Effects of Insular Cortex on Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
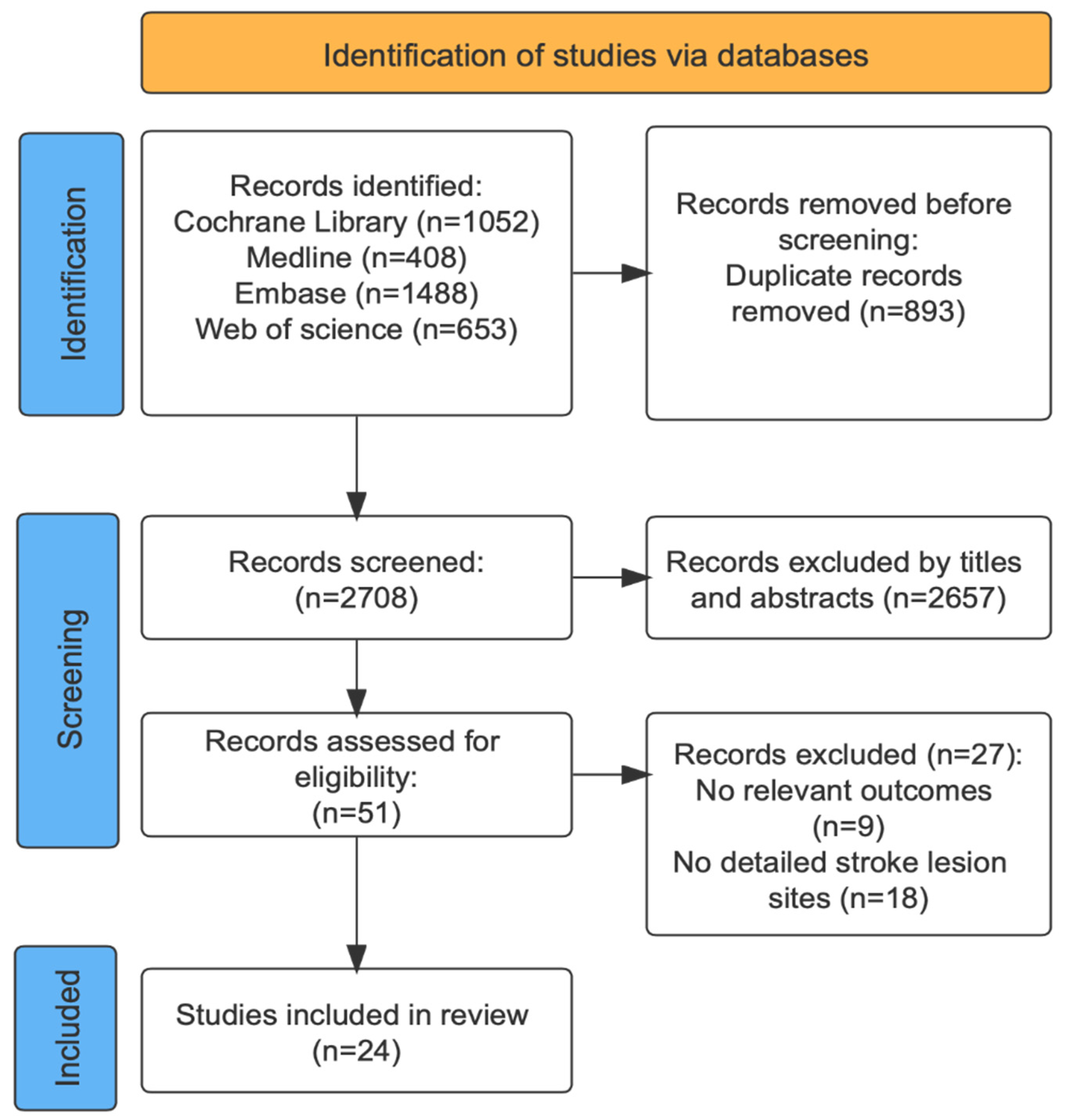
2. Method
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
2.2. Inclusion and Excluded Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
| Study | Number of Patients | Locations of Stroke | Phases of Stroke | Diagnosis Methods of Stroke | Image Analysis Methods | Evaluation of PSD | Days to Evaluation of Lesion Sites after Stroke | Days to Evaluation of PSD | Age (Mean ± SD, Years) | Gender (M/F) | Incidence of PSD | Presence of Dysphagia before Stroke-Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hess 2021 [11] | n = 132 | Supratentorial | Acute | CT | VLSM | WST | NA | NA | 71.20 ± 14.20 | 78/54 | 63.60% | NA |
| Zhang 2021 [43] | n = 275 | NA | Acute | MRI (DWI; DTI) | VLSM | WST; V-VST | Within 3 days | Within 24 h | 67.92 ± 12.22 | 182/93 | 41.10% | No |
| Galovic 2017 [17] | n = 62 | Supratentorial | Acute | MRI | VLSM | FOIS | 3 ± 2 days | Within 48 h | 75.00 ± 21.00 | 28/34 | NA | No |
| Moon 2018 [37] | n = 90 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | NA | MRI | VLSM | VFSS | NA | NA | 68.02 ± 13.21 | 57/33 | NA | No |
| Moon 2022 [36] | n = 40 | Cerebellar | NA | MRI | VLSM | VFSS(VDS) | NA | NA | 64.02 ± 13.21 | 24/16 | NA | No |
| Galovic 2013 [25] | n = 94 | Supratentorial | Acute | MRI | ROI | SSA | NA | Within 48 h | 74.00 ± 19.00 | 48/46 | 36.00% | NA |
| Nakamori 2021 [38] | n = 342 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | Acute | MRI (FLAIR) | NA | VFSS | Within 1 week | Within 14 days | 70.40 ± 12.60 | 200/142 | 13.20% | NA |
| Jang 2017 [28] | n = 82 | Supratentorial | Chronic | MRI | VLSM | VFSS | NA | NA | 73.90 ± 8.01 | 75/7 | 73.17% | No |
| Lapa 2021 [29] | n = 113 | Supratentorial | Acute | CT or MRI | ASPECTS | FEES(FEDSS) | NA | Within 24 h | 69.00 ± 13.00 | 67/45 | 54.90% | No |
| Wilmskoetter 2019 [13] | n = 68 | Supratentorial | Acute | DWI | VLSM | MBSImP; PAS | NA | NA | 68.21 ± 15.23 | 32/36 | NA | No |
| Suntrup 2015 [44] | n = 200 | NA | Acute | CT or MRI | NA | FEES(FEDSS) | Within 24–60 h | Within 96 h | 73.70 ± 16.50 | 101/99 | 82.50% | No |
| Flowers 2017 [14] | n = 160 | NA | Acute | MRI | NA | NA | Within 14 days | NA | 68.00 | 91/69 | 48.00% | NA |
| Kim 2016 [30] | n = 31 | Supratentorial | Subacute | DTI | FA value; ADC value | VFSS(VDS) | NA | NA | 61.10 ± 9.42 | 19/12 | 54.80% | No |
| Im 2018 [31] | n = 21 | Supratentorial | NA | MRI | NA | VFSS | NA | Within 14 days | 57.38 ± 12.71 | 13/8 | NA | No |
| Osawa 2013 [39] | n = 50 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | Acute | CT or MRI | SPECT data | VFSS; RSST; MWST | NA | NA | 70.20 ± 10.30 | 32/18 | 70.00% | No |
| Momosaki 2012 [32] | n = 20 | Supratentorial | NA | MRI | rCBF | MWST; FEES FOIS | NA | Within 7 days | 66.10 ± 5.10 | 14/6 | NA | No |
| Cola 2010 [12] | n = 20 | Supratentorial | Acute | MRI | NA | VFSS | NA | NA | 62.30 ± 12.20 | 19/1 | 35.00% | No |
| Saito 2016 [40] | n = 20 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | NA | MRI (DWI; FLAIR) | NA | VFSS | NA | Within 4 weeks | 76.40 ± 10.40 | 7/13 | NA | NA |
| Dehaghani 2016 [16] | n = 113 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | Acute | CT or MRI | NA | MASA | Within 24–72 h | Within 20 days | 64.37 ± 15.10 | 69/44 | 47.80% | No |
| Daniels 1996 [24] | n = 16 | Supratentorial | NA | CT or MRI | NA | VFSS | within 1 month | within 1 month | 66.60 ± 13.90 | 12/4 | NA | NA |
| Broadley 2003 [41] | n = 149 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | Acute | CT or MRI | NA | Parramatta Hospitals Assessment | NA | Within 72 h | 72.00 | 88/61 | 50.00% | NA |
| Steinhagen 2009 [42] | n = 60 | Supratentorial and Infratentorial | Acute | CT or MRI | NA | FEES | NA | NA | 74.60 ± 11.40 | 25/35 | NA | No |
| Gonzalez-Fernandez 2008 [34] | n = 14 | Supratentorial | Acute | MRI (FLAIR; DWI) | ROIs | NA | Within 24 h | Within 7 days | 62.60 ± 14.30 | 7/7 | NA | No |
| Galovic 2016 [35] | n = 119 | Supratentorial | Acute | MRI (DWI) | VLSM | Bogenhausen Dysphagia Score part 2 | NA | Within 48 h | 76.00 ± 9.00 | 65/54 | NA | No |
3.2. Study Design and Quality Assessment
| Study | Timeline for Data Capture | Assessor Blinded | Consistent Assessment for All Patients | Declared Operational Definition for Outcome | Outcome Addressed for All Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hess 2021 [11] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Zhang 2021 [43] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Galovic 2017 [17] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Moon 2018 [37] | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Moon 2022 [36] | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Galovic 2013 [25] | prospective | unclear | unclear | unclear | yes |
| Nakamori 2021 [38] | prospective | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Jang 2017 [28] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Lapa 2021 [29] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Wilmskoetter 2019 [13] | retrospective | yes | yes | unclear | yes |
| Suntrup 2015 [44] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Flowers 2017 [14] | unclear | unclear | yes | unclear | yes |
| Kim 2016 [30] | retrospective | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Im 2018 [31] | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Osawa 2013 [39] | retrospective | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Momosaki 2012 [32] | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Calo 2010 [12] | unclear | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Saito 2016 [40] | retrospective | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Dehaghani 2016 [36] | unclear | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Daniels 1996 [24] | retrospective | unclear | yes | yes | yes |
| Broadley 2003 [41] | prospective | yes | yes | unclear | no |
| Steinhagen 2009 [42] | prospective | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Gonzalez-Fernandez 2008 [34] | prospective | yes | yes | unclear | yes |
| Galovic 2016 [35] | unclear | unclear | yes | unclear | yes |
3.3. Swallowing Assessment
3.4. Diagnosis of Stroke
3.5. PSD-Related Lobar and Deep Brain Regions
| Study | Number of Patients | PSD-Related Brain Regions | Aspiration-Related Brain Regions | OTT-Related Brain Regions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hess 2021 [11] | n = 132 | Right insular cortex; Left basal ganglia; Left corona radiata; Left central region | NA | NA |
| Zhang 2021 [43] | n = 275 | Left inferior parietal gyrus | NA | NA |
| Galovic 2017 [17] | n = 62 | Superior corona radiata; Anterior insular cortex | NA | NA |
| Moon 2018 [37] | n = 90 | Superior frontal gyrus; Inferior frontal gyrus; Lentiform nucleus; Insular cortex | NA | Lentiform nucleus; Insular cortex |
| Moon 2022 [36] | n = 40 | Posterior lobe of the left cerebellum | NA | NA |
| Galovic 2013 [25] | n = 94 | Internal capsule; Insular cortex | Insular cortex | NA |
| Nakamori 2021 [38] | n = 342 | Parietal lobe lesion; Basal ganglia | Parietal lobe | NA |
| Jang 2017 [28] | n = 82 | Left inferior frontal lobe; Precentral gyrus; Right basal ganglia; Corona radiate; Putamen | Putamen | Precentral gyrus |
| Lapa 2021 [29] | n = 113 | Left lentiform nucleus; Left insular cortex; Left frontal operculum; Right insular cortex | NA | NA |
| Wilmskoetter 2019 [13] | n = 68 | Right inferior frontal gyrus; Pre- and postcentral gyrus; Supramarginal gyrus; Angular gyrus; Superior temporal gyrus; Insular cortex; Thalamus; Amygdala; Superior longitudinal fasciculus; Corona radiata; Internal capsule; External capsule; Ansalenticularis; Lenticular fasciculus | NA | NA |
| Suntrup 2015 [44] | n = 200 | Right pre- and post-central gyri; Opercular region; Supramarginal gyrus; Respective subcortical white matter tracts; Post-central lesion | NA | NA |
| Flowers 2017 [14] | n = 160 | Medullary; Insular cortex; Pontine | NA | NA |
| Kim 2016 [30] | n = 31 | Primary motor cortex on the contra-lesional side; Bilateral posterior limb of the internal capsule | NA | NA |
| Im 2018 [31] | n = 21 | Caudate nucleus; Insular cortex | Caudate nucleus | NA |
| Osawa 2013 [39] | n = 50 | Left precuneus; Left insular cortex; Anterior cingulate gyrus | Anterior cingulate gyrus | NA |
| Momosaki 2012 [32] | n = 20 | Brodmann area 4 | NA | NA |
| Calo 2010 [12] | n = 20 | Left periventricular white matter | NA | NA |
| Saito 2016 [40] | n = 20 | Middle frontal gyrus | NA | NA |
| Dehaghani 2016 [16] | n = 133 | Right primary sensory; Right insular cortex; Right internal capsule | NA | NA |
| Daniels 1996 [24] | n = 16 | Insular cortex | NA | NA |
| Broadley 2003 [41] | n = 149 | Frontal cortex; Insular cortex | NA | NA |
| Steinhagen 2009 [42] | n = 60 | NA | Insular cortex | NA |
| Gonzalez-Fernandez 2008 [34] | n = 14 | Primary somatosensory; Motor and motor supplementary areas; Putamen; Caudate; Basal ganglia; Internal capsule; | NA | NA |
| Galovic 2016 [35] | n = 119 | Anterior insular cortex | NA | NA |
3.6. Aspiration-Related and Oral Transit Time (OTT)-Related Brain Regions
3.7. The Incidence Rate of PSD
| Study | Number of Patients | PSD vs. No PSD | Male vs. Female | Ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic | Right vs. Left | Infratentorial vs. Supratentorial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hess 2021 [11] | n = 132 | 84/48 | 48/36 | NA | 36/48 | 10/74 |
| Zhang 2021 [43] | n = 275 | 113/162 | 75/38 | NA | 52/43 | NA |
| Galovic 2017 [17] | n = 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Moon 2018 [37] | n = 90 | 90/0 | 57/33 | 64/26 | 50/35 | 16/74 |
| Moon 2022 [36] | n = 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Galovic 2013 [25] | n = 94 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Nakamori 2021 [38] | n = 342 | 45/297 | 37/18 | NA | NA | NA |
| Jang 2017 [28] | n = 82 | 82/0 | 75/7 | 68/14 | 26/11 | NA |
| Lapa 2021 [29] | n = 113 | 62/51 | 27/24 | NA | 11/40 | NA |
| Wilmskoetter 2019 [13] | n = 68 | NA | 32/36 | NA | NA | NA |
| Suntrup 2015 [44] | n = 200 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Flowers 2017 [14] | n = 160 | 76/84 | 46/30 | NA | NA | NA |
| Kim 2016 [30] | n = 31 | 17/14 | 12/5 | NA | 13/14 | NA |
| Im 2018 [31] | n = 21 | 21/0 | 13/8 | 14/7 | 9/12 | NA |
| Osawa 2013 [39] | n = 50 | 27/23 | 13/14 | 19/8 | 4/12 | 13/3 |
| Momosaki 2012 [32] | n = 20 | 10/10 | 8/2 | 2/8 | NA | NA |
| Calo 2010 [12] | n = 20 | 7/14 | NA | NA | 10/10 | NA |
| Saito 2016 [40] | n = 20 | 20/0 | 7/13 | NA | 8/12 | NA |
| Dehaghani 2016 [36] | n = 133 | 54/79 | 24/30 | 8/12 | NA | NA |
| Daniels 1996 [24] | n = 16 | NA | NA | NA | 8/8 | NA |
| Broadley 2003 [41] | n = 149 | 74/75 | 41/33 | NA | NA | NA |
| Steinhagen 2009 [42] | n = 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16/44 |
| Gonzalez-Fernandez 2008 [34] | n = 29 | 14/15 | 7/7 | NA | 10/4 | NA |
| Galovic 2016 [35] | n = 119 | 12/107 | 6/6 | NA | 5/7 | NA |
4. Discussion
4.1. The Lobar and Deep Brain Regions Participate in the Swallowing Function Regulation
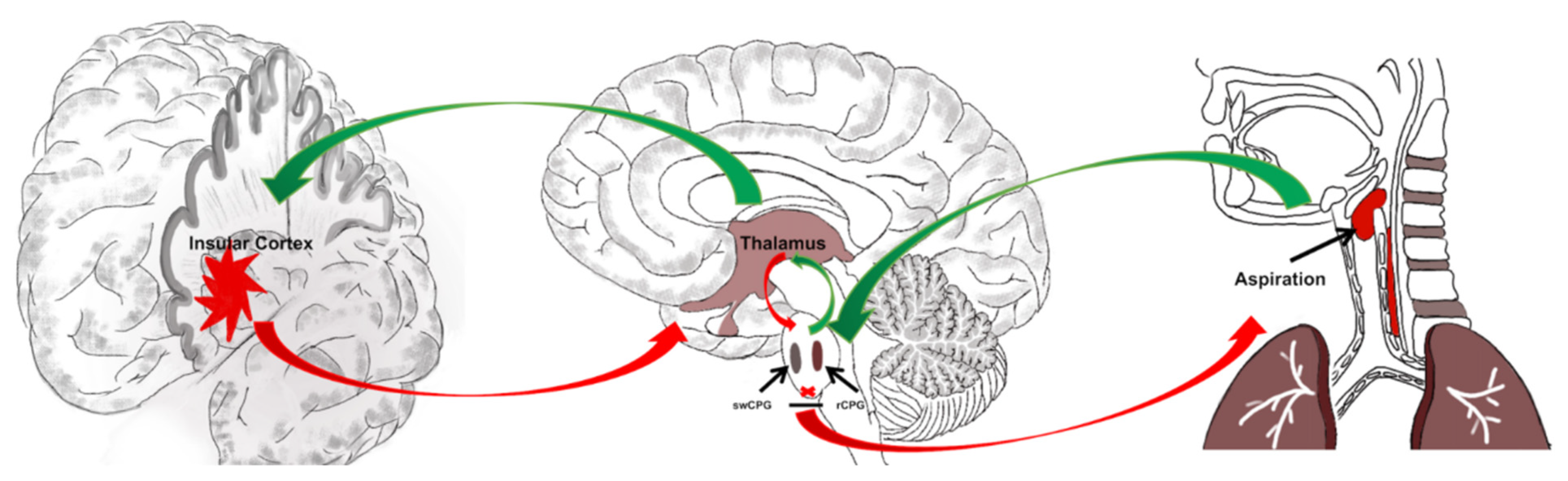
4.2. Insular Cortex May Be Most Relevant to PSD
4.3. Insular Cortex May Be Relevant to Aspiration after PSD
4.4. Clinical/Rehabilitative Implication of Normal Function for Insular Cortex
4.5. Limitations
4.6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saini, V.; Guada, L.; Yavagal, D.R. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology 2021, 97, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, R.; Beaton, D.; Diamant, N.E. Perceptions of psychological issues related to dysphagia differ in acute and chronic patients. Dysphagia 2010, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekberg, O.; Hamdy, S.H.; Woisard, V. Social and psychological burden of dysphagia: It’s impact on diagnosis and treatment. Dysphagia 2002, 17, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.J. Of proverbs and prevention: Aspiration and its consequences in older patients. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.L.; Roffe, C.; Beavan, J.; Blackett, B.; Fairfield, C.A.; Hamdy, S.; Havard, D.; McFarlane, M.; McLauglin, C.; Randall, M.; et al. Post-stroke dysphagia: A review and design considerations for future trials. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 4, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Rao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Peng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation at Different Sites for Dysphagia After Stroke: A Randomized, Observer-Blind Clinical Trial. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; Ferrillo, M.; Lippi, L.; Agostini, F.; de Sire, R.; Ferrara, P.E.; Raguso, G.; Riso, S.; Roccuzzo, A.; Ronconi, G.; et al. Sarcopenic Dysphagia, Malnutrition, and Oral Frailty in Elderly: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; Baricich, A.; Ferrillo, M.; Migliario, M.; Cisari, C.; Invernizzi, M. Buccal hemineglect: Is it useful to evaluate the differences between the two halves of the oral cavity for the multidisciplinary rehabilitative management of right brain stroke survivors? A cross-sectional study. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.C.; Abdala, A.P.; Borgmann, A.; Rybak, I.A.; Paton, J.F. Brainstem respiratory networks: Building blocks and microcircuits. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, K.K.; Segers, L.S.; Nuding, S.C.; O’Connor, R.; Alencar, P.A.; Davenport, P.W.; Bolser, D.C.; Pitts, T.; Lindsey, B.G.; Morris, K.F.; et al. Central Respiration and Mechanical Ventilation in the Gating of Swallow with Breathing. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, F.; Foerch, C.; Keil, F.; Seiler, A.; Lapa, S. Association of Lesion Pattern and Dysphagia in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2021, 52, 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cola, M.G.; Daniels, S.K.; Corey, D.M.; Lemen, L.C.; Romero, M.; Foundas, A.L. Relevance of subcortical stroke in dysphagia. Stroke 2010, 41, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmskoetter, J.; Bonilha, L.; Martin-Harris, B.; Elm, J.J.; Horn, J.; Bonilha, H.S. Mapping acute lesion locations to physiological swallow impairments after stroke. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, H.L.; AlHarbi, M.A.; Mikulis, D.; Silver, F.L.; Rochon, E.; Streiner, D.; Martino, R. MRI-Based Neuroanatomical Predictors of Dysphagia, Dysarthria, and Aphasia in Patients with First Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2017, 7, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.H.; Lim, M.H.; Seo, H.G.; Seong, M.Y.; Oh, B.M.; Kim, S. Development of a Novel Prognostic Model to Predict 6-Month Swallowing Recovery After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaghani, S.E.; Yadegari, F.; Asgari, A.; Chitsaz, A.; Karami, M. Brain regions involved in swallowing: Evidence from stroke patients in a cross-sectional study. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galovic, M.; Leisi, N.; Pastore-Wapp, M.; Zbinden, M.; Vos, S.B.; Mueller, M.; Weber, J.; Brugger, F.; Kägi, G.; Weder, B.J. Diverging lesion and connectivity patterns influence early and late swallowing recovery after hemispheric stroke. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keir, S.L.; Wardlaw, J.M. Systematic review of diffusion and perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, P.W.; Grant, P.E.; Gonzalez, R.G. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000, 217, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.L.; King, D.; Durkin, C.J.; Meagher, T.M.; Briley, D. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonanceimaging for acute stroke: Practical and popular. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, M.; Schaefer, P.W.; Sorensen, A.G.; Halpern, E.F.; Ay, H.; He, J.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Gonzalez, R.G. CT and conventional and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute stroke: Study in 691 patients at presentation to the emergency department. Radiology 2002, 224, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prichard, J.W.; Grossman, R.I. New reasons for early use of MRI in stroke. Neurology 1999, 52, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewas, R.; Michou, E.; Trapl-Grundschober, M.; Lal, A.; Arsava, E.M.; Bath, P.M.; Clavé, P.; Glahn, J.; Hamdy, S.; Pownall, S.; et al. European Stroke Organisation and European Society for Swallowing Disorders guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of post-stroke dysphagia. Eur. Stroke J. 2021, 6, LXXXIX-CXV. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.K.; Pathak, S.; Mukhi, S.V.; Stach, C.B.; Morgan, R.O.; Anderson, J.A. The relationship between lesion localization and dysphagia in acute stroke. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galovic, M.; Leisi, N.; Müller, M.; Weber, J.; Abela, E.; Kägi, G.; Weder, B. Lesion location predicts transient and extended risk of aspiration after supratentorial ischemic stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Q.I.; Baig, H.; Al Failakawi, A.; Majeed, S.; Khan, M.; Lucocq, J. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Healing Time in Patients Following Pilonidal Sinus Surgery: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e27777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 5.1.0; The Cochrane Collaboration Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2019. Available online: https://www.cochrane-handbook.org(accessed on 16 July 2020).
- Jang, S.; Yang, H.E.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, D.H. Lesion Characteristics of Chronic Dysphagia in Patients With Supratentorial Stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapa, S.; Foerch, C.; Singer, O.C.; Hattingen, E.; Luger, S. Ischemic Lesion Location Based on the ASPECT Score for Risk Assessment of Neurogenic Dysphagia. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Moon, W.J.; Kim, H.; Jung, E.; Lee, J. Association of Dysphagia With Supratentorial Lesions in Patients With Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Im, I.; Jun, J.P.; Hwang, S.; Ko, M.H. Swallowing outcomes in patients with subcortical stroke associated with lesions of the caudate nucleus and insula. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3552–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momosaki, R.; Abo, M.; Kakuda, W.; Uruma, G. Which cortical area is related to the development of dysphagia after stroke? A single photon emission computed tomography study using novel analytic methods. Eur. Neurol. 2012, 67, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.K.; Foundas, A.L.; Iglesia, G.C.; Sullivan, M.A. Lesion site in unilateral stroke patients with dysphagia. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1996, 6, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, M.; Kleinman, J.T.; Ky, P.K.; Palmer, J.B.; Hillis, A.E. Supratentorial regions of acute ischemia associated with clinically important swallowing disorders: A pilot study. Stroke 2008, 39, 3022–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galovic, M.; Leisi, N.; Müller, M.; Weber, J.; Tettenborn, B.; Brugger, F.; Abela, E.; Weder, B.; Kägi, G. Neuroanatomical correlates of tube dependency and impaired oral intake after hemispheric stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.I.; Jeong, Y.J.; Suh, J.H. Voxel-based lesion symptom mapping analysis for dysphagia in stroke patients with isolated cerebellar lesions. J. Neural. Transm. 2022, 129, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.I.; Yoon, S.Y.; Yi, T.I.; Jeong, Y.J.; Cho, T.H. Lesions Responsible for Delayed Oral Transit Time in Post-stroke Dysphagia. Dysphagia 2018, 33, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamori, M.; Hosomi, N.; Imamura, E.; Matsushima, H.; Maetani, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; Takeda, C.; Nagasaki, T.; Masuda, S.; et al. Association between stroke lesions and videofluoroscopic findings in acute stroke patients. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, A.; Maeshima, S.; Matsuda, H.; Tanahashi, N. Functional lesions in dysphagia due to acute stroke: Discordance between abnormal findings of bedside swallowing assessment and aspiration on videofluorography. Neuroradiology 2013, 55, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Hayashi, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Ota, T. Clinical Characteristics and Lesions Responsible for Swallowing Hesitation After Acute Cerebral Infarction. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broadley, S.; Croser, D.; Cottrell, J.; Creevy, M.; Teo, E.; Yiu, D.; Pathi, R.; Taylor, J.; Thompson, P.D. Predictors of prolonged dysphagia following acute stroke. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2003, 10, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhagen, V.; Grossmann, A.; Benecke, R.; Walter, U. Swallowing disturbance pattern relates to brain lesion location in acute stroke patients. Stroke 2009, 40, 1903–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Ding, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Diao, S.; Kong, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, C.; et al. Predictive Model of Dysphagia and Brain Lesion-Symptom Mapping in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 753364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntrup, S.; Kemmling, A.; Warnecke, T.; Hamacher, C.; Oelenberg, S.; Niederstadt, T.; Heindel, W.; Wiendl, H.; Dziewas, R. The impact of lesion location on dysphagia incidence, pattern and complications in acute stroke. Part 1: Dysphagia incidence, severity and aspiration. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Kemmling, A.; Warnecke, T.; Hamacher, C.; Oelenberg, S.; Niederstadt, T.; Heindel, W.; Wiendl, H.; Dziewas, R. The impact of lesion location on dysphagia incidence, pattern and complications in acute stroke. Part 2: Oropharyngeal residue, swallow and cough response, and pneumonia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntrup, S.; Warnecke, T.; Kemmling, A.; Teismann, I.K.; Hamacher, C.; Oelenberg, S.; Dziewas, R. Dysphagia in patients with acute striatocapsular hemorrhage. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogolla, N. The insular cortex. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venniro, M.; Zhang, M.; Caprioli, D.; Hoots, J.K.; Golden, S.A.; Heins, C.; Morales, M.; Epstein, D.H.; Shaham, Y. Volitional social interaction prevents drug addiction in rat models. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, A.; Ward, B.D.; Siwiec, R.M.; Ahmad, S.; Kern, M.; Nencka, A.; Li, S.J.; Shaker, R. Functional connectivity of the cortical swallowing network in humans. NeuroImage 2013, 76, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.D.; Zhou, L.F.; Wang, S.J.; Zhao, Y.S.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, L. Compensatory recombination phenomena of neurological functions in central dysphagia patients. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; Afsah, O.; Baz, H.; El-Regal, M.E.; Abou-Elsaad, T. Clinical and videofluoroscopic evaluation of feeding and swallowing in infants with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 150, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, I.; Guertin, P.A. Central pattern generators in the brainstem and spinal cord: An overview of basic principles, similarities and differences. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 107–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, N.K.; Lee, L.Y. Mechanisms of dyspnea. Chest 2010, 138, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevizan-Baú, P.; Dhingra, R.R.; Furuya, W.I.; Stanic, D.; Dutschmann, M. Forebrain projection neurons target functionally diverse respiratory control areas in the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. J. Comp. Neurol. 2021, 529, 2243–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, V.G.; Ivanova, T.G.; Alexandrova, N.P. Prefrontal control of respiration. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 5, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow, C.L.; Humbert, I.; Saxon, K.; Poletto, C.; Sonies, B.; Crujido, L. Effffects of surface electrical stimulation both at rest and during swallowing in chronic pharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia 2007, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, J.; Ye, Q.P.; Wu, Z.M.; Dai, Y.; Dou, Z.L. The Effect and Optimal Parameters of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Poststroke Dysphagia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 845737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Kurosu, A.; Coyle, J.L. A generalized equation approach for hyoid bone displacement and penetration–aspiration scale analysis. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Wu, Z.M.; Ye, Q.P.; Dai, M.; Dai, Y.; He, Z.T.; Dou, Z.L. Characteristics of dysphagia among different lesion sites of stroke: A retrospective study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 944688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, J.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Ye, Q.; Dai, M.; Dai, Y.; Dou, Z. Effects of Insular Cortex on Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101334
Qiao J, Wu Z, Cheng X, Ye Q, Dai M, Dai Y, Dou Z. Effects of Insular Cortex on Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(10):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101334
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Jia, Zhimin Wu, Xue Cheng, Qiuping Ye, Meng Dai, Yong Dai, and Zulin Dou. 2022. "Effects of Insular Cortex on Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis" Brain Sciences 12, no. 10: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101334
APA StyleQiao, J., Wu, Z., Cheng, X., Ye, Q., Dai, M., Dai, Y., & Dou, Z. (2022). Effects of Insular Cortex on Post-Stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Brain Sciences, 12(10), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101334





