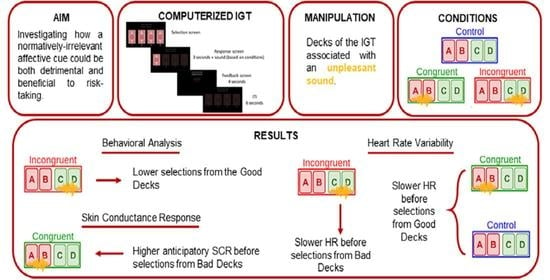
Normatively Irrelevant Affective Cues Affect Risk-Taking under Uncertainty: Insights from the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT), Skin Conductance Response, and Heart Rate Variability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Design and Procedure
2.3. Materials
2.3.1. Computerized IGT
2.3.2. Sound Manipulation
2.3.3. Physiological Indexes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Behavioral Data
2.4.2. Physiological Data
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Analysis
3.2. Physiological Analysis
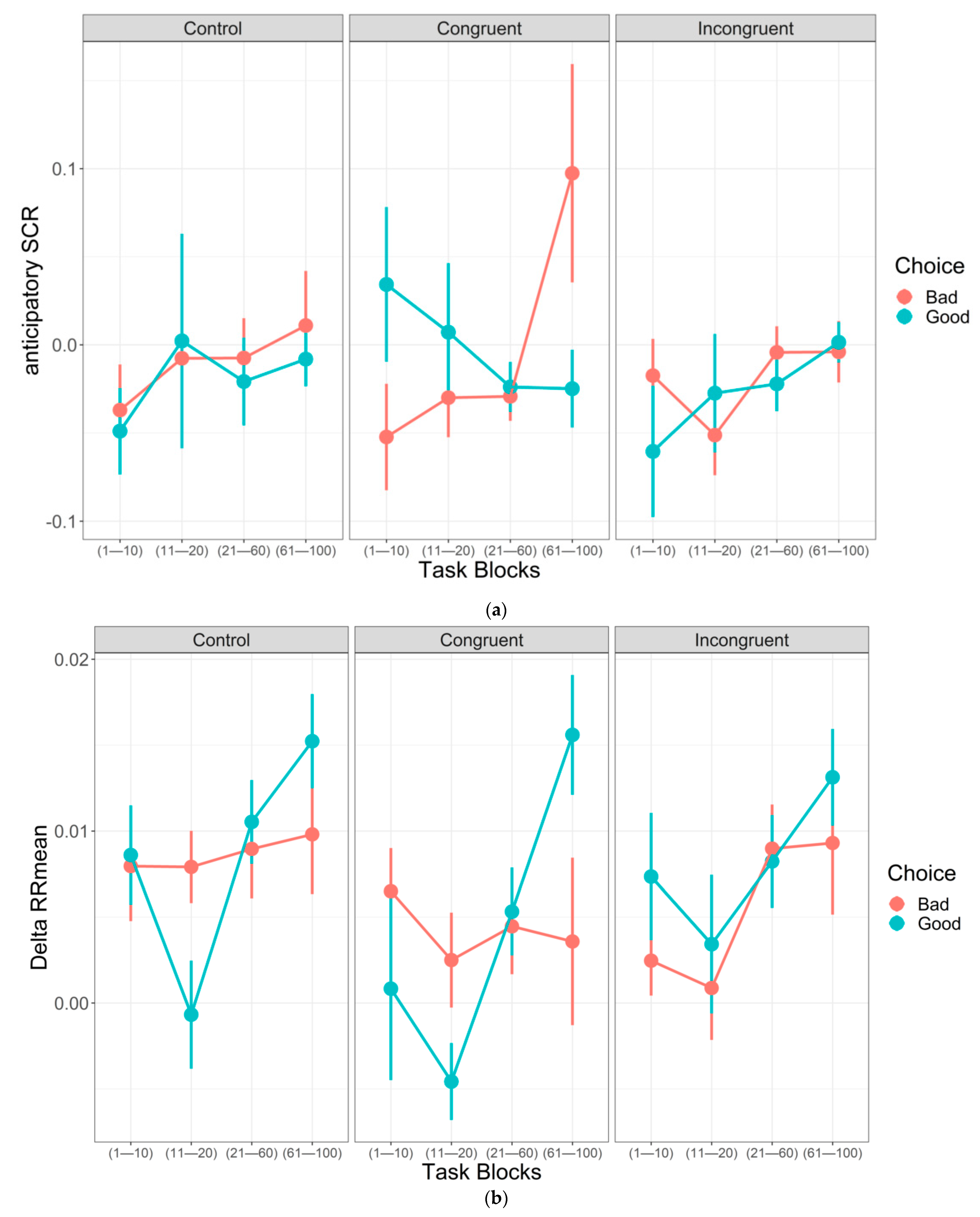
3.2.1. Skin Conductance Response
3.2.2. Cardiac activity
4. Discussion
Limits and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanchette, I.; Richards, A. The Influence of Affect on Higher Level Cognition: A Review of Research on Interpretation, Judgement, Decision Making and Reasoning. Cogn. Emot. 2010, 24, 561–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, J.S.; Li, Y.; Valdesolo, P.; Kassam, K.S. Emotion and Decision Making. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 799–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovic, P.; Finucane, M.L.; Peters, E.; MacGregor, D.G. Risk as Analysis and Risk as Feelings: Some Thoughts about Affect, Reason, Risk, and Rationality. Risk Anal. 2004, 24, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovic, P.; Finucane, M.; Peters, E.; MacGregor, D.G. Rational Actors or Rational Fools: Implications of the Affect Heuristic for Behavioral Economics. J. Socio-Econ. 2002, 31, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovic, P.; Finucane, M.L.; Peters, E.; MacGregor, D.G. The Affect Heuristic. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 177, 1333–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.R. The Somatic Marker Hypothesis: A Neural Theory of Economic Decision. Games Econ. Behav. 2005, 52, 336–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.R.; Damasio, H.; Anderson, S.W. Insensitivity to Future Consequences Following Damage to Human Prefrontal Cortex. Cognition 1994, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasio, A.R. Descartes’ Error: Emotion, Rationality and the Human Brain. N. Y. Putnam 1994, 352. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Xiang, P.; Huang, L. Bridging Ecological Rationality, Embodied Emotion, and Neuroeconomics: Insights from the Somatic Marker Hypothesis. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Recknor, E.C.; Grabenhorst, F.; Bechara, A. Decisions under Ambiguity and Decisions under Risk: Correlations with Executive Functions and Comparisons of Two Different Gambling Tasks with Implicit and Explicit Rules. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2007, 29, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R.; Lee, G.P. Different Contributions of the Human Amygdala and Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex to Decision-Making. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5473–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, H. Characterization of the Decision-Making Deficit of Patients with Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Lesions. Brain 2000, 123, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, M.; Bechara, A. The Somatic Marker Framework as a Neurological Theory of Decision-Making: Review, Conceptual Comparisons, and Future Neuroeconomics Research. J. Econ. Psychol. 2010, 31, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, A.R. Deciding Advantageously before Knowing the Advantageous Strategy. Science 1997, 275, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-C.; Huang, J.-T.; Duann, J.-R.; Lin, C.-H. Twenty Years After the Iowa Gambling Task: Rationality, Emotion, and Decision-Making. Front. Psychol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasio, A.R.; Everitt, B.J.; Bishop, D.; Roberts, A.C.; Robbins, T.W.; Weiskrantz, L. The Somatic Marker Hypothesis and the Possible Functions of the Prefrontal Cortex. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 351, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lerner, J.S.; Keltner, D. Feelings and Consumer Decision Making: The Appraisal-Tendency Framework. J. Consum. Psychol. 2007, 17, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, M.; Holland, R.W.; Witteman, C.L.M. In the Winning Mood: Affect in the Iowa Gambling Task. 2008. Available online: http://journal.sjdm.org/bb4.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Shukla, M.; Rasmussen, E.C.; Nestor, P.G. Emotion and Decision-Making: Induced Mood Influences IGT Scores and Deck Selection Strategies. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2019, 41, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rompay, T.J.L.; De Vries, P.W.; Bontekoe, F.; Tanja-Dijkstra, K. Embodied Product Perception: Effects of Verticality Cues in Advertising and Packaging Design on Consumer Impressions and Price Expectations. Psychol. Mark. 2012, 29, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, M.; Karlan, D.; Mullainathan, S.; Shafir, E.; Zinman, J. What’s Advertising Content Worth? Evidence from a Consumer Credit Marketing Field Experiment. Q. J. Econ. 2010, 125, 263–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, N.; Johnson, E.J. When Web Pages Influence Choice: Effects of Visual Primes on Experts and Novices. J. Consum. Res. 2002, 29, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darke, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ashworth, L. The Importance and Functional Significance of Affective Cues in Consumer Choice. J. Consum. Res. 2006, 33, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnambs, T.; Appel, M.; Oeberst, A. Red Color and Risk-Taking Behavior in Online Environments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Read, J.P.; Kahler, C.W.; Richards, J.B.; Ramsey, S.E.; Stuart, G.L.; Strong, D.R.; Brown, R.A. Evaluation of a Behavioral Measure of Risk Taking: The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 2002, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Aklin, W.M.; Jones, H.A.; Richards, J.B.; Strong, D.R.; Kahler, C.W.; Read, J.P. The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART) Differentiates Smokers and Nonsmokers. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2003, 11, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopko, D.R.; Lejuez, C.W.; Daughters, S.B.; Aklin, W.M.; Osborne, A.; Simmons, B.L.; Strong, D.R. Construct Validity of the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART): Relationship with MDMA Use by Inner-City Drug Users in Residential Treatment. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2006, 28, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovic, B.; Stupple, E.; Gale, M.; Sheffield, D. Sweating the Small Stuff: A Meta-Analysis of Skin Conductance on the Iowa Gambling Task. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 19, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porges, S.W. Cardiac Vagal Tone: A Physiological Index of Stress. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1995, 19, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porges, S.W. The Polyvagal Theory: Phylogenetic Substrates of a Social Nervous System. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2001, 42, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porges, S.W. The Polyvagal Perspective. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Åhs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J.; Wager, T.D. A Meta-Analysis of Heart Rate Variability and Neuroimaging Studies: Implications for Heart Rate Variability as a Marker of Stress and Health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-G.; Cheon, E.-J.; Bai, D.-S.; Lee, Y.H.; Koo, B.-H. Stress and Heart Rate Variability: A Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.M. Natural Selective Attention: Orienting and Emotion. Psychophysiology 2009, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Emotion and motivation. In Handbook of Psychophysiology, 3rd ed; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 581–607. ISBN 978-0-521-84471-0. [Google Scholar]
- Löw, A.; Lang, P.J.; Smith, J.C.; Bradley, M.M. Both Predator and Prey: Emotional Arousal in Threat and Reward. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, E.A.; Somsen, R.J.M.; Beek, B.V.; Molen, M.W.V.D. Heart Rate and Skin Conductance Analysis of Antecendents and Consequences of Decision Making. Psychophysiology 2004, 41, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, W.M.; Wedell, D.H. Autonomic Responses to Choice Outcomes: Links to Task Performance and Reinforcement-Learning Parameters. Biol. Psychol. 2020, 156, 107968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathôt, S.; Schreij, D.; Theeuwes, J. OpenSesame: An Open-Source, Graphical Experiment Builder for the Social Sciences. Behav. Res. 2012, 44, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Makita, K.; Nakao, T.; Kanayama, N.; Machizawa, M.G.; Sasaoka, T.; Sugata, A.; Kobayashi, R.; Hiramoto, R.; Yamawaki, S.; et al. Affective Auditory Stimulus Database: An Expanded Version of the International Affective Digitized Sounds (IADS-E). Behav. Res. 2018, 50, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzego, A.; Battisti, A.; Gabrieli, G.; Esposito, G.; Furlanello, C. Pyphysio: A Physiological Signal Processing Library for Data Science Approaches in Physiology. SoftwareX 2019, 10, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.J.; Levy, R.; Scheepers, C.; Tily, H.J. Random Effects Structure for Confirmatory Hypothesis Testing: Keep It Maximal. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 68, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. Likelihood of a Model and Information Criteria. J. Econom. 1981, 16, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H. Decision-Making and Addiction (Part I): Impaired Activation of Somatic States in Substance Dependent Individuals When Pondering Decisions with Negative Future Consequences. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumpu.com. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/6853895/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.5823 [stat]. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, T.V.; McClelland, J.L. A Reexamination of the Evidence for the Somatic Marker Hypothesis: What Participants Really Know in the Iowa Gambling Task. PNAS 2004, 101, 16075–16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, B.D.; Dalgleish, T.; Lawrence, A.D. The Somatic Marker Hypothesis: A Critical Evaluation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 239–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, N.; Vassileva, J.; Ahn, W.-Y. The Outcome-Representation Learning Model: A Novel Reinforcement Learning Model of the Iowa Gambling Task. Cogn. Sci. 2018, 42, 2534–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittig, A.; Pawlikowski, M.; Craske, M.G.; Alpers, G.W. Avoidant Decision Making in Social Anxiety: The Interaction of Angry Faces and Emotional Responses. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittig, A.; Alpers, G.W.; Niles, A.N.; Craske, M.G. Avoidant Decision-Making in Social Anxiety Disorder: A Laboratory Task Linked to in Vivo Anxiety and Treatment Outcome. Behav. Res. Ther. 2015, 73, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittig, A.; Brand, M.; Pawlikowski, M.; Alpers, G.W. The Cost of Fear: Avoidant Decision Making in a Spider Gambling Task. J. Anxiety Disord. 2014, 28, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Hirota, A.; Takasawa, N.; Shigemasu, K. Application of the Somatic Marker Hypothesis to Individual Differences in Decision Making. Biol. Psychol. 2003, 65, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, E.A.; Vendel, I.; Van der Molen, M.W. Decision-Making in Disinhibited Adolescents and Adults: Insensitivity to Future Consequences or Driven by Immediate Reward? Personal. Individ. Differ. 2003, 35, 1625–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R. Failure to Respond Autonomically to Anticipated Future Outcomes Following Damage to Prefrontal Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 1996, 6, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, M.; Thayer, J.F. How Heart Rate Variability Affects Emotion Regulation Brain Networks. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 19, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, B.M.; Luecken, L.J. Heart Rate Variability as an Index of Regulated Emotional Responding. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2006, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.P.; Cash, C.; Rankin, C.; Bernardi, A.; Koenig, J.; Thayer, J.F. Resting Heart Rate Variability Predicts Self-Reported Difficulties in Emotion Regulation: A Focus on Different Facets of Emotion Regulation. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Model | Parameters | AIC | Deviance | Chisq. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null Model | 4 | 18,974.02 | 18,966 | |
| Trial | 5 | 18,902.95 | 18,892 | 74.076 (p < 0.001) |
| Trial + Condition | 7 | 18,900.80 | 18,887 | 5.151 (p = 0.076) |
| Trial × Condition | 9 | 18,903.26 | 18,885 | 1.532 (p = 0.464) |
| Fixed Effects | Parameter | Estimate (SE) | z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.2807 (0.077) | −3.624 | <0.001 | |
| Trial | 1.3609 (0.141) | 9.704 | <0.001 | |
| Condition (Congr.) | −0.0414 (0.097) | −0.430 | 0.667 | |
| Condition (Incongr.) | −0.2081 (0.096) | −2.166 | 0.03 | |
| Random Effects | Parameter | Variance | Correlation | |
| Intercept | 0.259 | |||
| Trial (slope) | 2.307 | −0.65 |
| Condition | Choice | Block. Trend | SE | df | Lower. CL | Upper. CL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Bad | 0.01443 | 0.0138 | 345 | −0.01494 | 0.04124 |
| Congruent | Bad | 0.04497 | 0.0138 | 345 | 0.01746 | 0.07249 |
| Incongruent | Bad | 0.00875 | 0.0130 | 345 | −0.01682 | 0.03429 |
| Control | Good | 0.00997 | 0.0138 | 345 | −0.01745 | 0.03774 |
| Congruent | Good | −0.02372 | 0.0138 | 345 | −0.05081 | 0.00338 |
| Incongruent | Good | 0.01908 | 0.0130 | 345 | −0.00649 | 0.04465 |
| Contrast | Estimate | SE | df | t. Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contr. Bad–Contr. Good | 0.00445 | 0.0187 | 714 | 0.238 | 0.8117 |
| Congr. Bad–Congr. Good | 0.06584 | 0.0187 | 714 | 3.523 | 0.0005 |
| Incong. Bad–Incong. Good | −0.01033 | 0.0174 | 714 | −0.594 | 0.5522 |
| Condition | Choice | Block. Trend | SE | df | Lower. CL | Upper. CL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Bad | 0.000659 | 0.00145 | 390 | −0.002186 | 0.00350 |
| Congruent | Bad | −0.000679 | 0.00141 | 390 | −0.003450 | 0.00209 |
| Incongruent | Bad | 0.002862 | 0.00137 | 390 | 0.000159 | 0.00556 |
| Control | Good | 0.003108 | 0.00145 | 390 | 0.000263 | 0.00595 |
| Congruent | Good | 0.005418 | 0.00141 | 390 | 0.002647 | 0.00819 |
| Incongruent | Good | 0.002214 | 0.00137 | 390 | −0.000489 | 0.00492 |
| Contrast | Estimate | SE | df | t. Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contr. Bad–Contr. Good | −0.002449 | 0.00204 | 696 | −1.199 | 0.2310 |
| Congr. Bad–Congr. Good | −0.006097 | 0.00199 | 696 | −3.064 | 0.0023 |
| Incong. Bad–Incong. Good | 0.000648 | 0.00194 | 696 | 0.334 | 0.7385 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Priolo, G.; D’Alessandro, M.; Bizzego, A.; Bonini, N. Normatively Irrelevant Affective Cues Affect Risk-Taking under Uncertainty: Insights from the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT), Skin Conductance Response, and Heart Rate Variability. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030336
Priolo G, D’Alessandro M, Bizzego A, Bonini N. Normatively Irrelevant Affective Cues Affect Risk-Taking under Uncertainty: Insights from the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT), Skin Conductance Response, and Heart Rate Variability. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(3):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030336
Chicago/Turabian StylePriolo, Giulia, Marco D’Alessandro, Andrea Bizzego, and Nicolao Bonini. 2021. "Normatively Irrelevant Affective Cues Affect Risk-Taking under Uncertainty: Insights from the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT), Skin Conductance Response, and Heart Rate Variability" Brain Sciences 11, no. 3: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030336
APA StylePriolo, G., D’Alessandro, M., Bizzego, A., & Bonini, N. (2021). Normatively Irrelevant Affective Cues Affect Risk-Taking under Uncertainty: Insights from the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT), Skin Conductance Response, and Heart Rate Variability. Brain Sciences, 11(3), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030336