Deep Learning for the Prediction of the Survival of Midline Diffuse Glioma with an H3K27M Alteration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
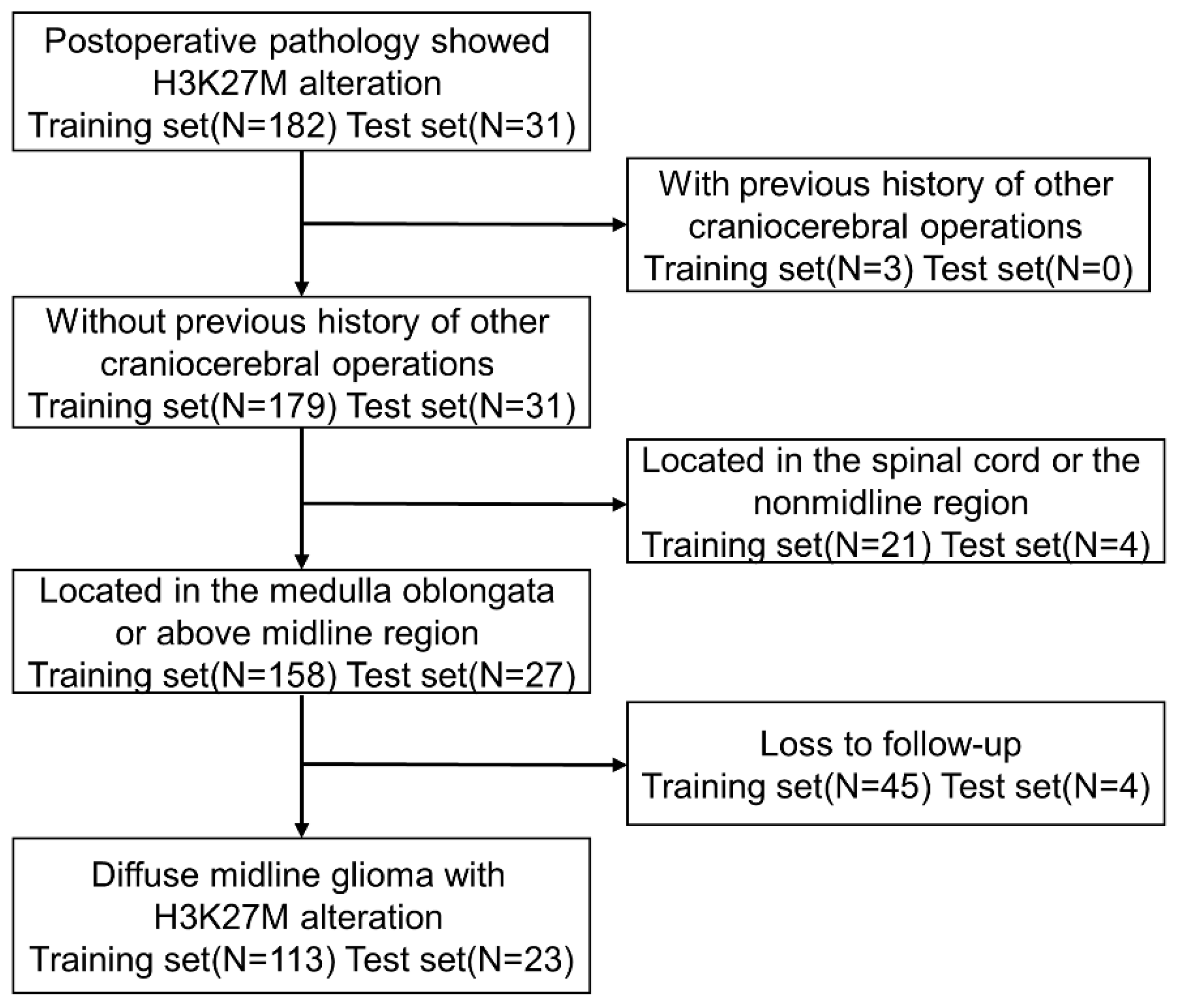
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Definitions
2.2. Feature Selection
2.3. Model Construction of Machine Learning
2.4. Model Training
2.5. Model Performance Measures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Feature Screening Results
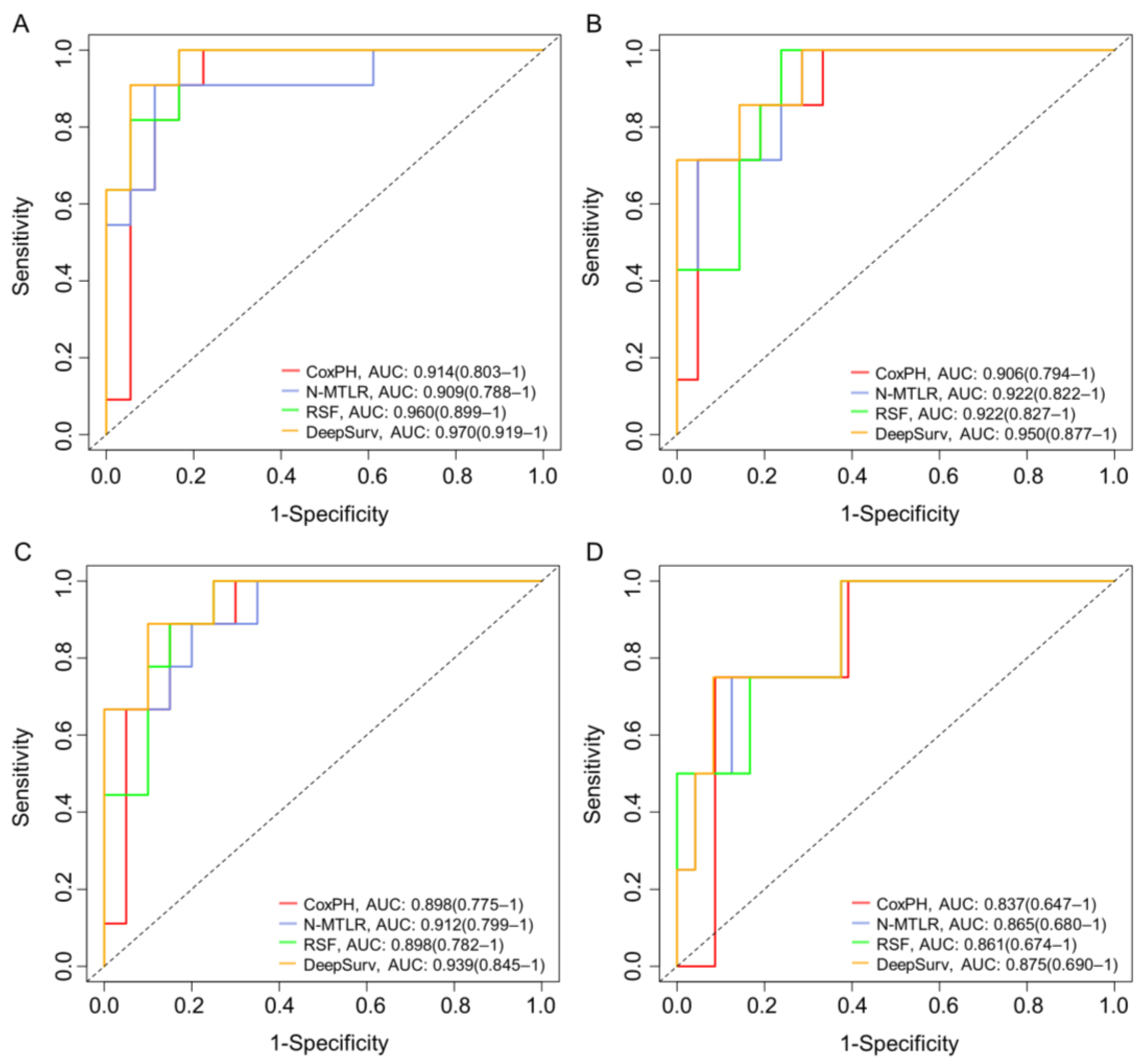
3.3. Model Performance
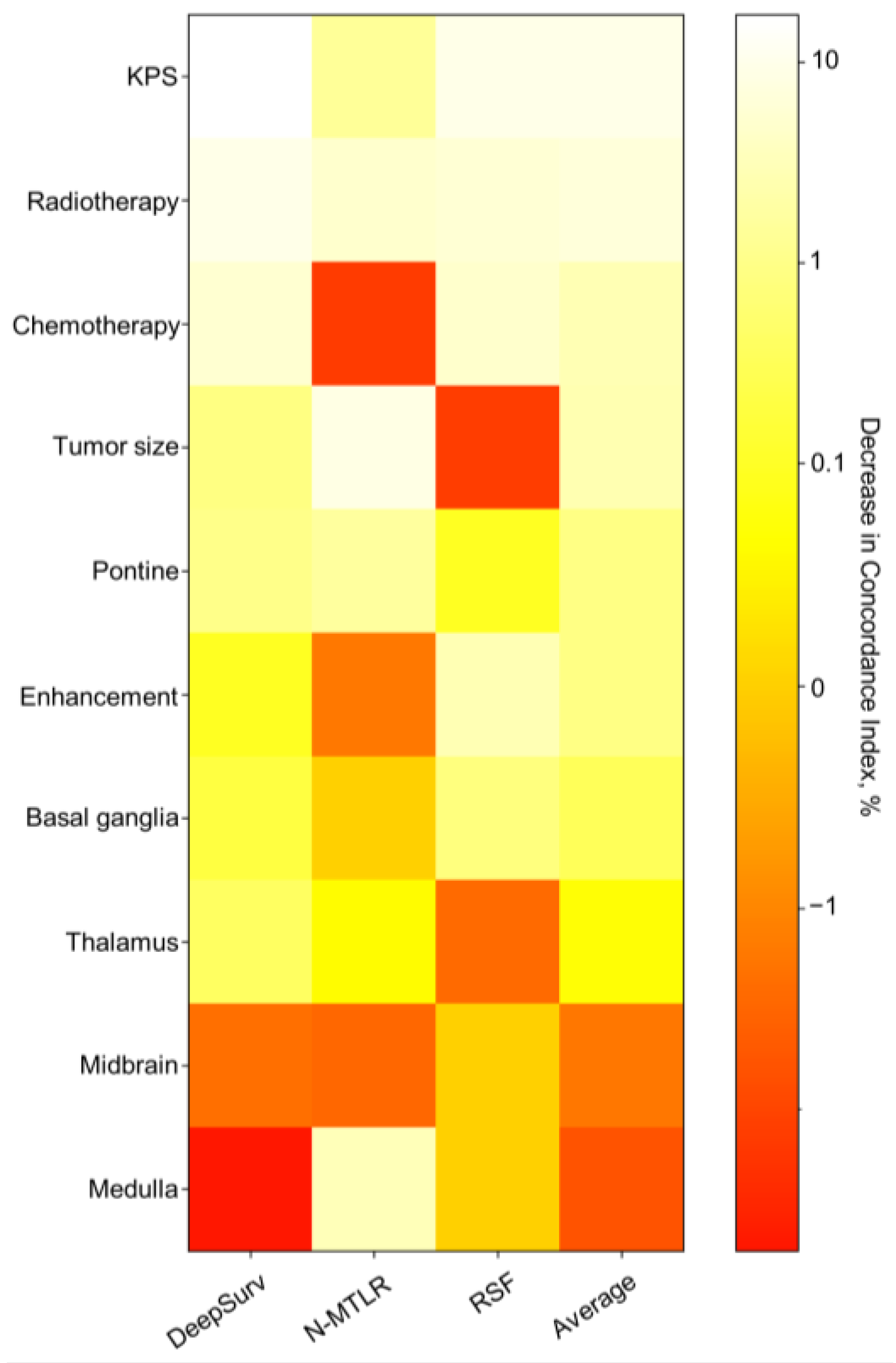
3.4. Model Visualization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, D.; Philippe, C.; Calmon, R.; Le Dret, L.; Truffaux, N.; Boddaert, N.; Pages, M.; Taylor, K.R.; Saulnier, P.; Lacroix, L.; et al. Histone H3F3A and HIST1H3B K27M mutations define two subgroups of diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas with different prognosis and phenotypes. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Broniscer, A.; McEachron, T.A.; Lu, C.; Paugh, B.S.; Becksfort, J.; Qu, C.; Ding, L.; Huether, R.; Parker, M.; et al. Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Aiyer, H.M. Diffuse midline glioma-H3K27M mutant. A novel entity with a defining and specific IHC marker. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.S.; Kulanthaivelu, K.; Kathrani, N.; Kotwal, A.; Bhat, M.D.; Saini, J.; Prasad, C.; Chakrabarti, D.; Santosh, V.; Uppar, A.M.; et al. Prediction of H3K27M mutation status of diffuse midline gliomas using MRI features. J. Neuroimaging 2021, 31, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20 (Suppl. S4), iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Harlay, V.; Appay, R.; Bequet, C.; Petrirena, G.; Campello, C.; Barrie, M.; Autran, D.; Boissonneau, S.; Graillon, T.; et al. Adult H3K27M mutated thalamic glioma patients display a better prognosis than unmutated patients. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 156, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Buczkowicz, P.; Rakopoulos, P.; Liu, X.Y.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; Albrecht, S.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Letourneau, L.; et al. K27M mutation in histone H3.3 defines clinically and biologically distinct subgroups of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, Y.; Saito, R.; Shibahara, I.; Sasaki, K.; Shoji, T.; Kanamori, M.; Sonoda, Y.; Kumabe, T.; Watanabe, M.; Tominaga, T. H3K27M and TERT promoter mutations are poor prognostic factors in surgical cases of adult thalamic high-grade glioma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Chanchotisatien, A.; Qin, Z.; Wu, J.; Du, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, F.; Yao, Z.; Chu, S. Imaging characteristics of adult H3 K27M-mutant gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin-Alamer, O.; Jimenez, A.E.; Azad, T.D.; Bettegowda, C.; Mukherjee, D. H3K27M-Altered Diffuse Midline Gliomas Among Adult Patients: A Systematic Review of Clinical Features and Survival Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 165, e251–e264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, H.G.; Ngo, T.N.M.; Le, H.T.; Jea, A.; Hrachova, M.; Battiste, J.; McNall-Knapp, R.; Dunn, I.F. Prognostic Implication of Patient Age in H3K27M-Mutant Midline Gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 858148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, F.M.; Kochanny, S.; Koshy, M.; Spiotto, M.; Pearson, A.T. Machine Learning-Guided Adjuvant Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Lin, J.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Xu, W.; Yu, C.; Qu, S.; Liu, X.; Qian, L.; Xu, C.; et al. Development of a Deep Learning Model for Malignant Small Bowel Tumors Survival: A SEER-Based Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.N.; Jv, D.W.; Meng, X.F.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Hong, N.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, N. Feasibility of machine learning-based modeling and prediction using multiple centers data to assess intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma outcomes. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzman, J.L.; Shaham, U.; Cloninger, A.; Bates, J.; Jiang, T.; Kluger, Y. DeepSurv: Personalized treatment recommender system using a Cox proportional hazards deep neural network. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoye, J.; Koohi-Moghadam, M.; Lo, A.W.I.; Tsang, R.K.; Chow, V.L.Y.; Zheng, L.W.; Choi, S.W.; Thomson, P.; Su, Y.X. Deep Learning Predicts the Malignant-Transformation-Free Survival of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. Cancers 2021, 13, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, J.; Brunnberg, A.; Holte, G.; Eldrup, N.; Sörelius, K. Artificial Intelligence Outperforms Kaplan-Meier Analyses Estimating Survival after Elective Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 65, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, P.; Gunavathi, C. A systematic review on machine learning and deep learning techniques in cancer survival prediction. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2022, 174, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steingrimsson, J.A.; Morrison, S. Deep learning for survival outcomes. Stat. Med. 2020, 39, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.M.; Veldhuijzen van Zanten, S.E.M.; Colditz, N.; Baugh, J.; Chaney, B.; Hoffmann, M.; Lane, A.; Fuller, C.; Miles, L.; Hawkins, C.; et al. Clinical, Radiologic, Pathologic, and Molecular Characteristics of Long-Term Survivors of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma (DIPG): A Collaborative Report From the International and European Society for Pediatric Oncology DIPG Registries. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, A.; Burford, A.; Carvalho, D.; Izquierdo, E.; Fazal-Salom, J.; Taylor, K.R.; Bjerke, L.; Clarke, M.; Vinci, M.; Nandhabalan, M.; et al. Integrated Molecular Meta-Analysis of 1,000 Pediatric High-Grade and Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 520–537.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, C.M.; Shumon, S.; Stummer, W.; Holling, M.; Surash, S. A Cohort Analysis of Truly Incidental Low-Grade Gliomas. World Neurosurg. 2022, 159, e347–e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ius, T.; Isola, M.; Budai, R.; Pauletto, G.; Tomasino, B.; Fadiga, L.; Skrap, M. Low-grade glioma surgery in eloquent areas: Volumetric analysis of extent of resection and its impact on overall survival. A single-institution experience in 190 patients: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.K.; Chaichana, K.L.; Weingart, J.D.; Redmond, K.J.; Lim, M.; Olivi, A.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Kleinberg, L.R. Progressive Low-Grade Glioma: Assessment of Prognostic Importance of Histologic Reassessment and MRI Findings. World Neurosurg. 2017, 99, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretti, V.; Bugiani, M.; Freret, M.; Schellen, P.; Jansen, M.; van Vuurden, D.; Kaspers, G.; Fisher, P.G.; Hulleman, E.; Wesseling, P.; et al. Subventricular spread of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittleman, H.; Sloan, A.E.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. An independently validated survival nomogram for lower-grade glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.L.; Hu, C.W.; Wang, X.R.; Yin, G.F.; Shang, J.X. Association between downexpression of miR-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4298–4303. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Piao, Y.; Chen, L.; Liang, H.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Teng, L.; et al. H3 K27M-mutant diffuse midline gliomas in different anatomical locations. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 78, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Bhutada, A.S.; Ladner, L.; Cuoco, J.A.; Entwistle, J.J.; Marvin, E.A.; Rogers, C.M. Prognostic Indicators for H3K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Glioma: A Population-Based Retrospective Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023, 178, e113–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Kuang, S.; Deng, D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C. Differences in survival prognosticators between children and adults with H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, K.; Purushotham, S.; Jiang, B.; Mandelbaum, R.S.; Takiuchi, T.; Liu, Y.; Roman, L.D. Survival outcome prediction in cervical cancer: Cox models vs. deep-learning model. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 381.e1–381.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doppalapudi, S.; Qiu, R.G.; Badr, Y. Lung cancer survival period prediction and understanding: Deep learning approaches. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2021, 148, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Huang, B.; Tang, J.; Jv, Y.; Mao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Y. A validated prognostic nomogram for patients with H3 K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.J.; Broniscer, A.; Glod, J. Pediatric glial tumors. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2001, 2, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Univariate Analysis (HR, 95% CI) | p | Multivariate Analysis (HR, 95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.988 (0.976–1.000) | 0.059 | 0.994 (0.940–0.970) | 0.434 |
| Gender | 0.674 | 0.890 | ||
| Female | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Male | 0.919 (0.620–1.362) | 1.036 (0.627–1.713) | ||
| Tumor size | 0.000 | 0.035 | ||
| ≥1 mm | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| ≥2 mm | 2.027 (0.728–5.644) | 4.069 (1.038–15.958) | ||
| ≥3 mm | 4.946 (2.069–11.825) | 4.848 (1.413–16.637) | ||
| ≥4 mm | 8.536 (3.504–20.793) | 6.771 (1.875–24.457) | ||
| Tumor location | 0.037 | 0.010 | ||
| Medulla | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Pontine | 0.981 (0.641–5.161) | 0.959 (0.145–6.347) | ||
| Midbrain | 0.733 (0.103–0.723) | 0.050 (0.03–0.718) | ||
| Thalamus | 0.801 (0.457–3.715) | 0.527 (0.082–3.402) | ||
| Basal ganglia | 0.942 (0.445–6.867) | 0.801 (0.117–5.487) | ||
| Extent of resection | 0.432 | 0.245 | ||
| Biopsy | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| PR | 1.035 (0.488–2.196) | 0.489 (0.200–1.191) | ||
| STR | 0.694 (0.308–1.562) | 0.404 (0.158–1.038) | ||
| GTR | 1.031 (0.455–2.336) | 0.598 (0.217–1.651) | ||
| Pre-op KPS | 0.964 (0.952–0.975) | 0.000 | 0.955 (0.940–0.970) | 0.000 |
| Enhancement | 0.000 | 0.031 | ||
| No | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Yes | 2.212 (1.462–3.347) | 1.733 (1.051–2.859) | ||
| Radiotherapy | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| No | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Yes | 0.203 (0.121–0.342) | 0.178 (0.089–0.355) | ||
| Chemotherapy | 0.000 | 0.002 | ||
| No | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Yes | 0.240 (0.146–0.395) | 0.345 (0.175–0.681) | ||
| ATRX expression | 0.845 | 0.112 | ||
| No | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Yes | 1.044 (0.674–1.617) | 1.586 (0.897–2.805) | ||
| P53 positive | 0.572 | 0.066 | ||
| No | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Yes | 0.858 (0.508–1.448) | 0.567 (0.309–1.039) | ||
| Ki67 expression | 10.186 (2.735–37.942) | 0.001 | 2.533 (0.511–12.565) | 0.255 |
| MGMT promoter methylation | 0.193 | 0.564 | ||
| Unmethylated | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Methylated | 0.713 (0.421–1.208) | 1.200 (0.647–2.225) |
| Models | C-Index | IBS | 6 Months AUC | 12 Months AUC | 18 Months AUC | 24 Months AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoxPH | Training set | 0.819 | 0.126 | 0.914 (0.803–1) | 0.906 (0.794–1) | 0.898 (0.775–1) | 0.837 (0.647–1) |
| Test set | 0.751 | 0.162 | 0.853 (0.781–0.952) | 0.836 (0.725–0.947) | 0.829 (0.711–0.924) | 0.773 (0.607–0.891) | |
| N-MTLR | Training set | 0.824 | 0.104 | 0.909 (0.788–1) | 0.922 (0.822–1) | 0.912 (0.799–1) | 0.865 (0.680–1) |
| Test set | 0.763 | 0.159 | 0.849 (0.742–0.957) | 0.853 (0.765–0.972) | 0.849 (0.762–0.974) | 0.807 (0.653–1) | |
| RSF | Training set | 0.845 | 0.112 | 0.960 (0.899–1) | 0.922 (0.827–1) | 0.898 (0.782–1) | 0.861 (0.674–1) |
| Test set | 0.786 | 0.150 | 0.871 (0.805–0.962) | 0.853 (0.761–0.985) | 0.821 (0.726–0.947) | 0.780 (0.637–1) | |
| DeepSurv | Training set | 0.862 | 0.093 | 0.970 (0.919–1) | 0.950 (0.877–1) | 0.939 (0.845–1) | 0.875 (0.690–1) |
| Test set | 0.811 | 0.147 | 0.893 (0.827–0.972) | 0.869 (0.782–0.961) | 0.866 (0.776–0.962) | 0.803 (0.667–1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, B.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Ju, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Lei, Y.; Ren, Y. Deep Learning for the Prediction of the Survival of Midline Diffuse Glioma with an H3K27M Alteration. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101483
Huang B, Chen T, Zhang Y, Mao Q, Ju Y, Liu Y, Wang X, Li Q, Lei Y, Ren Y. Deep Learning for the Prediction of the Survival of Midline Diffuse Glioma with an H3K27M Alteration. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(10):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101483
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Bowen, Tengyun Chen, Yuekang Zhang, Qing Mao, Yan Ju, Yanhui Liu, Xiang Wang, Qiang Li, Yinjie Lei, and Yanming Ren. 2023. "Deep Learning for the Prediction of the Survival of Midline Diffuse Glioma with an H3K27M Alteration" Brain Sciences 13, no. 10: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101483
APA StyleHuang, B., Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Mao, Q., Ju, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Li, Q., Lei, Y., & Ren, Y. (2023). Deep Learning for the Prediction of the Survival of Midline Diffuse Glioma with an H3K27M Alteration. Brain Sciences, 13(10), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101483






