Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Individuals with Down Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Cognitive Ability
2.2.2. ASD Symptom Severity
2.2.3. Expressive Language Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
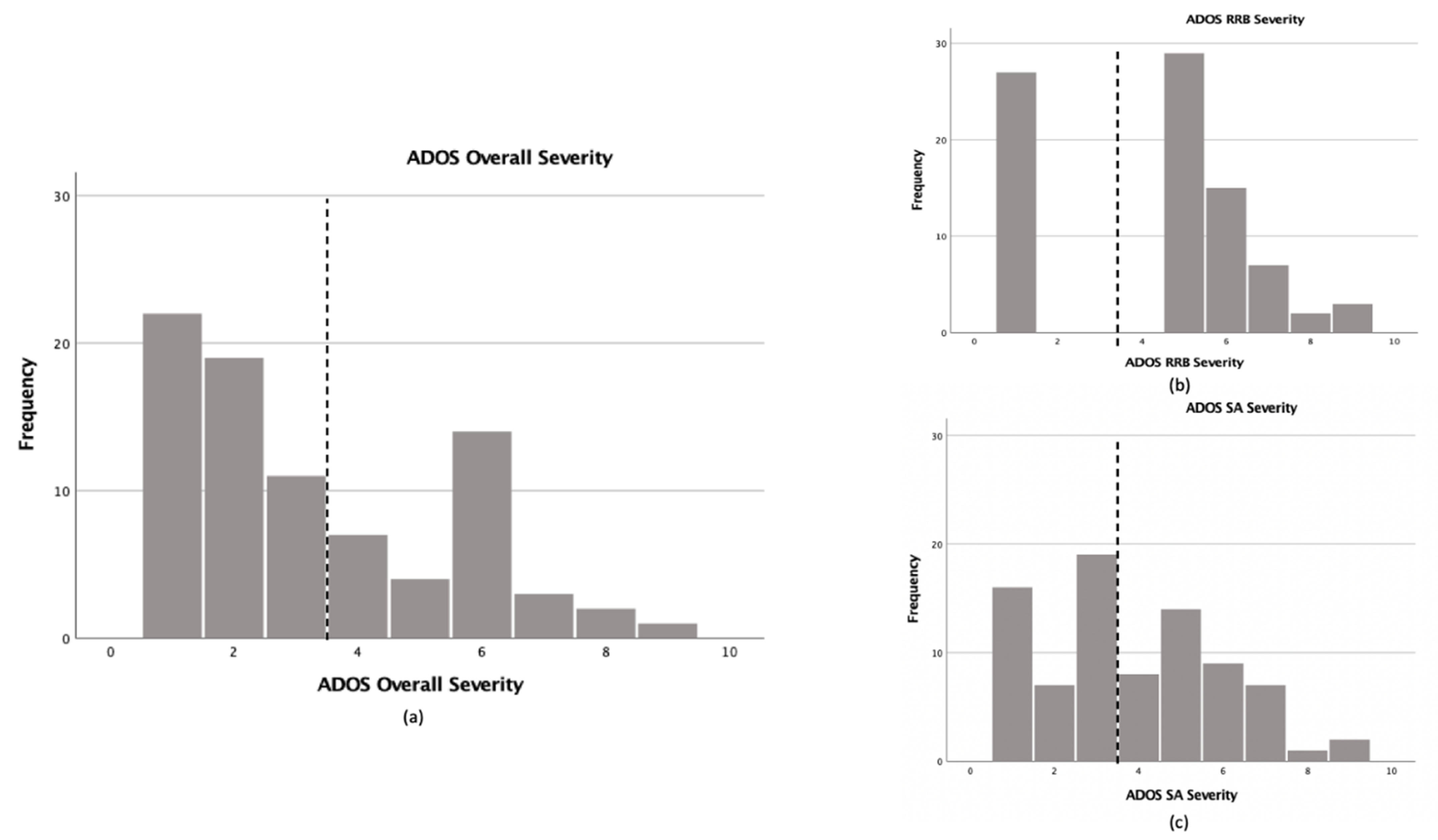
3.1. Prevalence of ASD
ASD Classification
3.2. Group Differences across Characteristics
3.3. Group Differences across ADOS-2 Items
3.3.1. Module 2 Items
3.3.2. Module 3 Items
4. Discussion
4.1. ASD Classification
4.2. Group Differences across Individual Characteristics
4.3. Group Differences across ADOS-2 Items
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mai, C.T.; Isenburg, J.L.; Canfield, M.A.; Meyer, R.E.; Correa, A.; Alverson, C.J.; Lupo, P.J.; Riehle-Colarusso, T.; Cho, S.J.; Aggarwal, D.; et al. National population-based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Res. 2019, 111, 1420–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, M.V.; Thorpe, J.G. Personality stereotype of noninstitutionalized down syndrome children. Am. J. Ment. Defic. 1983, 87, 601–605. [Google Scholar]
- Channell, M.M.; Project, T.D.S.C.; Hahn, L.; Rosser, T.C.; Hamilton, D.; Frank-Crawford, M.A.; Capone, G.T.; Sherman, S.L. Characteristics Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder Risk in Individuals with Down Syndrome. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 3543–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.J.; Hamrick, L.M.; Kelleher, B.L.; Roberts, J.E. Autism Spectrum Disorder-Associated Behaviour in Infants with Down Syndrome. J. Health Sci. Educ. 2020, 4, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Channell, M.M.; Phillips, B.A.; Loveall, S.J.; Conners, F.A.; Bussanich, P.M.; Klinger, L.G. Patterns of autism spectrum symptomatology in individuals with Down syndrome without comorbid autism spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2015, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Channell, M.M. The Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS-2) in school-age children with Down syndrome at low risk for autism spectrum disorder. Autism Dev. Lang. Impair. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, D.J. The Emerging Down Syndrome Behavioral Phenotype in Early Childhood. Infants Young-Child. 2005, 18, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurman, A.J.; Mervis, C.B. The regulatory function of social referencing in preschoolers with Down syndrome or Williams syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2013, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasari, C.; Freeman, S.F.N. Task-Related Social Behavior in Children With Down Syndrome. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 2001, 106, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.S.; Hesketh, L.J. Behavioral phenotype of individuals with Down syndrome. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2000, 6, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.S. Language learning in Down syndrome: The speech and language profile compared to adolescents with cognitive impairment of unknown origin. Down Syndr. Res. Pract. 2006, 10, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finestack, L.H.; Abbeduto, L. Expressive Language Profiles of Verbally Expressive Adolescents and Young Adults With Down Syndrome or Fragile X Syndrome. J. Speech Lang. Heart Res. 2010, 53, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiGuiseppi, C.; Hepburn, S.; Davis, J.M.; Fidler, D.J.; Hartway, S.; Lee, N.; Miller, L.; Ruttenber, M.; Robinson, C. Screening for Autism Spectrum Disorders in Children With Down Syndrome. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2010, 31, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxelgren, U.W.; Myrelid, Å.; Annerén, G.; Ekstam, B.; Göransson, C.; Holmbom, A.; Isaksson, A.; Åberg, M.; Gustafsson, J.; Fernell, E. Prevalence of autism and attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder in Down syndrome: A population-based study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 59, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, G.; Howlin, P.; Salomone, E.; Moss, J.; Charman, T. Profiles of children with Down syndrome who meet screening criteria for autism spectrum disorder (ASD): A comparison with children diagnosed with ASD attending specialist schools. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2016, 61, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maenner, M.J.; Shaw, K.A.; Baio, J.; Washington, A.; Patrick, M.; DiRienzo, M.; Christensen, D.L.; Wiggins, L.D.; Pettygrove, S.; Andrews, J.G.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2016. MMWR. Surveill. Summ. 2020, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamner, T.; Hepburn, S.; Zhang, F.; Fidler, D.; Rosenberg, C.R.; Robins, D.L.; Lee, N.R. Cognitive Profiles and Autism Symptoms in Comorbid Down Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2020, 41, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, M.; Hepburn, S.; Fidler, D.J.; Tapera, T.; Zhang, F.; Rosenberg, C.R.; Lee, N.R. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) symptom profiles of children with comorbid Down syndrome (DS) and ASD: A comparison with children with DS-only and ASD-only. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 89, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, C.A.; Murray, D.S.; Kinsman, A.; Castillo, H.; Mitchell, T.; Hickey, F.J.; Patterson, B. Differences in the clinical presentation of Trisomy 21 with and without autism. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2009, 53, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, J.; Richards, C.; Nelson, L.; Oliver, C. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder symptomatology and related behavioural characteristics in individuals with Down syndrome. Autism 2013, 17, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, G.T.; Grados, M.A.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Bernad-Ripoll, S.; Jewell, A. Down syndrome and comorbid autism-spectrum disorder: Characterization using the aberrant behavior checklist. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2005, 134A, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.Y.; Capone, G.T.; Kaufmann, W.E. Autism spectrum disorder in Down syndrome: Cluster analysis of Aberrant Behaviour Checklist data supports diagnosis. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2011, 55, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbeduto, L.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Sterling, A.; Sherman, S.; Edgin, J.O.; McDuffie, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Hamilton, D.; Nelson, M.; Aschkenasy, J.; et al. Expressive language sampling as a source of outcome measures for treatment studies in fragile X syndrome: Feasibility, practice effects, test-retest reliability, and construct validity. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurman, A.J.; Edgin, J.O.; Sherman, S.L.; Sterling, A.; McDuffie, A.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Hamilton, D.; Abbeduto, L. Spoken language outcome measures for treatment studies in Down syndrome: Feasibility, practice effects, test-retest reliability, and construct validity of variables generated from expressive language sampling. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, S.M.; Schneider, A.; Bickel, E.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Prescott, C.; Hessl, D. Improving IQ measurement in intellectual disabilities using true deviation from population norms. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2014, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roid, G. Stanford Binet Intelligence Scales, 5th ed.; Riverside Publishing: Rolling Meadows, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; DiLavore, P.; Risi, S.; Gotham, K.; Bishop, S.L. Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule-Second Edition (ADOS-2); Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gotham, K.; Pickles, A.; Lord, C. Standardizing ADOS Scores for a Measure of Severity in Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 39, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hus, V.; Lord, C. The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Module 4: Revised Algorithm and Standardized Severity Scores. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1996–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.; Chapman, R. Systematic Analysis of Language Transcripts (SALT), Research version; SALT Software LLC: Middleton, WI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennon, J.M.; D’Souza, H.; Mason, L.; Karmiloff-Smith, A.; Thomas, M.S. Visuo-attentional correlates of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children with Down syndrome: A comparative study with children with idiopathic ASD. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 104, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, S.L.; Moody, E.J. Diagnosing Autism in Individuals with Known Genetic Syndromes: Clinical Considerations and Implications for Intervention. In International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 40, pp. 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gotham, K.; Risi, S.; Pickles, A.; Lord, C. The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule: Revised Algorithms for Improved Diagnostic Validity. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2007, 37, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotham, K.; Risi, S.; Dawson, G.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Joseph, R.; Carter, A.; Hepburn, S.; McMahon, W.; Rodier, P.; Hyman, S.L.; et al. A Replication of the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) Revised Algorithms. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 47, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bal, V.H.; Kim, S.H.; Fok, M.; Lord, C. Autism spectrum disorder symptoms from ages 2 to 19 years: Implications for diagnosing adolescents and young adults. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.; Næss, K.-A.B.; Jarrold, C. Assessing pragmatic communication in children with Down syndrome. J. Commun. Disord. 2017, 68, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walden, T.A.; Blackford, J.U.; Carpenter, K.L. Differences in social signals produced by children with developmental delays of differing etiologies. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 1997, 102, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, D.J.; Most, D.E.; Booth-LaForce, C.; Kelly, J.F. Emerging Social Strengths in Young Children with Down Syndrome. Infants Young-Child. 2008, 21, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.J.; Loveall, S.J.; Savoy, M.T.; Neumann, A.M.; Ikuta, T. Joint attention in Down syndrome: A meta-analysis. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 78, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparella, T.; Goods, K.S.; Freeman, S.; Kasari, C. The emergence of nonverbal joint attention and requesting skills in young children with autism. J. Commun. Disord. 2011, 44, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbeduto, L.; McDuffie, A.; Thurman, A.J. The fragile X syndrome–autism comorbidity: What do we really know? Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDuffie, A.; Thurman, A.J.; Hagerman, R.J.; Abbeduto, L. Symptoms of Autism in Males with Fragile X Syndrome: A Comparison to Nonsyndromic ASD Using Current ADI-R Scores. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 1925–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurman, A.J.; McDuffie, A.; Kover, S.T.; Hagerman, R.J.; Abbeduto, L. Autism Symptomatology in Boys with Fragile X Syndrome: A Cross Sectional Developmental Trajectories Comparison with Nonsyndromic Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 2816–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, K.R.; Anderberg, E.I.; Huang-Storms, L.; Vasile, I.; Greene, R.K.; Duvall, S.W. Co-occurring Down Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Cognitive, Adaptive, and Behavioral Characteristics. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Overall Sample | Module 2 | Module 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Frequency | % | N | Frequency | % | N | Frequency | % | |
| Gender (M) | 83 | 45 | 54.2 | 45 | 28 | 62.2 | 38 | 17 | 44.7 |
| Race | 83 | 45 | 38 | ||||||
| African American/Black | 2 | 2.4 | 2 | 4.4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | 2.2 | 0 | 0 | |||
| White | 58 | 69.9 | 31 | 68.9 | 27 | 71.1 | |||
| Multiple Races | 9 | 10.8 | 6 | 13.3 | 3 | 7.9 | |||
| Unknown | 12 | 14.5 | 5 | 11.1 | 7 | 18.4 | |||
| Other | 1 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.6 | |||
| Ethnicity | 83 | 45 | 38 | ||||||
| Hispanic/Latino | 16 | 19.3 | 8 | 9.6 | 8 | 9.6 | |||
| Yearly Income | 81 | 43 | 38 | ||||||
| Less than 25,000 | 5 | 6.0 | 3 | 7.0 | 2 | 6.2 | |||
| 25,000–50,000 | 18 | 21.7 | 13 | 30.2 | 5 | 22.2 | |||
| 50,000–75,000 | 12 | 14.5 | 8 | 18.6 | 4 | 14.8 | |||
| 75,000–100,000 | 13 | 15.7 | 5 | 11.6 | 8 | 16.0 | |||
| 100,000–150,000 | 15 | 18.1 | 6 | 14.0 | 9 | 18.5 | |||
| 150,000–250,000 | 12 | 14.5 | 7 | 16.3 | 5 | 14.8 | |||
| Over 250,000 | 6 | 7.2 | 1 | 2.3 | 5 | 7.4 | |||
| N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | |
| CA (years) | 83 | 15.60 | 5.18 | 45 | 13.66 | 5.35 | 38 | 17.89 | 3.93 |
| Cognitive | |||||||||
| FSIQ Deviation | 71 | 46.66 | 11.21 | 38 | 40.77 | 8.53 | 33 | 53.44 | 10.12 |
| NVIQ Deviation | 77 | 50.91 | 11.29 | 41 | 45.85 | 9.81 | 36 | 56.68 | 10.12 |
| VIQ Deviation | 74 | 41.88 | 12.60 | 41 | 35.30 | 9.67 | 33 | 50.06 | 10.98 |
| ADOS-2 | |||||||||
| CSS | 83 | 3.27 | 2.16 | 45 | 3.73 | 2.19 | 38 | 2.71 | 2.04 |
| SA Severity | 83 | 3.83 | 2.12 | 45 | 4.27 | 2.05 | 38 | 3.32 | 2.11 |
| RRB Severity | 83 | 2.72 | 4.27 | 45 | 4.31 | 2.24 | 38 | 4.21 | 2.72 |
| Adaptive | 65 | 40 | 25 | ||||||
| Functioning | |||||||||
| Vineland ABC SS | 73.69 | 28.03 | 75.93 | 35.00 | 70.12 | 9.09 | |||
| Overall Sample | Module 2 | Module 3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | ||
| CA | DS-only | 52 | 15.14 | 5.21 | 24 | 11.87 | 4.77 | 28 | 17.93 | 3.78 |
| DS + ASD | 31 | 16.36 | 5.14 | 21 | 15.69 | 5.36 | 10 | 17.78 | 4.57 | |
| Total | 83 | 15.60 | 5.19 | 45 | 13.66 | 5.35 | 38 | 17.89 | 3.93 | |
| SB-5 NV Change Sensitive Score | DS-only | 47 | 464.47 | 13.80 | 21 | 455.95 | 11.63 | 26 | 471.35 | 11.50 |
| DS + ASD | 30 | 458.07 | 12.65 | 20 | 454.95 | 12.95 | 10 | 464.30 | 9.87 | |
| Total | 77 | 461.97 | 13.65 | 41 | 455.46 | 12.15 | 36 | 469.39 | 11.39 | |
| Syntactic Complexity | DS-only | 51 | 5.18 | 2.02 | 23 | 3.76 | 1.61 | 28 | 6.35 | 1.533 |
| DS + ASD | 30 | 3.38 | 1.86 | 20 | 2.52 | 1.42 | 10 | 5.09 | 1.40 | |
| Total | 81 | 4.51 | 2.14 | 43 | 3.19 | 1.63 | 38 | 6.02 | 1.58 | |
| Lexical Diversity | DS-only | 51 | 72.71 | 37.09 | 23 | 49.17 | 32.26 | 28 | 92.04 | 28.98 |
| DS + ASD | 30 | 50.63 | 32.38 | 20 | 35.50 | 23.07 | 10 | 80.90 | 26.99 | |
| Total | 81 | 64.53 | 36.81 | 43 | 42.81 | 28.87 | 38 | 89.11 | 18.54 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimachkie Nunnally, A.; Nguyen, V.; Anglo, C.; Sterling, A.; Edgin, J.; Sherman, S.; Berry-Kravis, E.; del Hoyo Soriano, L.; Abbeduto, L.; Thurman, A.J. Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Individuals with Down Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101278
Dimachkie Nunnally A, Nguyen V, Anglo C, Sterling A, Edgin J, Sherman S, Berry-Kravis E, del Hoyo Soriano L, Abbeduto L, Thurman AJ. Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Individuals with Down Syndrome. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(10):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101278
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimachkie Nunnally, Amanda, Vivian Nguyen, Claudine Anglo, Audra Sterling, Jamie Edgin, Stephanie Sherman, Elizabeth Berry-Kravis, Laura del Hoyo Soriano, Leonard Abbeduto, and Angela John Thurman. 2021. "Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Individuals with Down Syndrome" Brain Sciences 11, no. 10: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101278
APA StyleDimachkie Nunnally, A., Nguyen, V., Anglo, C., Sterling, A., Edgin, J., Sherman, S., Berry-Kravis, E., del Hoyo Soriano, L., Abbeduto, L., & Thurman, A. J. (2021). Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Individuals with Down Syndrome. Brain Sciences, 11(10), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101278






