Interpersonal Motor Interactions Shape Multisensory Representations of the Peripersonal Space
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Rubber Hand Illusion (RHI) | A bodily illusion based on synchronous tactile stimulation of an unseen self-hand, and observed tactile stimulation of a rubber [13,14,15] or virtual [51] hand, placed in a congruent position with the real hand. This induces feeling of ownership of the fake hand and changes in where the real hand is perceived in the space (proprioceptive drift). Interestingly, the sense of ownership over a virtual hand in Virtual Reality (VR) can be induced by its mere observation in a first-person perspective, inducing visuo-proprioceptive congruency [52,53]. |
| Rubber Foot Illusion | A bodily illusion based on the same multisensory integration principles of the RHI, but based on synchronous visuo-tactile stimulation or a rubber/virtual foot and consequent incorporation of the external foot [54,55,56]. |
| Enfacement Illusion | An illusion based on multisensory integration of tactile stimuli felt on one’s own face and synchronous observation of tactile stimulation delivered on another face. This illusion induces incorporation of the partner’s face onto the person’s identity representation [57,58,59,60]. |
| Full Body Illusion | A bodily illusion tested in immersive virtual reality, based on multisensory integration of tactile and visual information between stimulation received on the body and observed on a virtual body, inducing re-location of the self onto the virtual body, as shown by subjective (sense of ownership) and objective (self-location drift) measures [61,62,63,64,65]. Interestingly, the sense of ownership over a virtual body in VR can be induced by its mere observation in a first-person perspective, inducing visuo-proprioceptive congruency [66,67]. |
| Embreathment Illusion | A bodily illusion based on synchronous or asynchronous breathing with a virtual avatar in immersive virtual reality, mediated by multisensory integration of interoceptive and visual cues, showing incorporation, ownership, and sense of agency of the virtual body after congruent respiration [23]. |
| Crossmodal Congruency Effect (CCE) | The difference in reaction time in detecting a tactile stimulus on a body spot [11,12] when visual [2] or auditory stimuli [3,4,5,68] are presented on an incongruent location on the body. |
| Proprioceptive drift | A change of perceived hand location towards the rubber hand during the RHI [15]. |
| Self-location drift | A shift of perceived full-body location towards the virtual body during the full-body illusion [64]. |
2. Body Representations and the PPS
3. The PPS Is Shaped by Action Planning and Execution
4. Incorporating Tools in the PPS
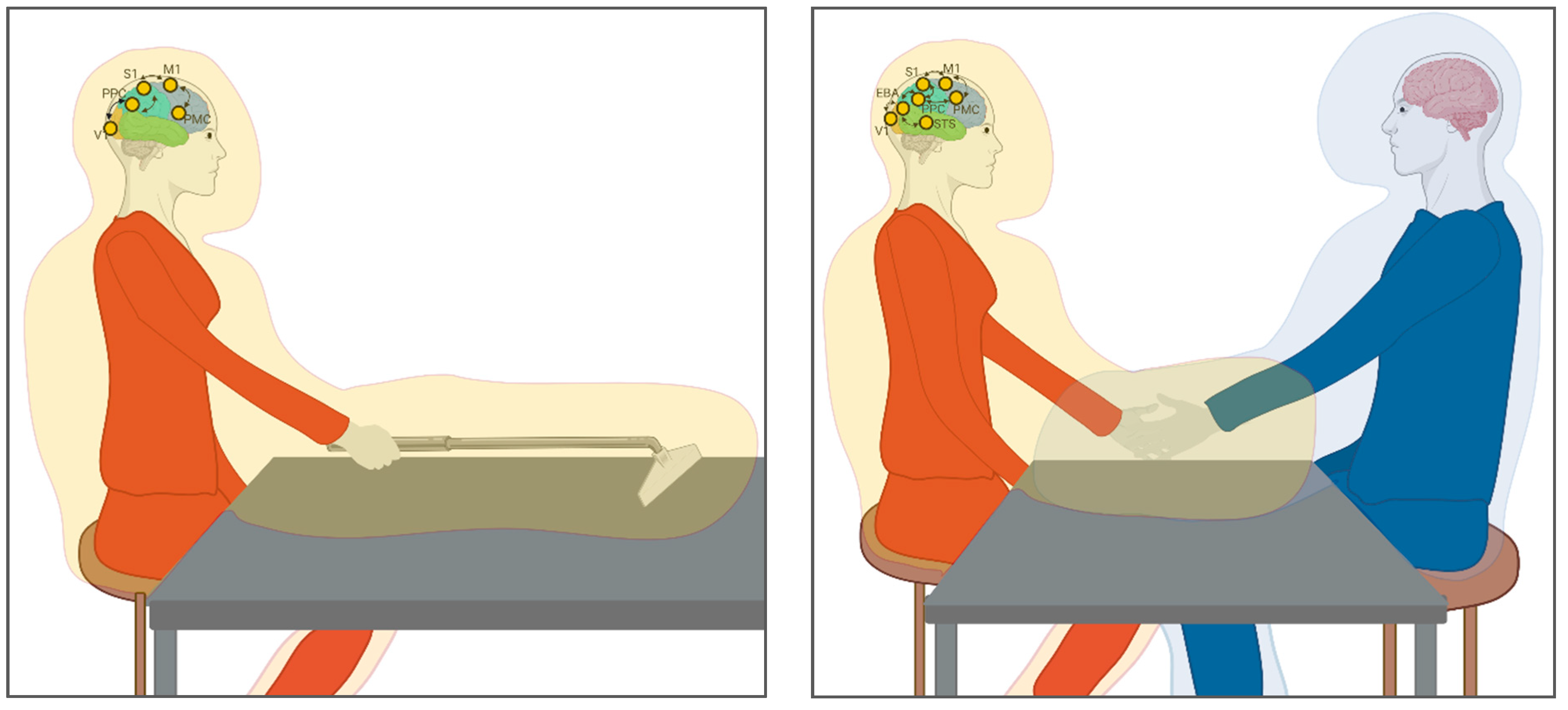
5. The PPS Is Modulated by Motor Interactions
6. Predictive Coding Accounts of PPS and Their Possible Role for Interpersonal Interactions
7. Plastic Representations of the Body and PPS in Typical and Atypical Development
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iriki, A.; Tanaka, M.; Iwamura, Y. Coding of Modified Body Schema during Tool Use by Macaque Postcentral Neurones. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravita, A.; Spence, C.; Kennett, S.; Driver, J. Tool-Use Changes Multimodal Spatial Interactions between Vision and Touch in Normal Humans. Cognition 2002, 83, B25–B34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzoneri, E.; Ubaldi, S.; Rastelli, V.; Finisguerra, A.; Bassolino, M.; Serino, A. Tool-Use Reshapes the Boundaries of Body and Peripersonal Space Representations. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 228, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.; Noel, J.P.; Canzoneri, E.; Blanke, O.; Serino, A. The Wheelchair as a Full-Body Tool Extending the Peripersonal Space. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galigani, M.; Castellani, N.; Donno, B.; Franza, M.; Zuber, C.; Allet, L.; Garbarini, F.; Bassolino, M. Effect of Tool-Use Observation on Metric Body Representation and Peripersonal Space. Neuropsychologia 2020, 148, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravita, A.; Spence, C.; Driver, J. Multisensory Integration and the Body Schema: Close to Hand and within Reach. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, R531–R539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravita, A.; Iriki, A. Tools for the Body (Schema). Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnè, A.; Serino, A.; Làdavas, E. Dynamic Size-Change of Peri-Hand Space Following Tool-Use: Determinants and Spatial Characteristics Revealed Through Cross-Modal Extinction. Cortex 2007, 43, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, N.P.; Spence, C. The Body Schema and the Multisensory Representation(s) of Peripersonal Space. Cogn. Process 2004, 5, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, N.P.; Calvert, G.A.; Spence, C. Extending or Projecting Peripersonal Space with Tools? Multisensory Interactions Highlight Only the Distal and Proximal Ends of Tools. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 372, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C.; Pavani, F.; Driver, J. Crossmodal Links between Vision and Touch in Covert Endogenous Spatial Attention. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2000, 26, 1298–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C.; Pavani, F.; Maravita, A.; Holmes, N. Multisensory Contributions to the 3-D Representation of Visuotactile Peripersonal Space in Humans: Evidence from the Crossmodal Congruency Task. J. Physiol. 2004, 98, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinick, M.; Cohen, J. Rubber Hands ‘Feel’ Touch That Eyes See. Nature 1998, 391, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavani, F.; Spence, C.; Driver, J. Visual Capture of Touch: Out-of-the-Body Experiences with Rubber Gloves. Psychol. Sci. 2000, 11, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, M.; Haggard, P. The Rubber Hand Illusion Revisited: Visuotactile Integration and Self-Attribution. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2005, 31, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Garfinkel, S.N.; Critchley, H.D.; Seth, A.K. Multisensory Integration across Exteroceptive and Interoceptive Domains Modulates Self-Experience in the Rubber-Hand Illusion. Neuropsychologia 2013, 51, 2909–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-D.; Bernasconi, F.; Bello-Ruiz, J.; Pfeiffer, C.; Salomon, R.; Blanke, O. Transient Modulations of Neural Responses to Heartbeats Covary with Bodily Self-Consciousness. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8453–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-D.; Bernasconi, F.; Salomon, R.; Tallon-Baudry, C.; Spinelli, L.; Seeck, M.; Schaller, K.; Blanke, O. Neural Sources and Underlying Mechanisms of Neural Responses to Heartbeats, and Their Role in Bodily Self-Consciousness: An Intracranial EEG Study. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 2351–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspell, J.E.; Heydrich, L.; Marillier, G.; Lavanchy, T.; Herbelin, B.; Blanke, O. Turning Body and Self Inside Out: Visualized Heartbeats Alter Bodily Self-Consciousness and Tactile Perception. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sel, A.; Azevedo, R.T.; Tsakiris, M. Heartfelt Self: Cardio-Visual Integration Affects Self-Face Recognition and Interoceptive Cortical Processing. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 5144–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciello, G.; Daum, M.M.; Menghini, C.; Brugger, P.; Lenggenhager, B. Not That Heart-Stopping After All: Visuo-Cardiac Synchrony Does Not Boost Self-Face Attribution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, H.D.; Harrison, N.A. Visceral Influences on Brain and Behavior. Neuron 2013, 77, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, A.; Porciello, G.; Tieri, G.; Aglioti, S.M. The “Embreathment” Illusion Highlights the Role of Breathing in Corporeal Awareness. J. Neurophysiol. 2020, 123, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, Á.; Ferentzi, E.; Bogdány, T.; Szolcsányi, T.; Witthöft, M.; Köteles, F. Proprioception but Not Cardiac Interoception Is Related to the Rubber Hand Illusion. Cortex 2020, 132, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiris, M.; Jiménez, A.T.; Costantini, M. Just a Heartbeat Away from One’s Body: Interoceptive Sensitivity Predicts Malleability of Body-Representations. Proc. R. Soc. B 2011, 278, 2470–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajadura-Jiménez, A.; Grehl, S.; Tsakiris, M. The Other in Me: Interpersonal Multisensory Stimulation Changes the Mental Representation of the Self. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajadura-Jiménez, A.; Longo, M.R.; Coleman, R.; Tsakiris, M. The Person in the Mirror: Using the Enfacement Illusion to Investigate the Experiential Structure of Self-Identification. Conscious. Cogn. 2012, 21, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajadura-Jiménez, A.; Tsakiris, M. Balancing the “Inner” and the “Outer” Self: Interoceptive Sensitivity Modulates Self–Other Boundaries. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2014, 143, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.E.; Tsakiris, M. Going at the Heart of Social Cognition: Is There a Role for Interoception in Self-Other Distinction? Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2018, 24, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzoli, C.; Ehrsson, H.H.; Farnè, A. Multisensory Representation of the Space Near the Hand: From Perception to Action and Interindividual Interactions. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebanz, N.; Bekkering, H.; Knoblich, G. Joint Action: Bodies and Minds Moving Together. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2006, 10, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallotti, M.; Frith, C.D. Social Cognition in the We-Mode. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzulo, G.; Iodice, P.; Ferraina, S.; Kessler, K. Shared Action Spaces: A Basis Function Framework for Social Re-Calibration of Sensorimotor Representations Supporting Joint Action. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, M.; Chung, A.J.; Shams, L. Perception of Body Ownership Is Driven by Bayesian Sensory Inference. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Blanke, O.; Serino, A. From Multisensory Integration in Peripersonal Space to Bodily Self-Consciousness: From Statistical Regularities to Statistical Inference: Multisensory Integration and Self-Consciousness. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1426, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Serino, A.; Wallace, M.T. Increased Neural Strength and Reliability to Audiovisual Stimuli at the Boundary of Peripersonal Space. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limanowski, J.; Blankenburg, F. Minimal Self-Models and the Free Energy Principle. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apps, M.A.J.; Tsakiris, M. The Free-Energy Self: A Predictive Coding Account of Self-Recognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 41, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilner, J.M.; Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D. Predictive Coding: An Account of the Mirror Neuron System. Cogn. Process. 2007, 8, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilner, J.M.; Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D. The Mirror-Neuron System: A Bayesian Perspective. NeuroReport 2007, 18, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Suzuki, K.; Grandi, L.C. Predictive Coding Accounts of Shared Representations in Parieto-Insular Networks. Neuropsychologia 2015, 70, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, A.; Tsakiris, M. Mentalizing Homeostasis: The Social Origins of Interoceptive Inference. Neuropsychoanalysis 2017, 19, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.C.; Brüne, M. The Role of Prediction in Social Neuroscience. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzoff, A.N.; Marshall, P.J. Chapter 2—Importance of body representations in social-cognitive development: New insights from infant brain science. In Progress in Brain Research; Hunnius, S., Meyer, M., Eds.; New Perspectives on Early Social-cognitive Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 254, pp. 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, Y. Predictive Learning: Its Key Role in Early Cognitive Development. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehl, S.; Bertenthal, B.I. An Interactionist Perspective on the Development of Coordinated Social Attention. PsyArXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candidi, M.; Aglioti, S.M.; Haggard, P. Embodying Bodies and Worlds. Rev. Philos. Psychol. 2012, 3, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Cascio, C.J.; Wallace, M.T.; Park, S. The Spatial Self in Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 179, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Failla, M.D.; Quinde-Zlibut, J.M.; Williams, Z.J.; Gerdes, M.; Tracy, J.M.; Zoltowski, A.R.; Foss-Feig, J.H.; Nichols, H.; Armstrong, K.; et al. Visual-Tactile Spatial Multisensory Interaction in Adults With Autism and Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 578401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Paredes, R.; Terrebonne, E.; Feldman, J.I.; Woynaroski, T.; Cascio, C.J.; Seriès, P.; Wallace, M.T. Inflexible Updating of the Self-Other Divide During a Social Context in Autism; Psychophysical, Electrophysiological, and Neural Network Modeling Evidence. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vives, M.V.; Spanlang, B.; Frisoli, A.; Bergamasco, M.; Slater, M. Virtual Hand Illusion Induced by Visuomotor Correlations. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieri, G.; Tidoni, E.; Pavone, E.F.; Aglioti, S.M. Mere Observation of Body Discontinuity Affects Perceived Ownership and Vicarious Agency over a Virtual Hand. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Tieri, G.; Aglioti, S.M. Influence of Cognitive Stance and Physical Perspective on Subjective and Autonomic Reactivity to Observed Pain and Pleasure: An Immersive Virtual Reality Study. Conscious. Cogn. 2019, 67, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crea, S.; D’Alonzo, M.; Vitiello, N.; Cipriani, C. The Rubber Foot Illusion. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenggenhager, B.; Hilti, L.; Brugger, P. Disturbed Body Integrity and the “Rubber Foot Illusion”. Neuropsychology 2015, 29, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, N.; Nakai, R.; Ino, T.; Mitani, A. Brain Activity Associated with the Rubber Foot Illusion. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 721, 134820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, M. Looking for Myself: Current Multisensory Input Alters Self-Face Recognition. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforza, A.; Bufalari, I.; Haggard, P.; Aglioti, S.M. My Face in Yours: Visuo-Tactile Facial Stimulation Influences Sense of Identity. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 5, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardini, F.; Tajadura-Jiménez, A.; Serino, A.; Tsakiris, M. It Feels like It’s Me: Interpersonal Multisensory Stimulation Enhances Visual Remapping of Touch from Other to Self. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2013, 39, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciello, G.; Bufalari, I.; Minio-Paluello, I.; Di Pace, E.; Aglioti, S.M. The ‘Enfacement’ Illusion: A Window on the Plasticity of the Self. Cortex 2018, 104, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenggenhager, B.; Tadi, T.; Metzinger, T.; Blanke, O. Video Ergo Sum: Manipulating Bodily Self-Consciousness. Science 2007, 317, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspell, J.E.; Lenggenhager, B.; Blanke, O. Keeping in Touch with One’s Self: Multisensory Mechanisms of Self-Consciousness. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Pfeiffer, C.; Blanke, O.; Serino, A. Peripersonal Space as the Space of the Bodily Self. Cognition 2015, 144, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, O.; Metzinger, T. Full-Body Illusions and Minimal Phenomenal Selfhood. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2009, 13, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, L.; Porciello, G.; Ciccarone, S.; Lenggenhager, B.; Tieri, G.; Marucci, M.; Dazzi, F.; Loriedo, C.; Bufalari, I. Characterizing Body Image Distortion and Bodily Self-Plasticity in Anorexia Nervosa via Visuo-Tactile Stimulation in Virtual Reality. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, M.; Spanlang, B.; Sanchez-Vives, M.V.; Blanke, O. First Person Experience of Body Transfer in Virtual Reality. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Lisi, M.P.; Tieri, G.; Aglioti, S.M. Heterosexual, Gay, and Lesbian People’s Reactivity to Virtual Caresses on Their Embodied Avatars’ Taboo Zones. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzoneri, E.; Magosso, E.; Serino, A. Dynamic Sounds Capture the Boundaries of Peripersonal Space Representation in Humans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roll, J.P.; Roll, R.; Velay, J.-L. Proprioception as a link between body space and extra-personal space. In Brain and Space; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 112–132. ISBN 978-0-19-854284-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzolatti, G.; Fadiga, L.; Fogassi, L.; Gallese, V. The Space Around Us. Science 1997, 277, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, H.; Holmes, G. Sensory Disturbances from Cerebral Lesions. Brain 1911, 34, 102–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, J. Body schema and body image—A double dissociation in deafferented patients. In Motor Control, Today and Tomorrow; Academic Publishing House: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Preester, H.D.; Knockaert, V. Body Image and Body Schema: Interdisciplinary Perspectives on the Body; John Benjamins Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 978-90-272-9440-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkerman, H.C.; de Haan, E.H.F. Somatosensory Processes Subserving Perception and Action. Behav. Brain Sci. 2007, 30, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, L.; Brozzoli, C.; Farnè, A. Peripersonal Space and Body Schema: Two Labels for the Same Concept? Brain Topogr. 2009, 21, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pellegrino, G.; Làdavas, E. Peripersonal Space in the Brain. Neuropsychologia 2015, 66, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziano, M.; Yap, G.; Gross, C. Coding of Visual Space by Premotor Neurons. Science 1994, 266, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogassi, L.; Raos, V.; Franchi, G.; Gallese, V.; Luppino, G.; Matelli, M. Visual Responses in the Dorsal Premotor Area F2 of the Macaque Monkey. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 128, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziano, M.S.; Hu, X.T.; Gross, C.G. Visuospatial Properties of Ventral Premotor Cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 77, 2268–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmer, F.; Schlack, A.; Duhamel, J.-R.; Graf, W.; Fink, G.R. Space Coding in Primate Posterior Parietal Cortex. NeuroImage 2001, 14, S46–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avillac, M.; Hamed, S.B.; Duhamel, J.-R. Multisensory Integration in the Ventral Intraparietal Area of the Macaque Monkey. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziano, M.S.A.; Gross, C.G. A Bimodal Map of Space: Somatosensory Receptive Fields in the Macaque Putamen with Corresponding Visual Receptive Fields. Exp. Brain Res. 1993, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.S.A. Coding the Locations of Objects in the Dark. Science 1997, 277, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.S.A. Where Is My Arm? The Relative Role of Vision and Proprioception in the Neuronal Representation of Limb Position. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 10418–10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.S.A.; Gross, C.G. The representation of extrapersonal space: A possible role for bimodal, visual-tactile neurons. In The cognitive neurosciences; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 1021–1034. ISBN 978-0-262-07157-4. [Google Scholar]
- Colby, C.L.; Duhamel, J.R.; Goldberg, M.E. Ventral Intraparietal Area of the Macaque: Anatomic Location and Visual Response Properties. J. Neurophysiol. 1993, 69, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, J.-R.; Colby, C.L.; Goldberg, M.E. Ventral Intraparietal Area of the Macaque: Congruent Visual and Somatic Response Properties. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guipponi, O.; Cléry, J.; Odouard, S.; Wardak, C.; Ben Hamed, S. Whole Brain Mapping of Visual and Tactile Convergence in the Macaque Monkey. NeuroImage 2015, 117, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cléry, J.; Guipponi, O.; Odouard, S.; Wardak, C.; Ben Hamed, S. Cortical Networks for Encoding near and Far Space in the Non-Human Primate. NeuroImage 2018, 176, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cléry, J.; Hamed, S.B. Frontier of Self and Impact Prediction. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cléry, J.; Guipponi, O.; Odouard, S.; Pinède, S.; Wardak, C.; Ben Hamed, S. The Prediction of Impact of a Looming Stimulus onto the Body Is Subserved by Multisensory Integration Mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 10656–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makin, T.R.; Holmes, N.P.; Zohary, E. Is That Near My Hand? Multisensory Representation of Peripersonal Space in Human Intraparietal Sulcus. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereno, M.I.; Huang, R.-S. A Human Parietal Face Area Contains Aligned Head-Centered Visual and Tactile Maps. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, G.; Petkova, V.I.; Ehrsson, H.H. Integration of Visual and Tactile Signals from the Hand in the Human Brain: An FMRI Study. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozzoli, C.; Gentile, G.; Petkova, V.I.; Ehrsson, H.H. FMRI Adaptation Reveals a Cortical Mechanism for the Coding of Space Near the Hand. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9023–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serino, A.; Canzoneri, E.; Avenanti, A. Fronto-Parietal Areas Necessary for a Multisensory Representation of Peripersonal Space in Humans: An RTMS Study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, A. Peripersonal Space (PPS) as a Multisensory Interface between the Individual and the Environment, Defining the Space of the Self. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 99, 138–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, F.; Noel, J.-P.; Park, H.D.; Faivre, N.; Seeck, M.; Spinelli, L.; Schaller, K.; Blanke, O.; Serino, A. Audio-Tactile and Peripersonal Space Processing Around the Trunk in Human Parietal and Temporal Cortex: An Intracranial EEG Study. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 3385–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladavas, E. Visual Peripersonal Space Centred on the Face in Humans. Brain 1998, 121, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzoli, C.; Gentile, G.; Ehrsson, H.H. That’s near My Hand! Parietal and Premotor Coding of Hand-Centered Space Contributes to Localization and Self-Attribution of the Hand. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14573–14582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, A.; Noel, J.-P.; Galli, G.; Canzoneri, E.; Marmaroli, P.; Lissek, H.; Blanke, O. Body Part-Centered and Full Body-Centered Peripersonal Space Representations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnè, A.; Làdavas, E. Dynamic Size-Change of Hand Peripersonal Space Following Tool Use. NeuroReport 2000, 11, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunley, S.B.; Lourenco, S.F. What Is Peripersonal Space? An Examination of Unresolved Empirical Issues and Emerging Findings. Wires Cogn. Sci. 2018, 9, e1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bufacchi, R.J.; Iannetti, G.D. An Action Field Theory of Peripersonal Space. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzoli, C.; Makin, T.R.; Cardinali, L.; Holmes, N.P.; Farne, A. Peripersonal space: A multisensory interface for body-object interactions. In The Neural Bases of Multisensory Processes; Murray, M.M., Wallace, M.T., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2011; pp. 449–466. [Google Scholar]
- Noel, J.-P.; Serino, A. High Action Values Occur Near Our Body. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Bertoni, T.; Terrebonne, E.; Pellencin, E.; Herbelin, B.; Cascio, C.; Blanke, O.; Magosso, E.; Wallace, M.T.; Serino, A. Rapid Recalibration of Peri-Personal Space: Psychophysical, Electrophysiological, and Neural Network Modeling Evidence. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 5088–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.S.A.; Cooke, D.F. Parieto-Frontal Interactions, Personal Space, and Defensive Behavior. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clery, J.; Guipponi, O.; Odouard, S.; Wardak, C.; Ben Hamed, S. Impact Prediction by Looming Visual Stimuli Enhances Tactile Detection. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4179–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vignemont, F.; Iannetti, G.D. How Many Peripersonal Spaces? Neuropsychologia 2015, 70, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambo, C.F.; Liang, M.; Cruccu, G.; Iannetti, G.D. Defensive Peripersonal Space: The Blink Reflex Evoked by Hand Stimulation Is Increased When the Hand Is near the Face. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 107, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossataro, C.; Sambo, C.F.; Garbarini, F.; Iannetti, G.D. Interpersonal Interactions and Empathy Modulate Perception of Threat and Defensive Responses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisio, A.; Garbarini, F.; Biggio, M.; Fossataro, C.; Ruggeri, P.; Bove, M. Dynamic Shaping of the Defensive Peripersonal Space through Predictive Motor Mechanisms: When the “Near” Becomes “Far”. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Grivaz, P.; Marmaroli, P.; Lissek, H.; Blanke, O.; Serino, A. Full Body Action Remapping of Peripersonal Space: The Case of Walking. Neuropsychologia 2015, 70, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozzoli, C.; Pavani, F.; Urquizar, C.; Cardinali, L.; Farnè, A. Grasping Actions Remap Peripersonal Space. NeuroReport 2009, 20, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzoli, C.; Cardinali, L.; Pavani, F.; Farnè, A. Action-Specific Remapping of Peripersonal Space. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, J.; Belardinelli, A.; Butz, M.V. Hands Ahead in Mind and Motion: Active Inference in Peripersonal Hand Space. Vision 2019, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Neumann, P.; Gail, A. Peri-Hand Space Expands beyond Reach in the Context of Walk-and-Reach Movements. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patané, I.; Cardinali, L.; Salemme, R.; Pavani, F.; Farnè, A.; Brozzoli, C. Action Planning Modulates Peripersonal Space. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 31, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, L.; Frassinetti, F.; Brozzoli, C.; Urquizar, C.; Roy, A.C.; Farnè, A. Tool-Use Induces Morphological Updating of the Body Schema. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R478–R479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, A.; Canzoneri, E.; Marzolla, M.; di Pellegrino, G.; Magosso, E. Extending Peripersonal Space Representation without Tool-Use: Evidence from a Combined Behavioral-Computational Approach. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi, S.; Farnè, A.; Rinaldesi, L.; Làdavas, E. Dynamic Size-Change of Peri-Hand Space through Tool-Use: Spatial Extension or Shift of the Multi-Sensory Area. J. Neuropsychol. 2007, 1, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, A.; O’Dowd, A.; Gherri, E. Tool Use Modulates Early Stages of Visuo-Tactile Integration in Far Space: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 145, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggio, M.; Bisio, A.; Avanzino, L.; Ruggeri, P.; Bove, M. This Racket Is Not Mine: The Influence of the Tool-Use on Peripersonal Space. Neuropsychologia 2017, 103, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggio, M.; Bisio, A.; Avanzino, L.; Ruggeri, P.; Bove, M. Familiarity with a Tool Influences Peripersonal Space and Primary Motor Cortex Excitability of Muscles Involved in Haptic Contact. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magosso, E.; Serino, A.; di Pellegrino, G.; Ursino, M. Crossmodal Links between Vision and Touch in Spatial Attention: A Computational Modelling Study. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2010, 2010, 304941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magosso, E.; Ursino, M.; di Pellegrino, G.; Làdavas, E.; Serino, A. Neural Bases of Peri-Hand Space Plasticity through Tool-Use: Insights from a Combined Computational-Experimental Approach. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, T.; Magosso, E.; Serino, A. From Statistical Regularities in Multisensory Inputs to Peripersonal Space Representation and Body Ownership: Insights from a Neural Network Model. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 611–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.E.; Fabio, C.; Ravenda, V.; Bahmad, S.; Koun, E.; Salemme, R.; Luauté, J.; Bolognini, N.; Hayward, V.; Farnè, A. Somatosensory Cortex Efficiently Processes Touch Located Beyond the Body. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 4276–4283.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammers, M.P.M.; de Vignemont, F.; Verhagen, L.; Dijkerman, H.C. The Rubber Hand Illusion in Action. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, L.; Brozzoli, C.; Urquizar, C.; Salemme, R.; Roy, A.C.; Farnè, A. When Action Is Not Enough: Tool-Use Reveals Tactile-Dependent Access to Body Schema. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 3750–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, L.; Brozzoli, C.; Luauté, J.; Roy, A.C.; Farnè, A. Proprioception Is Necessary for Body Schema Plasticity: Evidence from a Deafferented Patient. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, M.; Prabhu, G.; Haggard, P. Having a Body versus Moving Your Body: How Agency Structures Body-Ownership. Conscious. Cogn. 2006, 15, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, T.; Picot-Annand, A.; Neal, T.; Moore, C. Movement and the Rubber Hand Illusion. Perception 2009, 38, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newport, R.; Pearce, R.; Preston, C. Fake Hands in Action: Embodiment and Control of Supernumerary Limbs. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 204, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Hommel, B. Body-Ownership for Actively Operated Non-Corporeal Objects. Conscious. Cogn. 2015, 36, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Hommel, B. The Role of Agency for Perceived Ownership in the Virtual Hand Illusion. Conscious. Cogn. 2015, 36, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, S.; Unenaka, S.; Ohki, Y. The Relationship Between the Virtual Hand Illusion and Motor Performance. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grechuta, K.; Ulysse, L.; Rubio Ballester, B.; Verschure, P.F.M.J. Self Beyond the Body: Action-Driven and Task-Relevant Purely Distal Cues Modulate Performance and Body Ownership. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, J.-P.; Samad, M.; Doxon, A.; Clark, J.; Keller, S.; Di Luca, M. Peri-Personal Space as a Prior in Coupling Visual and Proprioceptive Signals. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossataro, C.; Rossi Sebastiano, A.; Tieri, G.; Poles, K.; Galigani, M.; Pyasik, M.; Bruno, V.; Bertoni, T.; Garbarini, F. Immersive Virtual Reality Reveals That Visuo-Proprioceptive Discrepancy Enlarges the Hand-Centred Peripersonal Space. Neuropsychologia 2020, 146, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohwy, J.; Paton, B. Explaining Away the Body: Experiences of Supernaturally Caused Touch and Touch on Non-Hand Objects within the Rubber Hand Illusion. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilteni, K.; Ehrsson, H.H. Sensorimotor Predictions and Tool Use: Hand-Held Tools Attenuate Self-Touch. Cognition 2017, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpert, D.M.; Doya, K.; Kawato, M. A Unifying Computational Framework for Motor Control and Social Interaction. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 358, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozzoli, C.; Gentile, G.; Bergouignan, L.; Ehrsson, H.H. A Shared Representation of the Space Near Oneself and Others in the Human Premotor Cortex. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, S. Situating Interaction in Peripersonal and Extrapersonal Space: Empirical and Theoretical Perspectives. In Situatedness and Place; Hünefeldt, T., Schlitte, A., Eds.; Contributions to Phenomenology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 95, pp. 67–79. ISBN 978-3-319-92936-1. [Google Scholar]
- Merleau-Ponty, M. The Visible and the Invisible: Followed by Working Notes; Northwestern University Press: Evanston, IL, USA, 1968; ISBN 978-0-8101-0457-0. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Press, C.; Haggard, P. Shared Representations in Body Perception. Acta Psychologica 2006, 121, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maister, L.; Cardini, F.; Zamariola, G.; Serino, A.; Tsakiris, M. Your Place or Mine: Shared Sensory Experiences Elicit a Remapping of Peripersonal Space. Neuropsychologia 2015, 70, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teneggi, C.; Canzoneri, E.; di Pellegrino, G.; Serino, A. Social Modulation of Peripersonal Space Boundaries. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellencin, E.; Paladino, M.P.; Herbelin, B.; Serino, A. Social Perception of Others Shapes One’s Own Multisensory Peripersonal Space. Cortex 2018, 104, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.A.; Ortega, P.A.; Wolpert, D.M. Motor Coordination: When Two Have to Act as One. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 211, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzulo, G.; Dindo, H. What Should I Do next? Using Shared Representations to Solve Interaction Problems. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 211, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, R.; Kujala, M.V. Brain Basis of Human Social Interaction: From Concepts to Brain Imaging. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilbach, L.; Timmermans, B.; Reddy, V.; Costall, A.; Bente, G.; Schlicht, T.; Vogeley, K. Toward a Second-Person Neuroscience. Behav. Brain Sci. 2013, 36, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, R.; Henriksson, L.; Malinen, S.; Parkkonen, L. Centrality of Social Interaction in Human Brain Function. Neuron 2015, 88, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heed, T.; Habets, B.; Sebanz, N.; Knoblich, G. Others’ Actions Reduce Crossmodal Integration in Peripersonal Space. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, T.M.; Ferguson, R.; Dexheimer, M.S.; Glenberg, A.M. Consequences of Joint Action: Entanglement with Your Partner. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2015, 144, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilner, J.M.; Paulignan, Y.; Blakemore, S.J. An Interference Effect of Observed Biological Movement on Action. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacheli, L.M.; Candidi, M.; Pavone, E.F.; Tidoni, E.; Aglioti, S.M. And Yet They Act Together: Interpersonal Perception Modulates Visuo-Motor Interference and Mutual Adjustments during a Joint-Grasping Task. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacheli, L.M.; Tidoni, E.; Pavone, E.F.; Aglioti, S.M.; Candidi, M. Kinematics Fingerprints of Leader and Follower Role-Taking during Cooperative Joint Actions. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 226, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacheli, L.M.; Candidi, M.; Era, V.; Aglioti, S.M. Causative Role of Left AIPS in Coding Shared Goals during Human–Avatar Complementary Joint Actions. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacheli, L.M.; Christensen, A.; Giese, M.A.; Taubert, N.; Pavone, E.F.; Aglioti, S.M.; Candidi, M. Prejudiced Interactions: Implicit Racial Bias Reduces Predictive Simulation during Joint Action with an out-Group Avatar. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candidi, M.; Curioni, A.; Donnarumma, F.; Sacheli, L.M.; Pezzulo, G. Interactional Leader–Follower Sensorimotor Communication Strategies during Repetitive Joint Actions. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candidi, M.; Sacheli, L.M.; Era, V.; Canzano, L.; Tieri, G.; Aglioti, S.M. Come Together: Human–Avatar on-Line Interactions Boost Joint-Action Performance in Apraxic Patients. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfo, M.; Era, V.; Tieri, G.; Sacheli, L.M.; Candidi, M. Interactor’s Body Shape Does Not Affect Visuo-Motor Interference Effects during Motor Coordination. Acta Psychologica 2019, 196, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Era, V.; Aglioti, S.M.; Candidi, M. Inhibitory Theta Burst Stimulation Highlights the Role of Left AIPS and Right TPJ during Complementary and Imitative Human–Avatar Interactions in Cooperative and Competitive Scenarios. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, C.; Era, V.; da Rold, F.; Candidi, M.; Borghi, A.M. Abstract Concepts in Interaction: The Need of Others When Guessing Abstract Concepts Smooths Dyadic Motor Interactions 2020. Available online: https://osf.io/wyqdm/ (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Era, V.; Aglioti, S.M.; Mancusi, C.; Candidi, M. Visuo-Motor Interference with a Virtual Partner Is Equally Present in Cooperative and Competitive Interactions. Psychol. Res. 2020, 84, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candidi, M.; Sacheli, L.M.; Aglioti, S. From Muscles Synergies and Individual Goals to Interpersonal Synergies and Shared Goals: Mirror Neurons and Interpersonal Action Hierarchies. Phys. Life Rev. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglioti, S.M.; Cesari, P.; Romani, M.; Urgesi, C. Action Anticipation and Motor Resonance in Elite Basketball Players. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candidi, M.; Maria Sacheli, L.; Mega, I.; Aglioti, S.M. Somatotopic Mapping of Piano Fingering Errors in Sensorimotor Experts: TMS Studies in Pianists and Visually Trained Musically Naïves. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiti, M.S.; Porciello, G.; Aglioti, S.M. The Bright and the Dark Sides of Motor Simulation. Neuropsychologia 2017, 105, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, W.; Launay, J.; Dunbar, R.I.M. Joint Attention, Shared Goals, and Social Bonding. Br. J. Psychol. 2016, 107, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Anna, A.; Fossataro, C.; Burin, D.; Bruno, V.; Salatino, A.; Garbarini, F.; Pia, L.; Ricci, R.; Leman, M.; Berti, A. Entrainment beyond Embodiment. Neuropsychologia 2018, 119, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, L.; Turgeon, M.; Atherton, G. How Moving Together Binds Us Together: The Social Consequences of Interpersonal Entrainment and Group Processes. Open Psychol. 2019, 1, 273–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patané, I.; Brozzoli, C.; Koun, E.; Frassinetti, F.; Farnè, A. Me, You, and Our Object: Peripersonal Space Recruitment During Executed and Observed Actions Depends on Object Ownership. J. Exp Psychol. General 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Anna, A.; Rosso, M.; Bruno, V.; Garbarini, F.; Leman, M.; Berti, A. Does Musical Interaction in a Jazz Duet Modulate Peripersonal Space? Psychol. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunik, E.; Frey, S.H.; Grafton, S.T. Virtual Lesions of the Anterior Intraparietal Area Disrupt Goal-Dependent on-Line Adjustments of Grasp. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmurget, M.; Epstein, C.M.; Turner, R.S.; Prablanc, C.; Alexander, G.E.; Grafton, S.T. Role of the Posterior Parietal Cortex in Updating Reaching Movements to a Visual Target. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.F.d.C.; Grafton, S.T. Goal Representation in Human Anterior Intraparietal Sulcus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacheli, L.M.; Tieri, G.; Aglioti, S.M.; Candidi, M. Transitory Inhibition of the Left Anterior Intraparietal Sulcus Impairs Joint Actions: A Continuous Theta-Burst Stimulation Study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Era, V.; Candidi, M.; Gandolfo, M.; Sacheli, L.M.; Aglioti, S.M. Inhibition of Left Anterior Intraparietal Sulcus Shows That Mutual Adjustment Marks Dyadic Joint-Actions in Humans. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, P.; Tucker, D.M.; Makeig, S. Frontal Midline Theta and the Error-Related Negativity: Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Action Regulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, E.F.; Tieri, G.; Rizza, G.; Tidoni, E.; Grisoni, L.; Aglioti, S.M. Embodying Others in Immersive Virtual Reality: Electro-Cortical Signatures of Monitoring the Errors in the Actions of an Avatar Seen from a First-Person Perspective. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, G.; Tieri, G.; Pavone, E.F.; Aglioti, S.M. Wronger than Wrong: Graded Mapping of the Errors of an Avatar in the Performance Monitoring System of the Onlooker. NeuroImage 2018, 167, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzetta, R.; Nicolardi, V.; Tidoni, E.; Aglioti, S.M. Error, Rather than Its Probability, Elicits Specific Electrocortical Signatures: A Combined EEG-Immersive Virtual Reality Study of Action Observation. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzetta, R.; Wokke, M.; Aglioti, S.M.; Ridderinkhof, R. Doing It Wrong: A Systematic Review on Electrocortical and Behavioral Correlates of Error Monitoring in Patients with Neurological Disorders. Neuroscience 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, G.; Scandola, M.; Feurra, M.; Pavone, E.F.; Rossi, S.; Aglioti, S.M. Midfrontal Theta Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Modulates Behavioural Adjustment after Error Execution. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 3159–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, Q.; Pavone, E.F.; Aglioti, S.M.; Candidi, M. Theta Synchronization over Occipito-Temporal Cortices during Visual Perception of Body Parts. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, Q.; Parrotta, E.; Era, V.; Martelli, M.L.; Candidi, M. Role of the Occipito-Temporal Theta Rhythm in Hand Visual Identification. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 123, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, G.; Fusaro, M.; Aglioti, S.M. Midfrontal-Occipital Ɵ-TACS Modulates Cognitive Conflicts Related to Bodily Stimuli. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, Q.; Candidi, M.; Era, V.; Tieri, G.; Aglioti, S.M. Midline Frontal and Occipito-Temporal Activity during Error Monitoring in Dyadic Motor Interactions. Cortex 2020, 127, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesper, C.; Butterfill, S.; Knoblich, G.; Sebanz, N. A Minimal Architecture for Joint Action. Neural Netw. 2010, 23, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Era, V.; Boukarras, S.; Candidi, M. Neural Correlates of Action Monitoring and Mutual Adaptation during Interpersonal Motor Coordination. Phys. Life Rev. 2019, 28, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, G.; Moreau, Q.; Tognoli, E.; Kelso, J.A.S. The Human Dynamic Clamp Reveals the Fronto-Parietal Network Linking Real-Time Social Coordination and Cognition. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 3271–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.P.N.; Ballard, D.H. Predictive Coding in the Visual Cortex: A Functional Interpretation of Some Extra-Classical Receptive-Field Effects. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K. A Theory of Cortical Responses. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Frith, C. A Duet for One. Conscious. Cogn. 2015, 36, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzulo, G. Studying Mirror Mechanisms within Generative and Predictive Architectures for Joint Action. Cortex J. Devoted Study Nerv. Syst. Behav. 2013, 49, 2968–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. Learning and Inference in the Brain. Neural Netw. 2003, 16, 1325–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzulo, G.; Rigoli, F.; Friston, K.J. Hierarchical Active Inference: A Theory of Motivated Control. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. Does Predictive Coding Have a Future? Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keysers, C.; Gazzola, V. Expanding the Mirror: Vicarious Activity for Actions, Emotions, and Sensations. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysers, C.; Kaas, J.H.; Gazzola, V. Somatosensation in Social Perception. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzulo, G.; Iodice, P.; Donnarumma, F.; Dindo, H.; Knoblich, G. Avoiding Accidents at the Champagne Reception: A Study of Joint Lifting and Balancing. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 28, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippsen, A.; Nagai, Y. A Predictive Coding Account for Cognition in Human Children and Chimpanzees: A Case Study of Drawing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, R.P. Interpersonally Situated Cognition. Int. J. Philos. Stud. 2008, 16, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, P.J.; Meltzoff, A.N. Body Maps in the Infant Brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2015, 19, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Pub: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-557-2. [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore, S.-J.; Tavassoli, T.; Calò, S.; Thomas, R.M.; Catmur, C.; Frith, U.; Haggard, P. Tactile Sensitivity in Asperger Syndrome. Brain Cogn. 2006, 61, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.R.; Robertson, A.E.; McKay, L.S.; Toal, E.; McAleer, P.; Pollick, F.E. Vision in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Vis. Res. 2009, 49, 2705–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, K. Auditory Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 836–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, G.; Webb, S.J.; McPartland, J. Understanding the Nature of Face Processing Impairment in Autism: Insights from Behavioral and Electrophysiological Studies. HDVN 2005, 27, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolphs, R.; Sears, L.; Piven, J. Abnormal Processing of Social Information from Faces in Autism. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliemann, D.; Dziobek, I.; Hatri, A.; Baudewig, J.; Heekeren, H.R. The Role of the Amygdala in Atypical Gaze on Emotional Faces in Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9469–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylliäinen, A.; Hietanen, J.K. Skin Conductance Responses to Another Person’s Gaze in Children with Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2006, 36, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.D.; Delmolino, L.; Tanaka, J.W.; Shiffrar, M. Comparison of Visual Sensitivity to Human and Object Motion in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2010, 3, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, C.M.; Konrad, C.; Häberlen, M.; Kleser, C.; von Gontard, A.; Reith, W.; Troje, N.F.; Krick, C. Perception of Biological Motion in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 1480–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grèzes, J.; Wicker, B.; Berthoz, S.; de Gelder, B. A Failure to Grasp the Affective Meaning of Actions in Autism Spectrum Disorder Subjects. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, B.; Wicker, B.; Moore, D.G.; Monfardini, E.; Duverger, H.; Fonséca, D.D.; Deruelle, C. Brief Report: Recognition of Emotional and Non-Emotional Biological Motion in Individuals with Autistic Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2007, 37, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, J.S.; Davies, M.; Quadt, L.; Critchley, H.D.; Garfinkel, S.N. Interoceptive Awareness Mitigates Deficits in Emotional Prosody Recognition in Autism. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 146, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mul, C.; Cardini, F.; Stagg, S.D.; Sadeghi Esfahlani, S.; Kiourtsoglou, D.; Cardellicchio, P.; Aspell, J.E. Altered Bodily Self-Consciousness and Peripersonal Space in Autism. Autism 2019, 23, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, C.J.; Foss-Feig, J.H.; Burnette, C.P.; Heacock, J.L.; Cosby, A.A. The Rubber Hand Illusion in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Delayed Influence of Combined Tactile and Visual Input on Proprioception. Autism 2012, 16, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.-P.; Lytle, M.; Cascio, C.; Wallace, M.T. Disrupted Integration of Exteroceptive and Interoceptive Signaling in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mul, C.; Stagg, S.D.; Herbelin, B.; Aspell, J.E. The Feeling of Me Feeling for You: Interoception, Alexithymia and Empathy in Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 2953–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curioni, A.; Minio-Paluello, I.; Sacheli, L.M.; Candidi, M.; Aglioti, S.M. Autistic Traits Affect Interpersonal Motor Coordination by Modulating Strategic Use of Role-Based Behavior. Mol. Autism 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, E.; Burr, D. When the World Becomes ‘Too Real’: A Bayesian Explanation of Autistic Perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevgi, M.; Diaconescu, A.O.; Henco, L.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Schilbach, L. Social Bayes: Using Bayesian Modeling to Study Autistic Trait-Related Differences in Social Cognition. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 87, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.A.; Hernandez, L.M.; Bowman, H.C.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Dapretto, M. Sensory Over-Responsivity and Social Cognition in ASD: Effects of Aversive Sensory Stimuli and Attentional Modulation on Neural Responses to Social Cues. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Ashwin, E.; Ashwin, C.; Tavassoli, T.; Chakrabarti, B. Talent in Autism: Hyper-Systemizing, Hyper-Attention to Detail and Sensory Hypersensitivity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.K.; Trivedi, M.H.; Garver, C.R.; Grannemann, B.D.; Andrews, A.A.; Savla, J.S.; Johnson, D.G.; Mehta, J.A.; Schroeder, J.L. The Pattern of Sensory Processing Abnormalities in Autism. Autism 2006, 10, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranek, G.T.; Boyd, B.A.; Poe, M.D.; David, F.J.; Watson, L.R. Hyperresponsive Sensory Patterns in Young Children With Autism, Developmental Delay, and Typical Development. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 2007, 112, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, C.L.; Harper, J.D.; Kueker, R.H.; Lang, A.R.; Abbacchi, A.M.; Todorov, A.; LaVesser, P.D. Sensory Responsiveness as a Predictor of Social Severity in Children with High Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2010, 40, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.; Hoadley, C.; Hughes, J.E.A.; Smith, P.; Allison, C.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Simner, J. Atypical Sensory Sensitivity as a Shared Feature between Synaesthesia and Autism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.J.; Ozonoff, S. Annotation: What Do We Know about Sensory Dysfunction in Autism? A Critical Review of the Empirical Evidence. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2005, 46, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boxtel, J.J.A.; Lu, H. A Predictive Coding Perspective on Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Lawson, R.; Frith, C.D. On Hyperpriors and Hypopriors: Comment on Pellicano and Burr. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, R.P.; Rees, G.; Friston, K.J. An Aberrant Precision Account of Autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Cruys, S.; Evers, K.; Van der Hallen, R.; Van Eylen, L.; Boets, B.; de-Wit, L.; Wagemans, J. Precise Minds in Uncertain Worlds: Predictive Coding in Autism. Psychol. Rev. 2014, 121, 649–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolis, D.; Schilbach, L. Observing and Participating in Social Interactions: Action Perception and Action Control across the Autistic Spectrum. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolis, D.; Balsters, J.; Wenderoth, N.; Becchio, C.; Schilbach, L. Beyond Autism: Introducing the Dialectical Misattunement Hypothesis and a Bayesian Account of Intersubjectivity. Psychopathology 2017, 50, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vygotsky, L.S. Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-674-07668-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss: Attachment; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss: Separation: Anxiety and Anger; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss: Loss: Sadness and Depression; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-465-04237-1. [Google Scholar]
- Filippetti, M.L.; Johnson, M.H.; Lloyd-Fox, S.; Dragovic, D.; Farroni, T. Body Perception in Newborns. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2413–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, G.; Meltzoff, A.N.; Osterling, J.; Rinaldi, J.; Brown, E. Children with Autism Fail to Orient to Naturally Occurring Social Stimuli. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1998, 28, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, G.; Toth, K.; Abbott, R.; Osterling, J.; Munson, J.; Estes, A.; Liaw, J. Early Social Attention Impairments in Autism: Social Orienting, Joint Attention, and Attention to Distress. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, R.P. Autism and the Development of Mind; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 1993; ISBN 978-0-86377-229-0. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fanghella, M.; Era, V.; Candidi, M. Interpersonal Motor Interactions Shape Multisensory Representations of the Peripersonal Space. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020255
Fanghella M, Era V, Candidi M. Interpersonal Motor Interactions Shape Multisensory Representations of the Peripersonal Space. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleFanghella, Martina, Vanessa Era, and Matteo Candidi. 2021. "Interpersonal Motor Interactions Shape Multisensory Representations of the Peripersonal Space" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020255
APA StyleFanghella, M., Era, V., & Candidi, M. (2021). Interpersonal Motor Interactions Shape Multisensory Representations of the Peripersonal Space. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020255





