Low-Grade Gliomas: Histological Subtypes, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatment Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Overview of the 2021 WHO Classification: Molecular Intricacies and the Pathway to Targeted Therapies
3. Specificities of WHO 2021 Classification of Brain Tumors
4. Rare Entities in Low-Grade Gliomas
4.1. MYB/MYBL1 Alterations
4.2. Angiocentric Glioma
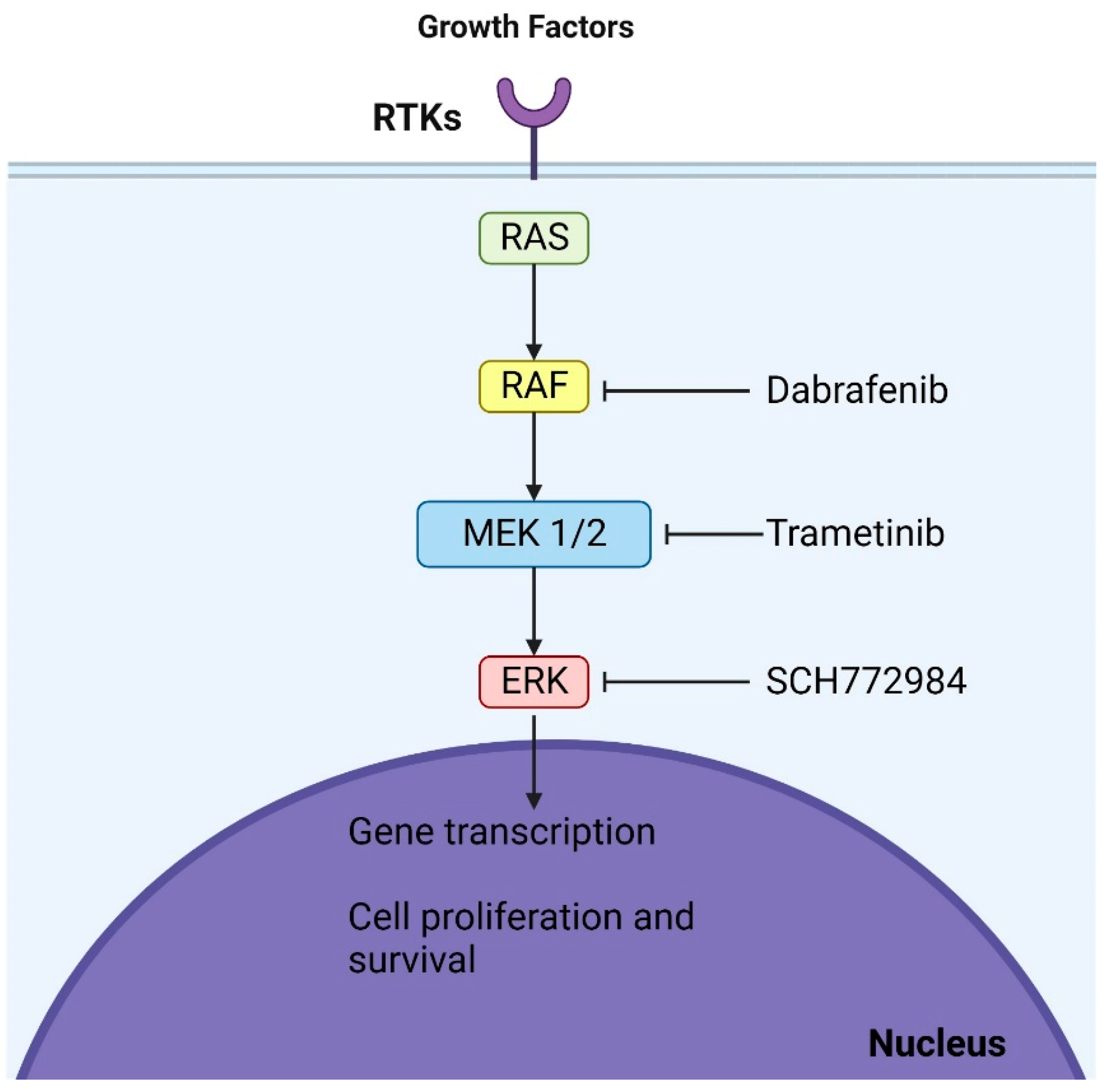
4.3. Diffuse Low-Grade MAPK Pathway-Altered Gliomas
4.4. Polymorphous Low-Grade Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Young (PLNTY)
5. Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas: A Special Consideration
6. Treatment Modalities, Approaches, Outcomes, and Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forst, D.A.; Nahed, B.V.; Loeffler, J.S.; Batchelor, T.T. Low-Grade Gliomas. Oncologist 2014, 19, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Chang, S.; Berger, M.S. Low-grade gliomas in adults: A review. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 948–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Burger, P.; Ellison, D.W.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Aldape, K.; Brat, D.; Collins, V.P.; Eberhart, C.; et al. International Society of Neuropathology-Haarlem Consensus Guidelines for Nervous System Tumor Classification and Grading. Brain Pathol. 2014, 24, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Xu, J.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, v1–v75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, D. Low-grade Gliomas. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2017, 23, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddoumi, I.; Orisme, W.; Wen, J.; Santiago, T.; Gupta, K.; Dalton, J.D.; Tang, B.; Haupfear, K.; Punchihewa, C.; Easton, J.; et al. Genetic alterations in uncommon low-grade neuroepithelial tumors: BRAF, FGFR1, and MYB mutations occur at high frequency and align with morphology. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; de Blank, P.M.; Kruchko, C.; Petersen, C.M.; Liao, P.; Finlay, J.L.; Stearns, D.S.; Wolff, J.E.; Wolinsky, Y.; Letterio, J.J.; et al. Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation Infant and Childhood Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 16 (Suppl. 10), x1–x36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22 (Suppl. 1), iv1–iv96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouke, S.J.; Benzinger, T.; Gibson, D.; Ryken, T.C.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Olson, J.J. The role of imaging in the management of adults with diffuse low grade glioma: A systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 125, 457–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomas, D.A.; Laack, N.N.I.; Rao, R.D.; Meyer, F.B.; Shaw, E.G.; O’Neill, B.P.; Giannini, C.; Brown, P.D. Intracranial low-grade gliomas in adults: 30-year experience with long-term follow-up at Mayo Clinic. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 11, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Raisanen, J.M.; Ganji, S.K.; Zhang, S.; McNeil, S.S.; An, Z.; Madan, A.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Vemireddy, V.; Sheppard, C.A.; et al. Prospective Longitudinal Analysis of 2-Hydroxyglutarate Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Identifies Broad Clinical Utility for the Management of Patients with IDH -Mutant Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4030–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Bent, M.J. Interobserver variation of the histopathological diagnosis in clinical trials on glioma: A clinician’s perspective. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, T.D.; Schiff, D. Update on molecular findings, management and outcome in low-grade gliomas. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, D.; Brown, P.D.; Giannini, C. Outcome in adult low-grade glioma: The impact of prognostic factors and treatment. Neurology 2007, 69, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balss, J.; Meyer, J.; Mueller, W.; Korshunov, A.; Hartmann, C.; Von Deimling, A. Analysis of the IDH1 codon 132 mutation in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Parsons, D.W.; Jin, G.; McLendon, R.; Rasheed, B.A.; Yuan, W.; Kos, I.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Jones, S.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations in Gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; Bennett, B.D.; Bittinger, M.A.; Driggers, E.M.; Fantin, V.R.; Jang, H.G.; Jin, S.; Keenan, M.C.; et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, D.J.; Aldape, K.; Colman, H.; Figrarella-Branger, D.; Fuller, G.N.; Giannini, C.; Holland, E.C.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.; Komori, T.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 5: Recommended grading criteria and terminologies for IDH-mutant astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 139, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, T. Grading of adult diffuse gliomas according to the 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsch, S.; Batchelor, T.T.; Castro, L.N.G. Diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications of the 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer 2022, 128, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive, Integrative Genomic Analysis of Diffuse Lower-Grade Gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesileanu, C.M.S.; Dirven, L.; Wijnenga, M.M.J.; Koekkoek, J.A.F.; E Vincent, A.J.P.; Dubbink, H.J.; Atmodimedjo, P.N.; Kros, J.M.; Van Duinen, S.G.; Smits, M.; et al. Survival of diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH1/2 wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV: A confirmation of the cIMPACT-NOW criteria. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ahluwalia, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Campian, J.L.; Clark, S.W.; Fabiano, A.J.; et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 1537–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plass, C.; Pfister, S.M.; Lindroth, A.M.; Bogatyrova, O.; Claus, R.; Lichter, P. Mutations in regulators of the epigenome and their connections to global chromatin patterns in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontebasso, A.M.; Gayden, T.; Nikbakht, H.; Neirinck, M.; Papillon-Cavanagh, S.; Majewski, J.; Jabado, N. Epigenetic dysregulation: A novel pathway of oncogenesis in pediatric brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; Kapoor, G.S.; Rohle, D.; Turcan, S.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Edwards, C.R.; Khanin, R.; Figueroa, M.E.; Melnick, A.; et al. IDH mutation impairs histone demethylation and results in a block to cell differentiation. Nature 2012, 483, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcan, S.; Rohle, D.; Goenka, A.; Walsh, L.A.; Fang, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Campos, C.; Fabius, A.W.M.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; et al. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype. Nature 2012, 483, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.W.; Müller, M.M.; Koletsky, M.S.; Cordero, F.; Lin, S.; Banaszynski, L.A.; Garcia, B.A.; Muir, T.W.; Becher, O.J.; Allis, C.D. Inhibition of PRC2 Activity by a Gain-of-Function H3 Mutation Found in Pediatric Glioblastoma. Science 2013, 340, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blank, P.; Fouladi, M.; Huse, J.T. Molecular markers and targeted therapy in pediatric low-grade glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 150, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Schrimpf, D.; Sturm, D.; Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Chavez, L.; Reuss, D.E.; et al. DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Jakacki, R.I.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Wu, S.; Nicolaides, T.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Fangusaro, J.; Phillips, J.; Perry, A.; Turner, D.; et al. A phase I trial of the MEK inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) in pediatric patients with recurrent or refractory low-grade glioma: A Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium (PBTC) study. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangusaro, J.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Wu, S.; Ligon, A.H.; Lindeman, N.; Banerjee, A.; Packer, R.J.; Kilburn, L.B.; Goldman, S.; et al. Selumetinib in paediatric patients with BRAF-aberrant or neurofibromatosis type 1-associated recurrent, refractory, or progressive low-grade glioma: A multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffet, E.; Kieran, M.; Hargrave, D.; Roberts, S.; Aerts, I.; Broniscer, A.; Geoerger, B.; Dasgupta, K.; Tseng, L.; Russo, M.; et al. LGG-46. Trametinib Therapy in Pediatric Patients with Low-Grade Gliomas (Lgg) with Braf Gene Fusion; A Disease-Specific Cohort in the First Pediatric Testing of Trametinib. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20 (Suppl. 2), i114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, N.; Pauly, J.; Malvar, J.; Gruber-Filbin, M.; de Mola, R.L.; Dorris, K.; Bendel, A.; Bowers, D.; Bornhorst, M.; Gauvain, K.; et al. LGG-44. A Phase I Dose Escalation Trial of the Mek1/2 Inhibitor Mek162 (Binimetinib) in Children with Low-Grade Gliomas and Other Ras/Raf Pathway-Activated Tumors. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20 (Suppl. 2), i114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, M.E.; Patel, A.; Danysh, B.P.; Dadu, R.; Kopetz, S.; Falchook, G. BRAF Inhibitors: Experience in Thyroid Cancer and General Review of Toxicity. Horm. Cancer 2015, 6, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavle, A.; Jones, J.; Lin, F.Y.; Malphrus, A.; Adesina, A.; Su, J. Dramatic clinical and radiographic response to BRAF inhibition in a patient with progressive disseminated optic pathway glioma refractory to MEK inhibition. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 34, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, A.; Stucklin, A.G.; Ramaswamy, V.; Zapotocky, M.; McKeown, T.; Hawkins, C.; Bouffet, E.; Tabori, U. Profound clinical and radiological response to BRAF inhibition in a 2-month-old diencephalic child with hypothalamic/chiasmatic glioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 2038–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karajannis, M.A.; Legault, G.; Fisher, M.J.; Milla, S.S.; Cohen, K.J.; Wisoff, J.H.; Harter, D.H.; Goldberg, J.D.; Hochman, T.; Merkelson, A.; et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in children with recurrent or progressive low-grade astrocytomas. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.D.; Zimmerman, M.A.; Fine, E.; Aspri, T.; Kieran, M.W.; Chi, S. LGG-26. Type II Braf Inhibitor Tak-580 Shows Promise for Upcoming Clinal Trial as Evidenced by Single Patient Ind Study. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20 (Suppl. 2), i110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selt, F.; van Tilburg, C.M.; Bison, B.; Sievers, P.; Harting, I.; Ecker, J.; Pajtler, K.W.; Sahm, F.; Bahr, A.; Simon, M.; et al. Response to trametinib treatment in progressive pediatric low-grade glioma patients. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; von Deimling, A. Grading of diffuse astrocytic gliomas: Broders, Kernohan, Zülch, the WHO… and Shakespeare. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Wesseling, P.; Aldape, K.; Brat, D.J.; Capper, D.; Cree, I.A.; Eberhart, C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Fouladi, M.; Fuller, G.N.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 6: New entity and diagnostic principle recommendations of the cIMPACT-Utrecht meeting on future CNS tumor classification and grading. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, P.; Sill, M.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; E Reuss, D.; Sturm, D.; Hench, J.; Frank, S.; Krskova, L.; Vicha, A.; et al. A subset of pediatric-type thalamic gliomas share a distinct DNA methylation profile, H3K27me3 loss and frequent alteration of EGFR. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.; Mackay, A.; Ismer, B.; Pickles, J.C.; Tatevossian, R.G.; Newman, S.; Bale, T.A.; Stoler, I.; Izquierdo, E.; Temelso, S.; et al. Infant High-Grade Gliomas Comprise Multiple Subgroups Characterized by Novel Targetable Gene Fusions and Favorable Outcomes. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 942–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, D.W.; Hawkins, C.; Jones, D.T.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; Louis, D.N. cIMPACT-NOW update 4: Diffuse gliomas characterized by MYB, MYBL1, or FGFR1 alterations or BRAF V600E mutation. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Patel, S.H.; Chi, A.S.; Snuderl, M.; Jain, R. There is an exception to every rule—T2-FLAIR mismatch sign in gliomas. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisoff, J.H.; Sanford, R.; Heier, L.; Sposto, R.; Burger, P.C.; Yates, A.J.; Holmes, E.J.; E Kun, L. Primary neurosurgery for pediatric low-grade gliomas: A prospective multi-institutional study from the Children’s Oncology Group. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, J.H.; Kim, S.-K. Clinical pearls and advances in molecular researches of epilepsy-associated tumors. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2019, 62, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Harreld, J.H.; Tinkle, C.L.; Moreira, D.C.; Li, X.; Acharya, S.; Qaddoumi, I.; Ellison, D.W. A single-center study of the clinicopathologic correlates of gliomas with a MYB or MYBL1 alteration. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 1091–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakur, S.F.; McGirt, M.J.; Johnson, M.W.; Burger, P.C.; Ahn, E.; Carson, B.S.; Jallo, G.I. Angiocentric glioma: A case series: Clinical article. J. Neurosurgery: Pediatr. 2009, 3, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tihan, T.; Rojiani, A.M.; Bodhireddy, S.R.; Prayson, R.A.; Iacuone, J.J.; Alles, A.J.; Donahue, D.J.; Hessler, R.B.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Monomorphous angiocentric glioma: A distinctive epileptogenic neoplasm with features of infiltrating astrocytoma and ependymoma. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, R.; Baba, A.; Emile, P.; Kurokawa, M.; Ota, Y.; Kim, J.; Capizzano, A.; Srinivasan, A.; Moritani, T. Neuroimaging features of angiocentric glioma: A case series and systematic review. J. Neuroimaging 2022, 32, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aronco, L.; Rouleau, C.; Gayden, T.; Crevier, L.; Décarie, J.C.; Perreault, S.; Jabado, N.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Ligon, K.L.; Ellezam, B. Brainstem angiocentric gliomas with MYB–QKI rearrangements. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orton, R.J.; Sturm, O.E.; Vyshemirsky, V.; Calder, M.; Gilbert, D.R.; Kolch, W. Computational modelling of the receptor-tyrosine-kinase-activated MAPK pathway. Biochem. J. 2005, 392, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, J.T.; Snuderl, M.; Jones, D.T.W.; Brathwaite, C.D.; Altman, N.; Lavi, E.; Saffery, R.; Sexton-Oates, A.; Blumcke, I.; Capper, D.; et al. Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young (PLNTY): An epileptogenic neoplasm with oligodendroglioma-like components, aberrant CD34 expression, and genetic alterations involving the MAP kinase pathway. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.R.; Giannini, C.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kim, D.K.; Kaufmann, T.J. Plenty of calcification: Imaging characterization of polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelotte, J.; Duprez, T.; Raftopoulos, C.; Michotte, A. Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young: Case report of a newly described histopathological entity. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2020, 120, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.R.; Giller, C.; Kolhe, R.; Forseen, S.E.; Sharma, S. Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young: A case report with genomic findings. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, V.P.; Caporalini, C.; Asioli, S.; Buccoliero, A. Paediatric-type diffuse low-grade gliomas: A clinically and biologically distinct group of tumours with a favourable outcome. Pathologica 2022, 114, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryall, S.; Tabori, U.; Hawkins, C. Pediatric low-grade glioma in the era of molecular diagnostics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, P.G.; Tihan, T.; Goldthwaite, P.T.; Wharam, M.D.; Carson, B.S.; Weingart, J.D.; Repka, M.X.; Cohen, K.J.; Burger, P.C. Outcome analysis of childhood low-grade astrocytomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 51, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listernick, R.; Ferner, R.E.; Liu, G.T.; Gutmann, D.H. Optic pathway gliomas in neurofibromatosis-1: Controversies and recommendations. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, A.J.; Fisher, M.J. Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas. J. Child Neurol. 2009, 24, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Sanford, R.; Heideman, R.; Jenkins, J.J.; Walter, A.; Li, Y.; Langston, J.W.; Muhlbauer, M.; Boyett, J.M.; Kun, L. Low-grade astrocytoma: A decade of experience at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 2792–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Dutt, M.; Suraweera, N.; Pfister, S.M.; von Deimling, A.; Brandner, S. Methylation array profiling of adult brain tumours: Diagnostic outcomes in a large, single centre. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Stichel, D.; Sahm, F.; Jones, D.T.W.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Schmid, S.; Hovestadt, V.; Reuss, D.E.; Koelsche, C.; et al. Practical implementation of DNA methylation and copy-number-based CNS tumor diagnostics: The Heidelberg experience. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 181–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.N.G.; Wesseling, P. The cIMPACT-NOW updates and their significance to current neuro-oncology practice. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2021, 8, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatti, F.; Bent, M.v.D.; Curran, D.; Debruyne, C.; Sylvester, R.; Therasse, P.; Áfra, D.; Cornu, P.; Bolla, M.; Vecht, C.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Survival in Adult Patients with Cerebral Low-Grade Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2076–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouratian, N.; Mut, M.; Jagannathan, J.; Lopes, M.B.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Schiff, D. Low-grade gliomas in older patients: A retrospective analysis of prognostic factors. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 90, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomas, D.A.; Laack, N.N.; Brown, P.D. Low-grade gliomas in older patients: Long-term follow-up from Mayo Clinic. Cancer 2009, 115, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Chang, E.F.; Lamborn, K.R.; Chang, S.M.; Prados, M.D.; Cha, S.; Tihan, T.; VandenBerg, S.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S. Role of Extent of Resection in the Long-Term Outcome of Low-Grade Hemispheric Gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, M.J.; Chaichana, K.L.; Attenello, F.J.; Weingart, J.D.; Than, K.; Burger, P.C.; Olivi, A.; Brem, H.; Quinoñes-Hinojosa, A. Extent of Surgical Resection Is Independently Associated with Survival in Patients with Hemispheric Infiltrating Low-Grade Gliomas. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Bansal, A.; Young, E.; Batchala, P.; Patrie, J.; Lopes, M.; Jain, R.; Fadul, C.; Schiff, D. Extent of Surgical Resection in Lower-Grade Gliomas: Differential Impact Based on Molecular Subtype. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairncross, G.; Wang, M.; Shaw, E.; Jenkins, R.; Brachman, D.; Buckner, J.; Fink, K.; Souhami, L.; Laperriere, N.; Curran, W.; et al. Phase III Trial of Chemoradiotherapy for Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma: Long-Term Results of RTOG 9402. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Barthel, F.P.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Salama, S.R.; Murray, B.A.; Morozova, O.; Newton, Y.; Radenbaugh, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell 2016, 164, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Bander, E.D.; A Venn, R.; Powell, T.; Cederquist, G.Y.-M.; Schaefer, P.M.; A Puchi, L.; Akhmerov, A.; Ogilvie, S.; Reiner, A.S.; et al. The Role of Extent of Resection in IDH1 Wild-Type or Mutant Low-Grade Gliomas. Neurosurgery 2018, 82, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schei, S.; Solheim, O.; Salvesen, Ø.; Hansen, T.I.; Sagberg, L.M. Patient-reported cognitive function before and after glioma surgery. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefel, J.S.; Noll, K.R.; Rao, G.; Cahill, D.P. Neurocognitive function varies by IDH1 genetic mutation status in patients with malignant glioma prior to surgical resection. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, K.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Sitskoorn, M.M.; Aaronson, N.K. Predictors of subjective versus objective cognitive functioning in patients with stable grades II and III glioma. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2015, 2, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffau, H.; Lopes, M.; Arthuis, F.; Bitar, A.; Sichez, J.-P.; Van Effenterre, R.; Capelle, L. Contribution of intraoperative electrical stimulations in surgery of low grade gliomas: A comparative study between two series without (1985–1996) and with (1996–2003) functional mapping in the same institution. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffau, H. Surgery of low-grade gliomas: Towards a ‘functional neurooncology’. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2009, 21, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Solheim, K.; Polley, M.-Y.; Lamborn, K.R.; Page, M.; Fedoroff, A.; Rabbitt, J.; Butowski, N.; Prados, M.; Chang, S.M. Quality of life in low-grade glioma patients receiving temozolomide. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 11, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.G.; Berkey, B.; Coons, S.W.; Brachman, D.; Buckner, J.C.; Stelzer, K.J.; Barger, G.R.; Brown, P.D.; Gilbert, M.R.; Mehta, M. Initial report of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 9802: Prospective studies in adult low-grade glioma (LGG). J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Taillandier, L.; Capelle, L. Radical surgery after chemotherapy: A new therapeutic strategy to envision in grade II glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 80, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururangan, S.; Fisher, M.J.; Allen, J.C.; Herndon, J.E.; Quinn, J.A.; Reardon, D.A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; Desjardins, A.; Phillips, P.C.; Watral, M.A.; et al. Temozolomide in Children with progressive low-grade glioma1. Neuro-Oncology 2007, 9, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouratian, N.; Schiff, D. Management of Low-Grade Glioma. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2010, 10, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bent, M.J.; Afra, D.; De Witte, O.; Hassel, M.B.; Schraub, S.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Malmström, P.-O.; Collette, L.; Piérart, M.; Mirimanoff, R.; et al. Long-term efficacy of early versus delayed radiotherapy for low-grade astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma in adults: The EORTC 22845 randomised trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surma-Aho, O.; Niemela, M.; Vilkki, J.; Kouri, M.; Brander, A.; Salonen, O.; Paetau, A.; Kallio, M.; Pyykkonen, L.J.; Jaaskelainen, J. Adverse long-term effects of brain radiotherapy in adult low-grade glioma patients. Neurology 2001, 56, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, B.G.; Stupp, R. Low-grade glioma: A challenge in therapeutic options: The role of radiotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, vii217–vii222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douw, L.; Klein, M.; Fagel, S.S.; van den Heuvel, J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Postma, T.J.; Vandertop, W.P.; Mooij, J.J.; Boerman, R.H.; et al. Cognitive and radiological effects of radiotherapy in patients with low-grade glioma: Long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Adjei, A.A. The clinical development of MEK inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, T.; Nazemi, K.J.; Crawford, J.; Kilburn, L.; Minturn, J.; Gajjar, A.; Gauvain, K.; Leary, S.; Dhall, G.; Aboian, M.; et al. Phase I study of vemurafenib in children with recurrent or progressive BRAFV600E mutant brain tumors: Pacific Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Consortium study (PNOC-002). Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, A.J.; Lang, S.-S.; Boucher, K.L.; Madsen, P.J.; Slaunwhite, E.; Choudhari, N.; Kellet, M.; Storm, P.B.; Resnick, A.C. Paradoxical activation and RAF inhibitor resistance of BRAF protein kinase fusions characterizing pediatric astrocytomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5957–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Aboian, M.; Nazemi, K.; Gauvain, K.; Yoon, J.; Minturn, J.; Leary, S.; AbdelBaki, M.S.; Goldman, S.; Elster, J.; et al. LGG-53. PNOC001 (NCT01734512): A Phase II Study of Everolimus for Recurrent or Progressive Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas (pLGG). Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22 (Suppl. S3), iii376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Krzykwa, E.; Greenspan, L.; Chi, S.; Yeo, K.K.; Prados, M.; Mueller, S.; Haas-Kogan, D. CTNI-19. Phase I Trial of Day101 in Pediatric Patients with Radiographically Recurrent or Progressive Low-Grade Glioma (LGG). Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22 (Suppl. 2), ii46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffet, E.; Hansford, J.; Garré, M.L.; Hara, J.; Plant-Fox, A.; Aerts, I.; Locatelli, F.; Van der Lugt, J.; Papusha, L.; Sahm, F.; et al. Primary analysis of a phase II trial of dabrafenib plus trametinib (dab + tram) in BRAF V600–mutant pediatric low-grade glioma (pLGG). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 40, LBA2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ater, J.L.; Zhou, T.; Holmes, E.; Mazewski, C.M.; Booth, T.N.; Freyer, D.R.; Lazarus, K.H.; Packer, R.J.; Prados, M.; Sposto, R.; et al. Randomized Study of Two Chemotherapy Regimens for Treatment of Low-Grade Glioma in Young Children: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, G.; Hamilton, J.; McKeown, T.; Bouffet, E.; Tabori, U.; Dirks, P.; Bartels, U. Trametinib Toxicities in Patients with Low-grade Gliomas and Diabetes Insipidus: Related Findings? J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 42, e248–e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toader, C.; Eva, L.; Costea, D.; Corlatescu, A.D.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Bratu, B.-G.; Glavan, L.A.; Costin, H.P.; Popa, A.A.; Ciurea, A.V. Low-Grade Gliomas: Histological Subtypes, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatment Strategies. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121700
Toader C, Eva L, Costea D, Corlatescu AD, Covache-Busuioc R-A, Bratu B-G, Glavan LA, Costin HP, Popa AA, Ciurea AV. Low-Grade Gliomas: Histological Subtypes, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatment Strategies. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(12):1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121700
Chicago/Turabian StyleToader, Corneliu, Lucian Eva, Daniel Costea, Antonio Daniel Corlatescu, Razvan-Adrian Covache-Busuioc, Bogdan-Gabriel Bratu, Luca Andrei Glavan, Horia Petre Costin, Andrei Adrian Popa, and Alexandru Vlad Ciurea. 2023. "Low-Grade Gliomas: Histological Subtypes, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatment Strategies" Brain Sciences 13, no. 12: 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121700
APA StyleToader, C., Eva, L., Costea, D., Corlatescu, A. D., Covache-Busuioc, R.-A., Bratu, B.-G., Glavan, L. A., Costin, H. P., Popa, A. A., & Ciurea, A. V. (2023). Low-Grade Gliomas: Histological Subtypes, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatment Strategies. Brain Sciences, 13(12), 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121700







