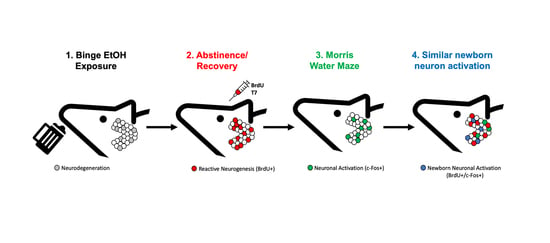
Functional Activation of Newborn Neurons Following Alcohol-Induced Reactive Neurogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
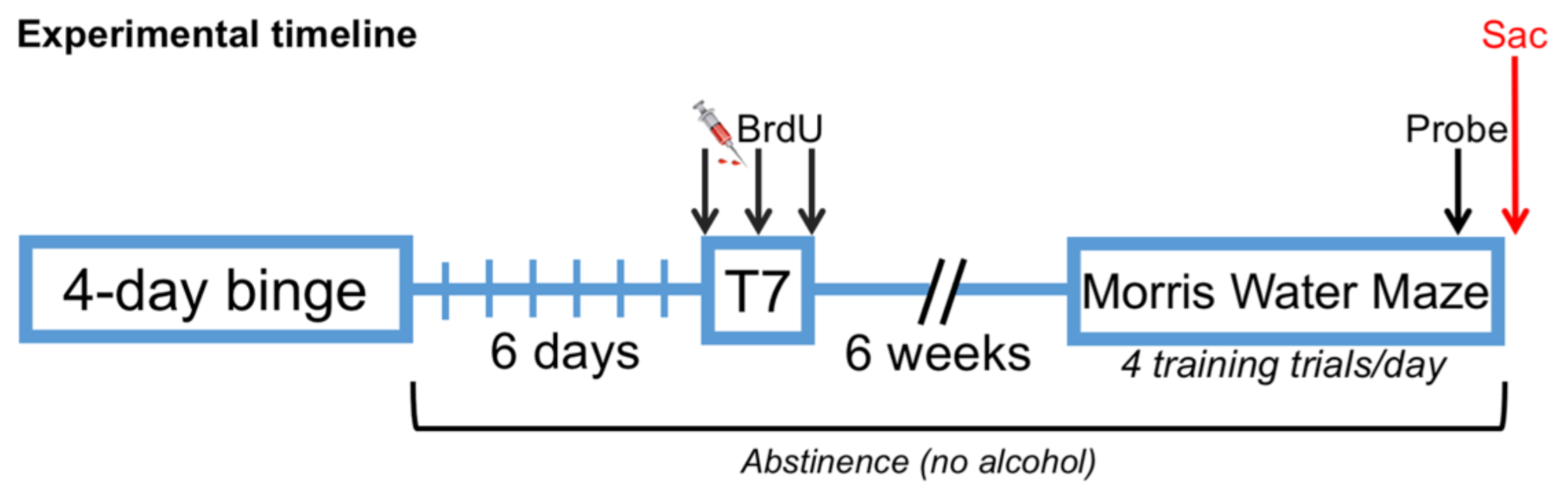
2.2. Binge Model of An Alcohol Use Disorder
2.2.1. Alcohol Exposure
2.2.2. Blood Ethanol Concentration (BEC)
2.2.3. Withdrawal Observation
2.3. Bromodeoxyuridine Administration
2.4. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
2.5. Tissue Preparation
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Quantification
2.8. Statistical Approaches
3. Results
3.1. AUD Model Data
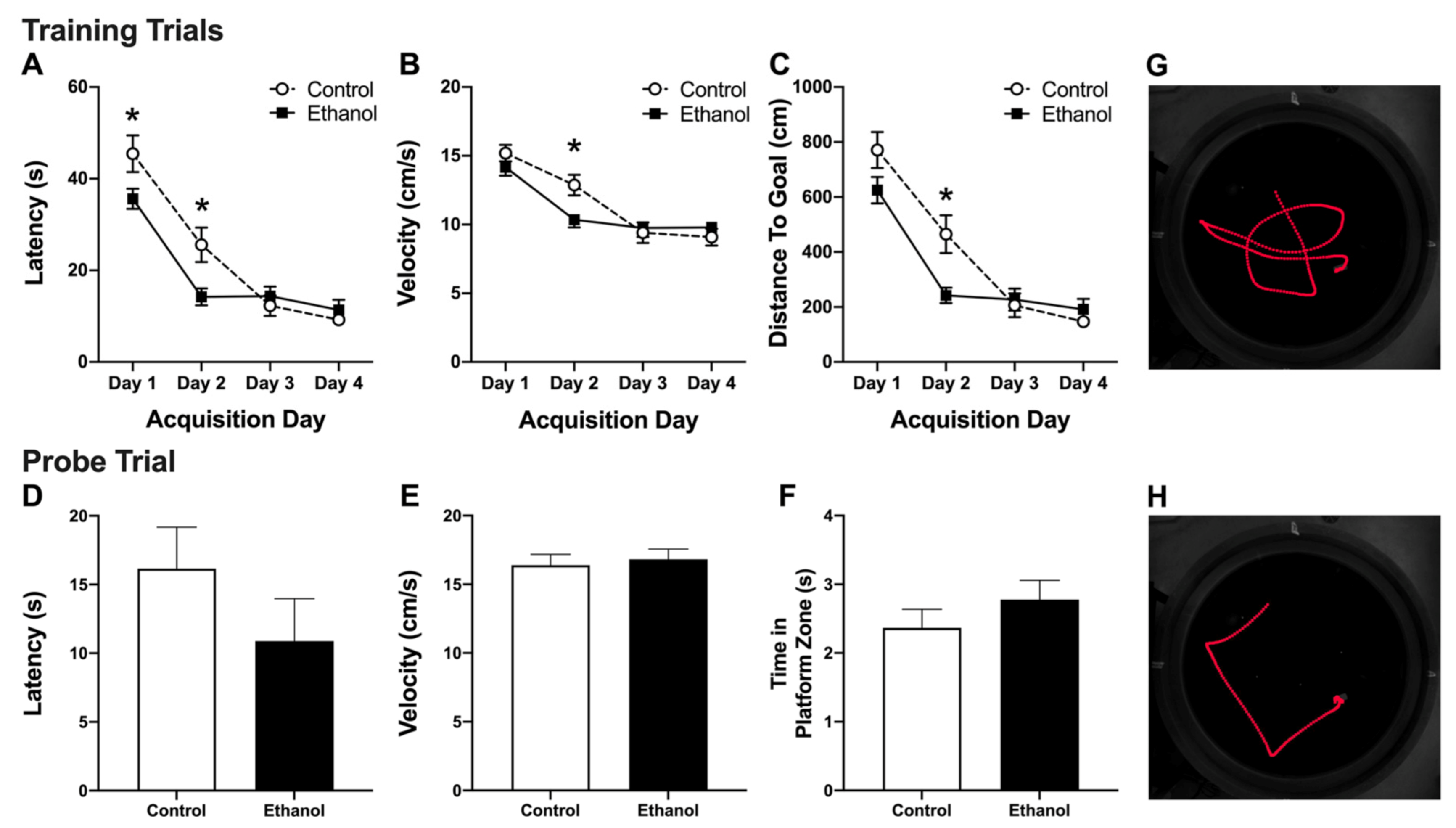
3.2. Abstinence from Alcohol Treatment Improves Acquisition of the MWM Task
3.3. Alcohol Treatment Has No Effect on Recall of the MWM
3.4. Abstinence from Ethanol Increases Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus (DG)
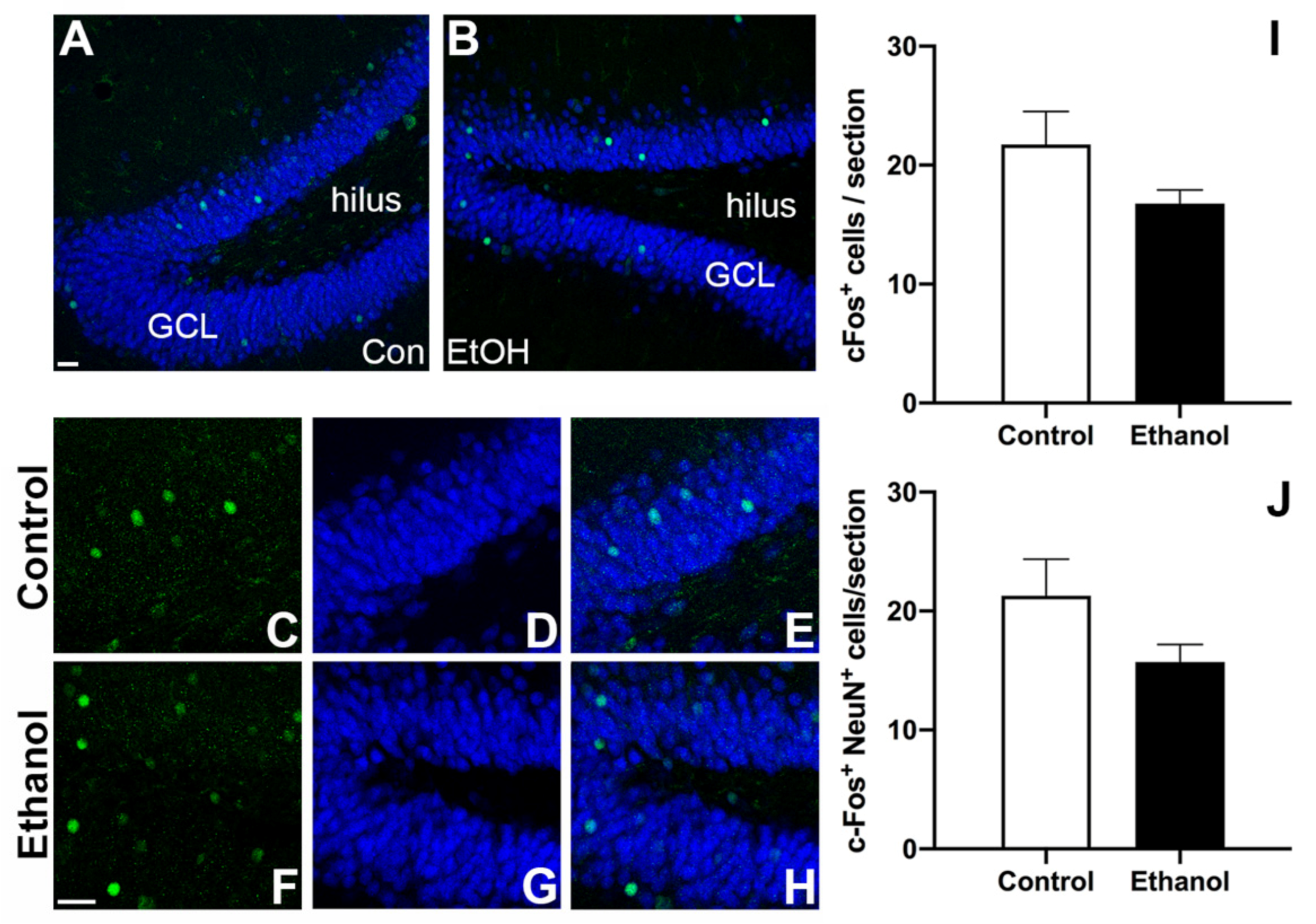
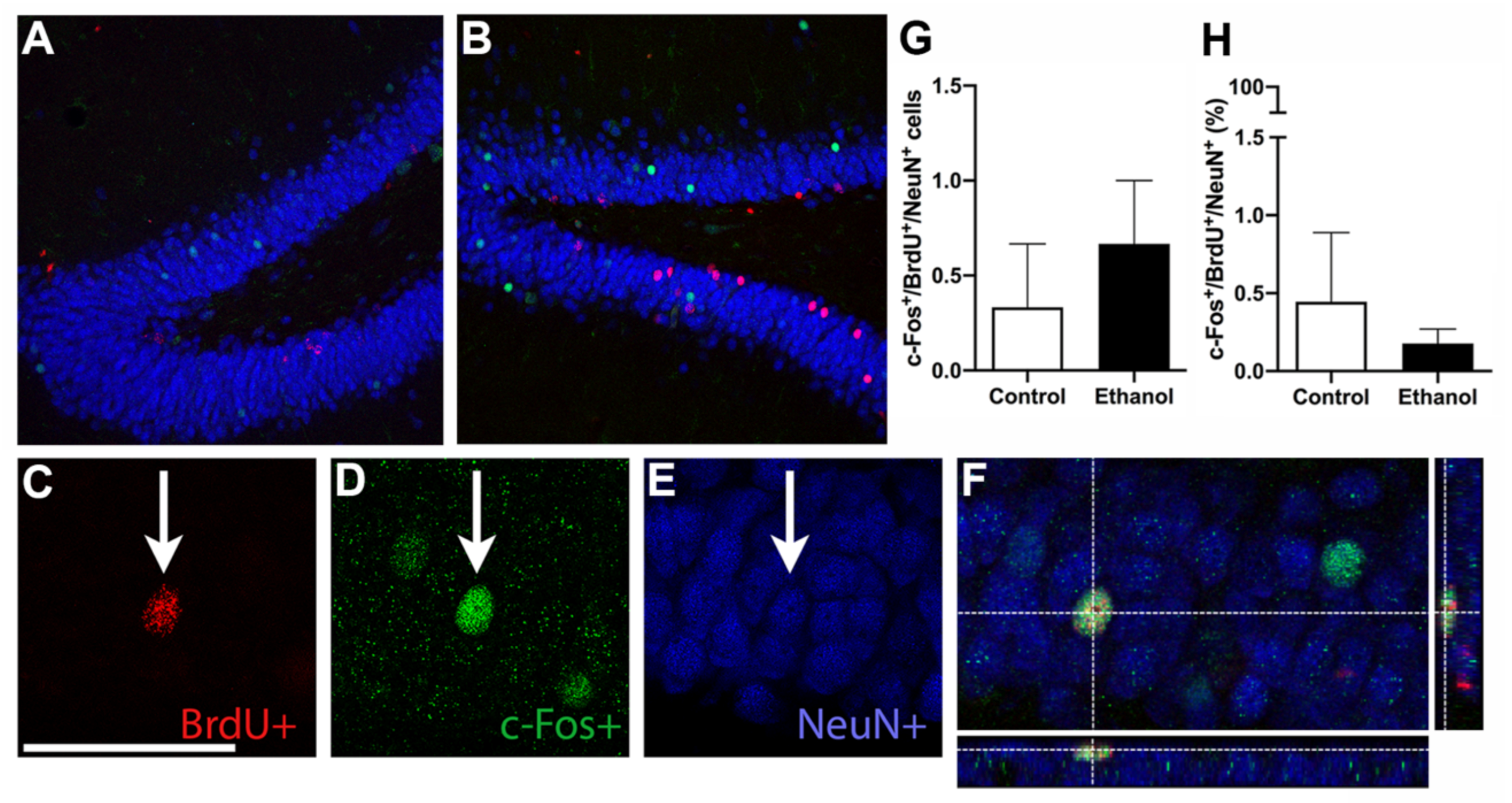
3.5. Prior Ethanol Exposure Has No Effect on MWM-Induced c-Fos Expression
3.6. Ethanol Does Not Alter MWM-Induced Activation of Adult Born Neurons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nutt, D.J.; King, L.A.; Phillips, L.D. Independent Scientific Committee on Drugs. Drug harms in the UK: A multicriteria decision analysis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Marks, J.S.; Stroup, D.F.; Gerberding, J.L. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA 2004, 291, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchery, E.E.; Harwood, H.J.; Sacks, J.J.; Simon, C.J.; Brewer, R.D. Economic costs of excessive alcohol consumption in the U.S., 2006. Am. J. Prev Med. 2011, 41, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NIAAA. Drinking Levels Defined. Available online: https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/moderate-binge-drinking (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health; Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, MS, USA, 2020.
- Grant, B.F.; Goldstein, R.B.; Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Jung, J.; Zhang, H.; Pickering, R.P.; Ruan, W.J.; Smith, S.M.; Huang, B.; et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 Alcohol Use Disorder: Results From the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckardt, M.J.; Martin, P.R. Clinical assessment of cognition in alcoholism. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1986, 10, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Nixon, K. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol 2009, 44, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stavro, K.; Pelletier, J.; Potvin, S. Widespread and sustained cognitive deficits in alcoholism: A meta-analysis. Addict. Biol. 2013, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, T.P.; Arciniegas, D.B.; Alfers, J.; Clapp, L.; Martin, B.; Du, Y.; Liu, D.; Shen, D.; Davatzikos, C. Hippocampus volume loss due to chronic heavy drinking. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsoy, S.; Durak, A.C.; Esel, E. Hippocampal volumes and cognitive functions in adult alcoholic patients with adolescent-onset. Alcohol 2013, 47, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Neurocircuitry in alcoholism: A substrate of disruption and repair. Psychopharmacology 2005, 180, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, M.C.; Mandyam, C.D. Thinking after Drinking: Impaired Hippocampal-Dependent Cognition in Human Alcoholics and Animal Models of Alcohol Dependence. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortez, I.; Rodgers, S.P.; Kosten, T.A.; Leasure, J.L. Sex and Age Effects on Neurobehavioral Toxicity Induced by Binge Alcohol. Brain Plast. 2020, 6, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, W.A. Are binge drinkers more at risk of developing brain damage? Alcohol 1993, 10, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obernier, J.A.; Bouldin, T.W.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure in adult rats causes necrotic cell death. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanraud, S.; Martelli, C.; Delain, F.; Kostogianni, N.; Douaud, G.; Aubin, H.J.; Reynaud, M.; Martinot, J.L. Brain morphometry and cognitive performance in detoxified alcohol-dependents with preserved psychosocial functioning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, D.W.; Barnes, D.E.; Zornetzer, S.F.; Hunter, B.E.; Kubanis, P. Neuronal loss in hippocampus induced by prolonged ethanol consumption in rats. Science 1980, 209, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geil, C.R.; Hayes, D.M.; McClain, J.A.; Liput, D.J.; Marshall, S.A.; Chen, K.Y.; Nixon, K. Alcohol and adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Promiscuous drug, wanton effects. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 54, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mechtcheriakov, S.; Brenneis, C.; Egger, K.; Koppelstaetter, F.; Schocke, M.; Marksteiner, J. A widespread distinct pattern of cerebral atrophy in patients with alcohol addiction revealed by voxel-based morphometry. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhanabalan, G.; Le Maitre, T.W.; Bogdanovic, N.; Alkass, K.; Druid, H. Hippocampal granule cell loss in human chronic alcohol abusers. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 120, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Marsh, L.; Mathalon, D.H.; Lim, K.O.; Pfefferbaum, A. Anterior hippocampal volume deficits in nonamnesic, aging chronic alcoholics. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengochea, O.; Gonzalo, L.M. Effect of chronic alcoholism on the human hippocampus. Histol. Histopathol. 1990, 5, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.; Bair, J.L.; Thomas, K.M.; Iacono, W.G. Problematic alcohol use and reduced hippocampal volume: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadete-Leite, A.; Tavares, M.A.; Uylings, H.B.; Paula-Barbosa, M. Granule cell loss and dendritic regrowth in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of the rat after chronic alcohol consumption. Brain Res. 1988, 473, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukoyanov, N.V.; Brandao, F.; Cadete-Leite, A.; Madeira, M.D.; Paula-Barbosa, M.M. Synaptic reorganization in the hippocampal formation of alcohol-fed rats may compensate for functional deficits related to neuronal loss. Alcohol 2000, 20, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, M.L.; Liput, D.J.; Eaves, D.W.; Nixon, K. Upregulated vimentin suggests new areas of neurodegeneration in a model of an alcohol use disorder. Neuroscience 2011, 197, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.Y.; Martinez, D.B.; Neafsey, E.J.; Collins, M.A. Binge ethanol-induced brain damage in rats: Effect of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.M.; Deeny, M.A.; Shaner, C.A.; Nixon, K. Determining the threshold for alcohol-induced brain damage: New evidence with gliosis markers. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cippitelli, A.; Damadzic, R.; Frankola, K.; Goldstein, A.; Thorsell, A.; Singley, E.; Eskay, R.L.; Heilig, M. Alcohol-induced neurodegeneration, suppression of transforming growth factor-beta, and cognitive impairment in rats: Prevention by group II metabotropic glutamate receptor activation. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, O.A.; Nixon, S.J. Neurobehavioral sequelae of alcoholism. Neurol. Clin. 1993, 11, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitel, A.L.; Beaunieux, H.; Witkowski, T.; Vabret, F.; Guillery-Girard, B.; Quinette, P.; Desgranges, B.; Eustache, F. Genuine episodic memory deficits and executive dysfunctions in alcoholic subjects early in abstinence. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawyer, K.S.; Adra, N.; Salz, D.M.; Kemppainen, M.I.; Ruiz, S.M.; Harris, G.J.; Oscar-Berman, M. Hippocampal subfield volumes in abstinent men and women with a history of alcohol use disorder. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernier, J.A.; White, A.M.; Swartzwelder, H.S.; Crews, F.T. Cognitive deficits and CNS damage after a 4-day binge ethanol exposure in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 72, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlen, P.L.; Wortzman, G.; Holgate, R.C.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Rankin, J.C. Reversible cerebral atrophy in recently abstinent chronic alcoholics measured by computed tomography scans. Science 1978, 200, 1076–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, J.; Butters, N.; Ryan, C.; Bayog, R. Cognitive loss and recovery in long-term alcohol abusers. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1983, 40, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, K. Alcohol and adult neurogenesis: Roles in neurodegeneration and recovery in chronic alcoholism. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, C.; Kunert, H.J.; Stawicki, S.; Kroner-Herwig, B.; Ehrenreich, H.; Krampe, H. Recovery of hippocampus-related functions in chronic alcoholics during monitored long-term abstinence. Alcohol Alcohol 2007, 42, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazdzinski, S.; Durazzo, T.C.; Yeh, P.H.; Hardin, D.; Banys, P.; Meyerhoff, D.J. Chronic cigarette smoking modulates injury and short-term recovery of the medial temporal lobe in alcoholics. Psychiatry Res. 2008, 162, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahr, N.M.; Mayer, D.; Rohlfing, T.; Hasak, M.P.; Hsu, O.; Vinco, S.; Orduna, J.; Luong, R.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Brain injury and recovery following binge ethanol: Evidence from in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Eijk, J.; Demirakca, T.; Frischknecht, U.; Hermann, D.; Mann, K.; Ende, G. Rapid partial regeneration of brain volume during the first 14 days of abstinence from alcohol. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefer, M.E.; Pennington, D.L.; Durazzo, T.C.; Mon, A.; Abe, C.; Truran, D.; Hutchison, K.E.; Meyerhoff, D.J. Genetic and behavioral determinants of hippocampal volume recovery during abstinence from alcohol. Alcohol 2014, 48, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 124, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.J.; Stevens, C.F.; Gage, F.H. Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imayoshi, I.; Sakamoto, M.; Ohtsuka, T.; Takao, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, K.; Ikeda, T.; Itohara, S.; Kageyama, R. Roles of continuous neurogenesis in the structural and functional integrity of the adult forebrain. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clelland, C.D.; Choi, M.; Romberg, C.; Clemenson, G.D., Jr.; Fragniere, A.; Tyers, P.; Jessberger, S.; Saksida, L.M.; Barker, R.A.; Gage, F.H.; et al. A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation. Science 2009, 325, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsufka, R.; Peng, H.; Newton, J.; Nixon, K. Alcohol effects on adult neural stem cells—A novel mechanism of neurotoxicity in alcohol use disorders. In Stem Cells in Toxicology and Teratology; Rasmussen, T., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, T.; Parylak, S.L.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, M.B. Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 1993, 11, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetsch, F.; Caille, I.; Lim, D.A.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 1999, 97, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, M.S.; Hinds, J.W. Neurogenesis in the adult rat: Electron microscopic analysis of light radioautographs. Science 1977, 197, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.D.; Takahashi, J.; Gage, F.H. The adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 1997, 8, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.S.; Perfilieva, E.; Bjork-Eriksson, T.; Alborn, A.M.; Nordborg, C.; Peterson, D.A.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Fulmore, C.A.; Tartt, A.N.; Simeon, L.R.; Pavlova, I.; Poposka, V.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Stankov, A.; Arango, V.; Dwork, A.J.; et al. Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Persists throughout Aging. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 589–599.e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempermann, G.; Gage, F.H.; Aigner, L.; Song, H.; Curtis, M.A.; Thuret, S.; Kuhn, H.G.; Jessberger, S.; Frankland, P.W.; Cameron, H.A.; et al. Human Adult Neurogenesis: Evidence and Remaining Questions. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastings, N.B.; Seth, M.I.; Tanapat, P.; Rydel, T.A.; Gould, E. Granule neurons generated during development extend divergent axon collaterals to hippocampal area CA3. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 452, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, N.; Teixeira, C.M.; Wang, A.H.; Frankland, P.W. Imaging activation of adult-generated granule cells in spatial memory. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 3033–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Praag, H.; Schinder, A.F.; Christie, B.R.; Toni, N.; Palmer, T.D.; Gage, F.H. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 2002, 415, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, E.; Beylin, A.; Tanapat, P.; Reeves, A.; Shors, T.J. Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Drew, M.R. Functional neurogenesis over the years. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 382, 112470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Burgin, A.; Schinder, A.F. Requirement of adult-born neurons for hippocampus-dependent learning. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winocur, G.; Wojtowicz, J.M.; Sekeres, M.; Snyder, J.S.; Wang, S. Inhibition of neurogenesis interferes with hippocampus-dependent memory function. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Hong, N.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Wojtowicz, J.M. A role for adult neurogenesis in spatial long-term memory. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Radik, R.; Wojtowicz, J.M.; Cameron, H.A. Anatomical gradients of adult neurogenesis and activity: Young neurons in the ventral dentate gyrus are activated by water maze training. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, J.S.; Choe, J.S.; Clifford, M.A.; Jeurling, S.I.; Hurley, P.; Brown, A.; Kamhi, J.F.; Cameron, H.A. Adult-born hippocampal neurons are more numerous, faster maturing, and more involved in behavior in rats than in mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14484–14495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.W.; Yang, Y.R.; Wang, P.S.; Wang, R.Y. Intermittent hypoxia after transient focal ischemia induces hippocampal neurogenesis and c-Fos expression and reverses spatial memory deficits in rats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, S.A.; Eaves, D.W.; Smith, A.R.; Nixon, K. Alcohol inhibition of neurogenesis: A mechanism of hippocampal neurodegeneration in an adolescent alcohol abuse model. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, D.G.; Yague, A.G.; Johnsen-Soriano, S.; Bosch-Morell, F.; Collado-Morente, L.; Muriach, M.; Romero, F.J.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M. Selective impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis by chronic alcoholism: Protective effects of an antioxidant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7919–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, K.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure decreases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, H.N.; Chan, S.H.; Crawford, E.F.; Lee, Y.K.; Funk, C.K.; Koob, G.F.; Mandyam, C.D. Permanent impairment of birth and survival of cortical and hippocampal proliferating cells following excessive drinking during alcohol dependence. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golub, H.M.; Zhou, Q.G.; Zucker, H.; McMullen, M.R.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N.; Ro, E.J.; Nagy, L.E.; Suh, H. Chronic Alcohol Exposure is Associated with Decreased Neurogenesis, Aberrant Integration of Newborn Neurons, and Cognitive Dysfunction in Female Mice. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Maitre, T.W.; Dhanabalan, G.; Bogdanovic, N.; Alkass, K.; Druid, H. Effects of Alcohol Abuse on Proliferating Cells, Stem/Progenitor Cells, and Immature Neurons in the Adult Human Hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, K.; Crews, F.T. Temporally specific burst in cell proliferation increases hippocampal neurogenesis in protracted abstinence from alcohol. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9714–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somkuwar, S.S.; Fannon, M.J.; Staples, M.C.; Zamora-Martinez, E.R.; Navarro, A.I.; Kim, A.; Quigley, J.A.; Edwards, S.; Mandyam, C.D. Alcohol dependence-induced regulation of the proliferation and survival of adult brain progenitors is associated with altered BDNF-TrkB signaling. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 4319–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansson, A.C.; Nixon, K.; Rimondini, R.; Damadzic, R.; Sommer, W.H.; Eskay, R.; Crews, F.T.; Heilig, M. Long-term suppression of forebrain neurogenesis and loss of neuronal progenitor cells following prolonged alcohol dependence in rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vetreno, R.P.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure during adolescence leads to a persistent loss of neurogenesis in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus that is associated with impaired adult cognitive functioning. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McClain, J.A.; Morris, S.A.; Marshall, S.A.; Nixon, K. Ectopic hippocampal neurogenesis in adolescent male rats following alcohol dependence. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maynard, M.E.; Leasure, J.L. Exercise enhances hippocampal recovery following binge ethanol exposure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taffe, M.A.; Kotzebue, R.W.; Crean, R.D.; Crawford, E.F.; Edwards, S.; Mandyam, C.D. Long-lasting reduction in hippocampal neurogenesis by alcohol consumption in adolescent nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11104–11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broadwater, M.A.; Liu, W.; Crews, F.T.; Spear, L.P. Persistent loss of hippocampal neurogenesis and increased cell death following adolescent, but not adult, chronic ethanol exposure. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Crews, F.T. Persistent Decreases in Adult Subventricular and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Following Adolescent Intermittent Ethanol Exposure. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, R.K.; Wooden, J.I.; Barton, E.A.; Leasure, J.L. Recurrent binge ethanol is associated with significant loss of dentate gyrus granule neurons in female rats despite concomitant increase in neurogenesis. Neuropharmacology 2019, 148, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.M.; Nickell, C.G.; Chen, K.Y.; McClain, J.A.; Heath, M.M.; Deeny, M.A.; Nixon, K. Activation of neural stem cells from quiescence drives reactive hippocampal neurogenesis after alcohol dependence. Neuropharmacology 2018, 133, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandyam, C.D.; Koob, G.F. The addicted brain craves new neurons: Putative role for adult-born progenitors in promoting recovery. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pineda, J.R.; Encinas, J.M. The Contradictory Effects of Neuronal Hyperexcitation on Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parent, J.M.; Yu, T.W.; Leibowitz, R.T.; Geschwind, D.H.; Sloviter, R.S.; Lowenstein, D.H. Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 3727–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdugo-Vega, G.; Arias-Gil, G.; Lopez-Fernandez, A.; Artegiani, B.; Wasielewska, J.M.; Lee, C.C.; Lippert, M.T.; Kempermann, G.; Takagaki, K.; Calegari, F. Increasing neurogenesis refines hippocampal activity rejuvenating navigational learning strategies and contextual memory throughout life. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Solway, K.; Messing, R.O.; Sharp, F.R. Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7768–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Nicola, D.; Suzzi, S.; Vargas-Caballero, M.; Fransen, N.L.; Al-Malki, H.; Cebrian-Silla, A.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Riecken, K.; Fehse, B.; Perry, V.H. Temporal dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in chronic neurodegeneration. Brain 2014, 137, 2312–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.S.; Washington, P.M.; Kernie, S.G. Injury-Induced Neurogenesis: Mechanisms and Relevance. Neuroscientist 2016, 22, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaiss, C.A.; Yu, T.S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Dimchev, G.; Parada, L.F.; Powell, C.M.; Kernie, S.G. Temporally specified genetic ablation of neurogenesis impairs cognitive recovery after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4906–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Daniels, T.E.; Rolfe, A.; Waters, M.; Hamm, R. Inhibition of injury-induced cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus impairs spontaneous cognitive recovery after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geibig, C.S.; Keiner, S.; Redecker, C. Functional recruitment of newborn hippocampal neurons after experimental stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, C.G.; Thompson, K.R.; Pauly, J.R.; Nixon, K. Recovery of Hippocampal-Dependent Learning Despite Blunting Reactive Adult Neurogenesis After Alcohol Dependence. Brain Plast. 2020, 6, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Urso, T.; Gavaler, J.S.; Van Thiel, D.H. Blood ethanol levels in sober alcohol users seen in an emergency room. Life Sci. 1981, 28, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoof, J.J.; Van Der Lely, N.; Bouthoorn, S.H.; Van Dalen, W.E.; Pereira, R.R. Adolescent alcohol intoxication in the Dutch hospital departments of pediatrics: A 2-year comparison study. J. Adolesc. Health 2011, 48, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.A.; Kelso, M.L.; Liput, D.J.; Marshall, S.A.; Nixon, K. Similar withdrawal severity in adolescents and adults in a rat model of alcohol dependence. Alcohol 2010, 44, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majchrowicz, E. Induction of physical dependence upon ethanol and the associated behavioral changes in rats. Psychopharmacologia 1975, 43, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, C.R.G.; Peng, H.; Hayes, D.M.; Chen, K.Y.; McClain, J.A.; Nixon, K. Type 2 Neural Progenitor Cell Activation Drives Reactive Neurogenesis after Binge-Like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescent Male Rats. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, M.A.; Corso, T.D.; Neafsey, E.J. Neuronal degeneration in rat cerebrocortical and olfactory regions during subchronic “binge” intoxication with ethanol: Possible explanation for olfactory deficits in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Braun, C.J.; Hoplight, B.; Switzer, R.C., 3rd; Knapp, D.J. Binge ethanol consumption causes differential brain damage in young adolescent rats compared with adult rats. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessberger, S.; Kempermann, G. Adult-born hippocampal neurons mature into activity-dependent responsiveness. Eur J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2707–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weig, B.C.; Richardson, J.R.; Lowndes, H.E.; Reuhl, K.R. Trimethyltin intoxication induces the migration of ventricular/subventricular zone cells to the injured murine hippocampus. Neurotoxicology 2016, 54, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbois, S.L.; Hopkins, D.M.; Scheff, S.W.; Pauly, J.R. Chronic intermittent nicotine administration attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced cognitive dysfunction. Neuroscience 2003, 119, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Y.; Hopkins, D.; Pauly, J.R.; Nixon, K. Binge Ethanol Produces Differential Effects on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Expression and Learning in Adolescent Versus Adult Rats. 2021; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Tayler, K.K.; Tanaka, K.Z.; Reijmers, L.G.; Wiltgen, B.J. Reactivation of neural ensembles during the retrieval of recent and remote memory. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates/George Paxinos, Charles Watson, 6th ed.; Elsevier Academic: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Noori, H.R.; Fornal, C.A. The appropriateness of unbiased optical fractionators to assess cell proliferation in the adult hippocampus. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar-Arredondo, A.; Zepeda, A. Memory retrieval-induced activation of adult-born neurons generated in response to damage to the dentate gyrus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 2859–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kramer, E.E.; Mercaldo, V.; Rashid, A.J.; Insel, N.; Frankland, P.W.; Josselyn, S.A. Neuronal Allocation to a Hippocampal Engram. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzowski, J.F.; McNaughton, B.L.; Barnes, C.A.; Worley, P.F. Environment-specific expression of the immediate-early gene Arc in hippocampal neuronal ensembles. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijmers, L.G.; Perkins, B.L.; Matsuo, N.; Mayford, M. Localization of a stable neural correlate of associative memory. Science 2007, 317, 1230–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chawla, M.K.; Guzowski, J.F.; Ramirez-Amaya, V.; Lipa, P.; Hoffman, K.L.; Marriott, L.K.; Worley, P.F.; McNaughton, B.L.; Barnes, C.A. Sparse, environmentally selective expression of Arc RNA in the upper blade of the rodent fascia dentata by brief spatial experience. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutgeb, J.K.; Leutgeb, S.; Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I. Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus and CA3 of the hippocampus. Science 2007, 315, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kernie, S.G.; Parent, J.M. Forebrain neurogenesis after focal Ischemic and traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallo, F.T.; Katche, C.; Morici, J.F.; Medina, J.H.; Weisstaub, N.V. Immediate Early Genes, Memory and Psychiatric Disorders: Focus on c-Fos, Egr1 and Arc. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawarawong, N.N.; Thompson, K.R.; Guerin, S.G.; Peng, H.; Nixon, K. Reactive, adult neurogenesis in female rats after alcohol dependence. Invited submission to: New Insights into Adult Neurogenesis and Neurodegeneration: Challengers for Brain Repair. Front. Neurosci. 2021. Under Review. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.F. Adult Neurogenesis in Injury-Induced Self-Repair: Use It or Lose It. Brain Plast. 2017, 2, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samokhvalov, A.V.; Irving, H.; Mohapatra, S.; Rehm, J. Alcohol consumption, unprovoked seizures, and epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Krishnan, B.; Zhang, H.; Park, H.R.; Ro, E.J.; Jung, Y.N.; Suh, H. Activity of hippocampal adult-born neurons regulates alcohol withdrawal seizures. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Lee, C.C.; Akamatsu, Y.; Wang, R.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Liu, J. Conditional ablation of neuroprogenitor cells in adult mice impedes recovery of poststroke cognitive function and reduces synaptic connectivity in the perforant pathway. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17314–17325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.S.; Grigereit, L.; Russo, A.; Seib, D.R.; Brewer, M.; Pickel, J.; Cameron, H.A. A Transgenic Rat for Specifically Inhibiting Adult Neurogenesis. eNeuro 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthe, A.; Roeder, I.; Kempermann, G. Mice in an enriched environment learn more flexibly because of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2016, 26, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, R.Q.; Cooke, M.; Seib, D.R.; Zhao, J.; Snyder, J.S. Adult neurogenesis promotes efficient, nonspecific search strategies in a spatial alternation water maze task. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 376, 112151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I.; Forrest, E.; Andersen, P.; Morris, R.G. Spatial learning with a minislab in the dorsal hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9697–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, P.J.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Miller, D.S.; Rhodes, J.S. Induction of c-Fos, Zif268, and Arc from acute bouts of voluntary wheel running in new and pre-existing adult mouse hippocampal granule neurons. Neuroscience 2011, 184, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, S.S.; Teixeira, C.M.; Zaslavsky, K.; Wheeler, A.L.; Martinez-Canabal, A.; Wang, A.H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Lozano, A.M.; Frankland, P.W. Functional convergence of developmentally and adult-generated granule cells in dentate gyrus circuits supporting hippocampus-dependent memory. Hippocampus 2011, 21, 1348–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G. The neurogenic reserve hypothesis: What is adult hippocampal neurogenesis good for? Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiskott, L.; Rasch, M.J.; Kempermann, G. A functional hypothesis for adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Avoidance of catastrophic interference in the dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V.; Mathalon, D.H.; Shear, P.K.; Rosenbloom, M.J.; Lim, K.O. Longitudinal changes in magnetic resonance imaging brain volumes in abstinent and relapsed alcoholics. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Score | Intoxication Behavior | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | 5 g/kg |
| 1 | Hypoactive, mild ataxia | 4 g/kg |
| 2 | Ataxia (abdomen elevated) | 3 g/kg |
| 3 | Delayed righting reflex Severe ataxia (abdomen drags) | 2 g/kg |
| 4 | Loss of righting reflex | 1 g/kg |
| 5 | Loss of eyeblink reflex | 0 g/kg |
| Score | Withdrawal Behaviors |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | hyperactivity |
| 1.4 | tail tremor |
| 1.6 | tail spasm |
| 2.0 | caudal tremor |
| 2.4 | splayed limbs |
| 2.6 | general tremor |
| 3.0 | head tremor |
| 3.4 | wet dog shake |
| 3.6 | chattering teeth |
| 3.8 | spontaneous convulsion |
| Group | Subjects | Intox Score | Dose (g/kg/day) | BEC (mg/dl) | Mean WD | Peak WD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWM | EtOH = 10; Con = 11 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 9.7 ± 0.2 | 401 ± 14 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 3.6 ± 0.1 |
| IHC | EtOH = 3; Con = 3 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 400 ± 10 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawarawong, N.N.; Nickell, C.G.; Hopkins, D.M.; Pauly, J.R.; Nixon, K. Functional Activation of Newborn Neurons Following Alcohol-Induced Reactive Neurogenesis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040499
Nawarawong NN, Nickell CG, Hopkins DM, Pauly JR, Nixon K. Functional Activation of Newborn Neurons Following Alcohol-Induced Reactive Neurogenesis. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(4):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040499
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawarawong, Natalie N., Chelsea G. Nickell, Deann M. Hopkins, James R. Pauly, and Kimberly Nixon. 2021. "Functional Activation of Newborn Neurons Following Alcohol-Induced Reactive Neurogenesis" Brain Sciences 11, no. 4: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040499
APA StyleNawarawong, N. N., Nickell, C. G., Hopkins, D. M., Pauly, J. R., & Nixon, K. (2021). Functional Activation of Newborn Neurons Following Alcohol-Induced Reactive Neurogenesis. Brain Sciences, 11(4), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040499