Subdural Effusion Evolves into Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
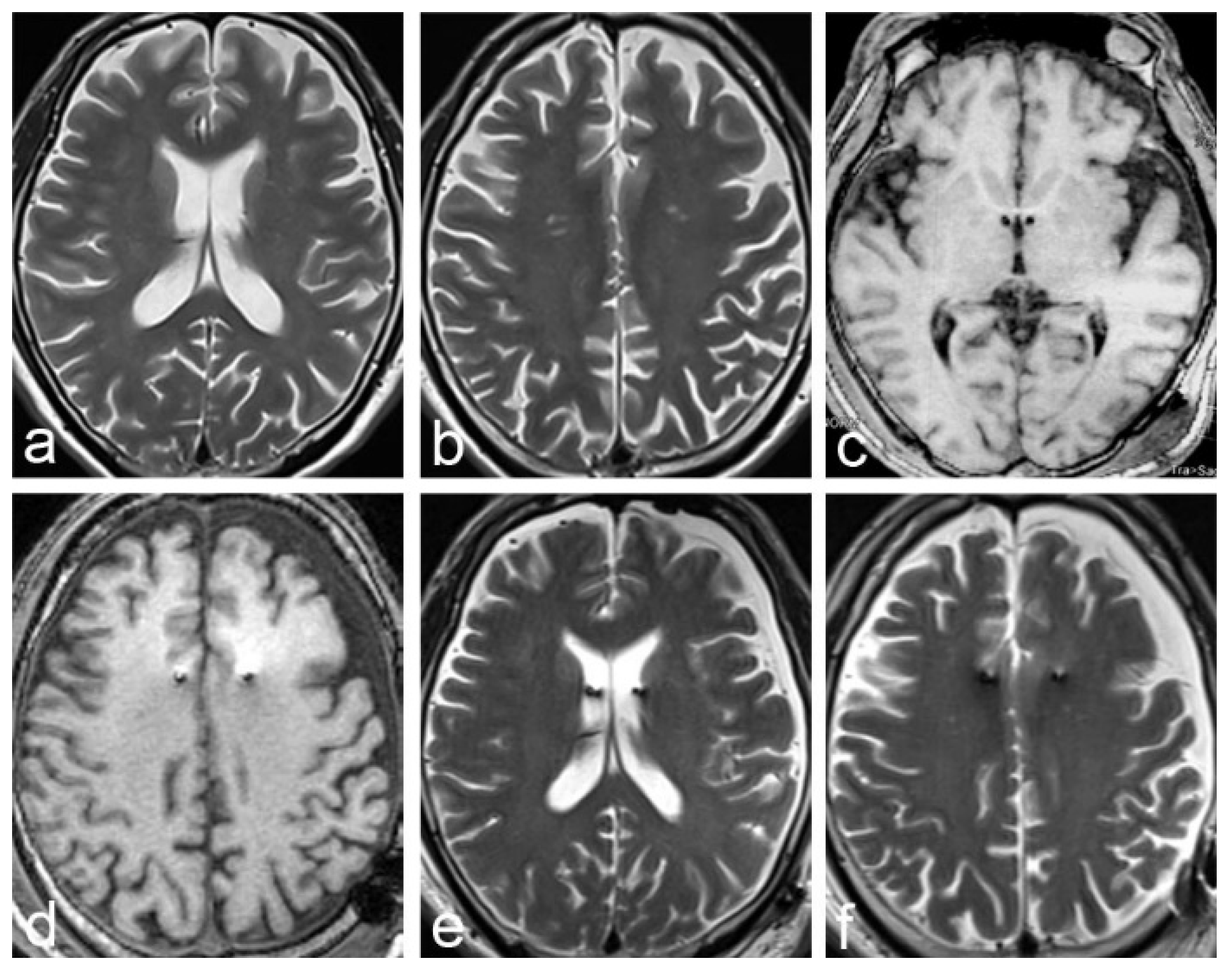
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
3. Systematic Review
Data Extraction Process
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Errico, A.P.; German, W.J. Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1930, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Putnam, T.J.; Cushing, H. Chronic subdural hematoma: Its pathology, its relation to pachymeningitis hemorrhagica and its surgical treatment. Arch. Surg. 1925, 11, 329–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.F.; Jiang, J.Y.; Bao, Y.H.; Liang, Y.M.; Pan, Y.H. Traumatic subdural effusion evolves into chronic subdural hematoma: Two stages of the same inflammatory reaction? Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, H.; Nomura, S.; Tsuchida, E.; Ito, H. Serum protein exudation in chronic subdural haematomas: A mechanism for haematoma enlargement? Acta Neurochir. 1998, 140, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Komai, T.; Mizukoshi, H. Role of local hyperfibrinolysis in the etiology of chronic subdural hematoma. J. Neurosurg. 1976, 45, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weir, B. Oncotic pressure of subdural fluids. J. Neurosurg. 1980, 53, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, H.; Saito, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Hasegawa, T. Tissue-type plasminogen activator in the chronic subdural hematoma. Surg. Neurol. 1988, 30, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S. ReviewNatural history of chronic subdural haematoma. Brain Inj. 2004, 18, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechli, H.; Nordmann, A.; Bucher, H.C.; Gratzl, O. Demographics and prevalent risk factors of chronic subdural haematoma: Results of a large single-center cohort study. Neurosurg. Rev. 2004, 27, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, M.A.; Marbet, G.; Radü, E.W.; Gratzl, O. Aspirin as a risk factor for hemorrhage in patients with head injuries. Neurosurg. Rev. 1992, 15, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintzen, A.R.; Tijssen, J.G.P. Subdural Hematoma and Oral Anticoagulant Therapy. Arch. Neurol. 1982, 39, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattle, H.; Kohler, S.; Huber, P.; Rohner, M.; Steinsiepe, K.F. Anticoagulation-related intracranial extracerebral haemorrhage. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1989, 52, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hylek, E.M.; Singer, D.E. Risk factors for intracranial hemorrhage in outpatients taking warfarin. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievink, W.I.; Maya, M.M.; Pikul, B.K.; Louy, C. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks as the cause of subdural hematomas in elderly patients on anticoagulation. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Cho, J.-H.; Goh, D.-H.; Kang, D.-H.; Shin, I.H.; Hamm, I.-S. Postoperative subdural hygroma and chronic subdural hematoma after unruptured aneurysm surgery: Age, sex, and aneurysm location as independent risk factors. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, K.; Suzuki, R.; Masaoka, H.; Matsushima, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Monma, S. Chronic subdural haematoma preceded by persistent traumatic subdural fluid collection. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.K.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, M.C.; Kang, J.K.; Choi, C.R. Spontaneous evolution of posttraumatic subdural hygroma into chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir. 1994, 127, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Doh, J.W.; Bae, H.G.; Yun, I.G. Relations among traumatic subdural lesions. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1996, 11, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.S.; Bae, W.K.; Park, Y.T.; Yun, I.G. The pathogenesis and fate of traumatic subdural hygroma. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 8, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Pan, L.; Liang, S.; Mao, Z.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Ling, Z. Early detection of cerebral ischemic events on intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging during surgical procedures for deep brain stimulation. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Pan, L.; Song, H.; Xu, X.; Xu, B.; Yu, X.; Ling, Z. Intraoperative MRI for optimizing electrode placement for deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson disease. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (prisma-p) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panov, F.; Levin, E.; de Hemptinne, C.; Swann, N.C.; Qasim, S.; Miocinovic, S.; Ostrem, J.L.; Starr, P.A. Intraoperative electrocorticography for physiological research in movement disorders: Principles and experience in 200 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponce, F.A.; Asaad, W.F.; Foote, K.D.; Anderson, W.S.; Rees Cosgrove, G.; Baltuch, G.H.; Beasley, K.; Reymers, D.E.; Oh, E.S.; Targum, S.D.; et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the fornix for Alzheimer’s disease: Surgical safety in the ADvance trial. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umemura, A.; Oka, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Okita, K.; Matsukawa, N.; Yamada, K. Complications of subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2011, 51, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voges, J.; Waerzeggers, Y.; Maarouf, M.; Lehrke, R.; Koulousakis, A.; Lenartz, D.; Sturm, V. Deep-brain stimulation: Long-term analysis of complications caused by hardware and surgery--experiences from a single centre. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Chung, S.J.; Lee, C.S.; Jeon, S.R. Analysis of hemorrhagic risk factors during deep brain stimulation surgery for movement disorders: Comparison of the circumferential paired and multiple electrode insertion methods. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgulho, A.; De Salles, A.A.F.; Frighetto, L.; Behnke, E. Incidence of hemorrhage associated with electrophysiological studies performed using macroelectrodes and microelectrodes in functional neurosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, D.K.; Rau, G.; Starr, P.A. Hemorrhagic complications of microelectrode-guided deep brain stimulation. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2003, 80, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Haim, S.; Asaad, W.F.; Gale, J.T.; Eskandar, E.N. Risk factors for hemorrhage during microelectrode-guided deep brain stimulation and the introduction of an improved microelectrode design. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Maeda, M. Risk factors for the occurrence of chronic subdural haematomas after neurosurgical procedures. Acta Neurochir. 2003, 145, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokmak, M.; Iplikcioglu, A.C.; Bek, S.; Gökduman, C.A.; Erdal, M. The role of exudation in chronic subdural hematomas. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Adachi, K.; Cho, K.; Ishimaru, S.; Maeda, M. Quantitative Kinetic Analysis of Blood Vessels in the Outer Membranes of Chronic Subdural Hematomas. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 1998, 38, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sajanti, J.; Majamaa, K. High concentrations of procollagen propeptides in chronic subdural haematoma and effusion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujisawa, H.; Ito, H.; Saito, K.; Ikeda, K.; Nitta, H.; Yamashita, J. Immunohistochemical localization of tissue-type plasminogen activator in the lining wall of chronic subdural hematoma. Surg. Neurol. 1991, 35, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Bae, W.K.; Bae, H.G.; Yun, I.G. The fate of traumatic subdural hygroma in serial computed tomographic scans. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2000, 15, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Su, W.; Wu, C. Clinical characteristics of chronic subdural hematoma evolving from traumatic subdural effusion. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2002, 40, 360–362. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, M.; Yamashima, T.; Yamashita, J.; Suzuki, M.; Shimada, S. Traumatic subdural hygroma: Pathology and meningeal enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 1992, 31, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhuo, W.; Sun, C.; Su, Z.; Yan, A.; Shen, L. Effects of atorvastatin on chronic subdural hematoma: A systematic review. Medicine 2017, 96, e7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, P.; Van Niftrik, C.H.B.; Muscas, G.; Scheffler, P.; Oertel, M.F.; Stieglitz, L.H. How to avoid pneumocephalus in deep brain stimulation surgery? Analysis of potential risk factors in a series of 100 consecutive patients. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Age (Year) | Sex | Diagnosis | DBS Target | SDE | Cerebral Atrophy | Days of Evacuation | Lead Shift | Effect of Stimulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 62 | F | Parkison’s disease | GPI | Yes | Yes | 36 days | description | poor |
| Case 2 | 56 | M | Alzheimer’s disease | fornix | Yes | Yes | 49 days | description | poor |
| Panov et al. 2017 [23] | — | — | Movement disorder | — | — | — | 2 months | — | — |
| Ponce et al. 2016 [24] | — | — | Alzheimer’s disease | fornix | Yes | — | 60 days | — | — |
| Umemura et al. 2011 [25] | — | — | Parkinson’s disease | STN | — | Yes | 2 months | No shift | — |
| Arachnoid | SDE after DBS | Traumatic SDE |
|---|---|---|
| Breakage | Clear | Unclear, Inference |
| Location of breakage | Bilateral forehead | Unclear location |
| Broken shape | Round hole | Irregular shape |
| Whether there is a valve | No | Possible |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, D.; Dang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, Z. Subdural Effusion Evolves into Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101375
Wu D, Dang Y, Wang J, Cui Z. Subdural Effusion Evolves into Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(10):1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101375
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Dongdong, Yuanyuan Dang, Jian Wang, and Zhiqiang Cui. 2022. "Subdural Effusion Evolves into Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery: Case Report and Review of the Literature" Brain Sciences 12, no. 10: 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101375
APA StyleWu, D., Dang, Y., Wang, J., & Cui, Z. (2022). Subdural Effusion Evolves into Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Brain Sciences, 12(10), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101375






