Cofilin and Neurodegeneration: New Functions for an Old but Gold Protein
Abstract
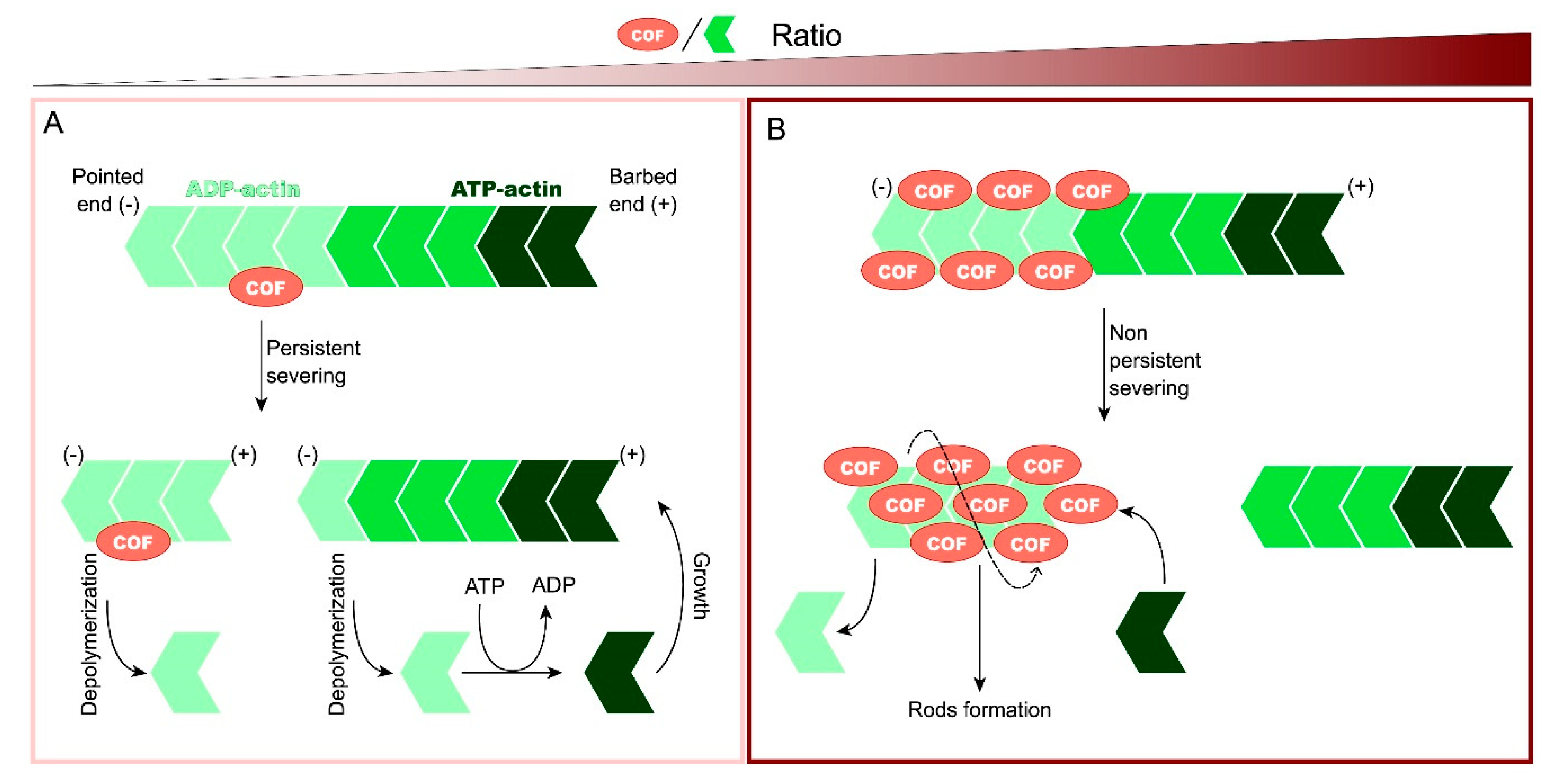
1. Introduction
2. Cofilin Regulation and Its Implication in Neurodegenerative Diseases
3. New Functions for Cofilin in Neurodegenerative Diseases
3.1. Cofilin Oxidation Leads to Cofilin–Actin Rod Formation
3.2. Cofilin Takes Part in Microglia Activation Which Leads to Neuroinflammation
3.3. Cofilin Mediates Actin Depolymerization for Myelin Wrapping
3.4. Cofilin Translocation into the Mitochondria Induces Apoptosis
3.5. Cofilin Induces Mitochondrial Fission
3.6. Cofilin Mediates Microtubule Instability
3.7. Cofilin Regulates Gene Expression
4. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid-β |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| CAP2 | Cyclase-associated protein 2 |
| CDK5 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 |
| CIN | Chronophin |
| Drp1 | Dynamin-related protein 1 |
| FRDA | Friedreich’s ataxia |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| LilrB2 | Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2 |
| LIMK1 | LIM-domain containing kinase 1 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MBP | myelin basic protein |
| PARK | Parkin 2 |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PLD1 | Phospholipase D1 |
| PP1/PP2 | Serine/threonine phosphatases 1 and 2 |
| ROCK | Rho-associated protein kinase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SSH1 | Slingshot 1 |
| TESK | Testis-specific kinase |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
References
- Bamburg, J.R.; Harris, H.E.; Weeds, A.G. Partial purification and characterization of an actin depolymerizing factor from brain. FEBS Lett. 1980, 121, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamburg, J.R. Proteins of the ADF/Cofilin Family: Essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchoin, L.; Boujemaa-Paterski, R.; Sykes, C.; Plastino, J. Actin dynamics, architecture and mechanics in cell motility. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamburg, J.R.; Bernstein, B.W. Roles of ADF/cofilin in actin polymerization and beyond. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2010, 2, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wioland, H.; Guichard, B.; Senju, Y.; Myram, S.; Lappalainen, P.; Jégou, A.; Romet-Lemonne, G. ADF/Cofilin accelerates actin dynamics by severing filaments and promoting their depolymerization at both ends. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1956–1967.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.W.; Chen, H.; Boyle, J.A.; Bamburg, J.R. Formation of actin-ADF/cofilin rods transiently retards decline of mitochondrial potential and ATP in stressed neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C828–C839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrianantoandro, E.; Pollard, T.D. Mechanism of actin filament turnover by severing and nucleation at different concentrations of ADF/Cofilin. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.; Frame, M.C. Cellular functions of the ADF/cofilin family at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-B.; Zhang, H.-W.; Fu, R.-Q.; Hu, X.-Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.-N.; Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.-J.; Deng, Q.; et al. Mitochondrial fission and mitophagy depend on cofilin-mediated actin depolymerization activity at the mitochondrial fission site. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.-A.A.; Liu, T.; Fang, C.C.; Cazzaro, S.; Kee, T.; LePochat, P.; Yrigoin, K.; Penn, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Activated cofilin exacerbates tau pathology by impairing tau-mediated microtubule dynamics. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Nakamura, K.; Iijima, M.; Sesaki, H. Mitochondrial dynamics in neurodegeneration. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.M. Does apoptosis have a role in neurodegeneration? BMJ 2001, 322, 1539–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McMurray, C.T. Neurodegeneration: Diseases of the cytoskeleton? Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, H.; Hablitz, L.M.; Xavier, A.L.R.; Feng, W.; Zou, W.; Pu, T.; Monai, H.; Murlidharan, G.; Castellanos Rivera, R.M.; Simon, M.J.; et al. Aquaporin-4-dependent glymphatic solute transport in the rodent brain. eLife 2018, 7, e40070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordone, M.P.; Salman, M.M.; Titus, H.E.; Amini, E.; Andersen, J.V.; Chakraborti, B.; Diuba, A.V.; Dubouskaya, T.G.; Ehrke, E.; Espindola de Freitas, A.; et al. The energetic brain—A review from students to students. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of astroglia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Parpura, V.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Haydon, P.G. Tripartite synapses: Glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsegiani, A.; Shah, Z. The role of cofilin in age-related neuroinflammation. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.E.; Woo, J.A. Cofilin, a master node regulating cytoskeletal pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 72, S131–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, C.; Huang, J.; Liu, W.; Lai, W.; Leng, F.; Tang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, M.; et al. ROCK1 induces dopaminergic nerve cell apoptosis via the activation of Drp1-mediated aberrant mitochondrial fission in Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munsie, L.; Caron, N.; Atwal, R.S.; Marsden, I.; Wild, E.J.; Bamburg, J.R.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Truant, R. Mutant huntingtin causes defective actin remodeling during stress: Defining a new role for transglutaminase 2 in neurodegenerative disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 1937–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K. Roles of cofilin in development and its mechanisms of regulation. Dev. Growth Differ. 2015, 57, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Nagata, K.; Maekawa, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Narumiya, S.; Mizuno, K. Rho-associated Kinase ROCK Activates LIM-kinase 1 by Phosphorylation at Threonine 508 within the Activation Loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 3577–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Troys, M.; Huyck, L.; Leyman, S.; Dhaese, S.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Ampe, C. Ins and outs of ADF/cofilin activity and regulation. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.Y.; Minamide, L.S.; Bamburg, J.R.; Bokoch, G.M. Chronophin mediates an ATP-sensing mechanism for cofilin dephosphorylation and neuronal cofilin-actin rod formation. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-S.; Huang, T.Y.; Bokoch, G.M. Reactive oxygen species regulate a slingshot-cofilin activation pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, J.M.; Gabrielsen, M.; Chim, Y.H.; Munro, J.; McGhee, E.J.; Sumpton, D.; Eaton, P.; Anderson, K.I.; Yin, H.; Olson, M.F. Polarized cell motility induces hydrogen peroxide to inhibit cofilin via cysteine oxidation. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, B.T.; Volbracht, C.; Tan, K.O.; Li, R.; Yu, V.C.; Li, P. Mitochondrial translocation of cofilin is an early step in apoptosis induction. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.W.; Shaw, A.E.; Minamide, L.S.; Pak, C.W.; Bamburg, J.R. Incorporation of cofilin into rods depends on disulfide intermolecular bonds: Implications for actin regulation and neurodegenerative disease. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6670–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hakala, M.; Lappalainen, P. ADF/cofilin binds phosphoinositides in a multivalent manner to act as a PIP(2)-density sensor. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.; Pope, B.; Mannherz, H.G.; Weeds, A. Determining the differences in actin binding by human ADF and cofilin. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 315, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.; Ho, H.J.; Wang, C.; Guan, J.-L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of cofilin at Y68 by v-Src leads to its degradation through ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Oncogene 2010, 29, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. The role of parkin in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25 (Suppl. 1), S32–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, D.P.; Scoles, D.R.; Ho, T.H.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Pulst, S.-M. Parkin is associated with actin filaments in neuronal and nonneural cells. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.K.; Kawamura, T.; Ohsawa, Y.; Ohtsubo, M.; Asakawa, S.; Takayanagi, A.; Shimizu, N. Parkin interacts with LIM Kinase 1 and reduces its cofilin-phosphorylation activity via ubiquitination. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2858–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Lasso, D.C.; Mollá, B.; Calap-Quintana, P.; García-Giménez, J.L.; Pallardo, F.V.; Palau, F.; Gonzalez-Cabo, P. Cofilin dysregulation alters actin turnover in frataxin-deficient neurons. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, E.; Mosser, S.; Fraering, P.C. Inactivation of brain Cofilin-1 by age, Alzheimer’s disease and γ-secretase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 2500–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Vidal, G.S.; Djurisic, M.; William, C.M.; Birnbaum, M.E.; Garcia, K.C.; Hyman, B.T.; Shatz, C.J. Human LilrB2 is a β-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer’s model. Science 2013, 341, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, S.; Vandermeulen, L.; Pizzamiglio, L.; Aksan, B.; Yan, J.; Konietzny, A.; Bonomi, E.; Borroni, B.; Padovani, A.; Rust, M.B.; et al. Cyclase-associated protein 2 dimerization regulates cofilin in synaptic plasticity and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehklau, K.; Hoffmann, L.; Gurniak, C.B.; Ott, M.; Witke, W.; Scorrano, L.; Culmsee, C.; Rust, M.B. Cofilin1-dependent actin dynamics control DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.; Zhou, J.; Patel, H.; Ridgway, R.A.; Huels, D.; Gurniak, C.B.; Sandilands, E.; Carragher, N.O.; Sansom, O.J.; Witke, W.; et al. ADF and cofilin1 control actin stress fibers, nuclear Integrity and cell survival. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopie, J.; Skarp, K.-P.; Kaisa Rajakylä, E.; Tanhuanpää, K.; Vartiainen, M.K. Active maintenance of nuclear actin by importin 9 supports transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E544–E552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Stope, M.B.; de Jesús, M.L.; Oude Weernink, P.A.; Urban, M.; Wieland, T.; Rosskopf, D.; Mizuno, K.; Jakobs, K.H.; Schmidt, M. Direct stimulation of receptor-controlled phospholipase D1 by phospho-cofilin. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4189–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamide, L.S.; Striegl, A.M.; Boyle, J.A.; Meberg, P.J.; Bamburg, J.R. Neurodegenerative stimuli induce persistent ADF/cofilin-actin rods that disrupt distal neurite function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichon, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, B.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X.A.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G. Cofilin aggregation blocks intracellular trafficking and induces synaptic loss in hippocampal neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3919–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.C.; Marsden, I.T.; Maloney, M.T.; Minamide, L.S.; Podlisny, M.; Selkoe, D.J.; Bamburg, J.R. Amyloid beta dimers/trimers potently induce cofilin-actin rods that are inhibited by maintaining cofilin-phosphorylation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, M.T.; Minamide, L.S.; Kinley, A.W.; Boyle, J.A.; Bamburg, J.R. Beta-secretase-cleaved amyloid precursor protein accumulates at actin inclusions induced in neurons by stress or amyloid beta: A feedforward mechanism for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11313–11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, E.; Iida, K.; Yonezawa, N.; Koyasu, S.; Yahara, I.; Sakai, H. Cofilin is a component of intranuclear and cytoplasmic actin rods induced in cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 5262–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Nishida, E.; Sakai, H.; Miyamoto, E. Dephosphorylation of cofilin accompanies heat shock-induced nuclear accumulation of cofilin. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 16143–16148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadidi, Q.; Shah, Z.A. Cofilin mediates LPS-induced microglial cell activation and associated neurotoxicity through activation of NF-κB and JAK-STAT Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1676–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, F.; Rotshenker, S. Galectin-3 (MAC-2) controls microglia phenotype whether amoeboid and phagocytic or branched and non-phagocytic by regulating the cytoskeleton. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.L.; Macklin, W.B. The Actin cytoskeleton in myelinating cells. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffaele, S.; Boccazzi, M.; Fumagalli, M. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaas, J.; van Veggel, L.; Schepers, M.; Tiane, A.; van Horssen, J.; Wilson, D.M., III; Moya, P.R.; Piccart, E.; Hellings, N.; Eijnde, B.O.; et al. Oxidative stress and impaired oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation in neurological disorders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4615–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntemer-Silveira, A.; Patil, N.; Brickner, M.A.; Parr, A.M. Strategies for oligodendrocyte and myelin repair in traumatic CNS injury. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuchero, J.B.; Fu, M.; Sloan, S.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Olson, A.; Zaremba, A.; Dugas, J.C.; Wienbar, S.; Caprariello, A.V.; Kantor, C.; et al. CNS myelin wrapping is driven by actin disassembly. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, J.; Burke, K.; Romito-DiGiacomo, R.R.; Miller, R.H.; Yang, Y. Oligodendrocyte-specific loss of Cdk5 disrupts the architecture of nodes of Ranvier as well as learning and memory. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 306, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, A.S.; Brown, T.L.; Jeffries, M.A.; Shang, Q.; Hashimoto, H.; Evangelou, A.V.; Kowalski, A.; Batish, M.; Macklin, W.B.; Wood, T.L. Mechanistic target of rapamycin regulates the oligodendrocyte cytoskeleton during myelination. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 2993–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.A.; Zhao, X.; Khan, H.; Penn, C.; Wang, X.; Joly-Amado, A.; Weeber, E.; Morgan, D.; Kang, D.E. Slingshot-Cofilin activation mediates mitochondrial and synaptic dysfunction via Aβ ligation to β1-integrin conformers. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.A.; Jung, A.R.; Lakshmana, M.K.; Bedrossian, A.; Lim, Y.; Bu, J.H.; Park, S.A.; Koo, E.H.; Mook-Jung, I.; Kang, D.E. Pivotal role of the RanBP9-cofilin pathway in Aβ-induced apoptosis and neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.A.; Boggess, T.; Uhlar, C.; Wang, X.; Khan, H.; Cappos, G.; Joly-Amado, A.; De Narvaez, E.; Majid, S.; Minamide, L.S.; et al. RanBP9 at the intersection between cofilin and Aβ pathologies: Rescue of neurodegenerative changes by RanBP9 reduction. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, F.; LePochat, P.; Woo, J.-A.A.; Bukhari, M.Z.; Hong, K.W.; Trotter, C.; Kang, D.E. Cofilin-mediated neuronal apoptosis via p53 translocation and PLD1 regulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-H.; Nakamura, T.; Lipton, S.A. Mitochondrial dynamics in cell death and neurodegeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 3435–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shen, L.; Shi, J.; Gao, N. ROCK1 activation-mediated mitochondrial translocation of Drp1 and cofilin are required for arnidiol-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Karbowski, M. Mitochondrial fission in apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Kang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Z.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Maimon, R.; Dowdy, S.F.; et al. Reversing a model of Parkinson’s disease with in situ converted nigral neurons. Nature 2020, 582, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.J. Tauopathies as clinicopathological entities. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 22 (Suppl. 1), S29–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, I.T.; Gervasio, O.L.; Cullen, K.M.; Guillemin, G.J.; Jeong, E.V.; Witting, P.K.; Antao, S.T.; Minamide, L.S.; Bamburg, J.R.; Goldsbury, C. Activated actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilin sequesters phosphorylated microtubule-associated protein during the assembly of Alzheimer-like neuritic cytoskeletal striations. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12994–13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venit, T.; El Said, N.H.; Mahmood, S.R.; Percipalle, P. A dynamic actin-dependent nucleoskeleton and cell identity. J. Biochem. 2021, 169, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Almuzzaini, B.; Drou, N.; Kremb, S.; Yousif, A.; Farrants, A.-K.Ö.; Gunsalus, K.; Percipalle, P. β-Actin-dependent global chromatin organization and gene expression programs control cellular identity. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1296–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Venit, T.; Drou, N.; Percipalle, P. In mitochondria β-actin regulates mtDNA transcription and is required for mitochondrial quality control. iScience 2018, 3, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liang, L.; Dong, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Gao, H. Cofilin 2 in serum as a novel biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease in Han Chinese. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldewachi, H.; Al-Zidan, R.N.; Conner, M.T.; Salman, M.M. High-Throughput screening platforms in the discovery of novel drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lapeña-Luzón, T.; Rodríguez, L.R.; Beltran-Beltran, V.; Benetó, N.; Pallardó, F.V.; Gonzalez-Cabo, P. Cofilin and Neurodegeneration: New Functions for an Old but Gold Protein. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070954
Lapeña-Luzón T, Rodríguez LR, Beltran-Beltran V, Benetó N, Pallardó FV, Gonzalez-Cabo P. Cofilin and Neurodegeneration: New Functions for an Old but Gold Protein. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(7):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070954
Chicago/Turabian StyleLapeña-Luzón, Tamara, Laura R. Rodríguez, Vicent Beltran-Beltran, Noelia Benetó, Federico V. Pallardó, and Pilar Gonzalez-Cabo. 2021. "Cofilin and Neurodegeneration: New Functions for an Old but Gold Protein" Brain Sciences 11, no. 7: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070954
APA StyleLapeña-Luzón, T., Rodríguez, L. R., Beltran-Beltran, V., Benetó, N., Pallardó, F. V., & Gonzalez-Cabo, P. (2021). Cofilin and Neurodegeneration: New Functions for an Old but Gold Protein. Brain Sciences, 11(7), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070954







