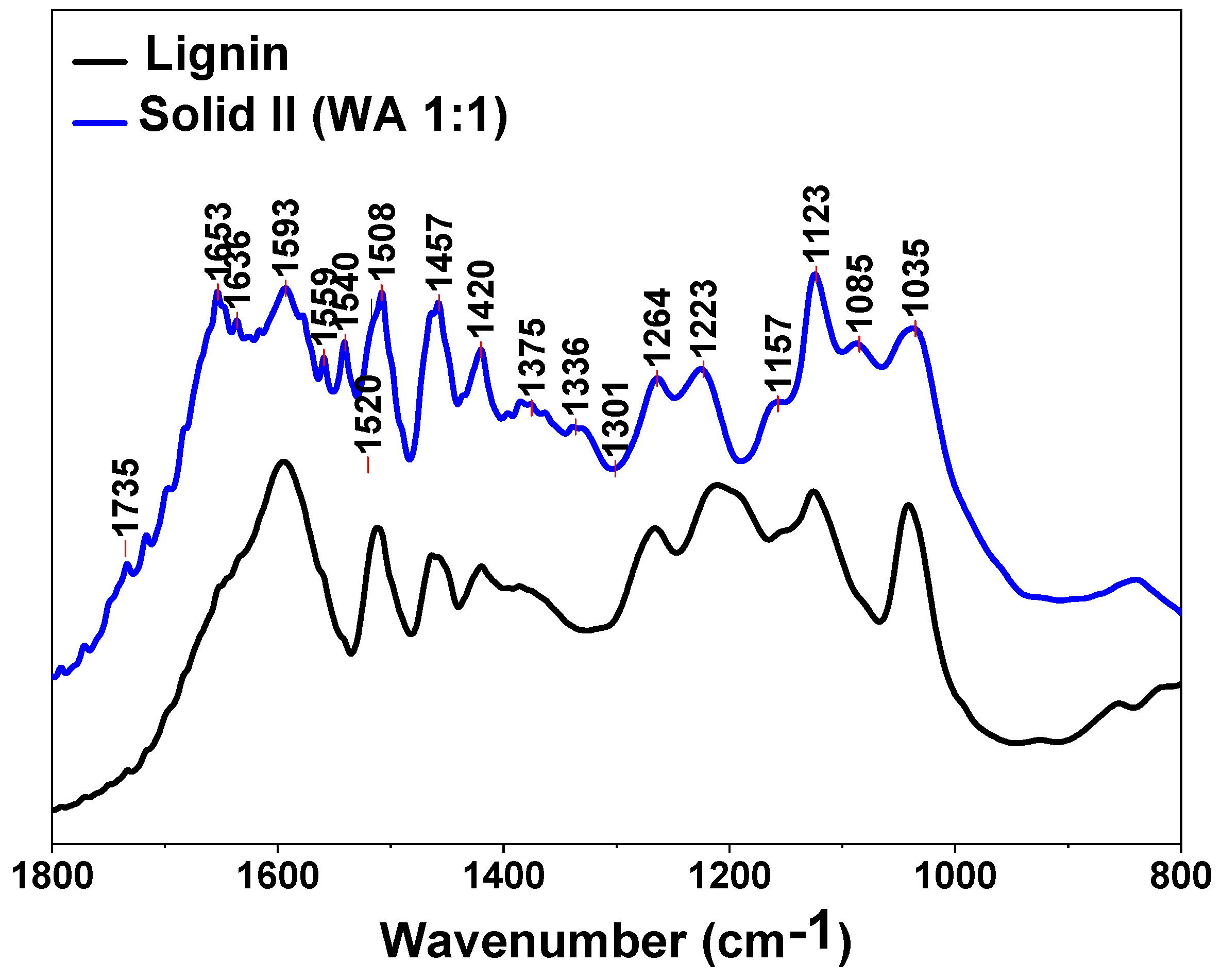
The spectra of Solid I, Solid II and references of commercial cellulose, xylan and lignin are displayed in the region between 1800 and 800 cm−1 in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. The bands are assigned to the characteristic bending or stretching modes of different specific groups of lignocellulosic biomass in the “fingerprint” region. The peak structure of this region is quite complicated, but the peaks can be assigned as follows [60,61,62,63]: 1735 cm−1 indicates unconjugated C=O in xylans (hemicellulose); 1653 cm−1 indicates absorbed O-H and conjugated C-O in lignin; 1593 cm−1 and 1508 cm−1 indicate C=C skeletal vibrations (aromatic ring) in lignin; 1457 cm−1 and 1420 cm−1 indicate C-H deformation in lignin and carbohydrates; 1375 cm−1 indicates C-H deformation in cellulose and hemicellulose; 1336 cm−1 and 1318 cm−1 indicate C-H vibration in cellulose and C-O vibration in syringyl derivatives; 1264 cm−1 indicates guaiacyl ring breathing, C-O stretching in lignin and C-O linkages in guaiacyl aromatic methoxyl groups; 1157 cm−1 indicates C-O-C vibration in cellulose and hemicellulose; 1118 cm−1 indicates aromatic skeletal vibration; 1085 and 1035 cm−1 indicate C-O deformation in aliphatic ether and guaiacyl aromatic methoxyl groups, respectively; 1048 cm−1 indicates C-O stretching in cellulose and hemicellulose; and 896 cm−1 indicates C-H deformation in cellulose [60,61,62,63].
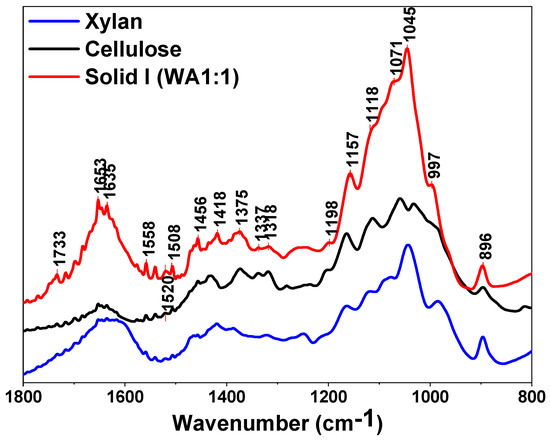
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of Solid I, commercial cellulose and xylan.
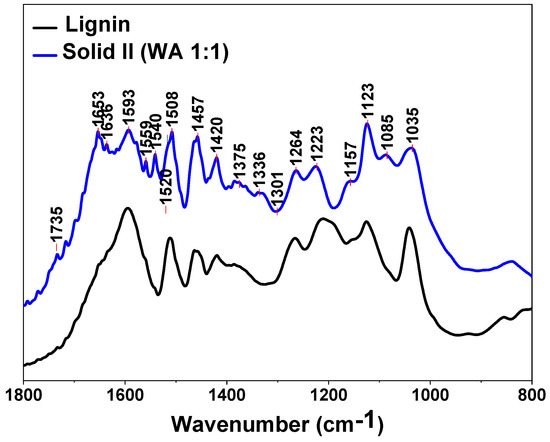
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra of Solid II and commercial lignin.
The presence of a peak at 1508 cm−1 is usually taken as an indication of the presence of lignin, especially when a weak band at 1520 cm−1 is present [63] (Figure 4), whereas the 1735, 1157, 1048 and 897 cm−1 peaks are characteristic of polysaccharides [60,63]. There are some weak bands typical of lignin in Figure 4, confirming that low amounts of lignin are retained in Solid I, as can be deduced from the mass balance data (Table 2). However, no peaks attributed to polysaccharides are evident in the spectrum of Solid II (Figure 4). In summary, the spectrum of Solid I is similar to that corresponding to the pure cellulose reference, whereas the spectrum of Solid II is similar to that corresponding to lignin. These data indicate that selective precipitation occurred, except for small amounts of lignin incorporated into Solid I.
3.3. NMR Analysis
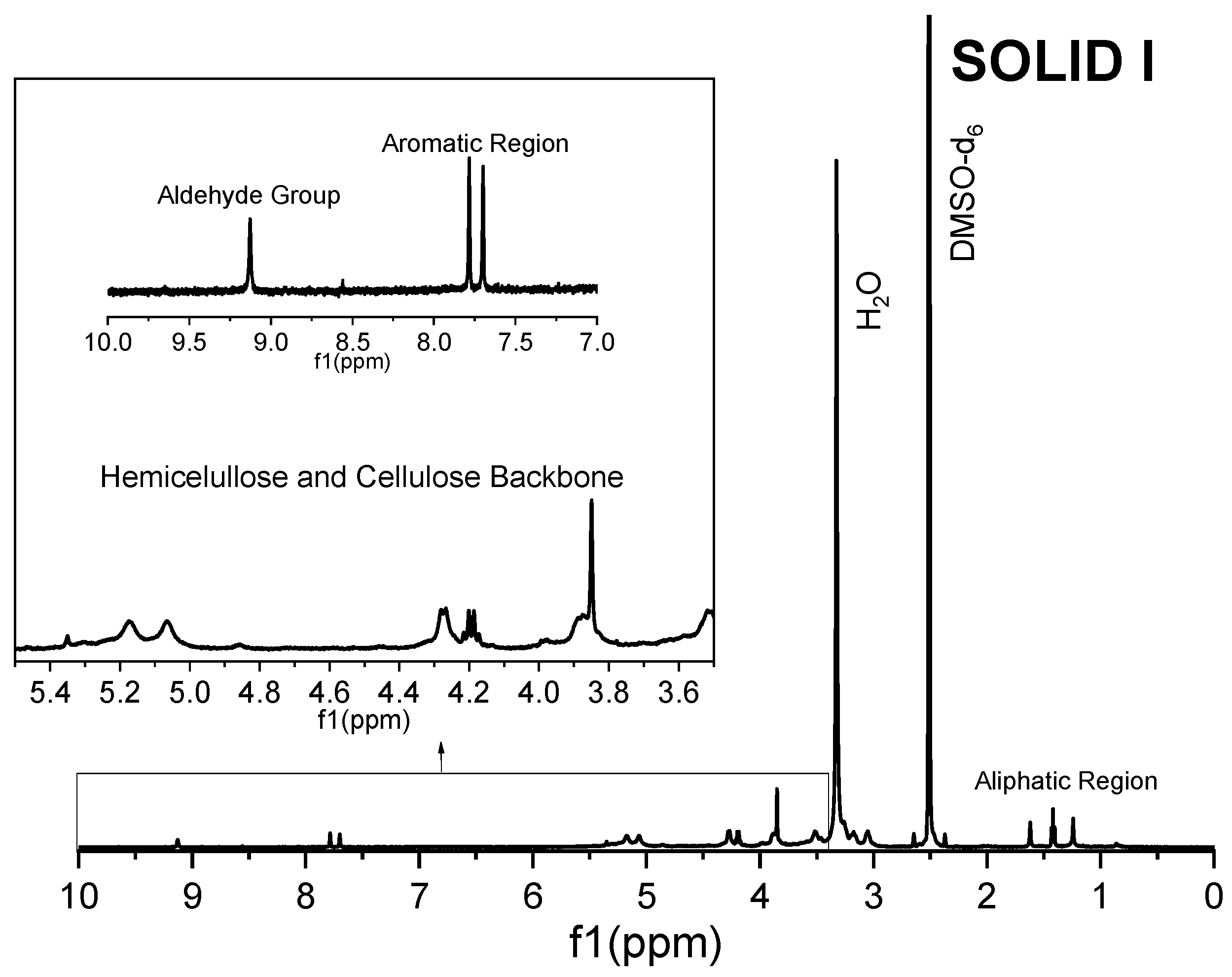
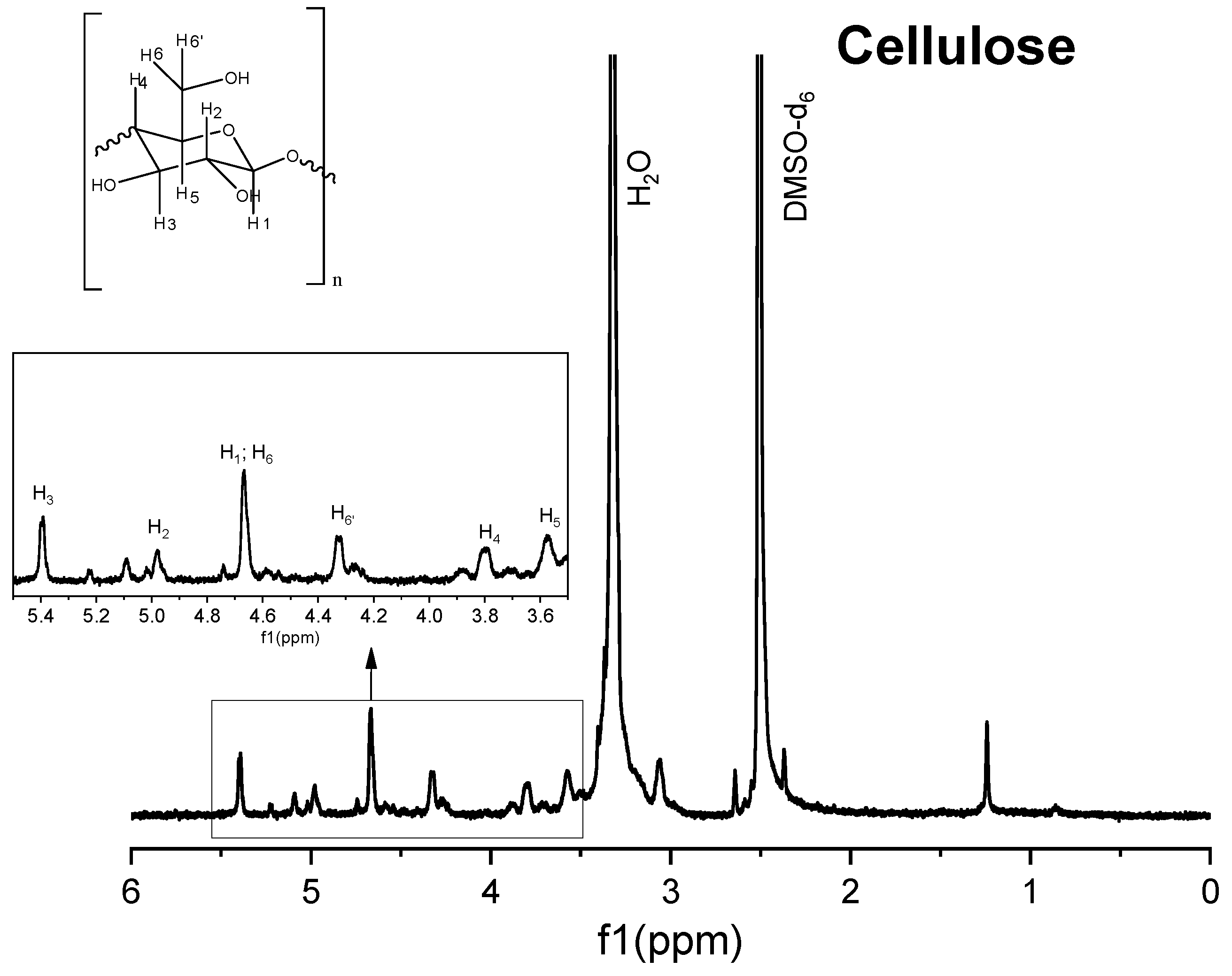
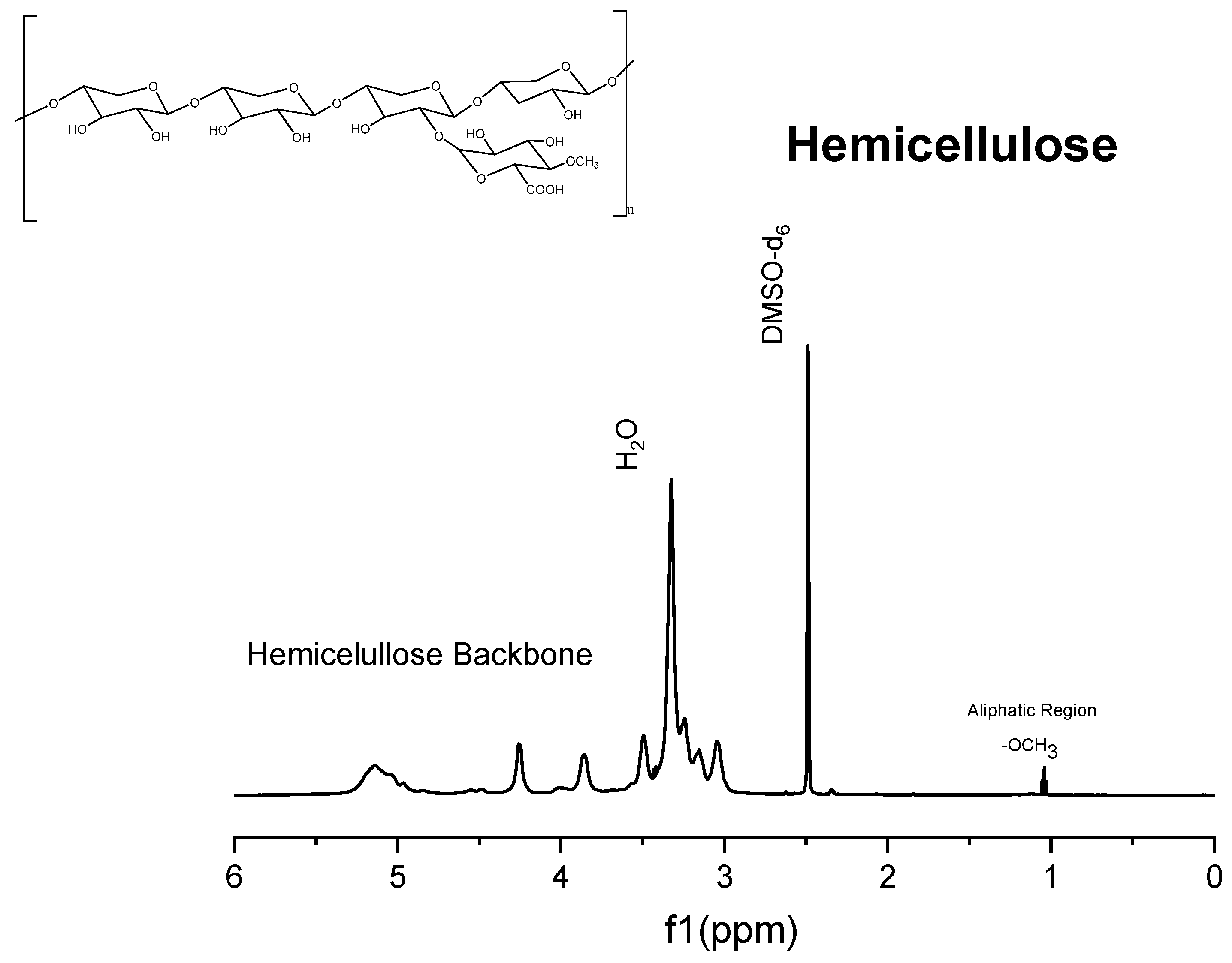
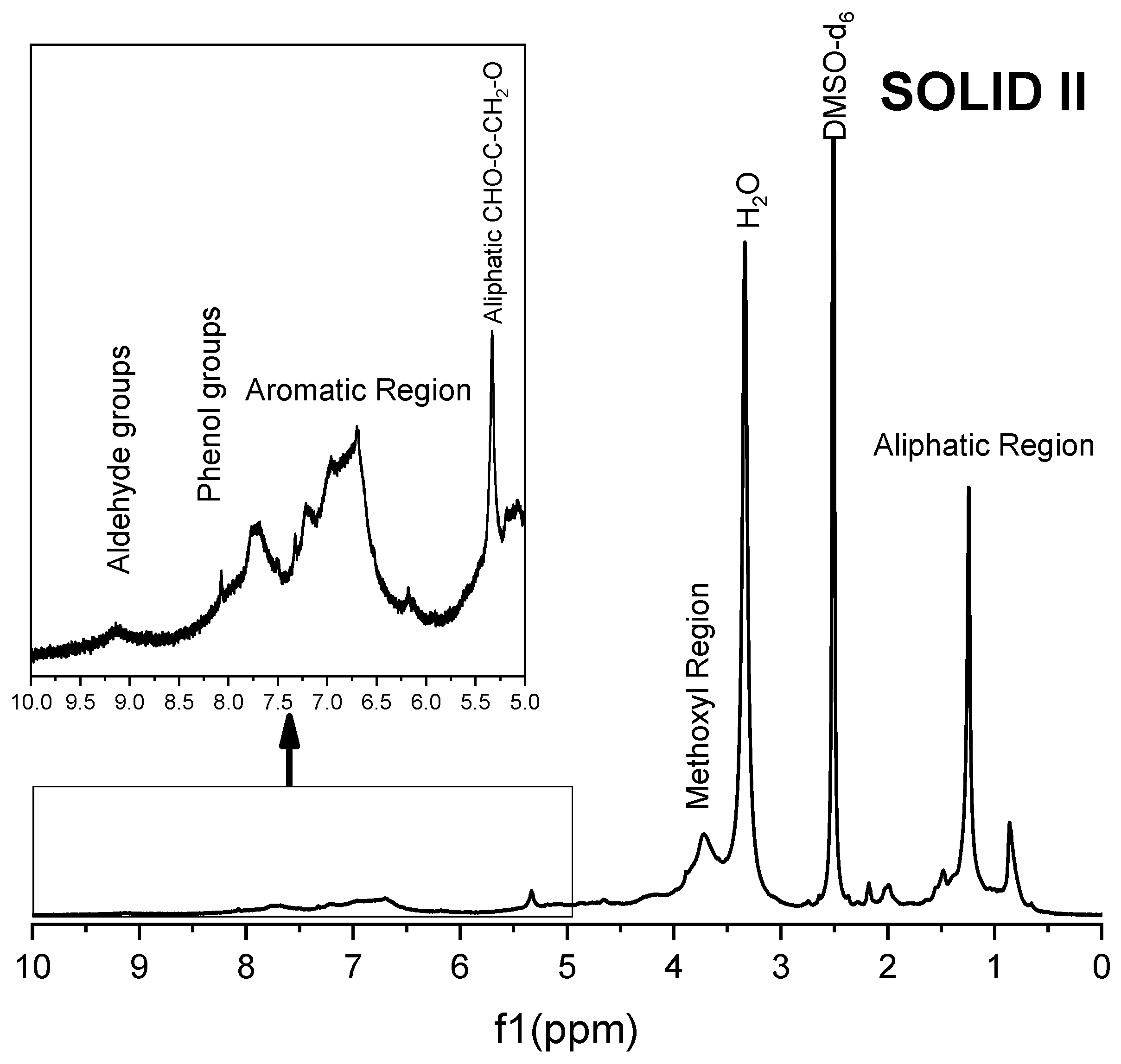
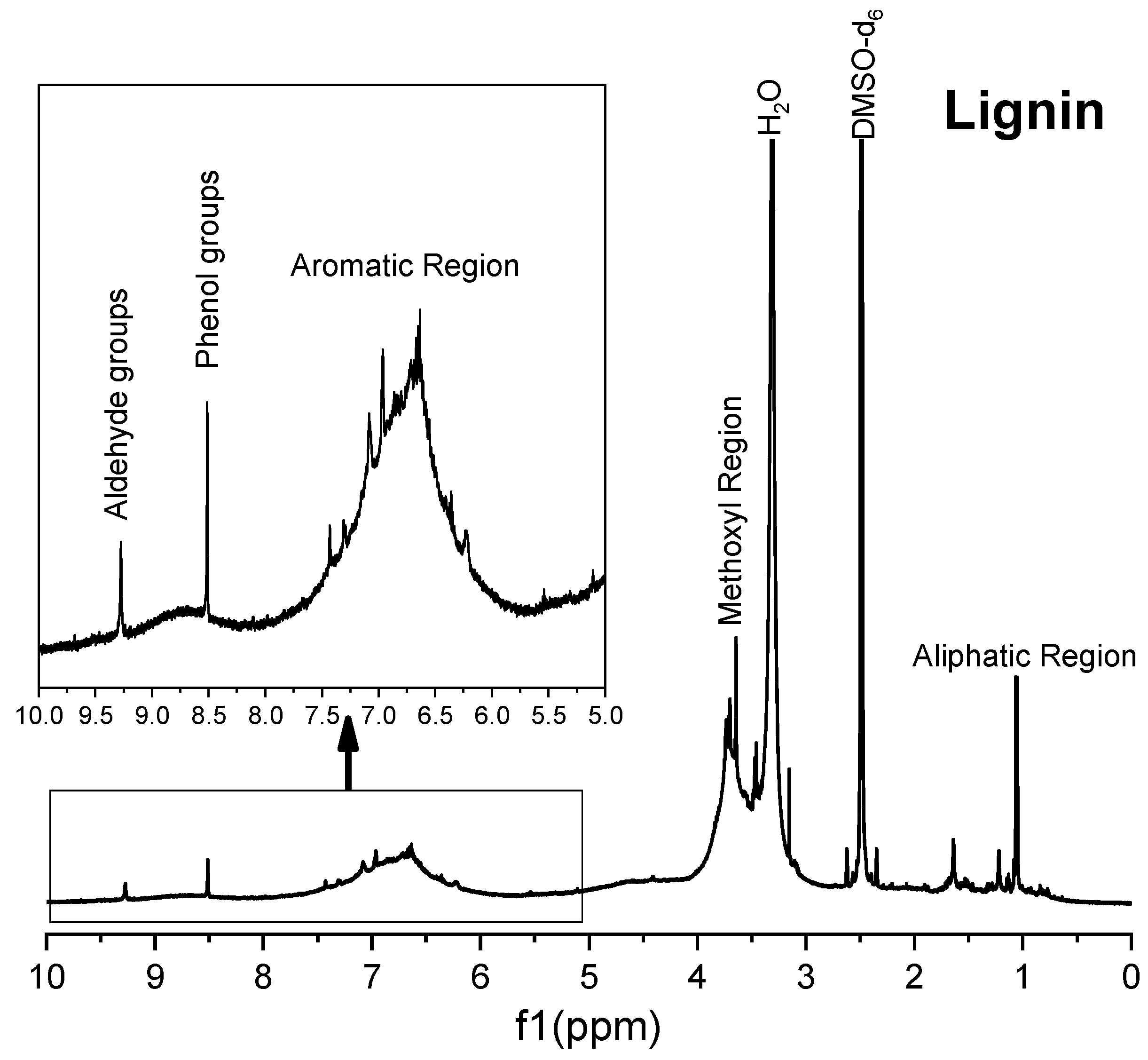
The Solid I and Solid II samples were analyzed by 1H magnetic resonance in DMSO-d6 solution and were compared with commercial reference materials of cellulose, xylans and lignin (Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9). The spectra of Solid I and Solid II are very different.
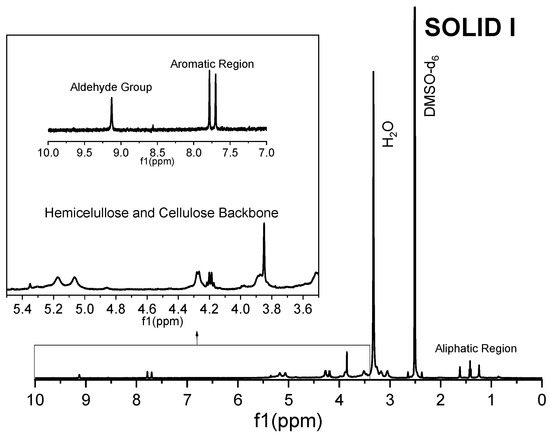
Figure 5.
1H NMR spectrum of Solid I.
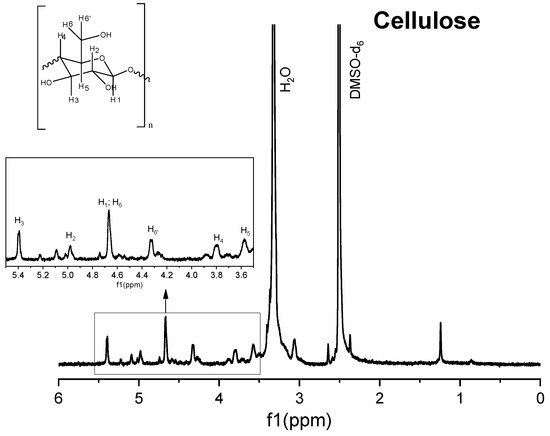
Figure 6.
1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum of commercial cellulose.
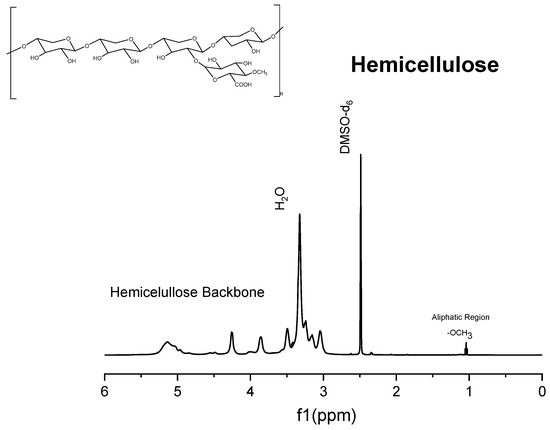
Figure 7.
1H NMR spectrum of commercial xylans.
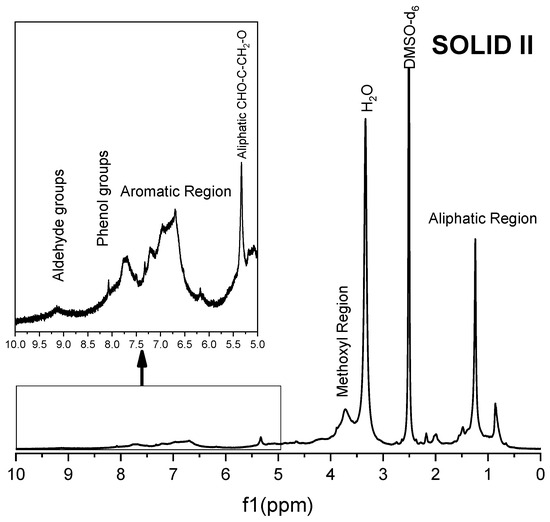
Figure 8.
1H NMR spectra of Solid II.
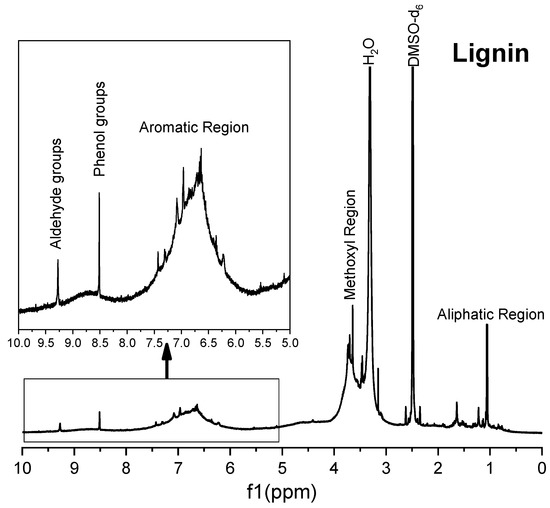
Figure 9.
1H NMR spectrum of commercial lignin.
The 1H spectrum of Solid I (Figure 5), obtained after the first filtration, was compared with the reference 1H spectra of commercial samples of cellulose and hemicellulose (Figure 6 and Figure 7). A combination of the structural skeletons of both sugars in the range of 5.5–3.5 ppm is observed [64,65]. This observation indicates that Solid I is mainly a combination of carbohydrates; however, in the spectrum of Solid I, peaks corresponding to aromatic rings at 7.8 and 7.7 ppm and aldehyde at 9.0 ppm, associated with lignin, were observed. These data are consistent with the mass balance, which indicated that the mass recovered in the first filtration was slightly higher than expected. This analysis confirms that a small amount of lignin was present in Solid I.
The 1H spectra of Solid II (Figure 8) and commercial lignin (Figure 9) are quite similar. In both spectra, signals appear at 9.2 ppm, corresponding to the strong shielding among guaiacyl groups, although a greater intensity is observed in the 1H spectrum of Solid II than that of the reference lignin. Methoxyl group protons are in the region of 4.0–3.4 ppm, very close to the water protons of aldehyde groups. signals in the region of 8.5–8.0 ppm correspond to the phenolic hydroxyl protons of lignin, and in the range of 8.0–6.0, the observed proton signals belong to the aromatic rings and vinyl protons of syringyl and guaiacyl. In the range of 6.0–4.0 ppm, signals of protons belonging to α, β, and γ saturated carbons of β-O-4, β-5 and β-β linkages appear because the lignin and Solid II are not completely dry and the DMSO-d6 is not 100% pure [66,67]. Finally, in the range of 2.0–1.0 ppm, the signals correspond to CH2, the aliphatic protons belonging to methyl or methylene groups, while the signals between 1.0 and 0.8 ppm were attributed to the protons in saturated aliphatic chains in lignin [66]. In summary, Solid II is essentially lignin. These observations are in agreement with the IR characterization: Solid I is a carbohydrate-rich solid with a small amount of lignin, and Solid II is essentially lignin.
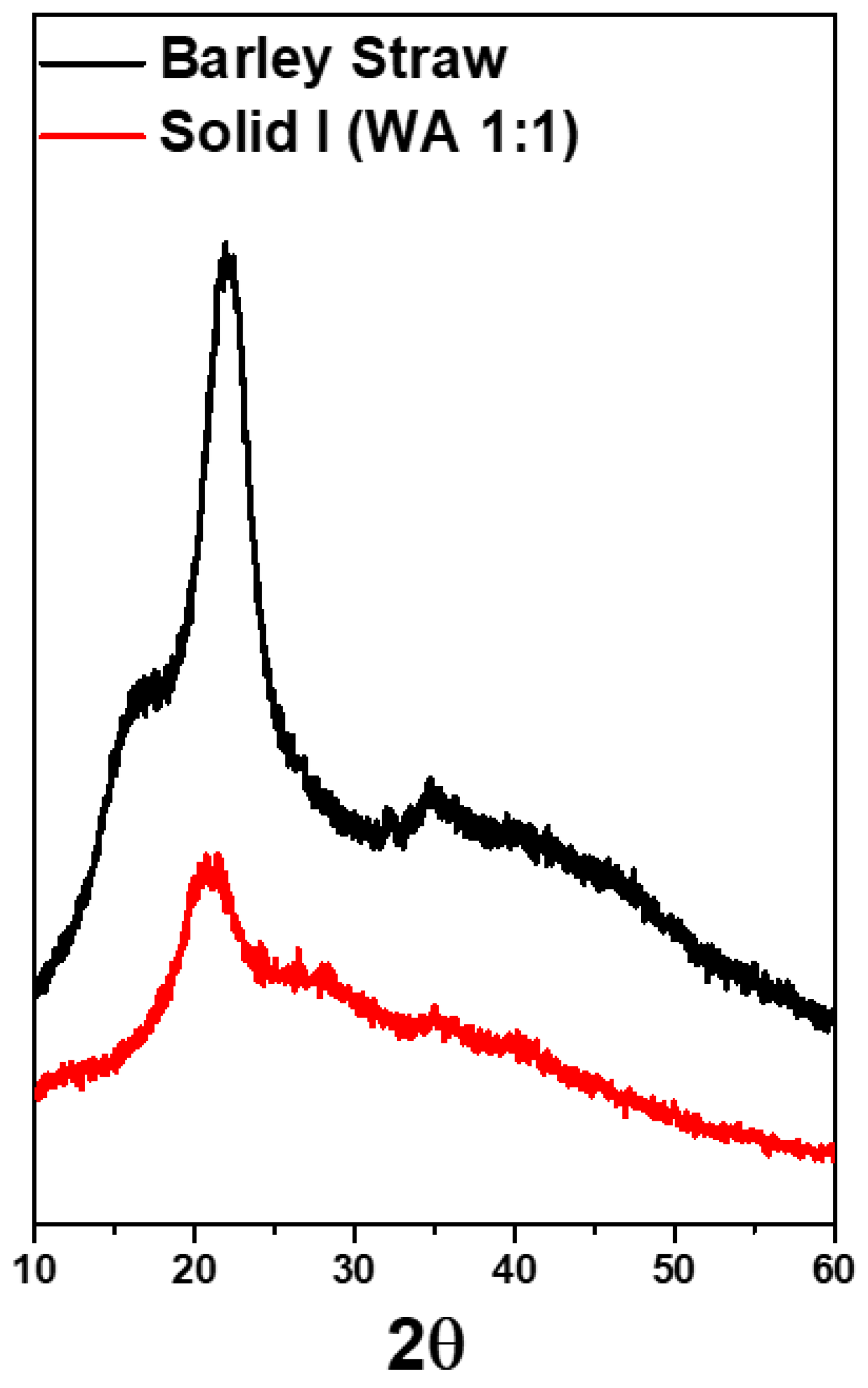
3.4. X-ray Diffraction
X-ray diffraction was employed to analyze the crystallinity of the materials. XRD profiles of the original barley straw and Solid I are depicted in Figure 10. The diffractogram of the original barley straw shows peaks typical of the crystalline structure of cellulose [57,68]. A prominent peak at 23° corresponds to the (200) reflection, and a wide peak from 15–17° represents the combination of the two reflections corresponding to (110) and (11). The pattern of Solid I, obtained after treating barley straw and selective precipitation, showed that the crystallinity was lost because these reflections were not found; the only peak found was at 21°. In this sample, almost no diffraction peaks are observed, indicating the nearly total disappearance of its crystallinity. This study indicates that the original barley straw has a certain crystallinity that is lost after [EMIMAcO] treatment. Other authors have also reported this behavior in different samples of lignocellulosic biomass and cellulose when the samples were treated with ionic liquids [33,55].
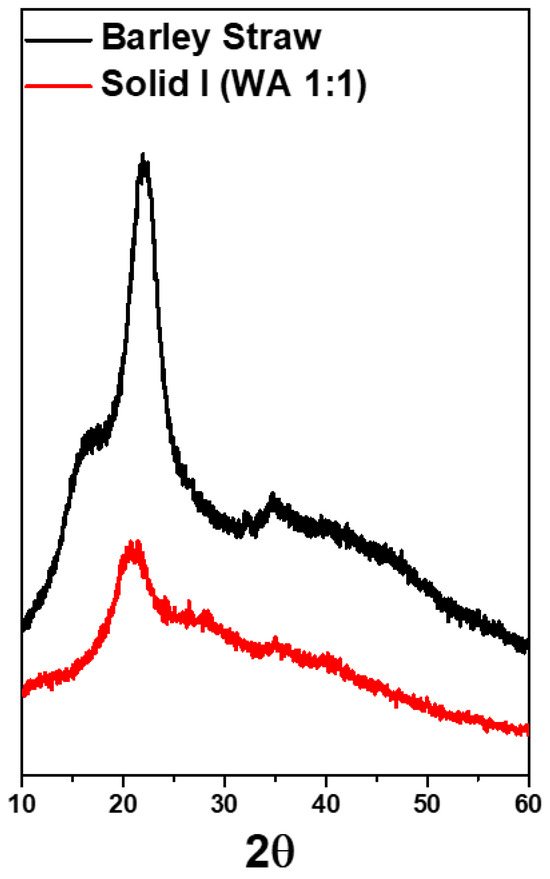
Figure 10.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra of raw barley straw and Solid I.
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
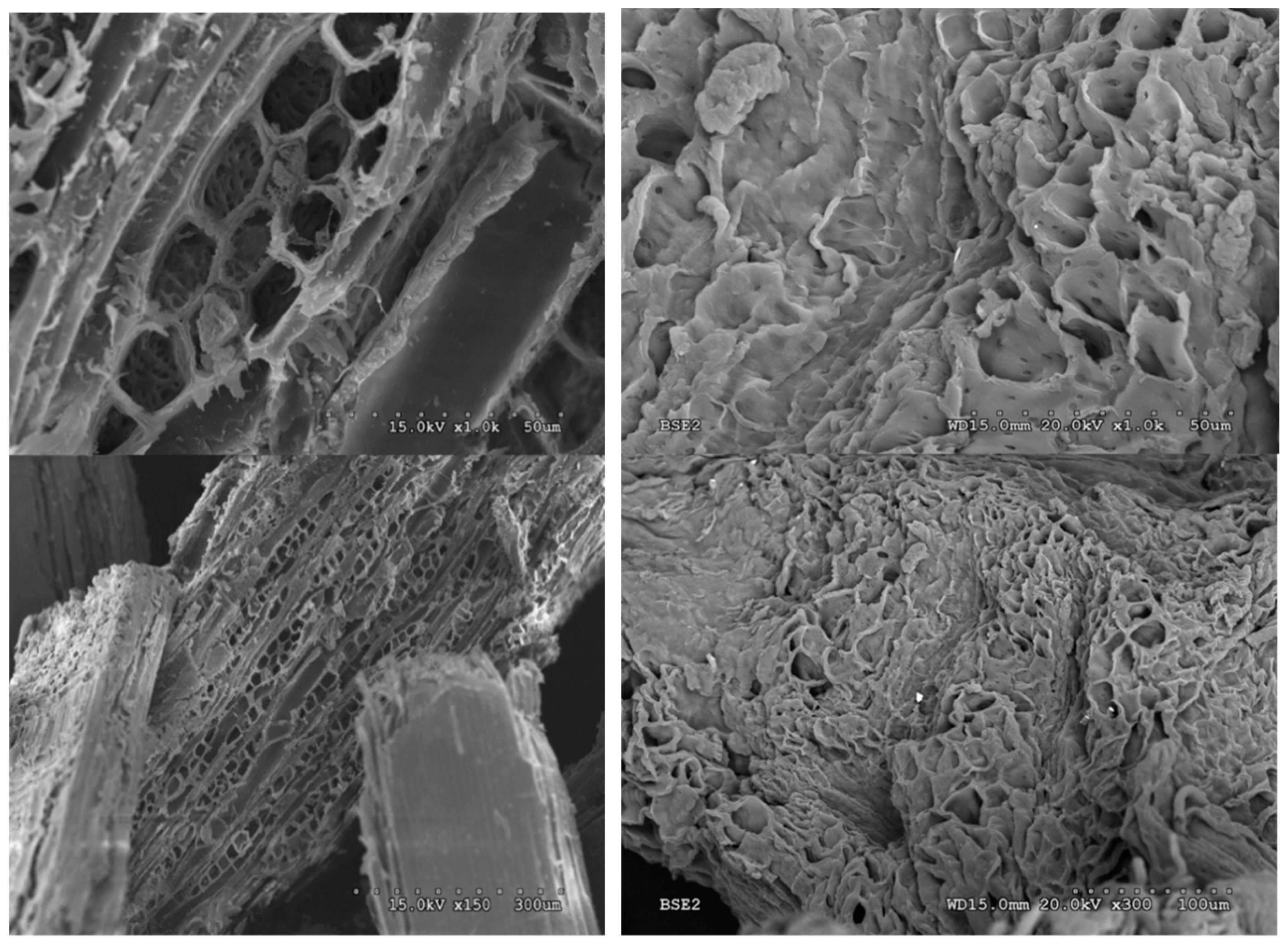
Solid I and raw barley straw were analyzed by SEM. The micrographs show a large difference between the starting sample and the precipitated sample (Figure 11). The sample of original barley straw (Figure 11) shows a regular structure typical of the vascularization of straw. However, the Solid I sample (Figure 11) lost practically all of its vascular structure. In addition, the images with higher magnification indicate that the treated sample was more porous than the original. These morphological changes are compatible with the structural changes observed in X-ray diffraction. The structure of the starting biomass was modified, giving rise to a more amorphous structure, which favors accessibility to the biomass components, making the material easier to transform. Destruction of the structure of lignocellulosic biomass has been observed in previous works [47] by other authors [69] and with other pretreatments [70].
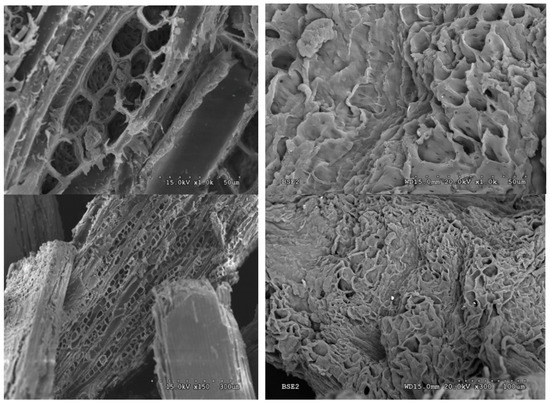
Figure 11.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of raw barley straw (left) and barley straw treated with [EMIMAcO] (Solid I, WA 1:1) (right).
3.6. Catalytic Activity
Original barley straw, cellulose and Solid I were subjected to hydrolysis in water media at 140 °C with 0.2 mol/L H2SO4. In Table 3, a comparison of the conversion values obtained with Solid I, the original barley straw and Avicel cellulose without treatment are shown. The conversion values were calculated by the weight difference between the sample initially added to the reaction and the sample obtained after reaction. The conversion values were different among the three samples studied; the lowest value was obtained for the cellulose sample, while the conversion values were higher for the other two samples. This trend is expected because the most complicated material to hydrolyze is cellulose, and samples of untreated barley straw only contain approximately 31% cellulose (Table 3). In Solid I, impurities of lignin in the sample were not taken into account to avoid complicating the calculations and reduce error since the amount of lignin in the sample was very small. The conversion of 90% in Solid I appears to be slightly high.

Table 3.
Results of conversion obtained after hydrolysis of untreated cellulose, untreated barley straw and barley straw treated (Solid I) with [EMIMAcO]. Reaction conditions: H2SO4 (0.2 mol/L), 140 °C and 5 h.
However, the conversion data are not conclusive because the hydrolysis schemes of cellulose and hemicellulose are complicated by consecutive reactions and can lead to the formation of humics and other products. For this reason, it is interesting to analyze the yields of the main products derived from glucans, glucose and levulinic acid, and the main products of xylans, xylose and furfural. It should be noted that under these reaction conditions and in aqueous media in the presence of an acid, the concentration of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural is very small because it easily transforms into levulinic acid.
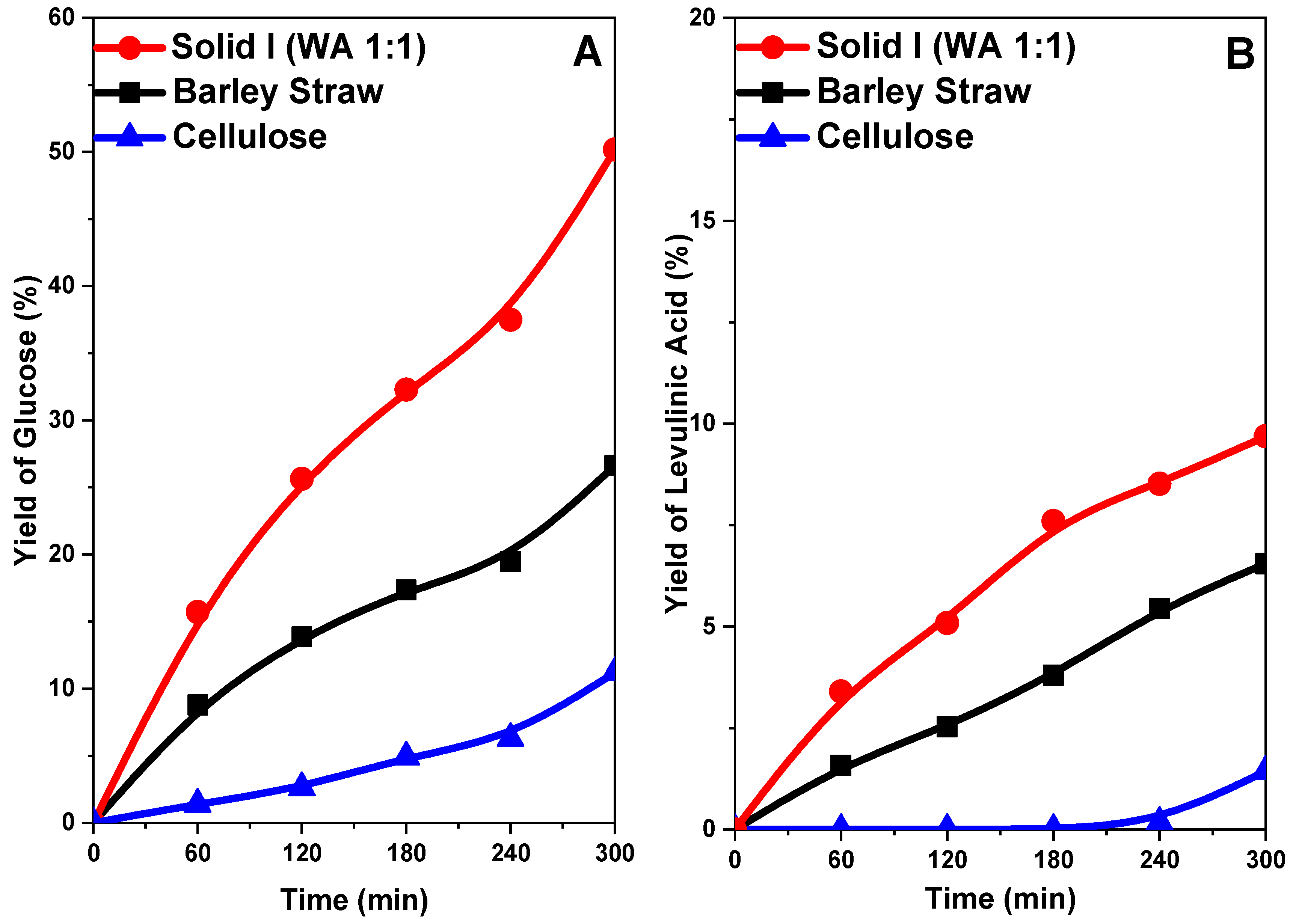
In Figure 12A, the yield of glucose decreases in the following order: Solid I > original barley straw > cellulose. Cellulose gave a very low yield of glucose (11%) after 5 h of reaction. The barley straw sample gave a higher yield of approximately 30%. However, with the Solid I sample, a yield of 65% was reached, which substantially affects acid hydrolysis to sugars. These glucose yield values follow an order inverse to that of sample crystallinity, as shown in Figure 10. This is because greater crystallinity (order) hinders the breakdown of the ß(1→4)-d-glucosidic bonds of cellulose because they are less accessible. However, treatment that reduces the crystallinity and increases the accessibility of said bonds favors hydrolysis, giving rise to higher yields of glucose [33,34,46,71].
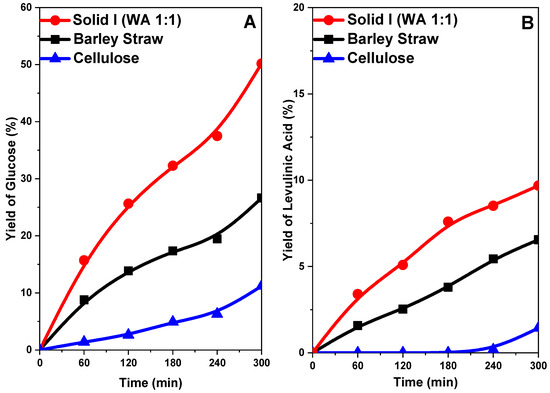
Figure 12.
Yield of glucose (A) and levulinic acid (B) from the hydrolysis of cellulose, untreated barley straw and barley straw treated (Solid I) with [EMIMAcO].
The yield of levulinic acid follows a profile very similar to that of glucose (Figure 12B) because levulinic acid is a byproduct of glucose; therefore, at higher glucose concentrations, more levulinic acid can be formed, but in all cases, the yield of levulinic acid is low with respect to that of glucose.
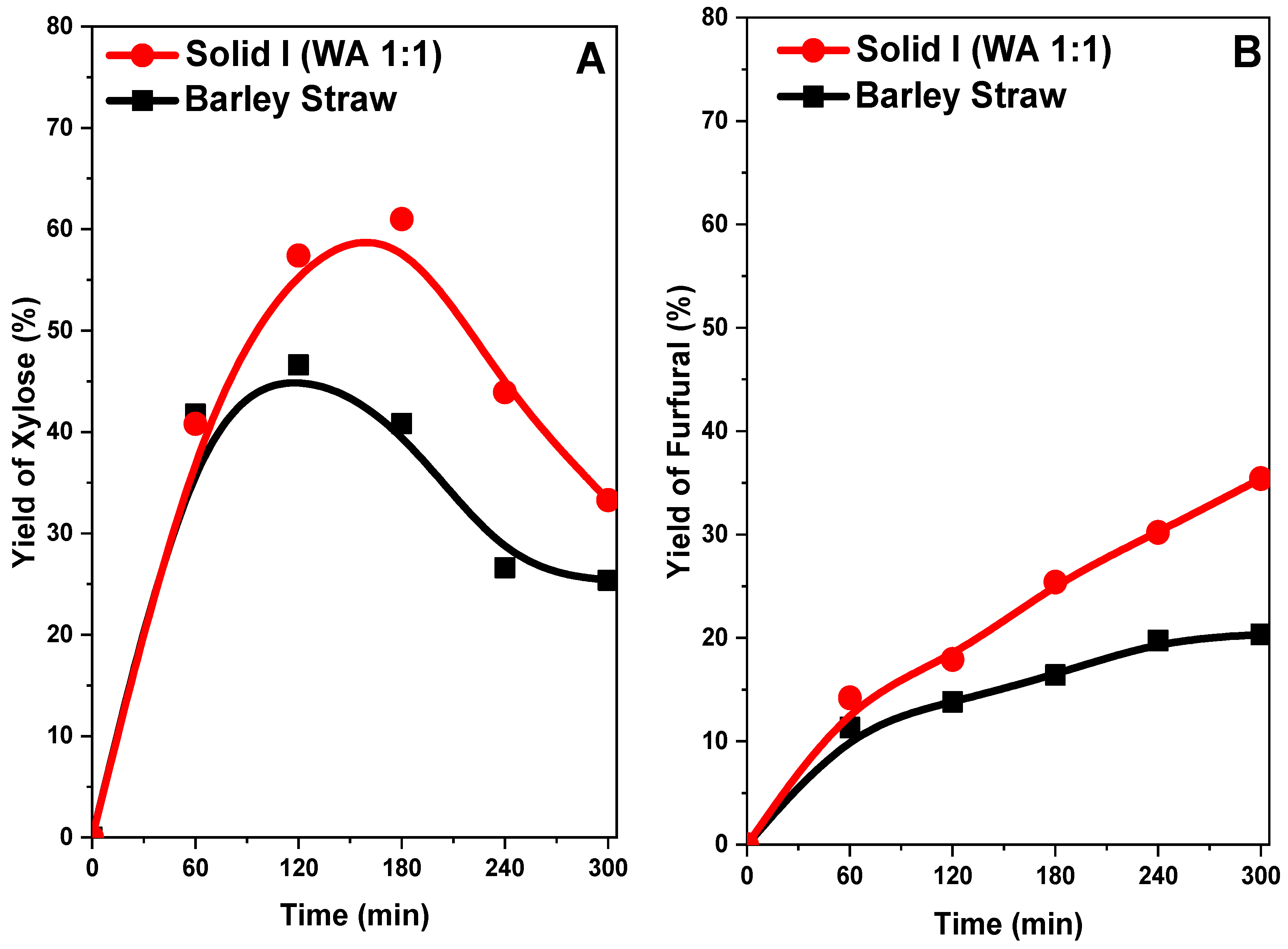
We compared the raw barley straw sample without treatment and Solid I in acid hydrolysis to obtain the concentration curves of the compounds xylose and furfural (Figure 13A,B) in both cases. The yield of xylose increased quickly with reaction time, reaching a maximum in both cases (Figure 13A). At 2 h, the barley straw obtained a yield of 45%, and Solid I achieved a yield of 58%, but the yield of Solid I reached a maximum of 60% at 3 h and then decreased until the end of the reaction, at which point the yield of xylose was 25% in barley straw and 35% in Solid I. This fact indicates that the pretreated sample (Solid I) can more easily hydrolyze hemicellulose, obtaining a higher yield of xylose more quickly, although the differences are less evident than with glucose (Figure 12A). This is because hemicellulose (polymer of origin of xylose) is much easier to hydrolyze than glucose and, therefore, even without treatment, hydrolysis can be effectively performed. In addition, presenting behavior typical of an intermediate reaction compound in consecutive reactions, the source of the xylose is consumed when in contact with the acid catalyst in the medium; then, dehydration takes place, and the material is transformed into furfural (Figure 13B).
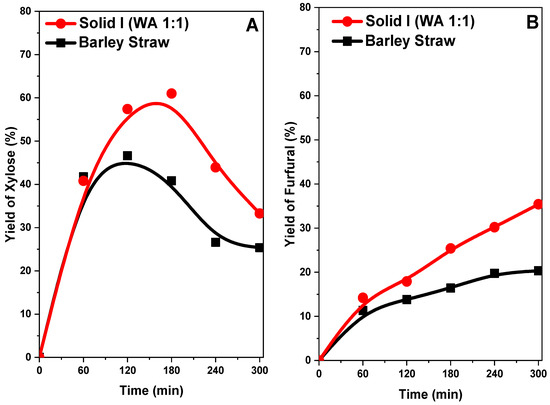
Figure 13.
Yields of xylose (A) and furfural (B) of barley straw treated and not treated with [EMIMAcO]
The furfural yield profiles indicate that the yield increases with reaction time, reaching, 36% with Solid I and 20% with untreated barley straw at 5 h. The Solid I sample had a higher concentration because the xylose concentration was higher than in the untreated sample.
In the hydrolysis process, the polymeric chains of cellulose and hemicellulose become smaller, and some of them become soluble in water; therefore, the reaction medium not only contains monomers such as glucose or xylose but can also contain oligomers with several units that are soluble. For this reason, we analyzed the final reaction samples and calculated the total reducing sugars (TRS) content, including the sugars in monomeric and oligomeric forms. The obtained results are shown in Table 4. The values of TRS are clearly higher than those obtained by the sum of sugars measured with HPLC (monomeric), which indicates that in the reaction medium, there is an appreciable amount of oligomeric sugars; this discrepancy is more evident for straw samples (original and Solid I). The yield to sugars decreases according to the order Solid I > original barley straw > cellulose, which coincides with the conversion values described in Table 3. However, the selectivity of total reducing sugars does not follow this trend (Table 4). It is clear that the selectivity of TRS is much higher for the Solid I sample than the untreated samples of cellulose and barley straw. The combination of high conversion and high selectivity in the Solid I sample produced one of the highest sugar yields in acid catalyzed hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass among those described in the literature [72,73,74,75,76,77,78].

Table 4.
Total reducing sugars (TRS) measurements obtained from the samples after the hydrolysis reaction.
4. Conclusions
Dissolution of barley straw in [EMIMAcO] and subsequent precipitation with water:acetone mixtures can be employed in the fragmentation of the main components. A water:acetone ratio of 1:1 is optimal for the efficient separation of carbohydrates with respect to lignin, with a high biomass recovery efficiency of approximately 90% with respect to the initial sample. The first precipitate (Solid I) is clearly enriched in carbohydrates (cellulose and hemicellulose), and the second precipitate is a lignin-rich solid, as evidenced by IR and NMR. The enriched carbohydrate solid (Solid I) presented large changes in structure (SEM) and crystallinity (XRD) with respect to those of the original barley straw. This carbohydrate-rich fraction is easier to hydrolyze, with a yield of total reducing sugars that is among the highest described in the literature.
Author Contributions
Experimental work: M.L.-S. and S.M.-d.; supervision: S.M.-d. and J.M.C.-M.; writing—original draft preparation: M.L.-S. and S.M.-d.; writing—review and editing: J.M.C.-M. and J.L.G.F.
Funding
This research was funded by Comunidad de Madrid (Spain) and ERDF (European Regional Development Fund), grant numbers S2013/MAE-2882 (RESTOENE-2-CM), S2018/EMT-4344 (BIOTRES-CM) and CSIC (201880E029). M.L.-S. acknowledges the support of the European Social Fund and Community of Madrid for her contract.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.F.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Nita, V. The role of biomass and bioenergy in a future bioeconomy: Policies and facts. Environ. Dev. 2015, 15, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, J. Sustainable Biofuels: Prospects and Challenge; The Royal Society: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scheller, H.V.; Ulvskov, P. Hemicelluloses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, E.M. Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature 2008, 454, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review of analytical methods in pretreatment of lignocelluloses: Composition, imaging, and crystallinity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, A.C. Cellulose: The structure slowly unravels. Cellulose 1997, 4, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, A. The hydrolysis of cellulose and its relation to structure. Part 2. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1958, 54, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, A. The hydrolysis of cellulose and its relation to structure. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1957, 53, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.; Muñoz-Dorado, J.; Rubia, T.D.L.; Martı´nez, J. Biodegradation and biological treatments of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: An overview. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvira, P.; Tomas-Pejo, E.; Ballesteros, M.; Negro, M.J. Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4851–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakzeski, J.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Jongerius, A.L.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The Catalytic Valorization of Lignin for the Production of Renewable Chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, N.; Wyman, C.; Dale, B.; Elander, R.; Lee, Y.Y.; Holtzapple, M.; Ladisch, M. Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, A.T.W.M.; Zeeman, G. Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Pan, Z.P.; Zhang, R.H. Overview of biomass pretreatment for cellulosic ethanol production. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2009, 2, 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- FitzPatrick, M.; Champagne, P.; Cunningham, M.F.; Whitney, R.A. A biorefinery processing perspective: Treatment of lignocellulosic materials for the production of value-added products. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8915–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on analysis in pretreatment of lignocelluloses: Degree of polymerization, adsorption/desorption, and accessibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, J.; Negro, M.; Manzanares, P.; Ballesteros, I.; Chamorro, M.; Sáez, F.; Ballesteros, M.; Moreno, A. A Sequential Steam Explosion and Reactive Extrusion Pretreatment for Lignocellulosic Biomass Conversion within a Fermentation-Based Biorefinery Perspective. Fermentation 2017, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipponen, M.H.; Pihlajaniemi, V.; Pastinen, O.; Laakso, S. Reduction of surface area of lignin improves enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose from hydrothermally pretreated wheat straw. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36591–36596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlajaniemi, V.; Sipponen, M.H.; Liimatainen, H.; Sirvio, J.A.; Nyyssola, A.; Laakso, S. Weighing the factors behind enzymatic hydrolyzability of pretreated lignocellulose. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, B.; Mu, X. Review of Alkali-Based Pretreatment to Enhance Enzymatic Saccharification for Lignocellulosic Biomass Conversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8691–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Dale, B.E. Global potential bioethanol production from wasted crops and crop residues. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Verma, J.P. Sustainable bio-ethanol production from agro-residues: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, S.; Malins, C. Availability of Cellulosic Residues and Wastes in the EU; The International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT): Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kilpeläinen, I.; Xie, H.; King, A.; Granstrom, M.; Heikkinen, S.; Argyropoulos, D.S. Dissolution of Wood in Ionic Liquids. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2007, 55, 9142–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosan, B.; Michels, C.; Meister, F. Dissolution and forming of cellulose with ionic liquids. Cellulose 2007, 15, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, M.E.; Bogel-Łukasik, E.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Solubility of Carbohydrates in Ionic Liquids. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Pale, M.; Meli, L.; Doherty, T.V.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Room temperature ionic liquids as emerging solvents for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Man, Z.; Bustam Khalil, M.A. Ionic liquid-a future solvent for the enhanced uses of wood biomass. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2011, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, H.; Luque, R. Advances on biomass pretreatment using ionic liquids: An overview. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3913–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquid processing of cellulose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnick, D.L.; Flores, R.A.; DeStefano, M.R.; Scurto, A.M. Cellulose Solubility in Ionic Liquid Mixtures: Temperature, Cosolvent, and Antisolvent Effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 7906–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Hou, H.; Hu, J. Pretreatment of eucalyptus with recycled ionic liquids for low-cost biorefinery. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Complete Chemical Hydrolysis of Cellulose into Fermentable Sugars through Ionic Liquids and Antisolvent Pretreatments. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 3467–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Chemical hydrolysis of cellulose into fermentable sugars through ionic liquids and antisolvent pretreatments using heterogeneous catalysts. Catal. Today 2018, 302, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Liu, C.F.; Sun, R.C. Fractionation of bagasse into cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin with ionic liquid treatment followed by alkaline extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8691–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Lopes, A.M.; João, K.G.; Rubik, D.F.; Bogel-Łukasik, E.; Duarte, L.C.; Andreaus, J.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Pre-treatment of lignocellulosic biomass using ionic liquids: Wheat straw fractionation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhong, L.-X.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Peng, X.-W.; Sun, R.-C. Studies on the structural characterization of lignin, hemicelluloses and cellulose fractionated by ionic liquid followed by alkaline extraction from bamboo. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H. Dissolution and regeneration of biopolymers in ionic liquids. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2014, 63, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, S.J.; Ma, H.H.; Zhang, B.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Hu, X.M. Fractionation of corn stover into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin using a series of ionic liquids. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.R.C.; Pinto, J.V.; Nunes, D.; Roseiro, L.B.; Oliveira, M.C.; Fortunato, E.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Imidazole: Prospect Solvent for Lignocellulosic Biomass Fractionation and Delignification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtar, S.S.; Tengku Malim Busu, T.N.; Md Noor, A.M.; Shaari, N.; Mat, H. An ionic liquid treatment and fractionation of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin from oil palm empty fruit bunch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathitsuksanoh, N.; George, A.; Zhang, Y.H.P. New lignocellulose pretreatments using cellulose solvents: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, G. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: A mini-review. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi Mood, S.; Hossein Golfeshan, A.; Tabatabaei, M.; Salehi Jouzani, G.; Najafi, G.H.; Gholami, M.; Ardjmand, M. Lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, G.; Yau, E.; Badal, K.; Collier, J.; Ramachandran, K.B.; Ramakrishnan, S. Chemical and physicochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: A review. Enzym. Res. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. High glucose yields from the hydrolysis of cellulose dissolved in ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Serrano, M.; Sáez Angulo, F.; Negro, M.J.; Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Second-Generation Bioethanol Production Combining Simultaneous Fermentation and Saccharification of IL-Pretreated Barley Straw. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7086–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, D.A.; Remsing, R.C.; Swatloski, R.P.; Moyna, P.; Moyna, G.; Rogers, R.D. Can ionic liquids dissolve wood? Processing and analysis of lignocellulosic materials with 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Visser, A.E.; Reichert, W.M.; Willauer, H.D.; Broker, G.A.; Rogers, R.D. Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem. 2001, 3, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Rahman, M.; Qin, Y.; Maxim, M.L.; Rodríguez, H.; Rogers, R.D. Complete dissolution and partial delignification of wood in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Rodriguez, H.; Rahman, M.; Rogers, R.D. Where are ionic liquid strategies most suited in the pursuit of chemicals and energy from lignocellulosic biomass? Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of Cellose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green and sustainable manufacture of chemicals from biomass: State of the art. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Sharma, M. Green solvents for the dissolution and processing of biopolymers. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 18, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gurau, G.; Pingali, S.V.; O’Neill, H.M.; Evans, B.R.; Urban, V.S.; Heller, W.T.; Rogers, R.D. Physical Insight into Switchgrass Dissolution in Ionic Liquid 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NREL. N.R.E.L. Biomass Compositional Analysis Laboratory Procedures. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/bioenergy/biomass-compositional-analysis.html (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Optimization of the process of chemical hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; García Fierro, J.L.; Campos-Martín, J.M. Method for the Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass. Patent WO2015/004296, 15 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Capel-Sanchez, M.C.; Barrio, L.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Silylation and surface properties of chemically grafted hydrophobic silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.K.; Pitman, A.J. FTIR studies of the changes in wood chemistry following decay by brown-rot and white-rot fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 52, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergert, H.L. Infrared Spectra of Lignin and Related Compounds. II. Conifer Lignin and Model Compounds1,2. J. Org. Chem. 1960, 25, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Hughes, S. Fractional extraction and physico-chemical characterization of hemicelluloses and cellulose from sugar beet pulp. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 36, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.C.; Geng, Z.C.; Fowler, P.; Baird, M.S. Characteristics of degraded hemicellulosic polymers obtained from steam exploded wheat straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuchi, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Endo, T.; Shibata, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Ikai, T.; Maeda, K.; Takahashi, K. Efficient and rapid direct transesterification reactions of cellulose with isopropenyl acetate in ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72071–72074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Daud, W.R.; Djuned, F.M. Cellulose acetate from oil palm empty fruit bunch via a one step heterogeneous acetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbag, I.; Mohamed Saleh, S. Studies on the formation of intermolecular interactions and structural characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/lignin film. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 73, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, A.; Serrano, L.; Garcia, A.; Mondragon, I.; Labidi, J. Comparative study of lignin fractionation by ultrafiltration and selective precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.; Santiago Cintrón, M. Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 2013, 20, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Simmons, B.A.; Vogel, K.P. Visualization of biomass solubilization and cellulose regeneration during ionic liquid pretreatment of switchgrass. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 104, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Mago, G.; Balan, V.; Wyman, C.E. Physical and chemical characterizations of corn stover and poplar solids resulting from leading pretreatment technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3948–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Procedimiento de Hidrólisis de Biomasa Lignocelulósica. Patent ES2528394, 9 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vanoye, L.; Fanselow, M.; Holbrey, J.D.; Atkins, M.P.; Seddon, K.R. Kinetic model for the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass in the ionic liquid, 1-ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Haverinen, J.; Jaakkola, M.; Lassi, U. Solid acid-catalyzed depolymerization of barley straw driven by ball milling. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Zhu, L.; Shen, F.; Qi, X. Black liquor-derived carbonaceous solid acid catalyst for the hydrolysis of pretreated rice straw in ionic liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Qian, X. Polymeric Solid Acid Catalysts for Lignocellulosic Biomass Fractionation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4514–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wei, S.A.; Wang, D. Enhanced hydrolysis of bamboo biomass by chitosan based solid acid catalyst with surfactant addition in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaye, S.; Pant, K.K.; Jain, S. Hydrolysis of cellulosic bamboo biomass into reducing sugars via a combined alkaline solution and ionic liquid pretreament steps. Renew. Energy 2017, 104, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, S.; Li, Y. Subcritical carbon dioxide-water hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse pith for reducing sugars production. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).