Revascularization Outcome Prediction for A Direct Aspiration-First Pass Technique (ADAPT) from Pre-Treatment Imaging and Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. CT Imaging
2.3. ADAPT Procedure and Outcome Determination
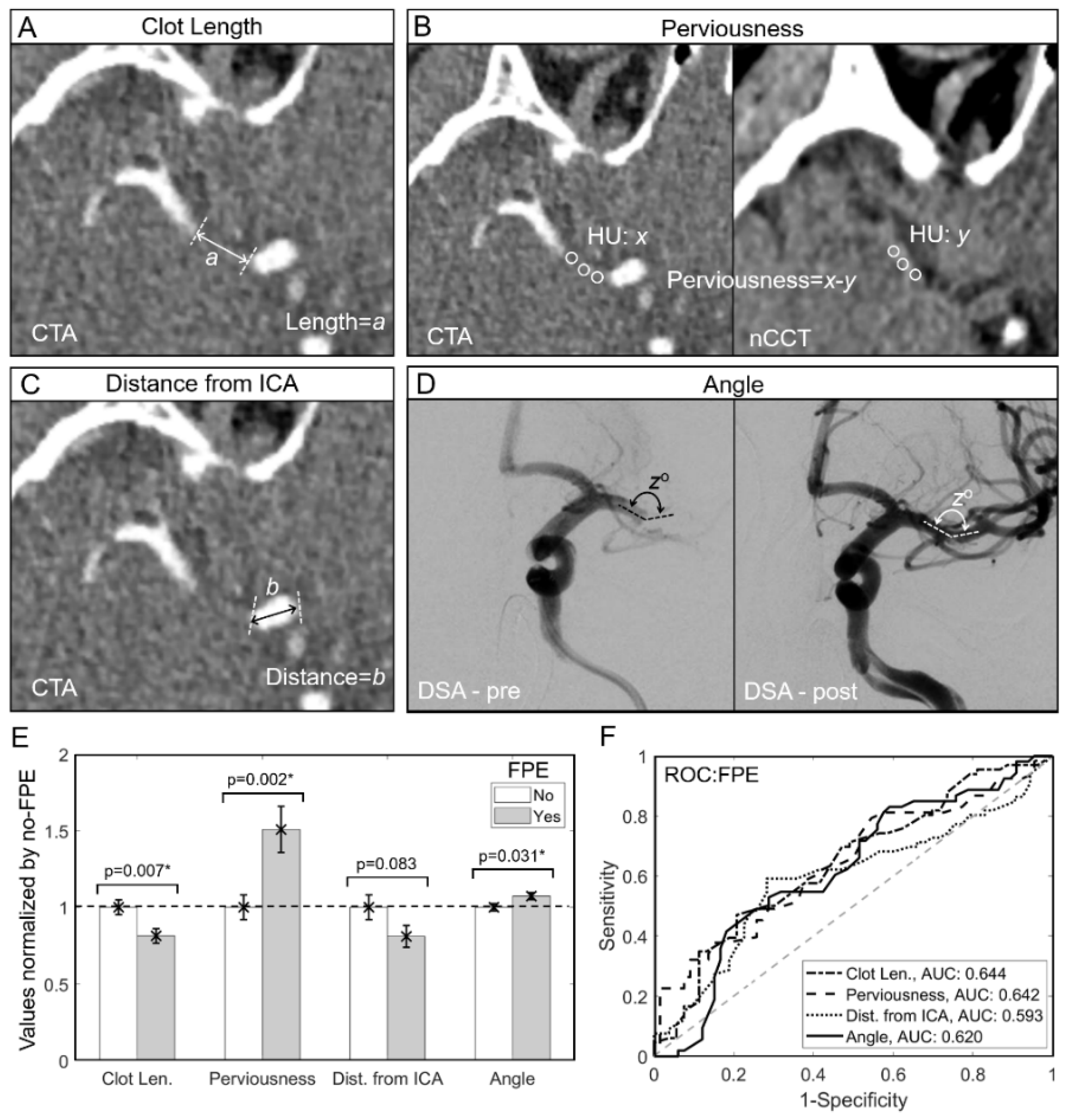
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Univariate Statistical Analysis
2.6. Multivariate Machine Learning Analyses
2.7. Model Stability Testing
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Shorter Length, Higher Perviousness and Larger AOI Are Associated with FPE
3.3. Machine Learning Models Predict FPE with Good Accuracy
3.4. The Logistic Regression Model Is Stable over 100 Training/Testing Randomizations
3.5. Interpreting the Logistic Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzzardi, G.; Del Sette, B.; Stanca, C.; Galbiati, A.; Cernigliaro, M.; Carriero, A.; Stecco, A. Mechanical Thrombectomy by a Direct Aspiration First Pass Technique (ADAPT) in Ischemic Stroke: Results of Monocentric Study Based on Multimodal CT Patient Selection. Stroke Res. Treat. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapergue, B.; Blanc, R.; Gory, B.; Labreuche, J.; Duhamel, A.; Marnat, G. Effect of Endovascular Contact Aspiration vs. Stent Retriever on Revascularization in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Large Vessel Occlusion. The ASTER Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 66, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadani, M.; Alawieh, A.; Vargas, J.; Chatterjee, A.R.; Turk, A.; Spiotta, A. First attempt recanalization with ADAPT: Rate, predictors, and outcome. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 11, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Castonguay, A.C.; Linfante, I.; Gupta, R.; Martin, C.O.; Holloway, W.E.; Mueller-Kronast, N.; English, J.D.; Dabus, G.; Malisch, T.W.; et al. First Pass Effect. Stroke 2018, 49, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascitelli, J.R.; Kellner, C.P.; Oravec, C.S.; De Leacy, R.A.; Oermann, E.K.; Yaeger, K.; Paramasivam, S.; Fifi, J.T.; Mocco, J. Factors associated with successful revascularization using the aspiration component of ADAPT in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernava, G.; Rosi, A.; Boto, J.; Brina, O.; Kulcsar, Z.; Czarnetzki, C.; Carrera, E.; Schaller, K.; Lovblad, K.-O.; Machi, P. Direct thromboaspiration efficacy for mechanical thrombectomy is related to the angle of interaction between the aspiration catheter and the clot. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 12, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, R.; Redjem, H.; Ciccio, G.; Smajda, S.; Desilles, J.-P.; Orng, E.; Taylor, G.; Drumez, E.; Fahed, R.; Labreuche, J.; et al. Predictors of the Aspiration Component Success of a Direct Aspiration First Pass Technique (ADAPT) for the Endovascular Treatment of Stroke Reperfusion Strategy in Anterior Circulation Acute Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, A.S.; Spiotta, A.; Frei, D.; Mocco, J.; Baxter, B.; Fiorella, D.; Siddiqui, A.; Mokin, M.; Dewan, M.; Woo, H.; et al. Initial clinical experience with the ADAPT technique: A direct aspiration first pass technique for stroke thrombectomy. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2014, 6, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokin, M.; Waqas, M.; Fifi, J.; De Leacy, R.; Fiorella, D.; Levy, I.E.; Snyder, K.; Hanel, R.; Woodward, K.; Chaudry, I.; et al. Clot perviousness is associated with first pass success of aspiration thrombectomy in the COMPASS trial. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 13, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashida, R.T.; Furlan, A.J. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2003, 34, e109–e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutra, B.G.; Tolhuisen, M.; Alves, H.C.; Treurniet, K.M.; Kappelhof, M.; Yoo, A.J.; Jansen, I.G.; Dippel, D.W.; Van Zwam, W.H.; Van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; et al. Thrombus Imaging Characteristics and Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Stroke 2019, 50, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokin, M.; Morr, S.; Natarajan, S.K.; Lin, N.; Snyder, K.V.; Hopkins, L.N.; Siddiqui, A.H.; I Levy, E. Thrombus density predicts successful recanalization with Solitaire stent retriever thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke: Table 1. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2015, 7, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Fricano, S.; Waqas, M.; Tso, M.; Dmytriw, A.; Mokin, M.; Kolega, J.; Tomaszewski, J.; Levy, E.; Davies, J.; et al. Increased Perviousness on CT for Acute Ischemic Stroke is Associated with Fibrin/Platelet-Rich Clots. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.R.; Waqas, M.; Fricano, S.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Levy, E.I.; Snyder, K.V.; Davies, J.M.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Tutino, V. Clot organization on histology is associated with radiomics features that predict treatment outcomes from mechanical thrombectomy. In Medical Imaging 2021: Digital Pathology; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; p. 116030L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.; Harris, G.; Williams, K. BRAINSFit: Mutual information rigid registrations of whole-brain 3D images, using the insight toolkit. Insight J. 2007, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.; Chandler, J.; Welch, A.V.; Higgins, J.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, T.; Wiesmann, M.; Nikoubashman, O.; Gopinathan, A.; Bhogal, P.; Yeo, L.L. The Aspirations of Direct Aspiration for Thrombectomy in Ischemic Stroke: A Critical Analysis. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, E.M.; Dankbaar, J.W.; Treurniet, K.M.; Horsch, A.D.; Roos, Y.B.; Kappelle, L.J.; Niessen, W.J.; Majoie, C.B.; Velthuis, B.; Marquering, H.A.; et al. Permeable Thrombi Are Associated with Higher Intravenous Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Treatment Success in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilgic, A.B.; Gocmen, R.; Arsava, E.M.; Topcuoglu, M.A. The Effect of Clot Volume and Permeability on Response to Intravenous Tissue Plasminogen Activator in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyselyova, A.A.; Fiehler, J.; Leischner, H.; Flottmann, F.; Buhk, J.H.; Frölich, A.M. Vessel diameter and catheter-to-vessel ratio affect the success rate of clot aspiration. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 13, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, A.; Valente, I.; Consoli, A.; Piano, M.; Renieri, L.; Gabrieli, J.; Russo, R.; Caragliano, A.; Ruggiero, M.; Saletti, A.; et al. Posterior Circulation Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large-Vessel Occlusion: Predictors of Favorable Clinical Outcome and Analysis of First-Pass Effect. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velagapudi, L.; Mouchtouris, N.; Schmidt, R.F.; Vuong, D.; Khanna, O.; Sweid, A.; Sadler, B.; Al Saiegh, F.; Gooch, M.R.; Jabbour, P.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach to First Pass Reperfusion in Mechanical Thrombectomy: Prediction and Feature Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, F.; Kyheng, M.; Consoli, A.; Desilles, J.-P.; Gory, B.; Richard, S.; Rodesch, G.; Labreuche, J.; Girot, J.-B.; Dargazanli, C.; et al. Identifying the predictors of first-pass effect and its influence on clinical outcome in the setting of endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: Results from a multicentric prospective registry. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 16, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.-S.; Nicholson, P.; A Hilditch, C.; Tsang, A.C.O.; Pereira, V.M.; Krings, T.; Fang, Y.; Brinjikji, W. Thrombus perviousness is not associated with first-pass revascularization using stent retrievers. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2019, 25, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagani, M.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W. Correlation between clot density and recanalization success or stroke etiology in acute ischemic stroke patients. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2017, 23, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, D.A.; Vélez, J.I.; Salazar, J.C. Comparison between SVM and logistic regression: Which one is better to discriminate? Rev. Colomb. Estadística 2012, 35, 223–237. [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro, V.; Valente, I.; Trombatore, P.; Ganimede, M.P.; Briatico, A.; Di Stasi, C.; Burdi, N.; Boero, G.; Prontera, M.P.; Gandini, R.; et al. Comparison Between Three Commonly Used Large-Bore Aspiration Catheters in Terms of Successful Recanalization and First-Passage Effect. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| FPE (n = 53) | No FPE (n = 66) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and Clinical Data | |||
| Male, n(%) | 21 (39.6) | 28 (42.4) | 0.852 |
| Female, n(%) | 32 (60.4) | 38 (57.6) | |
| Age, (mean ± SE) | 75.7 ± 2.0 | 70.5 ± 1.9 | 0.076 |
| Hypertension, n(%) | 42 (79.3) | 49 (74.2) | 0.663 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n(%) | 14 (26.4) | 18 (27.3) | 1.000 |
| Dyslipidemia, n(%) | 24 (45.3) | 32 (48.5) | 0.854 |
| Congestive heart failure, n(%) | 6 (11.3) | 10 (15.2) | 0.599 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n(%) | 17 (32.1) | 32 (48.5) | 0.092 |
| Current smoker, n(%) | 7 (13.2) | 7 (10.6) | 0.777 |
| Previous stroke, n(%) | 9 (17.0) | 17 (25.8) | 0.273 |
| Treatment Details | |||
| IV-tPA, n(%) | 33 (62.3) | 30 (45.5) | 0.065 |
| Stroke Presentation | |||
| Right-sided occlusion, n(%) | 33 (62.3) | 34 (51.5) | 0.268 |
| Left-sided occlusion, n(%) | 20 (37.7) | 32 (48.5) | |
| MCA M1 occlusion, n(%) | 44 (83.0) | 44 (66.7) | 0.058 |
| MCA M2 occlusion, n(%) | 9 (17.0) | 22 (33.3) | |
| Clot density-nCCT, HU (mean ± SE) | 42.5 ± 1.5 | 41.2 ± 1.3 | 0.540 |
| Image-Based Parameters (All parameters normally distributed based on SW test) | |||
| Clot length, mm (mean ± SE) | 9.79 ± 0.57 | 12.05 ± 0.58 | 0.007 † |
| Clot perviousness, HU (mean ± SE) | 37.60 ± 3.74 | 24.92 ± 2.02 | 0.002 † |
| Distance from ICA, mm (mean ± SE) | 11.64 ± 1.01 | 14.37 ± 1.28 | 0.083 |
| Angle of interaction (mean ± SE) | 149.1 ± 3.11 | 139.77 ± 3.32 | 0.031 † |
| Parameter. | Odds Ratio | Median | IQR | pchange |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clot Len. | 0.2859 ± 0.0148 | 10 mm | 7 mm | −25.87% |
| Perviousness | 1.6356 ± 0.0383 | 27 HU | 24 HU | 12.15% |
| Dist. From ICA | 0.3852 ± 0.0142 | 12 mm | 12.8 mm | −20.92% |
| AOI | 2.7292 ± 0.0382 | 150° | 29° | 24.06% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, T.R.; Waqas, M.; Sarayi, S.M.M.J.; Ren, Z.; Borlongan, C.V.; Dossani, R.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Snyder, K.V.; Davies, J.M.; et al. Revascularization Outcome Prediction for A Direct Aspiration-First Pass Technique (ADAPT) from Pre-Treatment Imaging and Machine Learning. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101321
Patel TR, Waqas M, Sarayi SMMJ, Ren Z, Borlongan CV, Dossani R, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Snyder KV, Davies JM, et al. Revascularization Outcome Prediction for A Direct Aspiration-First Pass Technique (ADAPT) from Pre-Treatment Imaging and Machine Learning. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(10):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101321
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Tatsat R., Muhammad Waqas, Seyyed M. M. J. Sarayi, Zeguang Ren, Cesario V. Borlongan, Rimal Dossani, Elad I. Levy, Adnan H. Siddiqui, Kenneth V. Snyder, Jason M. Davies, and et al. 2021. "Revascularization Outcome Prediction for A Direct Aspiration-First Pass Technique (ADAPT) from Pre-Treatment Imaging and Machine Learning" Brain Sciences 11, no. 10: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101321
APA StylePatel, T. R., Waqas, M., Sarayi, S. M. M. J., Ren, Z., Borlongan, C. V., Dossani, R., Levy, E. I., Siddiqui, A. H., Snyder, K. V., Davies, J. M., Mokin, M., & Tutino, V. M. (2021). Revascularization Outcome Prediction for A Direct Aspiration-First Pass Technique (ADAPT) from Pre-Treatment Imaging and Machine Learning. Brain Sciences, 11(10), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11101321






