Does Executive Function Training Impact on Communication? A Randomized Controlled tDCS Study on Post-Stroke Aphasia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Ethics Statement
2.4. Clinical Data
2.5. Materials
2.6. Procedure
2.6.1. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
2.6.2. Cognitive Treatments
2.6.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Data
3.1.1. Alertness
3.1.2. Selective Attention
3.1.3. Visuo-Spatial Working Memory
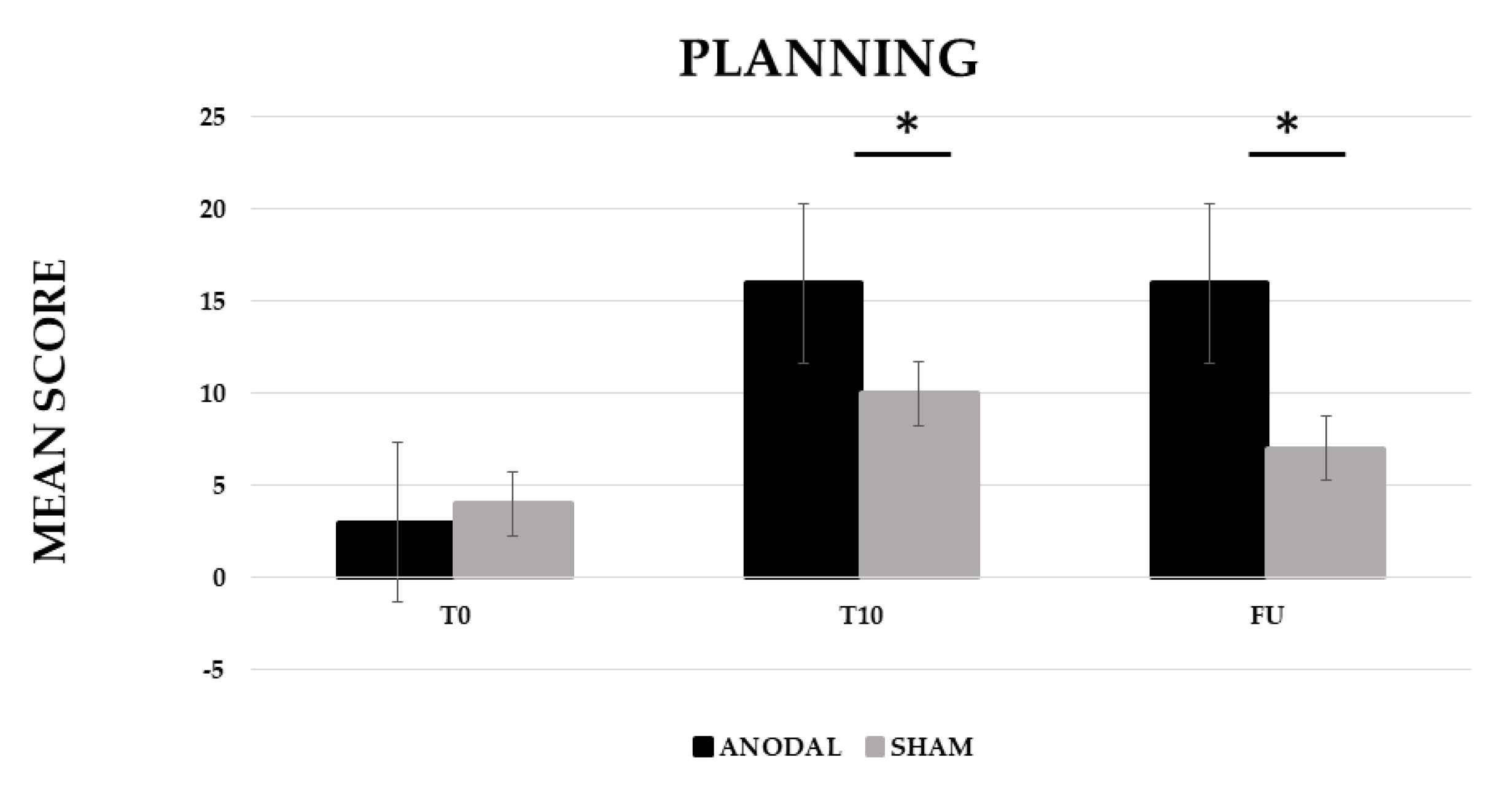
3.1.4. Planning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geranmayeh, F.; Brownsett, S.L.E.; Wise, R.J.S. Task-Induced Brain Activity in Aphasic Stroke Patients: What Is Driving Recovery? Brain 2014, 137, 2632–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickok, G.; Poeppel, D. Dorsal and Ventral Streams: A Framework for Understanding Aspects of the Functional Anatomy of Language. Cognition 2004, 92, 67–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.S.; Small, S.L. Imitation-Based Aphasia Therapy Increases Narrative Content: A Case Series. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, P.; Dick, A.S. Broca and Wernicke Are Dead, or Moving Past the Classic Model of Language Neurobiology. Brain Lang. 2016, 162, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulm, L.; Copland, D.; Meinzer, M. A New Era of Systems Neuroscience in Aphasia? Aphasiology 2018, 32, 742–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosson, B. Thalamic Mechanisms in Language: A Reconsideration Based on Recent Findings and Concepts. Brain Lang. 2013, 126, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, A.O.; Ojemann, G.A. The Thalamus and Language Revisited. Brain Lang. 2013, 126, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickok, G.; Poeppel, D. The Cortical Organization of Speech Processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariën, P.; Ackermann, H.; Adamaszek, M.; Barwood, C.H.S.; Beaton, A.; Desmond, J.; de Witte, E.; Fawcett, A.J.; Hertrich, I.; Küper, M.; et al. Consensus Paper: Language and the Cerebellum: An Ongoing Enigma. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 386–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.J. The Anatomy of Language: A Review of 100 FMRI Studies Published in 2009. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1191, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumstein, S.E.; Amso, D. Dynamic Functional Organization of Language: Insights from Functional Neuroimaging. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 8, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahana-Amitay, D.; Albert, M.L. Neuroscience of Aphasia Recovery: The Concept of Neural Multifunctionality. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, R.J.; Goldinger, S.D.; Lapointe, L.L. Auditory Vigilance in Aphasic Individuals: Detecting Nonlinguistic Stimuli with Full or Divided Attention. Brain Cogn. 1996, 30, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hula, W.D.; McNeil, M.R. Models of Attention and Dual-Task Performance as Explanatory Constructs in Aphasia. Semin. Speech Lang. 2008, 29, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leśniak, M.; Bak, T.; Czepiel, W.; Seniów, J.; Członkowska, A. Frequency and Prognostic Value of Cognitive Disorders in Stroke Patients. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2008, 26, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, L.L. Attention and Other Cognitive Deficits in Aphasia: Presence and Relation to Language and Communication Measures. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2012, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peach, R.K.; Rubin, S.S.; Newhoff, M. A Topographic Event-Related Potential Analysis of the Attention Deficit for Auditory Processing in Aphaisa. Clin. Aphasiol. 1994, 22, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Helm-Estabrooks, N. Cognition and Aphasia: A Discussion and a Study. J. Commun. Disoders 2002, 35, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.J. Auditory Vigilance during Divided Task Attention in Aphasic Individuals. Aphasiology 1991, 5, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, R.; Halai, A.D.; Lambon Ralph, M.A. Assessing and Mapping Language, Attention and Executive Multidimensional Deficits in Stroke Aphasia. Brain 2019, 142, 3202–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridriksson, J.; Nettles, C.; Davis, M.; Morrow, L.; Montgomery, A. Functional Communication and Executive Function in Aphasia. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2006, 20, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, K.; Kaszniak, A.W. Examining Executive Function in Individuals with Brain Injury: A Review. Aphasiology 2002, 16, 305–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsberger, G. Achieving Conversational Success in Aphasia by Focusing on Non-Linguistic Cognitive Skills: A Potentially Promising New Approach. Aphasiology 2005, 19, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrigrand, B.; Dutheil, S.; Michelet, V.; Rereau, S.; Rousseaux, M.; Mazaux, J.M. Communication Impairment and Activity Limitation in Stroke Patients with Severe Aphasia. Disabil. Rehabil. 2011, 33, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.; Arvidsson, P.; Blom Johansson, M. Relations between Executive Function, Language, and Functional Communication in Severe Aphasia. Aphasiology 2019, 33, 821–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.; Arvidsson, P.; Blom Johansson, M. Measuring Executive Function in People with Severe Aphasia: Comparing Neuropsychological Tests and Informant Ratings. NeuroRehabilitation 2020, 46, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, A.; Friedman, N.P.; Emerson, M.J.; Witzki, A.H.; Howerter, A.; Wager, T.D. The Unity and Diversity of Executive Functions and Their Contributions to Complex “Frontal Lobe” Tasks: A Latent Variable Analysis. Cogn. Psychol. 2000, 41, 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, A.; Friedman, N.P. The Nature and Organization of Individual Differences in Executive Functions: Four General Conclusions. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 21, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplak, M.E.; West, R.F.; Stanovich, K.E. Practitioner Review: Do Performance-Based Measures and Ratings of Executive Function Assess the Same Construct? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2013, 54, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchy, Y.; Ziemnik, R.E.; Niermeyer, M.A. Assessment of Executive Functions in Clinical Settings. In Executive Functions in Health and Disease; Goldberg, E., Ed.; Elsevier Science & Technology: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Bigler, E.D.; Tranel, D. Neuropsychological Assessment, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-539552-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stuss, D.T. Functions of the Frontal Lobes: Relation to Executive Functions. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2011, 17, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchy, Y. Executive Functioning: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinical Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, N.; Meier, E.L.; Johnson, J.P.; Kiran, S. Nonlinguistic Cognitive Factors Predict Treatment-Induced Recovery in Chronic Poststroke Aphasia. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simic, T.; Rochon, E.; Greco, E.; Martino, R. Baseline Executive Control Ability and Its Relationship to Language Therapy Improvements in Post-Stroke Aphasia: A Systematic Review. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2019, 29, 395–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Antal, A.; Ayache, S.S.; Benninger, D.H.; Brunelin, J.; Cogiamanian, F.; Cotelli, M.; de Ridder, D.; Ferrucci, R.; Langguth, B.; et al. Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Therapeutic Use of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 56–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangolo, P. The Potential Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) on Language Functioning: Combining Neuromodulation and Behavioral Intervention in Aphasia. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 719, 133329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Paulus, W. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation—Update 2011. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 463–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudbrack-Oliveira, P.; Razza, L.B.; Brunoni, A.R. Non-Invasive Cortical Stimulation: Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS). In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 159, pp. 1–22. ISBN 9780128222980. [Google Scholar]
- Fregni, F.; El-Hagrassy, M.M.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Carvalho, S.; Leite, J.; Simis, M.; Brunelin, J.; Nakamura-Palacios, E.M.; Marangolo, P.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; et al. Evidence-Based Guidelines and Secondary Meta-Analysis for the Use of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 256–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badre, D.; Wagner, A.D. Selection, Integration, and Conflict Monitoring: Assessing the Nature and Generality of Prefrontal Cognitive Control Mechanisms. Neuron 2004, 41, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassbender, C.; Foxe, J.J.; Garavan, H. Mapping the Functional Anatomy of Task Preparation: Priming Task-Appropriate Brain Networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2006, 27, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, H.; Radua, J.; Nakao, T.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Rubia, K. Meta-Analysis of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies of Inhibition and Attention in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Exploring Task-Specific, Stimulant Medication, and Age Effects. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Vanderhasselt, M.A. Working Memory Improvement with Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Cogn. 2014, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertrich, I.; Dietrich, S.; Blum, C.; Ackermann, H. The Role of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex for Speech and Language Processing. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 645209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, A.M.; Yalcin, O.; Baughman, F.D.; Vanman, E.J.; Hagger, M.S. The Impact of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Inhibitory Control in Young Adults. Brain Behav 2015, 5, e00332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friehs, M.A.; Frings, C. Pimping Inhibition: Anodal TDCS Enhances Stop-Signal Reaction Time. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2018, 44, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.Y.; Tseng, L.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Kuo, W.J.; Hung, D.L.; Tzeng, O.J.L.; Walsh, V.; Muggleton, N.G.; Juan, C.H. Modulating Inhibitory Control with Direct Current Stimulation of the Superior Medial Frontal Cortex. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapenta, O.M.; di Sierve, K.; de Macedo, E.C.; Fregni, F.; Boggio, P.S. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates ERP-Indexed Inhibitory Control and Reduces Food Consumption. Appetite 2014, 83, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, F. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Improves Response Inhibition. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 162, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehle, T.; Sandmann, P.; Thorne, J.D.; Jäncke, L.; Herrmann, C.S. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Prefrontal Cortex Modulates Working Memory Performance: Combined Behavioural and Electrophysiological Evidence. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedoncker, J.; Brunoni, A.R.; Baeken, C.; Vanderhasselt, M.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) Over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Healthy and Neuropsychiatric Samples: Influence of Stimulation Parameters. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.J.; Tseng, P.; Chang, C.F.; Pai, M.C.; Hsu, K.S.; Lin, C.C.; Juan, C.H. Modulating the Interference Effect on Spatial Working Memory by Applying Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation over the Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Brain Cogn. 2014, 91, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbo, M.C.; Matzen, L.E.; Coffman, B.A.; Hunter, M.A.; Jones, A.P.; Robinson, C.S.H.; Clark, V.P. Enhanced Working Memory Performance via Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: The Possibility of near and Far Transfer. Neuropsychologia 2016, 93, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Han, S.J. Improvement of the Working Memory and Naming by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giglia, G.; Birghina, F.; Rizzo, S.; Puma, A.; Indovino, S.; Maccora, S.; Baschi, R.; Cosentino, G.; Fierro, B. Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Ofthe Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Enhancesmemory-Guided Responses in a Visuospatialworking Memory Task. Funct. Neurol. 2014, 29, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harty, S.; Robertson, I.H.; Miniussi, C.; Sheehy, O.C.; Devine, C.A.; McCreery, S.; O’Connell, R.G. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation over Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Enhances Error Awareness in Older Age. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 3646–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, R.; Foxe, J.J.; Molholm, S.; Shpaner, M.; Garavan, H. Neural Mechanisms Involved in Error Processing: A Comparison of Errors Made with and without Awareness. Neuroimage 2005, 27, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, K.; Ruh, N.; Nitschke, K.; Reis, J.; Fritsch, B.; Unterrainer, J.M.; Rahm, B.; Weiller, C.; Kaller, C.P. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation over Left and Right DLPFC: Lateralized Effects on Planning Performance and Related Eye Movements. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 102, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, N.; Arnold, J.E.; Thompson-Schill, S.L. The Effects of Anodal Stimulation of the Left Prefrontal Cortex on Sentence Production. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.; Abdel Rahman, R.; Kuenecke, J.; Koenig, T.; Horn, H.; Sommer, W.; Dierks, T. Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) on Behaviour and Electrophysiology of Language Production. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 3989–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestalozzi, M.I.; di Pietro, M.; Martins Gaytanidis, C.; Spierer, L.; Schnider, A.; Chouiter, L.; Colombo, F.; Annoni, J.M.; Jost, L.B. Effects of Prefrontal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Lexical Access in Chronic Poststroke Aphasia. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2018, 32, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical Power Analyses Using G*Power 3.1: Tests for Correlation and Regression Analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.C. The Assessment and Analysis of Handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1971; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ciurli, P.; Marangolo, P.; Basso, A. Esame Del Linguaggio (II Versione); Organ. Spec.: Florence, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- de Renzi, E.; Vignolo, L.A. The Token Test: A Sensitive Test to Detect Receptive Disturbances in Aphasics. Brain 1962, 85, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, G.; Laudanna, A.; Burani, C.; Capasso, R. BADA: A Battery for the Assessment of Aphasic Disorders; CEPSAG: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pigliautile, M.; Chiesi, F.; Primi, C.; Inglese, S.; Mari, D.; Simoni, D.; Mossello, E.; Mecocci, P. Validation Study of the Italian Version of Communication Activities of the Daily Living (CADL 2) as an Ecologic Cognitive Assessment Measure in Older Subjects. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinnler, H.; Tognoni, G. Standardizzazione e Taratura Italiana Di Tests Neurpsicologici. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 6, 12–120. [Google Scholar]
- Monaco, M.; Costa, A.; Caltagirone, C.; Carlesimo, G.A. Forward and Backward Span for Verbal and Visuo-Spatial Data: Standardization and Normative Data from an Italian Adult Population. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turriziani, P.; Smirni, P. Standardizzazione Di Tre Nuovi Test Di Memoria Di Riconoscimento Verbale e Non Verbale: Uno Studio Preliminare. G. Ital. Psicol. 2010, XXXVII, 325–343. [Google Scholar]
- Krikorian, R.; Bartok, J.; Gay, N. Tower of London Procedure: A Standard Method and Developmental Data. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1994, 16, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandiga, P.C.; Hummel, F.C.; Cohen, L.G. Transcranial DC Stimulation (TDCS): A Tool for Double-Blind Sham-Controlled Clinical Studies in Brain Stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, N.E.; Cossar, J.; Marston, L.; Wand, B.M.; Bunce, D.; Moseley, G.L.; de Souza, L.H. Rethinking Clinical Trials of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: Participant and Assessor Blinding Is Inadequate at Intensities of 2mA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasker, J.P.; Garrett, K.L.; Fox, L.E. Severe Aphasia. In Augmentative Communication Strategies for Adults with Acute or Chronic Medical Conditions; Beukelman, D., Garrett, K.L., Yorkston, K.M., Eds.; Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 163–206. [Google Scholar]
- Light, J.; McNaughton, D. Communicative Competence for Individuals Who Require Augmentative and Alternative Communication: A New Definition for a New Era of Communication? AAC Augment. Altern. Commun. 2014, 30, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambini, V.; Arcara, G.; Aiachini, B.; Cattani, B.; Dichiarante, M.L.; Moro, A.; Cappa, S.F.; Pistarini, C. Assessing Functional Communication: Validation of the Italian Versions of the Communication Outcome after Stroke (COAST) Scales for Speakers and Caregivers. Aphasiology 2017, 31, 332–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, G.; Bambini, V.; Bechi, M.; Buonocore, M.; Spangaro, M.; Repaci, F.; Bianchi, L.; Guglielmino, C.; Sapienza, J.; Cavallaro, R.; et al. Communicative-Pragmatic Abilities Mediate the Relationship between Cognition and Daily Functioning in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychology 2021, 35, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani Rad, D. A Review on Adult Pragmatic Assessments. Iran. J. Neurol. 2014, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rofes, A.; Capasso, R.; Miceli, G. Verb Production Tasks in the Measurement of Communicative Abilities in Aphasia. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2015, 37, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, R.S.; Laures-Gore, J.; Dubay, M.; Williams, T.; Bryant, D. Unilateral Forced Nostril Breathing and Aphasia-Exploring Unilateral Forced Nostril Breathing as an Adjunct to Aphasia Treatment: A Case Series. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2015, 21, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persad, C. Retrospective Analysis of Outcomes from Two Intensive Comprehensive Aphasia Programs. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2013, 20, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saimanesh, M.; Pouretemad, H.R.; Amini, A.; Nillipour, R.; Ekhtiari, H. Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Working Memory in Patient with Non Fluent Aphasia Disorder. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Manenti, R.; Petesi, M.; Brambilla, M.; Rosini, S.; Miozzo, A.; Padovani, A.; Miniussi, C.; Cotelli, M. Efficacy of Semantic–Phonological Treatment Combined with TDCS for Verb Retrieval in a Patient with Aphasia. Neurocase 2015, 21, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownsett, S.L.E.; Warren, J.E.; Geranmayeh, F.; Woodhead, Z.; Leech, R.; Wise, R.J.S. Cognitive Control and Its Impact on Recovery from Aphasic Stroke. Brain 2014, 137, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geranmayeh, F.; Chau, T.W.; Wise, R.J.S.; Leech, R.; Hampshire, A. Domain-General Subregions of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Contribute to Recovery of Language after Stroke. Brain 2017, 140, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, R.A. The executive functions and self-regulation: An evolutionary neuropsychological perspective. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2001, 11, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne-Lavau, M.; Stip, E. Pragmatic and Executive Dysfunction in Schizophrenia. J. Neurolinguist. 2010, 23, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.; McDonald, S. Weak Coherence, No Theory of Mind, or Executive Dysfunction? Solving the Puzzle of Pragmatic Language Disorders. Brain Lang. 2003, 85, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipskaya-Velikovsky, L.; Zeilig, G.; Weingarden, H.; Rozental-Iluz, C.; Rand, D. Executive Functioning and Daily Living of Individuals with Chronic Stroke: Measurement and Implications. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2018, 41, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea-Shumsky, N.B.; Schoeneberger, S.; Grigsby, J. Executive Functioning as a Predictor of Stroke Rehabilitation Outcomes. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2019, 33, 854–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- el Hachioui, H.; Visch-Brink, E.G.; Lingsma, H.F.; van de Sandt-Koenderman, M.W.M.E.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Middelkoop, H.A.M. Nonlinguistic Cognitive Impairment in Poststroke Aphasia: A Prospective Study. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, M.; Hunsaker, E.; Guarino, A.J. The Relation between Language, Non-Verbal Cognition and Quality of Life in People with Aphasia. Aphasiology 2017, 31, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, J.V.; Dronkers, N.F.; Wilkins, D.; Ludy, C.; Raskin, P.; Kim, J. Is Problem Solving Dependent on Language? Brain Lang. 2005, 92, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.; Allen, C.M. A Disorder of Executive Function and Its Role in Language Processing. Semin. Speech Lang. 2008, 29, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, T.; Penn, C.; Ormond-Brown, D. Executive Dysfunction as an Explanatory Basis for Conversation Symptoms of Aphasia: A Pilot Study. Aphasiology 2007, 21, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, M.; Koch, A. Prediction of Strategy Usage by Adults with Aphasia. Aphasiology 2006, 20, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinidou, F.; Wertheimer, J.C.; Tsanadis, J.; Evans, C.; Paul, D.R. Assessment of Executive Functioning in Brain Injury: Collaboration between Speech-Language Pathology and Neuropsychology for an Integrative Neuropsychological Perspective. Brain Inj. 2012, 26, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchy, Y. Executive Functioning: Overview, Assessment, and Research Issues for Non-Neuropsychologists. Ann. Behav. Med. 2009, 37, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangolo, P.; Fiori, V.; Sabatini, U.; de Pasquale, G.; Razzano, C.; Caltagirone, C.; Gili, T. Bilateral Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Language Treatment Enhances Functional Connectivity in the Left Hemisphere: Preliminary Data from Aphasia. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 28, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkow, R.; Martin, A.; Würtz, A.; Flöel, A.; Meinzer, M. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Effects on Neural Processing in Post-Stroke Aphasia. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwigsen, G.; Saur, D. Neuroimaging of Stroke Recovery from Aphasia—Insights into Plasticity of the Human Language Network. Neuroimage 2019, 190, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, R.H.; Chrysikou, E.G.; Coslett, B. Mechanisms of Aphasia Recovery after Stroke and the Role of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation. Brain Lang. 2011, 118, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkeltaub, P.E. Brain Stimulation and the Role of the Right Hemisphere in Aphasia Recovery. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Dai, W.; Alsop, D.C.; Schlaug, G. Modulating Transcallosal and Intra-Hemispheric Brain Connectivity with TDCS: Implications for Interventions in Aphasia. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2016, 34, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| P | Sex | Age | Ed. Level | Time Post- Onset | Stroke Type | Lesion Side LH | Oral NN | Oral VN | Writ NN | Writ VN | WR | NWR | W Read | NW Read | WD | NW D | TT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 50 | 8 | 4 y | I | FTP | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 15 | 12.5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 2 | M | 58 | 13 | 3 y | I | FTP | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | M | 60 | 8 | 1 y | I | FT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17.5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 4 | F | 72 | 8 | 1 y | I | FTI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 5 | M | 66 | 13 | 1 y | I | FT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 12.5 | 15 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 6 | M | 67 | 17 | 2 y | I | FT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 7 | F | 58 | 13 | 2 y | H | FTI | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 8 | F | 72 | 8 | 1 y | I | FTP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 9 | M | 59 | 13 | 2 y | I | FTI | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 17.5 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 10 | M | 59 | 17 | 6 mo | I | FTI | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 11 | F | 72 | 8 | 2 y | I | FTP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 5 | 12.5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 |
| 12 | M | 54 | 17 | 6 mo | I | FTP | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 13 | F | 58 | 13 | 3 y | I | FTP | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 14 | F | 65 | 17 | 1 y | I | FT | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 15 | M | 69 | 8 | 2 y | I | FTP | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 16 | M | 55 | 13 | 3 y | I | FT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 17 | F | 52 | 17 | 6 mo | I | FTP | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 18 | F | 61 | 8 | 1 y | I | FTI | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 19 | F | 53 | 13 | 2 y | I | FTP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 20 | F | 68 | 13 | 4 y | I | FTP | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| P | Auditory Sentence Compreh | Written Sentence Compreh | CADL-2 | Visual Search | Corsi Backward | Smirni | TOL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 31 | 4 | 5 | 75 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 | 23 | 31 | 5 | 10 | 72 |
| 3 | 4 | 3 | 21 | 32 | 5 | 10 | 78 |
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 16 | 34 | 4 | 5 | 70 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 17 | 33 | 4 | 5 | 78 |
| 6 | 3 | 4 | 15 | 32 | 4 | 5 | 72 |
| 7 | 5 | 5 | 23 | 32 | 4 | 10 | 71 |
| 8 | 2 | 2 | 20 | 34 | 4 | 5 | 76 |
| 9 | 4 | 4 | 19 | 33 | 5 | 10 | 76 |
| 10 | 3 | 3 | 22 | 32 | 4 | 10 | 73 |
| 11 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 31 | 4 | 5 | 70 |
| 12 | 5 | 4 | 19 | 31 | 4 | 10 | 71 |
| 13 | 5 | 3 | 20 | 34 | 5 | 10 | 70 |
| 14 | 4 | 2 | 17 | 32 | 5 | 5 | 71 |
| 15 | 3 | 4 | 18 | 31 | 4 | 5 | 76 |
| 16 | 2 | 4 | 21 | 34 | 4 | 5 | 74 |
| 17 | 3 | 5 | 19 | 31 | 4 | 5 | 72 |
| 18 | 3 | 5 | 20 | 33 | 4 | 5 | 73 |
| 19 | 5 | 3 | 21 | 34 | 4 | 10 | 70 |
| 20 | 4 | 4 | 22 | 31 | 5 | 10 | 78 |
| P | C | ORAL NN | ORAL VN | AUDITORY SENT COMP | WRITTEN SENT COMP | CADL-2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T10 | FU | T0 | T10 | FU | T0 | T10 | FU | T0 | T10 | FU | T0 | T10 | FU | ||
| REAL FIRST | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 | R | 5 | 30 ^ | 30 | 5 | 30 ^ | 30 | 5 | 17 ** | 17 | 5 | 16 * | 14 | 20 | 48 ^ | 42 |
| S | 30 | 32.5 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 30 | 17 | 19 | 16 | 16 | 18 | 14 | 48 | 50 | 40 | |
| 3 | R | 0 | 17.5 ^ | 15 | 0 | 12.5 ^ | 15 | 4 | 15 * | 13 | 3 | 13 * | 13 | 21 | 50 ^ | 50 |
| S | 17.5 | 17.5 | 15 | 12.5 | 15 | 12.5 | 15 | 17 | 14 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 50 | 54 | 52 | |
| 5 | R | 0 | 15 ^ | 15 | 0 | 10 ** | 10 | 2 | 14 * | 13 | 4 | 13 * | 11 | 17 | 36 ** | 38 |
| S | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 36 | 40 | 38 | |
| 7 | R | 5 | 20 ** | 20 | 5 | 40 ^ | 42.5 | 5 | 15 * | 15 | 5 | 12 | 11 | 23 | 55 ^ | 50 |
| S | 20 | 25 | 20 | 40 | 45 | 40 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 55 | 59 | 48 | |
| 9 | R | 0 | 12.5 ^ | 15 | 5 | 30 ^ | 25 | 4 | 20 ^ | 20 | 4 | 18 ** | 18 | 19 | 36 ** | 40 |
| S | 12.5 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 19 | 18 | 36 | 40 | 40 | |
| 11 | R | 0 | 10 ** | 10 | 0 | 20 ^ | 20 | 4 | 12 | 13 | 2 | 11 * | 12 | 18 | 40^ | 40 |
| S | 10 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 40 | 46 | 44 | |
| 13 | R | 5 | 15 * | 15 | 0 | 10 ** | 10 | 5 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 14 ** | 15 | 20 | 51 ^ | 51 |
| S | 15 | 20 | 17.5 | 10 | 10 | 7.5 | 13 | 13 | 9 | 14 | 16 | 16 | 51 | 55 | 50 | |
| 15 | R | 5 | 20 ** | 20 | 5 | 30 ^ | 32.5 | 3 | 15 ** | 15 | 4 | 16 ** | 16 | 18 | 39 ** | 36 |
| S | 20 | 22.5 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 15 | 18 | 18 | 16 | 19 | 16 | 39 | 43 | 40 | |
| 17 | R | 0 | 20^ | 17.5 | 5 | 25 ^ | 25 | 3 | 10 | 11 | 5 | 13 | 12 | 19 | 44 ^ | 48 |
| S | 20 | 30 | 25 | 25 | 30 | 30 | 10 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 44 | 46 | 46 | |
| 19 | R | 0 | 17.5 ^ | 15 | 0 | 20 ^ | 17.5 | 5 | 14 * | 14 | 3 | 13 * | 14 | 21 | 48 ^ | 48 |
| S | 17.5 | 25 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 14 | 48 | 47 | 47 | |
| SHAM FIRST | ||||||||||||||||
| 2 | S | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 23 | 27 | 23 |
| R | 0 | 15 ^ | 12.5 | 10 | 35 ^ | 30 | 7 | 18 * | 15 | 4 | 14 * | 14 | 27 | 46 ** | 40 | |
| 4 | S | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| R | 5 | 25 ^ | 22.5 | 0 | 20 ^ | 15 | 8 | 18 * | 18 | 7 | 19 * | 17 | 20 | 44 ^ | 44 | |
| 6 | S | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 18 | 20 |
| R | 0 | 10 ** | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 17 * | 14 | 5 | 14 * | 13 | 18 | 42 ^ | 44 | |
| 8 | S | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| R | 0 | 12.5 | 15 | 0 | 15 ^ | 15 | 4 | 15 * | 15 | 4 | 19 ^ | 18 | 25 | 53 ^ | 50 | |
| 10 | S | 5 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 22 | 25 | 22 |
| R | 10 | 30 ^ | 30 | 5 | 25 ^ | 22.5 | 8 | 23 ** | 21 | 5 | 14 * | 13 | 25 | 55 ^ | 50 | |
| 12 | S | 5 | 7.5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 19 | 23 | 23 |
| R | 7.5 | 20 * | 20 | 0 | 20 ^ | 20 | 10 | 20 | 21 | 7 | 18 * | 19 | 23 | 47 ^ | 47 | |
| 14 | S | 5 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 17 | 22 | 20 |
| R | 10 | 25 ** | 20 | 0 | 20 ^ | 17.5 | 6 | 16 * | 15 | 4 | 15 ** | 16 | 22 | 46 ^ | 42 | |
| 16 | S | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 10 ** | 10 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 21 | 26 | 24 |
| R | 5 | 22.5 ^ | 20 | 10 | 35 ^ | 30 | 4 | 14 * | 14 | 6 | 16 * | 14 | 26 | 53 ^ | 48 | |
| 18 | S | 5 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 20 | 22 | 20 |
| R | 10 | 25 ** | 25 | 0 | 15 ^ | 15 | 5 | 17 ** | 19 | 9 | 18 | 19 | 22 | 41 ** | 41 | |
| 20 | S | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 22 | 24 | 24 |
| R | 0 | 10 ** | 7.5 | 10 | 30 ^ | 25 | 7 | 19 * | 19 | 8 | 20 * | 19 | 24 | 53 ^ | 53 | |
| P | C | VISUAL SEARCH | SMIRNI | TOL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T10 | FU | T0 | T10 | FU | T0 | T10 | FU | ||
| REAL FIRST | ||||||||||
| 1 | R | 31 | 40 | 40 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 75 | 90 ** | 85 |
| S | 40 | 40 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 90 | 90 | 80 | |
| 3 | R | 32 | 41 | 39 | 10 | 50 ^ | 50 | 78 | 92 ** | 90 |
| S | 41 | 40 | 38 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 92 | 92 | 90 | |
| 5 | R | 33 | 34 | 33 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 78 | 91 * | 94 |
| S | 34 | 34 | 33 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 94 | 94 | 92 | |
| 7 | R | 32 | 33 | 34 | 10 | 25 * | 25 | 71 | 79 | 75 |
| S | 33 | 35 | 34 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 79 | 73 | 73 | |
| 9 | R | 33 | 45 * | 46 | 10 | 25 * | 25 | 76 | 79 | 76 |
| S | 45 | 46 | 48 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 79 | 76 | 76 | |
| 11 | R | 31 | 40 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 70 | 88 ** | 89 |
| S | 40 | 39 | 40 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 88 | 88 | 90 | |
| 13 | R | 34 | 43 | 45 | 10 | 50 ^ | 50 | 70 | 92 ^ | 95 |
| S | 43 | 45 | 44 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 92 | 95 | 95 | |
| 15 | R | 31 | 42 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 76 | 88 * | 85 |
| S | 42 | 41 | 40 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 88 | 86 | 83 | |
| 17 | R | 31 | 32 | 32 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 72 | 74 | 72 |
| S | 32 | 32 | 31 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 74 | 73 | 72 | |
| 19 | R | 34 | 35 | 34 | 10 | 25 * | 25 | 70 | 85 * | 84 |
| S | 35 | 34 | 33 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 85 | 88 | 84 | |
| SHAM FIRST | ||||||||||
| 2 | S | 31 | 31 | 32 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 72 | 72 | 80 |
| R | 31 | 31 | 31 | 10 | 25 * | 25 | 72 | 88 * | 89 | |
| 4 | S | 34 | 35 | 38 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 70 | 75 | 73 |
| R | 35 | 44 | 33 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 75 | 88 * | 89 | |
| 6 | S | 32 | 33 | 33 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 72 | 72 | 71 |
| R | 33 | 41 | 43 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 72 | 69 | 70 | |
| 8 | S | 34 | 34 | 33 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 76 | 76 | 80 |
| R | 34 | 34 | 34 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 76 | 89 * | 91 | |
| 10 | S | 32 | 33 | 34 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 73 | 78 | 85 |
| R | 33 | 34 | 35 | 10 | 50 ^ | 50 | 78 | 100 ^ | 95 | |
| 12 | S | 31 | 32 | 31 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 71 | 4 | 75 |
| R | 32 | 32 | 32 | 10 | 50 ^ | 50 | 74 | 85 * | 80 | |
| 14 | S | 32 | 34 | 37 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 71 | 75 | 80 |
| R | 34 | 44 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 75 | 87 ** | 87 | |
| 16 | S | 34 | 38 | 35 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 74 | 76 | 75 |
| R | 38 | 40 | 38 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 76 | 75 | 75 | |
| 18 | S | 33 | 36 | 40 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 73 | 71 | 77 |
| R | 36 | 47 | 48 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 71 | 86 * | 88 | |
| 20 | S | 31 | 34 | 38 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 78 | 78 | 83 |
| R | 34 | 45 | 46 | 10 | 25 * | 25 | 78 | 93 ** | 95 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pisano, F.; Manfredini, A.; Castellano, A.; Caltagirone, C.; Marangolo, P. Does Executive Function Training Impact on Communication? A Randomized Controlled tDCS Study on Post-Stroke Aphasia. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091265
Pisano F, Manfredini A, Castellano A, Caltagirone C, Marangolo P. Does Executive Function Training Impact on Communication? A Randomized Controlled tDCS Study on Post-Stroke Aphasia. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(9):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091265
Chicago/Turabian StylePisano, Francesca, Alessio Manfredini, Andrea Castellano, Carlo Caltagirone, and Paola Marangolo. 2022. "Does Executive Function Training Impact on Communication? A Randomized Controlled tDCS Study on Post-Stroke Aphasia" Brain Sciences 12, no. 9: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091265
APA StylePisano, F., Manfredini, A., Castellano, A., Caltagirone, C., & Marangolo, P. (2022). Does Executive Function Training Impact on Communication? A Randomized Controlled tDCS Study on Post-Stroke Aphasia. Brain Sciences, 12(9), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091265










