The Role of the NF-kB Pathway in Intracranial Aneurysms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
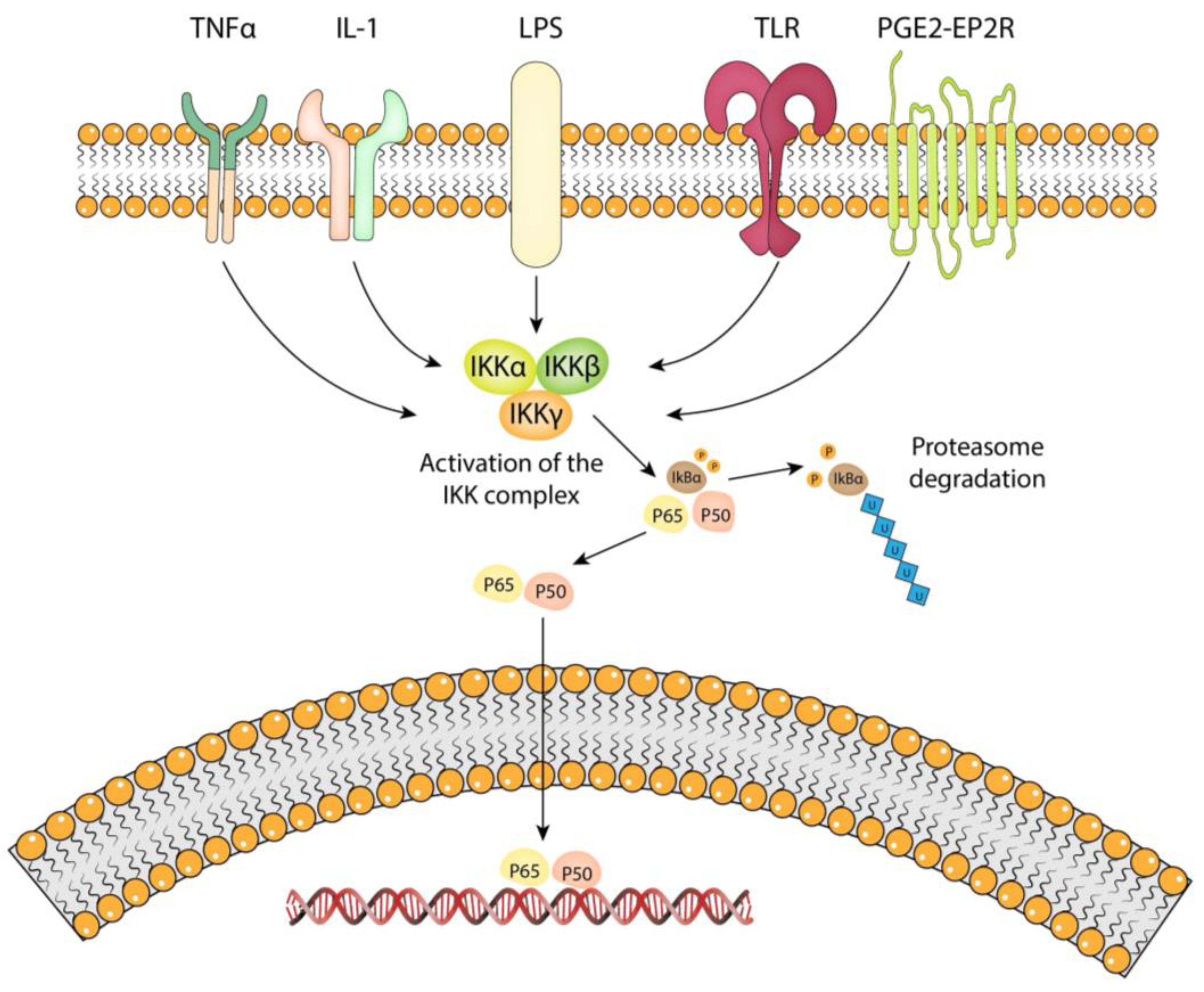
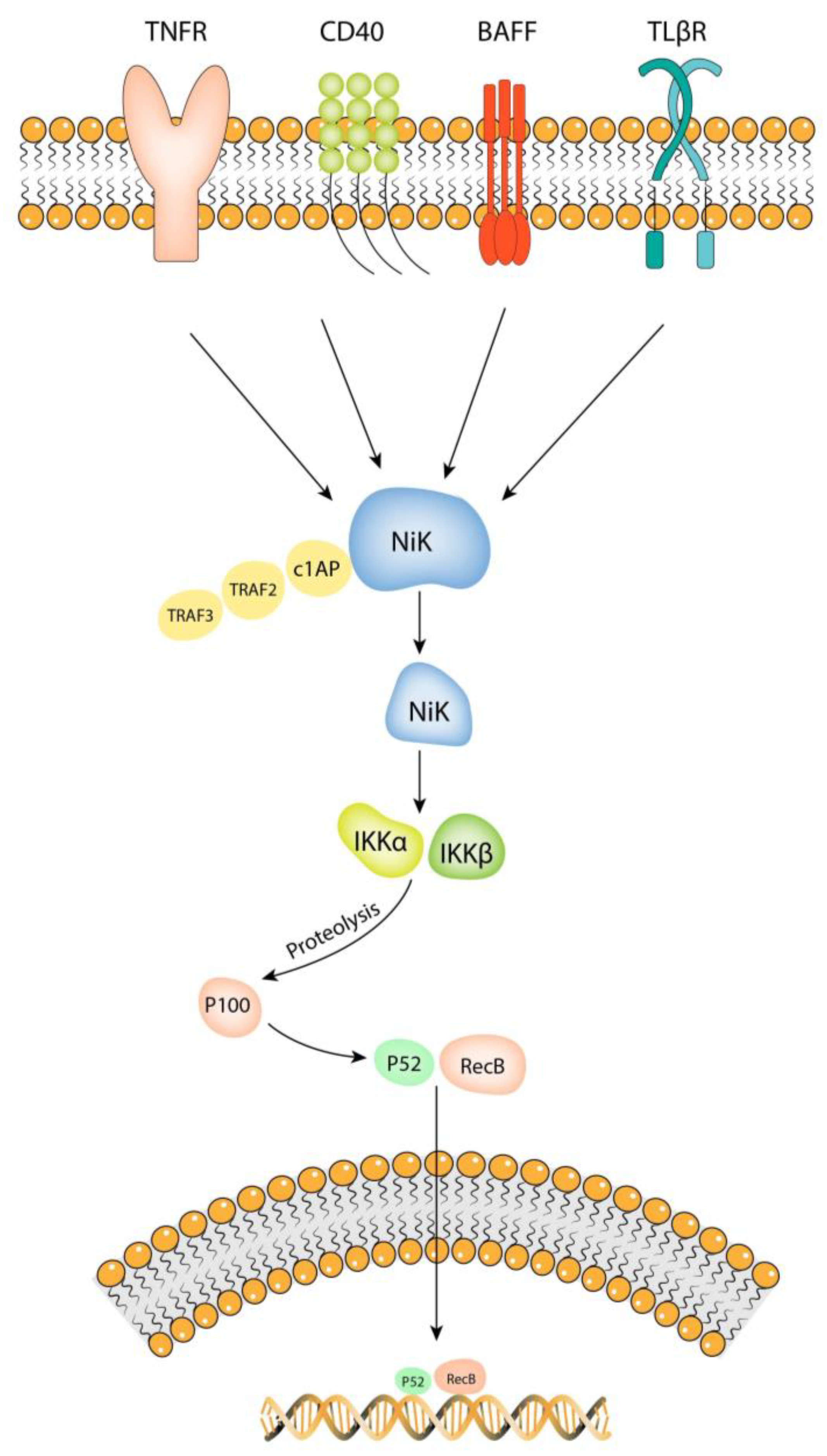
4.1. Overview of the NF-kB Pathway
4.2. Stimuli That Activate the NF-kB Pathway in IA Pathology
4.3. Transcriptional Targets of NF-kB Pathway in IA Pathology
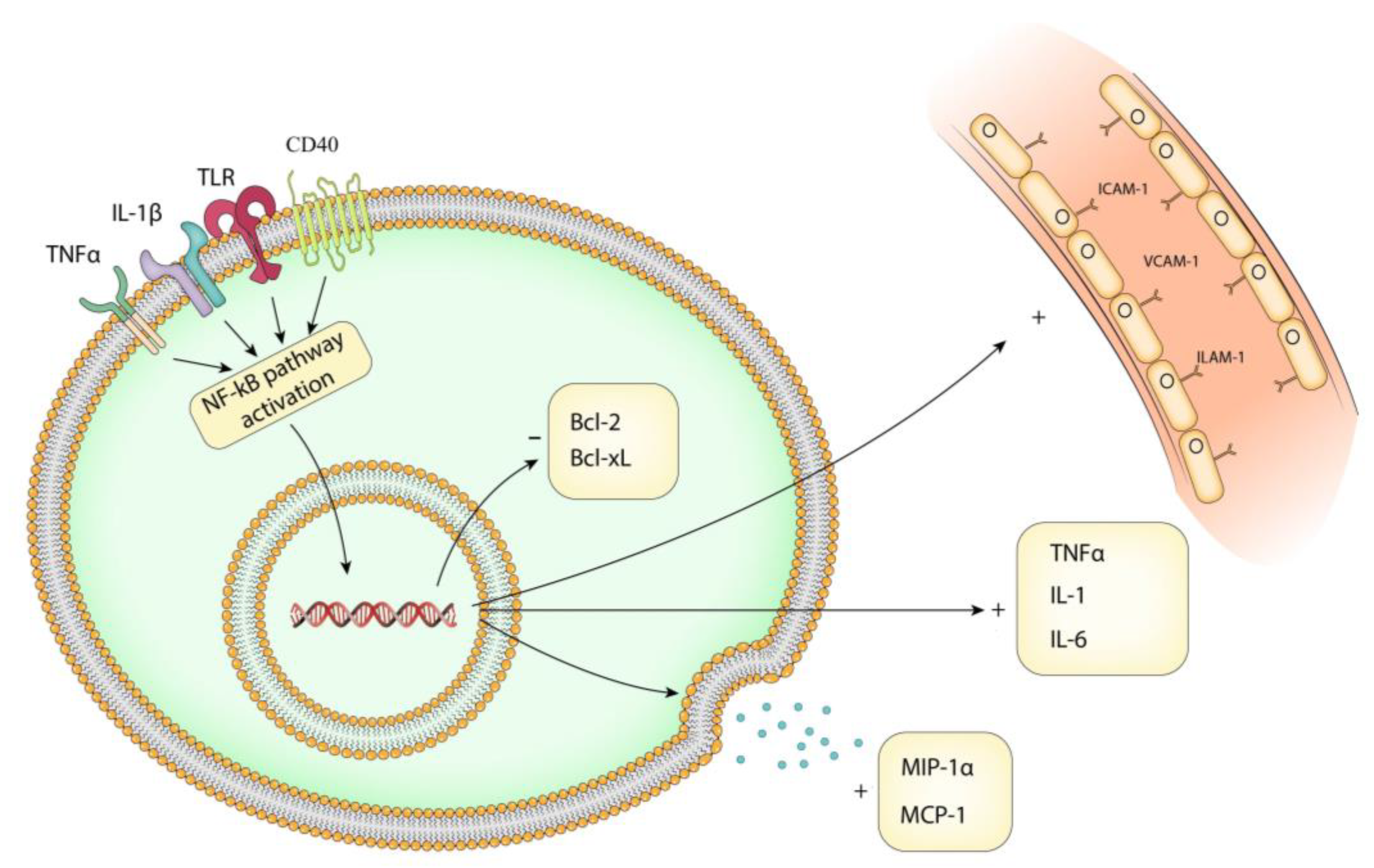
4.4. Role of NF-kB Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell
| Trigger | Mechanism | Effect | Treatment | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RANKL | p52 pathway | Pro-calcific effect | TRAIL | [47] |
| C. pneumoniae | PKC dependent pathway | Increased expression of ICAM-1 | Not specified | [48] |
| HSF-1 | Ang-II-induced inflammation | Activation of proinflammatory transcription factors | Hsp27 | [49,50] |
| Hyperglycemia | Activation of SGK 1 | Vascular calcification | Zinc supplementation | [51,52] |
| TNF-α | p65 pathway | Increased expression of Bfl-1/A1 and Bcl-xL | A20 protein | [54] |
4.5. Role of NF-kB Pathway in Extracellular Matrix Remodeling
4.6. The NF-kB Pathway in Endothelial Dysfunction
4.7. Current Strategies for Inhibiting NF-kB Activation
| Compound | Animal Model/Cell Culture | Mechanism of Action | Effect | Year | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pitvastin | Rats | Reduced binding to DNA for p56 subunit | Smaller aneurysm size, lower expression of MCP-1, VCAM-1, MMP-9, IL-1β, and iNOS | 2009 | [79] |
| Simvastin | Rats | Not specified | Reduced expression of MCP-1, VCAM-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 | 2008 | [80] |
| Aspirin | Rats | Not specified | Reduced expression of MCP-1, VCAM-1 | 2015 | [81] |
| Nifedipine | Rats | Inhibited translocation of p65 subunit into the nucleus | Reduced expression of MCP-1 and MMP-2 | 2008 | [83] |
| Zinc | Rats | Increased production of A20 protein | Smaller aneurysm size | 2021 | [84] |
| Etanecerpt | Rats | TNF-α inhibitor | Smaller aneurysm size and thicker internal elastic membrane | 2014 | [86] |
| BP-1-102 | Mice | STAT3 inhibitor | Reduced expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, IL-10, and MMP | 2020 | [88] |
| BMSCs | Cell culture/rabbits | Inhibition of KLF5 and suppression of PI3k/Akt/NF-kB pathway | Increased eNOS mRNA expression, decreased iNOS mRNA, MMP-2, and MMP-9 expression | 2020 | [89] |
| Resveratrol | Cell culture | MMP-3 inhibitor | Inhibits cell apoptosis by increasing the expression of Bcl-2 protein, decreased iNOS and NO expression | 2014 | [64] |
| Mice | Not specified | Lower IA incidence, reduced expression of MMP-2, and MMP-9 | 2022 | [90] | |
| Tanshione IIA | Rats | TNF-α inhibitor | Reduced expression of MCP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 | 2019 | [91] |
4.8. Clinical Trials Targeting Inflammation for Treating IA
4.9. Future Research Directions for Treating IA
4.10. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Texakalidis, P.; Sweid, A.; Mouchtouris, N.; Peterson, E.C.; Sioka, C.; Rangel-Castilla, L.; Reavey-Cantwell, J.; Jabbour, P. Aneurysm Formation, Growth, and Rupture: The Biology and Physics of Cerebral Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalouhi, N.; Ali, M.S.; Jabbour, P.M.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Koch, W.J.; Dumont, A.S. Biology of Intracranial Aneurysms: Role of Inflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Shintani, A.; Terada, T. Hemodynamic Characteristics at the Rupture Site of Cerebral Aneurysms: A Case Study. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, E1202–E1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorelli, F.; Sela, S.; Gesualdo, L.; Chevrel, S.; Tollet, F.; Pailler-Mattei, C.; Tacconi, L.; Turjman, F.; Vacca, A.; Schul, D.B. Hemodynamic Stress, Inflammation, and Intracranial Aneurysm Development and Rupture: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etminan, N.; Buchholz, B.A.; Dreier, R.; Bruckner, P.; Torner, J.C.; Steiger, H.-J.; Hänggi, D.; Macdonald, R.L. Cerebral Aneurysms: Formation, Progression, and Developmental Chronology. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgers, R.H.P.; Webb, R.C. Molecular Aspects of Arterial Smooth Muscle Contraction: Focus on Rho. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, M.; Chase, A.J.; Baker, A.H.; Newby, A.C. Inhibition of Transcription Factor NF-kB Reduces Matrix Metalloproteinase-1, -3 and -9 Production by Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 50, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Lu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, K.; Zhai, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Attenuation of TNF-α-Induced Inflammatory Injury in Endothelial Cells by Ginsenoside Rb1 via Inhibiting NF-κB, JNK and P38 Signaling Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, N.; Handa, H.; Hazama, F. Experimentally Induced Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats. Surg. Neurol. 1978, 10, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikori, M. Classical and Alternative NF-.KAPPA.B Activation Pathways and Their Roles in Lymphoid Malignancies. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2005, 45, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.; Baltimore, D. Multiple Nuclear Factors Interact with the Immunoglobulin Enhancer Sequences. Cell 1986, 46, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.; Ghosh, M.; Ghosh, J.; Das, J.; Sil, P.C. Contribution of Nano-Copper Particles to in Vivo Liver Dysfunction and Cellular Damage: Role of IκBα/NF-κB, MAPKs and Mitochondrial Signal. Nanotoxicology 2011, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Park, J.; Jung, K.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.; Park, J.; Park, E.-K.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, S.-H.K.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Magnolol and Honokiol Are Mediated through Inhibition of the Downstream Pathway of MEKK-1 in NF-κB Activation Signaling. Planta Medica 2005, 71, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinman, R.I.; Beg, A.A.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-Kappa B P100 (Lyt-10) Is a Component of H2TF1 and Can Function as an I Kappa B-like Molecule. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallett, M.A.; Lu, Y.; Smith, G.L. DDX50 Is a Viral Restriction Factor That Enhances IRF3 Activation. Viruses 2022, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Zou, J.; Fang, Y.; Ding, X. Renal Protection by Delayed Ischaemic Preconditioning Is Associated with Inhibition of the Inflammatory Response and NF-κB Activation. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2007, 25, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Interplay Between Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling and Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-B Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Scheidereit, C. The IκB Kinase Complex in NF-κB Regulation and Beyond. EMBO Rep. 2013, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. The IκB Kinase (IKK) Complex as a Critical Regulator of Immune Responses. Int. Congr. Ser. 2005, 1285, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Krimpenfort, P.; Berns, A.; Verma, I.M. Immunological Defects in Mice with a Targeted Disruption in Bcl-3. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Wang, Q.; Morgan, S.; Si, Y.; Ravichander, A.; Dou, C.; Kent, K.C.; Liu, B. Protein Kinase C-δ (PKCδ) Regulates Proinflammatory Chemokine Expression through Cytosolic Interaction with the NF-κB Subunit P65 in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9013–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Frȍsen, J.; Fukuda, M.; Bando, K.; Shioi, G.; Tsuji, K.; Ollikainen, E.; Nozaki, K.; Laakkonen, J.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin E2-EP2-NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Intracranial Aneurysms. Sci. Signal 2017, 10, eaah6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, Y.M.; Richmond, A. NF-κB Inducing Kinase: A Key Regulator in the Immune System and in Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinin, N.L.; Boldin, M.P.; Kovalenko, A.V.; Wallach, D. MAP3K-Related Kinase Involved in NF-kappaB Induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature 1997, 385, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Murti, A.; Pfeffer, L.M. Interferon Induces NF-κB-Inducing Kinase/Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor-Dependent NF-κB Activation to Promote Cell Survival*. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31530–31536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catz, S.D.; Johnson, J.L. Transcriptional Regulation of Bcl-2 by Nuclear Factor Kappa B and Its Significance in Prostate Cancer. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7342–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Fukuda, M.; Nishimura, M.; Nozaki, K.; Narumiya, S. Critical Role of TNF-Alpha-TNFR1 Signaling in Intracranial Aneurysm Formation. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nozaki, K.; Morishita, R.; Hashimoto, N. Reduced Collagen Biosynthesis Is the Hallmark of Cerebral Aneurysm: Contribution of Interleukin-1beta and Nuclear Factor-kappaB. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorelli, F.; Pailler-Mattei, C.; Gory, B.; Larquet, P.; Robinson, P.; Vargiolu, R.; Zahouani, H.; Labeyrie, P.-E.; Guyotat, J.; Pelissou-Guyotat, I.; et al. Biomechanical Characterization of Intracranial Aneurysm Wall: A Multiscale Study. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, e882–e889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Nishimura, M.; Ishibashi, R.; Kataoka, H.; Takagi, Y.; Hashimoto, N. Toll-like Receptor 4 Expression during Cerebral Aneurysm Formation. Laboratory Investigation. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, M.; Jiang, Z. Involvement of TLR2/4-MyD88-NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Intracranial Aneurysm. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Nishimura, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Furuyashiki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Kitaoka, S.; Ishibashi, R.; Ishibazawa, A.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. PGE(2) -EP(2) Signalling in Endothelium Is Activated by Haemodynamic Stress and Induces Cerebral Aneurysm through an Amplifying Loop via NF-κB. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeriswyl, D.C.; Prionisti, I.; Peach, T.; Tsolkas, G.; Chooi, K.Y.; Vardakis, J.; Morel, S.; Diagbouga, M.R.; Bijlenga, P.; Cuhlmann, S.; et al. Disturbed Flow Induces a Sustained, Stochastic NF-κB Activation Which May Support Intracranial Aneurysm Growth in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzasoma, L.; Antognelli, C.; Talesa, V.N. A Novel Role for Brain Natriuretic Peptide: Inhibition of IL-1 β Secretion via Downregulation of NF-kB/Erk 1/2 and NALP3/ASC/Caspase-1 Activation in Human THP-1 Monocyte. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5858315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Jacques, B.; Ma, W. Role of Prostaglandin E2 in the Synthesis of the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-6 in Primary Sensory Neurons: An in Vivo and in Vitro Study: PGE2 Induces IL-6 in DRG Neurons. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ruan, J.; Luo, L.; Long, F.; Tang, D. Chanling Gao Attenuates Bone Cancer Pain in Rats by the IKKβ/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Erl, W.; Pietsch, A.; Strobel, M.; Ziegler-Heitbrock, H.W.L.; Weber, P.C. Antioxidants Inhibit Monocyte Adhesion by Suppressing Nuclear Factor-icB Mobilization and Induction of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 in Endothelial Cells Stimulated to Generate Radicals. Arter. Thromb. 1994, 14, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhawan, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Emodin (3-Methyl-1,6,8-Trihydroxyanthraquinone) Inhibits TNF-Induced NF-kB Activation, IkB Degradation, and Expression of Cell Surface Adhesion Proteins in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Oncogene 1998, 17, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiani, F.; Catanzaro, M.; Buoso, E.; Basagni, F.; Di Marino, D.; Raniolo, S.; Amadio, M.; Frost, E.H.; Corsini, E.; Racchi, M.; et al. Targeting Cytokine Release through the Differential Modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways by Electrophilic/Non-Electrophilic Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalouhi, N.; Points, L.; Pierce, G.L.; Ballas, Z.; Jabbour, P.; Hasan, D. Localized Increase of Chemokines in the Lumen of Human Cerebral Aneurysms. Stroke 2013, 44, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nozaki, K.; Egashira, K.; Hashimoto, N. Impact of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Deficiency on Cerebral Aneurysm Formation. Stroke 2009, 40, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshiyuki, M.; Reed, J.C. Tumor Suppressor P53 Is a Direct Transcriptional Activator of the Human Bax Gene. Cell 1995, 80, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feoktistova, M.; Makarov, R.; Brenji, S.; Schneider, A.T.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Luedde, T.; Leverkus, M.; Yazdi, A.S.; Panayotova-Dimitrova, D. A20 Promotes Ripoptosome Formation and TNF-Induced Apoptosis via cIAPs Regulation and NIK Stabilization in Keratinocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Ning, K.; Liu, D.; Wu, D.; Wan, R.; Ge, J. MiR-140 Promotes the Progression of Intracranial Aneurysms by Targeting BCL2L2. NeuroReport 2023, 34, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, T.; An, Q.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Shi, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Cyclic Mechanical Stretch Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Changes in Cerebral Aneurysm Progress by Reducing Collagen Type IV and Collagen Type VI Levels. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, E.; Rochfort, K.D.; Forde, H.; Davenport, C.; Smith, D.; Cummins, P.M. Activation of the Non-Canonical NF-κB/P52 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells by RANKL Elicits pro-Calcific Signalling in Co-Cultured Smooth Muscle Cells. Cell. Signal. 2018, 47, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielma, S.A.; Krings, G.; Lopes-Virella, M.F. Chlamydophila pneumoniae Induces ICAM-1 Expression in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells via Protein Kinase C–Dependent Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Currie, R.W. Small Interfering RNA Knocks down Heat Shock Factor-1 (HSF-1) and Exacerbates pro-Inflammatory Activation of NF-kappaB and AP-1 in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegeli, T.S.; Currie, R.W. siRNA Knocks down Hsp27 and Increases Angiotensin II-Induced Phosphorylated NF-κB P65 Levels in Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, L.A.; Estepa, M.; Pieske, B.; Lang, F.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Alesutan, I.; Voelkl, J. Zinc Ameliorates the Osteogenic Effects of High Glucose in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelkl, J.; Tuffaha, R.; Luong, T.T.D.; Zickler, D.; Masyout, J.; Feger, M.; Verheyen, N.; Blaschke, F.; Kuro-o, M.; Tomaschitz, A.; et al. Zinc Inhibits Phosphate-Induced Vascular Calcification through TNFAIP3-Mediated Suppression of NF-κB. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.; Avellino, R.; Ferraro, P.; Romano, S.; Corcione, N.; Romano, M.F. Rapamycin Antagonizes NF-κB Nuclear Translocation Activated by TNF-α in Primary Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Enhances Apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H2459–H2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Xu, L.; Xu, O.; Li, R.; Chen, M.; Shen, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, F.; Yao, D.; Chen, Y.-F.; et al. O-Linked β-N-Acetylglucosamine Modification of A20 Enhances the Inhibition of NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-κB) Activation and Elicits Vascular Protection after Acute Endoluminal Arterial Injury. ATVB 2018, 38, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, M.P.; Coon, C.I.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Nuclear Factor kappaB/P50 Activates an Element in the Distal Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 Promoter in Interleukin-1beta-Stimulated Synovial Fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-T.; Yang, C.L.H.; Or, T.C.T.; Luo, D.; Li, J.C.B. Ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax Notoginseng Suppressed TNF-α-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 via the Suppression of Double-Strand RNA-Dependent Protein Kinase (PKR)/NF-κB Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirum-Connolly, K.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Lnterleukin-1 or Phorbol Induction of the Stromelysin Promoter Requires an Element That Cooperates with AP-1. Nuclic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambhore, N.S.; Kalidhindi, R.S.R.; Pabelick, C.M.; Hawse, J.R.; Prakash, Y.S.; Sathish, V. Differential Estrogen-Receptor Activation Regulates Extracellular Matrix Deposition in Human Airway Smooth Muscle Remodeling via NF-κB Pathway. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13935–13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Morimoto, M.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N. Macrophage-Derived Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 Promote the Progression of Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats. Stroke 2007, 38, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Overexpression of Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase 2 Up-Regulates NF-κB Activity in Melanoma Cells. JMS 2009, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizárraga, F.; Maldonado, V.; Meléndez-Zajgla, J. Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-2 Growth-Stimulatory Activity Is Mediated by Nuclear Factor-Kappa B in A549 Lung Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchavanakit, N.; Saengtong, W.; Manokawinchoke, J.; Pavasant, P. TNF-α Stimulates MMP-3 Production via PGE2 Signalling through the NF-kB and P38 MAPK Pathway in a Murine Cementoblast Cell Line. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, S. A Novel NF-κB/MMP-3 Signal Pathway Involves in the Aggressivity of Glioma Promoted by Bmi-1. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 12721–12727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Gao, D.; Jiang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Fei, Z. Resveratrol Inhibits Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation-Induced MMP-3 Expression and Cell Apoptosis in Primary Cortical Cells via the NF-κB Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheinberg, D.L.; McCarthy, D.J.; Elwardany, O.; Bryant, J.-P.; Luther, E.; Chen, S.H.; Thompson, J.W.; Starke, R.M. Endothelial Dysfunction in Cerebral Aneurysms. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, T.; Nikolopoulou, E.A.; Xu, Q.; Qu, A. Hypoxia Inducible Factor as a Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 183, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisk, C.; Kominsky, D.; Ehrentraut, S.; Bonaventura, J.; Nuss, R.; Hassell, K.; Nozik-Grayck, E.; Irwin, D.C. Hemoglobin-Induced Endothelial Cell Permeability Is Controlled, in Part, via a Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene–88–Dependent Signaling Mechanism. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, G.L.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Lawson, B.R.; Beske, S.D.; Seals, D.R. Nuclear Factor-κB Activation Contributes to Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction via Oxidative Stress in Overweight/Obese Middle-Aged and Older Humans. Circulation 2009, 119, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.J.; Duckles, S.P.; Krause, D.N. Dihydrotestosterone Stimulates Cerebrovascular Inflammation through NFjB, Modulating Contractile Function. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojima, M.; Oshima, M.; Takagi, K.; Torii, R.; Hayakawa, M.; Katada, K.; Morita, A.; Kirino, T. Magnitude and Role of Wall Shear Stress on Cerebral Aneurysm: Computational Fluid Dynamic Study of 20 Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysms. Stroke 2004, 35, 2500–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, D.A.; Wenzel, J.; Müller, K.; Töllner, K.; Tong, X.-K.; Assmann, J.C.; Stroobants, S.; Weber, T.; Niturad, C.; Fischer, L.; et al. Brain Endothelial TAK1 and NEMO Safeguard the Neurovascular Unit. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1529–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, R.; Gao, S.; Fan, J.; Xia, M.; Zhao, R.C.; Zhang, J. Melatonin Protects Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Permeability by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 via the NOTCH3/NF-κB Pathway. Aging 2019, 11, 11391–11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Ichiyama, T.; Sonaka, I.; Ohsaki, A.; Okada, S.; Wakiguchi, H.; Kudo, K.; Kittaka, S.; Hara, M.; Furukawa, S. Cysteine, Histidine and Glycine Exhibit Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Human Coronary Arterial Endothelial Cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takacs, P.; Kauma, S.W.; Sholley, M.M.; Walsh, S.W.; Dinsmoor, M.J.; Green, K. Increased Circulating Lipid Peroxides in Severe Preeclampsia Activate NF-κΒ and Upregulate ICAM-1 in Vascular Endothelial Cells. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flati, V.; Pastore, L.I.; Griffioen, A.W.; Satijn, S.; Toniat, E.; D’Alimonte, I.; Marchetti, P.; Gulin, A.; Martinottp, S. Endothelial Cell Anergy Is Mediated by bFGF through the Sustained Activation of P38-MAPK and NF-kappaB Inhibition. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2006, 19, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakil, P.; Ansari, S.A.; Cantrell, C.G.; Eddleman, C.S.; Dehkordi, F.H.; Vranic, J.; Hurley, M.C.; Batjer, H.H.; Bendok, B.R.; Carroll, T.J. Quantifying Intracranial Aneurysm Wall Permeability for Risk Assessment Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI: A Pilot Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, F.; Wang, M.; Ma, H.; Zhu, J. Simvastatin Modulates Interaction between Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell/Macrophage and TNF-α–Activated Endothelial Cell. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 71, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, K.; Shahbaz, S.K.; Mashayekhi, K.; Sadeghi, M.; Zayeri, Z.D.; Taba, M.Y.; Banach, M.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. Anti-Inflammatory Action of Statins in Cardiovascular Disease: The Role of Inflammasome and Toll-like Receptor Pathways. Clin. Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2021, 60, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nakagami, H.; Nozaki, K.; Morishita, R.; Hashimoto, N. Pitavastatin Suppresses Formation and Progression of Cerebral Aneurysms through Inhibition of the Nuclear Factor kappaB Pathway. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 357–365; discussion 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N. Simvastatin Suppresses the Progression of Experimentally Induced Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats. Stroke 2008, 39, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, J.-F.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, J. Aspirin Inhibits Degenerative Changes of Aneurysmal Wall in a Rat Model. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.P.; Galex, I.A.; Sadeghi, N.B.; Weledji, N.; Cabello Bermudez, S.I.; Mitchell, B.A.; Bush, D.M.; Yap, E.; Davis, N.C.; Catalino, M.P.; et al. Rabbit Elastase Aneurysm: Imaging and Histology Correlates for Inflammation and Healing. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e242–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N. Nifedipine Inhibits the Progression of an Experimentally Induced Cerebral Aneurysm in Rats with Associated Down-Regulation of NF-Kappa B Transcriptional Activity. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2008, 5, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Kataoka, H.; Minami, M.; Ikedo, T.; Miyata, T.; Shimizu, K.; Nagata, M.; Yang, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yokode, M.; et al. Association of Zinc Administration with Growth Suppression of Intracranial Aneurysms via Induction of A20. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holubova, M.; Axmanova, M.; Gumulec, J.; Raudenska, M.; Sztalmachova, M.; Babula, P.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Masarik, M. KRAS NF-κB Is Involved in the Development of Zinc Resistance and Reduced Curability in Prostate Cancer. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, T.; Isono, T.; Saitoh, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Nozaki, K. Suppression of Cerebral Aneurysm Formation in Rats by a Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitor. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.; Park, H.J.; Song, Y.-K.; Oh, Y.-J.; Kim, I.-W.; Oh, J.M. The Risk of Newly Diagnosed Cancer in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis by TNF Inhibitor Use: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huang, J.; You, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, B. Pharmacological Inhibition of STAT3 by BP-1-102 Inhibits Intracranial Aneurysm Formation and Rupture in Mice through Modulating Inflammatory Response. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, G. Exosomal microRNA-23b-3p from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Maintains T Helper/Treg Balance by Downregulating the PI3k/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Intracranial Aneurysm. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; An, Q.; Qin, X.; Qin, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, B.; Leng, B. Resveratrol Inhibits Cerebral Aneurysms in Mice via Downregulating the NF-κB Pathway. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2022, 69, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hou, D.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiao, G.; Liu, N. Tanshinone IIA Attenuates Cerebral Aneurysm Formation by Inhibiting the NF-κB-mediated Inflammatory Response. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia-Munne, J.C.; Ellis, J.A.; Feldstein, N.A.; Meyers, P.M.; Connolly, E.S. Moyamoya and Inflammation. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statin Treatment for Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Study (STUDIES). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04149483 (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Atorvastatin in the Treatment of Intracranial Unruptured VertebroBasilar Dissecting Aneurysms (ATREAT-VBD). Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04943783 (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Hasan, D.M.; Chalouhi, N.; Jabbour, P.; Dumont, A.S.; Kung, D.K.; Magnotta, V.A.; Young, W.L.; Hashimoto, T.; Richard Winn, H.; Heistad, D. Evidence That Acetylsalicylic Acid Attenuates Inflammation in the Walls of Human Cerebral Aneurysms: Preliminary Results. JAHA 2013, 2, e000019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm Aspirin Trial (UIAAT). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03661463 (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Güresir, E. Fight INflammation to Improve Outcome after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HEmorRhage. 2023. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, W.; Gu, S. Effect of Anti-CIRP Antibody on Inflammatory Response, Tumor Formation and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Rats. Trop. J. Pharm Res. 2020, 19, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yao, H.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Yang, S.; Cheng, K. miR-195 Suppresses Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm through the TNF-α/NF-κB and VEGF/PI3K/Akt Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Luo, K.; Bian, S.; Chen, J.; Qiu, R.; Wu, X.; Li, G. Paeonol Ameliorates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Progression by the NF-κB Pathway. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 77, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Bai, Y.-Q.; Qi, M. Daidzein Attenuates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm through NF-κB, p38MAPK and TGF-Β1 Pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarheydari, S.; Tahmasebi Birgani, M.; Rezaeijo, S.M. Auto-Segmentation of Head and Neck Tumors in Positron Emission Tomography Images Using Non-Local Means and Morphological Frameworks. Pol. J. Radiol. 2023, 88, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Gorji, A.; Fathi Jouzdani, A.; Rezaeijo, S.M.; Rahmim, A.; Salmanpour, M.R. Prediction of Cognitive Decline in Parkinson’s Disease Using Clinical and DAT SPECT Imaging Features, and Hybrid Machine Learning Systems. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blaj, L.A.; Cucu, A.I.; Tamba, B.I.; Turliuc, M.D. The Role of the NF-kB Pathway in Intracranial Aneurysms. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121660
Blaj LA, Cucu AI, Tamba BI, Turliuc MD. The Role of the NF-kB Pathway in Intracranial Aneurysms. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(12):1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121660
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlaj, Laurentiu Andrei, Andrei Ionut Cucu, Bogdan Ionel Tamba, and Mihaela Dana Turliuc. 2023. "The Role of the NF-kB Pathway in Intracranial Aneurysms" Brain Sciences 13, no. 12: 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121660
APA StyleBlaj, L. A., Cucu, A. I., Tamba, B. I., & Turliuc, M. D. (2023). The Role of the NF-kB Pathway in Intracranial Aneurysms. Brain Sciences, 13(12), 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121660






