The Effect of an α-7 Nicotinic Allosteric Modulator PNU120596 and NMDA Receptor Antagonist Memantine on Depressive-like Behavior Induced by LPS in Mice: The Involvement of Brain Microglia †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs and Treatment
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (rt-PCR)
2.5. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.6. Behavioral Tests
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
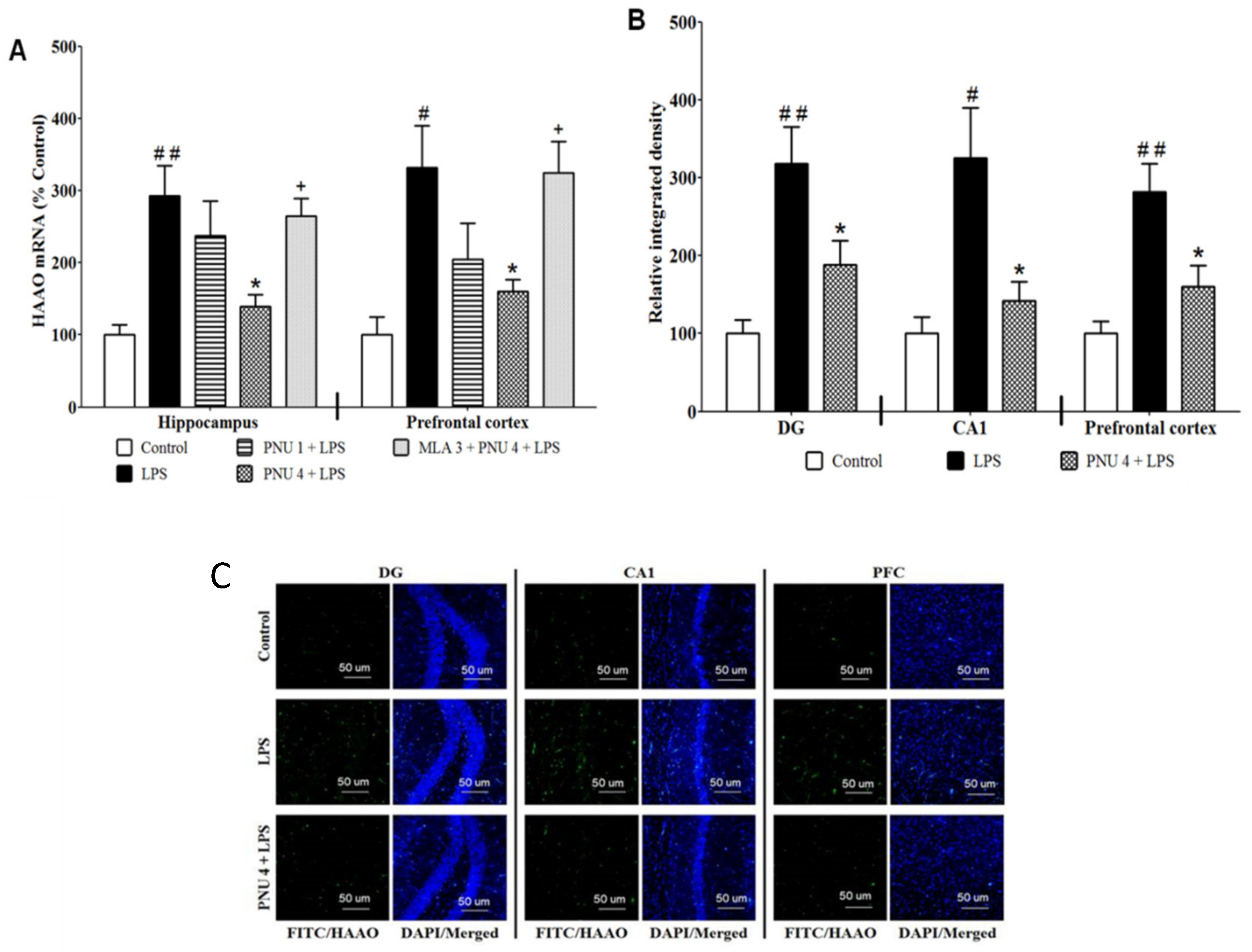
3.1. Effects of PNU120596 on HAAO Expression in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
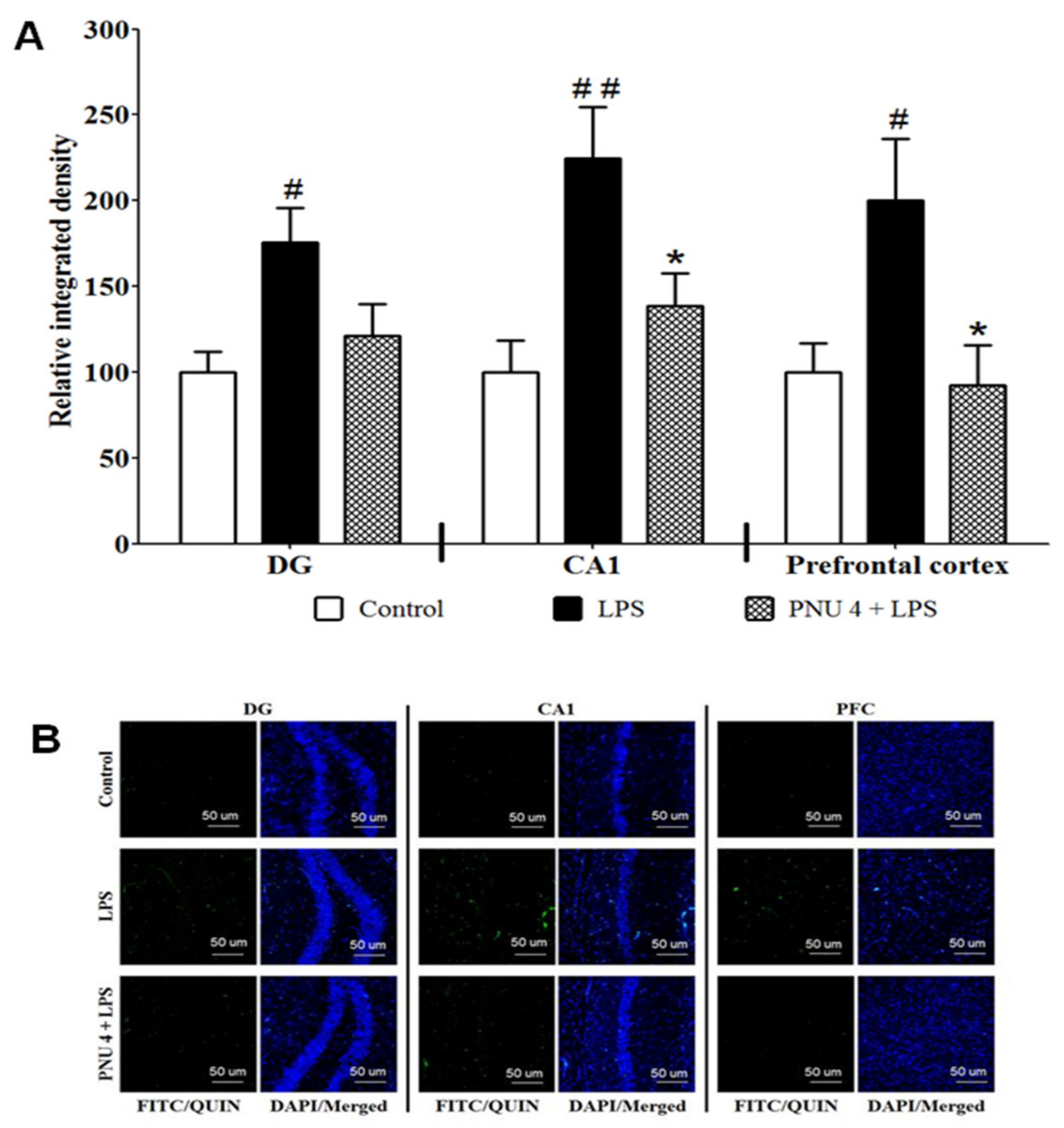
3.2. Effects of PNU120596 on QUIN Immunoreactivity in DG and CA1 Regions of the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
3.3. Effects of Memantine on LPS-Induced Depressive-like Behavior
3.4. Combinatorial Effects of PNU120596 and Memantine on LPS-Induced Depressive-like Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatova, E.; Shadrina, M.; Slominsky, P. Major Depression: One Brain, One Disease, One Set of Intertwined Processes. Cells 2021, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woelfer, M.; Kasties, V.; Kahlfuss, S.; Walter, M. The Role of Depressive Subtypes within the Neuroinflammation Hypothesis of Major Depressive Disorder. Neuroscience 2019, 403, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C.; e Cordeiro, T.M.; Suchting, R.; de Dios, C.; Leal, V.A.C.; Soares, J.C.; Dantzer, R.; Teixeira, A.L.; Selvaraj, S. Effect of immune activation on the kynurenine pathway and depression symptoms—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Alzarea, S. Glial mechanisms underlying major depressive disorder: Potential therapeutic opportunities. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 167, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vichaya, E.; Malik, S.; Sominsky, L.; Ford, B.G.; Spencer, S.J.; Dantzer, R. Microglia depletion fails to abrogate inflammation-induced sickness in mice and rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Cole, S.W. Reciprocal regulation of the neural and innate immune systems. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, M.P.; Achim, C.L.; Wiley, C.A.; Major, E.O.; Saito, K.; Markey, S.P. Human microglia convert l-tryptophan into the neurotoxin quinolinic acid. Biochem. J. 1996, 320, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, J.M.; Redus, L.; Coelho, D.S.; Morales, J.; Gao, X.; O’Connor, J.C. Neurotoxic kynurenine metabolism is increased in the dorsal hippocampus and drives distinct depressive behaviors during inflammation. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.K.; Budac, D.P.; Bisulco, S.; Lee, A.W.; A Smith, R.; Beenders, B.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. NMDA Receptor Blockade by Ketamine Abrogates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depressive-Like Behavior in C57BL/6J Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W.; A Lawson, M.; Woolwine, B.J.; Vogt, G.; Spivey, J.R.; Saito, K.; Miller, A.H. CSF concentrations of brain tryptophan and kynurenines during immune stimulation with IFN-α: Relationship to CNS immune responses and depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay-Richter, C.; Linderholm, K.R.; Lim, C.K.; Samuelsson, M.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Guillemin, G.J.; Erhardt, S.; Brundin, L. A role for inflammatory metabolites as modulators of the glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in depression and suicidality. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 43, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Alzarea, S.; Papke, R.L.; Rahman, S. The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor positive allosteric modulator attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of hippocampal IκB and CD11b gene expression in mice. Drug Discov. Ther. 2017, 11, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alzarea, S.; Rahman, S. Effects of alpha-7 nicotinic allosteric modulator PNU 120596 on depressive-like behavior after lipopolysaccharide administration in mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharm. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shytle, R.D.; Mori, T.; Townsend, K.; Vendrame, M.; Sun, N.; Zeng, J.; Ehrhart, J.; Silver, A.A.; Sanberg, P.R.; Tan, J. Cholinergic modulation of microglial activation by α7 nicotinic receptors. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Alzarea, S.; Papke, R.L.; Rahman, S. The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor positive allosteric modulator prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced allodynia, hyperalgesia and TNF-α in the hippocampus in mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzarea, S.; Rahman, S. Alpha-7 nicotinic receptor allosteric modulator PNU120596 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced anxiety, cognitive deficit and depression-like behaviors in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 366, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Gillevet, T.C.; Kabbani, N. A G protein-coupled α7 nicotinic receptor regulates signaling and TNF-α release in microglia. FEBS OpenBio 2017, 7, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, J.; Bouzat, C. Understanding the Bases of Function and Modulation of α7 Nicotinic Receptors: Implications for Drug Discovery. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbani, N.; Nichols, R.A. Beyond the Channel: Metabotropic Signaling by Nicotinic Receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.K.; Wang, J.; Papke, R.L. Positive allosteric modulators as an approach to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-targeted therapeutics: Advantages and limitations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, M.M.; Björkholm, C.; Malmerfelt, A.; Möller, A.; Påhlsson, N.; Konradsson-Geuken, Å.; Feltmann, K.; Jardemark, K.; Schilström, B.; Svensson, T.H. Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists and PAMs as adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia. An experimental study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, M.; Scheggi, S.; Carta, G.; Madeddu, C.; Lecca, S.; Luchicchi, A.; Cadeddu, F.; Frau, R.; Fattore, L.; Fadda, P.; et al. PPARα regulates cholinergic-driven activity of midbrain dopamine neurons via a novel mechanism involving α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, X.; Pan, L.; Zhu, W.; Fu, X.; Guo, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J. Pharmacologic activation of cholinergic alpha7 nicotinic receptors mitigates depressive-like behavior in a mouse model of chronic stress. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, R.L.; Kem, W.R.; Soti, F.; López-Hernández, G.Y.; Horenstein, N.A. Activation and Desensitization of Nicotinic α7-type Acetylcholine Receptors by Benzylidene Anabaseines and Nicotine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uteshev, V.V.; Meyer, E.M.; Papke, R.L. Activation and inhibition of native neuronal alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic ACh receptors. Brain Res. 2002, 948, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevets, W.C.; Price, J.L.; Furey, M.L. Brain structural and functional abnormalities in mood disorders: Implications for neurocircuitry models of depression. Anat. Embryol. 2008, 213, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.C.; A Lawson, M.; André, C.; Moreau, M.; Lestage, J.; Castanon, N.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roni, M.A.; Rahman, S. Antidepressant-like effects of lobeline in mice: Behavioral, neurochemical, and neuroendocrine evidence. Prog. Neuropsychopharm. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 41, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roni, M.A.; Rahman, S. The effects of lobeline on nicotine withdrawal-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 2989–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roni, M.A.; Rahman, S. Lobeline attenuates ethanol abstinence-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Alcohol 2017, 61, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabert, K.; Michoel, T.; Karavolos, M.H.; Clohisey, S.; Baillie, J.K.; Stevens, M.P.; Freeman, T.C.; Summers, K.M.; McColl, B.W. Microglial brain region−dependent diversity and selective regional sensitivities to aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.W.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Sharma, K.; Joseph, A.T.; Bisht, K.; Picard, K.; Tremblay, M.; Srivastava, L.K. Microglia in the developing prefrontal cortex of rats show dynamic changes following neonatal disconnection of the ventral hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2019, 146, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucault-Fruchard, L.; Doméné, A.; Page, G.; Windsor, M.; Emond, P.; Rodrigues, N.; Dollé, F.; Damont, A.; Buron, F.; Routier, S.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of the alpha 7 nicotinic receptor agonist PHA 543613 in an in vivo excitotoxic adult rat model. Neuroscience 2017, 356, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganong, A.H.; Cotman, C.W. Kynurenic acid and quinolinic acid act at N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1986, 236, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yirmiya, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Reshef, R. Depression as a Microglial Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, M.-N.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Z. Possible antidepressant effects and mechanisms of memantine in behaviors and synaptic plasticity of a depression rat model. Neuroscience 2011, 182, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Nakagawasai, O.; Nemoto, W.; Kadota, S.; Isono, J.; Odaira, T.; Sakuma, W.; Arai, Y.; Tadano, T.; Tan-No, K. Memantine ameliorates depressive-like behaviors by regulating hippocampal cell proliferation and neuroprotection in olfactory bulbectomized mice. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, E.; Rossi, S.; Szasz, B.; Juranyi, Z.; Fallon, S.; Pomara, N.; Sershen, H.; Lajtha, A. Changes in cerebral neurotransmitters and metabolites induced by acute donepezil and memantine administrations: A microdialysis study. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, H.; Pan, Z.; Park, C.; Brietzke, E.; Musial, N.; Shariq, A.S.; Iacobucci, M.; Yim, S.J.; Lui, L.M.W.; Rong, C.; et al. Recognition and Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rakoczy, S.; Brown-Borg, H. Assessment of spatial memory in mice. Life Sci. 2010, 87, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Arco, A.; Segovia, G.; Garrido, P.; de Blas, M.; Mora, F. Stress, prefrontal cortex and environmental enrichment: Studies on dopamine and acetylcholine release and working memory performance in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 176, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.J.; Stanton, M.E. Medial prefrontal administration of MK-801 impairs T-maze discrimination reversal learning in weanling rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, Glutamate, and Glia: A Trio of Trouble in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, F.N.; Menard, C. Inflamed Astrocytes: A Path to Depression Led by Menin. Neuron 2018, 100, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xiao, Q.; Xie, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, L.; Tu, J. Astrocyte, a Promising Target for Mood Disorder Interventions. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerhagen, C.; Veer, I.; Erk, S.; Mohnke, S.; Lett, T.; Wustenberg, T.; Walter, H. Amygdala functional connectivity in major depression-disentangling markers of pathology, risk and resilence. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 2740–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Edmiston, E.K.; Womer, F.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, X.; Wu, F.; Kong, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Abnormities of Amygdala and Prefrontal Cortex in Major Depressive Disorder with Suicide Attempts. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Nan, J.; Lan, Y. The Nucleus Accumbens: A Common Target in the Comorbidity of Depression and Addiction. Front. Neural Circuits 2020, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, K.; Ng, R.; Scott, H.; Kodavaganti, S.; Smyda, G.; Diwadkar, V.; Phillips, M. Ventral Striatum Functional Connectivity during Rewards and Losses and Symptomatology in Depressed Patients. Biol. Psychol. 2017, 123, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| HAAO | GGCTGGTGATTGAGAGAAGG (forward) GGTCCTTACAGTGGAACCATT (reverse) |
| GAPDH | GTGGAGTCATACTGGAACATGTAG (forward) AATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTG (reverse) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzarea, S.; Abbas, M.; Ronan, P.J.; Lutfy, K.; Rahman, S. The Effect of an α-7 Nicotinic Allosteric Modulator PNU120596 and NMDA Receptor Antagonist Memantine on Depressive-like Behavior Induced by LPS in Mice: The Involvement of Brain Microglia. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111493
Alzarea S, Abbas M, Ronan PJ, Lutfy K, Rahman S. The Effect of an α-7 Nicotinic Allosteric Modulator PNU120596 and NMDA Receptor Antagonist Memantine on Depressive-like Behavior Induced by LPS in Mice: The Involvement of Brain Microglia. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(11):1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111493
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzarea, Sami, Muzaffar Abbas, Patrick J. Ronan, Kabirullah Lutfy, and Shafiqur Rahman. 2022. "The Effect of an α-7 Nicotinic Allosteric Modulator PNU120596 and NMDA Receptor Antagonist Memantine on Depressive-like Behavior Induced by LPS in Mice: The Involvement of Brain Microglia" Brain Sciences 12, no. 11: 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111493
APA StyleAlzarea, S., Abbas, M., Ronan, P. J., Lutfy, K., & Rahman, S. (2022). The Effect of an α-7 Nicotinic Allosteric Modulator PNU120596 and NMDA Receptor Antagonist Memantine on Depressive-like Behavior Induced by LPS in Mice: The Involvement of Brain Microglia. Brain Sciences, 12(11), 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111493







