Research on Top Archer’s EEG Microstates and Source Analysis in Different States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Signal Acquisition
2.3. Signal Preprocessing
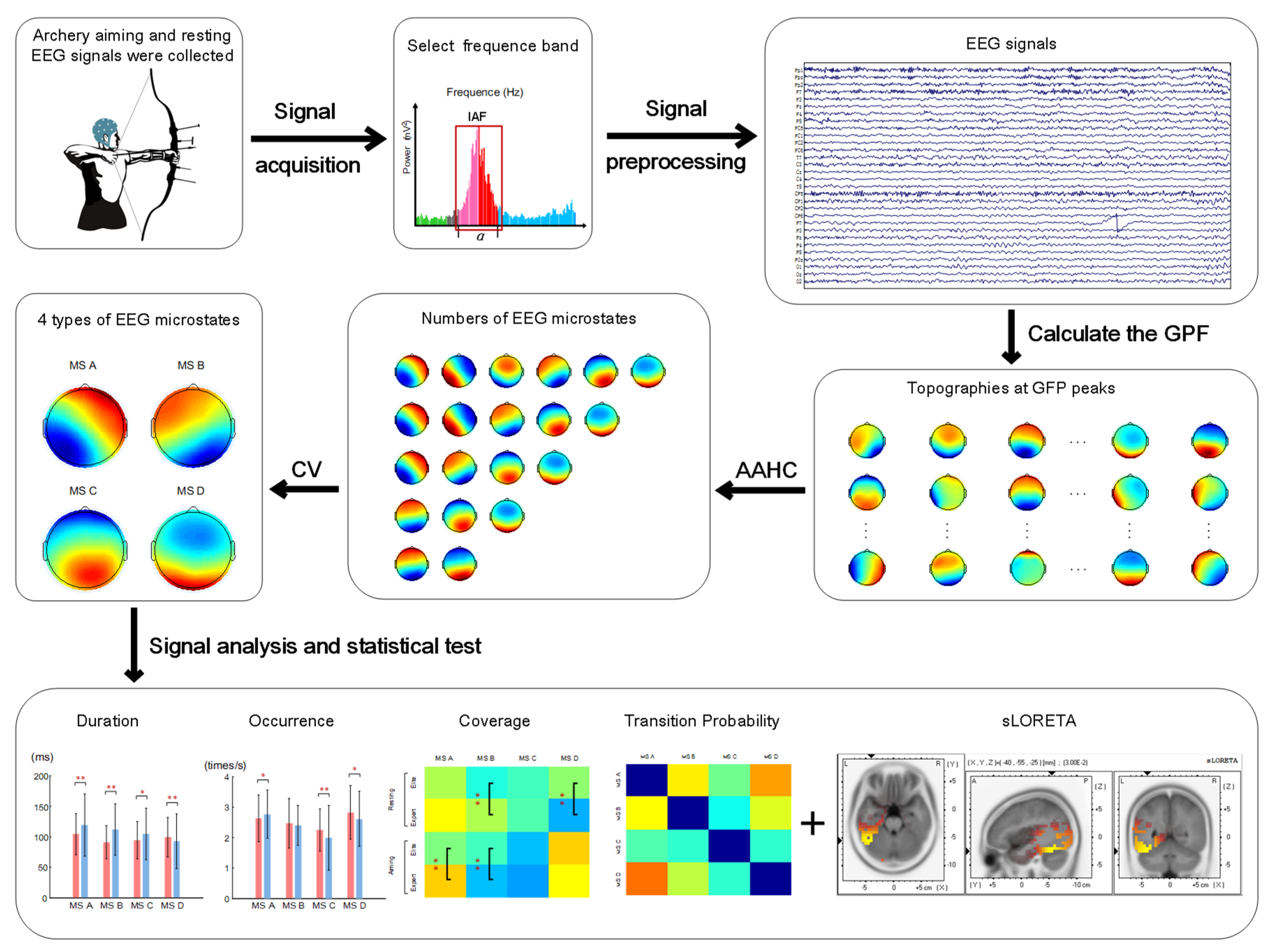
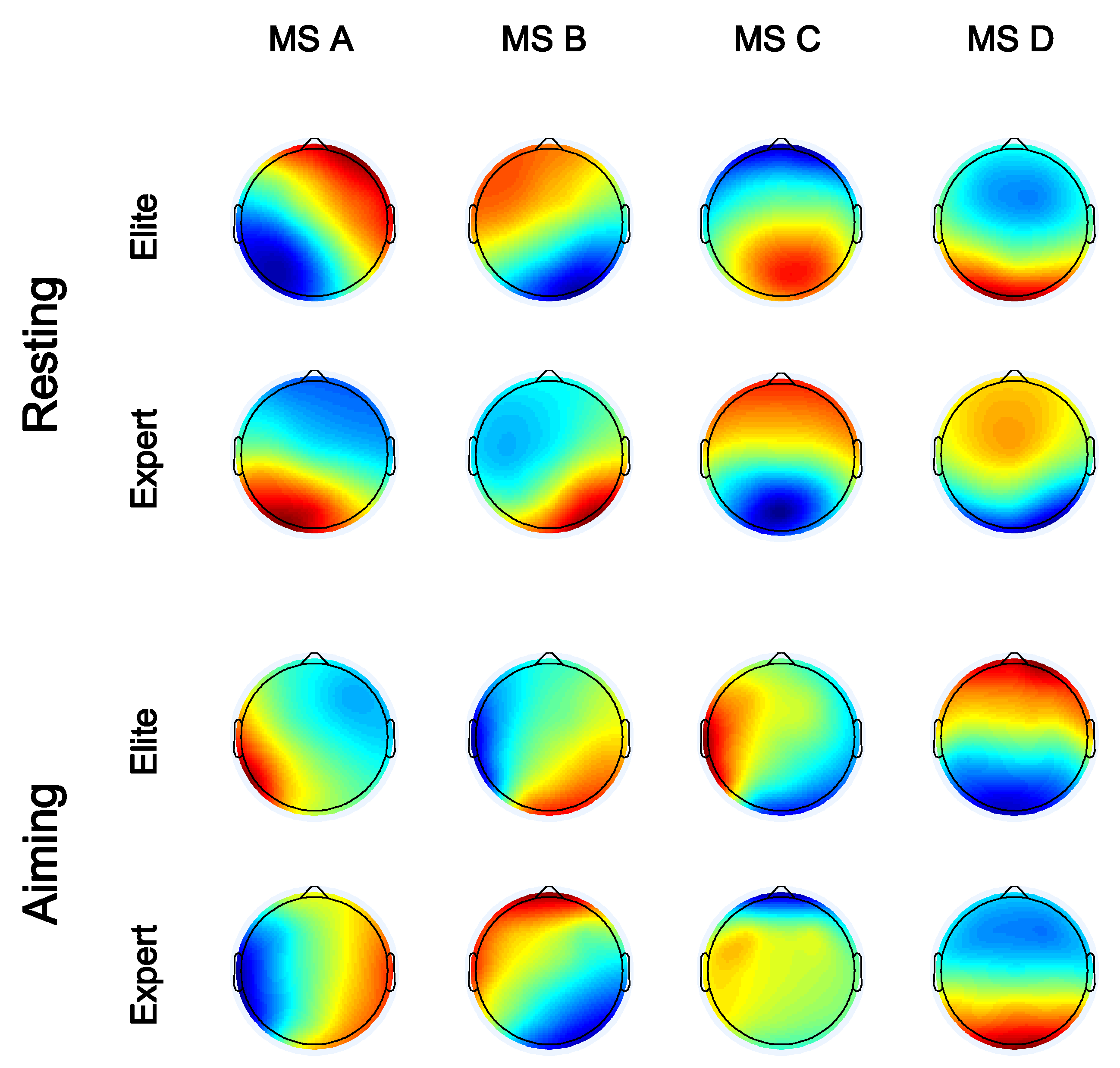
2.4. Microstate Analysis
2.5. Sources of Microstates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
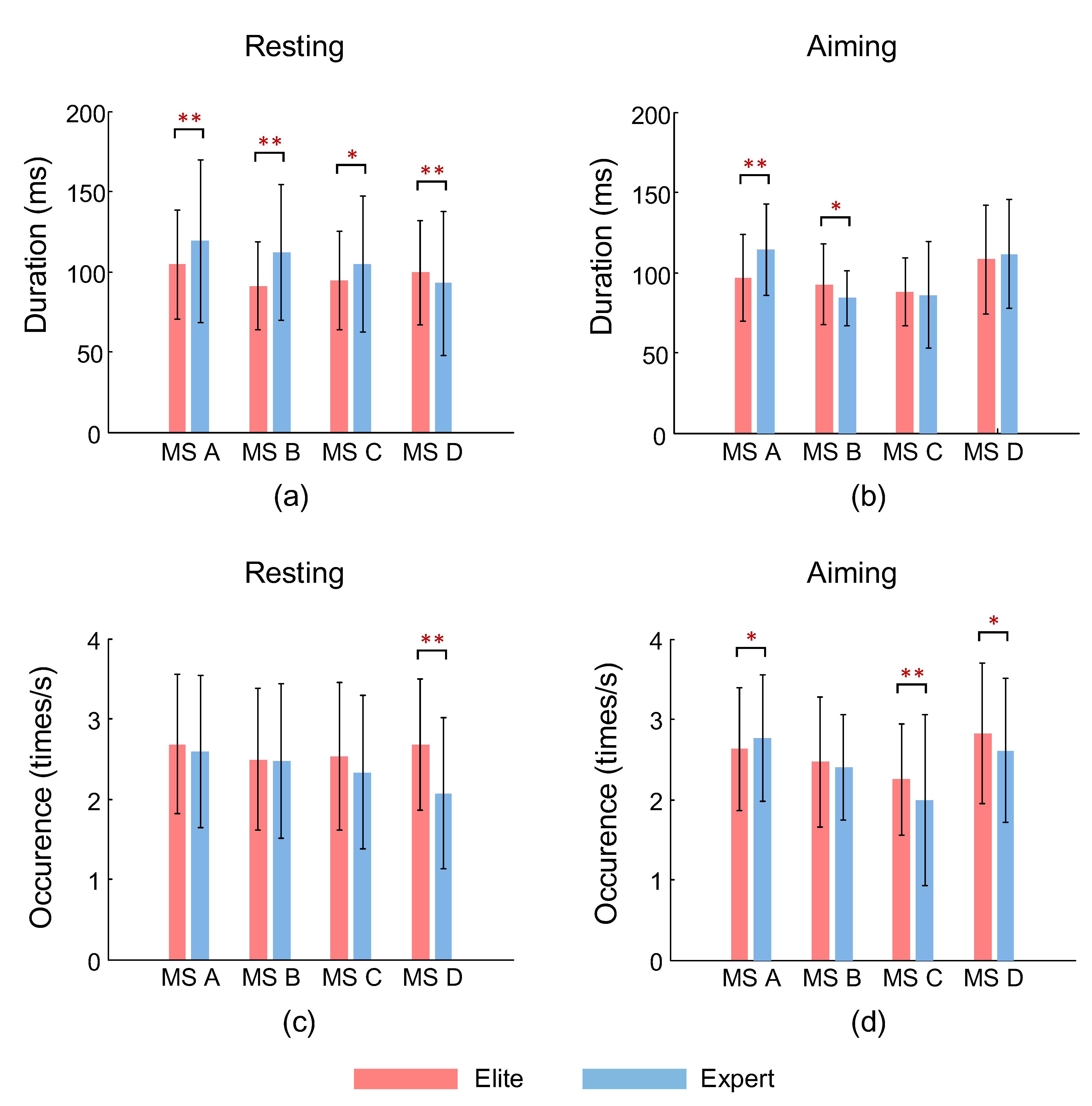
3.1. Microstate Duration
3.2. Occurrence of Microstates
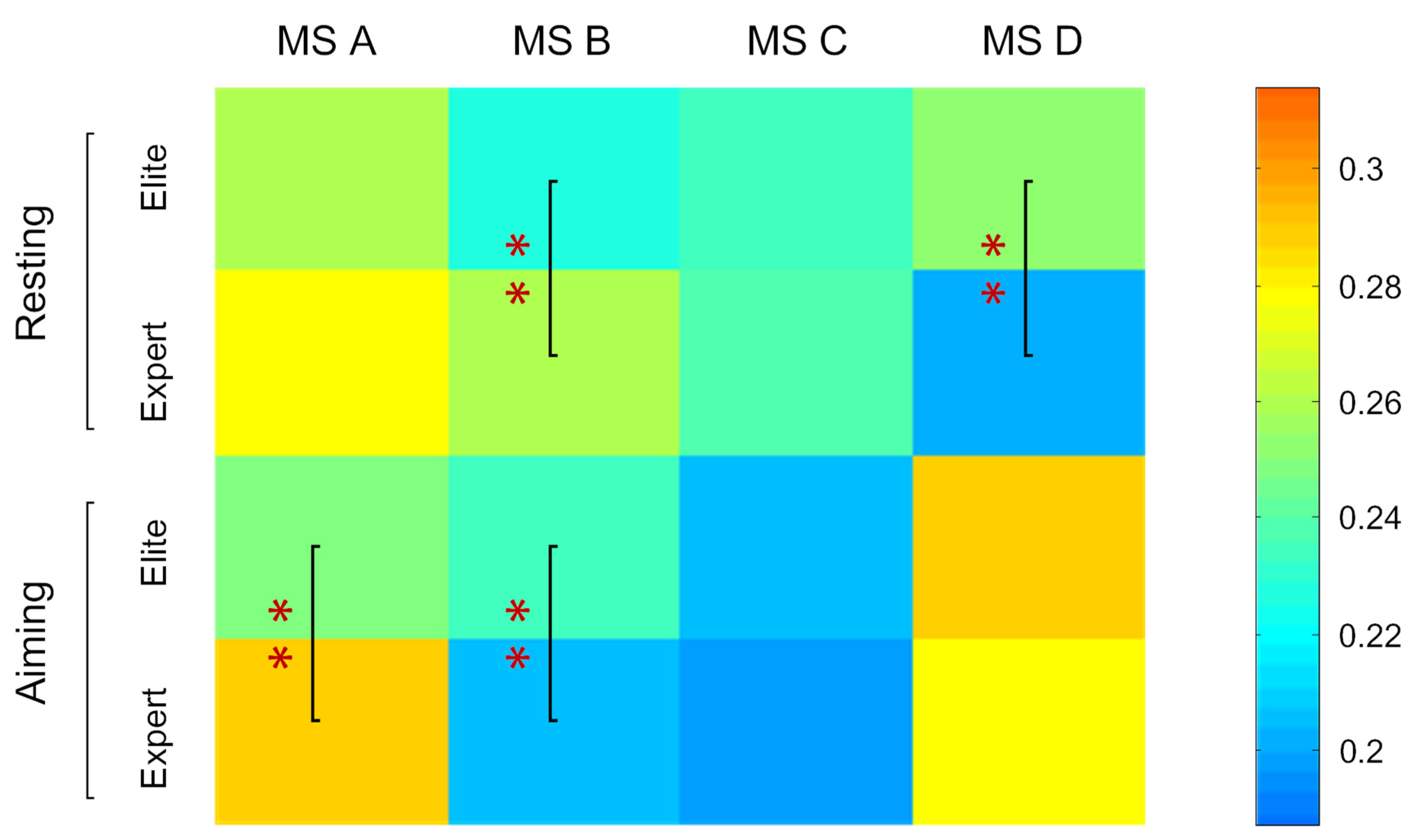
3.3. Coverage of Microstates in Total Time
3.4. Transition Probability between Different Microstates
3.5. Correlation between Microstate Parameters and Archery Performance
3.6. Source Localization of Microstates
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstate Analysis of Elite and Expert Archers in Resting State
4.2. Microstate Analysis of Elite and Expert Archers during Aiming
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ertan, H.; Soylu, A.R.; Korkusuz, F. Quantification the relationship between FITA scores and EMG skill indexes in archery. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2005, 15, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Èižmek, A.; Peršun, J. Exercise for development of specific coordination, balance and precision in archery. (Vježbe za razvoj specifiène koordinacije, ravnoteže i preciznosti u strelièarstvu.) U: Jukiæ i sur. ur. In Proceedings of the 9th Anual International Conference Conditioning of Athletes; Faculty of Kinesiology, University of Zagreb and Association of Conditioning Coaches of Croatia: Zagreb, Croatia,, 2011; pp. 412–414. [Google Scholar]
- Vrbik, A.; Bene, R.; Vrbik, I. Heart rate values and levels of attention and relaxation in expert archers during shooting. Hrvat. Športskomedicinski Vjesn. 2015, 30, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Caterini, R.; Delhomme, G.; Dittmar, A.; Economides, S.; Vernet-Maury, E. A model of sporting performance constructed from autonomic nervous system responses. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 67, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K. Total Archery; Samick Sports Company: Eumseong-gun, Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros Filho, E.S.; Moraes, L.C.; Tenenbaum, G. Affective and physiological states during archery competitions: Adopting and enhancing the probabilistic methodology of individual affect-related performance zones (IAPZs). J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2008, 20, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, T.E.; Lindsen, J.P.; de Jong, R. Pre-stimulus EEG effects related to response speed, task switching and upcoming response hand. Biol. Psychol. 2006, 72, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañal-Bruland, R.; van der Kamp, J.; Arkesteijn, M.; Janssen, R.G.; van Kesteren, J.; Savelsbergh, G.J. Visual search behaviour in skilled field-hockey goalkeepers. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2010, 41, 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, W.; Landers, D.M.; Petruzzello, S.J.; Han, M.; Crews, D.J.; Kubitzk, A. Hemispheric asymmetry, cardiac response, and performance in elite archers. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1999, 61, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, D.M.; Petruzzello, S.J.; Salazar, W.; Crewsd., J.; Kubitz, K.A.; Gannon, T.L.; Han, M. The influence of electrocortical biofeedback on performance in pre-elite archers. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 1991, 23, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H. Evaluation of attention and relaxation levels of archers in shooting process using brain wave signal analysis algorithms. Sci. Emot. Sensib. 2009, 12, 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, M.; Ganesan, S.; Sandhu, J.S. Effect of sensory motor rhythm neurofeedback on psycho-physiological, electro-encephalographic measures and performance of archery players. Ibnosina J. Med. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, C.R.; Villalobos, M.E.; Schultz, R.T.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Konrad, K.; Kohls, G. Atypical laterality of resting gamma oscillations in autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Li, H.; Yu, D. The relationship between ERP components and EEG spatial complexity in a visual Go/Nogo task. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, H.; Yu, D. The influence of vertical disparity gradient and cue conflict on EEG omega complexity in Panum’s limiting case. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 119, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, Z. EEG Signal Processing and Feature Extraction; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Michel, C.M.; Farzan, F. Microstates in resting-state EEG: Current status and future directions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D. Brain Electric Fields and Brain Functional States. Evolution of Dynamical Structures in Complex Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, D.; Skrandies, W. Reference-free identification of components of checkerboard-evoked multichannel potential fields. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1980, 48, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Strik, W.K.; Henggeler, B.; Koeniga, T.; Koukkouc, M. Brain electric microstates and momentary conscious mind states as building blocks of spontaneous thinking: I. Visual imagery and abstract thoughts. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1998, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, J.; Michel, C.M. Errors can be related to pre-stimulus differences in ERP topography and their concomitant sources. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 2774–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. Neuroimage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomescu, M.I.; Rihs, T.A.; Roinishvili, M.; Karahanoglu, F.I.; Schneider, S.; Menghetti, S.; De Ville, D.V.; Brand, A.; Chkonia, E.; Eliez, S.; et al. Schizophrenia patients and 22q11. 2 deletion syndrome adolescents at risk express the same deviant patterns of resting state EEG microstates: A candidate endophenotype of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2015, 2, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Koenig, T.; Wada, Y.; Higashima, M.; Koshino, Y.; Strik, W.; Dierks, T. Native EEG and treatment effects in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenic patients: Time and frequency domain approaches. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 97, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandeis, D.; Lehmann, D. Segments of event-related potential map series reveal landscape changes with visual attention and subjective contours. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 73, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, J.; Atienza, M.; Salas, R.; Gómez, C. Brain spatial microstates of human spontaneous alpha activity in relaxed wakefulness, drowsiness period, and REM sleep. Brain Topogr. 1999, 11, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodbeck, V.; Kuhn, A.; von Wegner, F.; Morzelewski, A.; Tagliazucchi, E.; Borisov, S.; Michel, C.M.; Laufs, H. EEG microstates of wakefulness and NREM sleep. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuraisingham, R.A.; Tran, Y.; Craig, A.; Wijesuriya, N.; Nguyen, H. Using microstate intensity for the analysis of spontaneous EEG: Tracking changes from alert to the fatigue state. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 4982–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, F.; Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.L.; Milz, P.; Gianotti, L.R. EEG microstates during resting represent personality differences. Brain Topogr. 2012, 25, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzagalli, D.; Lehmann, D.; Koenig, T.; Regard, M.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Face-elicited ERPs and affective attitude: Brain electric microstate and tomography analyses. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Thut, G.; Morand, S.; Khateb, A.; Pegna, A.J.; de Peralta, R.G.; Gonzalez, S.; Seeck, M.; Landis, T. Electric source imaging of human brain functions. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 36, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzman, B.A.; Abell, M.; Bartley, S.C.; Erickson, M.A.; Bolbecker, A.R.; Hetrick, W.P. Cognitive manipulation of brain electric microstates. Neuroimage 2017, 146, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Sun, S.; Huang, Z. Exploring differences for motor imagery using Teager energy operator-based EEG microstate analyses. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Long, Q.; Li, Q.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, A.; Huo, R. The modulation of salience and central executive networks by acute stress in healthy males: An EEG microstates study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 169, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsodyks, M.; Kenet, T.; Grinvald, A.; Karahanoglu, F.I.; Schneider, M.; Menghetti, S.; De Ville, D.V.; Brand, A. Linking spontaneous activity of single cortical neurons and the underlying functional architecture. Science 1999, 286, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, D.A.; Murayama, Y.; Logothetis, N.K. Very slow activity fluctuations in monkey visual cortex: Implications for functional brain imaging. Cereb. Cortex 2003, 13, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, C.; Marzano, N.; Iacoboni, M.; Infarinato, F.; Aschieri, P.; Buffo, P.; Cibelli, G.; Soricelli, A.; Eusebi, F.; Del Percio, C. Resting state cortical rhythms in athletes: A high-resolution EEG study. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Percio, C.; Infarinato, F.; Marzano, N.; Iacoboni, M.; Aschieri, P.; Lizio, R.; Soricelli, A.; Limatola, C.; Rossini, P.M.; Babiloni, C. Reactivity of alpha rhythms to eyes opening is lower in athletes than non-athletes: A high-resolution EEG study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 82, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, L.; Wu, G.; Jiang, C.; Fu, Y. Characteristic differences between the brain networks of high-level shooting athletes and non-athletes calculated using the phase-locking value algorithm. Biomed. Sign. Process. Control 2019, 51, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarin, V.; Morović, S. Neuroplasticity. Period. Biol. 2014, 116, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y. Reorganization and plastic changes of the human brain associated with skill learning and expertise. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, H.; Sandbakk, Ø.; Schubert, M.; Ettema, G.; Baumeiste, J. A comparison of frontal theta activity during shooting among biathletes and cross-country skiers before and after vigorous exercise. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, W. Research and Application of Competitive Sports Psychological Control; People’s Sports Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 110–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, D.; Ozaki, H.; Pal, I. EEG alpha map series: Brain micro-states by space-oriented Adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 67, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wegner, F.; Bauer, S.; Rosenow, F.; Triesch, J.; Laufs, H. EEG microstate periodicity explained by rotating phase patterns of resting-state alpha oscillations. Neuroimage 2021, 224, 117372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milz, P.; Faber, P.L.; Lehmann, D.; Koenig, T.; Kochi, K.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D. The functional significance of EEG microstates—Associations with modalities of thinking. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufler, A.J.; Spalding, T.W.; Santa Maria, D.L.; Hatfield, B.D. Neuro-cognitive activity during a self-paced visuospatial task: Comparative EEG profiles in marksmen and novice shooters. Biol. Psychol. 2000, 53, 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loze, G.M.; Collins, D.; Holems, P.S. Pre-shot EEG alpha-power reactivity during expert air-pistol shooting: A comparison of best and worst shots. J. Sport Sci. 2001, 19, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bréchet, L.; Brunet, D.; Perogamvros, L.; Tononi, G.; Michel, C.M. EEG microstates of dreams. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zou, G.; Liu, J.; Su, Z.; Zou, Q.; Gao, J.H. EEG microstates are correlated with brain functional networks during slow-wave sleep. Neuroimage 2020, 215, 116786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáčková, D.; Pánek, D.; Pavlů, D. Options for studying human motion: Neurophysiological program sLORETA. Auc Kinanthropol. 2019, 55, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paszkiel, S. Using the LORETA Method for Localization of the EEG Signal Sources in BCI Technology. In Analysis and Classification of EEG Signals for Brain–Computer Interfaces; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cevada, T.; Moreira, A.; Vilete, L.M.P.; Oertel-Knöchel, V.; Deslandes, A.C. Resilience, Psychological Characteristics, and Resting-state Brain Cortical Activity in Athletes and Non-athletes. Open Sports Sci. J. 2020, 13, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, H.; Wei, W.; Wang, G.; Du, Y.; Ruan, J. Altered peri-seizure EEG microstate dynamics in patients with absence epilepsy. Seizure 2021, 88, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Chang, Y.; Kim, J.; Seo, J.; Ryu, K.; Lee, E.; Woo, M.; Janelle, C.M. An fMRI study of differences in brain activity among elite, expert, and novice archers at the moment of optimal aiming. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2014, 27, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Michel, C.M.; Lehmann, D. Segmentation of brain electrical activity into microstates: Model estimation and validation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Prichep, L.; Lehmann, D.; Sosa, P.V.; Braeker, E.; Kleinlogel, H.; Isenhart, R.; John, E.R. Millisecond by millisecond, year by year: Normative EEG microstates and developmental stages. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R.; Walther, G. Cluster Validation by Prediction Strength. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2005, 14, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.M.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Topographic ERP analyses: A step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr. 2008, 20, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, A.T.; Pedroni, A.; Langer, N.; Hansen, L.K. Microstate EEGlab toolbox: An introductory guide. BioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenney, J.R.; Kadis, D.S.; Agler, W.; Rozhkov, L.; Altaye, M.; Xiang, J.; Vannest, J.; Glauser, T.A. Ictal connectivity in childhood absence epilepsy: Associations with outcome. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysoeva, M.V.; Vinogradova, L.V.; Kuznetsova, G.D.; Sysoev, I.V.; van Rijn, C.M. Changes in corticocortical and corticohippocampal network during absence seizures in WAG/Rij rats revealed with time varying Granger causality. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 64, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Daniel, B. Inappropriate assumptions about EEG state changes and their impact on the quantification of EEG state dynamics. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xu, Y.; Bian, C.; Li, M. Semantic congruent audiovisual integration during the encoding stage of working memory: An ERP and sLORETA study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5112–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, J.; Toga, A.; Evans, A.; Fox, P.; Lancaster, J.; Zilles, K.; Woods, R.; Paus, T. A four-dimensional probabilistic atlas of the human brain. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2001, 8, 401–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): Technical details. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E.T. Network-based statistic: Identifying differences in brain networks. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.D.; Cohen, A.L.; Nelson, S.M.; Wig, G.S.; Barnes, K.A.; Church, J.A.; Vogel, A.C. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron 2011, 72, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzbani, H.; Marateb, H.; Mansourian, M. Methodological note: Neurofeedback: A comprehensive review on system design, methodology and clinical applications. Basic Clin. Neurosci. J. 2016, 7, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chang, T.; Park, I. Visual scanning behavior and attention strategies for shooting among expert versus collegiate Korean archers. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2019, 126, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Liu, J.D.; Zhang, C.; Si, G.; Chung, P.K. Mindfulness training improves relaxation and attention in elite shooting athletes A single-case study. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2019, 50, 4–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Li, P.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y. Efficiency and Enhancement in Attention Networks of Elite Shooting and Archery Athletes. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossel, S.; Geng, J.J.; Fink, G.R. Dorsal and ventral attention systems: Distinct neural circuits but collaborative roles. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, T.; O’Sullivan, B.T.; Roland, P.E. Bilateral activation of fronto-parietal networks by incrementing demand in a working memory task. Cereb. Cortex 1997, 7, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantini, D.; Perrucci, M.G.; Del Gratta, C.; Romani, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13170–13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.J. Frontal-to-parietal top-down causal streams along the dorsal attention network exclusively mediate voluntary orienting of attention. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, S.; Dosenbach, N.U.F. The frontoparietal network: Function, electrophysiology, and importance of individual precision mapping. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.E.; Posner, M.I. The attention system of the human brain: 20 years after. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, M.I.; Petersen, S.E. The attention system of the human brain. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1990, 13, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Freudenthaler, H.H.; Pfurtscheller, G. Intelligence and spatiotemporal patterns of event-related desynchronization (ERD). Intelligence 1995, 20, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, C.; Cassetta, E.; Binetti, G.; Tombini, M.; Del Percio, C.; Ferreri, F.; Ferri, R.; Frisoni, G.; Lanuzza, B.; Nobili, F.; et al. Resting EEG sources correlate with attentional span in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 3742–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichle, M.E. The brain’s default mode network. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 38, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, L.A.; Haverkort, M.; Zwarts, F. Rethinking the neurological basis of language. Lingua 2005, 115, 997–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, A.; Bernal, B.; Rosselli, M. Language and visual perception associations: Meta-analytic connectivity modeling of Brodmann area 37. Behav. Neurol. 2015, 14, 565871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauseng, P.; Klimesch, W.; Stadler, W.; Schabus, M.; Doppelmayr, M.; Hanslmayr, S.; Gruber, W.R.; Birbaumer, N. A shift of visual spatial attention is selectively associated with human EEG alpha activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschman, T.J.; Miller, E.K. Top-down versus bottom-up control of attention in the prefrontal and posterior parietal cortices. Science 2007, 315, 1860–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanto, T.P.; Rubens, M.T.; Bollinger, J.; Gazzaley, A. Top-down modulation of visual feature processing: The role of the inferior frontal junction. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Elite | Expert | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject | Age | Sex | Training Years | Archery Performance | Subject | Age | Sex | Training Years | Archery Performance |
| Elite1 | 28 | Male | 6.0 | 8.9 | Expert1 | 25 | Male | 3.0 | 7.0 |
| Elite2 | 24 | Male | 11.0 | 8.3 | Expert2 | 22 | Female | 6.0 | 7.0 |
| Elite3 | 22 | Female | 8.0 | 7.7 | Expert3 | 24 | Male | 4.0 | 7.4 |
| Elite4 | 22 | Male | 8.0 | 8.7 | Expert4 | 21 | Male | 6.0 | 7.3 |
| Elite5 | 20 | Female | 6.0 | 8.8 | Expert5 | 26 | Female | 4.0 | 7.5 |
| Elite6 | 23 | Male | 9.0 | 9.1 | Expert6 | 23 | Male | 4.0 | 8.2 |
| Elite7 | 22 | Female | 6.0 | 8.8 | Expert7 | 26 | Female | 8.0 | 6.7 |
| Elite8 | 26 | Male | 12.0 | 9.2 | Expert8 | 24 | Male | 4.0 | 5.2 |
| Elite9 | 26 | Female | 10.0 | 8.8 | Expert9 | 23 | Female | 5.0 | 7.2 |
| Elite10 | 23 | Male | 10.0 | 9.2 | Expert10 | 22 | Female | 4.0 | 7.0 |
| Elite11 | 23 | Male | 9.0 | 8.3 | Expert11 | 22 | Male | 5.0 | 2.4 |
| Elite12 | 24 | Female | 7.0 | 9.4 | Expert12 | 20 | Female | 2.0 | 7.5 |
| Elite13 | 22 | Female | 5.0 | 8.0 | Expert13 | 19 | Male | 3.0 | 7.8 |
| Elite14 | 18 | Male | 7.0 | 9.0 | Expert14 | 25 | Male | 4.0 | 8.1 |
| Elite15 | 23 | Male | 8.0 | 9.3 | Expert15 | 23 | Male | 3.0 | 6.2 |
| Elite16 | 22 | Male | 7.0 | 7.7 | |||||
| Elite | p-Values Corrected by FDR | Expert | p-Values Corrected by FDR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resting Mean ± SD | Aiming Mean ± SD | Resting Mean ± SD | Aiming Mean ± SD | |||
| Duration (ms) | ||||||
| MS A | 104.70 ± 34.01 | 95.77 ± 37.3 | *↘ | 119.06 ± 50.59 | 114.09 ± 28.37 | — |
| MS B | 91.17 ±27.50 | 92.65 ± 24.99 | — | 112.15 ± 40.85 | 84.03 ± 17.06 | **↘ |
| MS C | 94.76 ± 30.58 | 88.63 ± 20.895 | — | 104.66 ± 42.44 | 85.88 ± 33.11 | **↘ |
| MS D | 99.43 ± 32.24 | 108.43 ± 33.98 | **↗ | 92.87 ± 44.90 | 111.51 ± 33.97 | **↗ |
| Occurrence (times/s) | ||||||
| MS A | 2.69 ± 0.86 | 2.63 ± 0.76 | — | 2.59 ± 0.94 | 2.76 ± 0.78 | *↗ |
| MS B | 2.50 ± 0.88 | 2.47 ± 0.81 | — | 2.48 ± 0.97 | 2.40 ± 0.66 | — |
| MS C | 2.53 ± 0.91 | 2.25 ± 0.70 | **↘ | 2.33 ± 0.96 | 1.99 ± 1.06 | **↘ |
| MS D | 2.68 ± 0.82 | 2.83 ± 0.88 | *↗ | 2.07 ± 0.94 | 2.61 ± 0.90 | *↗ |
| Coverage (%) | ||||||
| MS A | 27.49 ± 11.78 | 25.32 ± 12.14 | *↘ | 29.61 ± 13.53 | 31.41 ± 11.73 | — |
| MS B | 22.67 ±11.09 | 23.73 ± 12.92 | — | 27.14 ± 13.30 | 19.93 ± 7.63 | **↘ |
| MS C | 23.83 ± 11.74 | 19.83 ± 8.33 | **↘ | 24.01 ± 12.77 | 18.75 ± 14.83 | **↘ |
| MS D | 26.01 ± 10 28 | 31.12 ± 15.18 | **↗ | 19.24 ± 12.56 | 29.91 ± 14.03 | **↗ |
| Resting | Aiming | p-Values Corrected by FDR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microstate Transition | Elie (%) Mean ± SD | Expert (%) Mean ± SD | Elite (%) Mean ± SD | Expert (%) Mean ± SD | Elite vs. Expert | Resting vs. Aiming | ||||
| Resting | Aiming | Elite | Expert | |||||||
| A → B | 8.66 ± 4.11 | 7.85 ± 4.77 | 7.63 ± 3.30 | 9.53 ± 3.51 | 0.089 | ∗∗ | 0.019 ∗ | ↘ | ** | ↗ |
| A → C | 8.17 ± 3.73 | 9.56 ± 5.52 | 6.99 ± 2.56 | 7.26 ± 3.39 | 0.054 | 0.931 | 0.014 ∗ | ↘ | ∗∗ | ↘ |
| A → D | 7.64 ± 4.91 | 8.21 ± 4.27 | 10.51 ± 3.19 | 10.70 ± 5.68 | 0.553 | 0.985 | ∗∗ | ↗ | ∗∗ | ↗ |
| B → A | 7.89 ± 3.64 | 8.28 ± 4.57 | 8.21 ± 3.79 | 9.36 ± 3.34 | 0.779 | 0.006 ∗ | 0.919 | — | 0.021 ∗ | ↗ |
| B → C | 6.46 ± 3.46 | 8.29 ± 4.33 | 6.83 ± 3.05 | 5.86 ± 3.33 | ∗∗ | 0.007 ∗ | 0.333 | — | ∗∗ | ↘ |
| B → D | 8.48 ± 3.55 | 7.86 ± 4.75 | 8.38 ± 2.72 | 8.83 ± 3.44 | 0.235 | 0.512 | 0.962 | — | 0.017 ∗ | ↗ |
| C → A | 8.37 ± 3.75 | 9.66 ± 4.97 | 6.88 ± 2.61 | 6.59 ± 3.50 | 0.054 | 0.484 | ∗∗ | ↘ | ∗∗ | ↘ |
| C → B | 6.25 ± 2.85 | 8.68 ± 5.11 | 6.70 ± 3.09 | 6.10 ± 3.95 | ∗∗ | 0.053 | 0.333 | — | ∗∗ | ↘ |
| C → D | 8.45 ± 4.11 | 4.80 ± 3.30 | 7.82 ± 3.92 | 6.31 ± 2.77 | ∗∗ | 0.002 ∗ | 0.333 | — | ∗∗ | ↗ |
| D → A | 7.90 ± 3.94 | 7.57 ± 4.48 | 9.76 ± 3.49 | 11.38 ± 4.89 | 0.625 | 0.006 ∗ | ∗∗ | ↗ | ∗∗ | ↗ |
| D → B | 7.87 ± 3.71 | 7.95 ± 4.70 | 9.26 ± 3.02 | 8.22 ± 3.47 | 0.986 | 0.016 ∗ | 0.001 ∗ | ↗ | 0.380 | — |
| D → C | 8.72 ± 4.50 | 5.53 ± 3.58 | 7.59 ± 3.85 | 6.27 ± 2.86 | ∗∗ | 0.004 ∗ | 0.046 ∗ | ↘ | 0.039 ∗ | ↗ |
| Microstate Parameter | Correlation Indicator | MS A | MS B | MS C | MS D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elite | Duration | r | 0.299 | −0.124 | −0.798 ∗ | 0.250 |
| p | 0.319 | 0.687 | 0.001 | 0.409 | ||
| Occurrence | r | 0.294 | 0.217 | −0.542 | 0.327 | |
| p | 0.329 | 0.476 | 0.056 | 0.275 | ||
| Coverage | r | 0.314 | 0.066 | −0.726 ∗ | 0.261 | |
| p | 0.297 | 0.830 | 0.005 | 0.388 | ||
| Expert | Duration | r | 0.135 | −0.058 | −0.182 | 0.028 |
| p | 0.661 | 0.851 | 0.553 | 0.929 | ||
| Occurrence | r | 0.300 | 0.072 | 0.085 | 0.030 | |
| p | 0.320 | 0.816 | 0.782 | 0.922 | ||
| Coverage | r | 0.283 | −0.038 | −0.094 | 0.113 | |
| p | 0.348 | 0.908 | 0.761 | 0.714 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, F.; Gong, A.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Wu, J.; Nan, W.; Jiang, C.; Fu, Y. Research on Top Archer’s EEG Microstates and Source Analysis in Different States. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081017
Gu F, Gong A, Qu Y, Xiao H, Wu J, Nan W, Jiang C, Fu Y. Research on Top Archer’s EEG Microstates and Source Analysis in Different States. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(8):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081017
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Feng, Anmin Gong, Yi Qu, Hui Xiao, Jin Wu, Wenya Nan, Changhao Jiang, and Yunfa Fu. 2022. "Research on Top Archer’s EEG Microstates and Source Analysis in Different States" Brain Sciences 12, no. 8: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081017
APA StyleGu, F., Gong, A., Qu, Y., Xiao, H., Wu, J., Nan, W., Jiang, C., & Fu, Y. (2022). Research on Top Archer’s EEG Microstates and Source Analysis in Different States. Brain Sciences, 12(8), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081017





