Altered Emotional Phenotypes in Chronic Kidney Disease Following 5/6 Nephrectomy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. CKD Rat Model
2.3. Serum Biochemical Assays
2.4. Behavioral Tests
2.4.1. Anxiety Tests
2.4.2. Forced Swim Test
2.5. Local Field Potentials
2.6. Renal Histology
2.7. Quantification of Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of CKD Rat Models
3.2. Histological Analysis of Renal Fibrosis in CKD
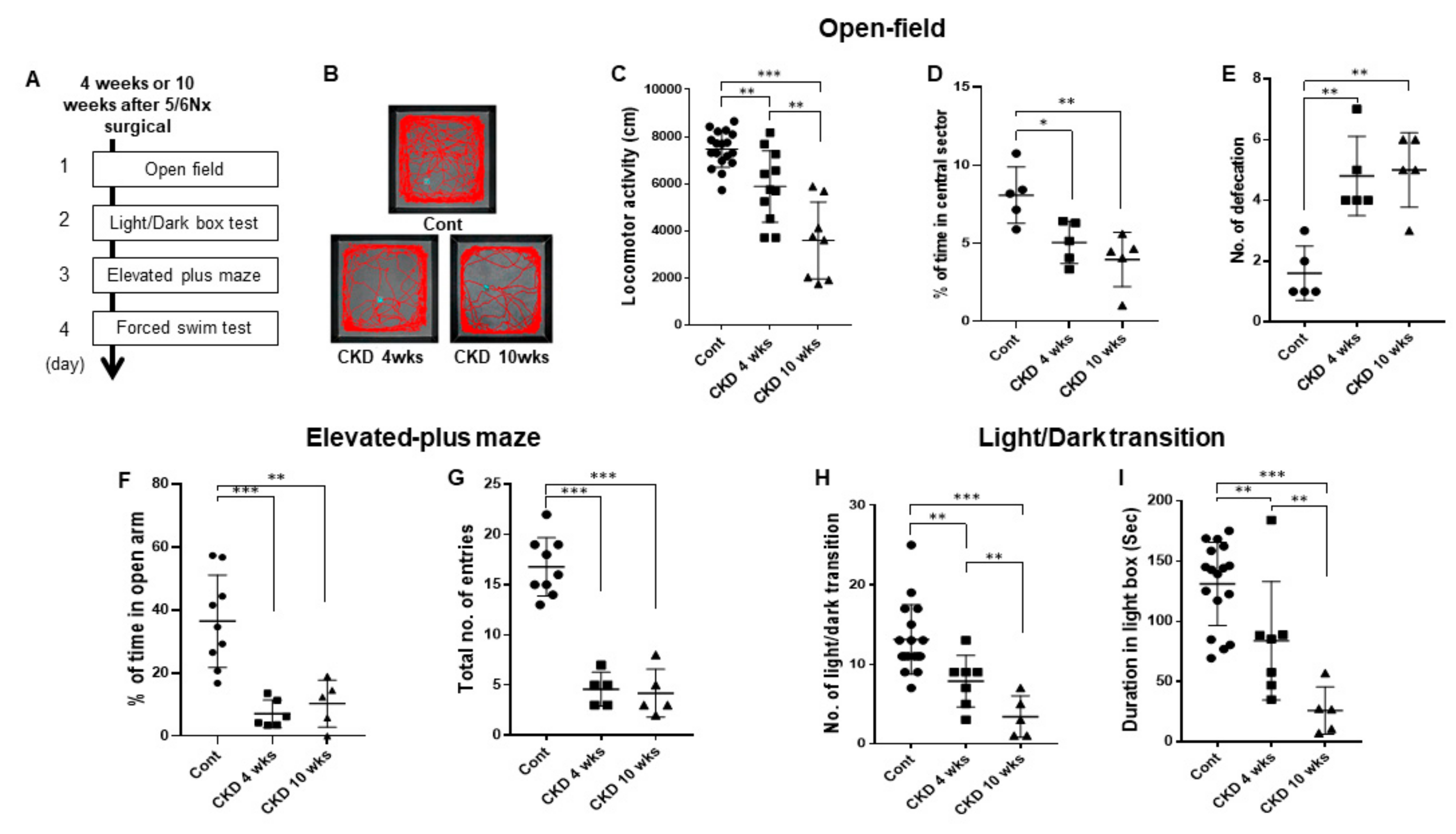
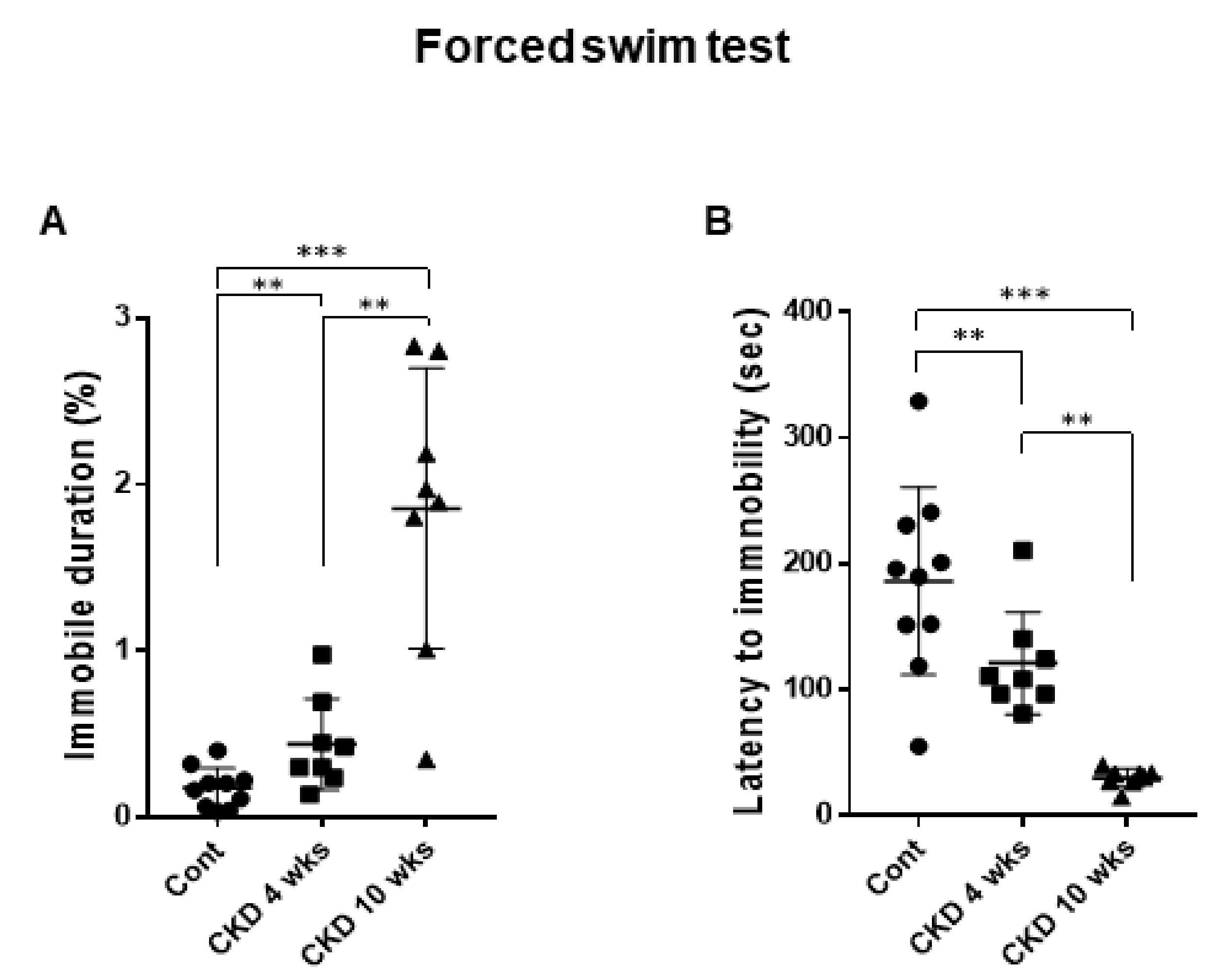
3.3. CKD Increases Anxiogenic Behaviors
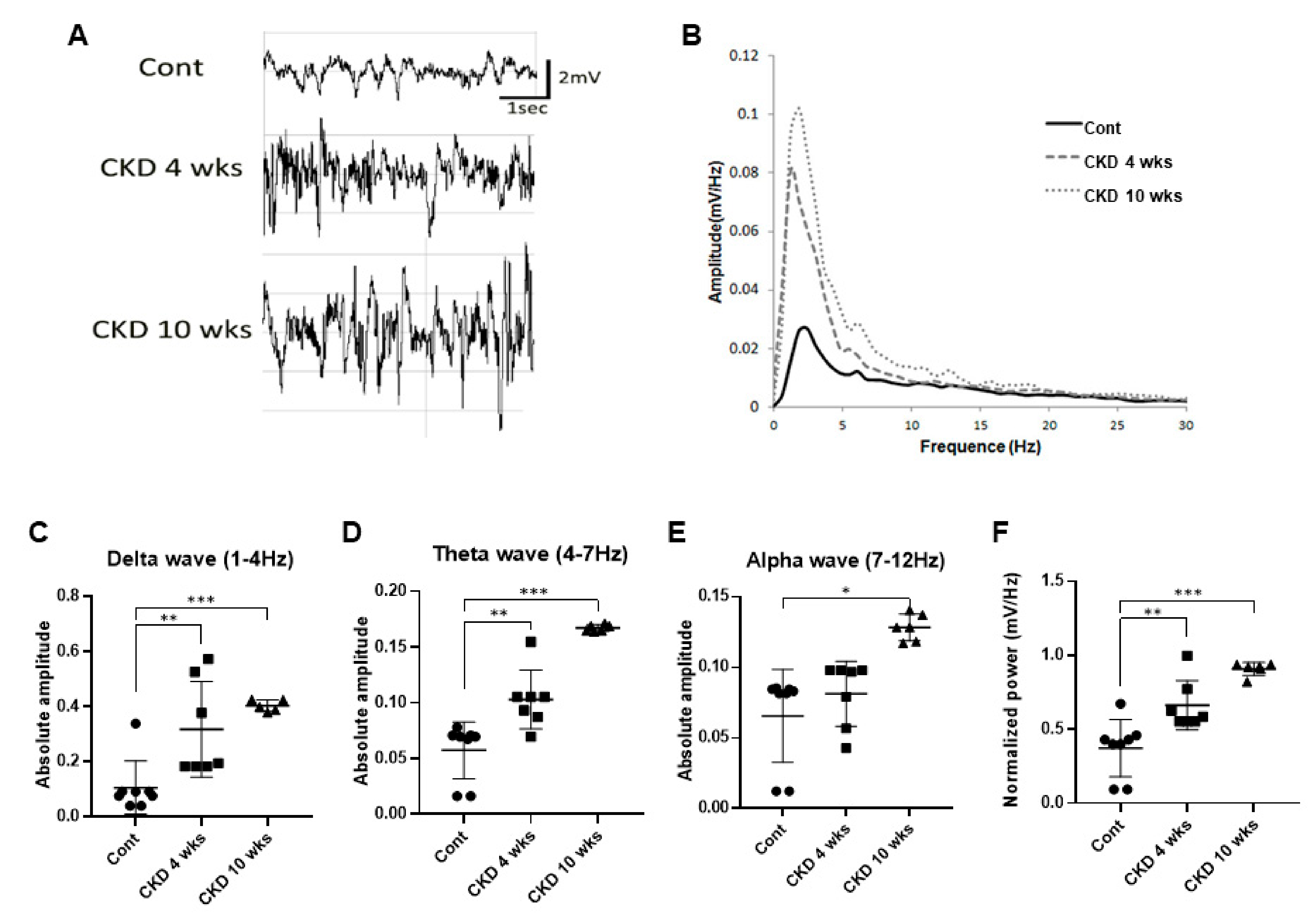
3.4. Representative Profile of LFP in CKD Rat Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zelnick, L.R.; Weiss, N.S.; Kestenbaum, B.R.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Heagerty, P.J.; Tuttle, K.; Hall, Y.N.; Hirsch, I.B.; de Boer, I.H. Diabetes and CKD in the United States Population, 2009–2014. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grams, M.E.; Juraschek, S.P.; Selvin, E.; Foster, M.C.; Inker, L.A.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J. Trends in the prevalence of reduced GFR in the United States: A comparison of creatinine- and cystatin C-based estimates. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, D.C.; Yun, S.R.; Lee, S.W.; Han, S.W.; Kim, W.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.K. Current characteristics of dialysis therapy in Korea: 2016 registry data focusing on diabetic patients. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 37, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Kiernan, M.C.; Murray, A.; Rosner, M.H.; Ronco, C. Kidney-brain crosstalk in the acute and chronic setting. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, J.M.; Godefroy, O.; Chillon, J.M.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. Cognitive disorders and dementia in CKD: The neglected kidney-brain axis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.H.; Livneh, H.; Yen, M.L.; Li, T.C.; Tsai, T.Y. Prevalence and correlates of depression among chronic kidney disease patients in Taiwan. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zalai, D.; Szeifert, L.; Novak, M. Psychological distress and depression in patients with chronic kidney disease. Semin. Dial. 2012, 25, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.; Vecchio, M.; Craig, J.C.; Tonelli, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Nicolucci, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Saglimbene, V.; Logroscino, G.; Fishbane, S.; et al. Prevalence of depression in chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soni, R.K.; Weisbord, S.D.; Unruh, M.L. Health-related quality of life outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2010, 19, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topczewska-Bruns, J.; Tankiewicz, A.; Pawlak, D.; Buczko, W. Behavioral changes in the course of chronic renal insufficiency in rats. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Chilcot, J.; Wellsted, D.; Vilar, E.; Farrington, K. An association between residual renal function and depression symptoms in haemodialysis patients. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 113, c117–c124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Ramkumar, A.; Madanagopal, T.T.; Waly, M.I.; Tageldin, M.; Al-Abri, S.; Fahim, M.; Yasin, J.; Nemmar, A. Motor and behavioral changes in mice with cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Yamato, M.; Toyonaga, J.; Noguchi, H.; Nakano, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Tokumoto, M.; Hirakata, H.; Kitazono, T. Cerebral oxidative stress induces spatial working memory dysfunction in uremic mice: Neuroprotective effect of tempol. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Ha, G.Y.; Jung, Y.W. Chronic renal failure induces cell death in rat hippocampal CA1 via upregulation of alphaCaMKII/NR2A synaptic complex and phosphorylated GluR1-containing AMPA receptor cascades. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 33, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, B.H.; Ziada, A.; Al Husseni, I.; Beegam, S.; Nemmar, A. Motor and behavioral changes in rats with adenine-induced chronic renal failure: Influence of acacia gum treatment. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tothova, L.; Babickova, J.; Borbelyova, V.; Filova, B.; Sebekova, K.; Hodosy, J. Chronic renal insufficiency does not induce behavioral and cognitive alteration in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolk, A.; Griffin, S.; van der Meij, R.; Dewar, C.; Saez, I.; Lin, J.J.; Piantoni, G.; Schoffelen, J.M.; Knight, R.T.; Oostenveld, R. Integrated analysis of anatomical and electrophysiological human intracranial data. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1699–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajan, C.; Porjesz, B. Advances in Electrophysiological Research. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 53–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, B.R.; Salvadore, G.; Colon-Rosario, V.; Latov, D.R.; Holroyd, T.; Carver, F.W.; Coppola, R.; Manji, H.K.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Grillon, C. Abnormal hippocampal functioning and impaired spatial navigation in depressed individuals: Evidence from whole-head magnetoencephalography. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNaughton, N.; Kocsis, B.; Hajós, M. Elicited hippocampal theta rhythm: A screen for anxiolytic and procognitive drugs through changes in hippocampal function? Behav. Pharmacol. 2007, 18, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsugi, M.; Mizuki, Y.; Ushijima, I.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsuchiya, K.; Aoki, T.; Watanabe, Y. Appearance of frontal midline theta activity in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2000, 41, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohl, J.E.; Harms, L.; Pommer, W. Quantitative EEG findings in patients with chronic renal failure. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2007, 12, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Madan, P.; Kalra, O.P.; Agarwal, S.; Tandon, O.P. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleck, C.; Scholle, T.; Schwertfeger, M.; Appenroth, D.; Stein, G. Determination of renal porphyrin handling in rats suffering from different kinds of chronic renal failure (CRF): Uranyl nitrate (UN) induced fibrosis or 5/6-nephrectomy (5/6NX). Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 54, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litbarg, N.O.; Vujicic, S.; Setty, S.; Sethupathi, P.; Dunea, G.; Arruda, J.A.; Singh, A.K. A novel model of surgical injury in adult rat kidney: A “pouch model”. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gangadharan, G.; Shin, J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, A.; Paydar, A.; Kim, D.S.; Miyazaki, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yanagawa, Y.; Kim, J.; et al. Medial septal GABAergic projection neurons promote object exploration behavior and type 2 theta rhythm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6550–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De la Mora, M.P.; Cardenas-Cachon, L.; Vazquez-Garcia, M.; Crespo-Ramirez, M.; Jacobsen, K.; Hoistad, M.; Agnati, L.; Fuxe, K. Anxiolytic effects of intra-amygdaloid injection of the D1 antagonist SCH23390 in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 377, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Brossard, G.; Hautbois, C.; Roux, S. Rodent models of depression: Forced swimming and tail suspension behavioral despair tests in rats and mice. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddenberg, T.E.; Komorowski, M.; Ruocco, L.A.; Silva, M.A.; Topic, B. Attenuating effects of testosterone on depressive-like behavior in the forced swim test in healthy male rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 79, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.E.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.C.; Kwon, O.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, T.C. Hyperthermic seizure induces persistent alteration in excitability of the dentate gyrus in immature rats. Brain Res. 2008, 1216, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.H.; Lee, K.; Sin, D.S.; Park, K.H.; Park, D.K.; Kim, D.S. Altered functional efficacy of hippocampal interneuron during epileptogenesis following febrile seizures. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 131, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.E.; Kwak, S.E.; Choi, K.C.; Kim, D.W.; Kwon, O.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, T.C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of astroglial death in the rat hippocampo-entorhinal complex following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 511, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.S. Lack of delta waves and sleep disturbances during non-rapid eye movement sleep in mice lacking alpha1G-subunit of T-type calcium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18195–18199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitch, W.E. Cachexia in chronic kidney disease: A link to defective central nervous system control of appetite. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1476–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwandt, A.; Denkinger, M.; Fasching, P.; Pfeifer, M.; Wagner, C.; Weiland, J.; Zeyfang, A.; Holl, R.W. Comparison of MDRD, CKD-EPI, and Cockcroft-Gault equation in relation to measured glomerular filtration rate among a large cohort with diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudchada, P.; Laehn, S. Comparisons of GFR estimation using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation and other creatinine-based equations in Asian population: A systematic review. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesta, J.J.; del Pozo, C.; Castello-Banyuls, J.; Faura, C.C. Selective down-regulation of alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain of uremic rats with cognitive impairment. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 236, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, M.K.; Giri, A.; Kumar, S.; Borah, A. A highly reproducible mice model of chronic kidney disease: Evidences of behavioural abnormalities and blood-brain barrier disruption. Life Sci. 2016, 161, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillon, J.M.; Brazier, F.; Bouquet, P.; Massy, Z.A. Neurological disorders in a murine model of chronic renal failure. Toxins 2014, 6, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, S.; Kim, S.R. Association of depression and anxiety with reduced quality of life in patients with predialysis chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2013, 67, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siesjö, B.K.; Katsura, K.; Mellergård, P.; Ekholm, A.; Lundgren, J.; Smith, M.L. Acidosis-related brain damage. Prog. Brain Res. 1993, 96, 23–48. [Google Scholar]
- Farnam, A. pH of soul: How does acid-base balance affect our cognition? Bioimpacts 2014, 4, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, L.L.; Strawn, J.R.; Sah, R. Acid-base dysregulation and chemosensory mechanisms in panic disorder: A translational update. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, D.V.; Miniussi, C.; Frisoni, G.B.; Geroldi, C.; Zanetti, O.; Binetti, G.; Rossini, P.M. Hippocampal atrophy and EEG markers in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2716–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Gireesh, G.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Watanabe, M.; Shin, H.S. Phospholipase C beta 4 in the medial septum controls cholinergic theta oscillations and anxiety behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15375–15385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeller, A.A.; Duzzioni, M.; Duarte, F.S.; Leme, L.R.; Costa, A.P.; Santos, E.C.; de Pieri, C.H.; dos Santos, A.A.; Naime, A.A.; Farina, M.; et al. GABA-A receptor modulators alter emotionality and hippocampal theta rhythm in an animal model of long-lasting anxiety. Brain Res. 2013, 1532, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.; Topiwala, M.A.; Gordon, J.A. Synchronized activity between the ventral hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex during anxiety. Neuron 2010, 65, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, A.; Topiwala, M.A.; Gordon, J.A. Single units in the medial prefrontal cortex with anxiety-related firing patterns are preferentially influenced by ventral hippocampal activity. Neuron 2011, 71, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dharmadhikari, A.S.; Tandle, A.L.; Jaiswal, S.V.; Sawant, V.A.; Vahia, V.N.; Jog, N. Frontal Theta Asymmetry as a Biomarker of Depression. East. Asian Arch. Psychiatry 2018, 28, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.F.; Kan, D.P.X.; Croarkin, P.; Phang, C.K.; Doruk, D. Neurophysiological correlates of depressive symptoms in young adults: A quantitative EEG study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.A.; Lacefield, C.O.; Kentros, C.G.; Hen, R. State-dependent alterations in hippocampal oscillations in serotonin 1A receptor-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6509–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimesch, W. α-band oscillations, attention, and controlled access to stored information. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Títoff, V.; Moury, H.N.; Títoff, I.B.; Kelly, K.M. Seizures, Antiepileptic Drugs, and CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorza, F.A.; Albuquerque, M.; Arida, R.M.; Cysneiros, R.M.; Henriques, T.M.; Scorza, C.A.; Cruz, J.; Kesrouani, S.; Gomes, R.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A. Seizure occurrence in patients with chronic renal insufficiency in regular hemodialysis program. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2005, 63, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Animal Model | Open-Field | Light-Dark Transition | Elevated Plus-Maze | Forced Swim Test | Blood Analysis | Local Field Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 23 | 18 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| CKD 4 weeks | 11 | 9 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 7 |
| CKD 10 weeks | 8 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, D.-K.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-S.; Gil, H.-W. Altered Emotional Phenotypes in Chronic Kidney Disease Following 5/6 Nephrectomy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070882
Yu YH, Kim S-W, Park D-K, Song H-Y, Kim D-S, Gil H-W. Altered Emotional Phenotypes in Chronic Kidney Disease Following 5/6 Nephrectomy. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(7):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070882
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yeon Hee, Seong-Wook Kim, Dae-Kyoon Park, Ho-Yeon Song, Duk-Soo Kim, and Hyo-Wook Gil. 2021. "Altered Emotional Phenotypes in Chronic Kidney Disease Following 5/6 Nephrectomy" Brain Sciences 11, no. 7: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070882
APA StyleYu, Y. H., Kim, S.-W., Park, D.-K., Song, H.-Y., Kim, D.-S., & Gil, H.-W. (2021). Altered Emotional Phenotypes in Chronic Kidney Disease Following 5/6 Nephrectomy. Brain Sciences, 11(7), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070882






