Neonatal Seizures: An Overview of Genetic Causes and Treatment Options
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epileptogenesis in the Neonatal Brain
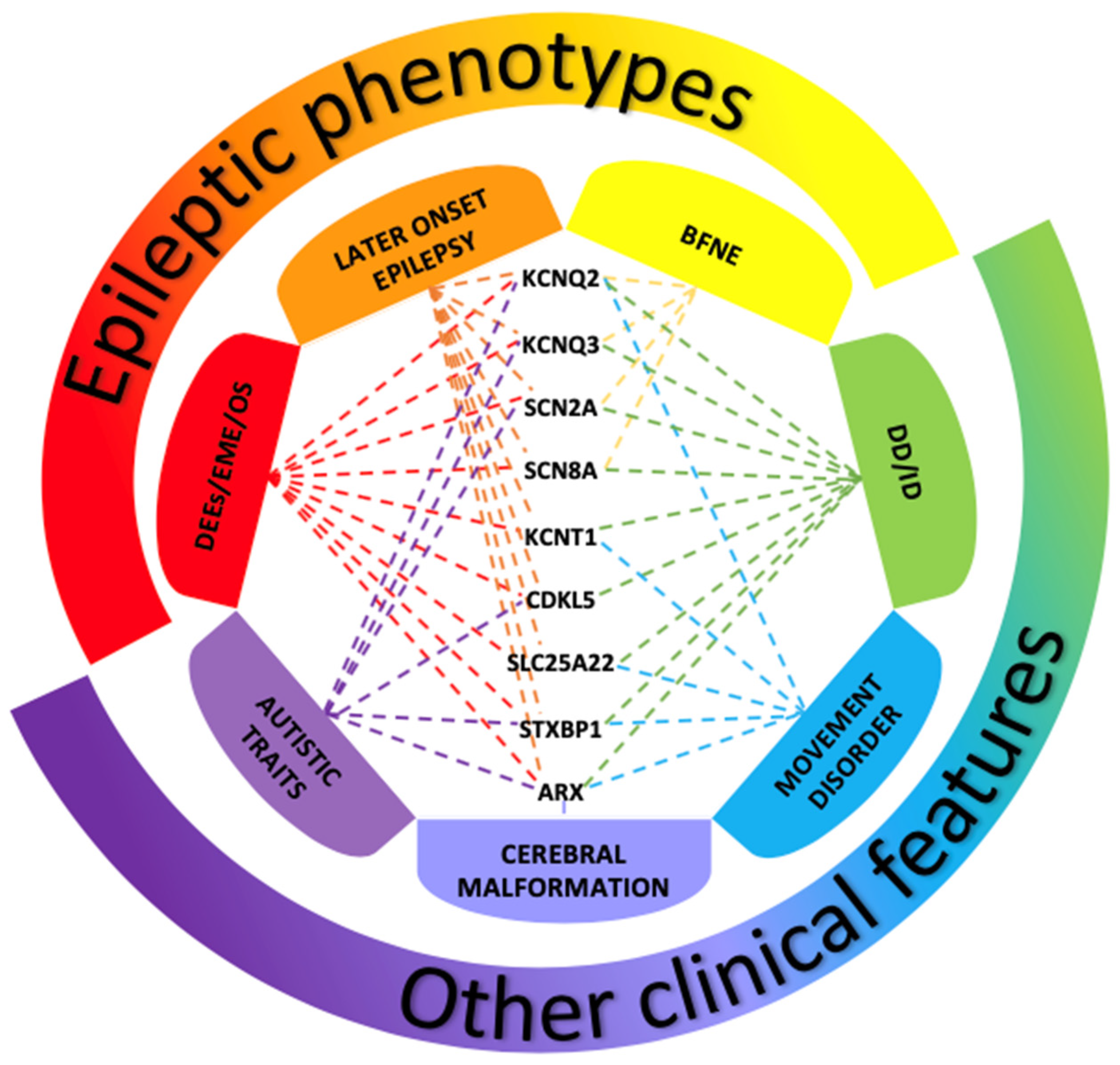
3. Epileptic Phenotypes of Newborns
3.1. Benign Familial Neonatal Epilepsy (BFNE)
3.2. Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies (DEEs)
3.2.1. Early Myoclonic Encephalopathy (EME)/Ohtahara Syndrome (OS)
3.2.2. Genes and Pathogenic Variants Mostly Involved in DEEs
4. The Role of EEG in Neonatal Seizures
5. Treatment
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shellhaas, R.A. Seizure classification, etiology, and management. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 162, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, F.; Percesepe, A.; Spagnoli, C. Genetic diagnosis in neonatal-onset epilepsies: Back to the future. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, H.C.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Chang, T.; Abend, N.S.; Chu, C.J.; Cilio, M.R.; Glidden, D.V.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Massey, S.; et al. Neonatal Seizure Registry Study Group. Contemporary Profile of Seizures in Neonates: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Pediatrics 2016, 174, 98–103.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramantani, G.; Schmitt, B.; Plecko, B.; Pressler, R.M.; Wohlrab, G.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Hagmann, C.; Pisani, F.; Boylan, G.B. Neonatal Seizures-Are We there Yet? Neuropediatrics 2019, 50, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsarou, A.M.; Galanopoulou, A.S.; Moshé, S. Epileptogenesis in neonatal brain. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plouin, P.; Kaminska, A. Neonatal seizures. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 111, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressler, R.M.; Cilio, M.R.; Mizrahi, E.M.; Moshé, S.L.; Nunes, M.L.; Plouin, P.; Vanhatalo, S.; Yozawitz, E.; de Vries, L.S.; Puthenveettil Vinayan, K.; et al. The ILAE classification of seizures and the epilepsies: Modification for seizures in the neonate. Position Pap. By ILAE Task Force Neonatal Seizures. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, A. Electroencephalography in neonatal epilepsies. Pediatrics Int. 2020, 62, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.T.; Berkovic, S.F.; Brodie, M.J.; Buchhalter, J.; Cross, J.H.; van Emde Boas, W.; Engel, J.; French, J.; Glauser, T.A.; Mathern, G.W.; et al. Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: Report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005–2009. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, C.; Fusco, C.; Percesepe, A.; Leuzzi, V.; Pisani, F. Genetic Neonatal-Onset Epilepsies and Developmental/Epileptic Encephalopathies with Movement Disorders: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, E.; Gardella, E.; Møller, R.S. Recent advances in treatment of epilepsy-related sodium channelopathies. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 24, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Tang, S.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, J. Electrophysiological features: The next precise step for SCN2A developmental epileptic encephalopathy. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyrer, J.; Maljevic, S.; Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.F.; Petrou, S.; Reid, C.A. Ion Channels in Genetic Epilepsy: From Genes and Mechanisms to Disease-Targeted Therapies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 142–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, A.; Bayat, M.; Rubboli, G.; Møller, R.S. Epilepsy Syndromes in the First Year of Life and Usefulness of Genetic Testing for Precision Therapy. Genes 2021, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, A. Therapeutic approaches to epileptogenesis—hope on the horizon. Epilepsia 2010, 51 (Suppl. S3), 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, S.W.; Galanopoulou, A.S. Altered GABA signaling in early life epilepsies. Neural Plast. 2011, 2011, 527605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanopoulou, A.S. Sexually dimorphic expression of KCC2 and GABA function. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 80, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanopoulou, A.S. Mutations affecting GABAergic signaling in seizures and epilepsy. Pflug. Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 460, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanopoulou, A.S.; Moshé, S. Pathogenesis and new candidate treatments for infantile spasms and early life epileptic encephalopathies: A view from preclinical studies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 79, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EuroEPINOMICS-RES Consortium; Epilepsy Phenome/Genome Project; Epi4K Consortium. De novo mutations in synaptic transmission genes including DNM1 cause epileptic encephalopathies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakhade, S.N.; Jensen, F.E. Epileptogenesis in the immature brain: Emerging mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boylan, G.B.; Kharoshankaya, L.; Mathieson, S.R. Diagnosis of seizures and encephalopathy using conventional EEG and amplitude integrated EEG. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 162, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieff, N.; Cotsapas, C.; Lee, P.H.; Purcell, S.M.; Smoller, J.W. Pleiotropy in complex traits: Challenges and strategies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClellan, J.; King, M.C. Genetic heterogeneity in human disease. Cell 2010, 141, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, N.M.; Weckhuysen, S.; Gorman, K.; King, M.D.; Lerche, H. Genetic potassium channel-associated epilepsies: Clinical review of the Kv family. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 24, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, C.; Levene, M. Epidemiology and aetiology of neonatal seizures. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.S.; Pan, Z.; Shi, W.; Brown, B.S.; Wymore, R.S.; Cohen, I.S.; Dixon, J.E.; McKinnon, D. KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel subunits: Molecular correlates of the M-channel. Science 1998, 282, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.A.; Charlier, C.; Stauffer, D.; DuPont, B.R.; Leach, R.J.; Melis, R.; Ronen, G.M.; Bjerre, I.; Quattlebaum, T.; Murphy, J.V.; et al. A novel potassium channel gene, KCNQ2, is mutated in an inherited epilepsy of newborns. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.B.; McMahon, J.M.; Carvill, G.L.; Tambunan, D.; Mackay, M.T.; Rodriguez-Casero, V.; Webster, R.; Clark, D.; Freeman, J.L.; Calvert, S.; et al. SCN2A encephalopathy: A major cause of epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures. Neurology 2015, 85, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, C.; King, M.D.; Gorman, K.M. The phenotypic spectrum of SCN2A-related epilepsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 24, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, M.; Brunklaus, A.; Zuberi, S.M. Phenotypic spectrum and genetics of SCN2A-related disorders, treatment options, and outcomes in epilepsy and beyond. Epilepsia 2019, 60 (Suppl. S3), S59–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, H.E.; Kelly, M.; LaCoursiere, C.M.; Pinsky, R.; Tambunan, D.; Shain, C.; Ramgopal, S.; Takeoka, M.; Libenson, M.H.; Julich, K.; et al. Genetics and genotype-phenotype correlations in early onset epileptic encephalopathy with burst suppression. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milh, M.; Cacciagli, P.; Ravix, C.; Badens, C.; Lépine, A.; Villeneuve, N.; Villard, L. Severe neonatal seizures: From molecular diagnosis to precision therapy? Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffrench-Constant, S.; Kachramanoglou, C.; Jones, B.; Basheer, N.; Syrmos, N.; Ganau, M.; Jan, W. Fetal and neonatal MRI features of ARX-related lissencephaly presenting with neonatal refractory seizure disorder. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammertse, H.; van Berkel, A.A.; Iacomino, M.; Toonen, R.F.; Striano, P.; Gambardella, A.; Verhage, M.; Zara, F. Homozygous STXBP1 variant causes encephalopathy and gain-of-function in synaptic transmission. Brain A J. Neurol. 2020, 143, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitsu, H.; Kato, M.; Mizuguchi, T.; Hamada, K.; Osaka, H.; Tohyama, J.; Uruno, K.; Kumada, S.; Nishiyama, K.; Nishimura, A.; et al. De novo mutations in the gene encoding STXBP1 (MUNC18-1) cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiberson, N.; Pineda, A.; Abramov, D.; Kharel, P.; Carnazza, K.E.; Wragg, R.T.; Dittman, J.S.; Burré, J. Mechanism-based rescue of Munc18-1 dysfunction in varied encephalopathies by chemical chaperones. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, F. The mitochondrial transporter family (SLC25): Physiological and pathological implications. Pflug. Eur. J. Physiol. 2004, 447, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicotera, A.G.; Dicanio, D.; Pironti, E.; Bonsignore, M.; Cafeo, A.; Efthymiou, S.; Mondello, P.; Salpietro, V.; Houlden, H.; Di Rosa, G. De novo mutation in SLC25A22 gene: Expansion of the clinical and electroencephalographic phenotype. J. Neurogenet. 2021, 35, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, S.; Erçal, D. Diagnostic Approach to Genetic Causes of Early-Onset Epileptic Encephalopathy. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodian, D.L.; Schreiber, J.M.; Vilboux, T.; Khromykh, A.; Hauser, N.S. Mutation in an alternative transcript of CDKL5 in a boy with early-onset seizures. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2018, 4, a002360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakimiec, M.; Paprocka, J.; Śmigiel, R. CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder-A Complex Epileptic Encephalopathy. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, E.; Yuan, L.; Seong, E.; Ligon, C.; DeKorver, N.; Gurumurthy, C.B.; Arikkath, J. Neuron-Type Specific Loss of CDKL5 Leads to Alterations in mTOR Signaling and Synaptic Markers. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4151–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.X.; Ricos, M.G.; Dibbens, L.M.; Heron, S.E. KCNT1 mutations in seizure disorders: The phenotypic spectrum and functional effects. J. Med Genet. 2016, 53, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Numis, A.L.; Nair, U.; Datta, A.N.; Sands, T.T.; Oldham, M.S.; Patel, A.; Li, M.; Gazina, E.; Petrou, S.; Cilio, M.R. Lack of response to quinidine in KCNT1-related neonatal epilepsy. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessi, M.; Chen, B.; Peng, J.; Tang, Y.; Olatoutou, E.; He, F.; Yang, L.; Yin, F. Intellectual Disability and Potassium Channelopathies: A Systematic Review. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yang, D.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.R.; Lee, S.T.; Kang, H.C. Genetic and clinical features of SCN8A developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 158, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, G.; Collett-White, F.; Orsini, A.; Thomas, S.; Jayapal, S.; Trump, N.; Zaiwalla, Z.; Jayawant, S. Autosomal dominant SCN8A mutation with an unusually mild phenotype. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesen, K.M.; Liu, Y.; Koko, M.; Gjerulfsen, C.E.; Sonnenberg, L.; Schubert, J.; Fenger, C.D.; Eltokhi, A.; Rannap, M.; Koch, N.A.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in SCN8A-related disorders reveal prognostic and therapeutic implications. Brain A J. Neurol. 2021, awab321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bye, A.M.; Flanagan, D. Spatial and temporal characteristics of neonatal seizures. Epilepsia 1995, 36, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B.; Ali, I.; Ryan, C.A.; Murphy, B.P.; Connolly, S. Defining the gap between electrographic seizure burden, clinical expression and staff recognition of neonatal seizures. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008, 93, F187–F191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, G.B.; Rennie, J.M.; Pressler, R.M.; Wilson, G.; Morton, M.; Binnie, C.D. Phenobarbitone, neonatal seizures, and video-EEG. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002, 86, F165–F170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scher, M.S.; Alvin, J.; Gaus, L.; Minnigh, B.; Painter, M.J. Uncoupling of EEG-clinical neonatal seizures after antiepileptic drug use. Pediatric Neurol. 2003, 28, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, M.C.; Morabito, V.; Lederer, D.; Glass, H.C.; Ferrao Santos, S.; Numis, A.L.; Ferriero, D.M.; Sands, T.T.; Cilio, M.R. Neonatal presentation of genetic epilepsies: Early differentiation from acute provoked seizures. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pressler, R.M.; Lagae, L. Why we urgently need improved seizure and epilepsy therapies for children and neonates. Neuropharmacology 2020, 170, 107854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, E.; Shaikh, Z.; Chavez, W.; Torres, A. Tratamiento de las convulsionesneonatales; Treatment of neonatal seizures. Medicina 2018, 78 (Suppl. S2), 30–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Hussain, A.M.; Sharma, S.S. Efficacy of Levetiracetam in neonatal seizures: A systematic review. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittigau, P.; Sifringer, M.; Ikonomidou, C. Antiepileptic drugs and apoptosis in the developing brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 993, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millichap, J.J.; Park, K.L.; Tsuchida, T.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Carmant, L.; Flamini, R.; Joshi, N.; Levisohn, P.M.; Marsh, E.; Nangia, S.; et al. KCNQ2 encephalopathy: Features, mutational hot spots, and ezogabine treatment of 11 patients. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millichap, J.J.; Miceli, F.; De Maria, M.; Keator, C.; Joshi, N.; Tran, B.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Ambrosino, P.; Shashi, V.; Mikati, M.A.; et al. Infantile spasms and encephalopathy without preceding neonatal seizures caused by KCNQ2 R198Q, a gain-of-function variant. Epilepsia 2017, 58, e10–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuersten, M.; Tacke, M.; Gerstl, L.; Hoelz, H.; Stülpnagel, C.V.; Borggraefe, I. Antiepileptic therapy approaches in KCNQ2 related epilepsy: A systematic review. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, M.P.; Fiannacca, M.; Smith, D.M.; Gertler, T.S.; Gunning, B.; Syrbe, S.; Verbeek, N.; Stamberger, H.; Weckhuysen, S.; Ceulemans, B.; et al. Treatment Responsiveness in KCNT1-Related Epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilena, R.; Striano, P.; Traverso, M.; Viri, M.; Cristofori, G.; Tadini, L.; Barbieri, S.; Romeo, A.; Zara, F. Dramatic effect of levetiracetam in early-onset epileptic encephalopathy due to STXBP1 mutation. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Cheng, M.; Wang, J.; Hong, S.; Li, M.; Liao, S.; Xie, L.; Jiang, L. De novo mutations of STXBP1 in Chinese children with early onset epileptic encephalopathy. Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, e12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialer, M. New antiepileptic drugs that are second generation to existing antiepileptic drugs. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 15, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matagne, A.; Margineanu, D.G.; Kenda, B.; Michel, P.; Klitgaard, H. Anti-convulsive and anti-epileptic properties of brivaracetam (ucb 34714), a high-affinity ligand for the synaptic vesicle protein, SV2A. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schubert-Bast, S.; Willems, L.M.; Kurlemann, G.; Knake, S.; Müller-Schlüter, K.; Rosenow, F.; Strzelczyk, A. Postmarketing experience with brivaracetam in the treatment of focal epilepsy in children and adolescents. Epilepsy Behav. EB 2018, 89, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustorino, G.; Spano, M.; Sgro, D.L.; Di Rosa, G.; Tricomi, G.; Bellantone, D.; Tortorella, G. Status gelasticus associated with levetiracetam as add-on treatment. Epileptic Disord. Int. Epilepsy J. Videotape 2007, 9, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, V.K.; Nagarajan, B.; Shivappa, S.K.; Benakappa, N. Effectiveness and Safety of Brivaracetam in Children. Indian J. Pediatrics 2021, 88, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissenkorn, A.; Tzadok, M.; Bar-Yosef, O.; Ben-Zeev, B. Treatment with brivaracetam in children—The experience of a pediatric epilepsy center. Epilepsy Behav. EB 2019, 101 Pt A, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, G.; Dicanio, D.; Nicotera, A.G.; Mondello, P.; Cannavò, L.; Gitto, E. Efficacy of Intravenous Hydrocortisone Treatment in Refractory Neonatal Seizures: A Report on Three Cases. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spoto, G.; Saia, M.C.; Amore, G.; Gitto, E.; Loddo, G.; Mainieri, G.; Nicotera, A.G.; Di Rosa, G. Neonatal Seizures: An Overview of Genetic Causes and Treatment Options. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101295
Spoto G, Saia MC, Amore G, Gitto E, Loddo G, Mainieri G, Nicotera AG, Di Rosa G. Neonatal Seizures: An Overview of Genetic Causes and Treatment Options. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(10):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101295
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpoto, Giulia, Maria Concetta Saia, Greta Amore, Eloisa Gitto, Giuseppe Loddo, Greta Mainieri, Antonio Gennaro Nicotera, and Gabriella Di Rosa. 2021. "Neonatal Seizures: An Overview of Genetic Causes and Treatment Options" Brain Sciences 11, no. 10: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101295
APA StyleSpoto, G., Saia, M. C., Amore, G., Gitto, E., Loddo, G., Mainieri, G., Nicotera, A. G., & Di Rosa, G. (2021). Neonatal Seizures: An Overview of Genetic Causes and Treatment Options. Brain Sciences, 11(10), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101295








