Itaconate Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Exerts Dopamine Neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal and PD Model Establishment
2.2. Behavioral Test
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.4. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.5. Cell Apoptosis
2.6. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP-Biotin Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) Staining
2.7. Intercellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection
2.8. Detection of Oxidative Stress-Related Factors
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.10. Western Blotting Analysis
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
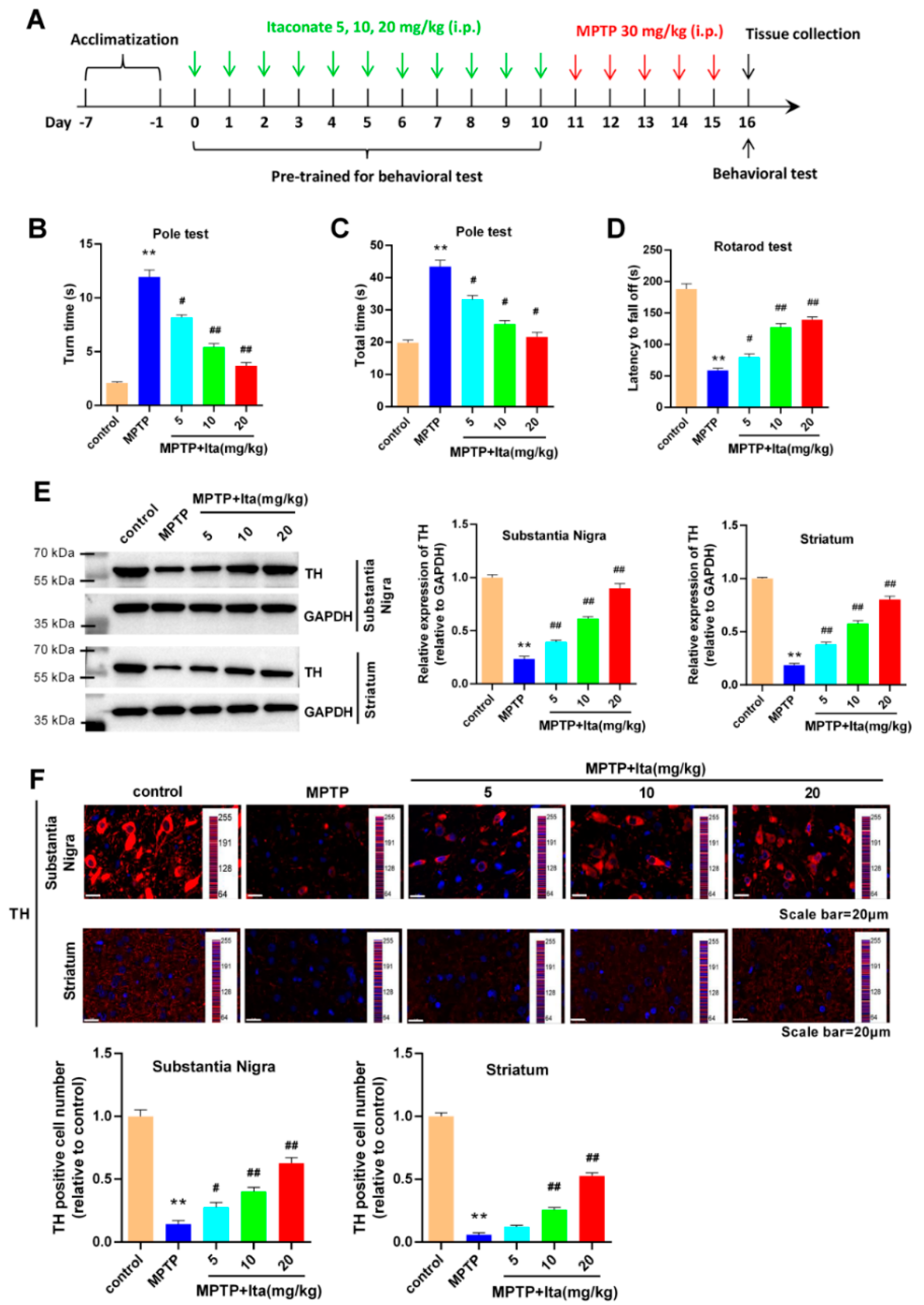
3.1. Itaconate Attenuated Motor Deficits and Dopamine Neuronal Damage in MPTP-Induced PD Mice
3.2. Itaconate Attenuated Microglia Activation and Inflammatary Response in MPTP-Caused PD Mice
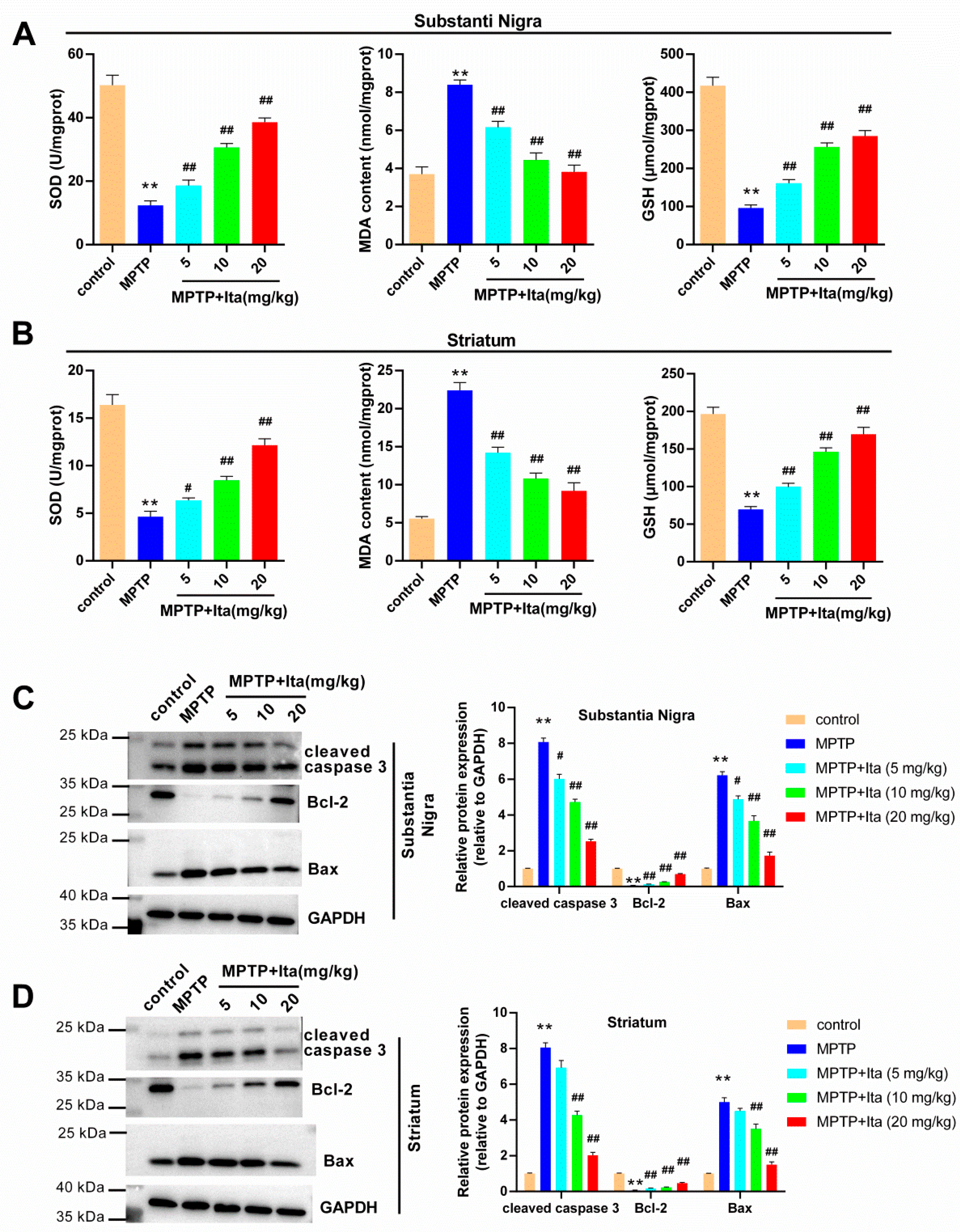
3.3. Itaconate Attenuated Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in MPTP-Induced PD Mice
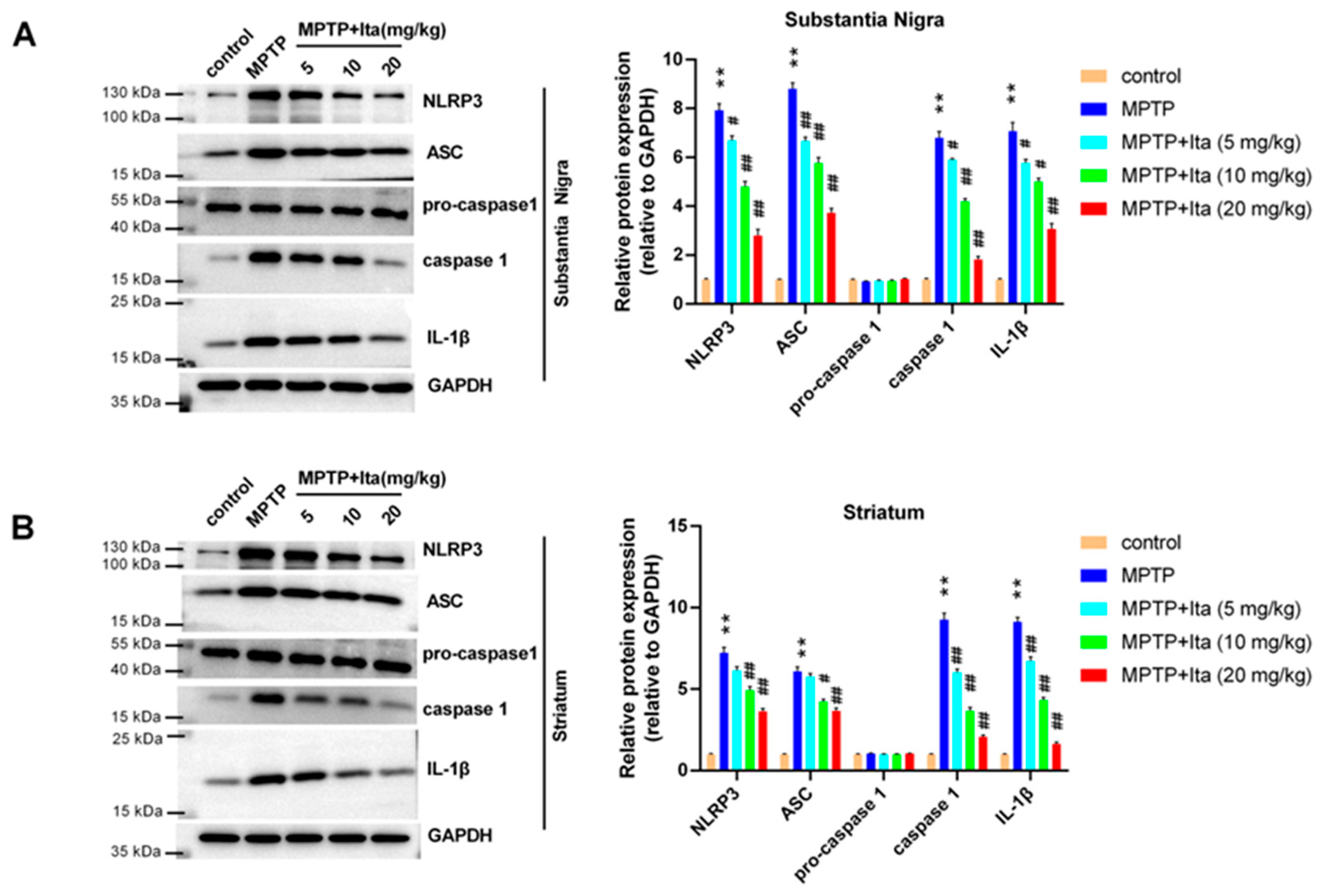
3.4. Itaconate Repressed NLRP3 Inflammasome in MPTP-Caused PD Mice
3.5. Itaconate Attenuated MPP+-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells Apoptosis
3.6. Itaconate Attenuated Dopamine Neuronal Damage in MPP+-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells
3.7. Itaconate Attenuated Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in MPP+-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells
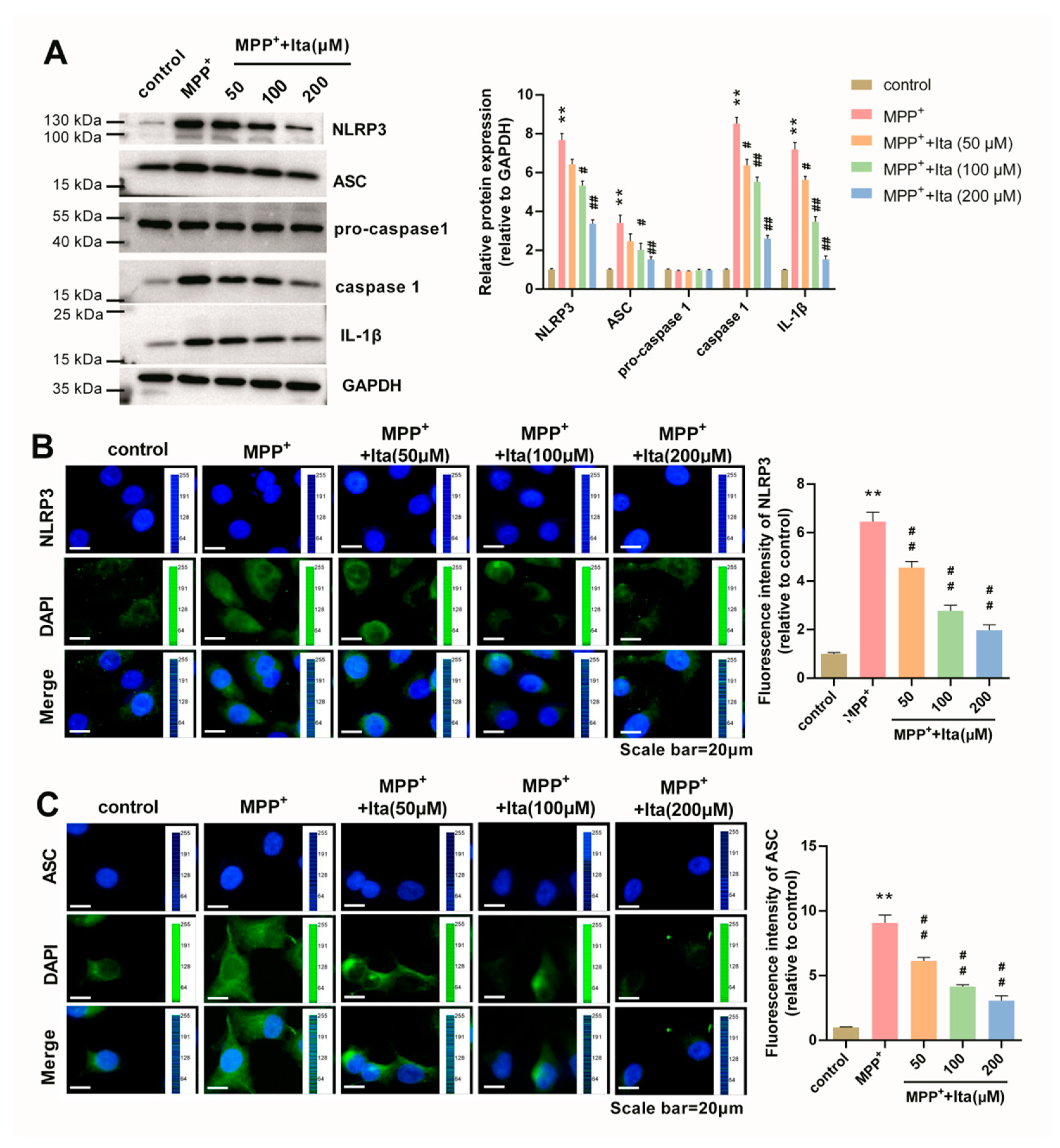
3.8. Itaconate Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome in MPP+-Caused SH-SY5Y Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Trist, B.G.; Hare, D.J.; Double, K.L. Oxidative stress in the aging substantia nigra and the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, J.; Cui, S.; He, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. Parkinson’s disease in China: A forty-year growing track of bedside work. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansey, M.G.; McCoy, M.K.; Frank-Cannon, T.C. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: Potential environmental triggers, pathways, and targets for early therapeutic intervention. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 208, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlDakheel, A.; Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Pathogenesis-targeted, disease-modifying therapies in Parkinson disease. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTherapeutics 2014, 11, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Bambouskova, M.; Nair, S.; Vincent, E.E.; Loginicheva, E.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, S.C.; Griss, T.; et al. Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, T.; Lucas, A.; Divakaruni, A.S.; Murphy, A.N.; Cabrales, P.; Metallo, C.M. Itaconate modulates tricarboxylic acid and redox metabolism to mitigate reperfusion injury. Mol. Metab. 2020, 32, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Di, G. Four-octyl itaconate activates Keap1-Nrf2 signaling to protect neuronal cells from hydrogen peroxide. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2018, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lu, D.L.; Chen, B.Q.; Liu, T.Y.; Wang, Z.X. Dimethyl Itaconate Reduces Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation in APPswe/PS1ΔE9 Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. NeuroMolecular Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Kim, J.K.; Silwal, P. An update on the regulatory mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1141–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, X.C.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.L.; Jiang, W.; Tan, L. NLRP3 polymorphisms are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in Han Chinese. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 265, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, J.A.; Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Caseley, E.; Lara-Reyna, S.; Poulter, J.A.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; Peckham, D.; McDermott, M.F. Neurodegenerative Disease and the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, R.; Zheng, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Xie, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.T.; Xu, J.; Jin, D.; et al. Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide Rescues Dopaminergic Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease Models by Inhibiting the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Ameliorating Mitochondrial Impairment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 794770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wei, X.; Jian, W.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, F.; Lou, H.; Zhang, B. Pharmacological Inhibition of HDAC6 Attenuates NLRP3 Inflammatory Response and Protects Dopaminergic Neurons in Experimental Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, C.G.; O’Neill, L.A. The role of itaconate in host defense and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e148548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooftman, A.; Angiari, S.; Hester, S.; Corcoran, S.E.; Runtsch, M.C.; Ling, C.; Ruzek, M.C.; Slivka, P.F.; McGettrick, A.F.; Banahan, K.; et al. The Immunomodulatory Metabolite Itaconate Modifies NLRP3 and Inhibits Inflammasome Activation. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 468–478.e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Shi, C.; Lv, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Jiang, L. SGLT2 inhibitor counteracts NLRP3 inflammasome via tubular metabolite itaconate in fibrosis kidney. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Liu, W.; Gao, J.; Jiang, C.; Fan, T.; Sun, Y. Andrographolide alleviates Parkinsonism in MPTP-PD mice via targeting mitochondrial fission mediated by dynamin-related protein 1. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 176, 4574–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.M.; Aller, M.I.; Leppä, E.; Rosenberg, P.H.; Wisden, W.; Korpi, E.R. K+ channel TASK-1 knockout mice show enhanced sensitivities to ataxic and hypnotic effects of GABA(A) receptor ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, K.; Sun, C. Thioredoxin-1 mediates neuroprotection of Schisanhenol against MPP(+)-induced apoptosis via suppression of ASK1-P38-NF-κB pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagetta, V.; Picconi, B.; Marinucci, S.; Sgobio, C.; Pendolino, V.; Ghiglieri, V.; Fusco, F.R.; Giampà, C.; Calabresi, P. Dopamine-dependent long-term depression is expressed in striatal spiny neurons of both direct and indirect pathways: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 12513–12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.; Jenner, P. Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, J. Significant roles of neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Therapeutic targets for PD prevention. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2019, 42, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Leem, Y.H.; Park, J.E.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, H.S. Neuroprotective Effect of β-Lapachone in MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model: Involvement of Astroglial p-AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Duan, J.; Ma, S.; Yin, Y.; Quan, W.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of protocatechuic aldehyde through PLK2/p-GSK3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway in both in vivo and in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease. Aging 2019, 11, 9424–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Costa, C.; Eixarch, H.; Keller, C.W.; Amman, L.; Martínez-Banaclocha, H.; Midaglia, L.; Sarró, E.; Machín-Díaz, I.; Villar, L.M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome as prognostic factor and therapeutic target in primary progressive multiple sclerosis patients. Brain 2020, 143, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, K.; AlHarthi, H.; Alghamdi, A.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Obesity-Mediated Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Meng, X.; Luo, X.Y.; Li, X.M.; Shuai, Z.W.; Ye, D.Q.; Pan, H.F. NLRP3: A promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.R.; Wang, M.; Jia, Y.Y.; Tian, D.D.; Liu, A.; Wang, W.J.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, R.; et al. Echinacoside protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 164, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, Q.; Hou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X. Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome by glibenclamide attenuated dopaminergic neurodegeneration and motor deficits in paraquat and maneb-induced mouse Parkinson’s disease model. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 349, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, P.; Cai, Y. Genkwanin suppresses MPP(+)-induced cytotoxicity by inhibiting TLR4/MyD88/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 2021, 87, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse IL-6 | 5′-TCTTGGGACTGATGCTGGTG-3′ | 5′-TTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTTTC-3′ |
| Mouse TNF-α | 5′-ACTGAACTTCGGGGTGATCG-3′ | 5′-CCACTTGGTGGTTTGTGAGT-3′ |
| Mouse COX-2 | 5′-GCTCAGCCAGGCAGCAAATC-3′ | 5′-CACCATAGAATCCAGTCCGGG-3′ |
| Mouse iNOS | 5′-CTCTAGTGAAGCAAAGCCCAACA-3′ | 5′-CACATACTGTGGACGGGTCG-3′ |
| Mouse β-actin | 5′-CACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCCA-3′ | 5′-CATCCATGGCGAACTGGTGG-3′ |
| Human IL-6 | 5′-ACTCCTTCTCCACAAGCGCC-3′ | 5′-TCTTCTCCTGGGGGTACTGG-3′ |
| Human TNF-α | 5′-CCCATGTTGTAGCAAACCCT-3′ | 5′-GAGGTACAGGCCCTCTGATG-3′ |
| Human COX-2 | 5′-CGCTCAGCCATACAGCAAAT-3′ | 5′-GTCCGGGTACAATCGCACTT-3′ |
| Human iNOS | 5′-GGAGACGGGAAAGAAGTCTCC-3′ | 5′-ACCCCAGGCAAGATTTGGAC-3′ |
| Human β-actin | 5′-GATTCCTATGTGGGCGACGA-3′ | 5′-AGGTCTCAAACATGATCTGGGT-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, G.; Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Meng, W.; Pang, Q. Itaconate Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Exerts Dopamine Neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091255
Sun G, Zhang R, Liu C, Meng W, Pang Q. Itaconate Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Exerts Dopamine Neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(9):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091255
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Guoqing, Rui Zhang, Chengxiao Liu, Wenjun Meng, and Qi Pang. 2022. "Itaconate Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Exerts Dopamine Neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome" Brain Sciences 12, no. 9: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091255
APA StyleSun, G., Zhang, R., Liu, C., Meng, W., & Pang, Q. (2022). Itaconate Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Exerts Dopamine Neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome. Brain Sciences, 12(9), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091255






