Effects of Ethanol Exposure during Lactation on Ultrasonic Vocalizations of Rat Pups upon Their Isolation: Increase in Pup Distress Calls †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. USV Recording
2.4. Statistical Analyses
- i.
- The fundamental frequencies at both start and end points were ≥30 and <70 kHz.
- ii.
- The duration was ≥20 ms.
- iii.
- The mean fundamental frequency was <90 kHz.
- iv.
- The bandwidth between the maximum and minimum fundamental frequencies was <60 kHz.
3. Results
3.1. Daily Consumption of Ethanol-Containing Water
3.2. Landmarks of Physical Growth
3.3. Body Weights of Dams
3.4. Body Weights of Pups
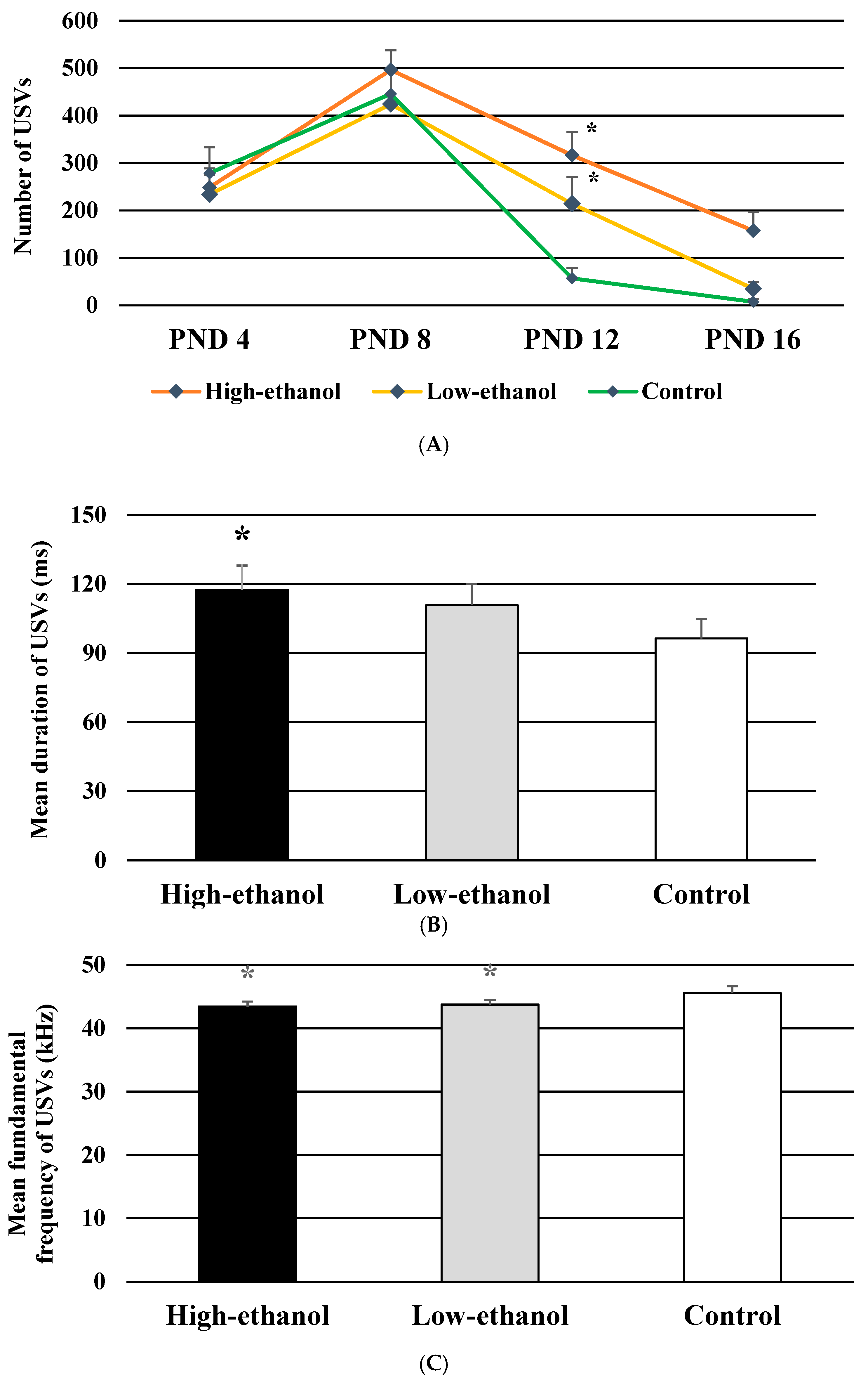
3.5. Number of USVs
3.6. Mean Duration of USVs
3.7. Mean Fundamental Frequency of USVs
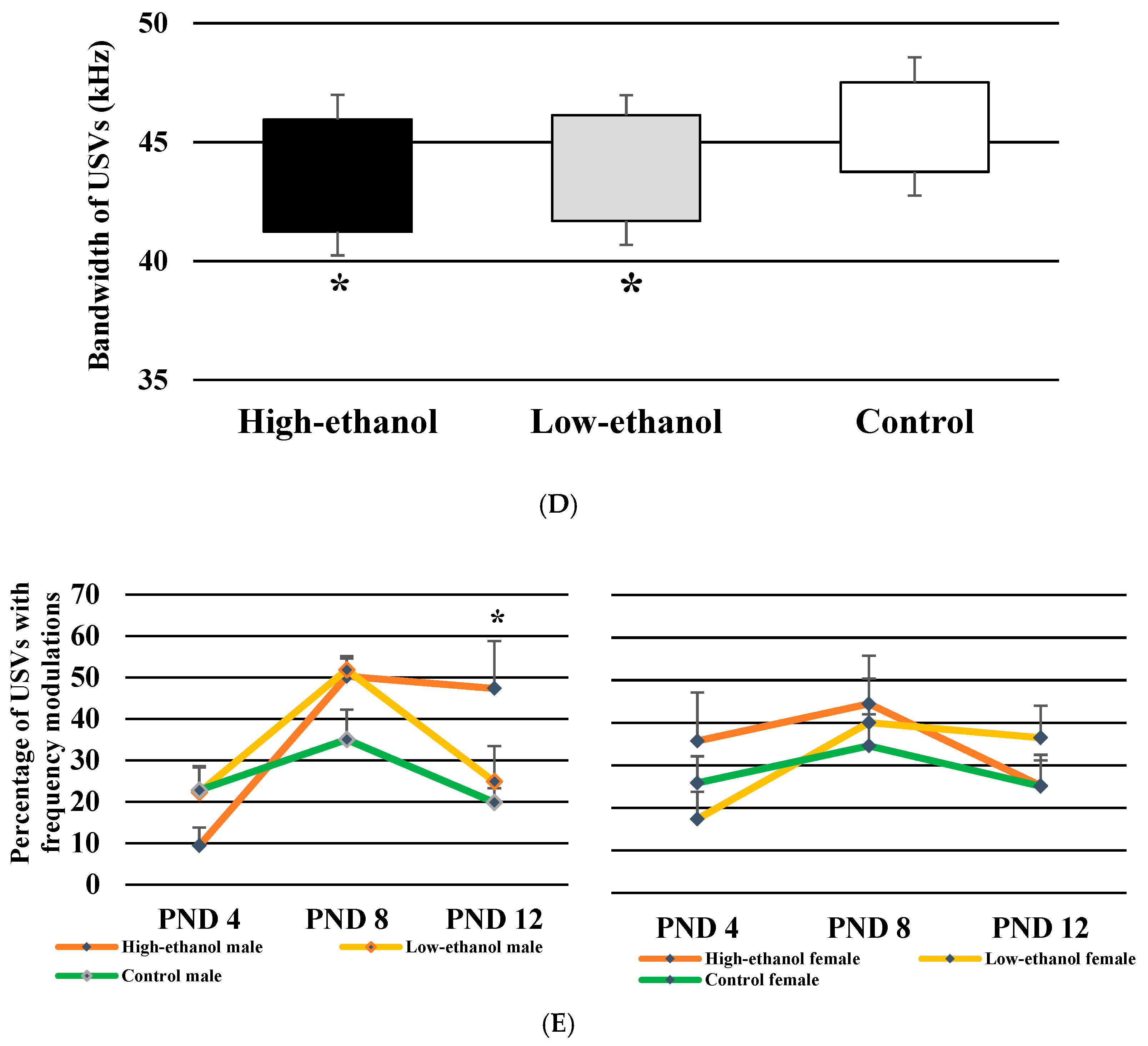
3.8. Bandwidth of USVs
3.9. Percentage of USVs with Frequency Modulations
3.10. Amplitude of USVs
4. Discussion
4.1. Physical Growth
4.2. USV Acoustic Parameters
4.3. Comparisons between Gestational and Lactational Exposure
4.4. Central Mechanisms of Ethanol Exposure and Negative Emotionality
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grossman, E.R. Beer, breast-feeding, and the wisdom of old wives. JAMA 1988, 259, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, J.A. The transfer of alcohol to human milk Sensory implications and effects on mother-infant interaction. In Alcohol and Alcoholism: Effects on Brain and Development; Hanningan, J.H., Spear, L.P., Spear, N.E., Goodlett, C.R., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 177–198. [Google Scholar]
- Mennella, J.A. Regulation of milk intake after exposure to alcohol in mothers’ milk. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, J.A. Short-term effects of maternal alcohol consumption on lactational performance. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglia, R.C.; Binns, C.W. Patterns of alcohol intake of pregnant and lactating women in Perth, Australia. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2007, 26, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennella, J.A. Alcohol use during lactation: The folklore versus the science. In Current Issues in Clinical Lactation; Auerbach, K.G., Ed.; Jones and Burtlett Publishers: Sudbury, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mennella, J.A.; Beauchamp, G.K. The transfer of alcohol to human milk: Effects on flavor and the infant’s behavior. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennella, J.A.; Beauchamp, G.K. Beer, breast feeding and folklore. Dev. Pychobiol. 1993, 26, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, J.A.; Garcia-Gomez, P.L. Sleep disturbances after acute exposure to alcohol in mothers’ milk. Alcohol 2001, 25, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, J.A.; Gerrish, C.J. Effects of exposure to alcohol in mother’s milk on infant sleep. Pediatrics 1998, 101, E21–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.E.; Anderson, K.W.; Ervin, C.H.; Worthington-Roberts, B.; Clarren, S.K. Maternal alcohol use during breast-feeding and infant mental and motor development at one year. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.; Porter, M. Drinking or smoking while breastfeeding and later cognition in children. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20174266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.E.; West, J.R. Alcohol and nutritional control treatments during neurogenesis in rat brain reduce total neuron number in locus coeruleus, but not in cerebellum or inferior olive. Alcohol 2003, 30, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.A.; West, J.R. Alcohol-induced brain damage during development: Potential risk factors. In Alcohol and Alcoholism: Effects on Brain and Development; Hannigan, J.H., Spear, L.P., Spear, N.E., Goodlett, C.R., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Goodlett, C.R.; Eilers, A.T. Alcohol-induced Purkinje cell loss with a single binge exposure in neonatal rats: A stereological study of temporal windows of vulnerability. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, M.G.; Chen, X.G.; Bergeski, B.A. Pattern and duration of the inhibitory effect of alcohol administered acutely on suckling-induced prolactin in lactating rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1990, 14, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, M.G. Evaluation of lactational parameters after alcohol administration for four days during early or midlactation in the rat. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares do Carmo, M.G.; Oller do Nascimento, C.M.; Martin, A.; Herrera, E. Ethanol intake during lactation impairs milk production in rats and affects growth and metabolism of suckling pups. Alcohol 1999, 18, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, S.; Kelly, S.J.; Riley, E.P. Neonatal alcohol exposure alters suckling behavior in neonatal rat pups. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 39, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.C.; Pepino, M.Y.; Johnson, J.; Spear, N.E. The infant rat learns about alcohol through interaction with an intoxicated mother. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melcer, T.; Gonzalez, S.; Barron, S.; Riley, E. Hyperactivity in preweanling rats following postnatal alcohol exposure. Alcohol 1994, 11, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Kotch, L.; Riley, E. Alterations in gait following ethanol exposure during the brain growth spurt in rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1990, 14, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, C.M.; Pauk, J.; Schanberg, S.M. Endocrine responses to mother–infant separation in developing rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 1990, 23, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerberg, B.; Shartrand, A.M. Temperature- dependent effects of maternal separation on growth, activity, and amphetamine sensitivity in the rat. Dev. Psychobiol. 1992, 25, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ise, S.; Ohta, H. Power spectrum analysis of ultrasonic vocalization elicited by maternal separation in rat pups. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portfors, C.V. Types and functions of ultrasonic vocalizations in laboratory rats and mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2007, 46, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting, R.K.W.; Wohr, M. On the relationships between ultrasonic calling and anxiety-related behavior in rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, S.A.; Shair, H.N.; Hofer, M.A. Hypothermic vocalizations of rat pups (Rattus norvegicus) elicit and direct maternal search behavior. J. Comp. Psychol. 1994, 108, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, M.A. Hidden regulators in attachment, separation, and loss. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child Dev. 1994, 59, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, S.; Gilbertson, R. Neonatal ethanol exposure but not neonatal cocaine selectively reduces specific isolation-induced vocalization waveforms in rats. Behav. Genet. 2005, 35, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, J.T.; Insel, T.R.; Trullas, R.; Skolnick, P. Rat pup isolation calls are reduced by functional antagonists of the NMDA receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 190, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.A.; Shair, H. Sensory processes in the control of isolation-induced ultrasonic vocalization by 2-week-old rats. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1980, 94, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carden, S.E.; Hernandez, N.; Hofer, M.A. The isolation and companion comfort responses of 7- and 3-day-old rat pups are modulated by drugs active at the opioid receptor. Behav. Neurosci. 1996, 110, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.A.; Masmela, J.R.; Brunelli, S.A.; Shair, H.N. Behavioral mechanism for active maternal potentiation of isolation calling in rat pups. Behav. Neurosci. 1999, 113, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, M.B. Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal responses to brief social separation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.A.; Brunelli, S.A.; Shair, H.N. Potentiation of isolation-induced vocalization by brief exposure of rat pups to maternal cues. Dev. Psychobiol. 1994, 27, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.N.; Thayer, J.E.; Frye, C.A. Prenatal stress suppresses rat pup ultrasonic vocalization and myoclonic twitching in response to separation. Dev. Psychobiol. 1999, 34, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanni, V.; Cagiano, R.; Carratu, M.R.; De Salvia, M.A.; Giustino, A.; Cuomo, V. Alterations in the ontogeny of rat pup ultrasonic vocalization produced by pre-natal exposure to nitrogen dioxide. Psychopharmacology 1994, 116, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, B.L.; Jauchem, J.R.; Mason, P.A.; Dooley, M.P.; Miller, S.A.; Ziriax, J.M.; Murphy, M.R. Neural and behavioral teratological evaluation of rats exposed to ultrawideband electromagnetic fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2000, 21, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, J.; Suter, D.; Alder, S. Microanalysis of ultrasound vocalizations of young rats: Assessment of the behavioral teratogenicity of methylmercury. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1990, 12, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, P.; Shoemaker, W. Opioid-dependent behaviors in infant rats: Effects of prenatal exposure to ethanol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 39, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.D.; Cronise, K.; Lugo, J.N., Jr.; Kelly, S.J. Ultrasonic vocalizations and maternal-infant interactions in a rat model of fetal alcohol syndrome. Dev. Psychobiol. 2002, 41, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerberg, B.; McDonald, B.C. Prenatal alcohol exposure influences the effects of neuroactive steroids on separation-induced ultrasonic vocalizations in rat pups. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1996, 55, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrier, M.A.; Wada, H. Effects of prenatal ethanol exposure on acoustic characteristics of ultrasonic vocalizations in rat pups. Neurotoxicology 2018, 69, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, S.; Segar, T.M.; Yahr, J.S.; Baseheart, B.J.; Willford, J.A. The effects of neonatal ethanol and/or cocaine exposure on isolation-induced ultrasonic vocalizations. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouette-Lahlou, I.; Vernet-Maury, E.; Vigouroux, M. Role of pups’ ultrasonic calls in a particular maternal behavior in Wistar rat: Pups’ anogenital licking. Behav. Brain Res. 1992, 50, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Fuentes, L.; Artillo, R.; Carreras, O.; Murillo, L. Effects of maternal chronic alcohol administration in the rat: Lactation performance and pup’s growth. Eur. J. Nutr. 2001, 40, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilaro, S.; Viñas, O.; Remesar, X.; Herrera, E. Effects of chronic ethanol consumption on lactational performance in rat: Mammary gland and milk composition and pups’ growth and metabolism. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1987, 27, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.H.; Kelly, S.J.; Wilson, M.A. Early postnatal alcohol exposure in rats: Maternal behavior and estradiol levels. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 59, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Land, C.I.; Campbell, J.; Spear, N.E.; Molina, J. Infantile experience with an alcohol-intoxicated mother: Responsiveness to isolation and to specific social interactions (abstract). Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 87A. [Google Scholar]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Abate, P.; Spear, N.E.; Molina, J.C. Disruption of maternal behavior by alcohol intoxication in the lactating rat: A behavioral and metabolic analysis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalant, A. Pharmacokinetics of ethanol: Absorption, distribution and elimination. In The Pharmacology of Alcohol and Alcohol Dependence; Begleiter, H., Kissin, B., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 15–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Spear, N.E.; Molina, J.C. Nursing experiences with an alcohol-intoxicated dam counteract appetitive conditioned responses toward alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, S.M.; Kehoe, P.; Callahan, M. Sonographic structure of isolation-induced ultrasonic calls of rat pups. Dev. Psychobiol. 1999, 34, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, S.A.; Keating, C.C.; Hamilton, N.A.; Hofer, M.A. Development of ultrasonic vocalization responses in genetically heterogenous National Institute of Health (N:NIH) rats: I. Influence of age, testing experience, and associated factors. Dev. Psychobiol. 1996, 29, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G.A.; Molina, V.A.; Spear, L.P. Repeated exposure of rat pups to isolation attenuates isolation-induced ultrasonic vocalization rates: Reversal with naltrexone. Dev. Psychobiol. 1994, 27, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.; Benno, R.; Schanz, N.; Phadia, E. The effects of prenatal cocaine exposure and genotype on the ultrasonic calls of infant mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrier, M.A.; Wada, H. Effects of prenatal ethanol exposure on acoustic characteristics of play fighting-induced ultrasonic vocalizations in juvenile rats. Neurotoxicology 2020, 79, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Moreno, L.M.; Cimadevilla, J.M. Acute and chronic ethanol intake: Effects on spatial and non-spatial memory in rats. Alcohol 2012, 46, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macieira, M.S.; Almeida, W.G.; Silva, E.A.; Schenberg, L.C.; Nakamura-Palacios, E.M. Alcohol dependence induced in rats by semivoluntary intermittent intake. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1997, 30, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nio, E.; Kogure, K.; Yae, T.; Onodera, H. The effects of maternal ethanol exposure on neurotransmission and second messenger systems: A quantitative auto radiographic study in the rat brain. Dev. Brain Res. 1991, 62, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, M.; Aghanouri, Z.; Rashidi, A.A.; Keshavarz, M. Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Dysfunction of Hippocampal Formation in Cognition. Int. J. Reprod. Med. 2004, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wellmann, K.A.; George, F.; Brnouti, F.; Mooney, S.M. Docosahexaenoic acid partially ameliorates deficits in social behavior and ultrasonic vocalizations caused by prenatal ethanol exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 286, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reno, J.M.; Marker, B.; Cormack, L.K.; Schallert, T.; Duvauchelle, C.L. Automating ultrasonic vocalization analyses: The WAAVES program. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 219, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, N.W. Postnatal alcohol exposure in the rat: Its effects on avoidance conditioning, Hebb-Williams maze performance, maternal behavior, and pup development. Physiol. Psychol. 1980, 8, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueta, M.; Abate, P.; Haymal, O.B.; Spear, N.E.; Molina, J.C. Ethanol exposure during late gestation and nursing in the rat: Effects upon maternal care, ethanol metabolism and infantile milk intake. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 91, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.C.; Martin, D.C.; Sigman, G.; Radow, B. Offspring survival, development, and operant performance following maternal ethanol consumption. Dev. Psychobiol. 1977, 10, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.G. Effects of chronic alcohol administration on lactational performance in the rat. Alcohol 1994, 12, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheslock, S.J.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Silveri, M.M.; Petrov, E.S.; Spear, L.P.; Spear, N.E. Acute effects of ethanol and the first suckling episode in the newborn rat. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, L.F.; Pautassi, R.M.; Spear, N.E.; Molina, J.C. Nursing from an ethanol-intoxicated dam induces short-and long-term disruptions in motor performance and enhances later self-administration of the drug. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, S.H.; Subramanian, M.G. Chronic alcohol exposure and lactation: Extended observations. Alcohol 2000, 21, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.G. Alcohol inhibits suckling-induced oxytocin release in the lactating rat. Alcohol 1999, 19, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, K.; Lewis, B.; Barron, S. Agmatine reduces ultrasonic vocalization deficits in female rat pups exposed neonatally to ethanol. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, N.W. Effects of postnatal alcohol exposure on maternal nesting behavior in the rat. Physiol. Psychol. 1979, 7, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerberg, B.; Rosenthal, A.J.; Stark, A.C. Neonatal social isolation alters both maternal and pup behaviors in rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2003, 42, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, S.M. Principles of Rat Communication: Quantitative Parameters of Ultrasonic Calls in Rats. Behav. Genet. 2005, 35, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, S.M.; Kadishevitz, L.; Fu, X.W. Mesolimbic component of the ascending cholinergic pathways: Electrophysiological pharmacological study. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brudzynski, S.M. (Ed.) . Handbook of Mammalian Vocalization: An Integrative Neuroscience Approach; Academic Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, S.M. Ethotransmission: Communication of emotional states through ultrasonic vocalization in rats. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, S.M.; Iku, A.; Harness, A. Activity of cholinergic neurons in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus during emission of 22kHz vocalization in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, P.; Callahan, M.; Daigle, A.; Mallinson, K. The Effect of Cholinergic Stimulation on Rat Pup Ultrasonic Vocalizations. Dev. Psychobiol. 2001, 38, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemis-Brown, J.E.; Johnson, E.D.; Blumberg, M.S. Separable brainstem and forebrain contributions to ultrasonic vocalizations in infant rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2005, 119, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Morales, M. Pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei contain distinct populations of cholinergic, glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, E.J.; McDougle, M.J.; Siegel, G.S.; Jhou, T.C.; Chandler, L.J. Role for the rostromedial tegmental nucleus in signaling the aversive properties of alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Chen, X.; Zuo, W.; Li, J.; Kang, S.; Zhou, L.H.; Siegel, A.; Bekker, A.; Ye, J.-H. Ablation of mu opioid receptor- expressing GABA neurons in rostromedial tegmental nucleus increases ethanol consumption and regulates ethanol-related behaviors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sheth, C.; Furlong, T.M.; Keefe, K.A.; Taha, S.A. Lesion of the rostromedial tegmental nucleus increases voluntary ethanol consumption and accelerates extinction of ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 3737–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhou, T.C.; Fields, H.L.; Baxter, M.G.; Saper, C.B.; Holland, P.C. The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), a GABAergic afferent to midbrain dopamine neurons, encodes aversive stimuli and inhibits motor responses. Neuron 2009, 61, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.M.; Penschuck, S.; Fritschy, J.M.; McCarthy, M.M. Developmental switch in the expression of GABAA receptor subunits α1 and α2 in the hypothalamus and limbic system of the rat. Dev. Brain Res. 2000, 119, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritschy, J.M.; Paysan, J.; Enna, A.; Mohler, H. Switch in the expression of rat GABAA-receptor subtypes during postnatal development: An immunohistochemical study. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5302–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pups | Incisor Eruption (PNDs) | Body Hair (PNDs) | Eye Opening (PNDs) | Timing of Death (PND) | Weaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-ethanol | 15.094 ± 0.222 | 11.844 ± 0.191 | 20 ± 0.174 | 18 ± 0.224 (n = 16) | PND 30 |
| Low-ethanol | 11 ± 0.179 | 8.75 ± 0.113 | 16.708 ± 0.168 | No death | PND 22 |
| Control | 9.271 ± 0.142 | 8.167 ± 0.124 | 15 ± 0.139 | No death | PND 22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahrier, M.A.; Wada, H. Effects of Ethanol Exposure during Lactation on Ultrasonic Vocalizations of Rat Pups upon Their Isolation: Increase in Pup Distress Calls. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091249
Shahrier MA, Wada H. Effects of Ethanol Exposure during Lactation on Ultrasonic Vocalizations of Rat Pups upon Their Isolation: Increase in Pup Distress Calls. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(9):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091249
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahrier, Mohd. Ashik, and Hiromi Wada. 2021. "Effects of Ethanol Exposure during Lactation on Ultrasonic Vocalizations of Rat Pups upon Their Isolation: Increase in Pup Distress Calls" Brain Sciences 11, no. 9: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091249
APA StyleShahrier, M. A., & Wada, H. (2021). Effects of Ethanol Exposure during Lactation on Ultrasonic Vocalizations of Rat Pups upon Their Isolation: Increase in Pup Distress Calls. Brain Sciences, 11(9), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091249





