Association between Visceral Adiposity Index, Binge Eating Behavior, and Grey Matter Density in Caudal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Severe Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasma Lipid Profile and Glucose Homeostasis Markers
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Adiposity Measurements
- Body Mass Index (BMI):
- Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR):
- Percentage of fat mass (%FM):
- Body fat mass index (BFMI):
- Visceral Adiposity Index (VAI) [5]:
2.4. Psychological Assessment
- Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II)
- UPPS Impulsive Behavior Scale (UPPS)
- Binge Eating Scale (BES)
2.5. T1-Weighted MRI Acquisition and Voxel-Based Morphometry Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Correlations between Adiposity Measurements and Binge Eating Scores
3.3. Comparison of Biological and Psychological Parameters between Participants with High-VAI Versus Low-VAI in Women and Men Separately
3.3.1. Women
3.3.2. Men
3.4. Comparison of Voxel-Based Morphometry Grey Matter Density in Selected ROIs between Men and Women with High- Versus Low-VAI
3.5. Exploratory Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burhans, M.S.; Hagman, D.K.; Kuzma, J.N.; Schmidt, K.A.; Kratz, M. Contribution of Adipose Tissue Inflammation to the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tchernof, A.; Despres, J.P. Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: An update. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 359–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłonowska-Lietz, B.; Wrzosek, M.; Włodarczyk, M.; Nowicka, G. New indexes of body fat distribution, visceral adiposity index, body adiposity index, waist-to-height ratio, and metabolic disturbances in the obese. Kardiol. Pol. 2017, 75, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amato, M.C.; Giordano, C.; Galia, M.; Criscimanna, A.; Vitabile, S.; Midiri, M.; Galluzzo, A. Visceral Adiposity Index: A reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z. Comparisons of Visceral Adiposity Index, Body Shape Index, Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference and Their Associations with Diabetes Mellitus in Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoli, S.; Leone, A.; Ponissi, V.; Bedogni, G.; Beggio, V.; Strepparava, M.G.; Battezzati, A. Prevalence of and risk factors for binge eating behaviour in 6930 adults starting a weight loss or maintenance programme. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCuen-Wurst, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Allison, K.C. Disordered eating and obesity: Associations between binge-eating disorder, night-eating syndrome, and weight-related comorbidities. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1411, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Pub.: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vainik, U.; García-García, I.; Dagher, A. Uncontrolled eating: A unifying heritable trait linked with obesity, overeating, personality and the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2019, 50, 2430–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.A.; Chiu, W.T.; Deitz, A.C.; Hudson, J.I.; Shahly, V.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Alonso, J.; Angermeyer, M.C.; Benjet, C.; et al. The prevalence and correlates of binge eating disorder in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Jonge, P.; Alonso, J.; Stein, D.J.; Kiejna, A.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Viana, M.C.; Liu, Z.; O’Neill, S.; Bruffaerts, R.; Caldas-de-Almeida, J.M.; et al. Associations between DSM-IV mental disorders and diabetes mellitus: A role for impulse control disorders and depression. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguin, P.; Fuentes, M.; Gabler, G.; Guerdjikova, A.I.; Keck, P.E., Jr.; McElroy, S.L. Medical comorbidity of binge eating disorder. Eat. Weight Disord. 2017, 22, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.M.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Yanovski, J.A.; Fox, C.S. Metabolic characterization of adults with binge eating in the general population: The Framingham Heart Study. Obesity 2014, 22, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raevuori, A.; Suokas, J.; Haukka, J.; Gissler, M.; Linna, M.; Grainger, M.; Suvisaari, J. Highly increased risk of type 2 diabetes in patients with binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.I.; Lalonde, J.K.; Coit, C.E.; Tsuang, M.T.; McElroy, S.L.; Crow, S.J.; Bulik, C.M.; Hudson, M.S.; Yanovski, J.A.; Rosenthal, N.R.; et al. Longitudinal study of the diagnosis of components of the metabolic syndrome in individuals with binge-eating disorder. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michels, N.; De Backer, F.; Dimakopoulou, M.; Mane, K.; Indave, I.; Huybrechts, I. Eating disorders and the risk of developing cancer: A systematic review. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T.B.; Smith, K.E. Delineating the Role of Binge Eating in Cancer Research. Eat. Weight Disord. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Perrini, P.; Rapone, B. Clinical Risk and Overall Survival in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperglycemia and Glioblastoma Multiforme. A Review of the Current Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Bedogni, G.; Ponissi, V.; Battezzati, A.; Beggio, V.; Magni, P.; Ruscica, M.; Bertoli, S. Contribution of binge eating behaviour to cardiometabolic risk factors in subjects starting a weight loss or maintenance programme. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, J.E. Medical comorbidity and medical complications associated with binge-eating disorder. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursey, K.M.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Burrows, T.L. The relationship between “food addiction” and visceral adiposity in young females. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 157, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawe, S.; Loxton, N.J. The role of impulsivity in the development of substance use and eating disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehr, E.J.; Krohmer, K.; Schag, K.; Dresler, T.; Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E. Emotion regulation model in binge eating disorder and obesity--a systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schag, K.; Schönleber, J.; Teufel, M.; Zipfel, S.; Giel, K. Food-related impulsivity in obesity and Binge Eating Disorder–a systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Vainik, U.; Garcia-Garcia, I.; Dagher, A. Overlapping Neural Endophenotypes in Addiction and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vainik, U.; Dagher, A.; Dube, L.; Fellows, L.K. Neurobehavioural correlates of body mass index and eating behaviours in adults: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Garcia, I.; Michaud, A.; Dadar, M.; Zeighami, Y.; Neseliler, S.; Collins, D.L.; Evans, A.C.; Dagher, A. Neuroanatomical differences in obesity: Meta-analytic findings and their validation in an independent dataset. Int. J. Obes. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.J.; Tesar, A.K.; Beier, J.; Berg, M.; Warrings, B. Grey matter alterations in obesity: A meta-analysis of whole-brain studies. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, N.; Ziauddeen, H.; Ersche, K.D.; Farooqi, I.S.; Bullmore, E.T.; Nathan, P.J.; Ronan, L.; Fletcher, P.C. Increased body mass index is associated with specific regional alterations in brain structure. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marqués-Iturria, I.; Pueyo, R.; Garolera, M.; Segura, B.; Junqué, C.; García-García, I.; José Sender-Palacios, M.; Vernet-Vernet, M.; Narberhaus, A.; Ariza, M.; et al. Frontal cortical thinning and subcortical volume reductions in early adulthood obesity. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 214, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuulari, J.J.; Karlsson, H.K.; Antikainen, O.; Hirvonen, J.; Pham, T.; Salminen, P.; Helmiö, M.; Parkkola, R.; Nuutila, P.; Nummenmaa, L. Bariatric Surgery Induces White and Grey Matter Density Recovery in the Morbidly Obese: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, V.; Derbyshire, K.; Rück, C.; Irvine, M.A.; Worbe, Y.; Enander, J.; Schreiber, L.R.; Gillan, C.; Fineberg, N.A.; Sahakian, B.J.; et al. Disorders of compulsivity: A common bias towards learning habits. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nevill, A.M.; Stewart, A.D.; Olds, T.; Duncan, M.J. A new waist-to-height ratio predicts abdominal adiposity in adults. Res. Sports Med. 2020, 28, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Gunn, P.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainson, M.G.; Batterham, A.M.; Tsakirides, C.; Rutherford, Z.H.; Hind, K. Prediction of whole-body fat percentage and visceral adipose tissue mass from five anthropometric variables. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, G.H. The Metabolic Phenotype in Obesity: Fat Mass, Body Fat Distribution, and Adipose Tissue Function. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Schutz, Y.; Dupertuis, Y.M.; Pichard, C. Body composition interpretation. Contributions of the fat-free mass index and the body fat mass index. Nutrition 2003, 19, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, S.; Valenta, V.; Wagner, R.; Tschritter, O.; Machann, J.; Häring, H.U.; Preissl, H.; Fritsche, A.; Heni, M. Brain insulin sensitivity is linked to adiposity and body fat distribution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kullmann, S.; Heni, M.; Hallschmid, M.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H.; Häring, H.U. Brain Insulin Resistance at the Crossroads of Metabolic and Cognitive Disorders in Humans. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1169–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, H.; Gourley, D.D.; Dekhtyar, M.; Haley, A.P. Cognition, Brain Structure, and Brain Function in Individuals with Obesity and Related Disorders. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczkurkin, A.N.; Raznahan, A.; Satterthwaite, T.D. Sex differences in the developing brain: Insights from multimodal neuroimaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.M.; Loughead, J.; Bakizada, Z.M.; Hopkins, C.M.; Geliebter, A.; Gur, R.C.; Wadden, T.A. Sex/gender differences in neural correlates of food stimuli: A systematic review of functional neuroimaging studies. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelle, M.G.; Diéguez, C. Updating gender differences in the control of homeostatic and hedonic food intake: Implications for binge eating disorder. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2019, 497, 110508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Downs, W.R.; Barrios, F.X.; Kopper, B.A.; Gutierrez, P.M.; Chiros, C.E. Factor structure and psychometric characteristics of the Beck Depression Inventory-II. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 1997, 19, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Ball, R.; Ranieri, W.F. Comparison of Beck Depression Inventories-IA and-II in psychiatric outpatients. J. Personal. Assess. 1996, 67, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourque, P.; Beaudette, D. Psychometric study of the Beck Depression Inventory on a sample of French-speaking university students. Can. J. Behav. Sci. /Rev. Can. Sci. Comport. 1982, 14, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Linden, M.; D’Acremont, M.; Zermatten, A.; Jermann, F.; Larøi, F.; Willems, S.; Juillerat, A.-C.; Bechara, A. A French Adaptation of the UPPS Impulsive Behavior Scale. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2006, 22, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, S.P.; Lynam, D.R. The Five Factor Model and impulsivity: Using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2001, 30, 669–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormally, J.; Black, S.; Daston, S.; Rardin, D. The assessment of binge eating severity among obese persons. Addict. Behav. 1982, 7, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunault, P.; Gaillard, P.; Ballon, N.; Couet, C.; Isnard, P.; Cook, S.; Delbachian, I.; Réveillère, C.; Courtois, R. Validation de la version française de la Binge Eating Scale: Étude de sa structure factorielle, de sa consistance interne et de sa validité de construit en population clinique et non clinique. L’Encéphale 2016, 42, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Dadar, M.; Pelletier, M.; Zeighami, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, I.; Iceta, S.; Yau, Y.; Nadeau, M.; Marceau, S.; Biertho, L.; et al. Neuroanatomical changes in white and grey matter after sleeve gastrectomy. Neuroimage 2020, 213, 116696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupe, P.; Yger, P.; Prima, S.; Hellier, P.; Kervrann, C.; Barillot, C. An Optimized Blockwise Nonlocal Means Denoising Filter for 3-D Magnetic Resonance Images. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2008, 27, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sled, J.G.; Zijdenbos, A.P.; Evans, A.C. A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 1998, 17, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collins, D.L.; Neelin, P.; Peters, T.M.; Evans, A.C. Automatic 3D Intersubject Registration of MR Volumetric Data in Standardized Talairach Space. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1994, 18, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manera, A.L.; Dadar, M.; Fonov, V.; Collins, D.L. CerebrA, registration and manual label correction of Mindboggle-101 atlas for MNI-ICBM152 template. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasser, M.F.; Coalson, T.S.; Robinson, E.C.; Hacker, C.D.; Harwell, J.; Yacoub, E.; Ugurbil, K.; Andersson, J.; Beckmann, C.F.; Jenkinson, M.; et al. A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex. Nature 2016, 536, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, M.; Poggiali, D.; Whitaker, K.; Marshall, T.R.; Van Langen, J.; Kievit, R.A. Raincloud plots: A multi-platform tool for robust data visualization. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Rockwood, N.J. Regression-based statistical mediation and moderation analysis in clinical research: Observations, recommendations, and implementation. Behav. Res. Therapy 2017, 98, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, L.A.; Arigo, D.; Mayer, L.E.; Sarwer, D.B.; Lowe, M.R. Examination of central body fat deposition as a risk factor for loss-of-control eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Succurro, E.; Segura-Garcia, C.; Ruffo, M.; Caroleo, M.; Rania, M.; Aloi, M.; De Fazio, P.; Sesti, G.; Arturi, F. Obese Patients With a Binge Eating Disorder Have an Unfavorable Metabolic and Inflammatory Profile. Medicine 2015, 94, e2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Vignati, L.; Battezzati, A.; De Amicis, R.; Ponissi, V.; Beggio, V.; Bedogni, G.; Vanzulli, A.; Bertoli, S. Association of Binge Eating Behavior with Total and Abdominal Adipose Tissue in a Large Sample of Participants Starting a Weight Loss or Maintenance Program. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morys, F.; Dadar, M.; Dagher, A. Association between mid-life obesity, its metabolic consequences, cerebrovascular disease and cognitive decline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Li, P.; Liu, H.; Nie, B.; Yin, X.; Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, T.; Wang, L.; et al. Gray matter reduction related to decreased serum creatinine and increased triglyceride, Hemoglobin A1C, and low-density lipoprotein in subjects with obesity. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowitz, D.; Wittfeld, K.; Terock, J.; Freyberger, H.J.; Hegenscheid, K.; Völzke, H.; Habes, M.; Hosten, N.; Friedrich, N.; Nauck, M.; et al. Association between waist circumference and gray matter volume in 2344 individuals from two adult community-based samples. Neuroimage 2015, 122, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Pelletier, S.; Richer, L.; Pike, G.B.; Gaudet, D.; Paus, T.; Pausova, Z. Adiposity-related insulin resistance and thickness of the cerebral cortex in middle-aged adults. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Aziz, N.A.; Diers, K.; Stöcker, T.; Reuter, M.; Breteler, M.M.B. Insulin resistance accounts for metabolic syndrome-related alterations in brain structure. Human Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2434–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazettes, F.; Cohen, J.I.; Yau, P.L.; Talbot, H.; Convit, A. Obesity-mediated inflammation may damage the brain circuit that regulates food intake. Brain Res. 2011, 1373, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bush, G.; Luu, P.; Posner, M.I. Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, W.W.; Menon, V.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Keller, J.; Glover, G.H.; Kenna, H.; Reiss, A.L.; Greicius, M.D. Dissociable Intrinsic Connectivity Networks for Salience Processing and Executive Control. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkin, A.; Egner, T.; Kalisch, R. Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahey, B.B.; Hinton, K.E.; Burgess, L.; Meyer, F.C.; Landman, B.A.; Villata-Gil, V.; Yang, X.; Rathouz, P.J.; Applegate, B.; Zald, D.H. Dispositional Negative Emotionality in Childhood and Adolescence Predicts Structural Variation in the Amygdala and Caudal Anterior Cingulate During Early Adulthood: Theoretically and Empirically Based Tests. Res. Child Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2021, 49, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, A.; Vaitl, D.; Schienle, A. Regional grey matter volume abnormalities in bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schienle, A.; Schäfer, A.; Hermann, A.; Vaitl, D. Binge-eating disorder: Reward sensitivity and brain activation to images of food. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balodis, I.M.; Molina, N.D.; Kober, H.; Worhunsky, P.D.; White, M.A.; Rajita, S.; Grilo, C.M.; Potenza, M.N. Divergent neural substrates of inhibitory control in binge eating disorder relative to other manifestations of obesity. Obesity 2013, 21, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hege, M.A.; Stingl, K.T.; Kullmann, S.; Schag, K.; Giel, K.E.; Zipfel, S.; Preissl, H. Attentional impulsivity in binge eating disorder modulates response inhibition performance and frontal brain networks. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, B.N. Research Domain Criteria: Toward future psychiatric nosologies. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 17, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildes, J.E.; Marcus, M.D. Application of the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) framework to eating disorders: Emerging concepts and research. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
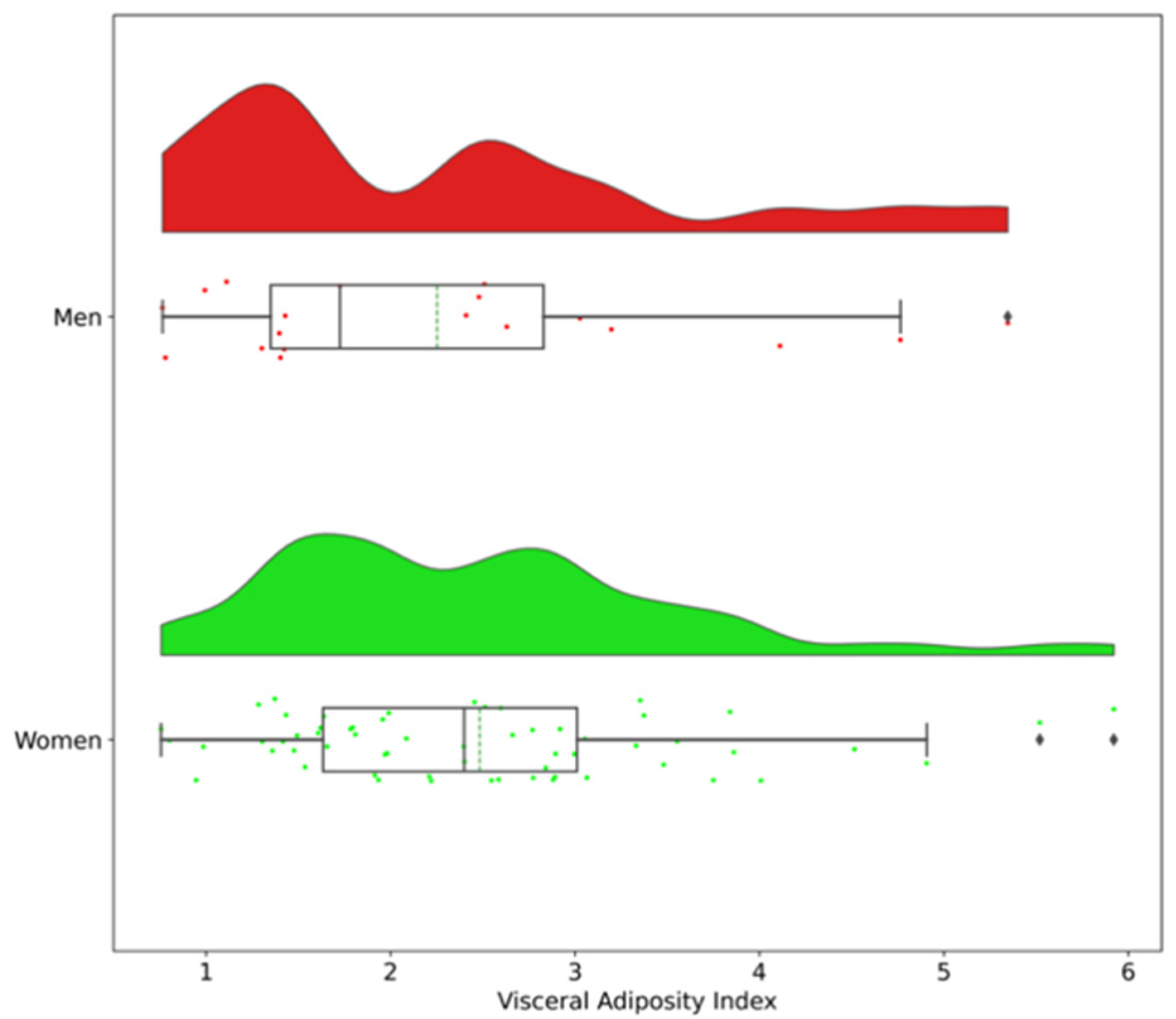

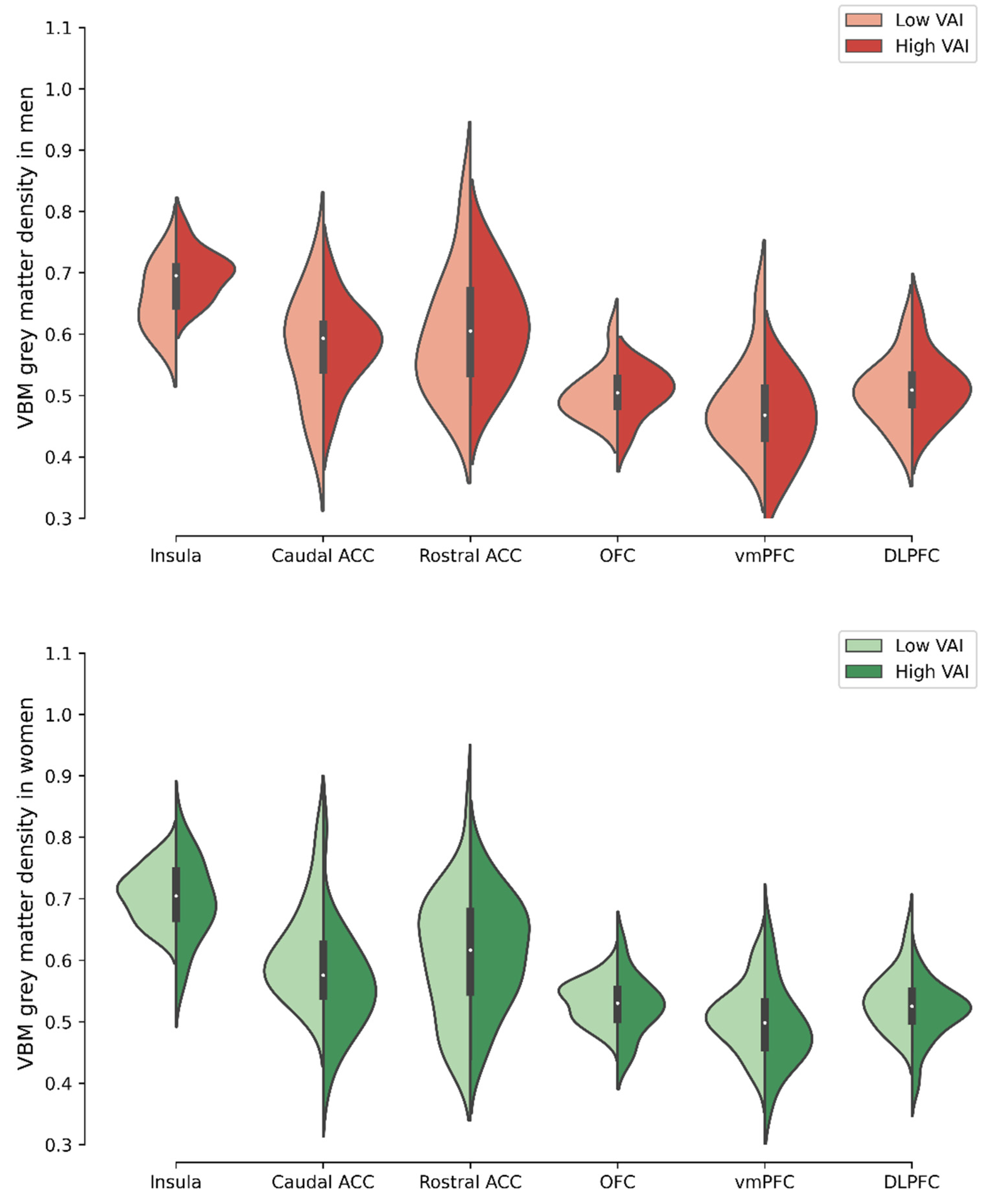
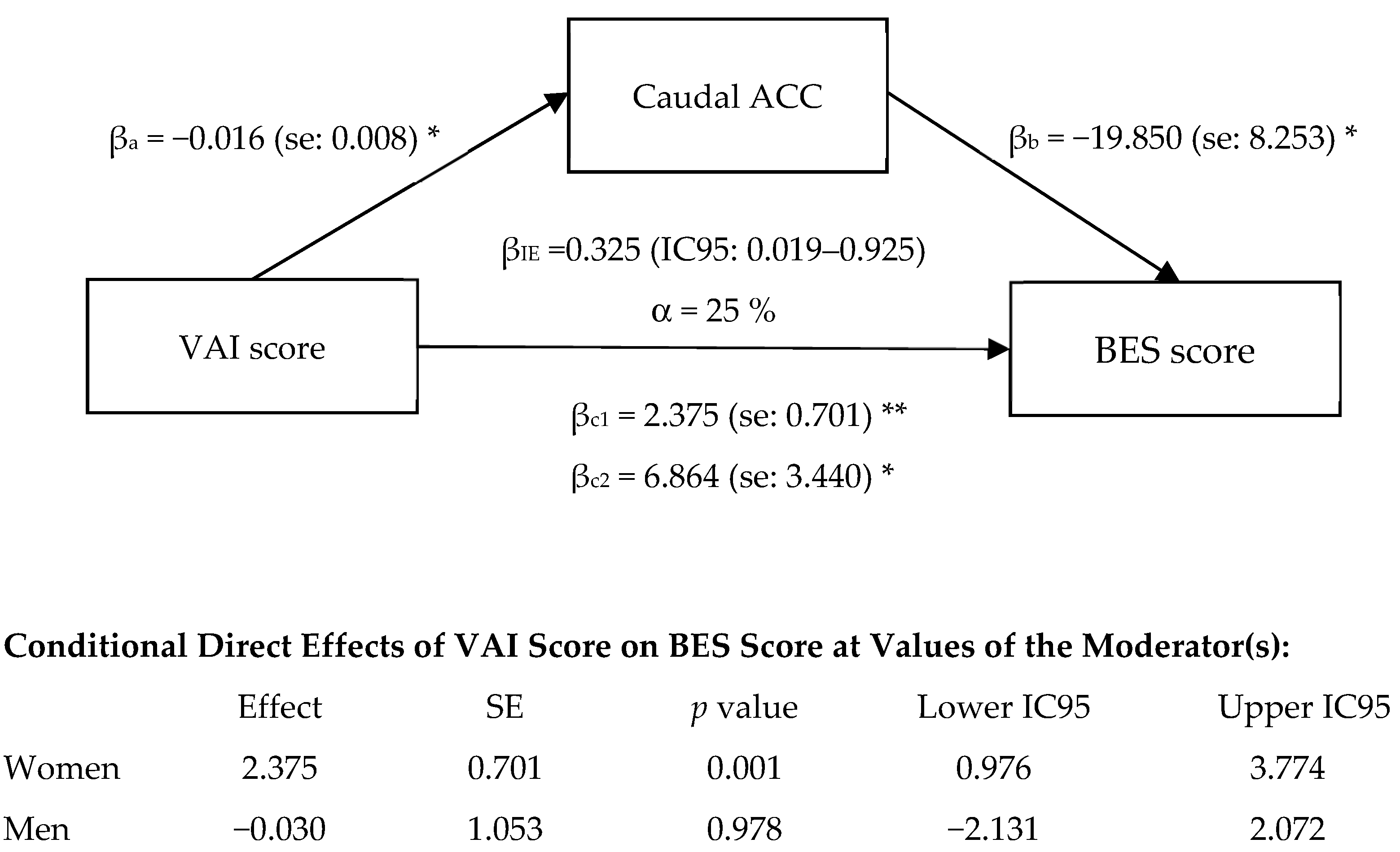
| MEN | WOMEN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOW-VAI | HIGH-VAI | LOW-VAI | HIGH-VAI | |||
| n = 10 | n = 9 | n = 32 | n = 28 | |||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p value * | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p value | |
| Visceral Adiposity Index | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | <0.001 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
| Anthropometric parameters | ||||||
| Age (yr) | 50.8 ± 6.6 | 44.4 ± 7.7 | 0.113 | 44.0 ± 7.4 | 42.7 ± 10.2 | 0.569 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 43.1 ± 4.9 | 40.9 ± 2.9 | 0.243 | 44.7 ± 4.0 | 43.4 ± 3.6 | 0.200 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 134 ± 12 | 130 ± 8 | 0.356 | 128 ± 10 | 129 ± 8 | 0.713 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 128 ± 12 | 122 ± 9 | 0.243 | 136 ± 9 | 131 ± 9 | 0.028 |
| Neck circumference (cm) | 46 ± 3 | 46 ± 2 | 0.780 | 39 ± 3 | 41 ± 2 | 0.033 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.661 | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.004 |
| Percentage of Fat Mass (%) | 41.8 ± 6.3 | 39.5 ± 5.0 | 0.315 | 52.3 ± 2.2 | 50.4 ± 2.2 | 0.001 |
| Body fat mass index (kg/m2) | 18.3 ± 4.5 | 16.2 ± 3.0 | 0.156 | 23.4 ± 2.8 | 21.9 ± 2.5 | 0.031 |
| Biological parameters | ||||||
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | <0.001 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.0 ± 1.2 | 4.6 ± 1.1 | 0.243 | 4.6 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | 0.653 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.028 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 2.5 ± 1.0 | 0.780 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 0.676 |
| Apolipoprotein B (g/L) | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.182 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.260 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 6.5 ± 1.1 | 5.8 ± 0.5 | 0.315 | 5.8 ± 0.7 | 6.8 ± 2.4 | 0.032 |
| Insulin (pmol/L) | 185.2 ± 102.2 | 209.8 ± 73.5 | 0.549 | 137.2 ± 93.3 | 186.9 ± 96.9 | 0.048 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 0.968 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 6.2 ± 1.2 | 0.005 |
| HOMA-IR index | 9.0 ± 5.5 | 9.1 ± 3.4 | 0.999 | 6.0 ± 4.3 | 9.8 ± 6.7 | 0.013 |
| TSH (mU/L) | 2.3 ± 1.5 | 2.8 ± 1.3 | 0.400 | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 2.7 ± 1.4 | 0.651 |
| MEN | WOMEN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOW-VAI | HIGH-VAI | LOW-VAI | HIGH-VAI | |||
| n = 8 | n = 9 | n = 30 | n = 27 | |||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p value * | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p value | |
| Psychological parameters | ||||||
| Binge Eating Scale | 14.4 ± 4.4 | 11.0 ± 6.2 | 0.277 | 9.1 ± 5.7 | 14.0 ± 6.6 | 0.004 |
| Beck Depression Inventory | 12.4 ± 6.8 | 8.3 ± 7.6 | 0.200 | 8.2 ± 7.3 | 11.1 ± 8.4 | 0.173 |
| UPPS Impulsive Behavior Scale | ||||||
| Negative urgency | 28.0 ± 6.5 | 25.9 ± 5.0 | 0.743 | 24.8 ± 4.8 | 26.6 ± 5.7 | 0.202 |
| Lack of premeditation | 19.4 ± 3.1 | 20.6 ± 4.5 | 0.423 | 20.9 ± 3.7 | 21.8 ± 5.8 | 0.514 |
| Lack of perseverance | 18.6 ± 4.1 | 18.2 ± 4.8 | 0.888 | 17.6 ± 3.3 | 18.3 ± 4.5 | 0.549 |
| Sensation seeking | 27.5 ± 5.6 | >33.7 ± 4.2 | 0.036 | 25.2 ± 6.6 | 24.3 ± 6.4 | 0.605 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iceta, S.; Dadar, M.; Daoust, J.; Scovronec, A.; Leblanc, V.; Pelletier, M.; Biertho, L.; Tchernof, A.; Bégin, C.; Michaud, A. Association between Visceral Adiposity Index, Binge Eating Behavior, and Grey Matter Density in Caudal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Severe Obesity. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091158
Iceta S, Dadar M, Daoust J, Scovronec A, Leblanc V, Pelletier M, Biertho L, Tchernof A, Bégin C, Michaud A. Association between Visceral Adiposity Index, Binge Eating Behavior, and Grey Matter Density in Caudal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Severe Obesity. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(9):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091158
Chicago/Turabian StyleIceta, Sylvain, Mahsa Dadar, Justine Daoust, Anais Scovronec, Vicky Leblanc, Melissa Pelletier, Laurent Biertho, André Tchernof, Catherine Bégin, and Andreanne Michaud. 2021. "Association between Visceral Adiposity Index, Binge Eating Behavior, and Grey Matter Density in Caudal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Severe Obesity" Brain Sciences 11, no. 9: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091158
APA StyleIceta, S., Dadar, M., Daoust, J., Scovronec, A., Leblanc, V., Pelletier, M., Biertho, L., Tchernof, A., Bégin, C., & Michaud, A. (2021). Association between Visceral Adiposity Index, Binge Eating Behavior, and Grey Matter Density in Caudal Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Severe Obesity. Brain Sciences, 11(9), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091158








